1. Introduction
Cratylia argentea (Cratylia) is a leguminous shrub species, native from the Brazilian Savanna (
Cerrado) [
1] but also found in other biomes such as the Amazon and
Caatinga [
2]. Some important characteristics of this leguminous shrub are its tolerance to acidic soils with high aluminum saturation and low fertility [
3], as well as its great palatability for ruminants [
4]. Cratylia stands out as a forage source with great potential for tropical areas with extended dry seasons [
5]. Cratylia also has a vigorous root development and a symbiotic capacity of biological nitrogen fixation (BNF). This enables the maintenance of green leaves over water deficient periods [
6] and could be an alternative to expensive protein concentrates for livestock [
7].
Studies have found advantageous animal performance [
8,
9] and optimal nutritive value [
10,
11] with Cratylia. Braga et al. [
11] evaluated the ruminal degradability of
Cratylia argentea, Flemingia macrophylla and
Stylosanthes guianensis harvested at 55 and 75 days and fed to growing sheep. The results showed a greater performance for sheep fed with
C. argentea and
F. macrophylla, which were recommended as protein banks and supplements for ruminants. The same study showed the bromatological composition of Cratylia samples harvested at 55 days, which had DM (dry matter), CP (crude protein), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), and acid detergent fiber (ADF) contents of 19.32%, 27.6%, 63.3%, and 55.6%, respectively. Andersson et al. [
10] assessed the bromatological composition parameters such as CP, ADF, and NDF of 38 Cratylia accessions harvested at 8 weeks of regrowth and reported mean CP of 20.6% and 22%, NDF of 44.5% and 46.2% and ADF of 26.6% and 30.6% for the rainy and dry season, respectively.
Reference methods for chemical analysis of forages is essential for the development of adjusted livestock diets and the inclusion of necessary feed supplements. Wet chemistry methods are typically used to analyze the chemical composition of biomass [
12]. However, this method is time-consuming, labor-intensive, expensive, and require many reagents [
13]. In addition, the wet chemical method produces considerable chemical waste, decreasing the analysis's environmental sustainability [
14].
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a technology that has successfully been used to predict the quality parameters of different forage crops [
15,
16,
17]. This method is considered fast, low cost, and minimizes labor requirement [
18] once accurate prediction models have been developed. With adjusted algorithms for the chemical parameters of Cratylia, the quality variation due to plant architecture, climate and season could be monitored within a lower timeframe [
19]. Given that, a greater frequency of sample analysis, according to changes in plants’ chemical composition, could result in adjusted livestock diets within a lower timeframe [
20].
To employ the NIRS for laboratory analysis, the development of multivariate calibration models is required. Thus, standardized laboratory procedure such as destructive harvest, drying, grinding, and bench analysis is still needed [
21].
Unfortunately, NIRS prediction models have not been developed for Cratylia argentea and are very limited for other leguminous shrubs. To date, there has been no report using NIRS to predict the chemical composition in dried C. argentea samples.
This study aims to evaluate the feasibility of using NIRS and chemometrics methods to predict concentrations of DM, CP, ADF, and NDF of C. argentea based on NIR spectroscopy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site description
The study was conducted at the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation – Embrapa Maize and Sorghum (Sete Lagoas, Minas Gerais, Brazil; 19º28′ S; 44º15′W, at 732 m altitude), where the Cratylia was planted and the NIR equipment was located. Cratylia was planted in a region with a Cwa climate type according to the Köppen classification system, i.e., savanna climate, with dry winters (May to September) and humid-rainy summers (October to April) [
23]. The average annual temperature is 22.9 °C, with 24.4 °C in the wet season and 22 °C for the dry season and an average annual precipitation of 1340 mm [
24].
A soil sample was collected on March 28th, 2013. Soils corresponded to Latossolos (
Oxisols) category [
22], with a pH 5.5, H+Al (7.11 dm
3), OM (3.44 dag kg
-1), NO3-N (18 mg kg
-1), P (2.18 mg kg
-1), CEC (10.23 dm
3), Ca (2.73), Mg (0.28) and K (39.26 mg kg
-1).
2.2. Cratylia cultivation
On December 11th, 2009, Cratylia seedlings were transplanted from a greenhouse to a 450 m2 experimental site at Embrapa Maize and Sorghum. The seedlings were 55 days old and planted in burrows spaced by 0,5 m in dual rows of 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 m, which was equivalent to 20,000, 10,000, 6,667, 5,000, and 4,000 plants ha-1, respectively. Several research was conducted in the area since its establishment and no fertilization was made in the area during this time.
