Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Diet composition and functional feed
2.3. Bovine blood collection
2.4. Serum concentrations of glucose and triglycerides
2.5. Serum levels of fT3, fT4 and 17β-Estradiol
2.6. Serum levels of hormonal parameters
2.7. Milk sampling
2.8. Analysis of fatty acid profile in milk
2.9. Lysozyme content and chemical-nutritional analysis of milk
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
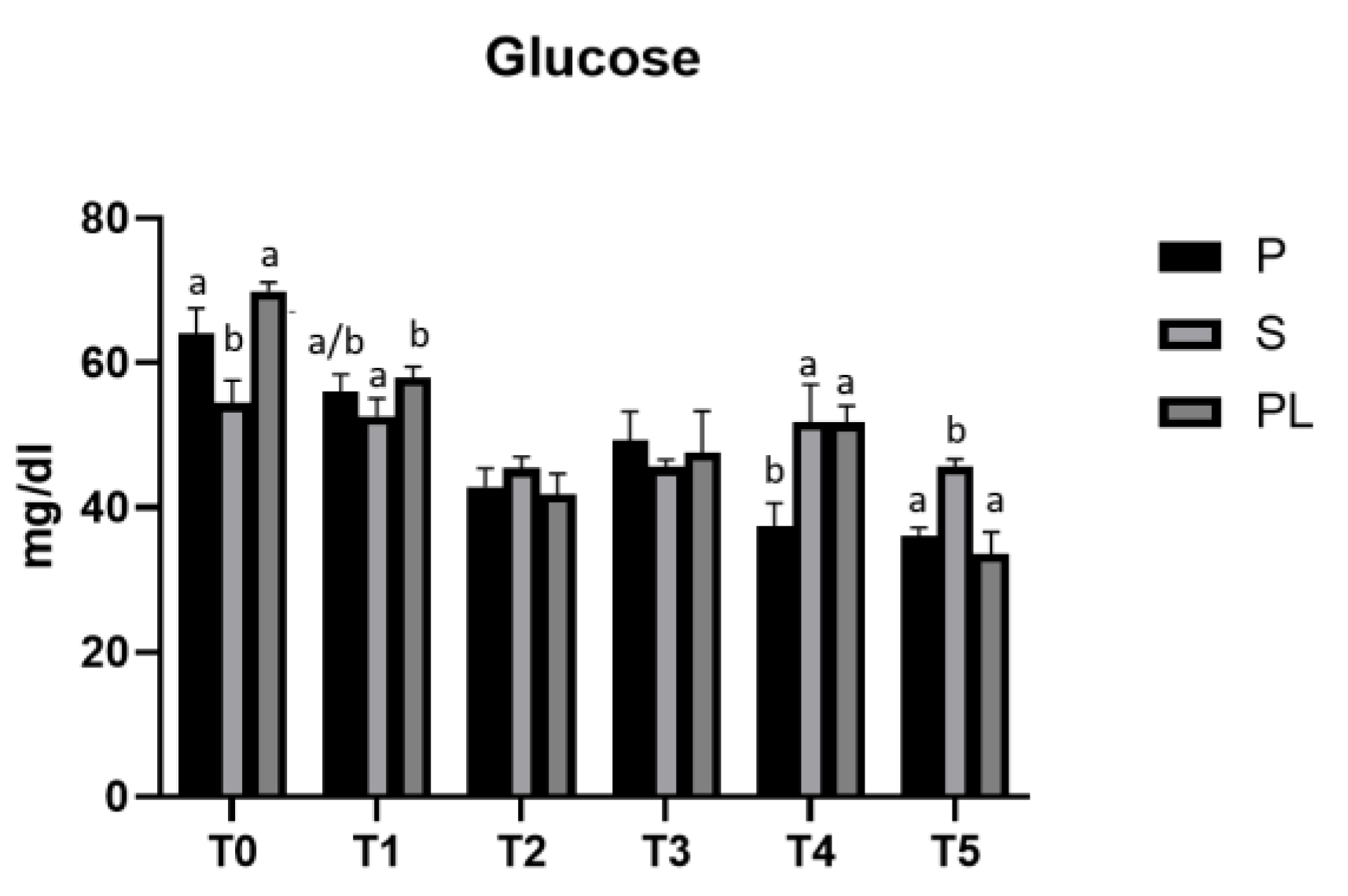
3.1. Serum glucose levels in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
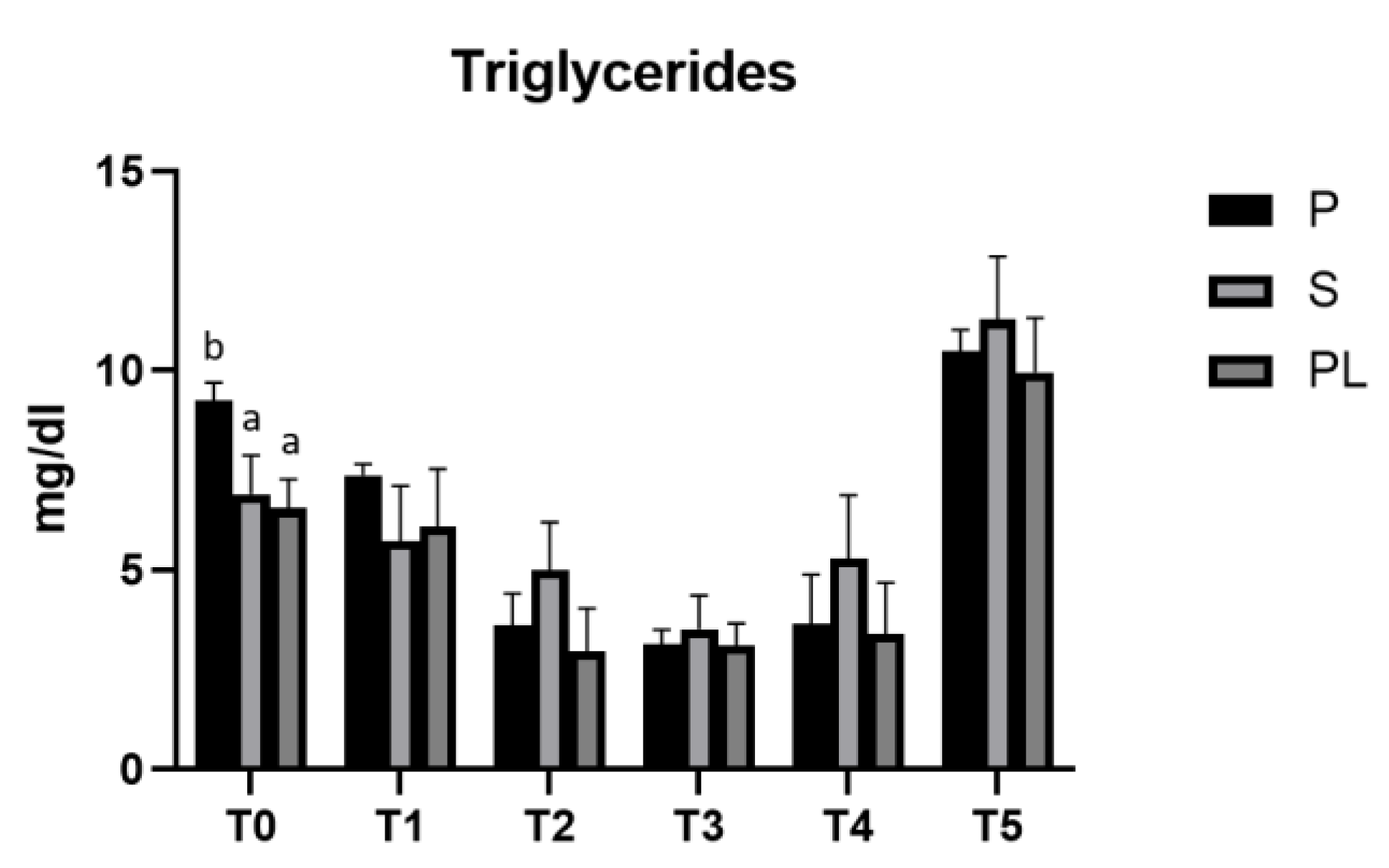
3.2. Serum levels of triglycerides in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
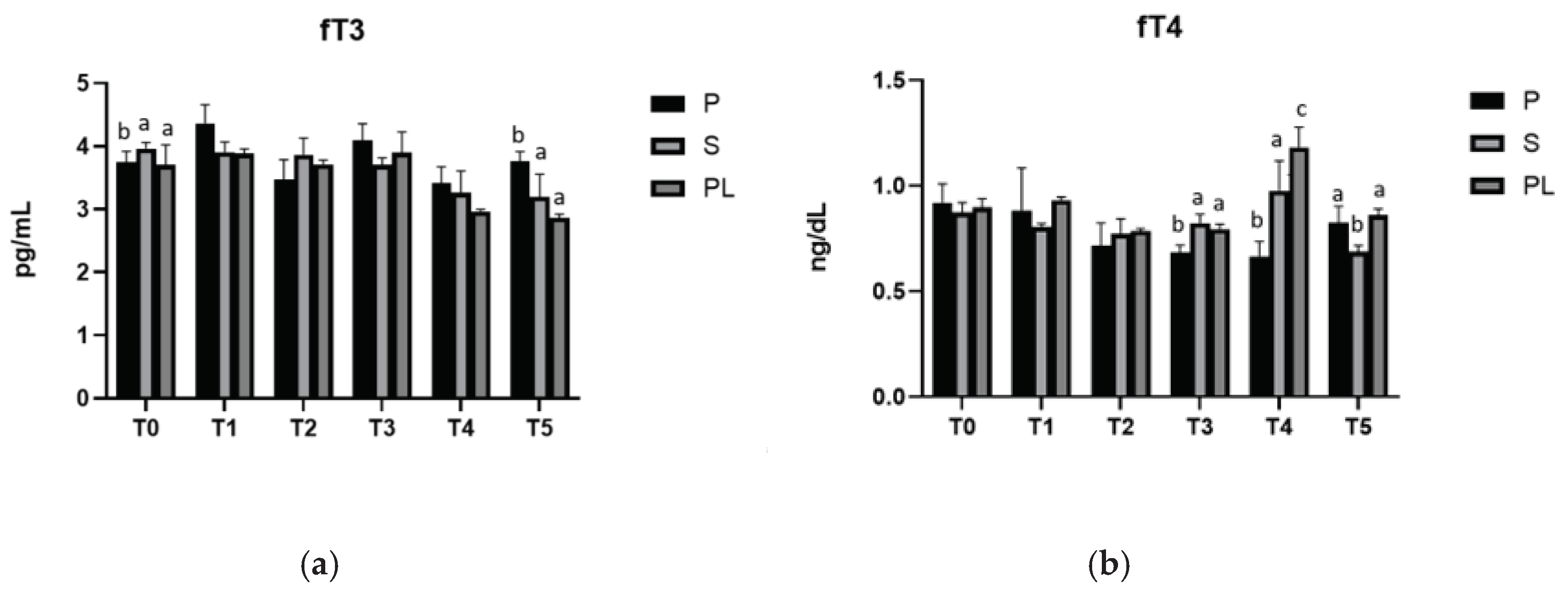
3.3. Serum levels of fT3 and fT4 in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
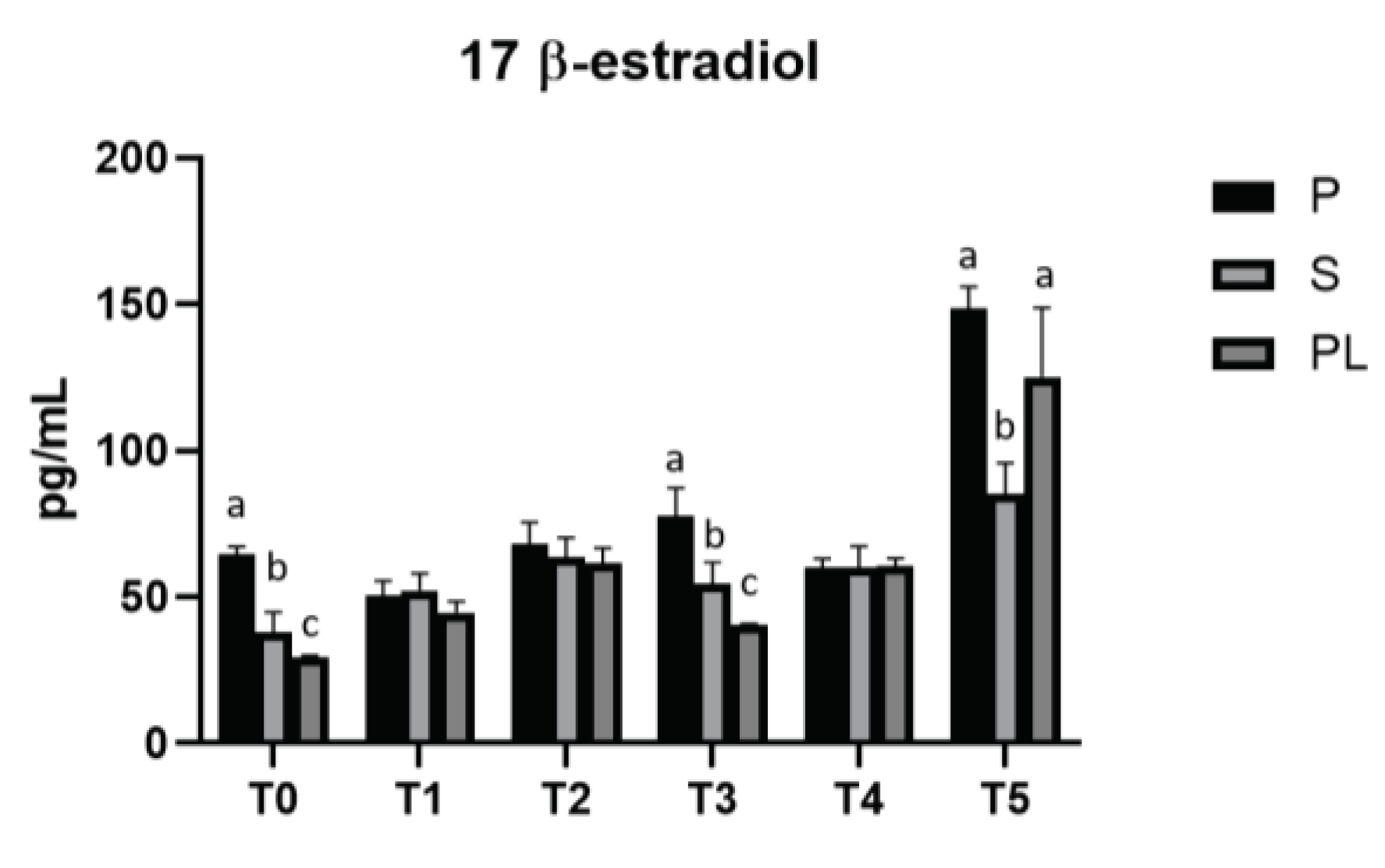
3.4. Serum levels of 17β-Estradiol in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
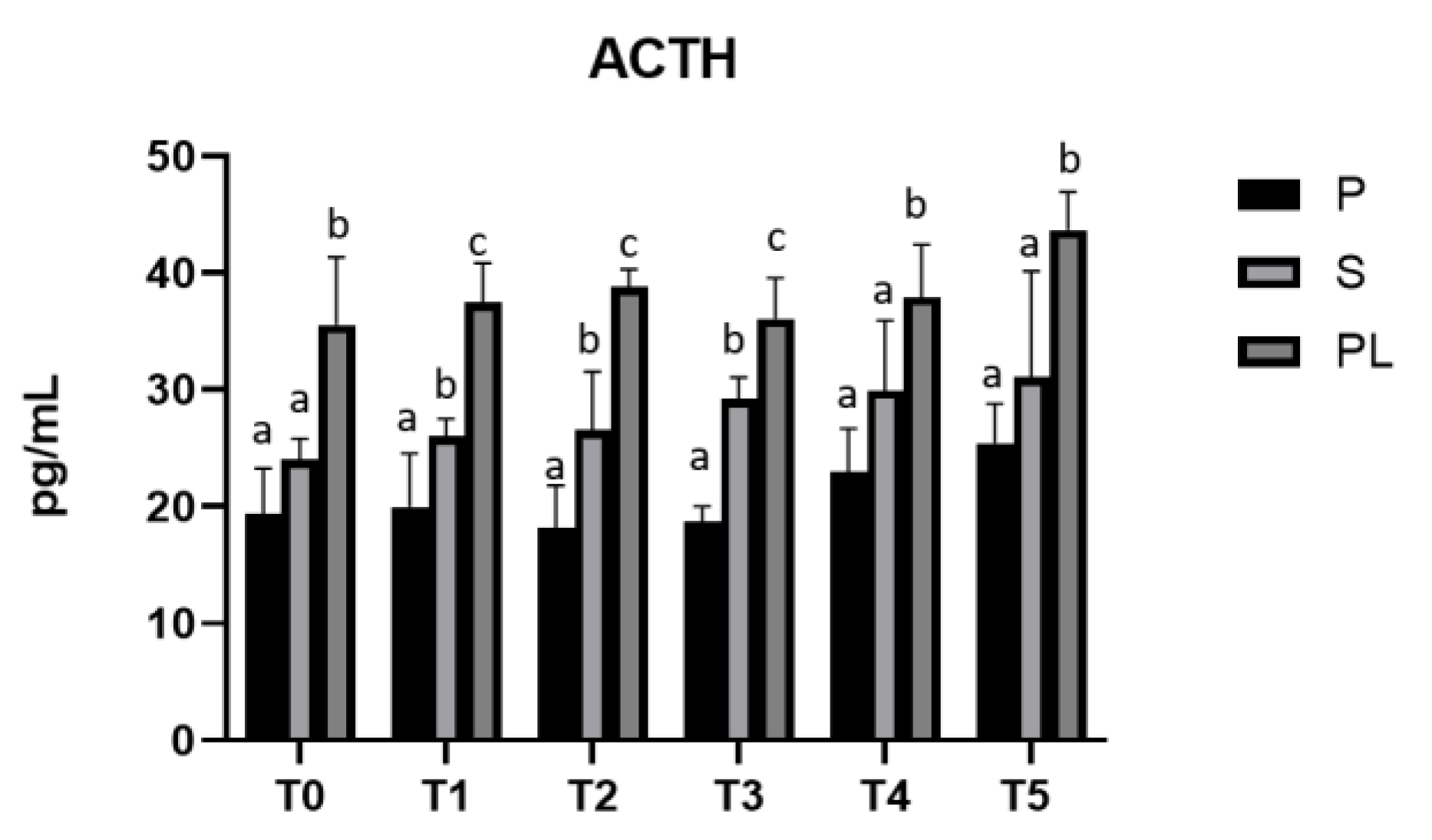
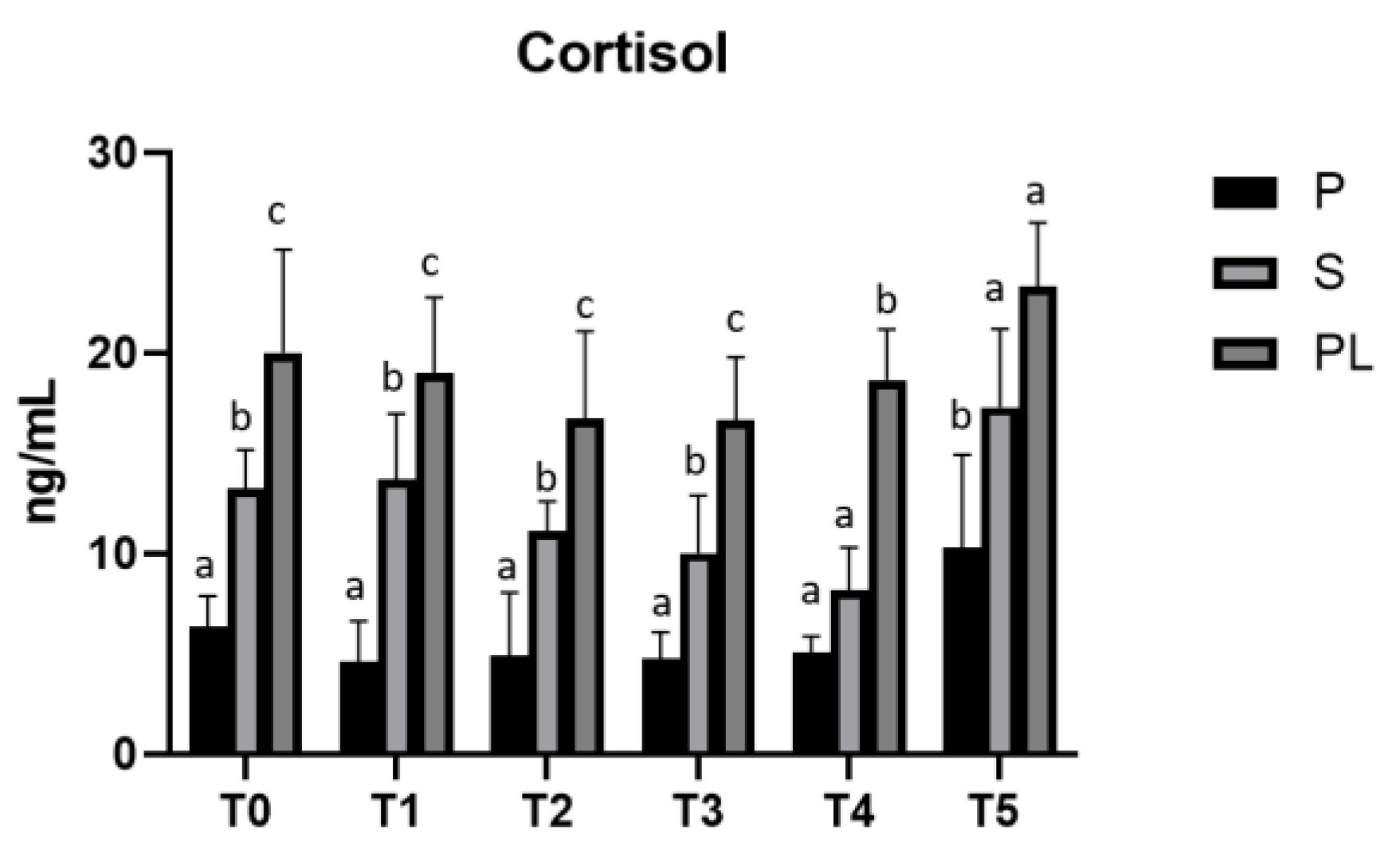
3.5. Serum levels of ACTH and cortisol in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
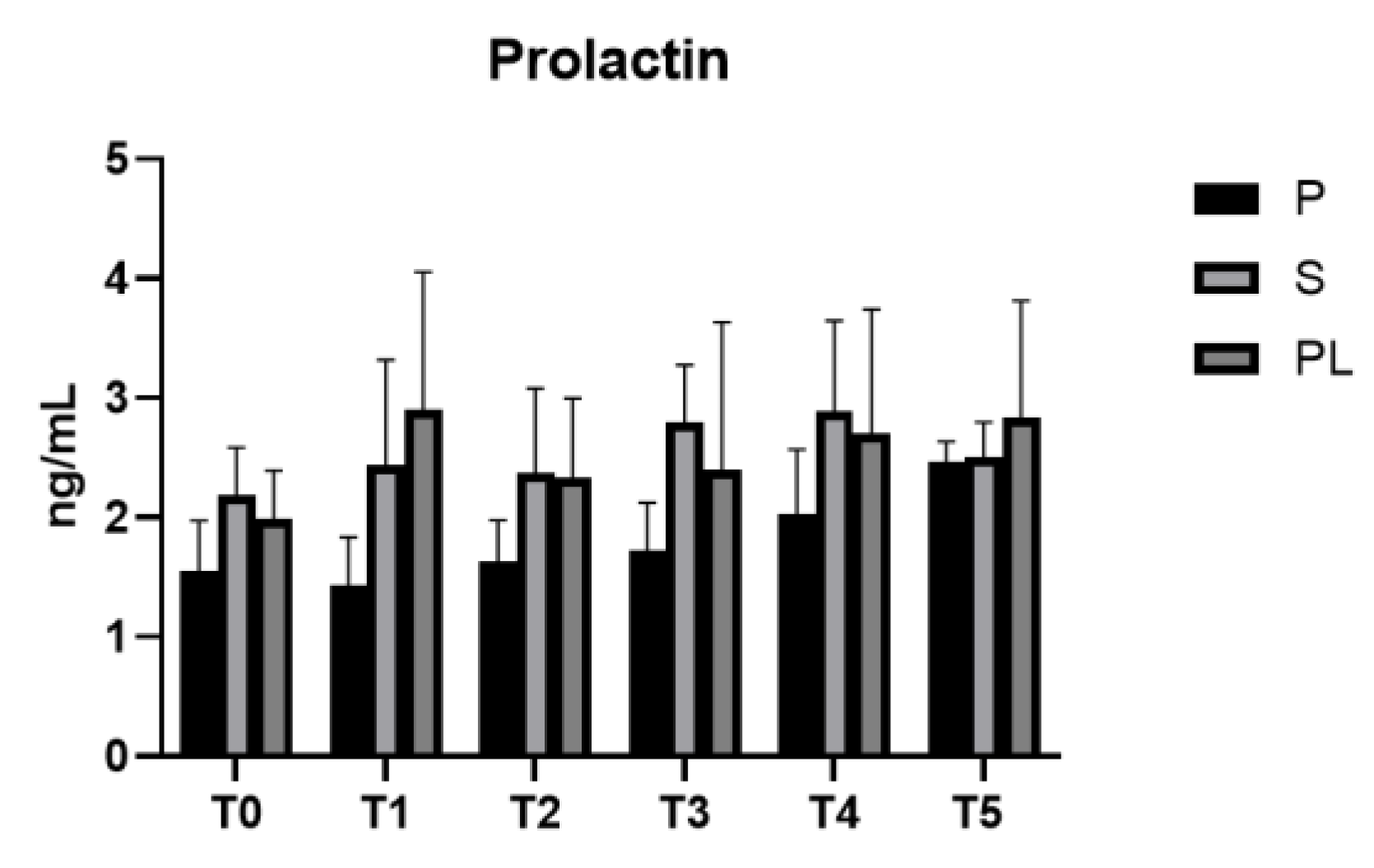
3.6. Serum levels of prolactin and oxytocin in P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
3.7. Fatty acids profile of milk from P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
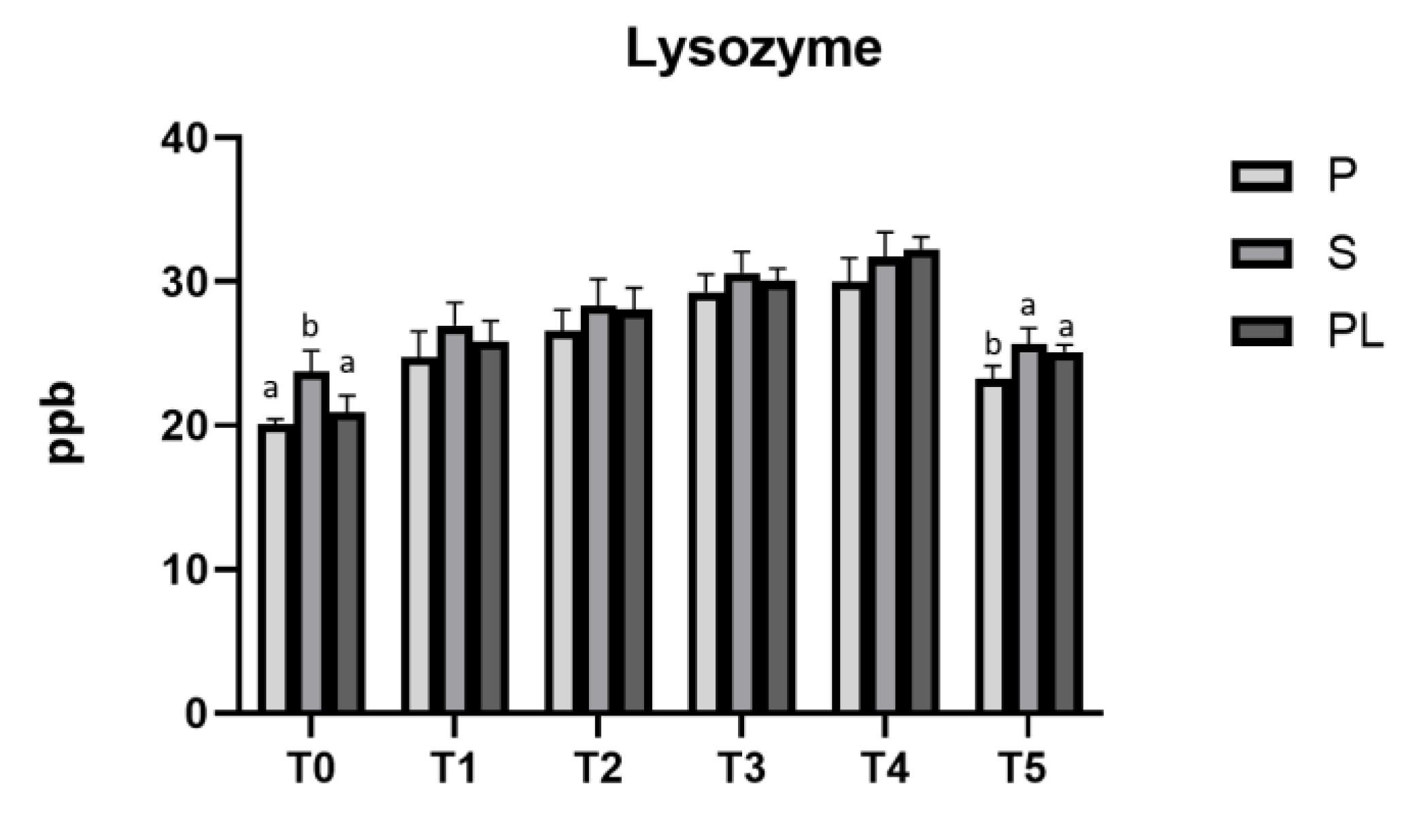
3.8. Lysozyme content and chemical-nutritional analysis in milk from P, S and PL cows upon polyphenol enriched diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashem, N.M.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Polyphenols in Farm Animals: Source of Reproductive Gain or Waste? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correddu, F.; Lunesu, M.F.; Buffa, G.; Atzori, A.S.; Nudda, A.; Battacone, G.; Pulina, G. . Can Agro-Industrial By-Products Rich in Polyphenols be Advantageously Used in the Feeding and Nutrition of Dairy Small Ruminants? Animals 2020, 10(1), 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchio, E.; Coccia, E.; Orso, G.; Lombardi, V.; Imperatore, R.; Vito, P.; Paolucci, M. Influence of polyphenols from olive mill wastewater on the gastrointestinal tract, alveolar macrophages and blood leukocytes of pigs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18(1), 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Attia, A. Effects of feeding sugar beet pulp and Avizyme supplementation on performance, egg quality, nutrient digestion and nitrogen balance of laying Japanese quail. Avian Biol. Res. 2015, 8(2), 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P. K.; DiPette, D. J.; Supowit, S. C. Protective effect of resveratrol against pressure overload-induced heart failure. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2(3), 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Interactions of tea polyphenols with intestinal microbiota and their implication for anti-obesity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100(3), 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, M. C.; De Cristofaro, G. A.; Imperatore, R.; Rocco, M.; Giaquinto, D.; Palladino, A.; Zotti, T.; Vito, P.; Paolucci, M.; Varricchio, E. