1. Introduction
Myelodysplastic neoplasm (MDS) is a group of clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorders, defined by cytopenias and morphologic dysplasia, leading to progressively ineffective hematopoiesis and an increased risk of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The term myelodysplastic neoplasm itself was introduced in the 5th edition of the WHO classification of haematolymphoid tumours [
1].
MDS is a heterogeneous group of preleukemic diseases with varying prognoses, clinical phenotype, and responses to treatment. It is crucial to use optimized risk stratification in individual patients for effective treatment strategies. To achieve this, different properly validated prognostic scoring systems, such as the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) or the Revised-IPSS (IPSS-R) are used worldwide. These widely accepted scoring systems utilize factors like the percentage of bone marrow blasts, the depth of cytopenia (hemoglobin, platelet, and absolute neutrophil count), and cytogenetic alterations to predict the survival time and the likelihood of AML evolution [
2,
3].
Apart from recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities, oncogenic mutations have been detected in 78% of patients with MDS or closely related myeloid neoplasms [
4]. Among the most frequently mutated genes in MDS, each plays a role in distinct cellular processes. For instance, some genes are involved in controlling RNA splicing (
SF3B1,
SRSF2, U2AF1, and
ZRSR2), others in epigenetic regulation of gene expression via DNA methylation (
TET2, DNMT3A, IDH1, and
IDH2), and a few participate in histone modification (ASXL1 and EZH2). Additionally, transcription factors (
RUNX1, NRAS, BCOR), signaling proteins (
CBL), the tumor suppressor p53 (
TP53), and the cohesin complex (
STAG2) are among the other commonly mutated genes [
5,
6,
7].
Certain mutations in MDS have strong associations with clinical phenotypes and outcomes, making them valuable prognostic biomarkers independent of conventional scoring systems [
7,
8]. Among these mutations,
TP53 aberrations hold particular significance in MDS, as they are detected in 7-11% of patients.
TP53 mutations are often linked to abnormalities of chromosome 5q, high cytogenetic complexity, or monosomal karyotypes [
9,
10,
11].
TP53 mutations are also frequently found in certain AML subgroups, such as AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MR) [
12]. These mutations are well-established adverse risk factors in both AML and MDS [
13,
14]. Patients with
TP53 alterations exhibit lower rates of complete remission, increased relapse rates, and inferior overall survival following intensive treatments [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. Similarly, those with
TP53 mutations experience shorter remission durations and inferior overall survival after non-intensive treatments [
18,
19]. Similar to solid neoplasms, various alterations of the
TP53 gene have been identified in myeloid neoplasms. These alterations include allelic losses at the cytogenetic level, as well as molecular mutations, insertions, and deletions. These aberrations can manifest as either heterozygous with a remaining wild-type allele or in a hemi-/homozygous state [
20,
21].
In the newest edition of WHO classification, MDS is divided into two main subcategories: those having defining genetic abnormalities and those that are defined morphologically. MDS with biallelic
TP53 inactivation (MDS-biTP53) falls into the group of MDS with defining genetic abnormalities. MDS-biTP53 is defined as a myeloid neoplasm with cytopenia, dysplasia, and less than 20% blasts or 30% erythroblasts, characterized by two or more
TP53 mutations or one
TP53 mutation and concurrent evidence of
TP53 copy loss or copy neutral loss of heterozygosity [
1].
Previous studies have examined the potential prognostic significance of p53 overexpression defined by immunohistochemistry and its relationship with
TP53 mutation. The evidence suggests that increased p53 labeling is linked to a higher risk of AML evolution, reduced overall survival, elevated bone marrow blast count, and poor risk karyotype [
23,
24,
25]. However, these studies vary in terms of the staining intensity and cut-off values used. Remarkably, there is only limited information about the topographic characteristics of p53 expression in different bone marrow lineages [
26].
This retrospective study aimed to analyze p53 expression in bone marrow samples with dysplasia, both in cases of MDS and dysplasia-related AML groups. We examined the correlation between TP53 mutation and p53 immunopositivity by employing various cut-off values for p53 expression. Additionally, we focused on understanding the relationship between p53 expression, TP53 mutation, and myeloblast count. Double immunohistochemical stains were used, which allowed us to precisely define the expression of p53 in different bone marrow cell lineages. Through these techniques, we aimed to gain a deeper understanding of the role of p53 in the bone marrow context and its potential implications for disease progression and patient outcomes in dysplasia-related conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
In this retrospective study, 46 adult cases of Myelodysplastic Neoplasm (MDS) and 26 adult cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) were evaluated. All cases exhibited dysplastic morphological changes in at least one bone marrow cell lineage. Additionally, four adult cases without evidence of a clonal alteration were selected as controls. A total of 76 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded bone-marrow biopsy samples were collected from the archives of the Department of Pathology, Medical Center, University of Debrecen. The patient's average age was 64.2 years (ranging from 25 to 90 years), and the female-to-male ratio was 42/34. The patients were managed and treated at the Department of Hematology, Medical Center, University of Debrecen. The latest edition of the WHO classification of hematolymphoid tumors was used for reclassifying the cases. The study protocol was approved by the respective Institutional Ethical Review Board for human subjects (IRB reference number: 60355-2/2016/EKU and IV/8465-3/2021/EKU).
2.2. Histology, immunohistochemistry
Bone marrow biopsies were routinely processed, fixed in formaldehyde (3.6% in phosphate buffer) for one day, followed by decalcification (EDTA-TRIS buffer at a concentration of 0.1 g/ml), and then embedded in paraffin wax. 4 μm slides were deparaffinized and used for subsequent stainings.
Retrospective p53 immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis was performed using the "Do-07" clone Dako antibody (Agilent Technologies Company, Santa Clara, California, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. Two independent pathologists evaluated the percentage of positive cells (0-100%) and the intensity of nuclear staining. The intensity of staining ranged from 0 to 3: 0 for negative, 1+ for weak, 2+ for moderate, and 3+ for strong expression. The total percentage of p53-positive cells (weak to strong) and the percentage of cells with strong (3+) p53 expression were assessed. Three cut-off values (1%, 5%, and 10%) for strong (3+) nuclear expression were separately correlated with the mutational status. Accuracy of strong (3+) and total p53 expression for prediction of TP53 mutation status were also analyzed. Specificity, sensitivity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were determined using different cut-off values. To analyze the p53 expression of different bone marrow cell populations, double immunohistochemical stainings were performed sequentially using the EnVision FLEX/HRP system. CD71 and CD34 antibodies were used in combination with p53 immunohistochemistry. Methyl-green counterstaining was performed for double staining.
2.3. DNA isolation
DNA extraction was carried out using the QIAamp DNA FFPE Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNA concentration was measured using the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit in a Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), following the manufacturer's instructions.
