Introduction
Viral illnesses continue to place a significant economic and public health cost on Healthcare Systems. This burden is caused by the viruses’ capacity to traverse species boundaries and produce unforeseen epidemics of viral illnesses in humans.1,2 The “one drug, one virus” paradigm relies on targeting viral-specific processes inside the cell to inhibit viral replication. The “one drug, multiple viruses” approach, which was introduced with the discovery of broad-spectrum antiviral agents (BSAAs), tiny compounds that block a variety of human viruses, provides a counterargument to this.3,4
The upper or lower respiratory tract is commonly challenged by respiratory virus infections such as the common cold caused by rhinovirus, coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), parainfluenza virus, bronchiolitis caused by RSV, pneumonia caused by coronaviruses or RSV, most influenza viruses, COVID-19, and influenza (flu), etc. Treatment of respiratory infection through conventional methods like oral or parenteral is challenging, as the microbes reside deep in the airways, where the conventionally administered drugs reach only in a small proportions. It is vital to find and develop innovative antivirals that can be used alone or in conjunction with existing medications to treat these serious respiratory virus infections.5,6
Virus specific drug development has been the preferred method of simplifying the drug discovery process when compared to the more complex design of broad spectrum antivirals, which frequently require targeting critical proteins belonging to different viruses or critical cellular processes used by different viruses.
Virus-specific antiviral research continues to be a viable and necessary technique for combating viral illnesses.
Taking an example of recent pandemic, the ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2′ (SARS-CoV-2) virus has caused widespread infections, with the most current form accounting for nearly 766 million illnesses and 6.94 million fatalities worldwide.7 SARS-CoV-2 has a distinct nucleic acid structure, with its RNA coding for structural proteins that trap lectins that recognise host cell sugar chains and avoid detection by the host’s immune system. Viruses elude the host’s immunological defence systems by attaching sugar chains to their spike proteins, and in other situations, they obtain easy entrance into host cells by being caught by lectins that recognise host cell sugar chains. Galectin-3 (Gal-3) is the one of these lectins which binds to β-galactosides. Human galectins-3 is highly expressed in activated T lymphocytes and epithelial and endothelial cells and fibroblasts. ProLectin–I and ProLectin-M belongs to the class of galectin antagonist thought to have the ability to neutralize viruses.8,9
Galectins have been linked to numerous distinct biological activities. Galectins are synthesised in the cytoplasm and excreted into the extracellular domain. Galectins are involved in both humoral and cellular adaptive immunity via endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine pathways. In SARS CoV-2 NMR studies, ProLectin-M attaches to the spike protein’s ‘galectin fold,’ effectively neutralizing the virus and preventing replication competent viruses from infecting neighbouring cells.8 Galectin antagonists may be used as a therapeutic tool and eventually serve as a substitute for current anti-viral medicines. Blocking viral entry utilizing a complex polysaccharide component of pectin [(1-6)- D-mannopyranose referred to as ProLectin-M and Rhamnogalacturonan-II (RG-II)] inhibits cellular entry and helps reduce the transmissibility of the host.9,10 The effect of limiting viral entry into cells and its downstream effect on viral replication was demonstrated in a clinical trial on mild to moderate COVID-19.10