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Olive Leaf from Five Italian Cultivars: Effects of Harvest-Time and Extraction Conditions on Phenolic Compounds and In Vitro Antioxidant Properties. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 2(1), 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, D. K.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Potential of plant polyphenols to combat oxidative stress and inflammatory processes in farm animals. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101(4), 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y. Potential and challenges of tannins as an alternative to in-feed antibiotics for farm animal production. Anim Nutr 2018, 4(2), 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipiński, K.; Mazur, M.; Antoszkiewicz, Z.; Purwin, C. Polyphenols in monogastric nutrition–a review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17(1), 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilbag, D.; Eren, M.; Agel, H.; Kovanlikaya, A.; Balci, F. Effects of dietary rosemary, rosemary volatile oil and vitamin E on broiler performance, meat quality and serum SOD activity. Br. Poult. Sci. 2011, 52(4), 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurson, G. C. “What a waste”—can we improve sustainability of food animal production systems by recycling food waste streams into animal feed in an era of health, climate, and economic crises? Sustainability 2020, 12(17), 7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, P.; Carta, P.; Ibba, I.; Manis, C.; Caboni, P. An untargeted metabolomic comparison of milk composition from sheep kept under different grazing systems. Dairy 2020, 1(1), 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, K.D.; Shittu, R.M.; Sabow, A.B.; Ebrahimi, M.; Sazili, A.Q. Influence of diet and post-mortem ageing on oxidative stability of lipids, myoglobin and myofibrillar proteins and quality attributes of gluteus medius muscle in goats. PLoS One 2016, 11(5), e0154603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Pereira, V.; Abuelo, Á.; Hernández, J. Effect of supplementation with antioxidants on the quality of bovine milk and meat production. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 616098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, R.; Barone, C.M.A.; Claps, S.; Varricchio, E.; Rufrano, D.; Caroprese, M.; Albenzio, M.; De Palo. P.; Campanile, G.; Neglia, G. Effects of dietary supplementation with polyphenols on meat quality in Saanen goat kids. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, N. K.; Singh, O. P.; Pandey, V.; Verma, P. K. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status during transition period in dairy cows. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24(4), 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, L. M.; Aitken, S. L. Impact of oxidative stress on the health and immune function of dairy cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128(1-3), 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poławska, E.; Bagnicka, A. W.; Niemczuk, K.; Lipińska, J. O. Relations between the oxidative status, mastitis, milk quality and disorders of reproductive functions in dairy cows—A review. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2012, 30(4), 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Tzamaloukas, O.; Neofytou, M. C.; Simitzis, P. E. Application of olive by-products in livestock with emphasis on small ruminants: Implications on rumen function, growth performance, milk and meat quality. Animals 2021, 11(2), 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, G.; Troilo, M.; Squeo, G.; Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F. Functional compounds from olive pomace to obtain high-added value foods–a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101(1), 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallem, U. Invited review: Roles of dietary n-3 fatty acids in performance, milk fat composition, and reproductive and immune systems in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101(10), 8641–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C. M.; Davis, D. R.; Heins, B. J.; Latif, M. A.; Leifert, C.; Peterman, L.; Butler, G.; Faergeman, O.; Abel-Caines, S.; Baranski, M. Enhancing the fatty acid profile of milk through forage-based rations, with nutrition modeling of diet outcomes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6(3), 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gengler, N.; Soyeurt, H.; Dehareng, F.; Bastin, C.; Colinet, F.; Hammami, H.; Vanrobays, M.L.; Laine, A.; Vanderick, S.; Grelet, C.; Vanlierde, A.; Froidmont, E.; Dardenne, P. Capitalizing on fine milk composition for breeding and management of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99(5), 4071–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Król, J.; Litwinczuk, Z.; Brodziak, A.; Barlowska, J. Lactoferrin, lysozyme and immunoglobulin G content in milk of four breeds of cows managed under intensive production system. Pol J Vet Sci 2010, 13(2), 357–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Antimicrobial activity of lysozyme with special relevance to milk. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7(25). [Google Scholar]
- Shahani, K. M.; Harper, W. J.; Jensen, R. G.; Parry Jr, R. M.; Zittle, C. A. Enzymes in bovine milk: a review. J. Dairy Sci. 1973, 56(5), 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, C.; Labella, C.; Elshafie, H. S.; Camele, I.; Musto, M.; Paolino, R.; D’Adamo, C.; Freschi, P. Effects of different heat treatments on lysozyme quantity and antimicrobial activity of jenny milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99(7), 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattem, H. E. Effect of heat treatments and seasons of the year on the protective proteins in milk of different animals. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 95(1), 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, F.; Ebani, V. V.; Ampola, M.; Innocenti, E.; Forzale, F.; Periccioli, M.; Cerri, D.; Andreani, E. Determinazione della concentrazione di lisozima in latte ovino normale e mastitico [Evaluation of lysozyme titration in normal and mastitic ewe milk]. S.P. Rum- Lugo (Ed.), Atti XIV Congresso Internazionale Fe.Me, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela Publicacions, Spain 2006.
- Scharfen, E. C.; Mills, D. A.; Maga, E. A. Use of human lysozyme transgenic goat milk in cheese making: effects on lactic acid bacteria performance. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90(9), 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, Å.; Björck, L.; Persson, K. Lactoferrin and lysozyme in milk during acute mastitis and their inhibitory effect in Delvotest P. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72(12), 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, R. C.; Parry Jr, R. M.; Shahani, K. M. Lysozyme, lipase, and ribonuclease in milk of various species. J. Dairy Sci. 1968, 51(4), 606–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, M. C.; Salzano, A.; Zotti, T.; Palladino, A.; Giaquinto, D.; Maruccio, L.; Romanucci, R.; Rocco, M.; Zarrelli, A.; D’Occhio, M. J.; Campanile, G.; Varricchio, E. Plasma fatty acid profile in Italian Holstein-Friesian dairy cows supplemented with natural polyphenols from the olive plant Olea europaea L. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzo, R.; Bianco, F.; Mazzoli, A.; Giacco, A.; Cancelliere, R.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A.; Liverini, G.; Iossa, S. Fat quality influences the obesogenic effect of high fat diets. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9475–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedea, V. S.; Pelmus, R. S.; Lazar, C.; Pistol, G. C.; Calin, L. G.; Toma, S. M.; Dragomir, C.; Taranu, I. Effects of a diet containing dried grape pomace on blood metabolites and milk composition of dairy cows. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97(8), 2516–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Moumen, A.; Ruiz, D.Y.; Alcaide, E.M. Chemical Composition and Nutrients Availability for Goats and Sheep of Two-Stage Olive Cake and Olive Leaves. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2003, 107, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Agricultural and aquacultural potential of olive pomace a review. J Agric Sci 2013, 5(7), 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghuei, M. J.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Salem, A.Z.M.; Zamiri, M. J. Nitrogen balance, blood metabolites and milk fatty acid composition of dairy cows fed pomegranate-peel extract. Livest. Sci. 2014, 164, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong R., Xiao W., Ren G., Zhou D., Tan C., Tan Z., Han Z., Tang S., Zhou C., &Wang M. Dietary tea catechin inclusion changes plasma biochemical parameters, hormone concentrations and glutathione redox status in goats. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24(12), 1681–1689. [CrossRef]
