1. Introduction
This paper describes a 3-level memory model that will be the basis for a new Artificial Intelligence system. The model includes a lower-level structure that stores source data, is Markov-like and unweighted. Then a middle-level ontology is created from 3 phases of aggregating this source information, by transposing from an ensemble to a hierarchy at each level. The ontology is useful for search processes, to find relevant information and it is shown that the aggregating process transposes the information from horizontal set-based sequences to more vertical typed-based clusters. The base memory is essentially neutral, with regards to what it should return, where any weighted constraints or preferences should be sent by the calling module. This therefore allows different weight sets to be imposed on the same linking structure. The success of the ontology typing is open to interpretation, but the author would suggest that when clustering text, the result was types based more on use and context, for example, ‘linking’ with ‘structure’ or ‘provide’ with ‘web,’ for a document describing distributed service-based networks. This allows the system to economise over symbol use, where links to related symbols will be clustered together. Or in a spatial sense, similar patterns would be clustered together. These two levels are essentially statistical and could be created from glial cells, for example.
The author then conjectures that a third memory substrate would be more neural in nature and would include functions or operations to be performed on the data, along with relevant memory information and possibly the operation results. This more cognitive level therefore may be more like the neocortex and will be a part of future work. This paper is concerned with describing the two lower memory structures only. A recent paper [
5] described how intelligence may be derived from internal structure in the brain and how evolution through the insect world may have made use of this. This paper will again try to relate the processes with internal structure and the insect world. Then with the human brain itself, the memory model may explain some of the big questions, like Gestalt and sub-conscious, but only in the context of this model and at a relatively simplistic level.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows: section 2 gives some related work.
Section 3 describes the new memory model, including some test results.
Section 4 shows how the model fits with Gestalt theory, while section 5 shows how it fits with the previous evolution theory. Finally, section 6 gives some conclusions on the work.
2. Related Work
This paper in some ways extends the work done in [