The area was managed with a recurrent harvest. At the beginning of the current research, on July 20th, 2021, Cratylia plots and inter rows were mowed to establish uniform regrowth and weed control, respectively. The destructive harvest for determination of agronomic parameters left a 50 cm stubble height and the collected material were composed of leaves and stems that were smaller than 5 mm, which was considered the Edible Feed Fraction [
25]. Each harvest happened at 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, and 126 days of regrowth on February 2nd, July 10th, August 7th of 2021, and January 9th, and April 14th of 2022, respectively. The goal with different harvest dates was to create different maturity levels and increase the robustness of the model. The samples were harvested with a Gardening scissor (Kotto, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.4. Research material and preparation
The samples were packed into paper bags and oven dried for 72 hours at 55°C. Subsequently, samples were ground in a Wiley mill (Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ, USA) to pass a 1 mm screen for wet chemical laboratory analysis of DM, CP, NDF, and ADF. The wet chemical analysis for DM was determined based on [
26] methodology. Crude protein was determined based on the Kjeldahl method [
27]. The neutral detergent fiber was determined based on [
28]. The ADF was determined based on [
29]. For NIRS spectra collection 15 g of milled Cratylia were placed on Petri dishes of borosilicate to obtain the spectrum of each sample in triplicate. The sample spectra were obtained with the NIRFlex 500 (Buchi Labortechnik, Flawil, Switzerland) in the region of 1,000-2,500 nm (4,000 to 10,000 cm
-1) at a resolution of 32 scans per spectra [
30] and corrected against the background spectrum which was performed routinely.
2.5. Model development
A total of 155 samples were used, where 107 were employed to construct the calibration model with the spectral data. For external validation model 48 samples of the Cratylia were used to predict the chemical properties (DM, CP, ADF, and NDF). Thus, the Kennard-Stone algorithm ensures the most representative samples are in the calibration set [
31]. The model performance was assessed on the external validation dataset.
The spectral data were preprocessed using standard normal variate (SNV) and the Savitzky–Golay first derivative method to eliminate variations such as baseline shifts and scattering of the light. The final preprocessed spectral data were mean centered before partial least square (PLS) analysis. All models were internally and externally validated. The internal validation was based on full cross-validation (CV) using the random method.
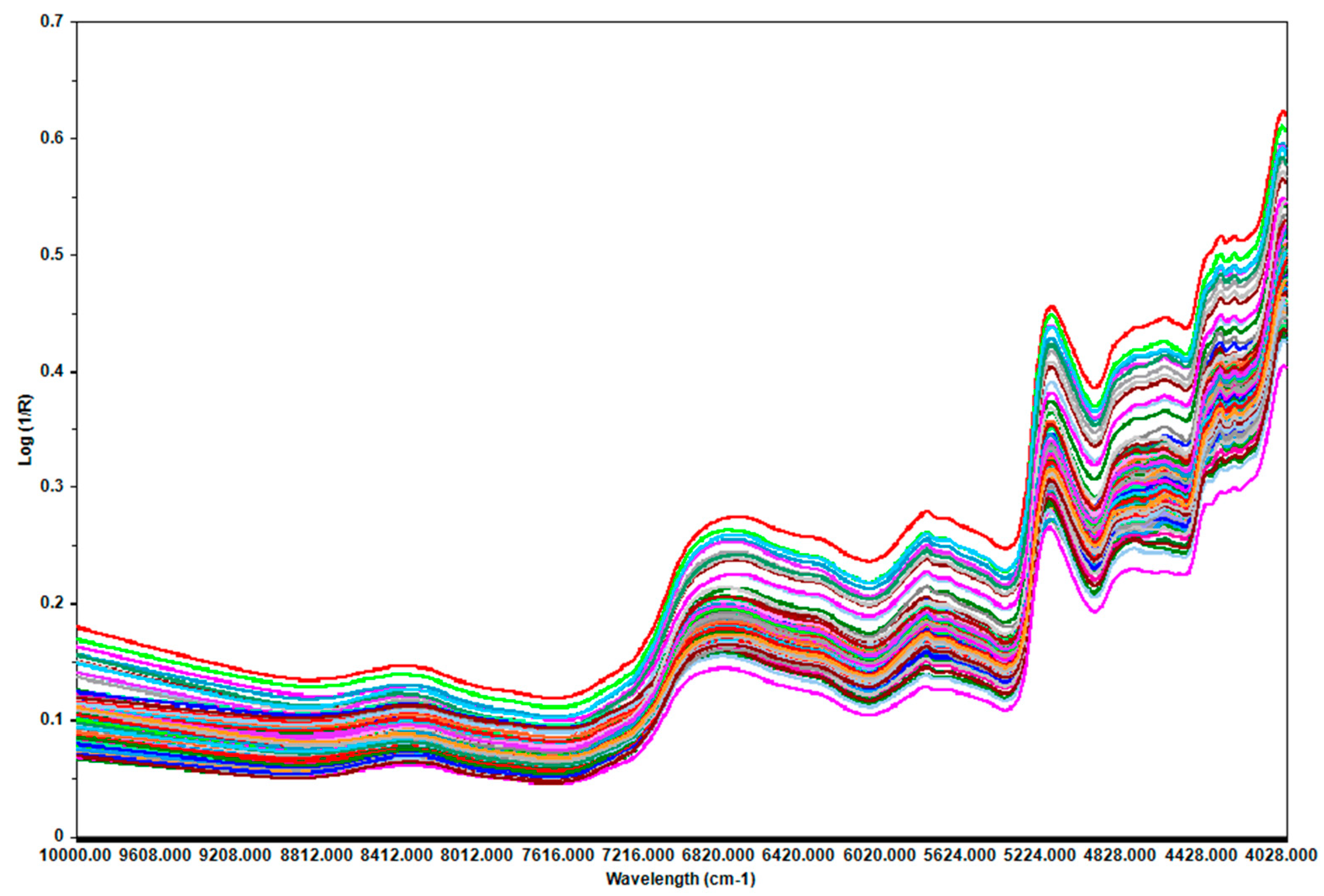
The average spectrum of three measurements (
Figure 1) was used as the final spectrum of each sample to assess the potential of prediction NIRS. The best models (having a small number of latent variables, small RMSECV, high R2C, and better predictive ability) were obtained using the PLS algorithm. Few outliers were detected based on leverage and studentized residuals and were removed.
