Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial strains
2.2. Antimicrobial susceptibility
2.3. Genomic DNA extraction and purification
2.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4.1. Detection and characterization of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons
2.4.1. PCR purification
2.5. Gel electrophoresis
2.6. Whole genome DNA Sequencing
2.7. Bioinformatics analyses
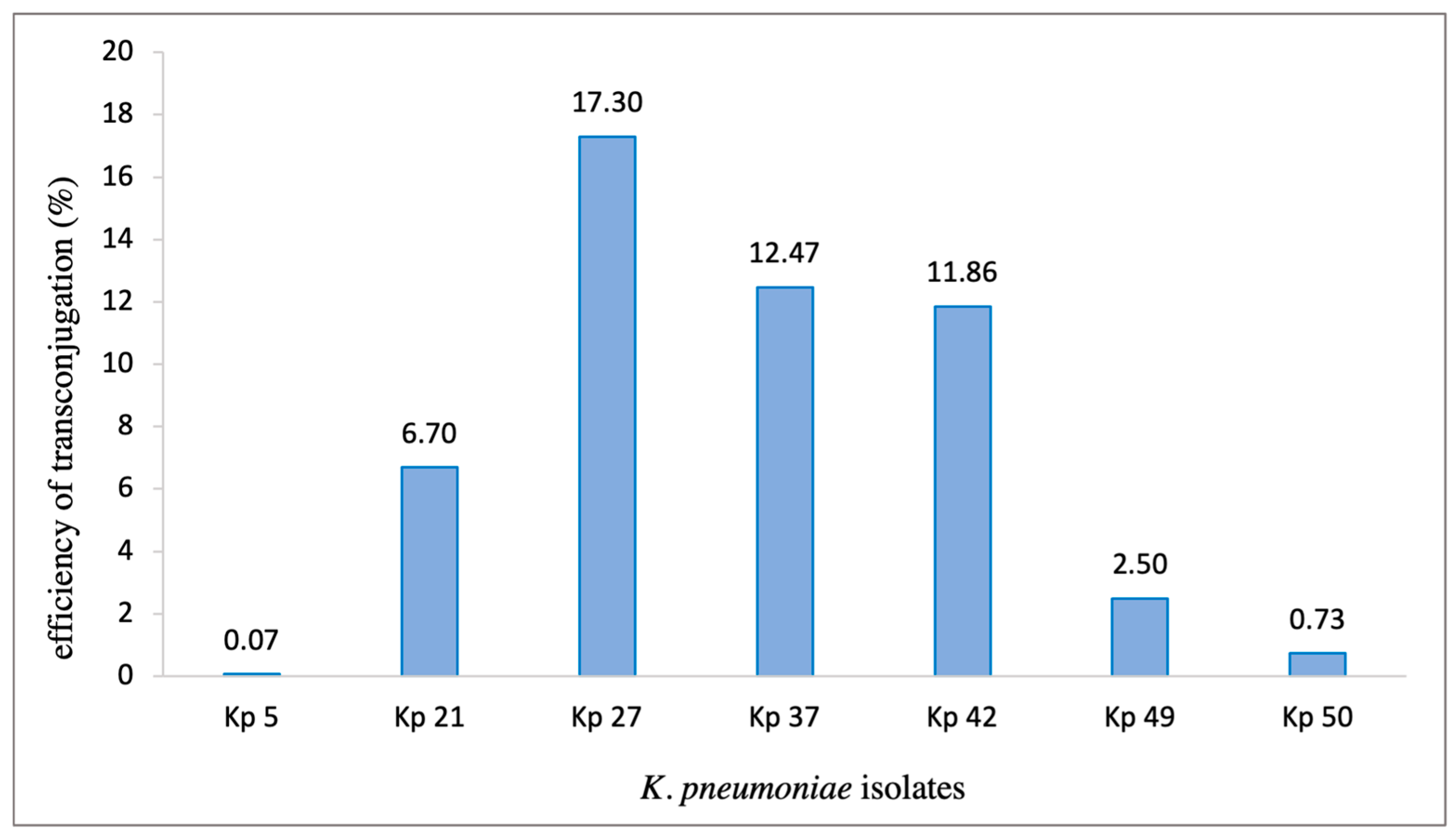
2.8. Conjugation experiment
3. Results
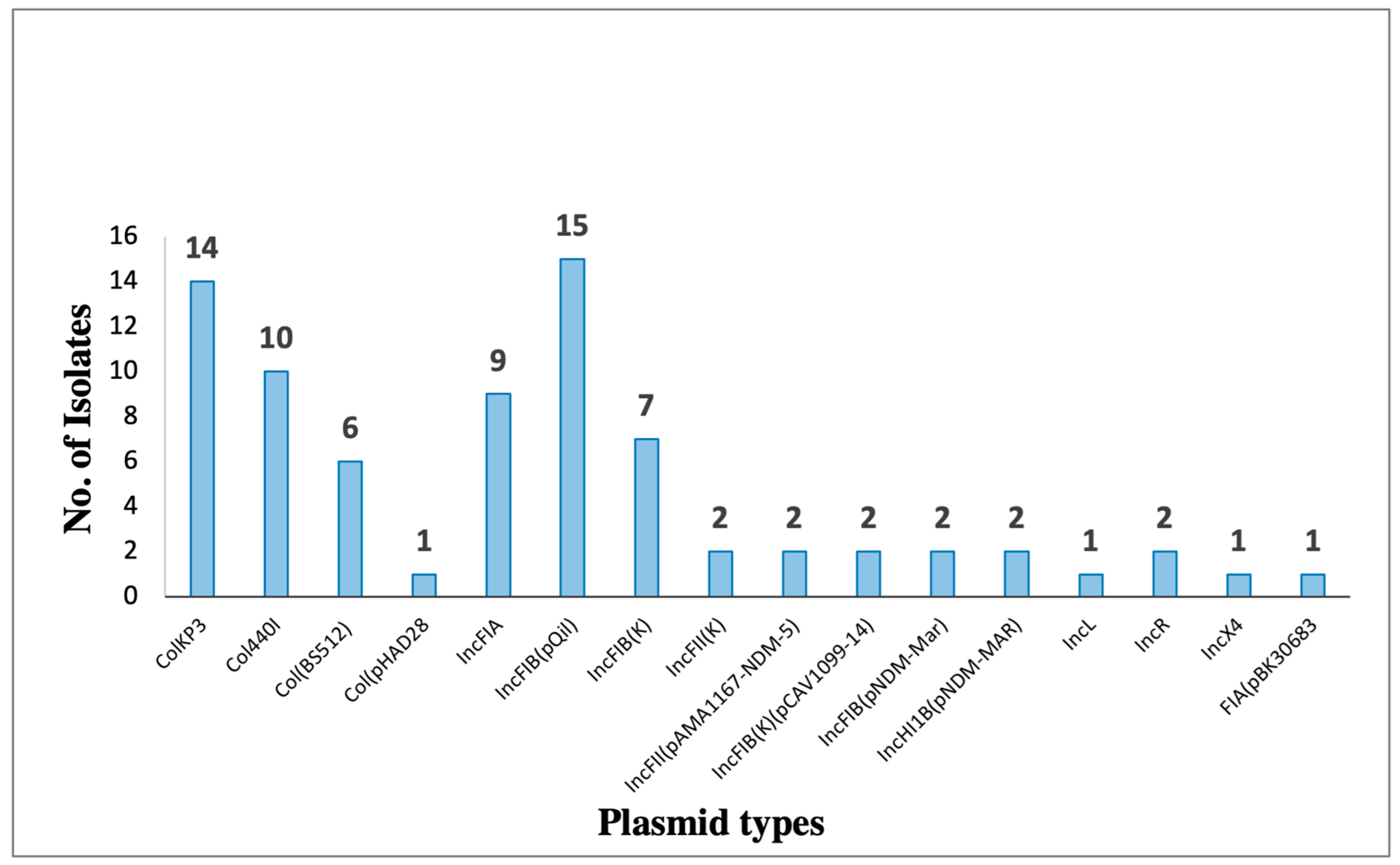
| isolate (KP) | Plasmid | Size (bp) | Replicon | Resistance genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 15, 16, 22, 28, 30, 41, 43, 44, 45, 50 | pKPQIL-IT | 115300 | IncFIB(QIL) |
blaTEM-1, blaKPC-3 |
| 5, 6, 11, 15, 16, 22, 28, 30, 41, 43, 44, 45, 49, 50 | pKP3-A | 7605 | ColKP3 |
BlaOXA-181 |
| 5, 6, 7, 15, 28, 30, 45 | pAMA1167-NDM-5 | 11310 | IncFII(pAMA1167-NDM-5) |
aadA5, aadA2, aac(3)-IId, aph(6)-Id, aph(3’’)-Ib, aac(6’)-Ib-cr5, blaNDM-5,blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15-1, blaTEM-1 dfrA17, dfrA12, Mph(A), Sul1, Sul2, emrE, tet(b), tet(C), cat |
| 10, 25, 27, 37, 42, 46 | pKPN-IT | 208191 | IncFIB(K) | aadA2, cat, Mph(A), Sul1, dfrA12 |
| 21, 40 | pCAV1099-14 | 113992 | IncFIB(K)(pCAV1099-14) | dfrA19, APH(3’’)-Ib, APH(3’)-Ia, QnrB52 |
| 41, 50 | pNDM-MAR | 267242 | IncFIB (pNDM-Mar) IncHI1B (pNDM-Mar) |
aac(6’)-Ib, blaOXA-1 , blaNDM-1, cat, QnrB1 |
| 27, 49 | pK245 | 98264 | IncR | aacC2, strA, strB, dfrA14, catA2, Qnrs, blaSH2A , blaTEM |
| 49 | pC15-1a | 92353 | IncFII | aac(6’)-Ib, aac(3)-II, blaTEM-1 , blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15-1 , tet(A) |
| 37 | pBK30683 |
139941 | FIA(pBK30683) | dfrA14, StrA, StrB, blaTEM-1, blaOXA-9, , blaKPC-3 Sul2,ant(3’’)-Ia |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Najafgholizadeh Pirzaman, A.; Mojtahedi, A. Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance and the Presence of Integron Genes among ESBL Producing Klebsiella Isolates. Meta Gene 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A. M.d.S.; de Melo, M. E. S.; Alves, L. C.; Brayner, F. A.; Lopes, A. C. S. Investigation of Class 1 Integrons in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical and Microbiota Isolates Belonging to Different Phylogenetic Groups in Recife, State of Pernambuco. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2014, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R. L.; Da Silva, B. C. M.; Rezende, G. S.; Nakamura-Silva, R.; Pitondo-Silva, A.; Campanini, E. B.; Brito, M. C. A.; Da Silva, E. M. L.; De Melo Freire, C. C.; Da Cunha, A. F.; Da Silva Pranchevicius, M. C. High Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Harboring Several Virulence and β-Lactamase Encoding Genes in a Brazilian Intensive Care Unit. Front Microbiol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, C. A.; Pierrat, G.; Tenaillon, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bercot, B.; Jaouen, E.; Jacquier, H.; Birgy, A. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase Variants Resistant to Ceftazidime-Avibactam: An Evolutionary Overview. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Bengoechea, J. A.; Sa Pessoa, J. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Infection Biology: Living to Counteract Host Defences. FEMS Microbiology Reviews. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mazel, D. Integrons: Agents of Bacterial Evolution. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Fluit, A. C.; Schmitz, F. J. Resistance Integrons and Super-Integrons. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M. R. Integrons: Past, Present, and Future. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2014, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C. H.; Huang, Y. T.; Mao, Y. C.; Lai, C. H.; Yeh, T. K.; Ho, C. M.; Liu, P. Y. Insight into the Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella Pneumoniae: A Study on IS26 Integrons, Beta-Lactamases, Porin Modifications, and Plasmidome Analysis. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozeh, F.; Mahluji, Z.; Khorshidi, A.; Zibaei, M. Molecular Characterization of Class 1, 2 and 3 Integrons in Clinical Multi-Drug Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Joshi, P.; Trivedi, P.; Akinwotu, O.; Gajjar, D. Genomic Islands in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. In Microbial Genomic Islands in Adaptation and Pathogenicity; 2023. [CrossRef]
- Di Pilato, V.; Principe, L.; Andriani, L.; Aiezza, N.; Coppi, M.; Ricci, S.; Giani, T.; Luzzaro, F.; Rossolini, G. M. Deciphering Variable Resistance to Novel Carbapenem-Based β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations in a Multi-Clonal Outbreak Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC)-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Resistant to Ceftazidime/Avibactam. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Polo, J. A.; Hernández-García, M.; Morosini, M. I.; Pérez-Viso, B.; Soriano, C.; De Pablo, R.; Cantón, R.; Ruiz-Garbajosa, P. Outbreak by KPC-62-Producing ST307 Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates Resistant to Ceftazidime/Avibactam and Cefiderocol in a University Hospital in Madrid, Spain. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2023, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Luo, M.; Liu, P.; Su, K.; Qing, Y.; Chen, S.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y. Molecular Characterisations of Integrons in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae in a Chinese Tertiary Hospital. Microb Pathog 2017, 104, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, F.; Mélançon, J.; Roy, P. H. The IntI-like Tyrosine Recombinase of Shewanella Oneidensis Is Active as an Integron Integrase. J Bacteriol 2002, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balushi, M. Al; Kumar, R.; Al-Rashdi, A.; Ratna, A.; Al-Jabri, A.; Al-shekaili, N.; Rani, R.; Sumri, S. Al; Al-Ghabshi, L.; Al-Abri, S.; Al-Jardani, A. Genomic Analysis of the Emerging Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Sequence Type 11 Harbouring Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC) in Oman. J Infect Public Health 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkhair, A.; Al-Muharrmi, Z.; Al’Adawi, B.; Al Busaidi, I.; Taher, H. B.; Al-Siyabi, T.; Al Amin, M.; Hassan, K. S. Prevalence and 30-Day All-Cause Mortality of Carbapenem-and Colistin-Resistant Bacteraemia Caused by Acinetobacter Baumannii, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, and Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Description of a Decade-Long Trend. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, A.; Al-Farsi, Y. M.; Al-Muharrmi, Z.; Al-Rashdi, R.; Al-Jabri, M.; Neilson, F.; Al-Adawi, S. S.; El-Beeli, M.; Al-Adawi, S. Epidemiology of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms in a Teaching Hospital in Oman: A One-Year Hospital-Based Study. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 19. CLSI. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd Edition. Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute, 2021.