5] and helps to further describe how neural processes may have evolved from the insects to humans. The number 3 is intrinsically linked with the memory architecture and it was also part of the whole cognitive model ([
10] and the ‘New Ideas in Brain Modelling’ papers [
8,
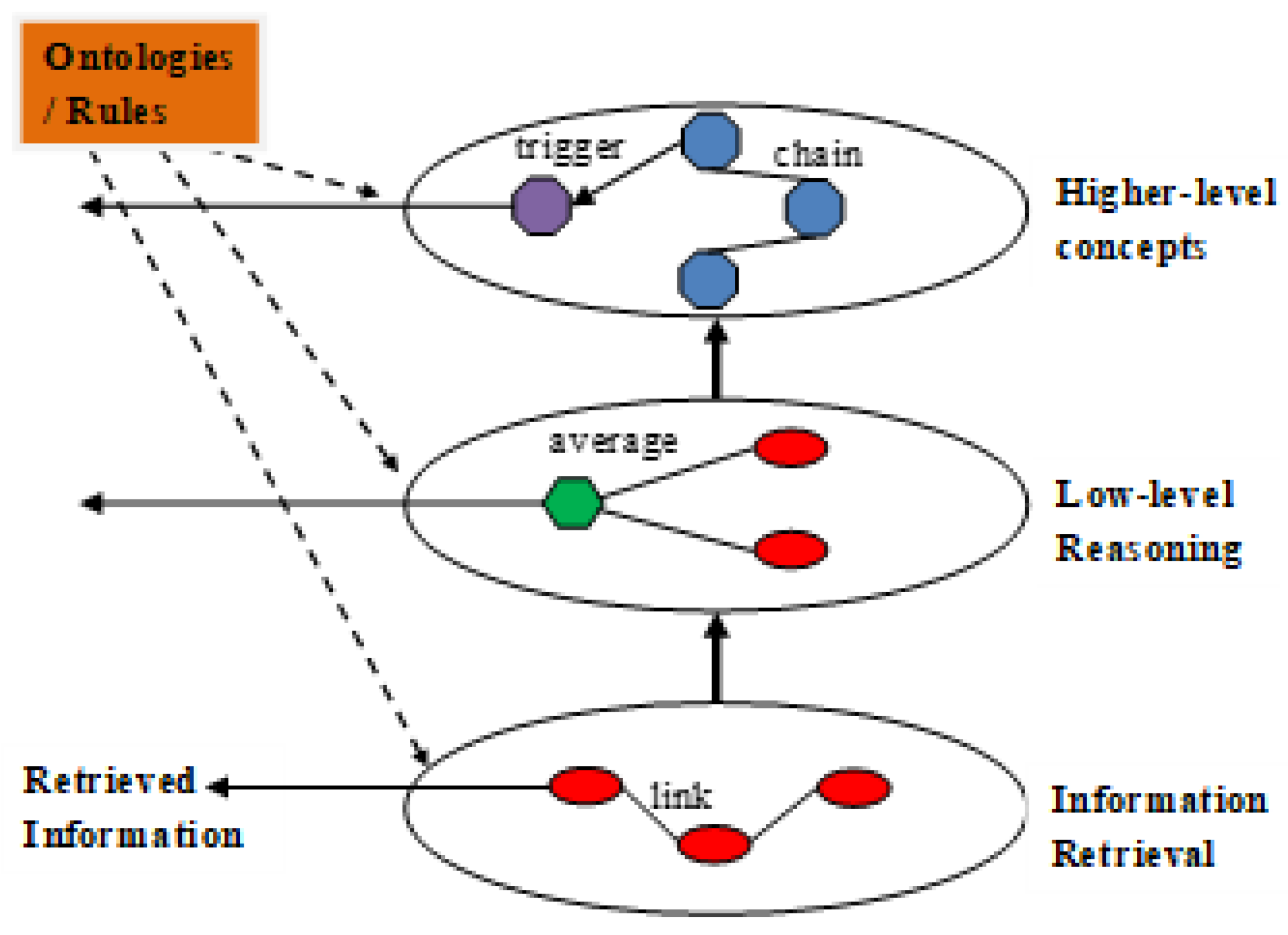
9]). The original architecture described 3 levels of increasing complexity. The lower-level optimised links locally, using stigmergy, for example. The middle-level aggregated the lower-level links and the upper-level aggregated those into more complex concepts. The original diagram is given in
Figure 1.
Section 3 describes that these levels now form the basis for the memory model as well. An ontology [
12] was also part of the original architecture and that is replaced by the new memory model. The memory model converts set-based instances into type-based context or use and is a statistical clustering process, rather than the normal semantics and rules. The author supposes that this effect is covered in modern NLP programs through the use of Word Vector models [
16] and Transformers [
22].
Gestalt theory has been mentioned in [
8]. With Gestalt psychology, objects are seen independently of their separate pieces. They have an ‘other’ interpretation of the sub-features and not just a summed whole of them. Gestalt theory makes use of ideas like similarity and proximity (and good continuation) to group objects and it believes that the brain has an internal order and structure that it places external stimuli into. It does not simply copy the input exactly as it appears. The booklet [
1] gives a formal description of the theory and a mathematical proof that links the psychology theories of memory span [
15,
2] and duality [
17]. Buffart states that:
This mathematical result should ring a bell to psychologists, since experimental psychology has long been aware of the important roles of the numbers 5, 6 and 7 as characterizing short-term memory span (e.g. Cavanagh, 1972; Miller, 1956) as well as of the duality phenomenon, viz. that people can hold two interpretations of an object simultaneously (Rock, 1977). From the theorem it follows that these phenomena are intrinsically related.
3. The Memory Model
The whole cognitive model was based on a 3-level architecture of increasing complexity, which also proposed an ontology that would be available to all the levels. Ontologies [
12] describe the relations between concepts in a very structured and formal way. They are themselves very high-level structures and it is not clear how they could be built simply from statistical processes. The 3-level cognitive model still has merit however and is still the underlying design that will guide the implementation process.