2.4. Next-Generation Sequencing
Following genomic DNA enzymatic fragmentation, libraries were created using the Accel-Amplicon Comprehensive TP53 panel (Swift Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Sequencing was performed using the MiSeq System (MiSeq Reagent kit v3 600 cycles, Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) as per the MiSeq instruction manual. Captured libraries were sequenced in a multiplexed fashion with a paired-end run, obtaining 2x150 bp reads with at least 250X depth of coverage. The coverage ranged between 250-69361, with a median of 4075 and a mean of 13769. The trimmed fastq files were generated using MiSeq reporter (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). NextGENe software (v.2.4.3.; SoftGenetics, State College, PA, USA) was used to analyze the raw sequence data for the presence of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (indels). The human reference genome GRCh37 (equivalent UCSC version hg19) was used for alignment. A 5% variant allele frequency (VAF) was used as a cut-off.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Statistical Analysis: Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 5.0.3 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). P values below 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Case distribution based on myeloblast count, p53 expression, and TP53 status
Considering myeloblast counts, the study included 26 cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with ≥20% bone marrow myeloblasts, 12 cases of myelodysplastic neoplasm (MDS) with an increased blast count (5-19% bone marrow myeloblasts), and 34 cases of MDS with a low blast count (<5% bone marrow myeloblasts). The cases were reevaluated and classified according to the diagnostic criteria of the 2022 WHO classification of hematolymphoid tumors. Among them, 23 cases met the criteria for "acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplasia-related (AML-MR)", while three AML cases were categorized under the "myeloid neoplasms post cytotoxic therapy (MN-pCT)" group showing significant myelodysplastic features. Among the 12 MDS cases with an increased blast count, two were classified as "myelodysplastic neoplasm with biallelic (or multi-hit)
TP53 alterations (MDS-
biTP53)", and two were categorized as MN-pCT. Additionally, eight cases lacked molecular or clinical evidence for a specific category and were defined morphologically as "myelodysplastic neoplasm with increased blasts (MDS-IB)". In the group of MDS with a low blast count, three cases were classified as “myelodysplastic neoplasm with low blasts and 5q deletion (MDS-5q)”, four cases as MN-pCT, four cases were morphologically defined as “hypoplastic MDS (h-MDS)”, and 23 cases as “myelodysplastic neoplasm with low blasts (MDS-LB)” (
Table 1 and
Figure 1A).
Different cut-off values for p53 expression were defined, including ≥10% total p53 expression, ≥1% strong (3+) p53 expression, ≥5% strong (3+) p53 expression, and ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression. The correlation between the total percentage of p53 positive cells, assessed by two independent pathologists, was found to be highly significant (Spearman r =0.7293, p<0.0001). An inter-reader agreement was nearly perfect using the ≥10% cut-off values for strong (3+) p53 expression, with a Kappa-value of 0.937.
Among the 72 neoplastic cases, 25 showed ≥10% total p53 expression (34.72%), 32 cases (44.44%) showed ≥1% strong (3+) p53 expression, 17 cases (23.61%) showed ≥5% strong (3+) p53 expression, and 12 cases (16.66%) showed ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression. Regarding the mutation status, 26/72 cases (36.11%) carried at least one
TP53 mutation, with eight cases (11.11%) having multiple
TP53 mutations (
Table 1). Six further cases (8.33%) harbored biallelic
TP53 alterations due to evidence of
TP53 copy loss. None of the reactive cases displayed strong (3+) p53 expression or carried
TP53 mutations. However, mild to moderate p53 expression was observed in three out of the four reactive cases, with a percentage of 1-20% (
Figure 2).
3.2. Correlation between p53 expression and myeloblast count
Myeloblast count showed a significant correlation with both total p53 expression (Spearman r=0.4470, p<0.0001), and strong (3+) p53 expression (Spearman r=0.4880, p<0.0001) (
Figure 1B). Cases were categorized based on the myeloblast count into three groups: AML (≥20% blast count, n=26), MDS-IB (5-19% blast count, n=12), MDS-LB (<5% blast count, n=34). A significant difference was detected between these subgroups both in total and strong (3+) p53 expression (p=0.0039 and p=0.0011 respectively as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test) (
Figure 1C).
We performed double immunohistochemical examinations on cases displaying ≥10% total p53 expression. Our observations revealed that p53 nuclear expression frequently occurs together with CD34 positivity, although not exclusively. On one hand, p53-/CD34+ cells could be observed, while conversely p53+/CD34- cell population was also identifiable. Despite statistical results indicating a significant correlation between the proportion of p53 positive bone marrow cells and the myeloblast ratio, based on the double immunohistochemical examinations, it could be concluded that p53 expression is not exclusively associated with the myeloblast cell population. Notably, the p53 expression was often associated with the erythroid cell lineage, which was confirmed by the double staining of p53+/CD71+. Furthermore, in several cases, p53 expression was observed in cells exhibiting megakaryocyte morphology,
Figure 3. The ratio of p53 positive cells ranged widely in all analyzed cell lineages. The ratio of p53 positive erythroblasts ranged between 0-50%, this range was 0-75% for megakaryocytes and 1-95% for CD34+ myeloblasts.
3.3. Correlation between TP53 mutation status and myeloblast count
The ratio of
TP53 mutated cases proportionally reflected the myeloblast count as 20.59% (7/34) of MDS cases, 33.33% (4/12) of MDS-IB cases, and 57.69% (15/26) AML cases were mutated. The ratio of multiple TP53 mutations showed a similar tendency: 2.94 % (1/34) of MDS cases, 16.67% (2/12) of MDS-IB cases, and 19.23% (5/26) of AML cases carried multiple mutations. The median of VAF values varied significantly between MDS-LB (VAF median: 10.81, mean: 11.39), MDS-IB (VAF median: 30.65, mean: 33.27), and AML (VAF median: 33.68, mean: 35.84) subgroups as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test, p=0.016. The VAF value was significantly higher in AML and MDS-IB compared with MDS as assessed with the Mann-Whitney test (p=0.0056 and p=0.303 respectively). While there was no significant difference between AML and MDS-IB (p=0.7539) (
Figure 1C). These findings are consistent with the observation that the VAF value showed a significant correlation with the myeloblast count (Spearman r=0.4757, p<0.0001) (
Figure 1B).
3.4. Correlation between p53 expression and TP53 mutation status
Out of the 26 TP53 mutated cases, 18 carried only one mutation, while eight had multiple mutations. The VAF value, which ranged from 5.04% to 88.04% with a mean of 22.75%, exhibited a significant correlation with both total and strong (3+) p53 expression (Spearman r=0.2953, p=0.0096 and Spearman r=0.4398, p<0.0001 respectively).
The percentage of bone marrow cells with strong (3+) p53 expression was significantly higher in the
TP53 mutant group compared to the
TP53 wild-type group, as assessed using the Mann-Whitney test (mean 14.15% versus 0.98% respectively, p=0.0005) (
Figure 1D).
A significant association was found between p53 expression and
TP53 mutation status using all the defined cut-off values. The highest specificity (0.9800) was observed with the ≥10% strong (3+) p53 cut-off value, indicating that 49 of the 50 wild-type cases were negative, but the sensitivity (0.4231) was low, with only 11 of the 26 mutant cases being positive. Conversely, the highest sensitivity (0.6154) was seen using the 1% strong (3+) p53 expression as a cut-off value, with 16 of the 26 mutant cases showing positivity, but the specificity (0.6800) was relatively lower, with 34 of the 50 wild-type cases being negative (
Table 2).
Out of the 26 TP53 mutated cases, 14 (53.85%) were considered ho harbor bi-allelic alteration. In eight cases multiple mutations were detected, in three cases the VAF value exceeded 50% and in three further cases one TP53 mutation was present together with chromosome 17 deletion. In 12 cases (46.15%) single TP53 mutation was detected without the evidence of a biallelic state. 33.33% (4/12) of cases with monoallelic TP53 alteration and 64.29% (9/14) of cases with biallelic TP53 alteration displayed ≥10% total p53 expression, this difference was not significant (p=0.2377). There was no significant difference in the percentage of strong (+3) p53 positive cells between cases with monoallelic and biallelic TP53 alterations (mean 8.83% vs. 19.64% respectively, Mann Whitney test, p=0.0754).
