Introduction
In 2017, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and American Nurses Association (ANA) emphasized the need for registered nurses (RN) to embrace a clearly defined, central role in antibiotic stewardship programs (ASP). [
1] The core elements of CDC’s Hospital ASP, highlight key areas for nursing-based interventions that each hospital can use to establish their individual pathways for fostering and supporting nursing engagement. (
Figure 1) [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]
In 2015, the Vermont Oxford Network (VON) in partnership with CDC launched ‘Choosing Antibiotics Wisely’, an internet-based, multicenter collaborative to address the overuse of antibiotics in newborn care and reported 34% reduction in median antibiotic usage rate (AUR; from16.7% to 12.1%) among 187 centers within three years of implementation. [
8,
9] Our hospital realized AUR reductions in both the newborn nursery (NBN) and in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) as part of the collaborative.
In our NICU, we created evidence-based, consensus derived- guidelines for evaluation and management of common infections, discouraged treating culture negative sepsis, empowered the charge nurses to become the center point of antibiotic stewardship efforts by initiating antibiotic time outs, discussing the need for continued antibiotic treatment in team huddle and educating parents on the plan for antibiotic usage. Additionally, we reduced central line infections by creating a nurse-led infection prevention and control group [
10]. Frequent audits and involvement of nursing team in planning and implementation of the ASP was a key element for our success.
In the NBN/mother-baby unit, we achieved a significant reduction in empiric antibiotic initiation rate in well appearing newborns with the implementation of the SRC in a two-phase approach. Phase 1 (2016-2017, SRC superimposition) was a retrospective prediction of the drop in antibiotic use with SRC superimposition. In Phase 2, we modified the use of SRC based on phase-1 results and tailored it to our patient demographics and hospital resources. Our use of empiric antibiotics dropped to 4% with the use of SRC Vs 12.6% with our previous guidelines based on 2010 CDC/AAP recommendations by the first half of the year in 2018 in infants ≥ 35weeks.
While our center achieved substantial decrease in empiric antibiotic use in infants admitted to our mother-baby unit, the involvement of the nurses in this antibiotic stewardship effort has been limited to routine discharge of nursing duties in the care of these infants.
Nurses in the mother-baby unit are unique in their responsibility for providing clinical care to the mother-baby dyad. With the expanding role of nurses in clinical decision making and in the care of their patients, it is imperative that we achieve greater involvement of nurses as important stakeholders in hospital-wide stewardship efforts. Because these nurses have many touch points with the newborns over the course of their shift, their observations are critically important for effective SRC implementation. Changes in clinical status as first recognized by nurses can change the recommendations of the SRC, including the need for laboratory evaluation or the empiric initiation of antibiotics.
Many factors can influence less nursing involvement in ASPs in the mother-baby unit compared to the NICU. It therefore becomes important to identify and address barriers to nursing engagement in this area of the hospital for antibiotic stewardship efforts and promote shared decision making among team members by implementing nurse-led sepsis risk assessment. Hence, we undertook this cross-sectional, survey-based study to assess nurses’ attitude and perception and to identify knowledge gaps in the implementation of nurse-led assessment of early-onset neonatal sepsis risk using the SRC in the mother-baby unit as part of ASP.
Methods
Research Setting and Participants:
This cross-sectional study utilized a researcher-developed, web-based survey of nurses who take care of newborn infants admitted after birth to the mother-baby unit of a safety-net maternity service in NE Florida. This hospital serves as the primary teaching site for Pediatric residents for their NBN and NICU rotations. The nurse managers of the mother-baby unit distributed the survey link to the full-time nursing staff via e-mail. This survey was preceded by educational sessions of mother-baby nurses on antibiotic stewardship program in the NICU and NBN and implementation of the SRC to replace the previous sepsis evaluation and management protocol based on AAP/CDC’s 2010 early onset sepsis practice guidelines.