3.1. Memory Model Levels
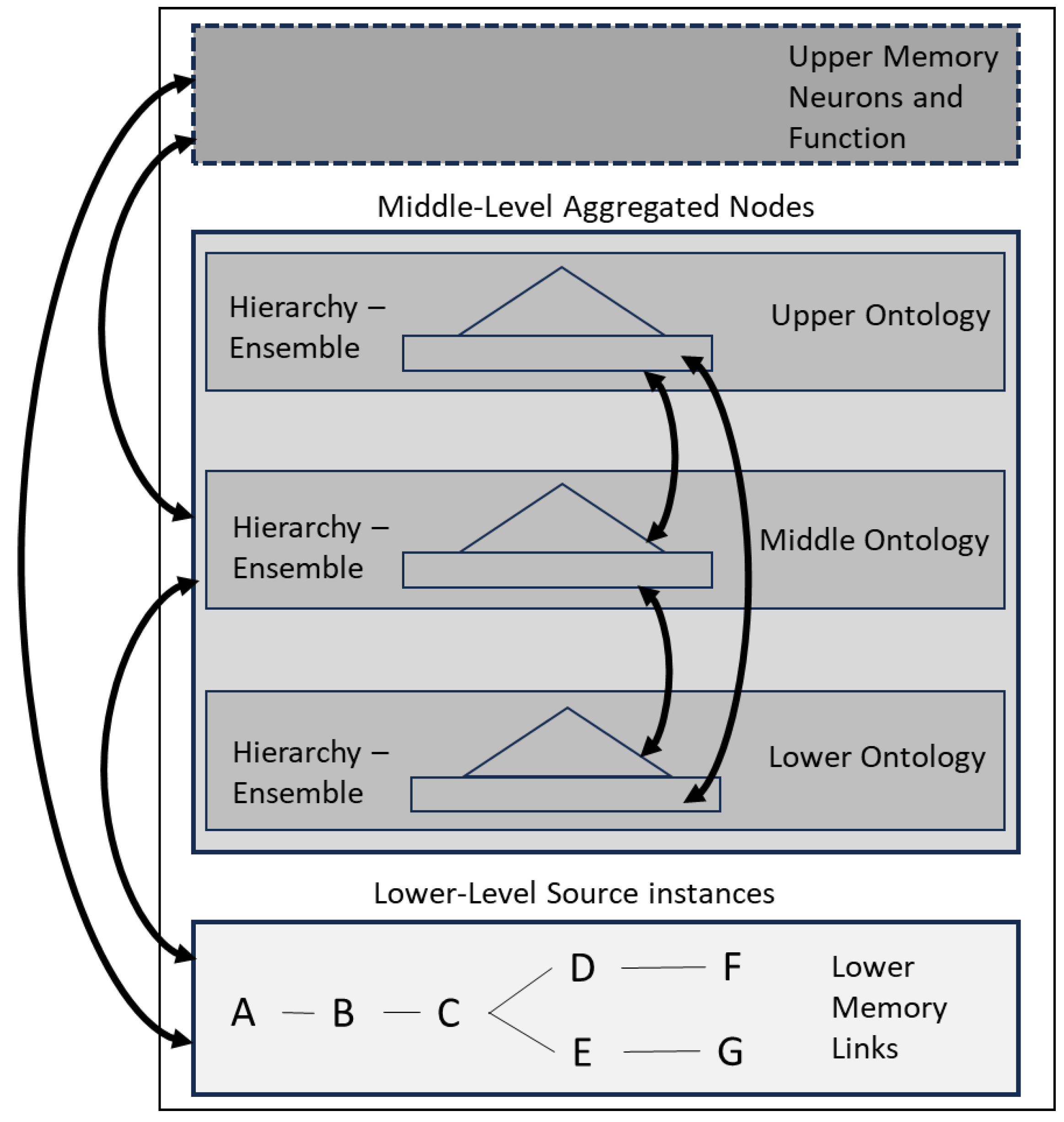
Like the whole architecture, the memory part will also be implemented as 3 different levels. This may not be surprising, when it is often thought that memory is stored in all parts of the brain. The 3 memory levels are as follows, also shown in
Figure 2:
- (1)
The lowest level is Markov-like sets of links only, between every source data concept that has been stored. The links describe any possible sequences through the source concepts.
- (2)
The middle level is an ontology that aggregates the source data through 3 phases and this converts it from set-based sequences into type-based clusters.
- (3)
The upper level would be a combination of the functional properties of the brain, with whatever input and resulting conversions they produce, being stored in the same memory substrate.
It may be that the first 2 levels can be made from glial cells instead of neurons. This was also the structure decided on in [
5], where the paper states that: ‘In the human brain, there are cells other than neurons, such as the more-simple glial and interneuron cells. More recently the perineuronal network [
20] has received a lot of attention and may be exactly the memory structure that the cognitive model will now use.’