3.5. Characteristics of cases with biallelic TP53 alterations
In three cases with a single TP53 mutation (3/18), the VAF value was over 50% which suggests the loss of the second allele. However, only one case had a conventional cytogenetic result available presented with a complex karyotype. Among the three cases with over 50% VAF value, two showed ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression while one case was completely negative for p53. In agreement with this discrepancy, the negative case carried the TP53 p.Y163Xfs mutation, leading to p53 protein truncation and instability. Clinically, two out of these cases were AML-MR and one was MDS-IB, consistent with ≥10% myeloblast count. The latter case was classified as MDS-biTP53.
In addition to the cases with >50% VAF values, eight further cases carried multiple
TP53 mutations: five cases carried two, one case three, one case four, and one case six mutations (
Table 3). Four of these cases (4/8) showed ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression, however in the other four cases (4/8) strong (3+) p53 expression was present in less than 10% of cells despite the presence of
TP53 mutations. Further analysis revealed that in three of these cases, more than two mutations were present resulting in potential p53 protein instability and consequent loss of expression. Moreover, two of these cases carried stop codon (p.C135X) or frame-shift mutation (p.K373Rfs). Finally, in two case the VAF values were relatively low (<10%). These factors may explain the low level p53 expression. Clinically, five cases were AML-MR, two cases were MN-pCT, and one case was MDS with increased blast count. This MDS case is classified as MDS-
biTP53. All cases with ≥10% p53 expression had >10% myeloblast count.
Three further cases were considered to harbor biallelic TP53 alteration due to the simultaneous presence of chromosome 17 deletion and TP53 mutation. Two of these cases (2/3) showed ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression, while one case was completely negative. The latter case carried a frame-shift mutation (p.E286Qfs). Clinically all of these cases were classified as AML-MR with >10% myeloblast count.
3.6. Characteristics of TP53 mutated cases without the evidence of bi-allelic state
In 12 cases only one TP53 mutation was present, the VAF value was <50%, and evidence of TP53 locus deletion in 17p13 was not present. Four cases showed ≥10% strong (3+) and five cases ≥10% total p53 expression, while in seven cases a discrepancy was present as both total and strong (3+) p53 expression were <10%. In one AML-MR cases, a truncating mutation was detected (p.L93Lfs), and in three AML-MR cases, the coverage was low (<500) indicating a minor TP53 mutant population in the sample. These circumstances may explain the negative IHC result. Further six TP53 mutant MDS cases showed negative IHC, two of which carried TP53 mutation with a relatively low VAF (5.94% and 7.52%). In four MDS-LB cases, however, no convincing explanation was found, as both VAF and coverage were satisfactory, and no truncating mutation was present. All cases with ≥10% p53 expression had ≥10% myeloblast count.
3.7. Inconsistency between TP53 status and p53 expressio
Among the 26
TP53 mutated cases, 15 were AML, 4 were MDS-IB, and 7 were MDS-LB. In 13 cases ≥10% total p53 expression was present (11/15 AML, 2/4 MDS-IB, 0/7 MDS-LB). In 13 further cases, total p53 expression was <10% (4/15 AML, 2/4 MDS-IB, 7/7 MDS-LB). The discrepancy was the most prominent in the MDS-LB group as none of the mutated cases showed ≥10% p53 expression. As it was described previously, satisfactory possible explanations were present in all the p53 low-expressor (<10%)
TP53 mutated AML and MDS-IB cases. Frameshift mutations, multiple mutations with protein instability, low VAF value with a minor clone or low coverage were present in these cases. On the other hand, in four MDS-LB cases, there was no apparent mutation-related explanation found for this inconsistency, however, the myeloblast count was low. It was also observed that all cases with mutated
TP53 and ≥10% total p53 expression also had a myeloblast count greater than 10% (
Figure 1A).
3.8. Correlation between CCSS score and p53 status
Comprehensive Cytogenetic Scoring System (CCSS) score was available in 60 neoplastic cases (
Table 1). There was a significant difference in CCSS score between
TP53 mutated and wild-type cases (p<0.0001, Chi-square test for trend). Complex karyotypes and a consequential very poor CCSS score were more frequent in
TP53 mutated cases. Very poor CCSS score was present in 52.38% (11/21) of
TP53 mutated cases and only in 7.14% (3/42) of
TP53 wild-type cases. Altogether very poor CCSS score was present in 14 cases, 11 of which were
TP53 mutated.
CCSS score also showed significant differences between p53 negative (<10%) and p53 positive (≥10%) cases (p<0.0001, Chi-square test). Very poor CCSS characterized 87.5% (7/8) of p53 positive cases and only 12.73% (7/55) of p53 negative cases.
3.9. Correlation between overall survival and p53 status
Excluding MN-pCT cases, overall survival was estimated in 23 AML cases and 40 MDS cases.
There was no significant difference in the overall survival between TP53 mutated (n=14, median 7.47 months) and TP53 wild type (n=9, median 11.37 months) AML cases (p=0.4655). There was no significant difference in overall survival between AML cases showing <10% strong 3+ p53 expression (n=15, median 5.8 months) and ≥10% strong 3+ p53 expression (n=8, median 2.25 months) (p=0.3394). AML cases with bi-allelic TP53 mutational status (n=9, median survival 5.450 months) were associated with significantly shorter overall survival compared with AML cases harboring single mutation or wild type TP53 status (n=14, median survival 11.37 months) (p=0.039).
The overall survival was significantly shorter in the TP53 mutated MDS group (n=9, median survival 10.30 months) compared with TP53 wild-type MDS cases (n=31, median survival 31.57 months) (p=0.0094). A similar result was found between MDS cases showing <10% strong 3+ p53 expression (n=37, median 31.90 months) and ≥10% strong 3+ p53 expression (n=3, median 4.067 months) (p=0.0030). MDS cases with bi-allelic TP53 mutational status (n=2, median survival 1.750 months) were associated with significantly shorter overall survival compared with MDS cases harboring single mutation or wild type TP53 status (n=38, median survival 31.57 months) (p<0.0001). This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
4. Discussion
Myelodysplastic neoplasm (MDS) represents a diverse group of clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorders. To ensure effective treatment strategies, optimizing risk stratification for individual MDS patients is essential.
TP53 mutations have been established as adverse risk factors, associated with high cytogenetic complexity and monosomal karyotypes in both MDS and AML. The 5th edition of the WHO classification of haematolymphoid tumors introduced the term "MDS with biallelic
TP53 inactivation" (MDS-
biTP53), requiring the presence of two or more
TP53 mutations or one
TP53 mutation combined with concurrent evidence of
TP53 copy loss or copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity [
1].
Several authors have explored the relationship between
TP53 mutation status and p53 protein expression, observing a strong correlation [
23,
24,
25,
26]. P53 immunohistochemistry is directed to the initial, non-involved region of the protein by the commonly used Do-7 antibody clone. Increase in labeling is an indirect sign of mutations resulting mutant/wild-type protein dimerization and delayed breakdown of the protein [
27,
28,
29,
30]. It has been published that p53 immunopositivity itself is associated with a poor prognosis. However, the precise cut-off value for p53 expression remains unclear. The distinction between biallelic and monoallelic alterations concerning immunopositivity is also subject to question. Additionally, further investigation is needed to determine the distribution of p53-positive cells among bone marrow hematopoietic cell lineages.
The results of this retrospective study revealed a significant correlation between TP53 mutation status and p53 protein expression. Various cut-off values for p53 expression were explored, and it was observed that a ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression cut-off provided the highest specificity, while a 1% strong (3+) p53 expression cut-off had the highest sensitivity. Moreover, the VAF value was found to be significantly correlated with both total and strong (3+) p53 expression. There was no significant difference in p53 expression between cases with monoallelic and biallelic alterations.