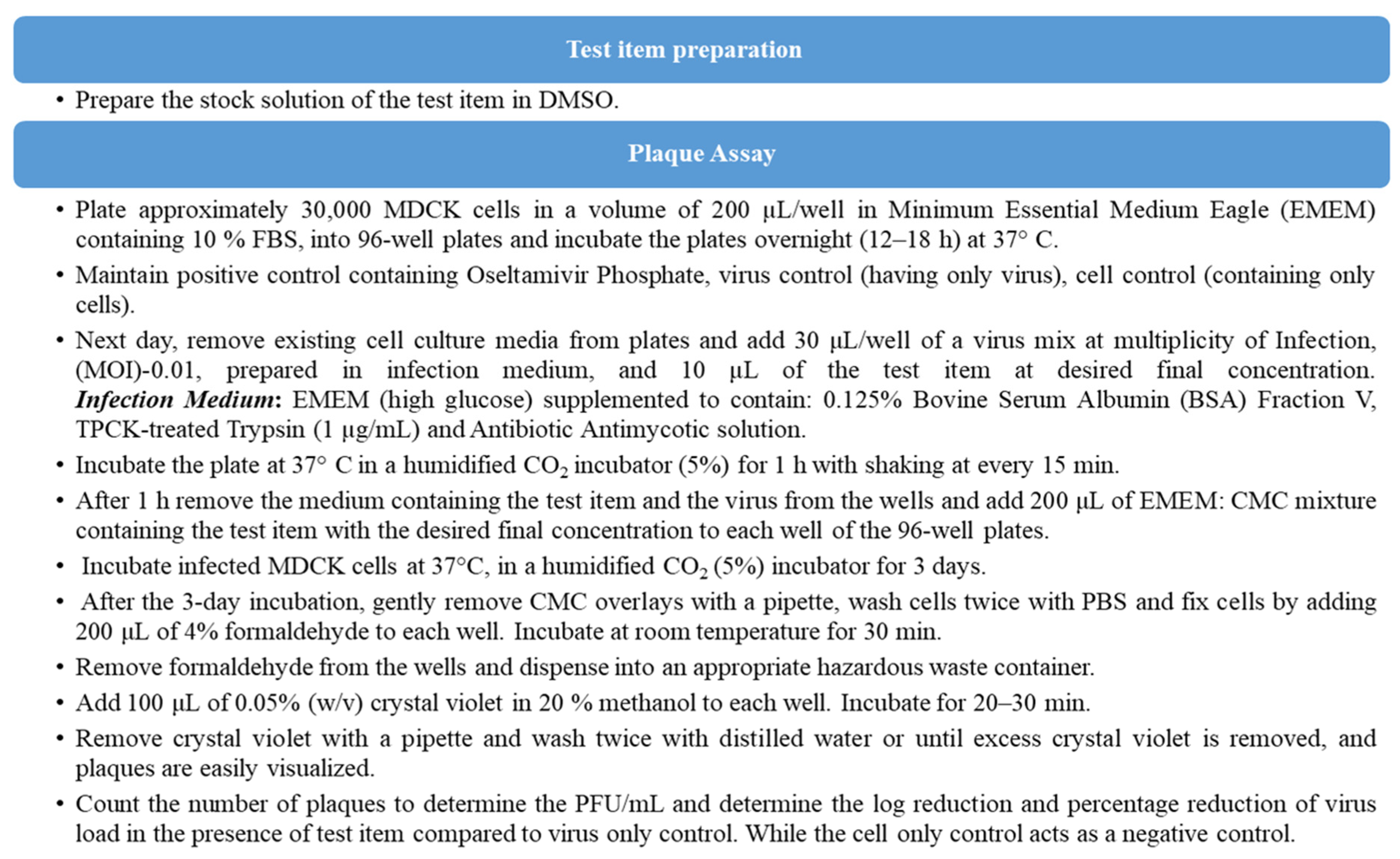
In virology, the precise isolation and measurement of live viral samples has always been an ongoing research objective. While technological and technique advancements continue to refine and alter the landscape, plaque assays remain the gold standard for determining viral concentrations for infectious lytic virons. To screen anti-viral activity of both ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I, three ‘in vitro’ studies have been conducted against (SARS-CoV-2) virus, Influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2. The plaque assay was used for screening and characterization of antiviral inhibitors against Influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2.
Materials and Methods
Evaluating anti-viral potency of ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M against COVID-19 virus strain:
Test drugs (coded as ALK001 [ProLectin-M] and ALK002 [ProLectin-I]) were evaluated for their anti-viral potency using SARS-CoV2 virus strain, at ‘The Centre for Cellular & Molecular Biology (CCMB)’, Hyderabad, India. Following parameters were evaluated for both the test drugs: (i) half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) (ii) cytotoxic concentrations (CC50).
Viral RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR assays were performed to determine IC50 whereas, CC
50 was evaluated by using MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay.
Table 1 describes the procedure for determining the IC50 and CC50 values; and
Table 2 denotes the concentration of test drug used in the study to determine the IC50 and CC50 value.
Evaluating anti-viral potency of ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M against H1N1 and hRSV strain A2:
Assay Procedure for
‘in vitro’ studies: The plaque assays were carried out to determine the antiviral activity of the test products (ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M) against ‘Influenza-A (H1N1)-A/PR/8/34 (TC adapted)’ and ‘Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2′ in a cell based in vitro setting. As, this is a cell-based assay it may not be reliable when the samples themselves are cytotoxic or when the virus is poorly cytopathic in each cell type. Thus, a highly permissive cell type (e.g., MDCK, Hep-2) is chosen for the assays for which Influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 causes substantive cell death.
Table 3 includes the plaque assay study summary and test medication concentrations utilised in the ‘in vitro’ study.
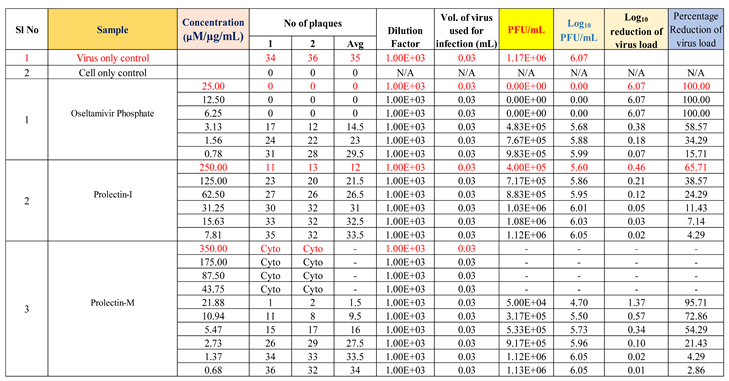
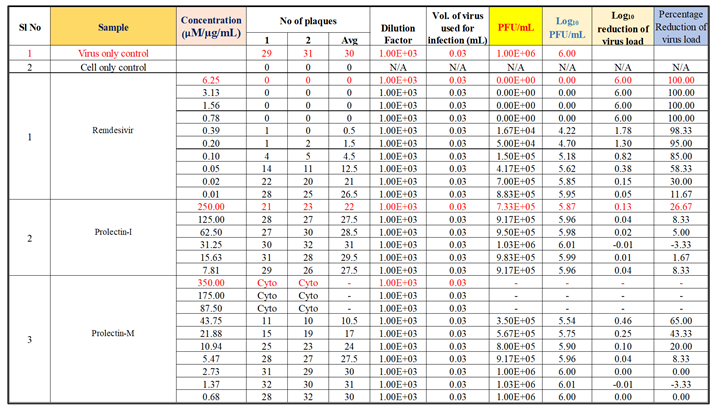
To determine the antiviral activity of the test items against ‘Influenza-A (H1N1)’ strain, “Oseltamivir Phosphate” was used as a reference standard, whereas “Remdesivir” was used as a reference standard to determine the antiviral activity of the test products against ‘human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2′.