- Antimicrobial, E. C. on. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 10.0, 2020. Http://Www.Eucast.Org. Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 10.0, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing A CLSI Supplement for Global Application. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kaas, R. S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F. M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R. S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M. C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R. L.; Rebelo, A. R.; Florensa, A. F.; Fagelhauer, L.; Chakraborty, T.; Neumann, B.; Werner, G.; Bender, J. K.; Stingl, K.; Nguyen, M.; Coppens, J.; Xavier, B. B.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Westh, H.; Pinholt, M.; Anjum, M. F.; Duggett, N. A.; Kempf, I.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Olkkola, S.; Wieczorek, K.; Amaro, A.; Clemente, L.; Mossong, J.; Losch, S.; Ragimbeau, C.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F. M. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2020, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Enright, M. C.; Godoy, D.; Spratt, B. G.; Larsen, A. R.; Skov, R. L. Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Staphylococcus Aureus: Revision of the Gmk Locus. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2012, 2538–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garciá-Fernández, A.; Larsen, M. V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F. M.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and PMLST: In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Davies, J.; Miao, V. Molecular Characterization of Class 3 Integrons from Delftia Spp. J Bacteriol 2007, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M. M.; Amer, F. A.; Allam, A. A.; El-Sokkary, R. H.; Gheith, T.; Arafa, M. A. Occurrence of Classes I and II Integrons in Enterobacteriaceae Collected from Zagazig University Hospitals, Egypt. Front Microbiol 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, Z.; Zamudio, R.; Horvath-Papp, E.; Ralph, J. D.; Al-Muharrami, Z.; Rajakumar, K.; Oggioni, M. R. Integrase-Controlled Excision of Metal-Resistance Genomic Islands in Acinetobacter Baumannii. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jabri, Z. J.; Busaidi, B. A.; Muzahmi, M. A.; Shabibi, Z. A.; Rizvi, M.; Rashdi, A. A.; Al-Jardani, A.; Farzand, R. Diversity of the Sequence Type Determines the Unique Genetic Arrangement of K-Loci in Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Strains I n r e v i e w. www.frontiersin.org.
- Dandachi, I.; Chaddad, A.; Hanna, J.; Matta, J.; Daoud, Z. Understanding the Epidemiology of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli in the Middle East Using a One Health Approach. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Quraini, M. AL; Jabri, Z. AL; Sami, H.; Mahindroo, J.; Taneja, N.; Muharrmi, Z. AL; Busaidi, I. AL; Rizvi, M. Exploring Synergistic Combinations in Extended and Pan-Drug Resistant (XDR and PDR) Whole Genome Sequenced Acinetobacter Baumannii. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quraini, M.; Rizvi, M.; Al-Jabri, Z.; Sami, H.; Al-Muzahmi, M.; Al-Muharrmi, Z.; Taneja, N.; Al-Busaidi, I.; Soman, R. Assessment of In-Vitro Synergy of Fosfomycin with Meropenem, Amikacin and Tigecycline in Whole Genome Sequenced Extended and Pan Drug Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Exploring A Colistin Sparing Protocol. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A. I. A.; Ahmed, A. M.; Sato, M.; Shimamoto, T. Characterization of Integrons and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Clinical Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Palestinian Hospitals. Microbiol Immunol 2009, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Peerayeh, S. N.; Fallah, F.; Bakhshi, B.; Rahbar, M.; Ashrafi, A. Detection of Class 1, 2, and 3 Integrons among Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from Children in Tehran Hospitals. Arch Pediatr Infect Dis 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Haddadi, A.; Harzandi, N. Prevalence of Integrons as the Carrier of Multidrug Resistance Genes among Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella; 2019; Vol. 8.
- Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, L.; Yang, J. Molecular Characteristics of Clinical IMP-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates: Novel IMP-90 and Integron In2147. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar F., H.; A. H. Ibrahim. THE PREVALENCE OF INTEGRON CLASS I AND II AMONG MULTI-DRUG RESISTANCE PRODUCING KLEBSIELLA Pneumonia. IRAQI JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES 2023, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, C. M.; Kim, M. J.; Partridge, S. R.; Stokes, H. W.; Hall, R. M. Characterization of the Class 3 Integron and the Site-Specific Recombination System It Determines. J Bacteriol 2002, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samah, G.; Hatem, M. E. S.; El, K. A. T.; Nikhat, M. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Klebsiella Isolates from Clinical Samples in a Saudi Hospital. Afr J Microbiol Res 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lin, C. J.; Chen, J. H.; Fung, C. P.; Chang, F. Y.; Lai, Y. K.; Lin, J. C.; Siu, L. K. Widespread Dissemination of Aminoglycoside Resistance Genes ArmA and RmtB in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates in Taiwan Producing CTX-M-Type Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Woo, P. C. Y.; Jing, H.; Zhu, B.; Liu, C. H. Structural Diversity of Class 1 Integrons and Their Associated Gene Cassettes in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates from a Hospital in China. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, C.; Piche, L.; Larose, C.; Roy, P. H. PCR Mapping of Integrons Reveals Several Novel Combinations of Resistance Genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1995, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Machado, J.; Sousa, J. C.; Peixe, L. Dissemination of Sulfonamide Resistance Genes (Sul1, Sul2, and Sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella Enterica Strains and Relation with Integrons. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.; Miranda, C. D.; Fuentes, O.; De La Fuente, M.; Godoy, F. A.; Bello-Toledo, H.; González-Rocha, G. Occurrence of Transferable Integrons and Suland Dfrgenes among Sulfonamide-and/or Trimethoprim-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Chilean Salmonid Farms. Front Microbiol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanchuen, R.; Koowatananukul, C.; Khemtong, S. Characterization of Class 1 Integrons with Unusual 3′ Conserved Region from Salmonella Enterica Isolates. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2008, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Evershed, N. J.; Levings, R. S.; Wilson, N. L.; Djordjevic, S. P.; Hall, R. M. Unusual Class 1 Integron-Associated Gene Cassette Configuration Found in IncA/C Plasmids from Salmonella Enterica. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, S.; da Silva, G. J.; Nielsen, K. M. Integrons: Vehicles and Pathways for Horizontal Dissemination in Bacteria. Mob Genet Elements 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lan, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, B. Characterization of Integrons and Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia Coli Sequence Type 131 Isolates. Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology 2020, 2020, 3826186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploy, M. C.; Chainier, D.; Thi, N. H. T.; Poilane, I.; Cruaud, P.; Denis, F.; Collignon, A.; Lambert, T. Integron-Associated Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhi from Asia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.; Hansen, L. H.; Sørensen, S. J. Conjugative Plasmids: Vessels of the Communal Gene Pool. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, P. R.; Evans, M. C.; Dyson, P. J. Low Target Site Specificity of an IS6100-Based Mini-Transposon, Tn1792, Developed for Transposon Mutagenesis of Antibiotic-Producing Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1999, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hou, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhou, D. Characterization of Novel Integrons, In1085 and In1086, and the Surrounding Genes in Plasmids from Enterobacteriaceae, and the Role for AttCaadA16 Structural Features during Atti1 × Attc Integration. Front Microbiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, S.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S.; Cancino-Diaz, M. E.; Cancino-Diaz, J. C. Extracellular Proteases of Staphylococcus Epidermidis: Roles as Virulence Factors and Their Participation in Biofilm. APMIS. Blackwell Munksgaard March 1, 2018, pp 177–185. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P. H.; Touchon, M.; Rocha, E. P. C. The Interplay of Restriction-Modification Systems with Mobile Genetic Elements and Their Prokaryotic Hosts. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, P. J.; Gupta, M.; Boyer, H. W.; Brown, W. E.; Rosenberg, J. M. Sequence Analysis of the DNA Encoding the Eco RI Endonuclease and Methylase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1981, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, V. P.; Akshay, S. D.; Rai, P.; Deekshit, V. K. Integrons as the Potential Targets for Combating Multidrug Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Using CRISPR- Cas9 Technique. Journal of applied microbiology. NLM (Medline) July 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wu, L.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Bao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xu, T.; Liang, J. Class 1 Integrons and Multiple Mobile Genetic Elements in Clinical Isolates of the Klebsiella Pneumoniae Complex from a Tertiary Hospital in Eastern China. Front Microbiol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Tai, C.; Tang, H.; He, X.; Wu, G.; Deng, Z.; Xu, P. The Genes Coding for the Conversion of Carbazole to Catechol Are Flanked by IS6100 Elements in Sphingomonas Sp. Strain XLDN2-5. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, X. X.; Ma, L. Xenogenetic Evolutionary of Integrons Promotes the Environmental Pollution of Antibiotic Resistance Genes — Challenges, Progress and Prospects. Water Research. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, G.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Molecular Epidemiology and Drug Resistant Mechanism in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from Pediatric Patients in Shanghai, China. PLoS One 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Torres, V. V. L.; Liu, H.; Rocker, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Bi, W.; Lin, J.; Strugnell, R. A.; Zhang, S.; Lithgow, T.; Zhou, T.; Cao, J. An Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae in an Intensive Care Unit of a Major Teaching Hospital in Wenzhou, China. Front Public Health 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascols, C.; Peirano, G.; Hackel, M.; Laupland, K. B.; Pitout, J. D. D. Surveillance and Molecular Epidemiology of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates That Produce Carbapenemases: First Report of OXA-48-like Enzymes in North America. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S. W.; Olsen, R. J.; Eagar, T. N.; Beres, S. B.; Zhao, P.; Davis, J. J.; Brettin, T.; Xia, F.; Musser, J. M. Population Genomic Analysis of 1,777 Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates, Houston, Texas: Unexpected Abundance of Clonal Group 307. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Momin, M. H. F.; Liakopoulos, A.; Phee, L. M.; Wareham, D. W. Emergence and Nosocomial Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant OXA-232-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Brunei Darussalam. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, J. W. P.; Kurup, A.; Lin, R. T. P.; Hsien, K. T. Emergence of Clinical Klebsiella Pneumoniae Producing OXA-232 Carbapenemase in Singapore. New Microbes New Infect 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, C.; Mathur, P.; Venkatesan, M.; Pragasam, A. K.; Anandan, S.; Khurana, S.; Veeraraghavan, B. Rapidly Disseminating Bla OXA-232 Carrying Klebsiella Pneumoniae Belonging to ST231 in India: Multiple and Varied Mobile Genetic Elements. BMC Microbiol 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, S.; Poirel, L.; Tritten, M. L.; Lienhard, R.; Bassi, C.; Nordmann, P. Emergence of an MDR Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST231 Producing OXA-232 and RmtF in Switzerland. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muggeo, A.; Guillard, T.; Klein, F.; Reffuveille, F.; François, C.; Babosan, A.; Bajolet, O.; Bertrand, X.; de Champs, C. Spread of Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST395 Non-Susceptible to Carbapenems and Resistant to Fluoroquinolones in North-Eastern France. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maida, C. M.; Bonura, C.; Geraci, D. M.; Graziano, G.; Carattoli, A.; Rizzo, A.; Torregrossa, M. V.; Vecchio, D.; Giuffrè, M. Outbreak of ST395 KPC-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Palermo, Italy. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Sonnevend, Á.; Ghazawi, A. A.; Hashmey, R.; Jamal, W.; Rotimi, V. O.; Shibl, A. M.; Al-Jardani, A.; Al-Abri, S. S.; Tariq, W. U. Z.; Weber, S.; Pál, T. Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae with High Rate of Autochthonous Transmission in the Arabian Peninsula. PLoS One 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortet, L.; Poirel, L.; Al Yaqoubi, F.; Nordmann, P. NDM-1, OXA-48 and OXA-181 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Sultanate of Oman. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, T. uz; Alrodayyan, M.; Albladi, M.; Aldrees, M.; Siddique, M. I.; Aljohani, S.; Balkhy, H. H. Clonal Diversity and Genetic Profiling of Antibiotic Resistance among Multidrug/Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Saudi Arabia. BMC Infect Dis 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataseje, L. F.; Boyd, D. A.; Fuller, J.; Haldane, D.; Hoang, L.; Lefebvre, B.; Melano, R. G.; Poutanen, S.; Van Caeseele, P.; Mulvey, M. R. Characterization of OXA-48-like Carbapenemase Producers in Canada, 2011-14. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, J.; Hopkins, K. L.; Loy, R.; Doumith, M.; Meunier, D.; Hill, R.; Pike, R.; Mustafa, N.; Livermore, D. M.; Woodford, N. OXA-48-like Carbapenemases in the UK: An Analysis of Isolates and Cases from 2007 to 2014. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2017, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Potron, A.; Nordmann, P. OXA-48-like Carbapenemases: The Phantom Menace. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2012, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Qin, Q.; Liu, S.; Ye, L.; Yang, J.; Li, B. Nosocomial Spread of OXA-232-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST15 in a Teaching Hospital, Shanghai, China. BMC Microbiol 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgring, J. D.; Zhu, W.; De Man, T. J. B.; Avillan, J. J.; Anderson, K. F.; Lonsway, D. R.; Rowe, L. A.; Batra, D.; Rasheed, J. K.; Limbago, B. M. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Enterobacteriaceae Producing Oxacillinase-48-like Carbapenemases, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfel, G.; Hoenigl, M.; Leitner, E.; Salzer, H. J. F.; Feierl, G.; Masoud, L.; Valentin, T.; Krause, R.; Grisold, A. J. Emergence of New Delhi Metallo- β-Lactamase, Austria. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2011. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, A. J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J. D. D. The Role of Epidemic Resistance Plasmids and International High- Risk Clones in the Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin Microbiol Rev 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Class D Ss-Lactamases : Diversity, Epidemiology and Genetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P. Polymyxins: Antibacterial Activity, Susceptibility Testing, and Resistance Mechanisms Encoded by Plasmids or Chromosomes Laurent Poirela,b,c, Aurélie Jayola,b,c and Patrice Nordmann. Clin Microbiol Rev 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, Z.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ganbarov, K.; Bialvaei, A. Z.; Mahmood, S. S.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kafil, H. S. Molecular Mechanisms Related to Colistin Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Infection and Drug Resistance. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Brink, A.; Poirel, L. Heteroresistance to Colistin in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Associated with Alterations in the PhoPQ Regulatory System. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M. S.; Suzuki, Y.; Jones, M. B.; Marshall, S. H.; Rudin, S. D.; Van Duin, D.; Kaye, K.; Jacobs, M. R.; Bonomo, R. A.; Adamsa, M. D. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Colistin-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Reveal Multiple Pathways of Resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. H.; Lin, T. L.; Pan, Y. J.; Wang, Y. P.; Lin, Y. T.; Wang, J. T. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains from Taiwan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J. M.; Di, Y. P. Determination of Mutational Timing of Colistin-Resistance Genes through Klebsiella Pneumoniae Evolution. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, L.; Shu, Q.; Ye, J.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Tan, L. Tigecycline Salvage Therapy for Critically Ill Children with Multidrug-Resistant/Extensively Drug-Resistant Infections after Surgery. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2018, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, Z.; Al-Shabibi, Z.; Al-Bimani, A.; Al-Hinai, A.; Al-Shabibi, A.; Rizvi, M. Whole Genome Sequencing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis Clinical Isolates Reveals Variable Composite SCCmec ACME among Different STs in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Oman. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournaras, S.; Koumaki, V.; Spanakis, N.; Gennimata, V.; Tsakris, A. Current Perspectives on Tigecycline Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Susceptibility Testing Issues and Mechanisms of Resistance. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Sun, J.; Ou, H. Y.; Qu, H. Whole-Genome-Sequencing Characterization of Bloodstream Infection-Causing Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae of Capsular Serotype K2 and ST374. Virulence 2018, 9, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veleba, M.; Schneiders, T. Tigecycline Resistance Can Occur Independently of the RamA Gene in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; He, F.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, F.; Xu, J.