1. Introduction
The genus
Nepovirus, family
Secoviridae, is one of the first group of plant viruses discovered and recognized by the
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) [
1,
2]. Nepoviruses have a bipartite positive-single stranded RNA genome (RNA1 and RNA2) and are divided into three subgroups (A, B and C) based on their sequences, genome organization and cleavage sites [
3]. Currently, this genus includes 48 recognized viral species [
4], of which
Artichoke Italian latent virus (AILV), firstly discovered in Italy from asymptomatic artichoke plants (
Cynara scolymus L.) [
5], belongs to the subgroup B [
4]. This subgroup has species with RNA2 of 4.4-4.7 Kb in size, present only in the M component; subgroup A has species with RNA2 of 3.7-4.0 Kb, present in both M and B components; whereas the subgroup C has species with RNA2 of 6.4-7.3 Kb, present in M component particles that are sometimes barely separable from those of B component [
6].
Following the discovery of AILV in Italy, this virus has been found in Bulgaria in several plant species, namely chicory (
Cichorium intybus) which showed leaf chlorotic mottle and yellow spots [
7], pelargonium (
Pelargonium zonale) with severe leaf malformations and stunting symptoms [
8], sow thistle (
Sonchus oleraceus) with yellow rings and line pattern on leaves [
9], gladiolus (
Gladiolus palustris) and grapevine (
Vitis vinifera) with fanleaf-like symptoms and reduced growth [
10,
11]. The presence of AILV was also reported from several weeds (
Crepis neglecta,
Helminthia chioides,
Hypochaeris aetnensis,
Lactuca virosa,
Urospermum dalechampii and
Lamium amplexicaule) [
12].
A comparative analysis conducted on three Bulgarian AILV isolates from sow thistle (AILV-S), gladiolus (AILV-G) and grapevine (AILV-V) and on one Italian isolate from artichoke (AILV-C), showed that all share common biological, serological, and physical-chemical properties [
10]. At the molecular level, only recently the genome of AILV-V has been completely sequenced [
13], whereas no sequence information is available from other isolates, including those reported on weeds.
Herein, we report the molecular information (sequence identities, genetic variability, recombination, and phylogenetic relationship), limitedly to the RNA2, gained on genomes of non-sequenced yet AILV isolates (AILV-C, G, S) and of a new isolate (AILV-B) found for the first time in this study in chard plants (
Beta vulgaris subsp
. vulgaris). Furthermore, since recombination is a recurring characteristic among nepoviruses,
i.e., the species of subgroup A [
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) [
14],
Arabis mosaic virus (ArMV) [
15],
Grapevine Deformation virus (GDefV) [
16], subgroup B [
Grapevine chrome mosaic virus (GCMV) and
Tomato black ring virus (TBRV) [
17],
Grapevine Anatolian ringspot virus (GARSV) [
18] and subgroup C [
Grapevine Bulgarian latent virus (GBLV) [
19],
Tomato ringspot virus (ToRSV) [
20], this aspect was investigated in the genomic RNA2 sequences of all AILV isolates, for which the results are here reported and discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Plant Material
Lyophilized leaves of different Nicotiana occidentalis (N. occidentalis) herbaceous plants infected with AILV-C, AILV-G and AILV-S isolates were used as viral sources.
Seven chard plants (
Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris) were collected from a chard plantation adjacent to an artichoke field (located in Bizerte, northern of Tunisia) that has been frequently monitored for some artichoke-infecting viruses, including AILV. The nucleic acids extracted from the chard plant samples were used as negative controls reactions to monitor the specificity of the molecular tests used for artichoke viruses’ identification [
21,
22].
All AILV isolates, including that found in some chard plants (AILV-B) (see details hereafter), were sap-inoculated onto
N. occidentalis plants and from which were purified after fractionation in 10-40% linear sucrose density gradients [
10].