Study Design:
This single-center study used a descriptive, cross-sectional survey-based design. A multi-disciplinary team consisting of physicians, advance practice providers, nurse educators, pharmacists, charge nurses and nurse representatives designed survey questions and independently validated by three reviewers to elicit nursing awareness of our antibiotic stewardship efforts including clinical application of the SRC and to identify gaps in knowledge and implementation challenges. The antibiotic stewardship program was a part of Vermont Oxford Network’s (VON) ‘Choosing wisely’ antibiotic stewardship campaign. The survey consisted mostly of multiple-choice questions but included several open-ended questions. Multiple choice questions allowed more than one response to some questions. We placed open-ended questions at the end of the survey that invited nurses to suggest interventions that would help them implement the nurse-led sepsis risk evaluation using the SRC. The survey did not request any personal information from the respondent so that responses were truly anonymous. Nurse managers sent periodic reminders to maximize participation. Nurse managers also shared serial increases in response rate with nursing staff during unit meetings.
The institutional review board of the institution approved this study as an element of the VON” Choosing antibiotics wisely” quality initiative for antibiotic stewardship.
Inclusion Criteria:
We solicited responses from all full-time nurses in the mother-baby unit.
Exclusion Criteria:
Part-time or traveling nurses were excluded from the study.
Data Analysis:
We analyzed survey data using descriptive statistics. Means (standard deviation) and percentages of various survey questions were calculated as appropriate. For open-ended question, we used thematic content analysis method to categorize recurring themes. Statistical software, SAS® was used for analyzing data.
Results
We surveyed 230 full-time registered nurses (RNs) in the mother-baby unit in three cycles. The initial response rate was low but improved to 89% (205/230) after periodic reminders to the team.
100% of respondents agreed that the implementation of the SRC has led to a reduction in empiric antibiotic use in well-appearing newborns. All respondents also agreed that use of the SRC represented an improvement over the previously used sepsis evaluation algorithm (based on 2010 CDC/AAP recommendations).
Most survey takers demonstrated good understanding of harmful effects of unnecessary antibiotics. 89% responded that antibiotics caused a reduction in healthy bacteria in the gut and increased the risk of bacterial resistance while 11% recognized alternation of gut flora
Questions that assessed nursing perception of nationwide efforts to establish nurse-initiated use of the SRC revealed that 66% of respondents favored greater nursing involvement in patient treatment but also noted the extra work burden. No respondents favored greater independence in patient management or judged that greater job satisfaction might derive from greater decision-making power.
33% of nurses responded that nurse-initiated use of the SRC should or could not be implemented in MB unit while 67% responded that mother-baby nurses could implement the SRC if they had adequate education and orientation. In a question asking nurses to identify the most difficult task associated with use of the SRC, 205 responses (100%) were in favor of the clinical assessment of infant as normal, equivocal or sick as being the most difficult task and commented in the free text box that with adequate education and orientation the initial reluctance will go away as the calculator gathers information from the EMR that is already available to them.
56% of nurses responded that the optimal way to implement nurse-initiated SRC was in close partnership with the physician and practitioner team. 44% of nurses did not wish to be participate in a nurse-initiated SRC.