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y. The Rapid Emergence of Tigecycline Resistance in BlaKPC-2 Harboring Klebsiella Pneumoniae, as Mediated in Vivo by Mutation in TetA during Tigecycline Treatment. Front Microbiol 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, P.; Galimand, M.; Bauraing, C.; Deplano, A.; Vanhoof, R.; De Mendonca, R.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H.; Struelens, M.; Glupczynski, Y. Emergence of ArmA and RmtB Aminoglycoside Resistance 16S RRNA Methylases in Belgium. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2007, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.; Drissi, M.; de Curraize, C.; Dupont, C.; Hartmann, A.; Solanas, S.; Siebor, E.; Amoureux, L.; Neuwirth, C. Occurence of ArmA and RmtB Aminoglycoside Resistance 16S RRNA Methylases in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases Producing Escherichia Coli in Algerian Hospitals. Front Microbiol 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathi, N. K. D.; Bakthavatchalam, Y. D.; Mathur, P.; Pragasam, A. K.; Walia, K.; Ohri, V. C.; Veeraraghavan, B. Plasmid Profiles among Some ESKAPE Pathogens in a Tertiary Care Centre in South India. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2019, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe-Magnus, D. A.; Guerout, A. M.; Ploncard, P.; Dychinco, B.; Davies, J.; Mazel, D. The Evolutionary History of Chromosomal Super-Integrons Provides an Ancestry for Multiresistant Integrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerminiaux, N. A.; Cameron, A. D. S. Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Clinical Environments. Can J Microbiol 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Isolate | Year of isolation | Type of resistance | Specimen type | Hospital unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kp1 | 2019 | XDR | Tracheal aspirate | Emergency |
| Kp 2 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 3 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Oncology |
| Kp 4 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Pediatrics |
| Kp 5 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Male Medical |
| Kp 6 | 2019 | PAN | Tracheal aspirate | ICU |
| Kp 7 | 2019 | XDR | Wound | Male Medical |
| Kp 8 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Day Care |
| Kp 9 | 2019 | ESBL | Biopsy | Surgery |
| Kp 10 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Oncology |
| Kp 11 | 2019 | PAN | Tracheal aspirate | Male Medical |
| Kp 12 | 2019 | ESBL | Pus | Surgery |
| Kp 13 | 2019 | XDR | Blood culture | Emergency |
| Kp 14 | 2019 | ESBL | Wound | Male Medical |
| Kp 15 | 2019 | XDR | Catheter urine | Male Medical |
| Kp 16 | 2019 | XDR | Sputum | ICU |
| Kp 17 | 2019 | ESBL | Catheter urine | Pediatrics |
| Kp 18 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 19 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Pediatrics |
| Kp 20 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Pediatrics |
| Kp 21 | 2019 | ESBL | urine | Emergency |
| Kp 22 | 2019 | XDR | Wound | ICU |
| Kp 23 | 2019 | ESBL | Blood culture | Emergency |
| Kp 24 | 2019 | XDR | Skin | Emergency |
| Kp 25 | 2019 | ESBL | Peritoneal fluid | Male Medical |
| Kp 26 | 2019 | ESBL | wound | Surgery |
| Kp 27 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 28 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Male Medical |
| Kp 29 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Day Care |
| Kp 30 | 2019 | XDR | Wound | Male Medical |
| Kp 31 | 2019 | XDR | Sputum | ICU |
| Kp 32 | 2019 | XDR | bronchial wash | Emergency |
| Kp 33 | 2019 | ESBL | wound | Female Medical |
| Kp 34 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Pediatrics |
| Kp 35 | 2019 | ESBL | Blood culture | Female Medical |
| Kp 36 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 37 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Urology |
| Kp 38 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 39 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Emergency |
| Kp 40 | 2019 | ESBL | Tracheal aspirate | Neonatal unit |
| Kp 41 | 2019 | XDR | Wound | Male Medical |
| Kp 42 | 2019 | ESBL | Blood culture | Neonatal unit |
| Kp 43 | 2019 | XDR | Tracheal aspirate | Male Medical |
| Kp 44 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Male Medical |
| Kp 45 | 2019 | XDR | Tracheal aspirate | Male Medical |
| Kp 46 | 2019 | ESBL | Tracheal aspirate | Neonatal unit |
| Kp 47 | 2019 | ESBL | Urine | Female Medical |
| Kp 48 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Surgery |
| Kp 49 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | Male Medical |
| Kp 50 | 2019 | XDR | Urine | ICU |
| Zone diameter breakpoints (mm) | ||||
| Antibiotic | Disk content | Susceptible | Intermediate | Resistant |
| Ampicillin | AMP 10mg | ≥17 | 14-16 | ≤13 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | TZP 110mg | ≥21 | 18–20 | ≤17 |