2.2. Extraction of Total Nucleic Acids, cDNA Synthesis and PCR
Nucleic acids were extracted from purified virus preparations after incubation with 1% SDS and extraction with 1 vol Tris-EDTA-saturated phenol and chloroform [
23]. cDNA was synthesized using 0.5µg of random DNA hexanucleotide mixture and\or OligodT primers and 200 units of
Moloney murine leukaemia virus (M-MLV) reverse transcriptase enzyme in a 20 µl reaction for 1 h at 42 °C, following the manufacturer’s instructions (LifeTechnologies, Milan, Italy).
A battery of sense and antisense primers (Supplementary
Table 1), designed on RNA2 sequence of AILV-V isolate reported in the GenBank (acc.no. LT608396), were used in RT-PCR and 5′\3′ RACE-PCR assays to amplify corresponding viral genomic regions of all AILV isolates. All RT-PCR runs consisted of 40 cycles, with an initial denaturing temperature of 94°C for 1 min, 58°C for 30 sec and an elongation time of 1 min at 72°C. RT-PCR products were electrophoresed in 1.2 % agarose gel in 1x TAE buffer and stained with RedGel nucleic acid stain (Biotium, Rome, Italy).
2.3. Cloning and Sequencing
All RT-PCR amplicons were ligated into StrataClone
TM PCR cloning vector pSC-A (Stratagene, CA, USA), subcloned into
Escherichia coli DH5α and custom sequenced (Eurofins Genomics, Germany). Nucleotide and protein sequences were analyzed with Geneious Prime vers. 2023.2 (
https://www.geneious.com, New Zealand). The BLAST programs (BlastX, and BlastP) of the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) were used to search for homologies in the protein information resources databases (PIR, release 47.0) [
24]. A tentative phylogenetic tree was performed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method in the Geneious Prime vers. 2023.2 analysis package. A bootstrap value for each node of NJ trees was calculated using 1,000 replicates.
2.4. Sequence and Recombination Analyses
The RNA2 sequences obtained were analyzed for the occurrence of genetic variability and possible recombination using the “Recombination Detection Program” (RDP4) version 4.22, with default parameters (the highest acceptable probability value = 0.05). The RDP4 package uses several programs to detect the occurrence of robust recombination events, namely RDP, GENECONV, BOOTSCAN, MAXCHI, CHIMAERA, 3SEQ, and SISCAN. Recombination sites identified by four or more programs and two or more types of methods were considered “significant recombination events”.
3. Results
3.1. Complete Sequence of Genomic RNA2 of AILV Isolates
All sequences derived from RACE and RT-PCR-generated amplicons, using sense and antisense AILV-specific primers were analyzed and the complete RNA2 sequences were constructed. The RNA2 sequences of AILV-C (acc.no. LT608397), AILV-G (acc.no. LT608398) and AILV-S (acc.no. MT294111) were found to be of 4,629 nt in size, whilst shorter by one nucleotide than that of AILV-V (acc.no. LT608396) reported in the GenBank.
ORF2 of all AILV isolates extended from nt 289 to 4,332 and coded for a polyprotein (p2) with a predicted molecular mass (Mr) of ca. 149.5 KDa, comprising in the 5’→ 3’ direction the homing protein (2A
HP), the movement protein (2B
MP) and the coat protein (2C
CP) domains. All AILV isolates showed a dipeptide (K/A) at aa position 835-836, which is also reported to be a cleavage site for TBRV CP [
17], cleaving the MP and the CP domains. However, for subgroup B nepoviruses, the cleavage site between HP and MP is still uncertain.
3.2. Identification of AILV in Chard Plants
Surprisingly, two out of seven collected chard plants used as negative controls reactions while checking in Dot blot hybridization assays the presence of AILV in the artichoke plantation in Tunisia, yielded positive reactions. To reconfirm this unexpected result, all the seven plants collected from that chard plantation were retested with RT-PCR assays using a couple of AILV-specific primers pairs, i.e., F1s\F1a and F2s\F2a which amplify two different portions of RNA2 of 330 bp and 420 bp in size, respectively (see supplementary Table). Both RT-PCR assays generated positive reactions from the two samples found to be infected with AILV in Dot blot hybridization, in addition to two other samples. The RT-PCR amplicons of AILV isolates from chard (AILV-B) were sequenced and further analyzed together with those obtained from other plant species.
