Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
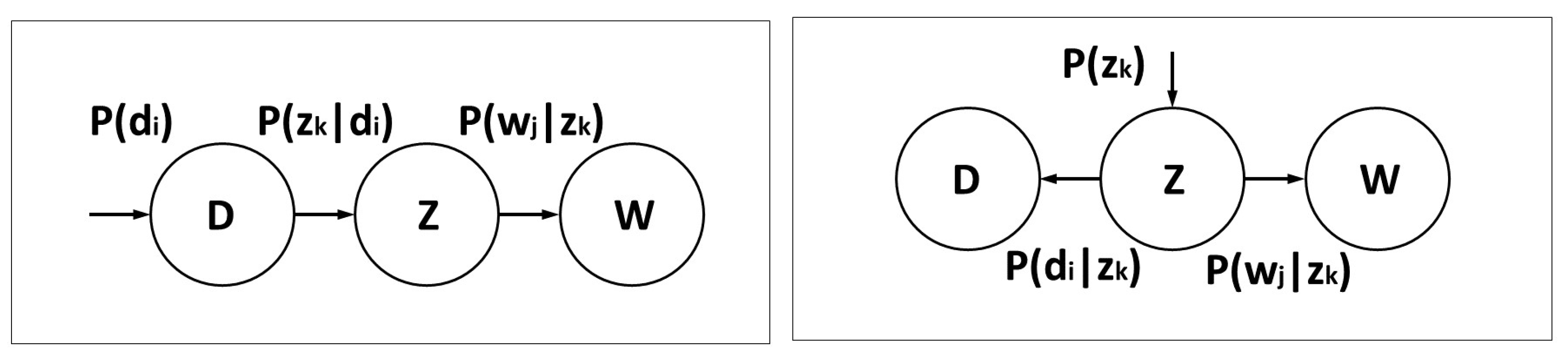
3. The Method: PLSA Formulas
| Aspect 1 | Aspect 2 | Aspect 3 | Aspect 4 |
| imag | video | region | speaker |
| SEGMENT | sequenc | contour | speech |
| color | motion | boundari | recogni |
| tissu | frame | descript | signal |
| Aspect1 | scene | imag | train |
| brain | SEGMENT | SEGMENT | hmm |
| slice | shot | precis | sourc |
| cluster | imag | estim | speakerindepend |
| mri | cluster | pixel | SEGMENT |
| algorithm | visual | paramet | sound |
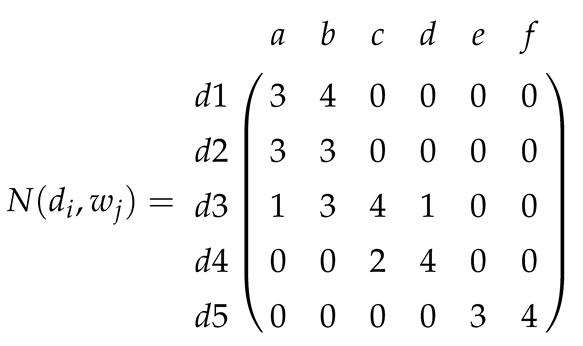 and the frequency matrix n
and the frequency matrix n3.1. Training and Prediction
4. Criticism: The LDA and Reformulations
4.1. Latent Dirichlet Allocation
4.2. Other Formulations
4.2.1. Extension to Continuous Data
4.2.2. Randomized Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis
4.2.3. Tensorial Approach
5. NMF Point of View
6. Extensions
6.1. Kernelization
6.2. Principal Component Analysis
6.3. Clustering
6.4. Information Theory Interpretation
6.5. Transfer Learning
6.6. Open Questions
7. PLSA Processing Steps and State of the Art of Solutions
7.1. Algorithm Initialization
7.2. Algorithms Based on Expectation Maximization Improvement
7.2.1. Tempered EM
7.2.2. Sparse PLSA
7.2.3. Incremental PLSA
7.3. Use of Computational Techniques
7.4. Open Questions
8. Discussion
9. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann, T. Probabilistic latent semantic indexing. SIGIR ’99: Proceedings of the 22nd annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval 1999.