The step-wise assay procedure performed in two
‘in vitro’ studies to determine antiviral activity of both test products ProLectin-I and ProLectin- M against Influenza-A (H1N1)-A/PR/8/34 (TC adapted) and Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 respectively, is mentioned in
Figure 1.
Objective
The objective of all 3 studies were to determine the antiviral potency/activity of the test products (ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M) against SARS-CoV-2, Influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 in a cell based in vitro setting.
Result
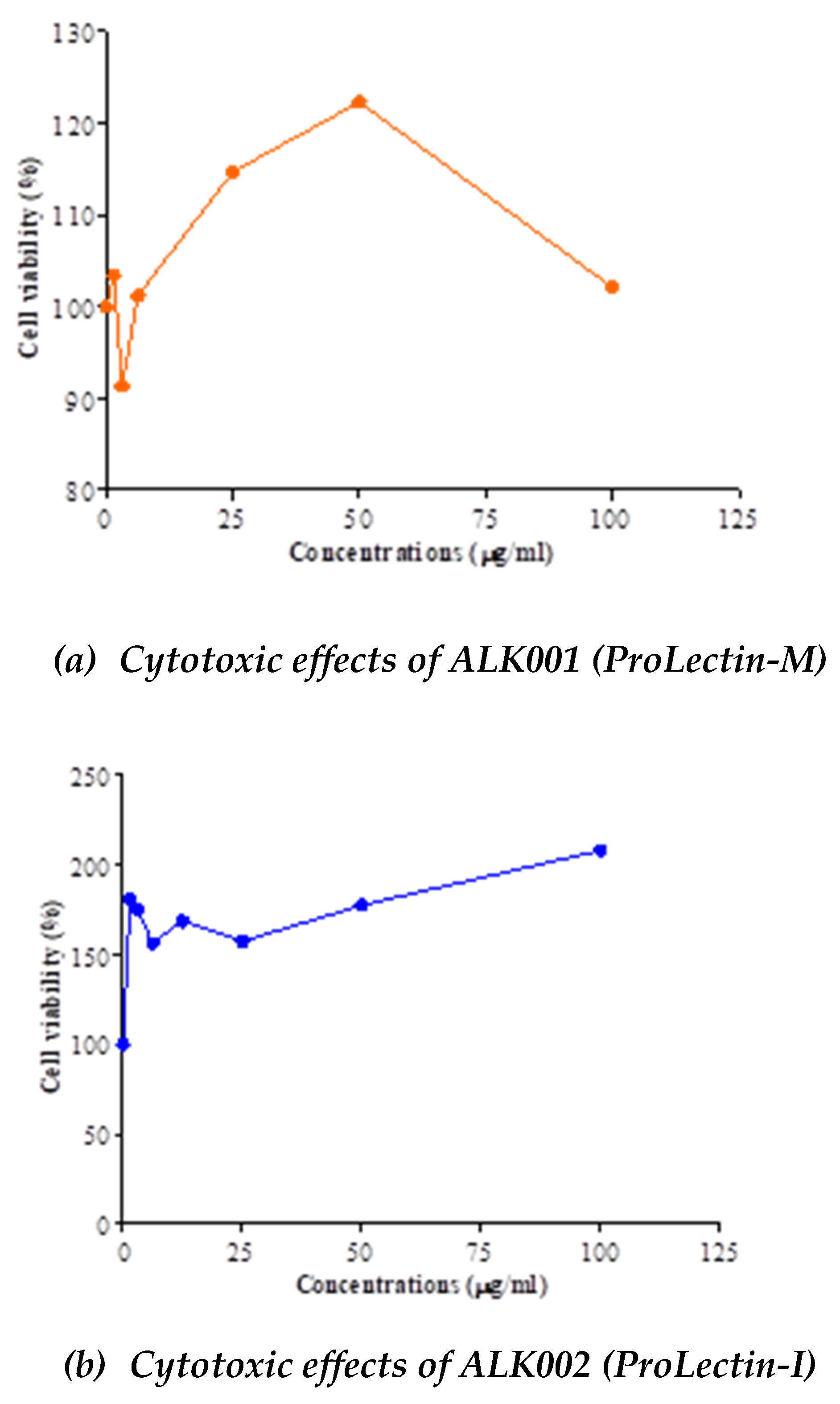
Anti-viral potency of ALK001 (ProLectin-M) and ALK002 (ProLectin-I) using COVID-19 strain:
The IC50, and CC50 values for both test products are described in
Table 4; and drug concentration vs response graphs are presented in
Figure 2. No cytotoxic effects observed by both compounds (ALK001 [ProLectin-M] and ALK002 [ProLectin-I]) on Vero cells. Both compounds increased the percent of viable cells: CC
