Submitted:
31 August 2023
Posted:
04 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction: Neurotrauma Preceding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
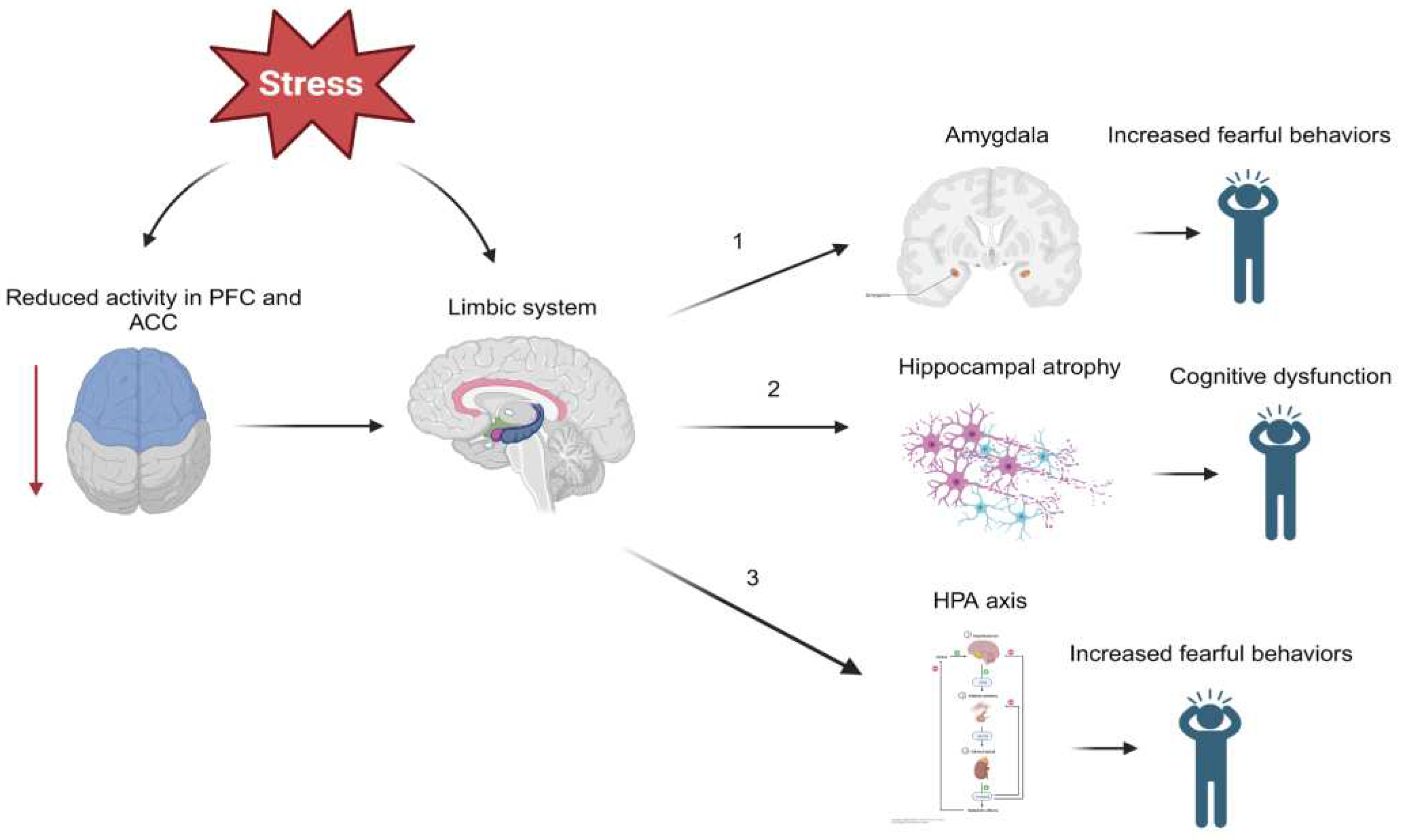
2. The Pathophysiology of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
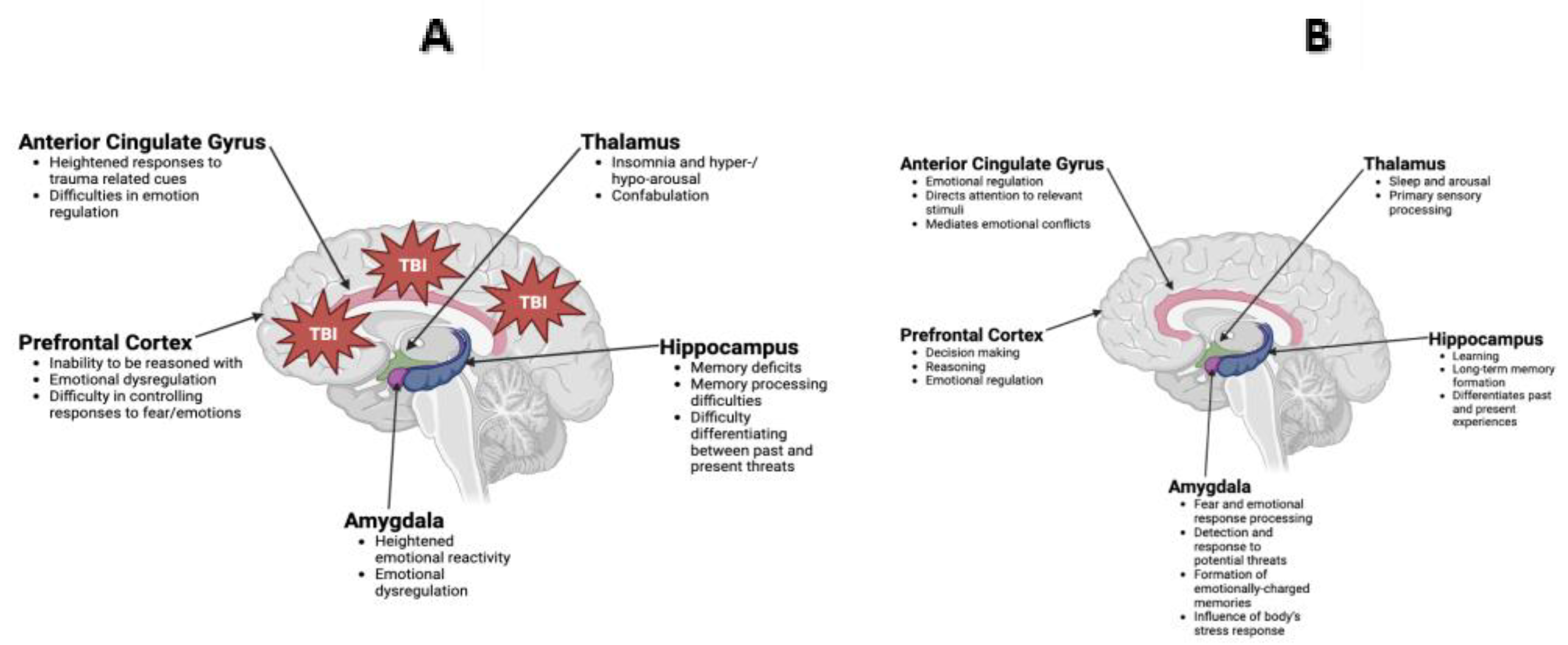
3. TBI
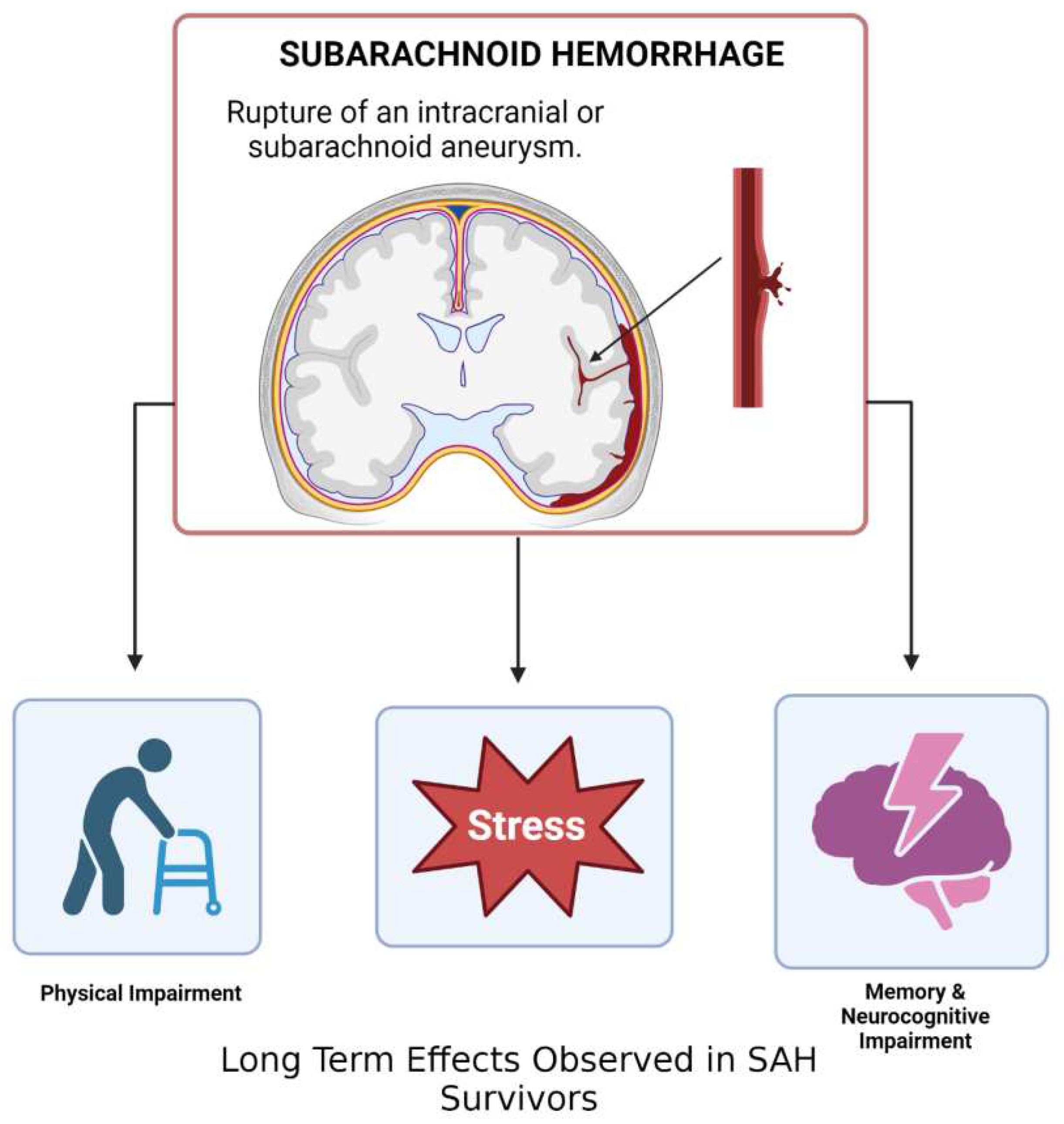
4. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
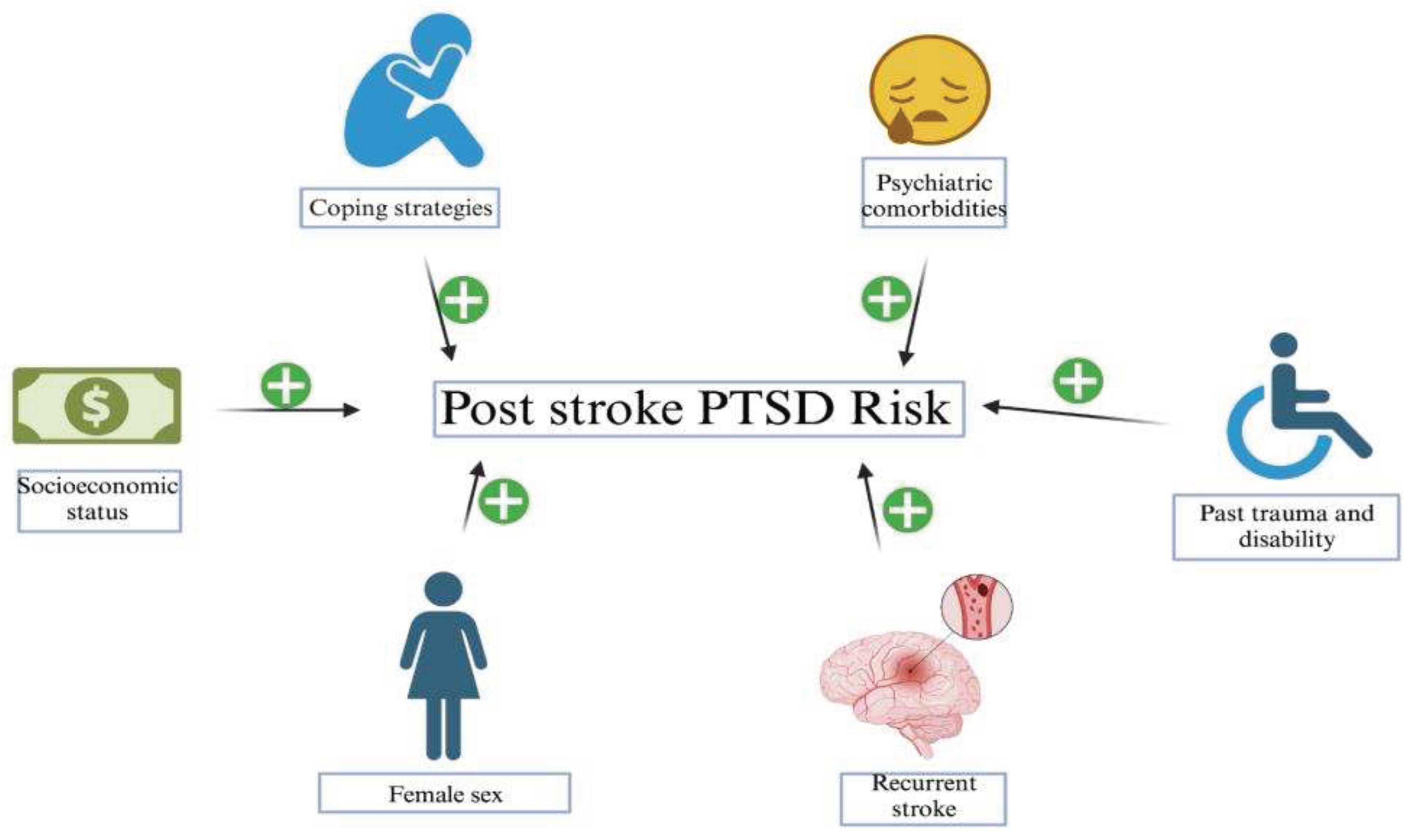
5. Stroke
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Arlington, VA, USA: 2013.
- Van Praag, D.L.; Cnossen, M.C.; Polinder, S.; Wilson, L.; Maas, A.I. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder after Civilian Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Rates. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 3220–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, G.A.; Dorr, N.P.; De Gasperi, R.; Sosa, M.A.G.; Shaughness, M.C.; Maudlin-Jeronimo, E.; Hall, A.A.; McCarron, R.M.; Ahlers, S.T. Blast Exposure Induces Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder-Related Traits in a Rat Model of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2564–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.B.; Leite-Morris, K.A.; Wang, L.; Rumbika, K.K.; Heinrichs, S.C.; Zeng, X.; Wu, L.; Arena, D.T.; Teng, Y.D.; Wang, W.; et al. Pathophysiological Bases of Comorbidity: Traumatic Brain Injury and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhou, E.W.; Sandhu, A.F.; Yuan, X.; Williams, G.E.; Cheng, J.; Sinha, B.; Akbar, M.; Bhattacharya, P.; et al. Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neil, M.E.; Klyce, D.W.P.; Pogoda, T.K.; Cifu, D.X.; Eggleston, B.E.M.; Cameron, D.C.M.; Wilde, E.A.; Walker, W.C.; Carlson, K.F. Associations Among PTSD and Postconcussive Symptoms in the Long-Term Impact of Military-Relevant Brain Injury Consortium–Chronic Effects of Neurotrauma Consortium Prospective, Longitudinal Study Cohort. J. Head Trauma Rehabilitation 2021, 36, E363–E372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merriman, C.; Norman, P.; Barton, J. Psychological correlates of PTSD symptoms following stroke. Psychol. Heal. Med. 2007, 12, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruggimann, L.; Annoni, J.M.; Staub, F.; von Steinbuchel, N.; Van der Linden, M.; Bogousslavsky, J. Chronic posttraumatic stress symptoms after nonsevere stroke. Neurology 2006, 66, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembi S, Tarrier N, O'Neill P, Burns A, Faragher B. Does post-traumatic stress disorder occur after stroke: a preliminary study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1998;13:315–322. [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.J.; Baisch, S.; Covey, J.; Mukerji, N.; Nath, F.; Schenk, T. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients' Fears of Recurrence Are Related to the Presence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 1994.