- Hofmann, T. Probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Prodeedings 1999.
- Hofmann, T. Unsupervised learning by probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Machine Learning 2001. [CrossRef]
- Deerwester, S.; Dumais, S.T.; Furnas, G.W.; Landauer, T.K.; Harshman, R. Indexing by latent semantic analysis. Journal of the American society for information science 1990, 41, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, L.; Pereira, F. Aggregate and mixed-order Markov models for statistical language processing. arXiv preprint cmp-lg/9706007 1997.
- Barde, B.V.; Bainwad, A.M. An overview of topic modeling methods and tools. 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS). IEEE, 2017, pp. 745–750.
- Ibrahim, R.; Elbagoury, A.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. Tools and approaches for topic detection from Twitter streams: survey. Knowledge and Information Systems 2018, 54, 511–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D. Research on PLSA model based semantic image analysis: A systematic review. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing 2018, 9, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, T. Collaborative filtering via gaussian probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Proceedings of the 26th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in informaion retrieval, 2003, pp. 259–266.
- Gaussier, E.; Goutte, C. Relation between PLSA and NMF and implications. In Proceedings 28th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval (SIGIR’05) 2005.
- Ding, C.; He, X.; Simon, H.D. On the equivalence of nonnegative matrix factorization and spectral clustering. Proceedings of the 2005 SIAM international conference on data mining. SIAM, 2005, pp. 606–610. [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T. Learning the similarity of documents: An information-geometric approach to document retrieval and categorization. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2000, pp. 914–920.
- Ding, C.H.; Li, T.; Jordan, M.I. Convex and semi-nonnegative matrix factorizations. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2008, 32, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, B.; Curry, J.; Dougherty, A. Non-negative matrix factorization: Ill-posedness and a geometric algorithm. Pattern Recognition 2009, 42, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.R.; Murty, M.N. On the Relation Between K-means and PLSA. 2012 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krithara, A.; Paliouras, G. TL-PLSA: Transfer learning between domains with different classes. 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining. IEEE, 2013, pp. 419–427. [CrossRef]
- Figuera, P.; García Bringas, P. On the Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis Generalization as the Singular Value Decomposition Probabilistic Image. Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications 2020, 19, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Huang, C.L.; Tan, Y.K.; Ma, B. Language models learning for domain-specific natural language user interaction. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), 2009, pp. 2480–2485. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Schuurmans, D.; Peng, F.; Zhao, Y. Combining statistical language models via the latent maximum entropy principle. Machine Learning 2005, 60, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagie, M.; Van Der Loos, M.; Van Wezel, M. Including item characteristics in the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model for collaborative filtering. Ai Communications 2009, 22, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Huang, C.L.; Wu, C.H. Spoken document summarization using topic-related corpus and semantic dependency grammar. 2004 International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing. IEEE, 2004, pp. 333–336. [CrossRef]
- Madsen, R.E.; Larsen, J.; Hansen, L.K. Part-of-speech enhanced context recognition. Proceedings of the 2004 14th IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop Machine Learning for Signal Processing, 2004. IEEE, 2004, pp. 635–643.
- Tsai, F.S.; Chan, K.L. Detecting cyber security threats in weblogs using probabilistic models. Pacific-Asia Workshop on Intelligence and Security Informatics. Springer, 2007, pp. 46–57. [CrossRef]
- Farhadloo, M.; Rolland, E. Fundamentals of sentiment analysis and its applications. In Sentiment Analysis and Ontology Engineering; Springer, 2016; pp. 1–24.
- Xie, X.; Ge, S.; Hu, F.; Xie, M.; Jiang, N. An improved algorithm for sentiment analysis based on maximum entropy. Soft Computing 2019, 23, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monay, F.; Gatica-Perez, D. On image auto-annotation with latent space models. Proceedings of the eleventh ACM international conference on Multimedia, 2003, pp. 275–278.