3.3. Mechanical Transmission of AILV Chard Plants onto Herbaceous Host
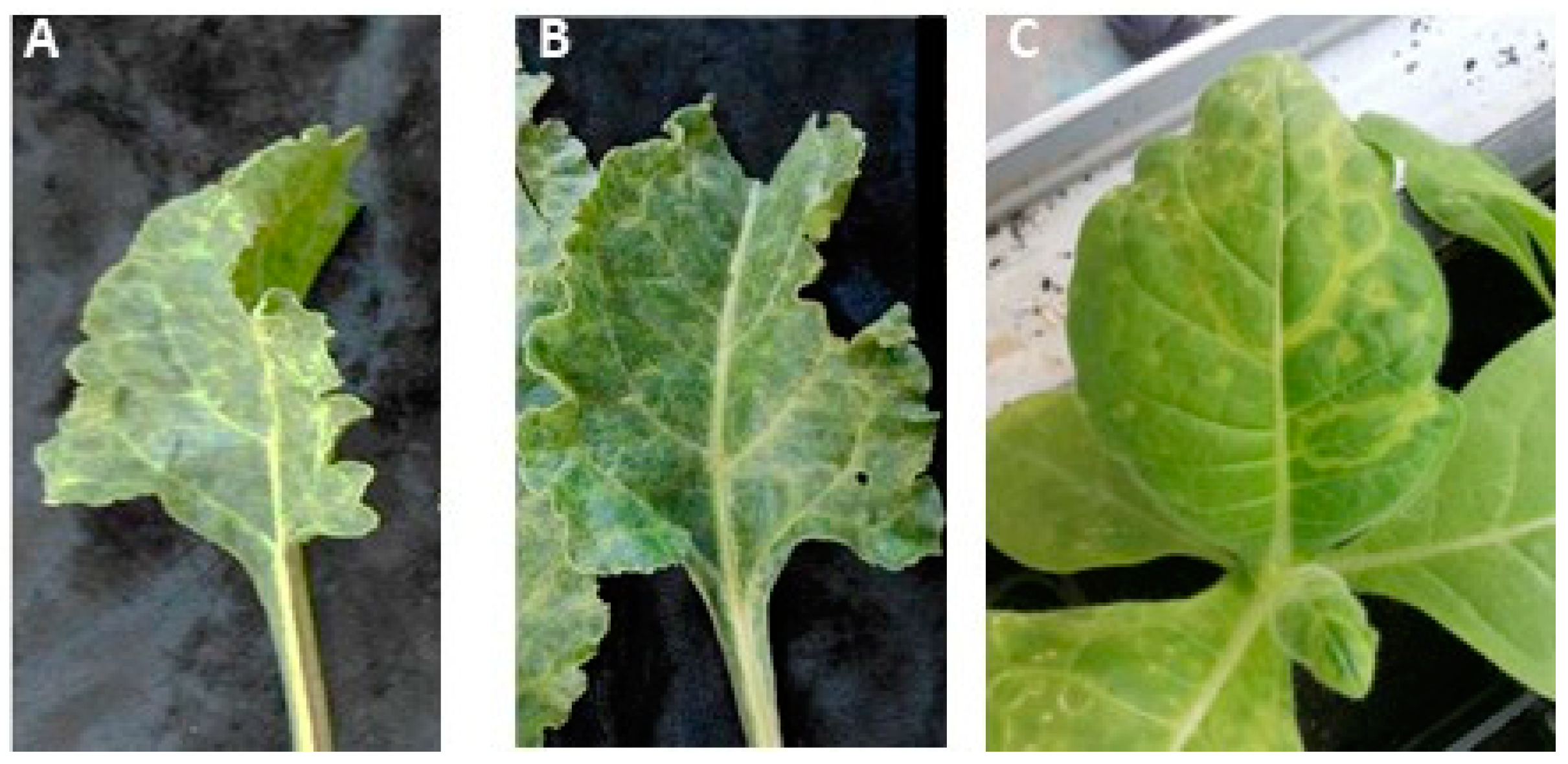
The saps extracted from the two chard plants, found positive to AILV infection in RT-PCR and Dot blot hybridization assays, and showing mottling and vein clearing symptoms, were used to transmit AILV onto
N. occidentalis plants, which showed 8 days post-inoculation ringspots and vein mottling symptoms (
Figure 1). To ascertain the presence of only AILV in the affected
N. occidentalis, all plants were screened by RT-PCR and real-time PCR assays for the presence
of common chard-infecting viruses,
i.e., cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) [
25], beet curly top virus (BCTV) [
26], beet mosaic virus (BtMV) [
27], beet yellows virus (BYV) [
28], turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) [
29] and cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) [
30]. RT-PCR results showed that none of these viruses were present in the diseased inoculated herbaceous plants, except AILV, thus the symptoms developed were attributed to AILV infection.
3.4. Genetic Variability of Genomic RNA2 of AILV Isolates
The 5’ and 3’NCR of RNA2 of all AILV isolates under study showed to have different levels of nucleotides variation between them (