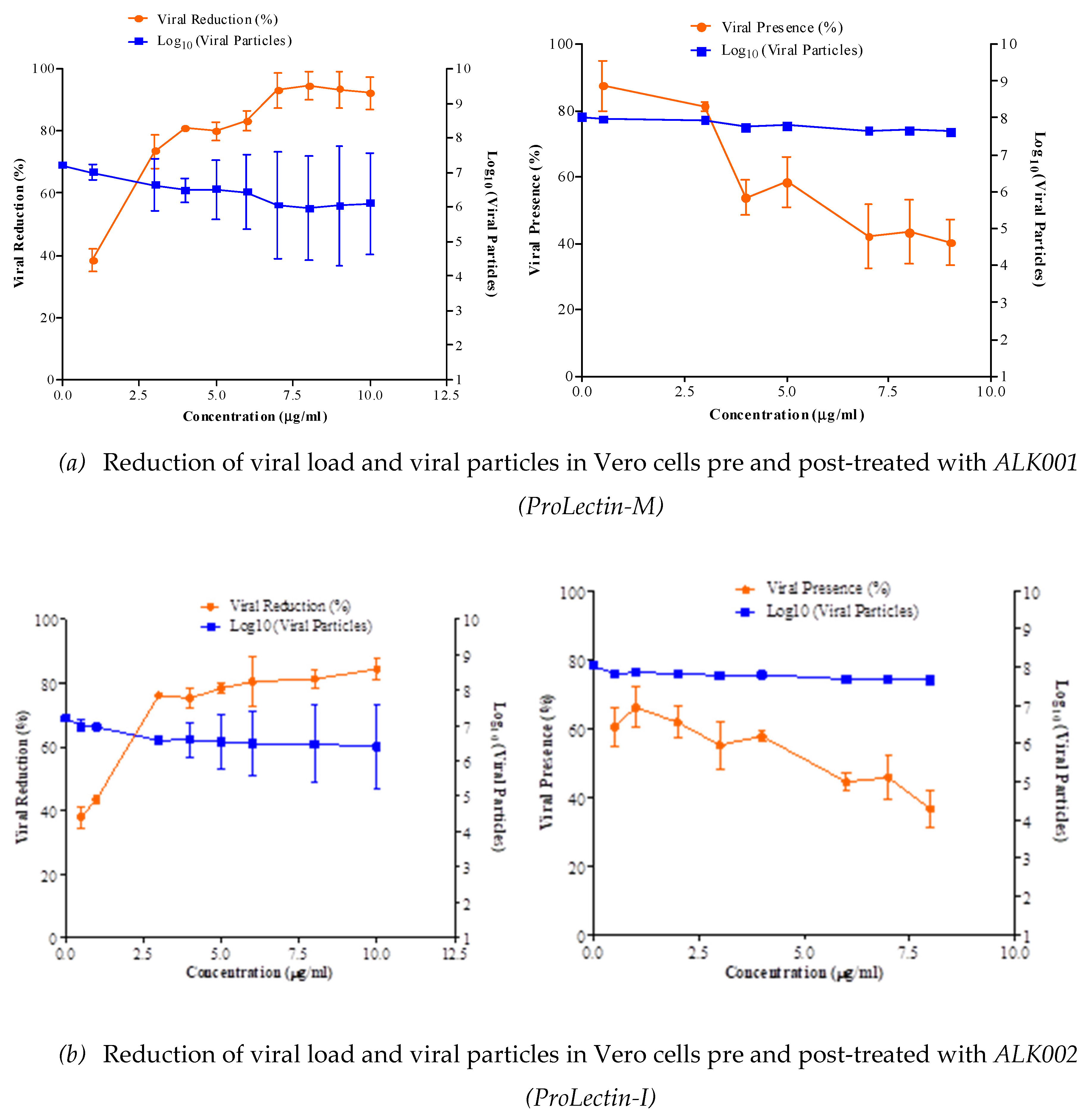
50 = >100 μg/ml. Anti-SARS-CoV2 efficacy of ALK001 (ProLectin-M) and ALK002 (ProLectin-I) is presented in
Figure 3. Reduction of viral load and viral particles in Vero cells pre-treated with ALK002 (ProLectin-I) was observed to reduce from 10
6.8 to 10
5.1; whereas, in post-treatment viral particles are reduced from 10
6.8 to 10
5.2.
Result of ‘in vitro’ studies using influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2
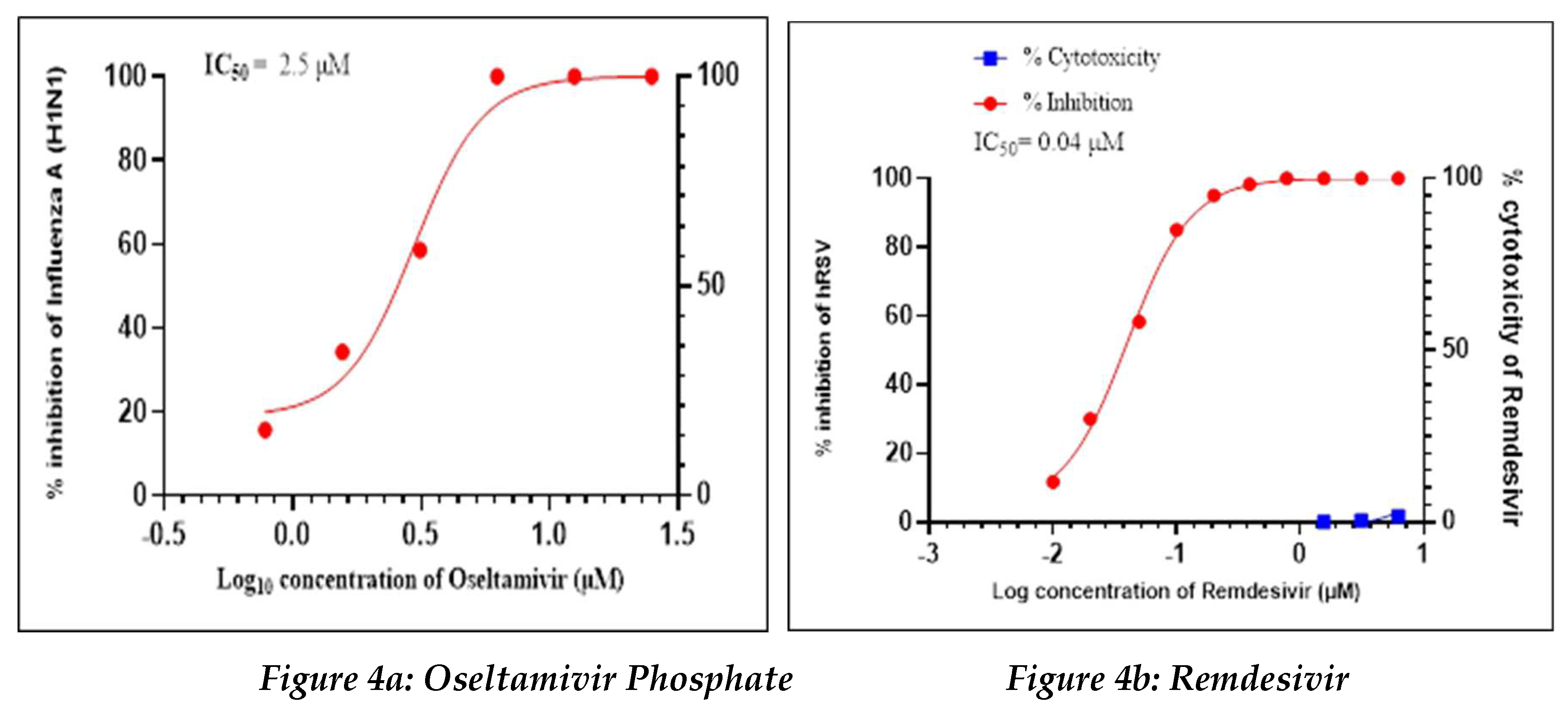
Positive Control
Oseltamivir Phosphate was used as a positive control in this study to assess the antiviral activity against influenza-A (H1N1), whereas Remdesivir was used as a positive control to assess the antiviral activity against human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 (
Figure 4a, 4b).