The following was written in [
8] about the whole cognitive model, where a comparison with the new memory model can be made as follows:
3.2. Lower Memory Level
The lowest level is also Markov-like [
4], where each node contains links to each possible next node, as defined by the input over time. Thus, tracing through these links can return different sequences. It would also be possible to note start or end nodes in a sequence, to help with definition and maybe also use an n-gram [
4] count to make the next node more accurate. Unlike neural representations however, this structure does not have to be weighted. A link between nodes in a region is noted only once, no matter how often it occurs during the input. The structure therefore only stores equally possible sequence paths, where preferences or weighted choices are transferred over to the query, which overlays the structure. If this structure is sufficient, then the theory would state that a Markov process may be sufficient to describe a Gestalt process. This is discussed further in section 4.
3.3. Middle Ontology Level
The lower-level therefore organises the data into linked sequences only, without any preference to what gets linked. Another design that is central to the cognitive model is an ensemble-hierarchy [
8]. Again, these are loosely-structured constructs that can probably be produced through statistical counting methods and the source data. The ensemble, for example, can provide a global ordering for the popularity of each concept, while the hierarchy or tree can build a linked structure based on the input sequences, but possibly re-organised based on the global preferences. The final hierarchy in the upper ontology level is more like single lists of concepts than trees. The formal ontology of the cognitive model in
Figure 1 is now replaced by this simpler version. While this is still a low-level structure, it may contain one important property in that it is able to convert set-based sequences into type-based clusters. This would introduce a small amount of knowledge into the ontology that a search process can make use of.
3.4. Ontology Typing Tests
A computer program, written in Java, has implemented the two lower memory model levels for basic testing. The lower-level is fairly straightforward, but the middle ontology level is too complicated to explain in detail. There would be more than 1 way to implement the aggregation process and it makes use of the Frequency Grid [
8] to generate word clusters that from the basis of the aggregations. The author has chosen a version that prunes the most nodes from the result, so as to save on time and resources, for running on a laptop. This means that a text document the size of a book may return at the top ontology hierarchy, only a few words clustered together (see
Appendix A), but as the search would move back down the structure to the lower levels and then to the base source data, it will be able to discover most of the text from matching there as well.
Test Results
The success of a test is measured rather arbitrarily, by judging if the words in a cluster have some relation and preferably, are not simply part of the same sentence. The author has judged that this is often the case. Each result is only from clustering on a single book however. It is even more difficult to judge how accurate the clusters are when texts are combined, but this will be part of the future work. One problem that has occurred with the frequency grid before is when 2 or more smaller clusters are joined together. This can result in a single cluster with apparently 2 or more meanings in it. This also occurs in some of the final upper ontology clusters, described in
Appendix A. Rather than the program recognising associated antonyms, or something like that, it may have combined 2 lower clusters somewhere, but the algorithms in this paper are quite different to what was used previously. The problem for a self-organising system was to some extent solved in [
7] through averaging over multiple solutions, but that would also be a future project.
Appendix A therefore lists some well-known texts [
19], together with the final upper ontology cluster sets that the program produced. The resulting structures were very narrow, where each node was a child node of the one before. However, this would be consistent with a conversion from a horizontal set-based description to a vertical type-based one. The results are very subjective, but the author hopes that it is possible to see how some level of real meaning in the words has been derived from the statistical process.
3.5. Upper Functional Level
It is then conjectured that there would also be an upper level that would relate to the brain function operating on the memory. The 2 lower levels would be used to find information, where the upper level would perform higher-level operations and possibly save the result. This would probably be quite a common view, for example [
13], but the 3-level memory architecture is probably new.
3.6. Sub-Conscious
The second ontology level and above is an aggregation of a selection of the concepts that occurred in the levels below. It is therefore only a partial representation of the instances of whole concepts that may be stored as source memories. For example, if only a window concept was triggered, the brain would not necessarily be driven to think about houses. One may think that the lower level with a more complete description of each memory instance would also be linked more closely with the sensory system. If that system is also part of the thinking process, then it may require that whole memory instances are activated before they can be sent to the appropriate sense for recognition. Therefore, the middle and upper ontology levels could activate a lot of aggregated nodes and even complete local circuits that may not register with the sensory system. It would only be when the search at these levels started to agree on some more holistic view that would then trigger whole patterns in the lower level, that the senses would then start to recognise the activity. This would therefore allow for a lot of activity to remain silent, as in the sub-conscious.