- Bryant, R. Post-traumatic stress disorder vs traumatic brain injury. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.R.; Noble, L.J.; McIntyre, C.K. Using the Single Prolonged Stress Model to Examine the Pathophysiology of PTSD. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, R.C.; Raskind, M.A. Noradrenergic dysregulation in the pathophysiology of PTSD. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 284, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieweg, W.V.R.; Julius, D.A.; Fernandez, A.; Beatty-Brooks, M.; Hettema, J.M.; Pandurangi, A.K. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Clinical Features, Pathophysiology, and Treatment. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.P.; Etkin, A.; Furman, D.J.; Lemus, M.G.; Johnson, R.F.; Gotlib, I.H. Functional Neuroimaging of Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-Analysis and New Integration of Baseline Activation and Neural Response Data. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.L.; Shin, L.M.; Orr, S.P.; Carson, M.A.; Rauch, S.L.; Macklin, M.L.; Lasko, N.B.; Metzger, L.J.; Dougherty, D.D.; Alpert, N.M.; et al. Decreased regional cerebral blood flow in medial prefrontal cortex during trauma-unrelated stressful imagery in Vietnam veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Yamasue, H.; Gilbertson, M.W.; Shenton, M.E.; Rauch, S.L.; Pitman, R.K. Evidence for Acquired Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Gray Matter Loss from a Twin Study of Combat-Related Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, N.; Quinn, S.; Bremner, J.D. Smaller volume of anterior cingulate cortex in abuse-related posttraumatic stress disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2006, 90, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, L.M.; Rauch, S.L.; Pitman, R.K. Amygdala, Medial Prefrontal Cortex, and Hippocampal Function in PTSD. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2006, 1071, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jeong, D.-U.; Sim, M.E.; Bae, S.C.; Chung, A.; Kim, M.J.; Chang, K.H.; Ryu, J.; Renshaw, P.F.; Lyoo, I.K. Asymmetrically Altered Integrity of Cingulum Bundle in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2006, 54, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, T.R.; Mason, J.W.; Giller, E.L.; Ostroff, R.B.; Harkness, L. Sustained urinary norepinephrine and epinephrine elevation in post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1987, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, I.; Abelson, J.L.; Ph. D; Bs, S.B.F.; Raz, J.; A Young, E. Neuroendocrine and Psychophysiologic Responses in PTSD: A Symptom Provocation Study. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 21, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, I.; López, J.F.; Flagel, S.B.; Vázquez, D.M.; Young, E.A. Differential regulation of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors mRNA and fast feedback: Relevance to post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Neuroendocrinol. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.A.; Breslau, N. Cortisol and Catecholamines in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geracioti, T.D.; Baker, D.G.; Ekhator, N.N.; West, S.A.; Hill, K.K.; Bruce, A.B.; Schmidt, D.; Rounds-Kugler, B.; Yehuda, R.; Keck, P.E.; et al. CSF Norepinephrine Concentrations in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, R.H.; Gallezot, J.-D.; Ding, Y.-S.; Henry, S.; Potenza, M.N.; Southwick, S.M.; Krystal, J.H.; Carson, R.E.; Neumeister, A. Association of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder With Reduced In Vivo Norepinephrine Transporter Availability in the Locus Coeruleus. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigs, M.; Grafman, J. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: The Role of Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Amygdala. Neurosci. 2009, 15, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassens, E.R.; Giltay, E.J.; Cuijpers, P.; van Veen, T.; Zitman, F.G. Adulthood trauma and HPA-axis functioning in healthy subjects and PTSD patients: A meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterwald, C.; Alberini, C.M. Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: From adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2013, 112, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, H.C.; Figner, B.; Tyborowska, A.; van Peer, J.M.; Cillessen, A.H.; Roelofs, K. Defensive freezing links Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal-axis activity and internalizing symptoms in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 82, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Stegeren, A.H.; Wolf, O.T.; Everaerd, W.; Rombouts, S.A. Interaction of endogenous cortisol and noradrenaline in the human amygdala. 2007, 167, 263–268. [CrossRef]
- Zuj, D.V.; Palmer, M.A.; Malhi, G.S.; Bryant, R.A.; Felmingham, K.L. Endogenous cortisol reactivity moderates the relationship between fear inhibition to safety signals and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 78, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M.; Krey, L.C.; McEWEN, B.S. The Neuroendocrinology of Stress and Aging: The Glucocorticoid Cascade Hypothesis*. Endocr. Rev. 1986, 7, 284–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Why Stress Is Bad for Your Brain. Science 1996, 273, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.D.; Tumpap, A.M. Posttraumatic stress disorder symptom severity is associated with left hippocampal volume reduction: a meta-analytic study. CNS Spectrums 2016, 22, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Doherty, D.C.; Chitty, K.M.; Saddiqui, S.; Bennett, M.R.; Lagopoulos, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging measurement of structural volumes in posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 232, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laryea, G.; Arnett, M.G.; Muglia, L.J. Behavioral Studies and Genetic Alterations in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) Neurocircuitry: Insights into Human Psychiatric Disorders. Behav. Sci. 2012, 2, 135–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolber, B.J.; Roberts, M.S.; Howell, M.P.; Wozniak, D.F.; Sands, M.S.; Muglia, L.J. Central amygdala glucocorticoid receptor action promotes fear-associated CRH activation and conditioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 12004–12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haufler, D.; Nagy, F.Z.; Pare, D. Neuronal correlates of fear conditioning in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacella, M.L.; Hruska, B.; Steudte-Schmiedgen, S.; George, R.L.; Delahanty, D.L. The utility of hair cortisol concentrations in the prediction of PTSD symptoms following traumatic physical injury. Soc. Sci. Med. 2017, 175, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatzer-Levy, I.R.; Steenkamp, M.M.; Brown, A.D.; Qian, M.; Inslicht, S.; Henn-Haase, C.; Otte, C.; Yehuda, R.; Neylan, T.C.; Marmar, C.R. Cortisol response to an experimental stress paradigm prospectively predicts long-term distress and resilience trajectories in response to active police service. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 56, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Hellman, N.; Abelson, J.L.; Rao, U. Cortisol, heart rate, and blood pressure as early markers of PTSD risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 49, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Büki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). (2023, ). National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih. 7 February.
- Hoge, C.W.; McGurk, D.; Thomas, J.L.; Cox, A.L.; Engel, C.C.; Castro, C.A. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in U.S. Soldiers Returning from Iraq. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, A.N.; Yi, G.; Patch, M.; Alter, Y.; Campbell, J.C.; Gundersen, K.K.; Tang, J.T.; Tsuyuki, K.; Stockman, J.K. The Effect of Intimate Partner Violence and Probable Traumatic Brain Injury on Mental Health Outcomes for Black Women. J. Aggress. Maltreatment Trauma 2019, 28, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachar, R.J. , Park L.S., Dennis M. Mental health implications of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in children and youth. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2015;24(2):100–108.