2.6. Model evaluation and Statistical analysis
To test the robustness of the PLS models, PLS regression was cross-validated using the leave-one-out method, where a single sample is removed, and the model is rebuilt without the sample. The best calibration model between the chemical reference value and NIRS data was evaluated based on the highest coefficient of determination (R2c) and smallest root mean square error in calibration (RMSEC) and in external validation (R2p, RMSEP), respectively. The RMSEC, which suggests information about the adjustment of the model to the calibration data, was calculated considering the number of samples, the results of the reference analysis, and the estimated results by the NIRS model. The goodness and accuracy of models were tested using the residual prediction deviation (RPD) calculated, according to Williams and Norris [
32], as the ratio of the standard deviation of reference values to the RMSEC.
The means of the observed and NIRS-predicted datasets were compared using a student’s t-test to determine significance on a 5% level using RBio software [
33]. For CP, NDF, ADF, and DM the models were produced that predicted concentrations on a DM basis.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. General
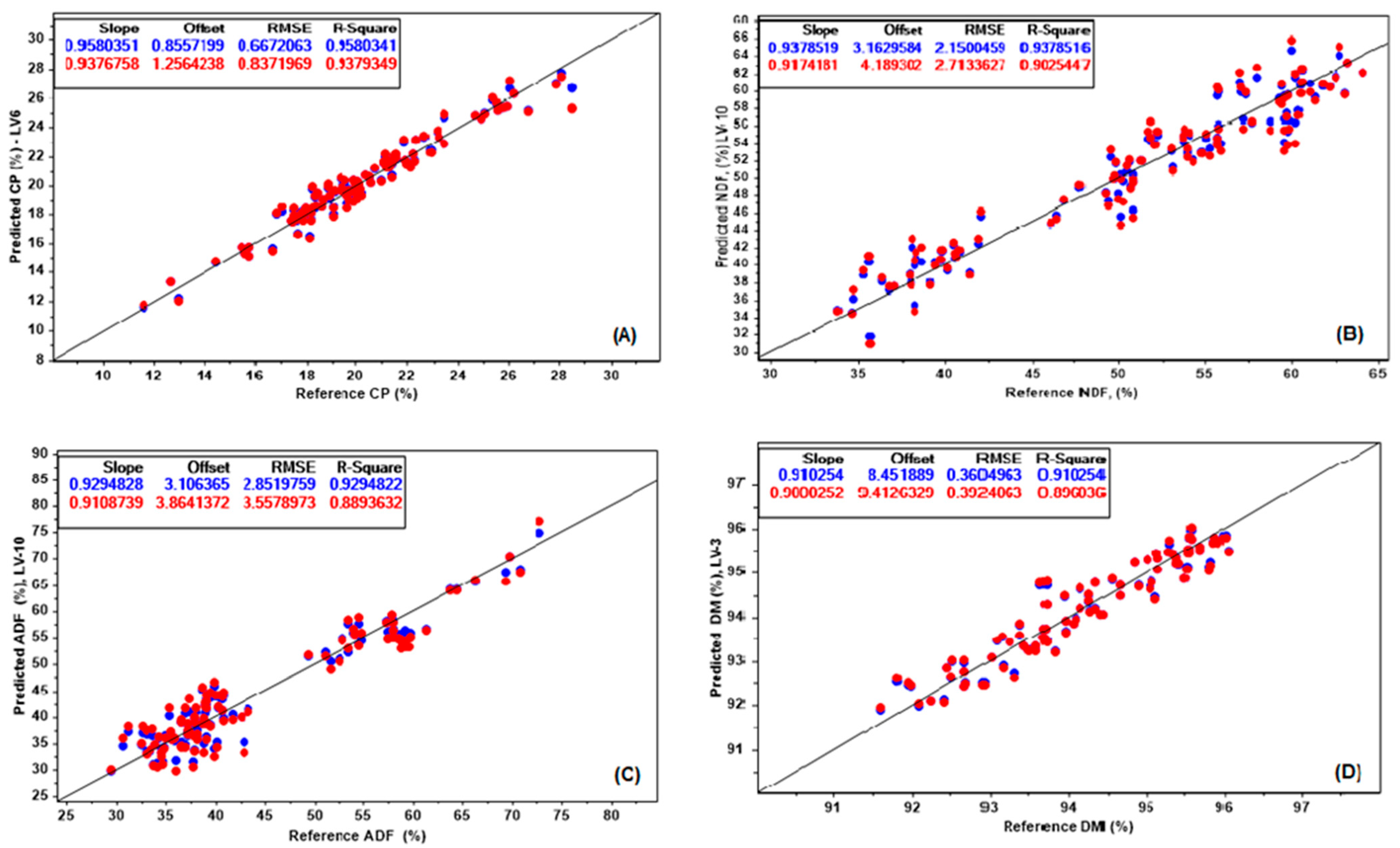
The wide variation within the evaluated chemical properties (CP, NDF, ADF, and DM) were used to develop NIRS calibration and prediction models, based on NIRS and chemometric analysis. The calibration and validation results of NIRS for chemical parameters of Cratylia are shown in
Table 1 and
Figure 2.
3.2. Calibration and validation: R2, RMSEC and RMSEP
The RMSEC values were 0.66, 2.15, 2.85, and 0.36 while the RMSEP was 0.83, 2.71, 3.55, and 0.39, for CP, NDF, ADF, and DM models, respectively (
Figure 2). The results from the coefficient of determination (R
2) for calibration (R
2cal) and validation (R
2val) also contributed to demonstrating the predictive ability of the evaluated models to estimate the chemical parameters. The R