4. Gestalt
Gestalt theory can be implemented in the lowest level of the memory structure. Because the links are unbiassed, one interesting aspect of the structure is that it may not return exactly what was input, thus satisfying the theory that the whole may be different to the parts. As part of the computer model, an n-gram depth can add accuracy, requiring that 2 or more previous concepts are present. But even with this, sequences may get combined, even if they were added separately during input. Kolmogorov and Shannon were written about in [
6], with regards to trying to measure intelligence. Shannon bases his Information Theory [
18] on Entropy and a Markov model. Kolmogorov Complexity theory ([
3], chapter 7) states that the shortest sequence is the most likely and also the best. This idea is also associated with Gestalt theory and would be compatible with the architecture, because shorter sequences are likely to have fewer transitions to other sequences and so a shorter sequence that satisfies the query is more likely to be true.
4.1. Example of a Gestalt Process
Consider this example where the following 2 sentences are added to the lowest-level memory:
The cat sat on the mat and drank some milk.
The dog barked at the moon and chased its tail.
Start words would now include ‘the’ and end words would include ‘milk’ and ‘tail.’ Each word in the sequence also has a link to any words that immediately follow it. If, for example, the memory system is asked to retrieve a sequence that results in the ‘and’ word being considered, then there are two possibilities after that – ‘drank’ or ‘chased.’ Therefore, a question about a dog could retrieve either of the following two sentences:
The dog barked at the moon and chased its tail, or
The dog barked at the moon and drank some milk.
If the second sentence was returned, then it would not be violating the memory system and the person would probably not have a reason to disbelieve it. It could therefore be a legitimate answer, even though it is different to what was originally entered. It can also be argued that changing the information in this way is not a creative process, but simply taking a different route through the linked structure. This means that the process is still mechanical at this level and the creative constraints would be moved to the more cognitive query request. But these constraints can now be different for different modules, thereby allowing for different interpretations of the source data by those modules.
5. Brain Evolution
This section follows-on from [
5] that proposes an evolutionary model to explain the neural correlates that may sustain intelligence and adaptation, from invertebrates to the human brain. The paper [
9] showed how an inward-firing, full-linking network can demonstrate colonic movement, or possibly the movement of worms. The paper [
23] maps the whole connectome for the C. elegans worm and it appears to be fully-linked. If the worm is then associated with the lowest memory level only, that could still give it the ability to move randomly, which means that it would not have to make a decision that way. Then the middle memory level converts from sequences to types, but it is a typing from use, not necessarily meaning, which means what it links with. If this level could be included in the ants, for example, it may help to explain how they can recognise different chemical 'road-signs' inside of the nest [
14] without understanding meaning. Then the human would also have the upper level with neocortex-related regions, to perform higher functions.
6. Conclusions
This paper describes a new 3 level architecture for memory in an AI system. While it is essentially for a computer model, it is based strongly on our understanding of the human brain. The number 3 occurs a lot in the architecture and this is in contrast to the numbers 7 (memory span) and 2 (duality) that occur in psychology. A value of 3 would allow something to be rooted (1), while two parts are being compared (2 and 3). If the brain likes to synchronise to balanced states, for example, then this might encourage the system to explore a step further, even when parts match. The development is still at an early stage and the algorithms will probably change, but they appear to give different views to what is usually found. The lower level can allow for a simplistic version of Gestalt, while the middle-level ontology also gives a different view that is more akin to the word use, or what it links with. Creating the ontology uses nothing more than a statistical count, without any external knowledge and so it has to rely on the source and internal ‘structures’ for generating clusters. The idea of a sub-conscious can be included, but may be linked to the idea that external senses are used when we think. However, this would then encourage the lower level to be searched over and a balance achieved there as well.
Appendix A. Upper Ontology Hierarchy for Book Texts
This appendix lists the upper-level ontology hierarchy that was created for some well-known books. The clustering relates to the use of the word. Each row is a child node of the row immediately before it, leading to a very narrow and vertical structure.
Thinking Networks – the Large and Small of it, Kieran Greer [
11].