- Oetzel, G. R. Monitoring and testing dairy herds for metabolic disease. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2004, 20(3), 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F. D.; Muiño, R.; Pereira, V.; Campos, R.; Benedito, J. L. Relationship among blood indicators of lipomobilization and hepatic function during early lactation in high-yielding dairy cows. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 12(3), 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamanc, H.; Stojić, V.; Kirovski, D.; Jovanović, M.; Cernescu, H.; Vujanac, I. Thyroid hormones concentrations during the mid-dry period: An early indicator of fatty liver in Holstein-Friesian dairy cows. J. Thyroid Res. 2010, 2010, 897602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi-Fani, M.; Nazifi, S.; Rowghani, E.; Bahrami, S.; Jamshidi, O. Thyroid hormones and their correlations with serum glucose, beta hydroxybutyrate, nonesterified fatty acids, cholesterol, and lipoproteins of high-yielding dairy cows at different stages of lactation cycle. Comp Clin Path 2009, 18, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanovic, R.; Nedic, S.; Vujanac, I.; Bojkovski, J.; Nedic, S.; Jovanovìc, L.; Kirovski, D.; Borozan, S. Dietary Supplementation of Chestnut Tannins in Prepartum Dairy Cows Improves Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms Interacting with Thyroid Status. Metabolites 2023, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier-Dodier, P.; Girard, C. L.; Talbot, B. G.; Lacasse, P. Effect of dry period management on mammary gland function and its endocrine regulation in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94(10), 4922–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgorlon, S.; Fanzago, M.; Guiatti, D.; Gabai, G.; Stradaioli, G.; Stefanon, B. Factors affecting milk cortisol in mid lactating dairy cows. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11(1), 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertulat, S.; Fischer-Tenhagen, C.; Suthar, V.; Möstl, E.; Isaka, N.; Heuwieser, W. Measurement of fecal glucocorticoid metabolites and evaluation of udder characteristics to estimate stress after sudden dryoff in dairy cows with different milk yields. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96(6), 3774–37878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, N. I. A.; Kawu, M. U.; Bako, I. G. Effects of Launaea taraxacifolia and resveratrol on milk yield and serum prolactin and oxytocin levels: a lactogenic study. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2019, 7(1), 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Otmani, S.; Chebli, Y.; Chentouf, M.; Hornick, J. L.; Cabaraux, J. F. Effects of olive cake and cactus cladodes as alternative feed resources on goat milk production and quality. Agriculture 2020, 11(1), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, R. A.; Buckley, F.; Prendiville, R.; Murphy, J. J.; Callan, J.; Kenny, D. A. A comparison between Holstein-Friesian and Jersey dairy cows and their F1 hybrid on milk fatty acid composition under grazing conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93(5), 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Pertíñez, M.; Martín-García, I.; Mena, Y.; Zarazaga, L. Á.; Guzmán, J. L. Supplementing the diet of dairy goats with dried orange pulp throughout lactation: II effect on milk fatty acids profile, phenolic compounds, fat-soluble vitamins and antioxidant capacity. Animals 2021, 11(8), 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ineichen, S.; Künzler, A. D.; Kreuzer, M.; Marquardt, S.; Reidy, B. Digestibility, nitrogen utilization and milk fatty acid profile of dairy cows fed hay from species rich mountainous grasslands with elevated herbal and phenolic contents. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz-Kęszycka, M.; Czyżak-Runowska, G.; Lipińska, P.; Wójtowski, J. Fatty acid profile of milk-a review. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 57(2), 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terramoccia, S.; Bartocci, S.; Taticchi, A.; Di Giovanni, S.; Pauselli, M.; Mourvaki, E.; Urbani, S.; Servili, M. Use of dried stoned olive pomace in the feeding of lactating buffaloes: Effect on the quantity and quality of the milk produced. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26(7), 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Vera, R. R.; Aguilar, C.; Lira, R.; Peña, I.; Fernández, J. Feeding olive cake to ewes improves fatty acid profile of milk and cheese. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 184(1-4), 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiofalo, B.; Liotta, L.; Zumbo, A.; Chiofalo, V. Administration of olive cake for ewe feeding: effect on milk yield and composition. Small Rumin. Res. 2004, 55(1-3), 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj Malla, B. A.; Tran, L. V.; Sharma, A. N.; Kumar, S.; Tyagi, A. K. Seasonal variation in fatty acid profile in the milk of different species under popularly followed feeding system in India. Indian J Anim Sci 2017, 87(4), 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reklewska, B.; Bernatowicz, E.; Reklewski, Z.; Nałęcz-Tarwacka, T.; Kuczyńska, B.; Zdziarski, K.; Oprządek, A. Concentration of milk functional components in Black-and-White cows, depending on the season and feeding system. Zesz. Nauk. Prz. Hod. 2003, 68, 85–98. [Google Scholar]

| Fatty Acid (g/100g) |
Experimental Time |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | ||||||||||||||
| P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | ||
| C14:0 | 1.09±0.04a | 16.19±0.25b | 15.35±0.33c | 1.00±0.03 | 14.87±0.29 | 13.35±0.29 | 0.90±0.02 | 14.23±0.32 | 12.99±0.20 | 0.80±0.09 | 12.18±0.10 | 10.76±0.13 | 0.68±0.10 | 9.70±0.18 | 8.09±0.16 | 0.60±0.09 | 9.15±0.17 | 7.10±0.13 | |