Interestingly, some cases exhibited TP53 mutations without ≥10% p53 protein expression, and vice versa. This incongruence could be attributed to the presence of multiple TP53 mutations, leading to protein instability and subsequent loss of p53 expression. Other contributing factors may include truncating mutations, low VAF value, or low coverage during analysis. Protein instability and truncation lead to a completely negative staining pattern in solid tumors; however, this pattern is challenging to discern in bone marrow samples. Residual non-neoplastic bone marrow cells may express p53 with variable frequency. The reactive cells with physiological p53 expression are intermixed with the neoplastic cells and prevent the entirely negative “null” phenotype that is typical of solid tumors with truncating mutations.
Notably, the most prominent discrepancy was observed within the MDS-LB group, suggesting that this subgroup may be particularly affected by the conflicting results. Furthermore, it was observed that all cases with mutated TP53 and p53-positive immunostaining had a myeloblast count greater than 10%. This finding implies that p53 immunopositivity is not solely dependent on the presence of TP53 mutations but also correlates with the myeloblast count in the analyzed samples.
Low myeloblast counts indicate the parallel occurrence of clonal and normal, non-clonal hemopoesis. Their actual balance may influence the particular TP53/p53 findings.
TP53 mutation and p53 expression showed a correlation with the myeloblast count. Specifically, the ratio of TP53 mutated cases proportionally increased with the myeloblast count, with 20.59% of MDS cases, 33.33% of MDS with increased blast count (MDS-IB) cases, and 57.69% of AML cases carrying TP53 mutations. The VAF value was significantly higher in AML and MDS-IB cases compared to MDS cases, indicating a potential association between higher VAF and a higher percentage of myeloblasts. The myeloblast count showed a significant correlation with both total and strong (3+) p53 expression. Cases with higher blast counts were more likely to exhibit increased p53 expression.
Based on these observations, one would expect that p53 protein expression is exclusively present only in myeloblasts. However, double immunohistochemical stainings of samples with more than 10% total p53 expression revealed that, in most cases, erythroid cells and megakaryocytes exhibit partial p53 expression. These cells showed a p53+/CD34- pattern. We should consider that at least a portion of these lineages are part of the process and also derivate from the mutant stem cell clone. The ratio of positively stained erythroids ranged between 1-50%, while this range was 0-75% in megakaryocytes. The CD34+ myeloblasts also exhibited only partial p53 expression (1-95%), as p53-/CD34+ cells were also present.
The correlation between TP53 mutation status and the Comprehensive Cytogenetic Scoring System (CCSS) score was significant. TP53-mutated cases were more likely to exhibit complex karyotypes and poorer CCSS scores, indicating a higher-risk disease phenotype associated with TP53 mutations. This finding aligns with previous studies that have identified TP53 mutations as adverse risk factors in MDS and AML.
5. Conclusions
The findings from this study contribute to a better understanding of the role of TP53 mutations and p53 protein as an indicator of the mutant phenotype in MDS and AML.. The finding suggests that with proper interpretation, p53 immunohistochemistry can be a valuable tool for the identification of cases with TP53 mutations with excellent specificity but a low sensitivity. Immunohistochemistry could be especially useful in cases with increased blast counts. However, this tool is not sufficient for the distinction between monoallelic and biallelic alterations. The observations underscore the complex relationship between TP53 mutations and p53 protein load and highlight the need for further investigations to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M. and J.B.; methodology, A.M, K.M; software, K.M, J.B.; validation, J.B., S.M. and Á.M.; formal analysis, J.B.; investigation, J.B., S.M, K.M., and Á.M; resources, J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, J.B.; writing—review and editing, G.M, A.M and Zs.M..; visualization, J.B.; supervision, G.M..; project administration, J.B.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of University of Debrecen (IRB reference number: 60355-2/2016/EKU and IV/8465-3/2021/EKU).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Haematolymphoid tumours [Internet; beta version ahead of print]. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2022 [cited 2023.08.25]. (WHO classification of tumours series, 5th ed.; vol. 11). Available from: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/chapters/63.
- Greenberg, P. L., Tuechler, H., Schanz, J., Sanz, G., Garcia-Manero, G., Solé, F., Bennett, J. M., Bowen, D., Fenaux, P., Dreyfus, F., Kantarjian, H., Kuendgen, A., Levis, A., Malcovati, L., Cazzola, M., Cermak, J., Fonatsch, C., le Beau, M. M., Slovak, M. L., … Haase, D. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood, 2012 120 (12). [CrossRef]
- Jonas, B. A., & Greenberg, P. L. MDS prognostic scoring systems – Past, present, and future. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2015 28(1), 3–13. [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E., Gerstung, M., Malcovati, L., Tauro, S., Gundem, G., van Loo, P., Yoon, C. J., Ellis, P., Wedge, D. C., Pellagatti, A., Shlien, A., Groves, M. J., Forbes, S. A., Raine, K., Hinton, J., Mudie, L. J., McLaren, S., Hardy, C., Latimer, C., … Campbell, P. J. Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013, 122(22), 3616–3627. [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, T., Nagata, Y., Grossmann, V., Okuno, Y., Bacher, U., Nagae, G., Schnittger, S., Sanada, M., Kon, A., Alpermann, T., Yoshida, K., Roller, A., Nadarajah, N., Shiraishi, Y., Shiozawa, Y., Chiba, K., Tanaka, H., Koeffler, H. P., Klein, H.-U., … Ogawa, S. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014, 28(2), 241–247. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M., Wang, F., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Cao, P., Nie, D., Fang, J., Wang, M., Liu, M., & Liu, H. Gene mutation spectrum of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and progression to acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol Oncol 2021 10(2). [CrossRef]
- Cook, M. R., Karp, J. E., & Lai, C. The spectrum of genetic mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome: Should we update prognostication? EJHaem 2022 3(1), 301–313. [CrossRef]
- Bejar, R., Stevenson, K., Abdel-Wahab, O., Galili, N., Nilsson, B., Garcia-Manero, G., Kantarjian, H., Raza, A., Levine, R. L., Neuberg, D., & Ebert, B. L. Clinical Effect of Point Mutations in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N Engl J Med 2011, 364(26), 2496–2506. [CrossRef]
- Haase, D., Stevenson, K. E., Neuberg, D., Maciejewski, J. P., Nazha, A., Sekeres, M. A., Ebert, B. L., Garcia-Manero, G., Haferlach, C., Haferlach, T., Kern, W., Ogawa, S., Nagata, Y., Yoshida, K., Graubert, T. A., Walter, M. J., List, A. F., Komrokji, R. S., Padron, E., … Bejar, R. TP53 mutation status divides myelodysplastic syndromes with complex karyotypes into distinct prognostic subgroups. Leukemia 2019, 33(7), 1747–1758. [CrossRef]