Table 1), whilst the AILV-B isolate was the most variable at both 5’ and 3’UCR. However, despite the nucleotide variations found in all isolates, the 5’ and 3’UCR showed to encompass conserved and repeated sequences which can form stem-loop structures (data not shown). Normally, these structures are reported to be involved in replication, translation efficiency and viral infection cycle, or in host/virus interactions [
31].
The comparative sequence analysis between the CR of RNA2 of all isolates showed that AILV-V was the most variable isolate, with the lowest sequence identities of 83.2% and 84.7% at the nucleotides and amino acids levels, respectively (
Table 2).
At the CP level, the sequence variability found among the AILV isolates under study was in line with that reported for the nepovirus species, whilst the AILV-V and AILV-C were the most variable with 12.7% and 5.1% of difference at the nt and aa levels, respectively (
Table 3).
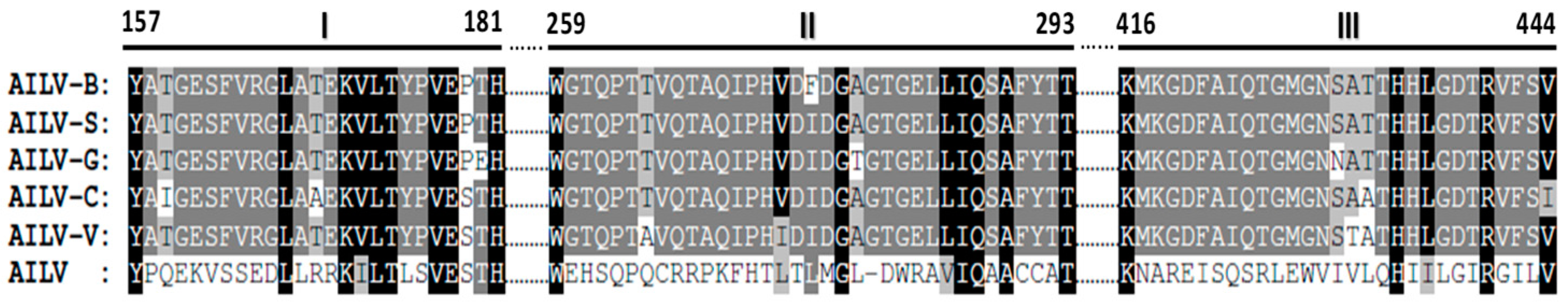
However, the variability within the CP gene was accentuated when the unique sequence of an AILV-X28754 isolate, of unknown origin and of host species, reported in the GenBank (acc.no. X28754), was included in the comparative analysis.