2 results for calibration were 0.95, 0.93, 0.92, and 0.91 whereas the results for validation were 0.93, 0.90, 0.88, and 0.89, for CP, NDF, ADF, and DM, respectively. Williams et al. [
34] determined that R
2 results between 0.66 to 0.81 are considered
approximate, 0.82 to 0.90,
good, and above 0.91,
excellent. Based on the calibration results in this research, CP, NDF, ADF and DM, fall in the excellent category. Nevertheless, while the validation results were considered
excellent for CP and
good for ADF, NDF and DM. Even though the R
2val was lower on NDF, ADF and DM, the results were still positive. In all, variables led to low relative RMSEP (<10% of the observed mean), and no significant difference between the observed and predicted means (
Table 2).
3.3. Ratio of Performance to Deviation
The RPD results were higher than 3.0 for all the chemical properties evaluated (
Table 2). This ratifies the accuracy and good predictive ability these models showed in external validation. Based on the literature, RPD equations greater than 2.4 are
desirable, and equations lower than 1.5, are
unusable [
32]. The RPD measures the strength of the relationship between the values of a constituent and the error of the results predicted by NIRS [
35]. Thus, the greater the RPD, the lower the predictive error [
36]. The RPD results obtained were 4.8, 4,0, 3.8, and 3.4 for CP, NDF, ADF, and DM models, respectively. Thus, the results were considered
excellent [
34] for all the models developed.
Mazabel et al. [
37] built a chemometric model from
Brachiaria humidicola and reported an RPD of 2.56 for CP in Colombia. The result was lower than other evaluated parameters such as ADF (4.4), NDF (3.62) and IVDMD (3.63). However, considered
desirable, based on Williams and Norris [
32] scale. The authors associated the lower prediction with a smaller size of samples (
n = 20) used for external validation. Nevertheless, the overall results were positive.