- Bremner, J.D. Traumatic stress: effects on the brain. Dialog- Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, C.M. Decoding Hippocampal Signaling Deficits After Traumatic Brain Injury. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.A.; Koch, P.F. Disruption of Network Synchrony and Cognitive Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Shimada, R.; Okada, Y.; Kibayashi, K. Traumatic brain injury decreases serotonin transporter expression in the rat cerebrum. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson-Campbell, M.; Shaw, L.; O'Brien, J.; Holmes, J.; Magalhaes, L. A scoping review on occupational and self identity after a brain injury. Work 2013, 44, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasterling, J.J.; Jacob, S.N.; Rasmusson, A. Traumatic Brain Injury and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Conceptual, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic Considerations in the Context of Co-Occurrence. J. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 30, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, S. , & Rayi, A. (2022). Anatomy, Head and Neck, Subarachnoid Space. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Lawton, M.T.; Vates, G.E. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, I.; Kayahara, T.; Kawashima, A.; Okada, A.; Miyamoto, S.; Kataoka, H.; Kurita, H.; Ishii, A.; Aoki, T. Hypoxic microenvironment as a crucial factor triggering events leading to rupture of intracranial aneurysm. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deem, S.; Diringer, M.; Livesay, S.; Treggiari, M.M. Hemodynamic Management in the Prevention and Treatment of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocritical Care 2023, 39, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; van Gelder, J.M. The Probability of Sudden Death from Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Vu, L.D.; Mai, T.D.; Dao, C.X.; Ngo, H.M.; Hoang, H.B.; Do, S.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Pham, D.T.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Predictive validity of the prognosis on admission aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage scale for the outcome of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, J.W.; Rinkel, G.J.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Case-Fatality Rates and Functional Outcome After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 1997, 28, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.S.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Carhuapoma, J.R.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Dion, J.E.; Higashida, R.T.; Hoh, B.L.; Kirkness, C.J.; Naidech, A.M.; Ogilvy, C.S.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 2012, 43, 1711–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.I. Diagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2015, 21, 1263–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, C.Q.; Ngo, H.M.; Hoang, H.B.; Pham, D.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Tran, T.A.; Nguyen, D.N.; Do, S.N.; Nguyen, M.H.; Vu, H.D.; et al. Clinical characteristics and factors relating to poor outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Vietnam: A multicenter prospective cohort study. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0256150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, A.S.; Fernandez, L.; Schmidt, J.M.; Mayer, S.A.; Claassen, J.; Lee, K.; Connolly, E.S.; Badjatia, N. Effect of rebleeding on the course and incidence of vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 2011, 78, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengart, A.J.; Schultheiss, K.E.; Tolentino, J.; Macdonald, R.L.; A, A.; J, G.; M, B.; F, R.; R, B.; M, H.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Outcome in Patients With Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 2007, 38, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baisch, S.B.; Schenk, T.; Noble, A.J. What is the cause of post-traumatic stress disorder following subarachnoid haemorrhage? Post-ictal events are key. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 153, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütter, B.-O.; Kreitschmann-Andermahr, I. Subarachnoid hemorrhage as a psychological trauma. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, A.J.; Baisch, S.; Schenk, T.; Mendelow, A.D.; Allen, L.; Kane, P. POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER EXPLAINS REDUCED QUALITY OF LIFE IN SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE PATIENTS IN BOTH THE SHORT AND LONG TERM. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D. An Enduring Somatic Threat Model of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Due to Acute Life-Threatening Medical Events. Soc. Pers. Psychol. Compass 2014, 8, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslau, N.; Schultz, L. Neuroticism and post-traumatic stress disorder: a prospective investigation. Psychol. Med. 2012, 43, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, C.R.; Andrews, B.; Valentine, J.D. Meta-analysis of risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder in trauma-exposed adults. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2000, 68, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Sonnega, A.; Bromet, E.; Hughes, M.; Nelson, C.B. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1995, 52, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parslow, R.A.; Jorm, A.F. Pretrauma and Posttrauma Neurocognitive Functioning and PTSD Symptoms in a Community Sample of Young Adults. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, K.; Pietrzak, R.H.; Mackenzie, C.S.; Chou, K.L.; Sareen, J. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Across the Adult Lifespan: Findings From a Nationally Representative Survey. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajer, I.M.H.; Smits, A.R.; Rinkel, G.J.; van Zandvoort, M.J.; Meij, L.W.-D.; Visser-Meily, J.M. Exploratory study of the course of posttraumatic stress disorder after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2018, 53, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, R.; Tarrier, N.; Berry, E.; Kincey, J. Post-traumatic stress disorder and illness perceptions over time following myocardial infarction and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br. J. Heal. Psychol. 2006, 11, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, M.; Zetterling, M.; Ronne-Engström, E.; Carlsson, M.; Ekselius, L. Depression and post-traumatic stress disorder after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage in relation to lifetime psychiatric morbidity. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 25, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, N.; Brooks, S.; Dunn, R. Latest developments in post-traumatic stress disorder: diagnosis and treatment: Table 1. Br. Med Bull. 2015, 114, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; A Mensah, G.; Connor, M.; A Bennett, D.; E Moran, A.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013, 383, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, D.; Richardson, S.; Fausett, J.K.; Falzon, L.; Howard, V.J.; Kronish, I.M. Prevalence of PTSD in Survivors of Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Meta-Analytic Review. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e66435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronish, I.M.; Edmondson, D.; Goldfinger, J.Z.; Fei, K.; Horowitz, C.R.; A, G.; J, S.; V, G.; B, C.; E, C.; et al. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Adherence to Medications in Survivors of Strokes and Transient Ischemic Attacks. Stroke 2012, 43, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, J.M.; Caeiro, L.; Figueira, M.L. Neuropsychiatric sequelae of stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.A.; Goldmann, E.; Zamzam, A.; Luciano, J.M.; Messé, S.R.; Cucchiara, B.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Mullen, M.T. Association Between Anxiety, Depression, and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder and Outcomes After Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, S.S.; Williams, L.S.; Swindle, R.W. Depression and Other Mental Health Diagnoses After Stroke Increase Inpatient and Outpatient Medical Utilization Three Years Poststroke. Med Care 2005, 43, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zulkifly, M. F. , Ghazali, S. E., Che Din, N., Desa, A., & Raymond, A. A. (2015). The Ability of Recovery Locus of Control Scale (RLOC) and Post-traumatic Stress Symptoms (PTSS) to Predict the Physical Functioning of Stroke Patients. Malaysian Journal of Medical Science, 22(5), 31–41.