The sequence alignment of the five 2C
CP of AILV isolates together with the AILV-X28754 showed particularly three non-conserved aa stretches that were completely different from all AILV sequences under study (
Figure 2); whilst the variability has reached 15.2% and 20% at the nt and aa levels, respectively.
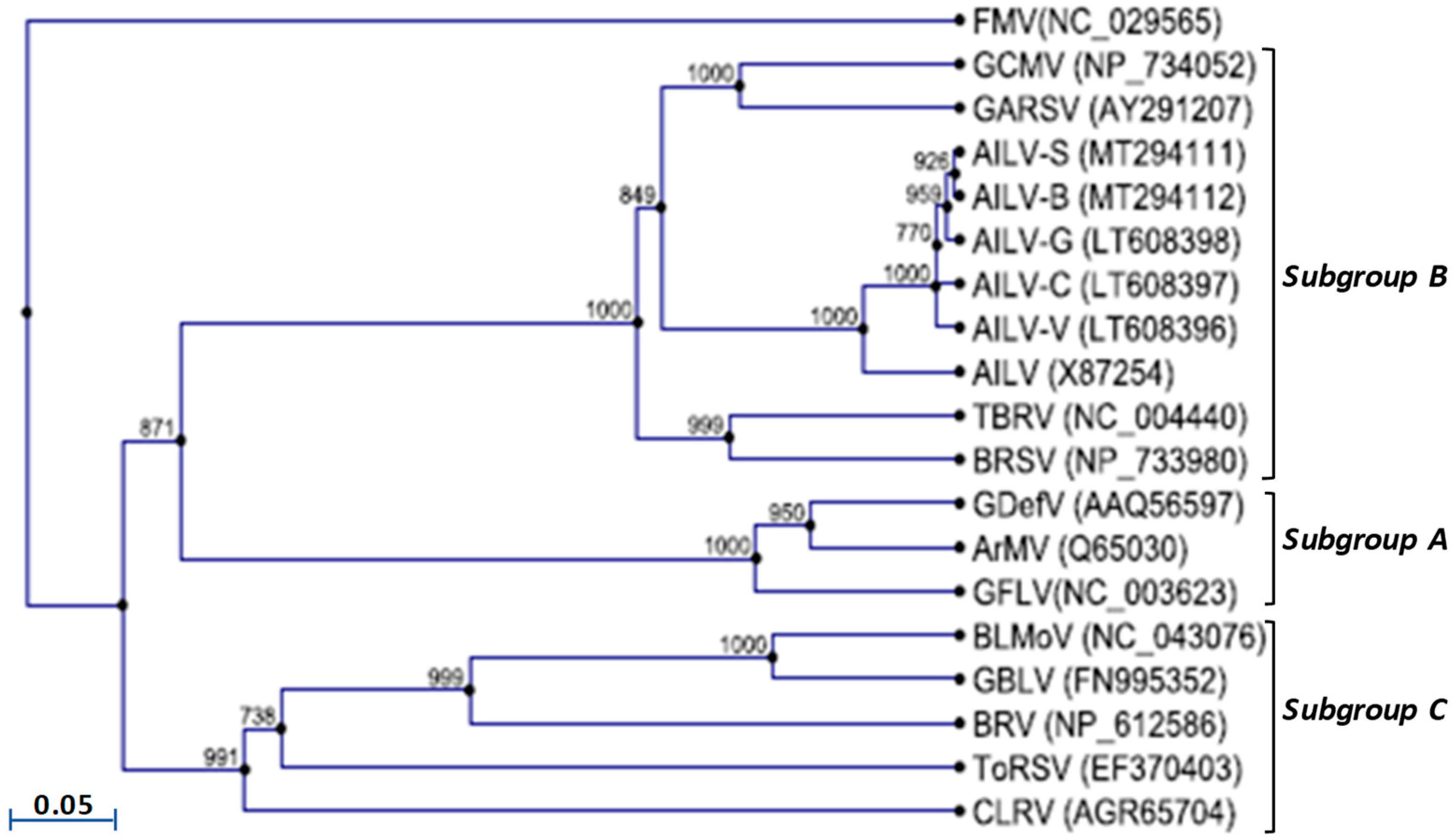
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of AILV Isolates
The phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acids sequence alignment of the 2C
CP genes of all AILV isolates and those of other nepoviruses of subgroup’s A, B and C, allocated the AILV isolates in two clusters within a clade composed of species belonging to the subgroup B; however, the AILV-X87254 was allocated in one cluster separated from all the other isolates (
Figure 3).