3.4. External Cross-Validation
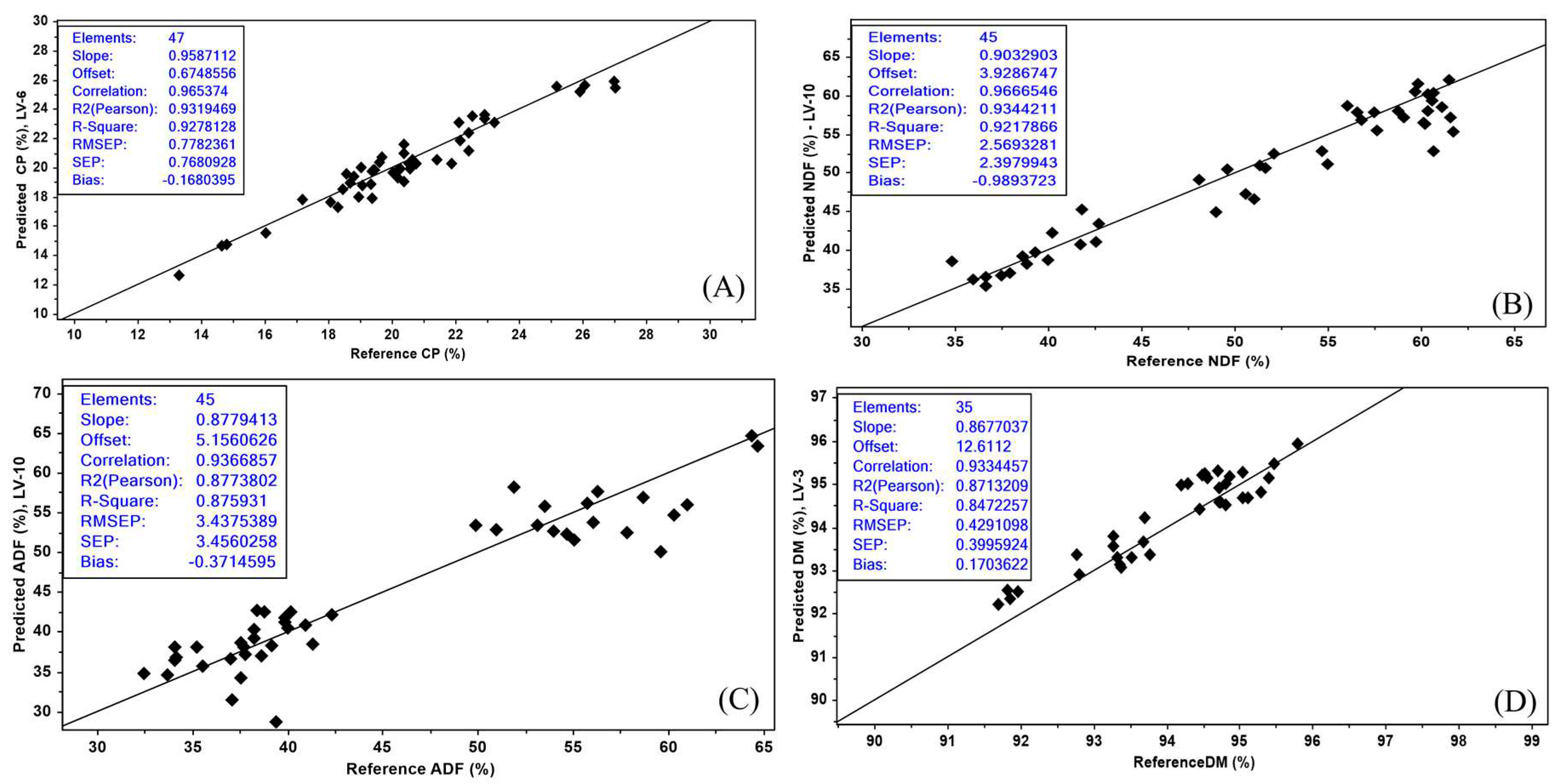
The external validation for CP showed an R
2 (0.92) and RMSEP of 0.77 for (
Figure 3A). It is important to reemphasize that CP showed the highest RPD (
Table 2), R
2 (cal and val) and second lowest RMSEC and RMSEP (
Table 1,
Figure 2A) among the four evaluated chemical properties. A similar characteristic was observed by Norman et al. [
38] when evaluating 102 forage species in Australia. The authors associated better results for CP with the fact of having different plant biotypes within the tested model. This was similar to the current research since the Cratylia plant materials used did not go through any breeding process, therefore, had a high genetic variability, which was visually observed in the field. Andueza et al. [
39] also showed an increased predictive capacity of CP when evaluating plant materials with greater diversity in France (
n = 1034).
The NDF had an external validation R
2 of 0.92 and RMSEP of 2.56 (
Figure 3B). Norman et al. [
39] found similar R
2 (0.94) and RPD (3.9) when evaluating annual legumes. The same research observed an R
2 (0.96) and RPD (5.8) for ADF. Although the R
2 results for ADF (0.87) and RMSEP (3.43) (
Figure 3C) in our research were a little lower for external validation, the current results fall in the category of
good and
excellent [
34] for NDF and ADF, respectively. Serrano et al. [
40] found external validation results with R
2 (0.91) and RPD (3.48) for NDF, and R
2 (0.93) and RPD (4.01) for CP, when evaluating several pasture mixes (legumes and grasses) in Portugal. Both research work mentioned above aligns with the current results, supporting our findings.