- Lienhart, R.; Hauke, R. Filtering adult image content with topic models. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. IEEE, 2009, pp. 1472–1475.
- Shah-Hosseini, A.; Knapp, G.M. Semantic image retrieval based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on Multimedia, 2006, pp. 703–706. [CrossRef]
- Foncubierta-Rodríguez, A.; García Seco de Herrera, A.; Müller, H. Medical image retrieval using bag of meaningful visual words: unsupervised visual vocabulary pruning with PLSA. Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on Multimedia indexing and information retrieval for healthcare, 2013, pp. 75–82.
- Cao, Y.; Steffey, S.; He, J.; Xiao, D.; Tao, C.; Chen, P.; Müller, H. Medical image retrieval: a multimodal approach. Cancer informatics 2014, 13, CIN–S14053. [CrossRef]
- Fasel, B.; Monay, F.; Gatica-Perez, D. Latent semantic analysis of facial action codes for automatic facial expression recognition. Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGMM international workshop on Multimedia information retrieval, 2004, pp. 181–188. [CrossRef]
- Quelhas, P.; Monay, F.; Odobez, J.M.; Gatica-Perez, D.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Modeling scenes with local descriptors and latent aspects. Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1. IEEE, 2005, Vol. 1, pp. 883–890.
- Zhu, S. Pain expression recognition based on pLSA model. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haloi, M. A novel plsa based traffic signs classification system. pre-print 2015, [1503.06643].
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Lu, H. Co-regularized plsa for multi-view clustering. Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2012, pp. 202–213. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.M.; Su, E.C.Y.; Lo, A.; Chiu, H.S.; Sung, T.Y.; Hsu, W.L. PSLDoc: Protein subcellular localization prediction based on gapped-dipeptides and probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 2008, 72, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masseroli, M.; Chicco, D.; Pinoli, P. Probabilistic latent semantic analysis for prediction of gene ontology annotations. The 2012 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, 2012, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Pulido, A.; Rueda, A.; Romero, E. Extracting regional brain patterns for classification of neurodegenerative diseases. IX International Seminar on Medical Information Processing and Analysis; Brieva, J.; Escalante-Ramírez, B., Eds. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, 2013, Vol. 8922, p. 892208. [CrossRef]
- Su, E.C.Y.; Chang, J.M.; Cheng, C.W.; Sung, T.Y.; Hsu, W.L. Prediction of nuclear proteins using nuclear translocation signals proposed by probabilistic latent semantic indexing. BMC bioinformatics. Springer, 2012, Vol. 13, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Qian, F.; Ou, X. 3D seismic waveform classification study based on high-level semantic feature. 2015 1st International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management (GISTAM). IEEE, 2015, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Geng, T.; Elsayed, Y.; Saaj, C.; Lekakou, C. A unified system identification approach for a class of pneumatically-driven soft actuators. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2015, 63, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K. Probabilistic latent semantic analysis of composite excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectra of multicomponent system. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2020, 239, 118518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, M.; Smets, T.; Waelkens, E.; De Moor, B. A Mathematical Comparison of Non-negative Matrix Factorization-Related Methods with Practical Implications for the Analysis of Mass Spectrometry Imaging Data. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 2021, e9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L. A tutorial on probabilistic latent semantic analysis. pre-print 2012, [1212.3900].
- Dempster, A.; Laird, N.; Rubin, D. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data via the EM Agorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, Methodological 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Jebara, T.; Pentland, A. On reversing Jensen’s inequality. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2001, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C.; Clustering, C.R.D. Algorithms and Applications; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, 2014.
- Brants, T.; Chen, F.; Tsochantaridis, I. Topic-based document segmentation with probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Proceedings of the eleventh international conference on Information and knowledge management, 2002, pp. 211–218.