| Cefepime | FEP 30mg | ≥ 25 | 19– 24 | ≤ 18 |
| Cefotaxime | CTX 30mg | ≥26 | 23-25 | ≤22 |
| Cefoxitin | FOX 30mg | ≥18 | 15-17 | ≤ 14 |
| Ceftazidime | CAZ 30mg | ≥21 | 18-20 | ≤ 17 |
| Imipenem | IMP 10mg | ≥23 | 20-22 | ≤ 19 |
| Meropenem | MEM 10mg | ≥23 | 20-22 | ≤ 18 |
| Gentamicin | CN 30mg | ≥15 | 13-14 | ≤ 12 |
| Amikacin | AK 10mg | ≥17 | 15-16 | ≤ 14 |
| Ciprofloxacin | CIP 5mg | ≥31 | 21-30 | ≤ 20 |
| Step | Temperature | Time |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | 95 °C | 2 min |
| Denaturation | 95°C | 30 s |
| Annealing | 30 s | |
| Extension | 72°C | 1 min / kb |
| Final extension | 72°C | 10 min |
| Hold | 15°C |
| gene | Annealing temperature | Nucleotide sequence (5’ -3’ ) | Expected size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 integrase gene | Intl1 | 56 °C | IntI1F (ACGAGCGCAAGGTTTCGGT) IntI1R (GAAAGGTCTGGTCATACATG) |
565 |
| Class 2 integrase gene | Intl2 | 52 °C | IntI2F (GTGCAACGCATTTTGCAGG) IntI2R (CAACGGAGTCATGCAGATG) |
403 |
| Class 3 integrase gene | Intl3 | 57 °C | IntI3F (CATTTGTGTTGTGGACGGC) IntI3R (GACAGATACGTGTTTGGCAA) |
717 |
| Variable regions | 52 °C | 5’ -CS (GGCATCCAAGCAGCAAG) 3’-CS (AAGCAGACTTGACCTGAT) |
Uncertain |
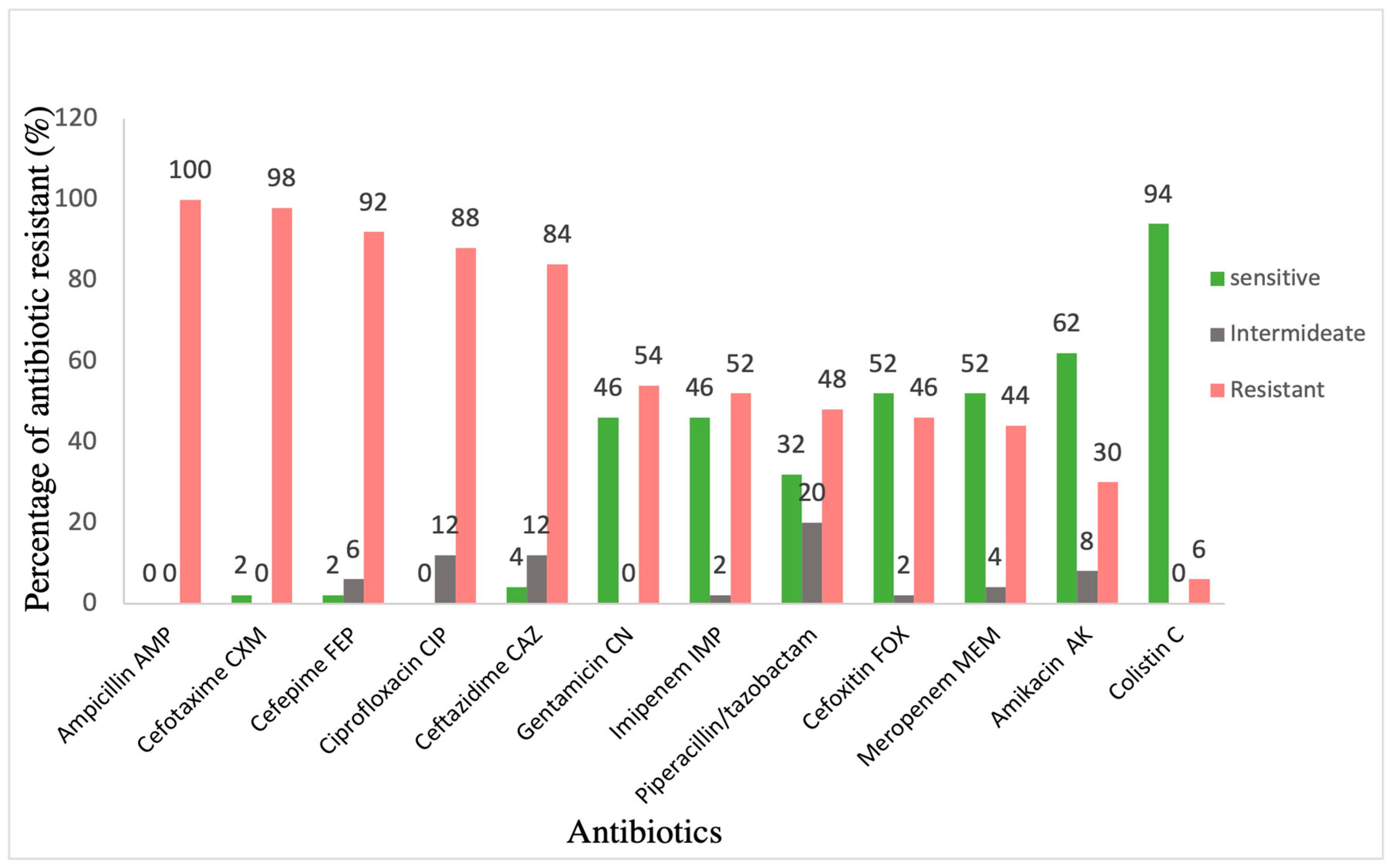
| Isolate | AMP | CTX | FEP | CIP | CAZ | TZP | FOX | IPM | MEM | CN | AK | CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kp 1 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | S |
| Kp 2 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | I | R |
| Kp 5 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 6 PDR | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Kp 7 | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | S | S | R | R | S |
| Kp 11 PDR | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Kp 13 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 15 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 16 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| Kp 22 | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | S | S | R |
| Kp 24 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| Kp 28 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 29 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 30 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 31 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 32 | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 41 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| Kp 43 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| Kp 44 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | S |
| Kp 45 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 48 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 49 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| Kp 50 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R |
| Demographic and Clinical Characteristics | Case Patients, n = 13 |
|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 12 (92%) |
| Age | |
| Adults <=24 years, n (%) | 1 (7.7%) |
| From 25-50 years, n (%) | 3 (23.1%) |
| More than 50 years, n (%) | 9 (69.2%) |
| Age at first positive culture | |
| Mean age of adults, years (range) | 59.7 (20-86) |
| Length of stay | |
| Median length of stay to a first positive culture, days (range) | 48 (1–134) |
| Hospital location | |
| Intensive care unit (ICU), n (%) | 8 (61.5%) |
| Intermediate care ward, n (%) | 5 (83.5 %) |
| Isolate (KP) | PhoP | PhoQ |
|---|---|---|
| Kp 6 and Kp 11 | 3 SNPs | -Ve |
| (Gln147His) | ||
| (Gln131Glu) | ||
| (Pro129Thr) | ||
| Kp 22 and Kp 50 | 3 SNPs | -Ve |
| (Val129Glu) (Gln147His) | ||
| (Gln131Glu) |
| K. Pneumoniae (n=23) | Phenotypic resistance | Genes positive | Level of agreement- genotypic with phenotypic expression % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Amikacin | 9 | 21 | 42.90% |
| Gentamicin | 15 | 21 | 71.40% | |
| Quinolones | 23 | 23 | 100% | |
| Carbapenems | 14 | 14 | 100% | |
| Cephalosporins | 23 | 23 | 100% | |
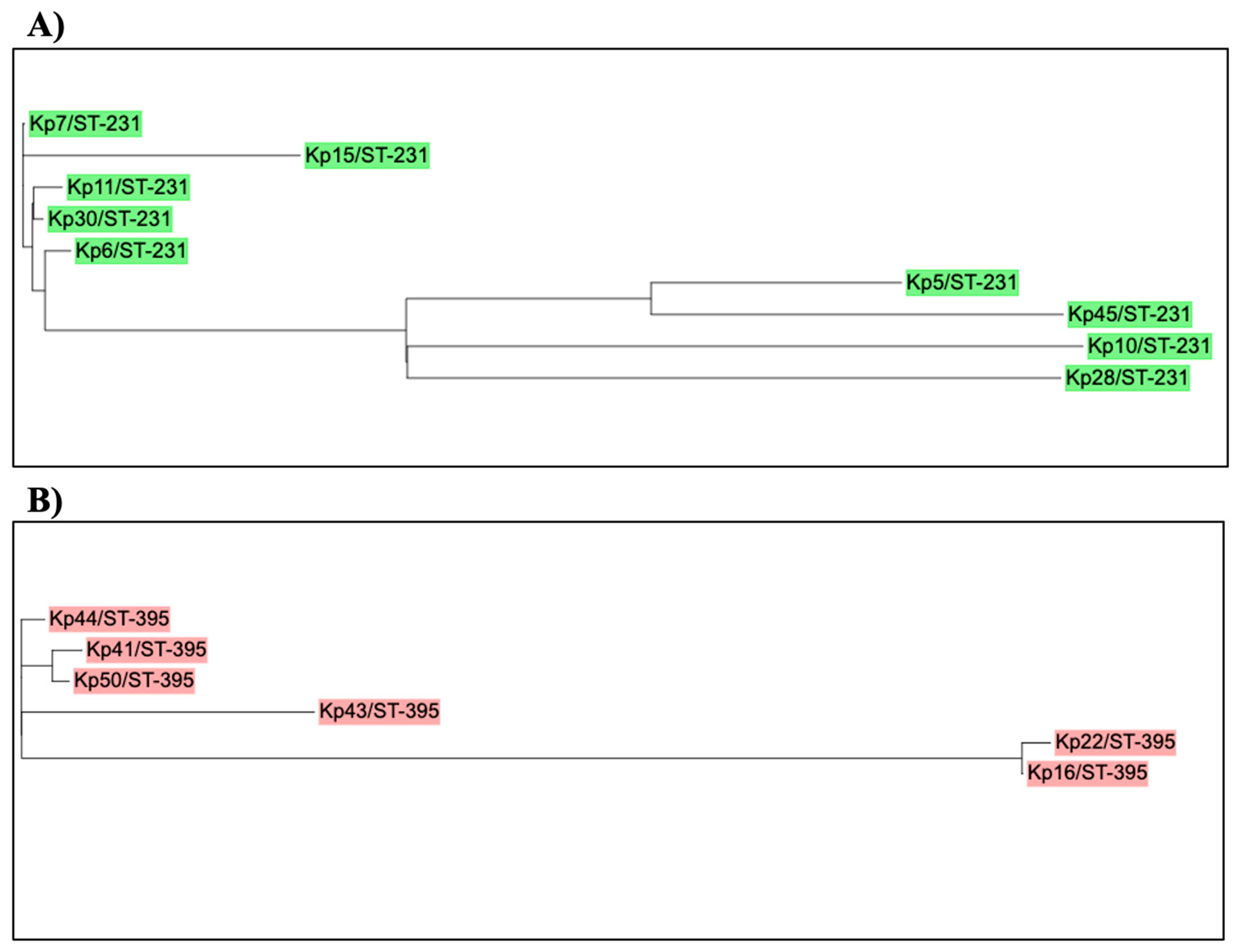
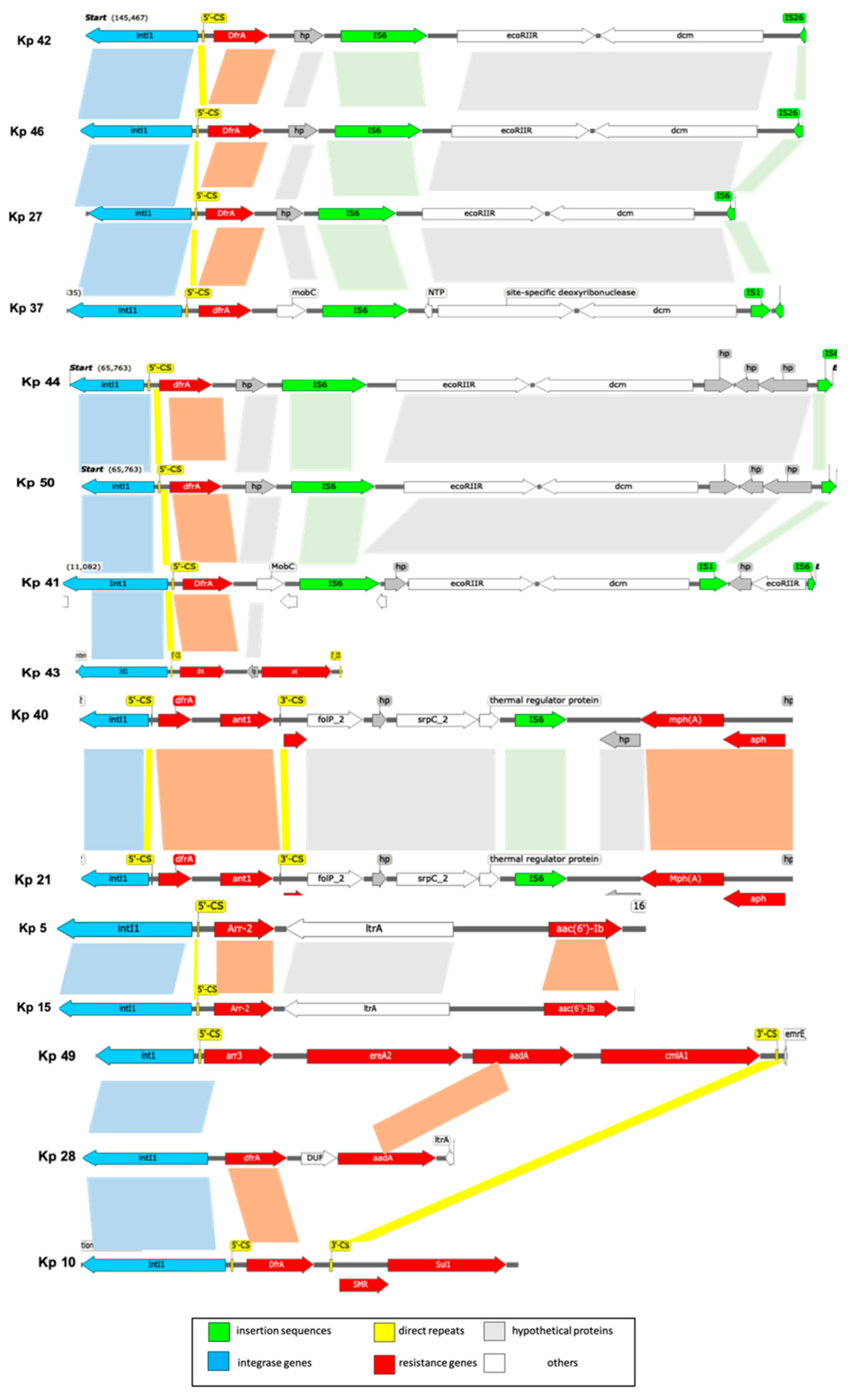
| Isolate | ST type | Gene cassette |
|---|---|---|
| Kp 40 | 37 | dfrA12,ant1 |
| Kp 49 | 147 | Arr3, ereA2, aadA, cmlA1 |
| Kp 21 | 45 | dfra12,ant1 |
| Kp 41 | 395 | dfrA14, |
| Kp 43 | 395 | dfrA12, APH(3”)-Ia, |
| Kp 44 | 395 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 50 | 395 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 16 | 395 | In0 |
| Kp 22 | 395 | In0 |
| Kp 5 | 231 | aac(6')-Ib, arr2, |
| Kp 6 | 231 | dfrA12, emrE, ant1 |
| Kp 7 | 231 | dfrA12, emrE, ant1 |
| Kp 10 | 231 | dfrA5 |
| Kp 11 | 231 | aacA4, cat1, ant1, |
| Kp 15 | 231 | aacA4, emrE, ant1 |
| Kp 28 | 231 | Ant1, erm, cat1 |
| Kp 30 | 231 | aacA4 |
| Kp 45 | 231 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 42 | 405 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 46 | 405 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 27 | 280 | dfrA14 |
| Kp 25 | 1741 | In0 |
| Kp 37 | 1710 | dfrA14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