Oseltamivir Phosphate had shown IC50 value of 2.5 µM and Remdesivir had shown IC50 value of 0.04 µM. The IC50 value for both positive controls found to be in acceptable ranges based on literature data.
Test drugs (ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I)
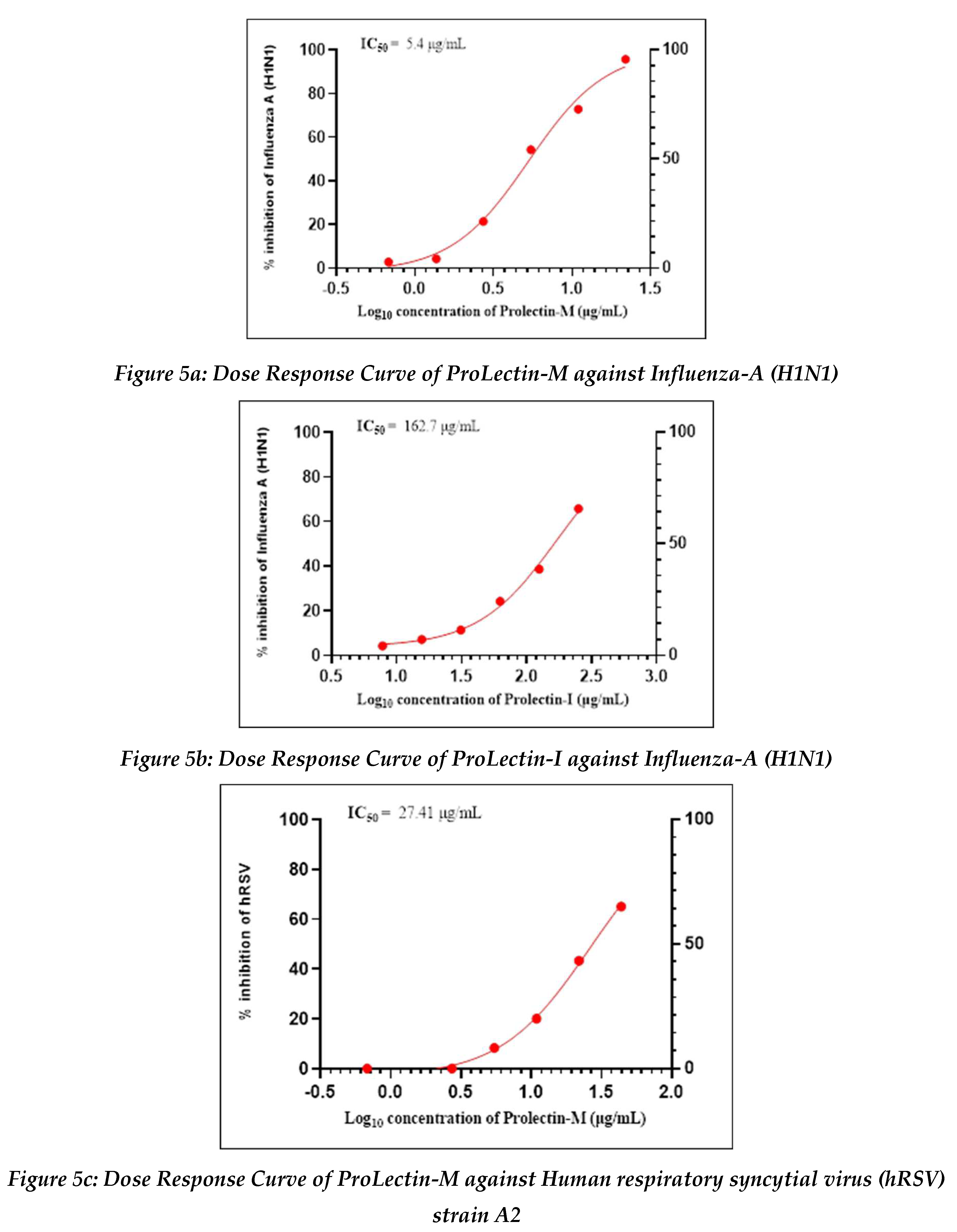
Antiviral activity against influenza-A (H1N1): The assay was conducted to determine the cytotoxicity of ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I using highly permissive cell type (e.g., MDCK) for which Influenza-A (H1N1) causes substantive cell death. Up-to concentration of 21.88 µg/mL, ProLectin-M was found to be non-cytotoxic. The cytotoxicity of ProLectin-M was observed for top 4 concentrations (350 µg/mL, 175 µg/mL, 87.5 µg/mL, and 43.75 µg/mL), i.e., less than 50% healthy cells in the well were observed. The IC50 values of the test items ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I were found to be 5.4 µg/mL and 162.7 µg/mL respectively (Figures 5a, 5b).