- Brants, T. Test data likelihood for PLSA models. Information Retrieval 2005, 8, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brants, T.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Hofmann, T.; Chen, F. Computer controlled method for performing incremental probabilistic latent semantic analysis of documents, involves performing incremental addition of new term to trained probabilistic latent semantic analysis model, 2006. US Patent Number US2006112128-A1.
- Zhuang, L.; She, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, K.; Yu, N. Image classification via semi-supervised pLSA. 2009 Fifth International Conference on Image and Graphics. IEEE, 2009, pp. 205–208.
- Niu, L.; Shi, Y. Semi-supervised plsa for document clustering. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops. IEEE, 2010, pp. 1196–1203.
- Blei, D.M.; Lafferty, J.D. Dynamic topic models. Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, 2006, pp. 113–120.
- Girolami, M.; Kabǿn, A. On an equivalence between PLSI and LDA. SIGIR 03 Proceedings of the 26th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval 2003.
- Teh, Y.W.; Jordan, M.I.; Beal, M.J.; Blei, D.M. Hierarchical Dirichlet Processes. Journal of the American Statistical Association 2006, 101, 1566–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimno, D.; Li, W.; McCallum, A. Mixtures of hierarchical topics with pachinko allocation. Proceedings of the 24th international conference on Machine learning, 2007, pp. 633–640.
- Koltcov, S.; Ignatenko, V.; Terpilovskii, M.; Rosso, P. Analysis and tuning of hierarchical topic models based on Renyi entropy approach, 2021, [arXiv:stat.ML/2101.07598]. arXiv:stat.ML/2101.07598].
- Bosch, A.; Zisserman, A.; Muñoz, X. Scene classification via pLSA. European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2006, pp. 517–530.
- Hörster, E.; Lienhart, R.; Slaney, M. Continuous visual vocabulary modelsfor plsa-based scene recognition. Proceedings of the 2008 international conference on Content-based image and video retrieval, 2008, pp. 319–328.
- Li, Z.; Shi, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, Z. Modeling continuous visual features for semantic image annotation and retrieval. Pattern Recognition Letters 2011, 32, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodner, E.; Denzler, J. Randomized probabilistic latent semantic analysis for scene recognition. Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition. Springer, 2009, pp. 945–953.
- Ho, T.K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1998, 20, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashua, A.; Hazan, T. Non-negative tensor factorization with applications to statistics and computer vision. Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on Machine learning, 2005, pp. 792–799.
- Peng, W.; Li, T. On the equivalence between nonnegative tensor factorization and tensorial probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Applied Intelligence 2011, 35, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, R.A. others. Foundations of the PARAFAC procedure: Models and conditions for an explanatory multimodal factor analysis. University of California at Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 1970.
- Balažević, I.; Allen, C.; Hospedales, T.M. Tucker: Tensor factorization for knowledge graph completion. pre-print 2019, [1901.09590].
- Yoo, J.; Choi, S. Probabilistic matrix tri-factorization. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. IEEE, 2009, pp. 1553–1556.
- Cichocki, A.; Zdunek, R.; A.H., P.; Amary, S. Nonnegative Matrix and Tensor Factorizations; John Willey and Sons Ltd, 2009.
- Shashanka, M.; Raj, B.; Smaragdis, P. Probabilistic latent variable models as nonnegative factorizations. Computational intelligence and neuroscience 2008, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajori, F. A history of mathematical notations; Vol. 1, Courier Corporation, 1993.
- Biletch, B.D.; Yu, H.; Kay, K.R. An analysis of mathematical notations: for better or for worse, 2015.
- Cayley, A. Remarques sur la notation des fonctions algébriques., 1855.
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The nonnegative rank factorizations of nonnegative matrices. Linear Algebra and its Applications 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D. Matrix analysis and applications; Cambridge University Press, 2017.