3.6. Recombination Analysis
The recombination analysis conducted on the RNA2 sequences of AILV isolates generated extremely high P-values, at least in 5 implemented methods, which were taken as indicators of significant intraspecific recombination sites occurring in different regions of the genomic RNAs of AILV isolates (Table 2).
Table 2.
Recombination crossover analysis of genomic RNA2 of AILV isolates, using the ‘Recombination Detecting Program’ RDP4. a RDP4-implemented methods supporting the corresponding recombination sites: R (RDP), G (GENECONV), B (BOOTSCAN), M (MAXCHI), C (CHIMAERA), 3Seq (3s) and S (SISCAN). The reported P-value within brackets is the greatest P-value among the calculated using RDP4-implemented methods and the corresponding method is shown in bold.
Table 2.
Recombination crossover analysis of genomic RNA2 of AILV isolates, using the ‘Recombination Detecting Program’ RDP4. a RDP4-implemented methods supporting the corresponding recombination sites: R (RDP), G (GENECONV), B (BOOTSCAN), M (MAXCHI), C (CHIMAERA), 3Seq (3s) and S (SISCAN). The reported P-value within brackets is the greatest P-value among the calculated using RDP4-implemented methods and the corresponding method is shown in bold.
| Domain |
Position (nt) |
Parental isolates (Major × minor) |
RDP4 (P value) a
|
| 2A |
251-300 |
AILV-V x AILV-B |
RGBMC3sS (4.516 x 10-64) |
| 2A |
730-800 |
AILV-S x AILV-V |
RGBMC3sS (1.462 x 10-67) |
| 2B |
1292-1406 |
AILV-V x AILV-C |
RGBMC3sS (1.124 x 10-71) |
| 2B |
1304-1408 |
AILV-V x AILV-B |
RGBMC3sS (4.734 x 10-38) |
| 2C |
2245- 2851 |
AILV-B x AILV-V |
RGBMC3sS (1.561 x 10-27) |
| 2C |
2762-2961 |
AILV-B x AILV-V |
RGBMC3sS (1.053 x 10-29) |
| 3’NCR |
4450-4621 |
AILV-B x AILV-C |
RGBMC3sS (2.573 x 10-45) |
5. Discussions and Conclusions
AILV is an important nepovirus and represents the fourth member of nepoviruses of subgroup B to be completely sequenced and characterized, after TBRV, GCMV and GARSV. The scope of this study was to retrieve more genome sequence information of AILV isolates infecting different host plant species, since only one complete genomic sequence (RNA1 and 2) of an AILV isolate from grapevine is available in the GenBank. The complete sequencing of four RNA2 segments of AILV from different host plant species has highlighted the presence of high genomic variability (ca. 18%) never reported before among isolates of nepoviruses of subgroup B. Another thread of this study was the first-time finding of AILV in a new host never reported before, i.e., chard (Beta vulgaris), and to find that the vein mottling and yellow symptoms observed on infected chard plants are attributed to AILV infection. Unfortunately, it was not possible to corroborate more this result by observing additional AILV-infected chard plants in the field, since the discovery of AILV in chard has occurred after the eradication of chard plantation in the field. However, comforting was the symptoms observed on chard plants and on N. occidentalis plants, from which after PCR assays, all confirmed the presence and accordingly the role of AILV in the diseased plants. This study highlighted the sequence variations in RNA2 of AILV from different hosts, and in particular manner the presence of three stretches of amino acids sequences in the CP gene of an AILV-X87254 isolate that were particularly different from those found in our isolates. However, the nucleotide sequence comparisons between this partial fragment (1,820 nt long and spanning the CP and a portion of the 3’NCR region) of RNA2 and our sequences from AILV isolates showed 85% to 95% identity. Whether these variations are the results of some errors ocured in the 80’s during sequencing this partial fragment or due to some recombinations in the genome of this AILV isolate