Technical book on artificial intelligence, the Internet and autonomous, service-based systems.
| Clusters |
| knowledge, link, value |
| system |
| answer, example |
| linking, structure |
| provide, web |
| concept, data, different, each, environment, language, level, one, process, use |
| more, source, used |
| information, query |
| allow, architecture, described, distributed, over, reasoning |
| autonomic, between, mechanism, model, new, number, ontology, problem, rule, search, semantic, set, type |
| computer, user |
| based, describe, need, such |
| network, service |
| node, through |
Romeo and Juilet, William Shakespeare [
19].
| Clusters |
| romeo, shall |
| day, give, lady, make, one, out, up, well |
| love, o, thy |
| go, good, here, ill, night, now |
| thou |
| death, eye, hath |
| man, more, tybalt |
| come, thee |
The Wonderful Wizard of Oz, L. Frank Baum [
19].
| Clusters |
| dorothy |
| asked, came, see |
| city, emerald |
| great, oz |
| again, answered, away, before, down, made, now, shall, toto, up |
| scarecrow |
| lion, woodman |
| back, come, girl, go, green, head, heart, man, one, over, upon, very, witch |
| little, out, tin |
The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes, Arthur Conan Doyle [
19].
| Clusters |
| back, before, came |
| down, know |
| more, room, think, well |
| day, eye, face, found, matter, tell |
| upon |
| holmes, very |
| little, man, now |
| one |
| away, case, good, heard, house, much, nothing, quite, street, such, through, two, ye |
| go, here |
| come, hand, over, shall, time |
| asked, never |
| door, saw |
| mr, see |
| out, up |
| made, way |
Computing Machinery and Intelligence, A.M. Turing [
21].
| Clusters |
| answer, computer, man, question, think |
| machine |
| one |
| such |
References
- Buffart, H. (2017). A formal approach to Gestalt theory, Blurb, ISBN: 9781389505577.
- Cavanagh, J.P. Relation between the immediate memory span and the memory search rate. Psychol. Rev. 1972, 79, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M. and Joy, A.T. (1991). Elements of Information Theory, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-06259-6 Online ISBN 0-471-20061-1.
- Fink, G.A. (2014). Markov models for pattern recognition: from theory to applications. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Greer, K. Neural Assemblies as Precursors for Brain Function. NeuroSci 2022, 3, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, K. (2021). Is Intelligence Artificial? Euroasia Summit, Congress on Scientific Researches and Recent Trends-8, -4, The Philippine Merchant Marine Academy, Philippines, pp. 307 - 324. 2 August.
- Greer, K. A Pattern-Hierarchy Classifier for Reduced Teaching. WSEAS Trans. Comput. 2020, 19, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, K. New ideas for brain modelling 3. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 55, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, K. New Ideas for Brain Modelling 2. 2015, 23–39. [CrossRef]
- Greer, K. (2012). Turing: Then, Now and Still Key, in: X-S. Yang (eds.), Artificial Intelligence, Evolutionary Computation and Metaheuristics (AIECM) - Turing 2012, Studies in Computational Intelligence., Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 2013, Vol. 427/2013, pp. 43-62. [CrossRef]
- Greer, K. (2008). Thinking Networks - the Large and Small of it: Autonomic and Reasoning Processes for Information Networks, published with LuLu.com, ISBN: 1440433275. Online version available on Google Books.
- Gruber, T.R. A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowl. Acquis. 1993, 5, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.; Lewis, M.; Klukas, M.; Purdy, S.; Ahmad, S. A Framework for Intelligence and Cortical Function Based on Grid Cells in the Neocortex. Front. Neural Circuits 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, Y.; Shental, N.; Brandis, A.; Hefetz, A.; Feinerman, O. Ants regulate colony spatial organization using multiple chemical road-signs. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.A. The magical number seven, plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol. Rev. 1956, 63, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolov, T. , Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S. and Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2013, 26.
- Rock, I. (1977). In defence of unconscious inference. In W. Epstein (Ed.), Stability and constancy in visual perception: mechanisms and processes. New York, N. Y.: John Wiley & Sons.
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication, The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27, 379–423.
- The Gutenberg Project. Available online: https://www.gutenberg.org/browse/scores/top (accessed on 2 September 23).
- Tsien, R.Y. Very long-term memories may be stored in the pattern of holes in the perineuronal net. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 12456–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind 1950, 49, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. , Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L. and Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30.
- Yan, G.; Vértes, P.E.; Towlson, E.K.; Chew, Y.L.; Walker, D.S.; Schafer, W.R.; Barabási, A.-L. Network control principles predict neuron function in the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome. Nature 2017, 550, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).