- Beltrami, E. Sulle funzioni bilineari. Giornale di Matematiche ad Uso degli Studenti Delle Universita 1873, 11, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.D.; Porter, M.A. The extraordinary SVD. The American Mathematical Monthly 2012, 119, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.L. Every waking moment Ky Fan (1914–2010). Notices of the AMS 2010, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Moslehian, M.S. Ky fan inequalities. Linear and Multilinear Algebra 2012, 60, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, N.J.; Lin, L. Matrix functions: A short course. Matrix Functions and Matrix Equations 2013, 19, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Eckart, C.; Young, G. A principal axis transformation for non-Hermitian matrices. Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 1939, 45, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. The Singular Value Decomposition, Applications and Beyond. arXiv preprint 2015, [1510.08532].
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; T., L.; W., P. On the equivalence between non-negative matrix factorization and probabilistic latent semantic indexing. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2008.
- Mnih, A.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Probabilistic matrix factorization. Advances in neural information processing systems 2007, 20, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Khuri, A.I. Advanced calculus with applications in statistics (Second Edition); Vol. 486, John Wiley & Sons, 2003.
- Amari, S.I. Information geometry of the EM and em algorithms for neural networks. Neural networks 1995, 8, 1379–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappelier, J.C.; Eckard, E. Plsi: The true fisher kernel and beyond. Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Springer, 2009, pp. 195–210.
- Hofmann, T.; Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Kernel methods in machine learning. The annals of statistics 2008, 1171–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K.; Akaho, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Müller, K.R. Asymptotic properties of the Fisher kernel. Neural computation 2004, 16, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, M.C.; Wang, L.; Lyu, S. Efficient algorithms for graph regularized PLSA for probabilistic topic modeling. Pattern Recognition 2019, 86, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuera, P.; Bringas, P.G. A Non-parametric Fisher Kernel. International Conference on Hybrid Artificial Intelligence Systems. Springer, 2021, pp. 448–459.
- Bishop, C.M. Bayesian pca. Advances in neural information processing systems 1999, pp. 382–388.
- Kim, D.; Lee, I.B. Process monitoring based on probabilistic PCA. Chemometrics and intelligent laboratory systems 2003, 67, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Del Buono, N.; Mencar, C. Nonnegative matrix factorizations for intelligent data analysis. In Non-negative Matrix Factorization Techniques; Springer, 2016; pp. 49–74. [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, R.; Pöppel, G.; Tomé, A.; Lang, E. From binary NMF to variational bayes NMF: A probabilistic approach. In Non-negative Matrix Factorization Techniques; Springer, 2016; pp. 1–48. [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, K.; Wang, G.; Ebrahimi, N. A unified statistical approach to non-negative matrix factorization and probabilistic latent semantic indexing. Machine Learning 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, E.R.; Brun, M. A probabilistic theory of clustering. Pattern Recognition 2004, 37, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J. Alternative clustering analysis: A review. Data Clustering 2018, pp. 535–550. [CrossRef]
- Shashanka, M. Simplex decompositions for real-valued datasets. 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing. IEEE, 2009, pp. 1–6.
- Rao, C.R. Diversity and dissimilarity coefficients: a unified approach. Theoretical population biology 1982, 21, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R. Diversity: Its measurement, decomposition, apportionment and analysis. Sankhyā: The Indian Journal of Statistics, Series A 1982, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.R. Differential metrics in probability spaces. Differential geometry in statistical inference 1987, 10, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.; Mitchell, A.F. Rao’s distance measure. Sankhyā: The Indian Journal of Statistics, Series A 1981, 345–365. [Google Scholar]
- Sejdinovic, D.; Sriperumbudur, B.; Gretton, A.; Fukumizu, K. Equivalence of distance-based and RKHS-based statistics in hypothesis testing. The Annals of Statistics 2013, 2263–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhler, C. Geometry of maximum likelihood estimation in Gaussian graphical models; University of California, Berkeley, 2011.
- Amari, S.i. Information geometry and its applications; Vol. 194, Springer, 2016.