ProLectin-M exhibited 95 % reduction in the viral load at the test concentration of 21.8 µg/mL with an IC
50 value of 5.4 µg/mL. ProLectin-I did not show any cytotoxicity till 250 µg/mL concentration. Details about the drug concentration, number of plaques, log
10 and percentage reduction of viral load is described in
Table 5.
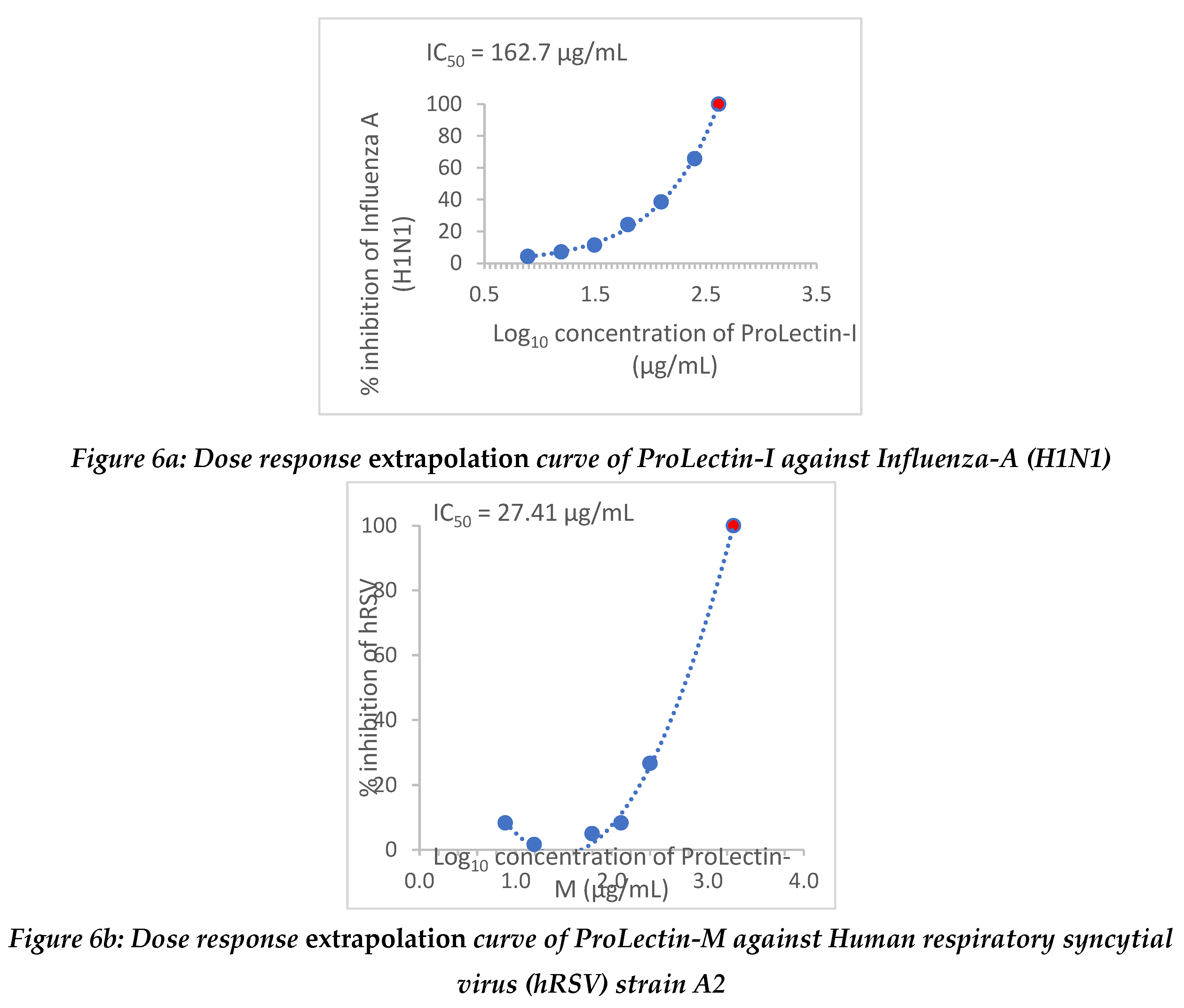
Extrapolation of the dose response curve for ProLectin-M resulted in ˜100% reduction in the viral load at 22.9 µg/mL concentration; whereas, extrapolation of the dose response curve for ProLectin-I resulted in ˜100% reduction in the viral load at 412 µg/mL concentration. Dose response extrapolation graphs for both the test products are presented in
Figure 6a, 6b.