is hard to be determined. In this context, our analysis predicted different recombination sites that has involved the AILV genomes from different hosts and in particular those from grapevine (AILV-G), artichoke (AILV-C) and chard (AILV-B). This recombination, and specifically in these host types, was somehow expected being host species that often share the same agricultural habitat. Most probably these recombinations, and consequently the evolution of AILV, are the result of the existence of a common vector that have facilitated the encounter of different AILV isolates and their transmission from one plant species to another in nature. An experiment to investigate the capacity of Longidorus attenuatus and L. apulus to inoculate AILV isolates from one host plant species to another would clarify the evolutionary pathway of this virus.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
T.E.: writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, validation, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, conceptualization, resources. A. B.S.: visualization, methodology, data curation. I.B.: visualization, methodology, validation, investigation, formal analysis, data curation. M.M.H.: visualization, investigation. R.S.: visualization, methodology, data curation. M.D.: visualization, validation, data curation. A.A.; validation, methodology, data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
No ethics approval was required for this work.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgment
Authors would like to thank Prof. Donato Gallitelli (University of Bari, Italy) for providing the AILV isolates (AILV-C, -S, -G, -V) analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cadman, C.H. Biology of Soil-Borne Viruses. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1963, 1, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.D.; Murant, A.F. Nepovirus Group. CMI/AAB Descriptions of Plant Viruses 1977, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Sanfacon, H. Secoviridae: A Family of Plant Picorna-Like Viruses with Monopartite or Bipartite Genomes. eLS 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- ICTV. 2023. https://ictv.global.
- Majorana, G.; Rana, G.L. Un nuovo virus latente isolato da Carciofo in Puglia/a new latent virus isolated from Artichoke in Apulia. Phytopathol Medit. 1970, 9, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, M.; Schmitt-Keichinger, C.; Sanfaçon, H. A renaissance in nepovirus research provides new insights into their molecular interface with hosts and vectors. Adv. Virus Res. 2017, 97, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Vovlas, C.; Martelli, G.P.; Quacquarelli, A. Le virosi delle piante ortensi in Puglia. VI. II complesso delle maculature anulari della Cicoria. Phytopathol. Medit. 1971, 10, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Vovlas, C. Le malformazioni fogliari, una nuova virosi del Geranio. Phytopathol. Medit. 1974, 13, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Quacquarelli, A.; Martelli, G.P. Ricerche sull’agente dell’arricciamento maculato del carciofo. Ospiti differenziali e proprietà. In: Proceedings of the 1st Congresso dell’Unione Fitopatologica Mediterranea, Bari-Napoli 1996, 168-177.
- Savino, V.; Gallitelli, D.; Jankulova, M.; Rana, G.L. A comparison of four isolates of artichoke Italian latent virus (AILV). Phytopathol. Medit. 1977, 16, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Jankulova, M.; Savino, V.; Gallitelli, D.; Quacquarelli, A.; Martelli, G.P. Isolation of artichoke Italian latent virus from the grapevine in Bulgaria. In: Proceedings of 6th ICVG Meeting, vol 18. Cordoba, 1976, Monografias INIA, 143–148.
- Quacquarelli, A.; Rana, G.L.; Martelli, G.P. Poljopr Znan Smotra 1976, 39, 561.