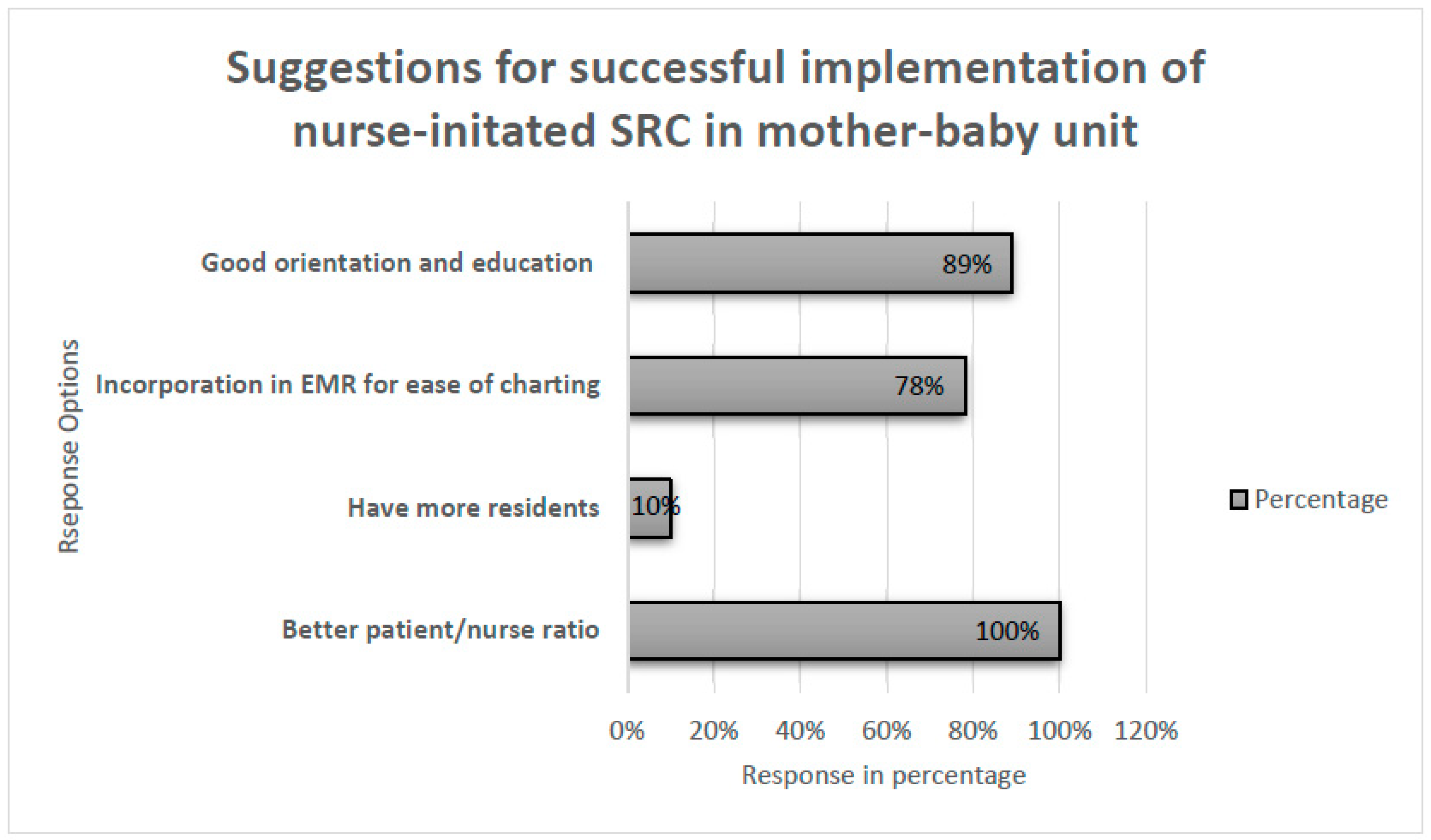
We sought input on factors that might facilitate nursing adoption of the SRC in the mother-baby unit. 100% of respondents suggested a greater nurse to patient ratio and 88% of respondents suggested a targeted program of education and orientation (
Figure 2).
42% nurses were less than 30 years of age and 30% of today cohort was <5 years of completing training. There was no significant correlation to age (p=0.15) or experience (p=0.28) however, greater number of fresh grads (< 5 years) were interested in championing this effort.