- Cook, M. R., Karp, J. E., & Lai, C. The spectrum of genetic mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome: Should we update prognostication? EJHaem 2022, 3(1), 301–313. [CrossRef]
- Jädersten, M., Saft, L., Smith, A., Kulasekararaj, A., Pomplun, S., Göhring, G., Hedlund, A., Hast, R., Schlegelberger, B., Porwit, A., Hellström-Lindberg, E., & Mufti, G. J. TP53 Mutations in Low-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes With del(5q) Predict Disease Progression. J Clin Oncol 2011, 29(15), 1971–1979. [CrossRef]
- Devillier, R., Mansat-De Mas, V., Gelsi-Boyer, V., Demur, C., Murati, A., Corre, J., Prebet, T., Bertoli, S., Brecqueville, M., Arnoulet, C., Recher, C., Vey, N., Mozziconacci, M.-J., Delabesse, E., & Birnbaum, D. Role of ASXL1 and TP53 mutations in the molecular classification and prognosis of acute myeloid leukemias with myelodysplasia-related changes. Oncotarget 2015, 6(10), 8388–8396. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y., Gao, S.-J., Soubise, B., Douet-Guilbert, N., Liu, Z.-L., & Troadec, M.-B. TP53 in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Cancers 2021, 13(21), 5392. [CrossRef]
- Cumbo, C., Tota, G., Anelli, L., Zagaria, A., Specchia, G., & Albano, F. TP53 in Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Recent Biological and Clinical Findings. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(10), 3432. [CrossRef]
- Ohgami, R. S., Ma, L., Merker, J. D., Gotlib, J. R., Schrijver, I., Zehnder, J. L., & Arber, D. A. Next-generation sequencing of acute myeloid leukemia identifies the significance of TP53, U2AF1, ASXL1, and TET2 mutations. Mod Pathol 2015, 28(5), 706–714. [CrossRef]
- Kuykendall, A., Duployez, N., Boissel, N., Lancet, J. E., & Welch, J. S. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2018, 38, 555–573. [CrossRef]
- Terada, K., Yamaguchi, H., Ueki, T., Usuki, K., Kobayashi, Y., Tajika, K., Gomi, S., Kurosawa, S., Miyadera, K., Tokura, T., Omori, I., Marumo, A., Fujiwara, Y., Yui, S., Ryotokuji, T., Osaki, Y., Arai, K., Kitano, T., Kosaka, F., … Inokuchi, K. Full-length mutation search of the TP53 gene in acute myeloid leukemia has increased significance as a prognostic factor. Ann Hematol 2018, 97(1), 51–61. [CrossRef]
- Sill, H., Zebisch, A., & Haase, D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes with TP53 Aberrations — A Distinct Stem Cell Disorder. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26(20), 5304–5309. [CrossRef]
- George, B., Kantarjian, H., Baran, N., Krocker, J. D., & Rios, A. TP53 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Molecular Aspects and Patterns of Mutation. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(19), 10782. [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M., Hollstein, M., & Hainaut, P. TP53 Mutations in Human Cancers: Origins, Consequences, and Clinical Use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010, 2(1), a001008–a001008. [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, A. O., Yang, X., Lintner, R. E., McFarland, J. M., Duby, M., Kim, J., Howard, T. P., Takeda, D. Y., Ly, S. H., Kim, E., Gannon, H. S., Hurhula, B., Sharpe, T., Goodale, A., Fritchman, B., Steelman, S., Vazquez, F., Tsherniak, A., Aguirre, A. J., … Hahn, W. C. Mutational processes shape the landscape of TP53 mutations in human cancer. Nature Genetics 2018, 50(10), 1381–1387. [CrossRef]
- Molteni, A., Ravano, E., Riva, M., Nichelatti, M., Bandiera, L., Crucitti, L., Truini, M., & Cairoli, R. Prognostic Impact Of Immunohistochemical P53 Expression In Bone Marrow Biopsy In Higher Risk Mds: A Pilot Study. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 2019, 11(1), e2019015. [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K. L., Nguyen, J., Komrokji, R. S., Sallman, D., al Ali, N. H., Padron, E., Lancet, J. E., Moscinski, L. C., List, A. F., & Zhang, L. Immunohistochemical pattern of p53 is a measure of TP53 mutation burden and adverse clinical outcome in myelodysplastic syndromes and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101(8), e320–e323. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Pol, S., Ma, L., Ohgami, R. S., & Arber, D. A. Immunohistochemistry for p53 is a useful tool to identify cases of acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes that are TP53 mutated, have complex karyotype, and have poor prognosis. Mod Pathol 2017, 30(3), 382–392. [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K. J., Abukhiran, I. M., Syrbu, S., Tomasson, M., Bates, M., Dhakal, P., & Bhagavathi, S. Utilizing digital pathology and immunohistochemistry of p53 as an adjunct to molecular testing in myeloid disorders. Acad Pathol 2023, 10(1), 100064. [CrossRef]
- Ruzinova, M. B., Lee, Y.-S., Duncavage, E. J., & Welch, J. S. TP53 immunohistochemistry correlates with TP53 mutation status and clearance in decitabine-treated patients with myeloid malignancies. Haematologica 2019, 104(8), e345–e348. [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, K., & Lane, D. P. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J Mol Cell Biol 2019, 11(4), 317–329. [CrossRef]
- Madarász, K., Mótyán, J. A., Bedekovics, J., Miltényi, Z., Ujfalusi, A., Méhes, G., & Mokánszki, A. Deep Molecular and In Silico Protein Analysis of p53 Alteration in Myelodysplastic Neoplasia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2022, 11(21), 3475. [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, N., Brosh, R., Oren, M., & Rotter, V. Mutations in the p53 Tumor Suppressor Gene: Important Milestones at the Various Steps of Tumorigenesis. Genes & Cancer 2011, 2(4), 466–474. [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumaran, R., Tan, K. H., Miranda, P. J., Haupt, S., & Haupt, Y. Regulation of Mutant p53 Protein Expression. Front Oncol 2015, 5:284. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Correlation between TP53 status, p53 expression, and myeloblast count in bone marrow biopsy specimens with dysplasia-related alterations (n=76); (a) Heat map summarizing the distribution of cases according to myeloblast count (AML, MDS-IB, and MDS-LB), TP53 status, total and strong (3+) p53 expression, and Comprehensive Cytogenetic Scoring System (CCSS). TP53 mutated cases showing a VAF value of less than 10%, coverage below 500, frameshift mutations, or having more than two mutations are highlighted as these mutated cases were frequently associated with a low-level p53 expression. (b) Correlation of strong (+) p53 expression and TP53 VAF value with bone marrow myeloblast count. Both the percentage of p53 3+ cells and TP53 mutation VAF value showed a significant correlation with the percentage of CD34+ myeloblasts (Spearman r=0.4880, p<0.0001 and Spearman r=0.4757, p<0.0001 respectively). (c) P53 expression and TP53 VAF value in different disease subgroups. A significant difference was detected between these subgroups both in total and strong (3+) p53 expression (p=0.0039 and p=0.0011 respectively as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test). The median VAF values varied significantly between MDS-LB, MDS-IB, and AML subgroups (Kruskal-Wallis test, p=0.016). (d) Correlation between p53 expression and TP53 mutation status. The percentage of bone marrow cells with total or strong (3+) p53 expression was significantly higher in the TP53 mutant group compared to the TP53 wild-type group, as assessed using the Mann-Whitney test (p=0.0417 and p=0.0005 respectively). The VAF value showed a significant correlation with strong (3+) p53 expression (p<0.0001).
Figure 1.