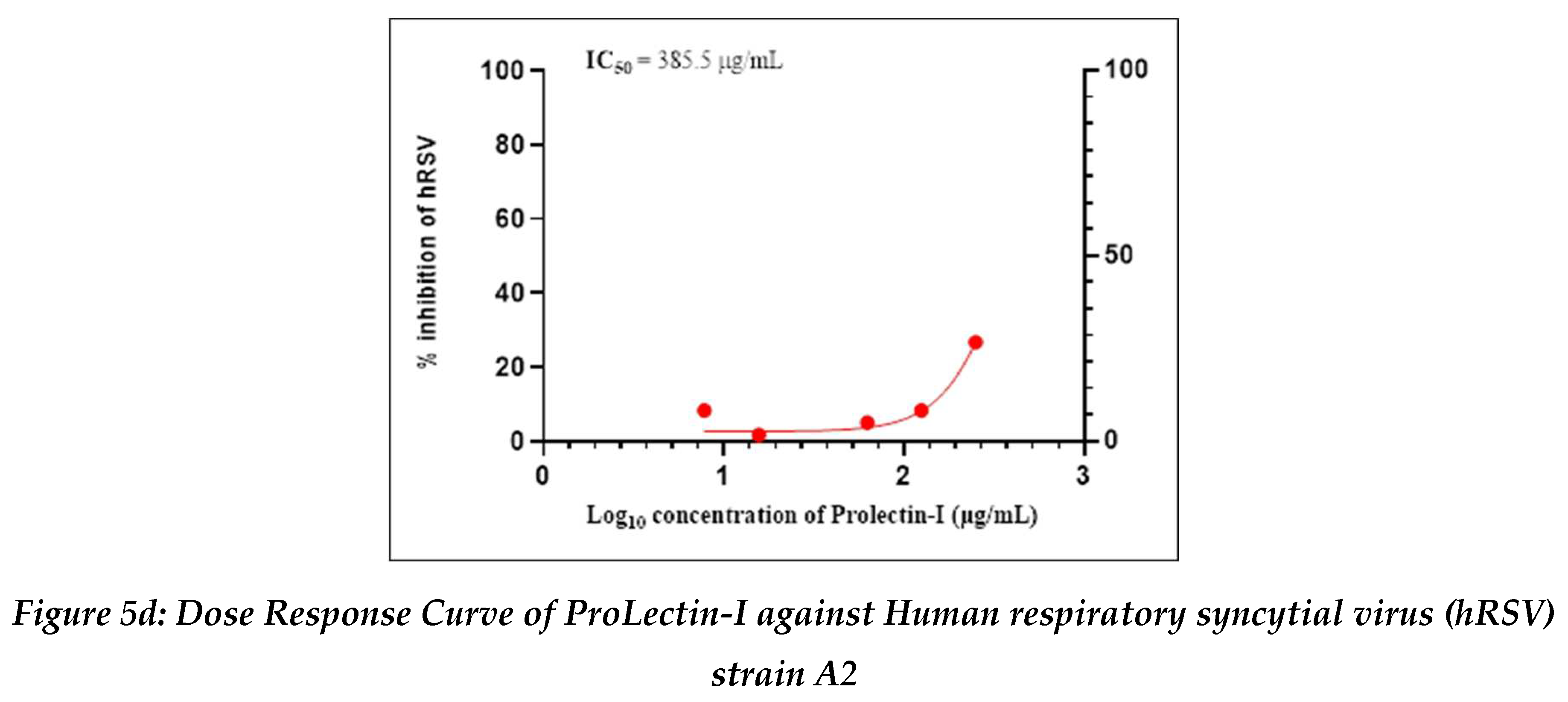
Antiviral activity against human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2: The test item (ProLectin-M) was found to be cytotoxic at top three concentrations from 350 µg/mL, 175 µg/mL, and 87.5 µg/mL, i.e., less than 50% healthy cells in the well were observed. The IC50 values of the test items ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I were found to be 27.41 µg/mL and 385.5 µg/mL respectively (Figures 5c, 5d).
The test item ProLectin-M exhibited 65 % reduction in the viral load at the test concentration of 43.75 µg/mL with an IC
50 value of 27.41 µg/mL. ProLectin-I did not show any cytotoxicity till 250 µg/mL concentration. Details about the drug concentration, number of plaques, log
10 and percentage reduction of viral load is described in
Table 6.