Discussion
We undertook this qualitative, cross-sectional, survey-based study to evaluate nurses’ attitudes and perception and to identify knowledge gaps in the implementation of nurse-initiated SRC for the evaluation and management of early onset sepsis in newborns ≥ 35 weeks’ gestational age admitted to the mother-baby unit in our safety-net maternity service. The responsibilities of a mother-baby nurse far exceed just provision of medical care to a mother and her newborn baby together as a couplet. They form the primary support for the new mother during this vulnerable post-partum period and play a very important role in providing initial education in the care of infants to new parents. With frequent close interaction with the mother-baby couplet, the mother-baby nurse can play a central and clinically important role in initiating and updating the sepsis risk calculator which requires initial entry of objective perinatal factors known at the time of infant’s birth into the calculator and specification of the infant’s clinical status. The algorithm provides a quantitative risk estimate with recommendations for evaluation and treatment based on the risk.
In our survey, all respondents recognized that the use of the SRC represented an improvement over the prior 2010 CDC/AAP algorithm that had been based on the presence of categorical risk factors. Nurses also recognized that there has been a decrease in antibiotic use in well-appearing infants with the use of SRC. But in regard to implementation, the responses favored good education and orientation of nurses to SRC as well as implementation in close partnership with the clinical team. In identifying the barriers, nurses felt that amelioration of inadequate nursing-patient ratios, deficiencies in training and education, and lack of incorporation of the SRC into the EMR represented opportunities for achieving greater buy-in.
In some birthing centers, nurses have stepped up their role and call the physician if infant has a greater than normal risk for developing early onset sepsis based on their use of the SRC. However, reports from such units are few.
Other centers have investigated the role of nursing in antibiotic stewardship efforts. Van Huizen et al did a scoping review to investigate nurse’s role in ASP related to judicious use of antibiotics. These investigators found that there was limited research in terms of policies and best practice guidelines when it came to the role of nursing in preparation, administration, and disposal of intravenous antibiotics. They emphasized that nurses’ role in ASP should be supported through education and evidence-based guidelines [
11]. Kirby et al, in their multisite study in 2020, described the barriers to integrating nurses’ input in ASP as lack of knowledge, professional jurisdictions and social dynamics [
12]. Another study assessing pediatric nurses’ perception of their role in ASP details that nurses affirm that their role is crucial to antimicrobial stewardship. Similar to the findings of our study, they stressed the need for additional education and engagement in antibiotic stewardship efforts [
13,
14].
Our study has some shortcomings. Our single center data may not accurately represent the full cadre of full-time nurses. We also did not rigorously evaluate the validity and reliability of the survey questions. In a 2021 policy statement, the AAP Committee on Infectious Disease and Pediatric Infectious Disease Society clearly recognized that nurses can be valuable partners in antibiotic stewardship efforts and advocate for their active integration into these efforts [
15]. Our study is consistent with the recommendations of the policy statement and underlines the key role mother-baby nurses can play in the successful implementation of nurse-led antibiotic stewardship efforts in newborn nurseries and mother-baby units in the setting of adequate education and support from hospital leadership. Each institution should better define the nature and scope of nurse’s engagement in these stewardship efforts and tailor them to the resources and missions of the different work-areas of the hospital.
Author Contributions
Sfurti Nath: Conceptualized and designed the study, collected data, performed data analysis, drafted the manuscript and approved the submitted version. Rana Alissa: Contributed in conceptualization and designing of the study, edited the manuscript and approved the submitted version. Mark Hudak: Provided critical input to the study, edited the manuscript and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- American Nurses Association; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Redefining the antibiotic stewardship team: recommendations from the American Nurses Association/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention workgroup on the role of registered nurses in hospital antibiotic stewardship practices. White paper. https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/healthcare/pdfs/ANA-CDC-whitepaper.pdf. Published 2017. Accessed Aug 18, 2021.
- The White House. National action plan for combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria, 2015. Available at: https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/docs/national_action_plan_for_combating_antibotic-resistant_bacteria.pdf. Accessed Aug 31,2023.
- CDC. Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2019. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/hospital.html. Accessed Aug 31,2023.