Regarding the external validation in DM, the R
2 result was 0.84 and RMSEP was 0.42 (
Figure 3D), considered in the
good category of William’s scale [
34]. The increased dispersion might be related to the lower number of samples used (
n = 35), compared to the other chemical parameters (
n = 45 ~ 47). Therefore, a lower plant variability was covered. Andrade Ribeiro et al. [
41] evaluated the ability of NIRS to predict DM of
Brachiaria brizantha cv. Piatã grass and found an R
2val of 0.75 in Southern Brazil. This result was below the R
2val for the other chemical parameters evaluated such as CP, ADF, and NDF, which were 0.94, 0.85, and 0.92, respectively. Beside a low R
2 for DM, the RPD were also lower than our research with values of 2.01, 3.98, 3.49, and 2.56 for DM, CP, NDF and ADF, respectively. The authors associated the lower prediction capacity of the model with a lack of uniformity of the grinded samples and the number of samples (
n = 84). Oluk et al. [
42] found an R
2 of 0.76 when validating NIRS models to predict DM of Dalisgrass (
Paspalum dilatatum) in Turkey. The RPD was somewhat lower (2.15) at validation and 2.66 at calibration. The authors found the same R
2 (0.76) for DM, when calibrating the model. Based on Williams et al. [
34], this DM results would be considered
approximate.
Several factors such as laboratory error, plant stage, maturity, and edaphoclimatic conditions play an important role in the development of NIRS models. The low error involved in the chemistry analysis and plant variability (genetic and of different growth stages) of the harvested material might have been the main factors leading the success of the current models.
5. Conclusions
The obtained calibration models to CP, NDF, ADF, and DM showed validation errors like those obtained for wet chemistry method, indicating the suitability of NIRS and reliability of our developed models to predict the chemical properties of Cratylia argentea. Nevertheless, the addition of more samples should improve the robustness of the model.
These results could assist livestock producers to expediate and cheapen the process of estimating the nutritive value of Cratylia for cattle diet adjustment, as well as for researchers and breeding programs to assess chemical parameters of Cratylia in a timely manner.
Future research may evaluate the performance of current equations in different Cratylia cultivars to validate and establish new prediction models.
Author Contributions
Writing – original draft, L.F.A; Visualization, L.F.A., E.P.B., L.C.C.; Project administration, L.F.A.; Investigation, L.F.A., L.C.C., E.B., W.J.R.M.; Supervision, A.M.Q.L., W.J.R.M., E.P.B., K.T.S., E.A.S.; Conceptualization, A.M.Q.L., L.C.C.; Resources, A.M.Q.L., W.J.R.M., K.T.S.; Writing – review & editing, A.M.Q.L., W.J.R.M., M.L.F.S., J.E.R.; Data Curation, L.C.C., W.J.R.M.; Methodology, M.L.F.S.; Formal analysis, M.L.F.S.; Software; M.L.F.S. Funding acquisition, A.M.Q.L, J.E.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel of Education (CAPES, Brazil nº 88887.667823/2022-00) and the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research (FFAR, United States nº DSnew-0000000028). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The authors would like to also acknowledge the funding agencies National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and Minas Gerais State Agency for Research and Development – (FAPEMIG).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Queiroz, L. P. O gênero Cratylia Martius ex Bentham (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae, Phaseoleae): revisão taxonômica e aspectos biológicos 1991, Masters Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, 129p.
- Queiroz, L.P.; Coradin, L. Biogeografía de Cratylia en áreas prioritarias para Coleta. In: E.A. Pizarro and L. Coradin (eds), Memorias del taller Potencial del género Cratylia como leguminosa forrajera, EMBRAPA/Cenargen/CPAC/CIAT 1996, 19–20, Brasilia, Brasil, 1–12.
- Argel, P.; Gonzalez, J.; Lobo, M. Cratylia argentea: A Shrub Legume for Livestock Production in the Tropics, in: Holmann, F., Lascano, C. (Eds.), Feeding Systems with Legumes to Intensify Dairy Farms. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical; Tropileche Consortium; International Livestock Research Institute 2004, Cali, Colombia, p. 164.
- Hohnwald, S.; Trautwein, J.; Camarão, A. P.; Wollny, C. B. Relative palatability and growth performance of capoeira species as supplementary forages in the NE-amazon. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2016, 218, 107–115. [CrossRef]
- Raaflaub, M.; Lascano, C.E. The effect of wilting and drying on intake rate and acceptability by sheep of the shrub legume Cratylia argentea. Tropical Grasslands 1995, 29, 97–101.
- Matrangolo, W.J.; da Silva, I.H.; Almeida, L.G.; Cruz, S.B.; Malta, P.; Gomes, S.X.; Aspectos ecológicos de Cratylia argentea na região central de Minas Gerais. In: Embrapa Milho e Sorgo. Cadernos de Agroecologia 2018, v. 13, n.1.