Correlation between TP53 status, p53 expression, and myeloblast count in bone marrow biopsy specimens with dysplasia-related alterations (n=76); (a) Heat map summarizing the distribution of cases according to myeloblast count (AML, MDS-IB, and MDS-LB), TP53 status, total and strong (3+) p53 expression, and Comprehensive Cytogenetic Scoring System (CCSS). TP53 mutated cases showing a VAF value of less than 10%, coverage below 500, frameshift mutations, or having more than two mutations are highlighted as these mutated cases were frequently associated with a low-level p53 expression. (b) Correlation of strong (+) p53 expression and TP53 VAF value with bone marrow myeloblast count. Both the percentage of p53 3+ cells and TP53 mutation VAF value showed a significant correlation with the percentage of CD34+ myeloblasts (Spearman r=0.4880, p<0.0001 and Spearman r=0.4757, p<0.0001 respectively). (c) P53 expression and TP53 VAF value in different disease subgroups. A significant difference was detected between these subgroups both in total and strong (3+) p53 expression (p=0.0039 and p=0.0011 respectively as assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test). The median VAF values varied significantly between MDS-LB, MDS-IB, and AML subgroups (Kruskal-Wallis test, p=0.016). (d) Correlation between p53 expression and TP53 mutation status. The percentage of bone marrow cells with total or strong (3+) p53 expression was significantly higher in the TP53 mutant group compared to the TP53 wild-type group, as assessed using the Mann-Whitney test (p=0.0417 and p=0.0005 respectively). The VAF value showed a significant correlation with strong (3+) p53 expression (p<0.0001).
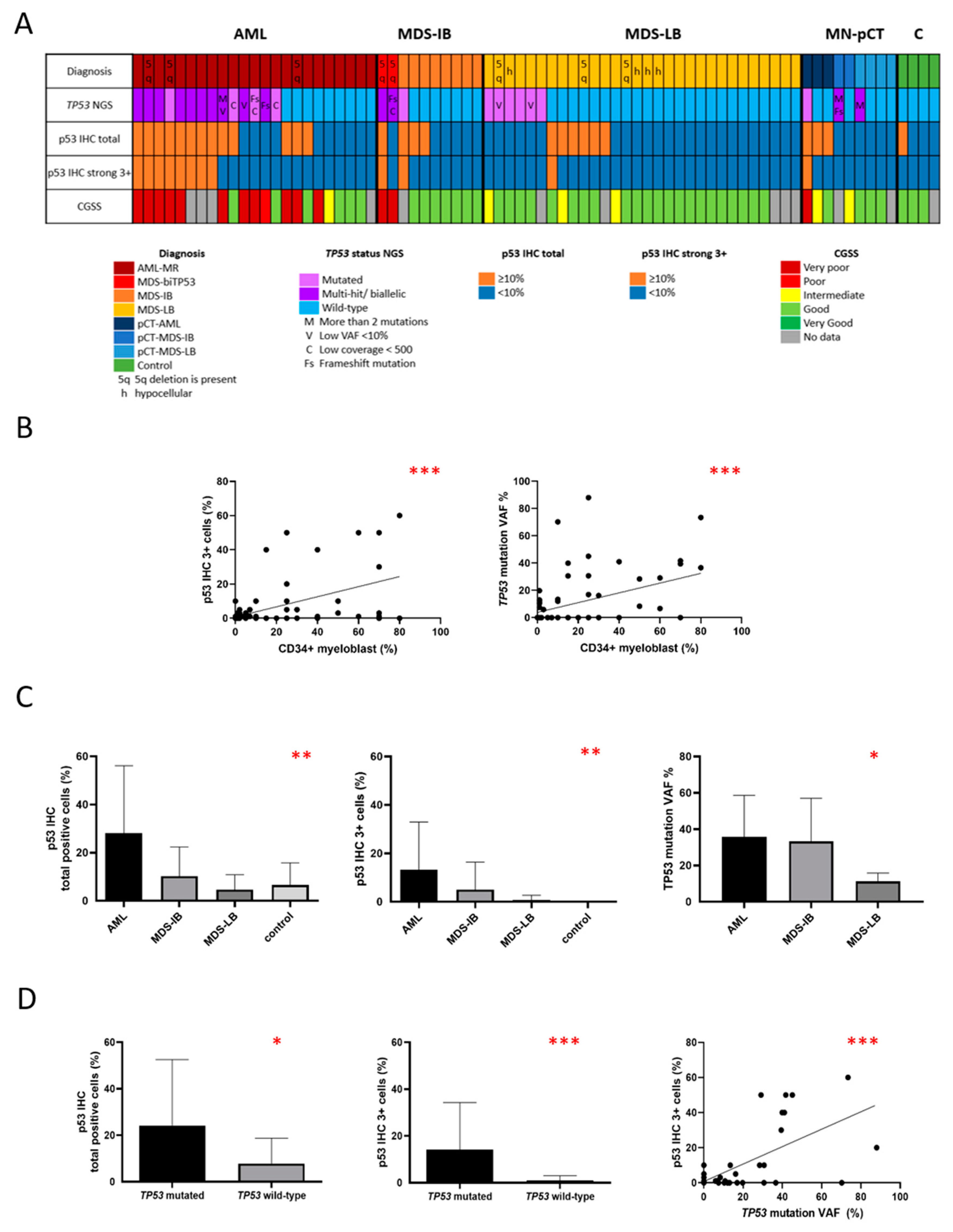
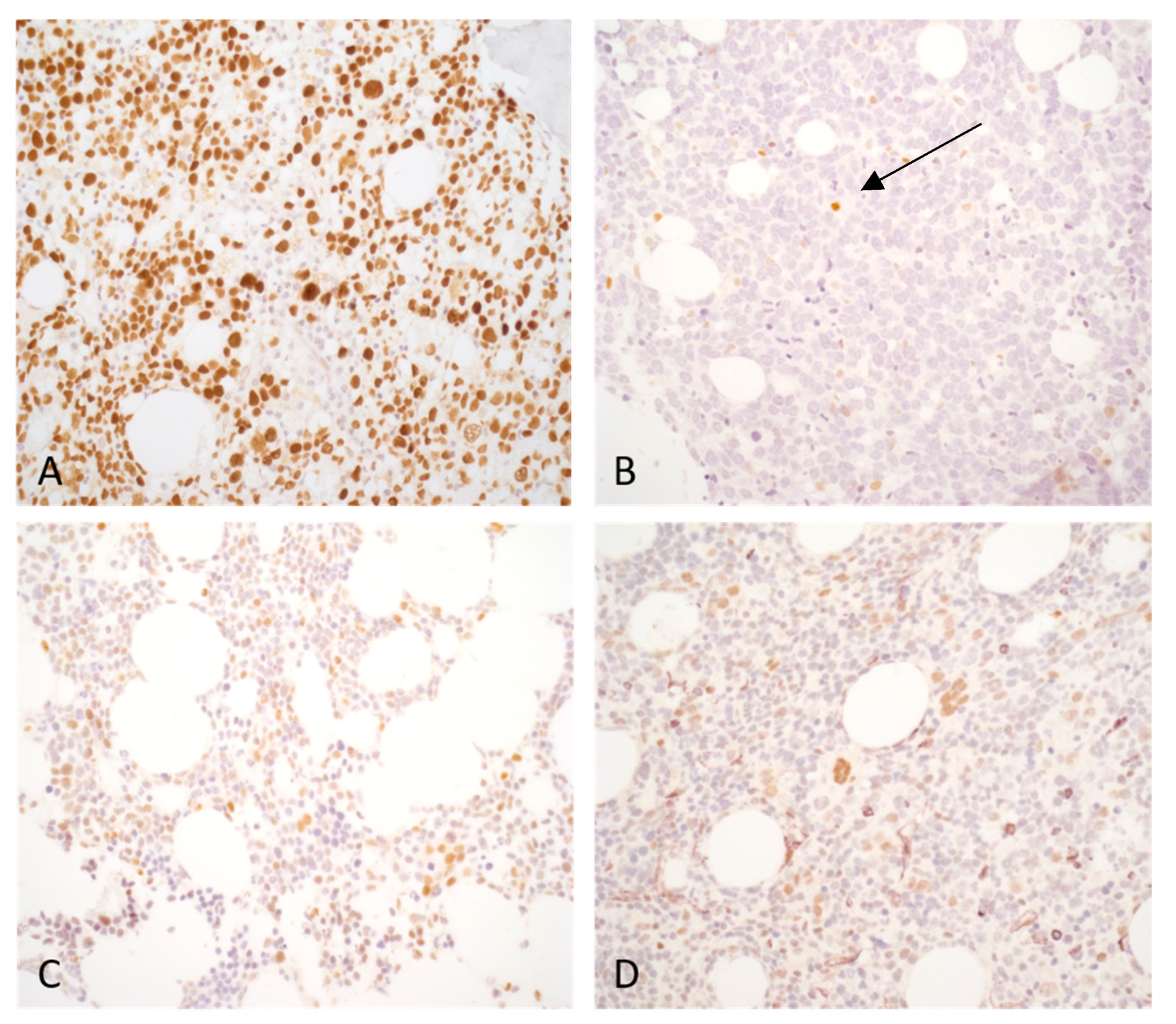
Figure 2.