- Chuanqi, T.; Sun, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, C. A Survey on Deep Transfer Learning. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:cs.LG/1808.01974]. [Google Scholar]
- Bozinovski, S. Reminder of the first paper on transfer learning in neural networks, 1976. Informatica 2020, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Mao, K. Supervised adaptive-transfer PLSA for cross-domain text classification. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop. IEEE, 2014, pp. 259–266.
- Mirsky, L. An introduction to linear algebra; Dover Publications Inc., 1990.
- Huang, K.; Sidiropoulos, N.D.; Swami, A. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Revisited: Uniqueness and Algorithm for Symmetric Decomposition. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING 2014, 62, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Anh, V.N.; Mamitsuka, H. Efficient probabilistic latent semantic analysis through parallelization. Asia Information Retrieval Symposium. Springer, 2009, pp. 432–443. [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. Matrix computations. Johns Hopkins studies in the mathematical sciences; Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD, 1996.
- Anderson, E.; Bai, Z.; Bischof, C.; Blackford, L.S.; Demmel, J.; Dongarra, J.; Du Croz, J.; Greenbaum, A.; Hammarling, S.; McKenney, A. others. LAPACK Users’ guide; SIAM, 1999.
- Farahat, A.; Chen, F. Improving probabilistic latent semantic analysis with principal component analysis. 11th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2006.
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, Z.Y. Improved text clustering algorithm of probabilistic latent with semantic analysis [J]. Journal of Computer Applications 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Gong, S.; Liu, C.; Zeng, J.; Jia, N.; Zhang, Y. Online belief propagation algorithm for probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Frontiers of Computer Science 2013, 7, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottou, L.; others. Online learning and stochastic approximations. On-line learning in neural networks 1998, 17, 142. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yamaguchi, K. The EM algorithm and related statistical models; CRC Press, 2003.
- Meng, X.L.; Van Dyk, D. The EM algorithm—an old folk-song sung to a fast new tune. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology) 1997, 59, 511–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A. EM algorithm and variants: An informal tutorial. pre-print 2011, [1105.1476].
- Hinton, G.E.; Zemel, R.S. Autoencoders, minimum description length, and Helmholtz free energy. Advances in neural information processing systems 1994, 6, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, R.M.; Hinton, G.E. A view of the EM algorithm that justifies incremental, sparse, and other variants. In Learning in graphical models; Springer, 1998; pp. 355–368. [CrossRef]
- Hazan, T.; Hardoon, R.; Shashua, A. Plsa for sparse arrays with Tsallis pseudo-additive divergence: noise robustness and algorithm. 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2007, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Tsallis, C. Possible generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs statistics. Journal of statistical physics 1988, 52, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzawa, Y. On Tsallis Entropy-Based and Bezdek-Type Fuzzy Latent Semantics Analysis. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). IEEE, 2018, pp. 3685–3689. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, G.; Wang, Y.; Herman, G.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J. Incremental EM for Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis on Human Action Recognition. 6th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X. Incremental probabilistic latent semantic analysis for automatic question recommendation. Proceedings of the 2008 ACM conference on Recommender systems, 2008, pp. 99–106. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Luo, W.; Yang, K.; Zhuang, F.; He, Q.; Shi, Z. Self-organizing weighted incremental probabilistic latent semantic analysis. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics 2018, 9, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiou, N.; Kotropoulos, C. Rplsa: A novel updating scheme for probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Computer Speech & Language 2011, 25, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanovic, K.; Bodik, R.; Catanzaro, B.C.; Gebis, J.J.; Husbands, P.; Keutzer, K.; Patterson, D.A.; Plishker, W.L.; Shalf, J.; Williams, S.W. others. The landscape of parallel computing research: A view from berkeley, 2006.
- Hong, C.; Chen, W.; Zheng, W.; Shan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Parallelization and characterization of probabilistic latent semantic analysis. 2008 37th International Conference on Parallel Processing. IEEE, 2008, pp. 628–635.
- Dean, J.; Ghemawat, S. MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Communications of the ACM 2008, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y. P 2 LSA and P 2 LSA+: Two paralleled probabilistic latent semantic analysis algorithms based on the MapReduce model. International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning. Springer, 2011, pp. 385–393.