- Elbeaino, T.; Belghacem, I.; Mascia, T.; Gallitelli, D.; Digiaro, M. Next generation sequencing and molecular analysis of artichoke Italian latent virus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1805–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, O.; Lanneau, M.; Candresse, T.; Dunez, J. The nucleotide sequence of the RNA-2 of an isolate of the English serotype of tomato black ring virus: RNA recombination in the history of nepoviruses. J. General Virol. 1995, 76, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigne, E.; Marmonier, A.; Fuchs, M. Multiple interspecies recombination events within RNA2 of Grapevine fanleaf virus and Arabis mosaic virus. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Gerbermeskel, S.; Martelli, G.P. Grapevine deformation virus: Complete sequencing and evidence of recombination events derived from Grapevine fanleaf virus and Arabis mosaic virus. Virus Res. 2012, 166, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digiaro, M.; Yahyaoui, E.; Martelli, G.P.; Elbeaino, T. The sequencing of the complete genome of a Tomato black ring virus (TBRV) and of the RNA2 of three Grapevine chrome mosaic virus (GCMV) isolates from grapevine reveals the possible recombinant origin of GCMV. Virus Genes 2015, 50, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digiaro, M.; Nehdi, S.; Elbeaino, T. Complete sequence of RNA1 of Grapevine Anatolian ringspot virus. Arch Virol 2012, 157, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M; Fallanaj, F. ; Kuzmanovic, S.; Martelli, G.P. Complete nucleotides sequence and genome organization of Grapevine Bulgarian latent virus. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.; Chisholm, J.; Wei, T.; Ghoshal, B.; Saeed, H.; Rott, M.; Sanfaçon, H. Complete genome sequence of three tomato ringspot virus isolates: evidence for reassortment and recombination. Arch. Virol. 2015, 60, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, W.; Minutillo, S.A.; Spano, R.; Zammouri, S.; Gallitelli, D.; Mnari-Hattab, M. Occurrence of artichoke-infecting viruses in Tunisia. EPPO Bulletin 2017, 47, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutillo, S.A.; Mascia, T.; Gallitelli, D. A DNA probe mix for the multiplex detection of ten artichoke viruses. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, T.O.; Schneider, I.R. Virus degradation and nucleic acid release in single-phase phenol systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968, 124, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieco, F.; Saponari, M.; Alkowni, R.; Savino, V.; Garau, R.; Martelli, G.P. Progress in diagnosis of olive viruses. Informat. Fitopatol. 2000, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Brannigan, K.; Clark, R.; Gilbertson, R.L. Characterization of curtoviruses associated with curly top disease of tomato in California and monitoring for these viruses in beet leafhoppers. Plant Disease 2010, 94, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemchinov, L.G.; Hammond, J.; Jordan, R.; Hammond, R.W. The complete nucleotide sequence, genome organization, and specific detection of Beet mosaic virus. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, K.; Rysánek, P. Detection of beet yellows virus by RT-PCR and immunocapture RT-PCR in Tetragonia expansa and Beta vulgaris. Acta Virol. 2004, 48, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sabokkhiz, M.A.; Jafarpour, B.; Shahriari Ahmadi, F.; Tarighi, S.I. dentification of Turnip mosaic virus isolated from Canola in northeast area of Iran. African J. Biotechnol, 2012, 11, 14553–14560. [Google Scholar]
- Chaouachi, M.; Fortabat, M.N.; Geldreich, A.; Yot, P.; Kerlan, C.; Kebdani, N.; Audeon, C.; Romaniuk, M.; Bertheau, Y. An accurate real-time PCR test for the detection and quantification of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV): applicable in GMO screening. Eur Food Res Technol. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Brault, V.; Hibrand, L.; Candresse, T.; Le Gall, O.; Dunez, J. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of Hungarian grapevine chrome mosaic nepovirus RNA2. Nucl. Acids Res. 1989, 17, 7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).