Typical p53 expression pattern of bone marrow biopsy samples: (a) Acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplasia-related (AML-MR) case with two TP53 mutations. The VAF value was higher than 10% for both mutations. More than 10% of bone marrow cells display strong (3+) p53 expression. (b) AML-MR case harboring one TP53 mutation without the evidence of a biallelic state, VAF: 36.66%. The TP53 alteration in this case is a frameshift mutation causing protein truncation and instability. Both total and strong (3+) p53 expression were under 10%. A few isolated positive cells are detectable (arrow) and likely belong to the residual reactive hematopoiesis. (c) AML-MR, TP53 wild-type. Strong (3+) p53 expression is not present. Some scattered cells display weak to moderate p53 expression. (d) Reactive case with transient cytopenia, TP53 wild-type. Isolated bone marrow cells show p53 expression with variable intensity.
Figure 2.
Typical p53 expression pattern of bone marrow biopsy samples: (a) Acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplasia-related (AML-MR) case with two TP53 mutations. The VAF value was higher than 10% for both mutations. More than 10% of bone marrow cells display strong (3+) p53 expression. (b) AML-MR case harboring one TP53 mutation without the evidence of a biallelic state, VAF: 36.66%. The TP53 alteration in this case is a frameshift mutation causing protein truncation and instability. Both total and strong (3+) p53 expression were under 10%. A few isolated positive cells are detectable (arrow) and likely belong to the residual reactive hematopoiesis. (c) AML-MR, TP53 wild-type. Strong (3+) p53 expression is not present. Some scattered cells display weak to moderate p53 expression. (d) Reactive case with transient cytopenia, TP53 wild-type. Isolated bone marrow cells show p53 expression with variable intensity.
Figure 3.
Double immunohistochemical stains of two cases with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Double immunohistochemical staining underscores the complexity of interpreting p53 immunohistochemistry. The p53 expression varies in intensity and can manifest across various cell lineages. Reactive, non-clonal and clonal cells are admixed which adds further complexity to the evaluation. (a-b) An AML case harboring one TP53 mutation with a 41.73% VAF value, the myeloblast ratio is 70%, the total p53 labeling is 80%. A: The p53/CD34 double immunohistochemical stain reveals three distinct patterns – cells with p53+/CD34- (scattered throughout the sample), p53+/CD34+ (red circle) and p53-/CD34+ (black circle) cells pattern could be observed. One p53-positive (arrow) and one p53-negative (arrowhead) dysplastic megakaryocyte are also present (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD34 – purple, VIP). B: The p53/CD71 double immunohistochemical stain detects p53-/CD71+ (black circle) and p53+/CD71+ (red circle) erythroid cells. A p53+/CD71- population is also present, which probably corresponds to myeloblasts (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD71 – purple, VIP). (c-d) An AML case harboring one TP53 mutation with a 16.20% VAF value, the myeloblast ratio is 30%, the total p53 labeling is 40%. C: The p53/CD34 immunohistochemical stain highlights a lot of p53+/CD34- cells with variable p53 labeling intensity (arrows) (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD34 – purple, VIP). Considering the relatively low VAF value, it is possible that weak p53 labeling is associated with non-mutated cells exhibiting physiologic p53 expression. D.: The p53/CD71 highlights p53-/CD71+ (black circle) as well as p53+/CD71+ (red circle) erythroid cells (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD71 – purple, VIP).
Figure 3.
Double immunohistochemical stains of two cases with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Double immunohistochemical staining underscores the complexity of interpreting p53 immunohistochemistry. The p53 expression varies in intensity and can manifest across various cell lineages. Reactive, non-clonal and clonal cells are admixed which adds further complexity to the evaluation. (a-b) An AML case harboring one TP53 mutation with a 41.73% VAF value, the myeloblast ratio is 70%, the total p53 labeling is 80%. A: The p53/CD34 double immunohistochemical stain reveals three distinct patterns – cells with p53+/CD34- (scattered throughout the sample), p53+/CD34+ (red circle) and p53-/CD34+ (black circle) cells pattern could be observed. One p53-positive (arrow) and one p53-negative (arrowhead) dysplastic megakaryocyte are also present (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD34 – purple, VIP). B: The p53/CD71 double immunohistochemical stain detects p53-/CD71+ (black circle) and p53+/CD71+ (red circle) erythroid cells. A p53+/CD71- population is also present, which probably corresponds to myeloblasts (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD71 – purple, VIP). (c-d) An AML case harboring one TP53 mutation with a 16.20% VAF value, the myeloblast ratio is 30%, the total p53 labeling is 40%. C: The p53/CD34 immunohistochemical stain highlights a lot of p53+/CD34- cells with variable p53 labeling intensity (arrows) (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD34 – purple, VIP). Considering the relatively low VAF value, it is possible that weak p53 labeling is associated with non-mutated cells exhibiting physiologic p53 expression. D.: The p53/CD71 highlights p53-/CD71+ (black circle) as well as p53+/CD71+ (red circle) erythroid cells (original magnification: 400x; p53 –brown, DAB/ CD71 – purple, VIP).