- Gonzalez, J.; Di Palma, M.V.L.; Acuña, V.R.; Argel, P.J.; Hidalgo, C.A.; Romero, F.; Utilization of the shrub Cratylia argentea cv. Veraniega as protein supplement for milking cows during the dry season in Costa Rica, in: Ibrahim, M. (Ed.), International Symposium on Silvopastoral Systems: Second Congress on Agroforestry and Livestock Production in Latin America. CATIE/IICA 2001. Costa Rica, p. 478.
- Silva, M.E.; Araújo, J.V.; Silveira, W.F.; Carvalho, L.M.; Ribeiro, R.R.; Effectiveness of cratylia argentea as an animal feed supplement in the control of gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep. Semina: Ciências Agrárias 2018, 39, 657. [CrossRef]
- Valles-de la Mora, B.; Castillo-Gallegos, E.; Alonso-Díaz, M.; Ocaña-Zavaleta, E.; Jarillo-Rodríguez, J. Live-weight gains of Holstein × zebu heifers grazing a Cratylia argentea/Toledo-grass (Brachiaria Brizantha) association in the mexican humid tropics. Agroforestry Systems 2016, 91, 1057–1068. [CrossRef]
- ANDERSSON, M. S.; PETERS, M.; SCHULTZE-KRAFT, R.; FRANCO, L. H.; LASCANO, C. E. Phenological, agronomic and forage quality diversity among germplasm accessions of the tropical legume shrub cratylia argentea. The Journal of Agricultural Science 2006, 144, 237–248. [CrossRef]
- Braga, E.; Braga Filho, E.; Silva, J.A.; Faturi, C.; Domingues, F.N.; Lourenço Júnior, J.D. Ruminal degradability of tropical leguminous plants from Eastern Amazonia. Semina: Ciências Agrárias 2018, 39, 845. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-Y.; Lee, E.-J.; Ban, S.-E.; Lee, J.-W. Near infrared spectroscopy model for analyzing chemical composition of biomass subjected to Fenton oxidation and hydrothermal treatment. Renewable Energy 2021, 172, 1341–1350. [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, C. C.; Assis, C.; Simeone, M. L.; Sena, M. M. Use of near-infrared spectroscopy, partial least-squares, and ordered predictors selection to predict four quality parameters of sweet sorghum juice used to produce bioethanol. Energy & Fuels 2016, 30, 4137–4144. [CrossRef]
- Moros, J.; Garrigues, S.; Guardia, M. de Vibrational Spectroscopy provides a green tool for multi-component analysis. Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2010, 29, 578–591.
- Norris, K. H.; Barnes, R. F.; Moore, J. E.; Shenk, J. S. Predicting forage quality by infrared replectance spectroscopy. Journal of Animal Science 1976, 43, 889–897. [CrossRef]
- Deinum, B.; Struik, P. C. Genetic variation in digestibility of forage maize (Zea mays L.) and its estimation by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS). an analysis. Euphytica 1989, 42, 89–98. [CrossRef]
- Harris, P. A.; Nelson, S.; Carslake, H. B.; Argo, C. McG.; Wolf, R.; Fabri, F. B.; Brolsma, K. M.; van Oostrum, M. J.; Ellis, A. D. Comparison of NIRS and wet chemistry methods for the nutritional analysis of Haylages for horses. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 2018, 71, 13–20. [CrossRef]
- Tibola, C.S.; de Miranda, M.Z.; Guarienti, E.M. Avaliação de Parâmetros de Qualidade de Trigo por Espectroscopia no Infravermelho Próximo. In: Tibola, C.S.; de Medeiros, E.P.; Simeone, M.L.F. (Eds.) Espectroscopia No Infravermelho Próximo Para Avaliar Indicadores De Qualidade Tecnológica e Contaminantes Em Grãos. Embrapa 2018, Brasília, DF, pp. 1–200.
- Dillon, P. Achieving high dry-matter intake from pasture with grazing dairy cows. In: Elgersma, A.; Dijkstra. J.; Tamminga, S.; editors. Fresh Herb. Dairy cattle key to a Sustain. Food Chain, New York, USA: Springer 2006, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J. M.; Allen, J. D.; Tunnicliffe, R.; Smith, M.; Garnsworthy, P. C. Variation in composition of pre-grazed pasture herbage in the United Kingdom, 2006–2012. Animal Feed Science and Technology 2014, 196, 139–144. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, G.B.; Nogueira, A.R.A.; Olivares, I.R.B.; de Oliveira, M.A. Controle de Qualidade para Espectroscopia no Infravermelho Próximo, in: Tibola, C.S., de Medeiros, E.P., Simeone, M.L.F. (Eds.), Espectroscopia No Infravermelho Próximo Para Avaliar Indicadores De Qualidade Tecnológica e Contaminantes Em Grãos. Embrapa 2018, Brasília, DF, pp. 1–200.