- Marques, P.T.; Beltrami, L.P.B.; Rosa, C.T.; Massuda, R.; Barbosa, F.J.L.; Zétola, V.F.; Lange, M.C. Post-traumatic stress disorder in non-disabled ischemic stroke patients. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2020, 67, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Assayag, E.; Tene, O.; Korczyn, A.D.; Solomon, Z.; Bornstein, N.M.; Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S.; Seyman, E.; Niry, D.; Molad, J.; Hallevi, H. Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms After Stroke: The Effects of Anatomy and Coping Style. Stroke 2022, 53, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfinger, J.Z.; Edmondson, D.; Kronish, I.M.; Fei, K.; Balakrishnan, R.; Tuhrim, S.; Horowitz, C.R. Correlates of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in Stroke Survivors. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favrole, P.; Jehel, L.; Levy, P.; Descombes, S.; Muresan, I.-P.; Manifacier, M.-J.; Alamowitch, S. Frequency and predictors of post-traumatic stress disorder after stroke: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 327, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letamendia, C.; LeBlanc, N.J.; Pariente, J.; Simon, N.M.; Thomas, C.L.; Chabrol, H.; Chollet, F.; Raposo, N.; Schmitt, L.; Birmes, P.; et al. Peritraumatic distress predicts acute posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms after a first stroke. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2012, 34, e11–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzi, S.A.; Wood, A.G.; Chen, J.; Vaddadi, K.; Phan, T.G. Imaging predictors of poststroke depression: methodological factors in voxel-based analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutovic, S.; Kadojic, D.; Dikanovic, M.; Solic, K.; Malojcic, B. Prevalence and correlates of post-traumatic stress disorder after ischaemic stroke. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2019, 121, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, R.K.; Rasmusson, A.M.; Koenen, K.C.; Shin, L.M.; Orr, S.P.; Gilbertson, M.W.; Milad, M.R.; Liberzon, I. Biological studies of post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garton, A.L.; Sisti, J.A.; Gupta, V.P.; Christophe, B.R.; Connolly, E.S.; M, L.; A, S.; A, C.; S, S.; J, B.; et al. Poststroke Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Stroke 2017, 48, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, J.; Yahalom, H.; Kozlovsky, N.; Cwikel-Hamzany, S.; Matar, M.A.; Kaplan, Z.; Yehuda, R.; Cohen, H. High dose hydrocortisone immediately after trauma may alter the trajectory of PTSD: Interplay between clinical and animal studies. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiphuth, I.C.; Utz, K.S.; Noble, A.J.; Köhrmann, M.; Schenk, T.; A, G.; J, S.; V, G.; B, C.; E, C.; et al. Increased Prevalence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Patients After Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2014, 45, 3360–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Du, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, G.; et al. Supportive psychological therapy can effectively treat post-stroke post-traumatic stress disorder at the early stage. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1007571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, C.M. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for post-stroke post-traumatic stress disorder: Case report using the three-phase approach. Brain Inj. 2022, 36, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang W., K. , Wang L., Tsoi K. K. F., Rutovic S., Kim J. S. (2022). Post-traumatic stress disorder after stroke: a systematic review. Neurol. India 70, 1887–1895. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