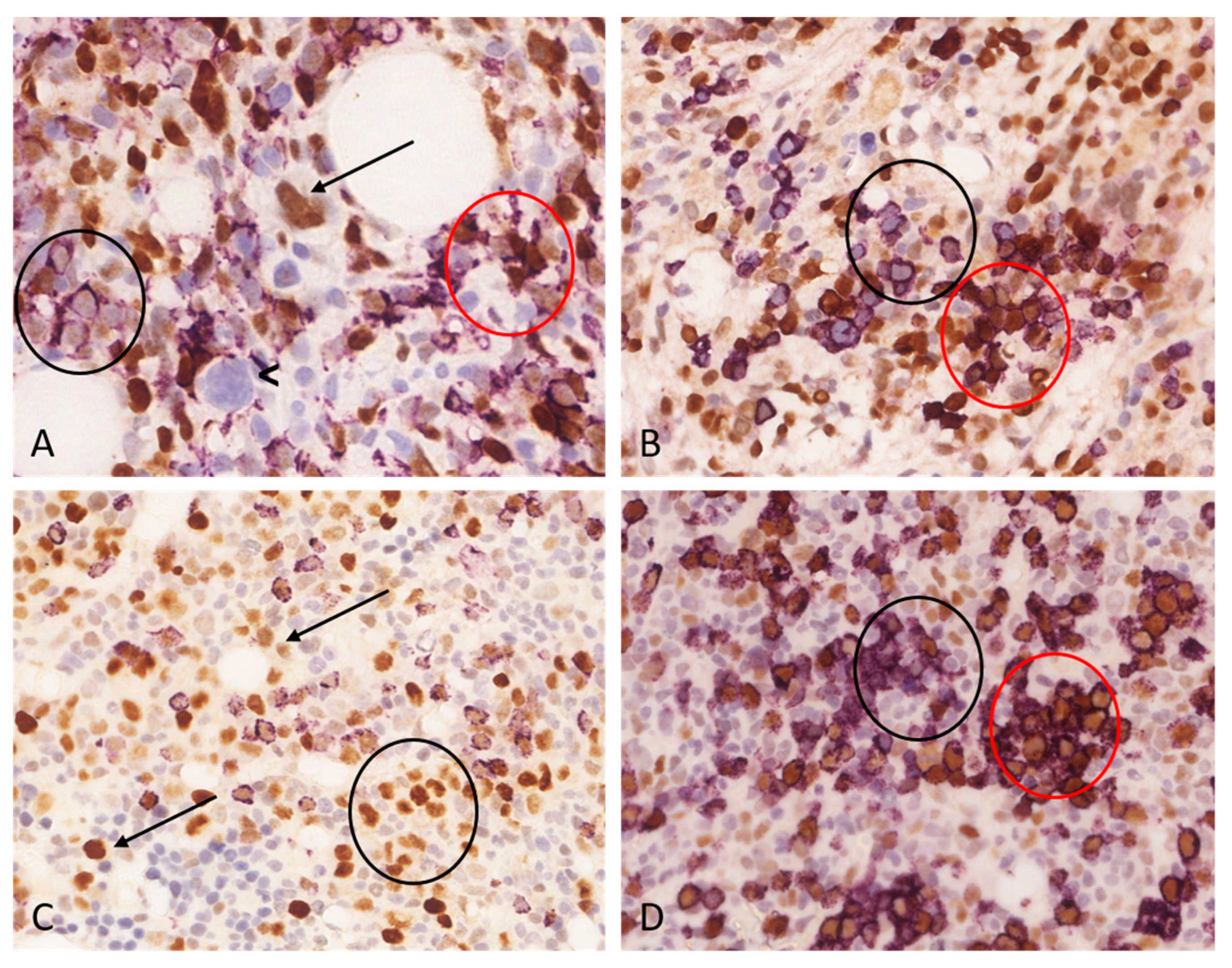
Table 1.
Distribution of cases (n=76) according to different parameters.
Table 1.
Distribution of cases (n=76) according to different parameters.
| WHO diagnosis according to 5th edition, 2022 |
|
| Acute myeloid leukaemia, myelodysplasia-related (AML-MR) |
23 |
| Myelodysplastic neoplasm with biallelic (or multi-hit) TP53 alterations |
2 |
| Myelodysplastic neoplasm with low blasts and 5q deletion |
3 |
| Myelodysplastic neoplasm with increased blasts (morphologically defined) |
8 |
| Myelodysplastic neoplasm with low blasts (morphologically defined) |
23 |
| Hypoplastic MDS (morphologically defined) |
4 |
| Myeloid neoplasms post cytotoxic therapy (MN-pCT) - AML |
3 |
| Myeloid neoplasms post cytotoxic therapy (MN-pCT) – MDS with increased blasts |
2 |
| Myeloid neoplasms post cytotoxic therapy (MN-pCT) – MDS with low blasts |
4 |
| Reactive, control |
4 |
| Sex of patients |
| Male |
34 |
| Female |
42 |
| TP53 mutational status by NGS |
|
TP53 wild-type |
49 |
|
TP53 mutated |
27 |
|
TP53 mutated with multiple mutations |
8 |
| p53 expression by immunohistochemistry |
|
| p53 total expression ≥10% |
25 |
| p53 strong (3+) expression ≥1% |
32 |
| p53 strong (3+) expression ≥5% |
17 |
| p53 strong (3+) expression ≥10% |
12 |
| Karyotype according to CCSS1 |
|
| Good |
38 |
| Intermediate |
6 |
| Poor |
2 |
| Very poor |
14 |
| No data |
13 |
Table 2.
Accuracy of strong (3+) and total p53 expression for the predicting TP53 mutations. The highest specificity and positive predictive value were present with ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression, while the highest sensitivity and negative predictive value were observed with a threshold of ≥1 strong (3+) p53 expression.
Table 2.
Accuracy of strong (3+) and total p53 expression for the predicting TP53 mutations. The highest specificity and positive predictive value were present with ≥10% strong (3+) p53 expression, while the highest sensitivity and negative predictive value were observed with a threshold of ≥1 strong (3+) p53 expression.
| |
Strong (3+) p53 expression ≥1% |
Strong (3+) p53 expression ≥5% |
Strong (3+) p53 expression ≥10% |
Total p53 expression ≥10% |
| Sensitivity |
0.6154 |
0.4615 |
0.4231 |
0.5000 |
| Specificity |
0.6800 |
0.9000 |
0.9800 |
0.7600 |
| Positive predictive value |
0.5000 |
0.7059 |
0.9167 |
0.5200 |
| Negative predictive value |
0.7727 |
0.7627 |
0.7656 |
0.7451 |
Table 3.
Characteristics of TP53 mutated cases with multiple mutations (n=8). Cases with more than two mutations were associated with a low level (<10%) strong (3+) p53 expression (Case 4, 6, and 7). One additional case with a low VAF value (<10%) also displayed a similarly low p53 expression (Case 3). In contrast, the other four cases showed ≥ 10% strong (3+) p53 expression.
Table 3.
Characteristics of TP53 mutated cases with multiple mutations (n=8). Cases with more than two mutations were associated with a low level (<10%) strong (3+) p53 expression (Case 4, 6, and 7). One additional case with a low VAF value (<10%) also displayed a similarly low p53 expression (Case 3). In contrast, the other four cases showed ≥ 10% strong (3+) p53 expression.
| Case |
WHO diagnosis |
TP53 AA change |
VAF (%) |
Number of mutations |
Total p53 expression |
Strong (3+) p53 expression |
Myeloblast count |
Cytogenetics |
| 1 |
AML-MR |
p.E271K |
27,8 |
2 |
80% |
50% |
60% |
CK |
| p.N239D |
29,14 |
| 2 |
AML-MR |
p.V272M |
30,7 |
2 |
20% |
10% |
25% |
ND |
| p.Y220X |
8,38 |
| 3 |
AML-MR |
p.E271K |
6,08 |
2 |
3% |
1% |
60% |
CK |
| p.N239D |
6,67 |
| 4 |
AML-MR |
p.E271K |
8,28 |
3 |
10% |
3% |
50% |
modal chromosomenumber:78-83 |
| p.M246K |
8,35 |
| p.C135X |
5,65 |
| 5 |
AML-MR |
p.V216M |
39,44 |
2 |
70% |
30% |
70% |
CK |
| p.G245S |
38,22 |
| 6 |
MN-pCT |
p.S215N |
30,65 |
6 |
3% |
0% |
15% |
ND |
| p.K373Rfs |
11,59 |
| p.T256I |
6,82 |
| p.P98L |
6,25 |
| p.Q375E |
5,6 |
| p.T253I |
5,45 |
| 7 |
MN-pCT |
p.S362N |
5,19 |
4 |
1% |
1% |
1% |
46, xy |
| p.G334R |
5,04 |
| p.V272M |
6,27 |
| p.N239D |
10,81 |
| 8 |
MDS-biTP53 |
p.R248Q |
39,93 |
2 |
40% |
40% |
15% |
CK |
| p.P152Q |
38,21 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).