| C16:0 | 15.31±0.33a | 47.50±0.62b | 38.77±0.67c | 15.00±0.28 | 33.76±0.82 | 29.28±0.68 | 14.70±0.20 | 30.39±0.76 | 28.79±0.14 | 13.41±0.13 | 28.00±0.20 | 27.03±0.18 | 12.09±0.10 | 27.33±0.18 | 25.18±0.17 | 11.18±0.11 | 27.10±0.17 | 24.40±0.16 | |
| C16:1 n7t | 4.74±0.05b | n.d.a | n.d.a | 5.08±0.04 | 0.10±0.02 | 0.03±0.01 | 5.37±0.05 | 0.22±0.05 | 0.07±0.01 | 6.01±0.16 | 0.56±0.11 | 0.26±0.09 | 6.23±0.13 | 0.86±0.08 | 0.40±0.04 | 6.90±0.11 | 0.90±0.09 | 0.55±0.04 | |
| C16:1 n7 | n.d.a | 0.85±0.02b | n.d.a | 0.10±0.02 | 0.98±0.03 | 0.05±0.02 | 0.13±0.03 | 1.56±0.10 | 0.10±0.02 | 0.16±0.06 | 2.91±0.11 | 0.25±0.07 | 0.20±0.06 | 3.56±0.10 | 0.42±0.02 | 0.25±0.05 | 4.02±0.10 | 0.58±0.05 | |
| C18:0 | 8.45±0.17a | 9.89±0.13b | 14.43±0.26c | 7.64±0.16 | 6.24±0.17 | 10.22±0.19 | 7.43±0.20 | 5.77±0.10 | 9.81±0.11 | 6.15±0.09 | 5.09±0.08 | 8.56±0.11 | 5.48±0.11 | 4.39±0.09 | 7.98±0.08 | 5.00±0.10 | 3.06±0.08 | 6.17±0.12 | |
| C18:1 n9 | 9.36±0.18a | 21.01±0.42b | 26.38±0.53c | 9.60±0.17 | 24.14±0.34 | 29.00±0.26 | 9.80±0.21 | 27.64±0.25 | 29.80±0.30 | 11.00±0.14 | 29.80±0.32 | 32.34±0.36 | 11.90±0.02 | 30.75±0.35 | 35.13±0.36 | 12.26±0.16 | 31.14±0.31 | 36.50±0.34 | |
| C18:2 n6t | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| C18:2 n6 | 17.96±0.27a | 3.42±0.09b | 3.02±0.10c | 18.19±0.26 | 12.90±0.11 | 11.07±0.17 | 18.23±0.32 | 13.00±0.18 | 11.20±0.16 | 18.45±0.20 | 13.80±0.20 | 12.46±0.15 | 19.10±0.22 | 15.20±0.21 | 13.00±0.18 | 19.16±0.23 | 16.01±0.17 | 14.03±0.12 | |
| C18:3 n6 | 1.01±0.12a | 0.07±0.03b | 0.27±0.01c | 1.10±0.03 | 0.50±0.03 | 1.89±0.10 | 1.10±0.02 | 0.54±0.10 | 1.90±0.07 | 1.11±0.05 | 0.59±0.09 | 2.00±0.10 | 1.13±0.04 | 0.75±0.05 | 2.50±0.10 | 1.14±0.08 | 0.80±0.03 | 2.60±0.10 | |
| C20:1 n9 | 3.98±0.08a | n.d.b | 0.49±0.04c | 4.30±0.07 | 0.05±0.01 | 0.78±0.06 | 4.47±0.08 | 0.19±0.06 | 0.82±0.05 | 5.28±0.16 | 0.29±0.11 | 1.68±0.13 | 5.74±0.20 | 0.35±0.03 | 1.90±0.08 | 6.10±0.10 | 0.45±0.02 | 2.33±0.09 | |
| C18:3 n3 | 0.10±0.04b | 0.21±0.08a | 0.26±0.03a | 0.11±0.02 | 1.27±0.03 | 0.99±0.06 | 0.13±0.03 | 1.28±0.14 | 1.01±0.12 | 0.15±0.08 | 1.30±0.11 | 1.03±0.10 | 0.17±0.03 | 1.40±0.09 | 1.13±0.03 | 0.18±0.05 | 1.58±0.09 | 1.20±0.08 | |
| C20:2 n6 | 2.83±0.06b | 0.07±0.02a | 0.09±0.01a | 3.00±0.06 | 1.13±0.05 | 0.78±0.05 | 3.01±0.07 | 1.15±0.03 | 0.86±0.01 | 3.08±0.10 | 1.16±0.06 | 0.90±0.02 | 3.10±0.10 | 1.20±0.11 | 1.08±0.09 | 3.12±0.11 | 1.22±0.07 | 1.12±0.03 | |
| C20:3 n6 | 2.60±0.03b | 0.25±0.10a | 0.33±0.04a | 2.78±0.03 | 1.29±0.12 | 0.65±0.05 | 2.80±0.05 | 1.30±0.20 | 0.68±0.09 | 2.85±0.07 | 1.35±0.20 | 0.70±0.06 | 3.00±0.10 | 1.38±0.10 | 0.88±0.05 | 3.03±0.04 | 1.40±0.06 | 0.90±0.03 | |
| C20:4 n6 | 16.97±0.27b | 0.33±0.13a | 0.38±0.03a | 17.40±0.27 | 1.97±0.11 | 1.25±0.10 | 17.45±0.26 | 1.98±0.10 | 1.27±0.09 | 17.50±0.30 | 2.04±0.05 | 1.30±0.10 | 17.65±0.29 | 2.09±0.15 | 1.42±0.09 | 17.67±0-27 | 2.10±0.11 | 1.46±0.09 | |