- gpgpu.org. General-Purpose Computation Graphics Hardware. https://web.archive.org/web/20051231024709/http://www.gpgpu.org/, 2006.
- Kouassi, E.K.; Amagasa, T.; Kitagawa, H. Efficient probabilistic latent semantic indexing using graphics processing unit. Procedia Computer Science 2011, 4, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saâdaoui, F. Randomized extrapolation for accelerating EM-type fixed-point algorithms. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 2023, 196, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J. On the convergence properties of the EM algorithm. The Annals of statistics 1983, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyles, R.A. On the convergence of the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) 1983, 45, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.D. Additive non-negative matrix factorization for missing data. pre-print 2010, [1007.0380].
- Archambeau, C.; Lee, J.A.; Verleysen, M. ; others. On Convergence Problems of the EM Algorithm for Finite Gaussian Mixtures. ESANN, 2003, Vol. 3, pp. 99–106.
- Schmidt, Erhard. Zur Theorie der linearen und nichtlinearen Integralgleichungen. In Integralgleichungen und Gleichungen mit unendlich vielen Unbekannten; Springer, 1989; pp. 190–233.
- Valiant, L.G. A theory of the learnable. Communications of the ACM 1984, 27, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Notation in areas with strong mathematical content is nontrivial and has a secular history [71]. In many cases, the notation determines conceptual developments [72]. The classical matrix notation, attributed to Cayley [73], among others, remains useful today. However, in the case of NMF, it is more convenient to write, at least in elementary statements, the product as
|
| 2 | Several authors have referred to the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence as
|
| 3 | PCA dimension refers to the geometric multiplicity of the eigenvalues of the SVD theorem and corresponds to , with being and vectors of and , respectively. The nonzero roots of such that , or characteristic polynomial is the algebraic multiplicity . Both ideas play a fundamental role in the canonical forms [113, Chap. 10] and the interpretation of dimensionality in matrix analysis. |
| Year | Contribution | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | PLSA | PLSA formulation in conference proceedings [1,2]. [3] comments on the connections among NMF, SVD and information geometry. |
| 2003 | LDA | Criticism of PLSA: LDA formulation [9]. |
| 2003 | Gaussian PLSA | Assumption of Gaussian mixtures [10]. |
| 2005 | NMF | PLSA solves the NMF problem [11]. Introduction to stochastic matrices [12]. |
| 2008 | Kernelization | Fisher kernel derivation from PLSA [13]. |
| 2008 | k-means | Equivalence between k-means and NMF [14]. |
| 2009 | PCA | Comparison of NMF, PLSA and PCA [15]. |
| 2012 | Information Geometry | Relationship between Fisher information matrix and variance from the PLSA context [16]. |
| 2018 | Neural Networks | Neural network interpretation of PLSA for transfer learning [17]. |
| 2020 | SVD | Establishment of conditions for equivalence among NMF, PLSA and SVD [18]. |
| Discipline | Research Area | % |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering (45%) | Mechanics & Robotics | 37 |
| Acoustics | 4 | |
| Telecommunications & Control Theory | 3 | |
| Materials Science | 1 | |
| Computer Science (34%) | Clustering | 18 |
| Information retireval | 9 | |
| Networks | 4 | |
| Machine Learning Applications | 3 | |
| Semantic image analysis (10%) | Image classification | 4 |
| Image retrieval | 3 | |
| Image classification | 3 | |
| Life Sciences (5%) | Mathematical Computational Biology | 2 |
| Biochemistry Molecular Biology | 2 | |
| Environmental Sciences Ecology | 1 | |
| Methodological (4%) | - | 3 |
| Fundamental Sciences (2%) | Geochemistry Geophysics | 1 |
| Instruments Instrumentation | 1 |
| Asymmetric formulation | Symmetric formulation | |
|---|---|---|
| E-step | ||
| M-step | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