- Tamar F. Barlam, Sara E. Cosgrove, Lilian M. Abbo, Conan MacDougall, Audrey N. Schuetz, Edward J. Septimus, Arjun Srinivasan, Timothy H. Dellit, Yngve T. Falck-Ytter, Neil O. Fishman, Cindy W. Hamilton, Timothy C. Jenkins, Pamela A. Lipsett, Preeti N. Malani, Larissa S. May, Gregory J. Moran, Melinda M. Neuhauser, Jason G. Newland, Christopher A. Ohl, Matthew H. Samore, Susan K. Seo, Kavita K. Trivedi, Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 62, Issue 10, 15 May 2016, Pages e51–e77. [CrossRef]
- Monsees E, Popejoy L, Jackson MA, Lee B, Goldman J. Integrating staff nurses in antibiotic stewardship: Opportunities and barriers. Am J Infect Control. 2018 Jul;46(7):737-742. Epub 2018 May 2. PMID: 29729830. [CrossRef]
- Carter EJ, Greendyke WG, Furuya EY, Srinivasan A, Shelley AN, Bothra A, Saiman L, Larson EL. Exploring the nurses' role in antibiotic stewardship: A multisite qualitative study of nurses and infection preventionists. Am J Infect Control. 2018 May;46(5):492-497. Epub 2018 Feb 1. PMID: 29395509; PMCID: PMC6495548. [CrossRef]
- McGregor JC, Fitzpatrick MA, Suda KJ. Expanding Antimicrobial Stewardship Through Quality Improvement. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e211072. [CrossRef]
- Ho T, Dukhovny D, Zupancic JA, Goldmann DA, Horbar JD, Pursley DM. Choosing Wisely in Newborn Medicine: Five Opportunities to Increase Value. Pediatrics. 2015 Aug;136(2):e482-9. Epub 2015 Jul 20. PMID: 26195536. [CrossRef]
- Dukhovny D, Buus-Frank ME, Edwards EM, Ho T, Morrow KA, Srinivasan A, Pollock DA, Zupancic JAF, Pursley DM, Goldmann D, Puopolo KM, Soll RF, Horbar JD. A Collaborative Multicenter QI Initiative to Improve Antibiotic Stewardship in Newborns. Pediatrics. 2019 Dec; 144(6):e20190589. Epub 2019 Nov 1. PMID: 31676682. [CrossRef]
- Shukla S, Cortez J, Renfro B, Makker K, Timmons C, Nandula PS, Hazboun R, Dababneh R, Hoopes C, VanRavestein J, McCarter Y, Middlebrooks M, Ingyinn M, Alvarez A, Hudak ML. Charge Nurses Taking Charge, Challenging the Culture of Culture-Negative Sepsis, and Preventing Central-Line Infections to Reduce NICU Antibiotic Usage. Am J Perinatol. 2020 Nov 3. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33142341. [CrossRef]
- van Huizen P, Kuhn L, Russo PL, Connell CJ. The nurses' role in antimicrobial stewardship: A scoping review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Jan;113:103772. Epub 2020 Sep 9. PMID: 33080476. [CrossRef]
- Kirby E, Broom A, Overton K, Kenny K, Post JJ, Broom J. Reconsidering the nursing role in antimicrobial stewardship: a multisite qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(10):e042321. Published 2020 Oct 29. [CrossRef]
- Rana F. Hamdy, Wayne Neal, Laura Nicholson, Emily Ansusinha, Simmy King, Pediatric Nurses' Perceptions of Their Role in Antimicrobial Stewardship: A Focus Group Study, Journal of Pediatric Nursing, Volume 48, 2019,.Pages 10-17, ISSN 0882-5963. [CrossRef]
- Gotterson F, Buising K, Manias E. Nurse role and contribution to antimicrobial stewardship: An integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 May;117:103787. Epub 2020 Oct 8. PMID: 33647845. [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey S Gerber, Mary Anne Jackson, Pranita D Tamma, Theoklis E Zaoutis, AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases and Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, Policy Statement: Antibiotic Stewardship in Pediatrics, Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, Volume 10, Issue 5, May 2021, Pages 641–649. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).