| C24:0 | 7.00±0.14b | 0.09±0.02a | 0.07±0.01a | 5.98±0.13 | 0.08±0.04 | 0.08±0.01 | 5.73±0.09 | 0.08±0.03 | 0.06±0.03 | 5.07±0.14 | 0.05±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 4.36±0.20 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.02±0.01 | 4.11±0.16 | 0.01±0.01 | 0.01±0.01 | |
| C20:5 n3 | 1.00±0.05b | n.d.a | n.d.a | 1.08±0.06 | 0.10±0.05 | 0.23±0.08 | 1.08±0.04 | 0.11±0.05 | 0.27±0.10 | 1.10±0.11 | 0.13±0.05 | 0.29±0.11 | 1.13±0.09 | 0.15±0.06 | 0.33±0.04 | 1.15±0.11 | 0.16±0.05 | 0.40±0.12 | |
| C24:1 n9 | 0.10±0.04b | 0.02±0.03a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.10±0.03 | 0.08±0.04 | 0.07±0.01 | 0.13±0.05 | 0.15±0.05 | 0.08±0.01 | 0.20±0.06 | 0.20±0.09 | 0.10±0.04 | 0.25±0.05 | 0.26±0.05 | 0.19±0.04 | 0.27±0.08 | 0.28±0.07 | 0.25±0.04 | |
| C22:6 n3 | 7.50±0.15b | 0.10±0.05a | 0.13±0.04a | 7.54±0.15 | 0.54±0.07 | 0.28±0.10 | 7.54±0.17 | 0.54±0.05 | 0.29±0.12 | 7.68±0.15 | 0.55±0.13 | 0.30±0.11 | 7.79±0.18 | 0.60±0.11 | 0.35±0.09 | 7.88±0.12 | 0.62±0.10 | 0.40±0.12 | |
| Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| SFA | 31.95±4.14a | 73.69±0.26b | 68.65±0.20c | 29.62±0.100002 | 54.95±0.33 | 52.93±1.17 | 28.76±0.13 | 50.34±0.30 | 51.65±0.12 | 25.43±0.32 | 45.32±0.10 | 46.39±0.11 | 22.61±0.13 | 41.45±0.12 | 41.27±0.11 | 20.89±0.12 | 39.32±0.08 | 37.68±0.11 | |
| MUFA | 18.08±0.09 a | 21.86±0.45 b | 26.87±0.12 c | 19.18±0.33 | 25.35±0.44 | 29.93±0.36 | 19.90±0.08 | 29.76±0.10 | 30.87±0.17 | 22.65±0.12 | 33.76±0.15 | 34.63±0.14 | 24.32±0.09 | 35.78±0.12 | 38.04±0.11 | 25.78±0.10 | 36.79±0.26 | 40.21±0.11 | |
| PUFA | 49.97±0.12 b | 4.45±0.13 a | 4.48±0.04 a | 51.20±0.11 | 19.70± 0.07 | 17.14±0.09 | 51.34±0.12 | 19.90±0.11 | 17.48±0.10 | 51.92±0.13 | 20.92±0.11 | 18.98±0.10 | 53.07±0.13 | 22.77±0.11 | 20.69±0.08 | 53.33±0.13 | 23.89±0.09 | 22.11±0.11 | |
| SFA/MUFA | 1.77 a | 3.37 b | 2.55 c | 1.54 | 2.17 | 1.77 | 1.45 | 1.69 | 1.67 | 1.12 | 1.34 | 1.34 | 0.92 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 0.81 | 1.07 | 0.94 | |
| ITEMS | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | P | S | PL | |
| Lactose % | 4.57± 0.05a/b | 4.54±0.04a | 4.65±0.06b | 4.72±0.05 | 4.68±0.06 | 4.75±0.07 | 4.76±0.05 | 4.72±0.05 | 4.76±0.03 | 4.79±0.05 | 4.75±0.04 | 4.78±0.05 | 4.80±0.05 | 4.82±0.07 | 4.87±0.04 | 4.79±0.05a | 4.80±0.05a | 4.89±0.05b |
| Protein % | 3.22±0.04 | 3.27±0.03 | 3.30±0.03 | 3.30±0.05 | 3.39±0.05 | 3.36±0.04 | 3.45±0.07 | 3.48±0.03 | 3.46±0.04 | 3.48±0.11 | 3.53±0.05 | 3.50±0.04 | 3.50±0.05 | 3.54±0.04 | 3.56±0.05 | 3.50±0.03 | 3.55±0.04 | 3.55±0.11 |
| Fat % | 4.00±0.05a/b | 4.04±0.04a | 3.93±0.05b | 3.94±0.03 | 3.97±0.05 | 3.90±0.04 | 3.91±0.05 | 3.94±0.04 | 3.92±0.03 | 3.89±0.07 | 3.89±0.08 | 3.90±0.04 | 3.74±0.06 | 3.75±0.04 | 3.80±0.05 | 3.70±0.03 | 3.73±0.04 | 3.75±0.07 |
| Somatic cell count (SCC) 103/ml | 400±50 | 300±55 | 350±56 | 300±50 | 250±40 | 300±50 | 285±50 | 235±40 | 278±50 | 250±40 | 200±45 | 250±50 | 150±40 | 145±40 | 186±45 | 150±50 | 150±50 | 190±45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