- Santos, H.G., P.K.T. Jacomine, L.H.C. Anjos, V.A. Oliveira, J.F. Lumbreras, M.R. Coelho, J.A. Almeida, J.C. Araujo Filho, J.B. Oliveira, Cunha TJF. Brazilian soil classification system. Embrapa 2018, Brasília, Brazil.
- de Sá Júnior, A.; de Carvalho, L. G.; da Silva, F. F.; de Carvalho Alves, M. Application of the Köppen Classification for climatic zoning in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 2011, 108, 1–7.
- Campos, A.; Silva, B.; Freitas, D.; Fernandes, M. Qualidade Física do Latossolo Vermelho Distrófico Cultivado com Milho https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/203319/1/Circ-253.pdf (accessed Aug 30, 2023).
- Navas Panadero, A., Daza Cárdenas, J.I., Montaña Barrera, V. Desempeño de Bancos Forrajeros de Cratylia argentea (Desv.) kuntze, em suelos degradados em el Departamento de Casanare. Revista de Medicina Veterinaria 2020, 1, 29–42. [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.J.; Queiroz, A.C. Análise de Alimentos: Métodos Químicos e Biológicos, 3 rd. ed 2006, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, MG.
- Official methods of analysis (16th ed.). Association of Official Analytical Chemists 1995, Arlington, VA.
- Van Soest, P. J.; Robertson, J. B.; Lewis, B. A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to Animal Nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J. Collaborative study of acid-detergent fiber and lignin. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists 1973, 56(4), pp.781-784. [CrossRef]
- Neto, M.; Simeone, M. L.; Guimarães, C.; Andrade, H. M.; Queiroz, L.; Simão, E. de P. Predição do Teor de Carbono Total em Solos de Áreas Experimentais de Integração Lavoura- Pecuária por Meio da Espectroscopia NIR https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/953275/predicao-do-teor-de-carbono-total-em-solos-de-areas-experimentais-de-integracao-lavoura-pecuaria-por-meio-da-espectroscopia-nir (accessed Aug 10, 2023).
- Kennard, R.W.; Stone, L.A. Computer Aided Design of Experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.C. Implementation of Near-Infrared Technology. In: Williams, P.C.; Norris, K. Eds. Near-Infrared Technology in the Agricultural and Food Industries, 2nd Edition, American Association of Cereal Chemists 2001, St. Paul, MN, USA, 145-169.
- Bhering, L.L. Rbio: A Tool for Biometric and Statistical Analysis Using the R Platform. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology 2017, v.17: 187-190p. [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Manley, M.; Antoniszyn, J. Near infrared technology: getting the best out of light. PDK Grain 2003, Nanaimo, Canada.
- Williams, P. The RPD statistic: A tutorial note. NIR News 2014, 25, 22–26. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. J.; O’ Brien, B.; O’ Donovan, M.; Condon, T.; Murphy, M. D. A near infrared spectroscopy calibration for the prediction of fresh grass quality on Irish pastures. Information Processing in Agriculture 2022, 9, 243–253.
- Mazabel, J.; Worthington, M.; Castiblanco, V.; Peters, M.; Arango, J. Using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for estimating nutritional quality of brachiaria humidicola in breeding selections. Agrosystems, Geosciences Environment 2020, 3. [CrossRef]
- Norman, H. C.; Hulm, E.; Humphries, A. W.; Hughes, S. J.; Vercoe, P. E. Broad near-infrared spectroscopy calibrations can predict the nutritional value of >100 forage species within the Australian feedbase. Animal Production Science 2020, 60, 1111. [CrossRef]
- Andueza, D.; Picard, F.; Jestin, M.; Andrieu, J.; Baumont, R. NIRS prediction of the feed value of temperate forages: Efficacy of four calibration strategies. Animal 2011, 5, 1002–1013. [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Shahidian, S.; Carapau, Â.; Rato, A. E. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and optical sensors for estimating protein and fiber in dryland Mediterranean Pastures. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 73–91. [CrossRef]
- Andrade Ribeiro, M. C.; Loures Guerra, G.; Cano Serafim, C.; Nóbrega de Carvalho, L.; Galbeiro, S.; Vendrame, P. R.; Monteiro do Carmo, J. P.; Rodrigues Franconere, E. R.; Ferracini, J. G.; do Prado, I. N.; Prado Calixto, O. P.; Mizubuti, I. Y. Prediction models of the nutritional quality of fresh and dry Brachiaria Brizantha cv. Piatã Grass by near infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Animal Research 2023, 51, 193–203.
- Oluk, A. C.; Yucel, H.; Bilgin, F. D.; Serbester, U. Estimation of forage quality by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in dallisgrass, paspalum dilatatum, Poir. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy 2022, 30, 189–196. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).