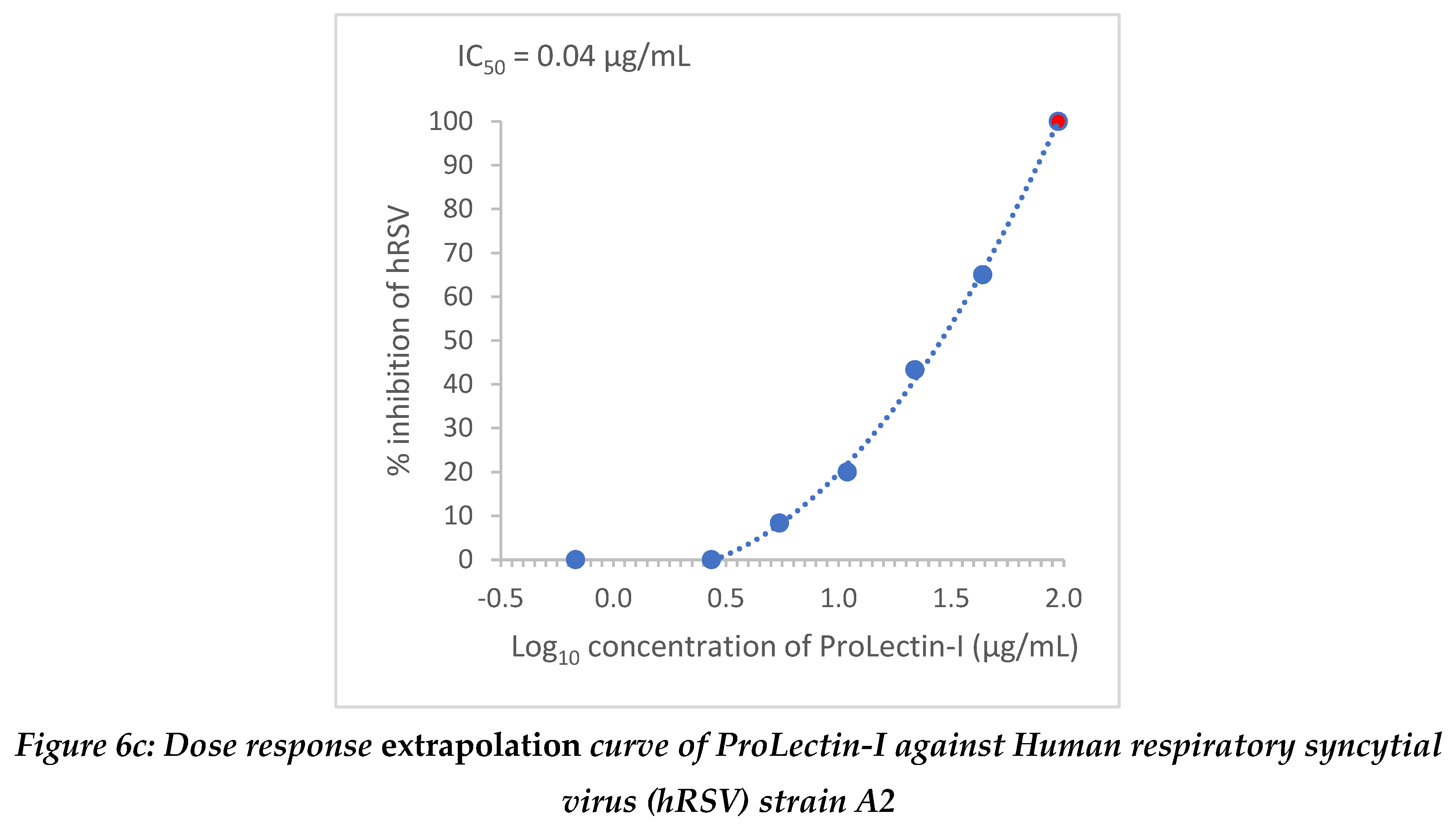
Extrapolation of the dose response curve for ProLectin-M resulted in ˜100% reduction in the viral load at 1848 µg/mL concentration; whereas, extrapolation of the dose response curve for ProLectin-I resulted in ˜100% reduction in the viral load at 94.7 µg/mL concentration. Dose response extrapolation graphs for both test products are presented in
Figure 6.
Discussion
Respiratory viral infections or upper respiratory tract infections are a worldwide public health concern because they are the major cause of symptomatic sickness, resulting in a significant economic burden. The influenza (A and B) viruses and the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are the two most common causes of respiratory viral infection.13,14 Broad acting antivirals are needed to prevent existing and new strains of viruses. Due to the lack of available treatments, the emergence /re-emergence of viruses with epidemic and/or pandemic potential such as ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 1 and 2 (SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2)’ viruses or variety strains of influenza, poses significant human health threats. However, in the event of a public health emergency many factors may hinder the immediate deployment of vaccines due to restricted evidences of safety and efficacy data. This is the rationale behind the need for the creation of broad-spectrum antiviral compounds for rapid reaction in the case of an outbreak crisis, as well as bioweapon defences..
At the first phase, anti-viral potency of test drugs (coded as ALK001 [ProLectin-M] and ALK002 [ProLectin-I]) were evaluated for their using SARS-CoV2 virus strain. Various anti-viral parameters were evaluated such as, IC50 and CC50. Viral RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR assays were performed to determine IC50 whereas, CC50 was evaluated by using MTT assay.
The IC50 ALK001 and AALK002 was found to be 6248 ng/ml (6.2µg/ml) and 4207 ng/ml (4.2μg/ml) respectively. The CC50 value was similar in both the test products i.e., >100 µg/ml.
In two ‘in vitro’ studies, anti-viral activity of ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M against Influenza-A (H1N1) and human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 had been studied by using positive control drugs. In both the studies, the plaque assay was used to test for screening and characterization of antiviral inhibitors. Plaque assays continue to be one of the most accurate methods for directly quantifying infectious viruses and antiviral drugs in cell culture by counting distinct plaques. Among two ‘in vitro’ studies, one uses a highly permissive cell type (e.g., MDCK) for the assay in which Influenza-A (H1N1) causes substantive cell death, while another uses a highly permissive cell type (e.g., Hep-2) for the assay in which human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2 causes substantive cell death. “Oseltamivir Phosphate” was used as a reference standard to determine the antiviral activity of the test products against ‘Influenza A (H1N1)’ strain, whereas “Remdesivir” was used as a reference standard to determine the antiviral activity of the test products against ‘human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) strain A2’.
In two ‘in vitro’ studies following observation were noted:
The ‘in vitro’ study of two test products had shown antiviral activity on different ranges of concentration. ProLectin-M showed 95% reduction in influenza-A (H1N1) strain of virus and 65% reduction in hRSC strain A2. Extrapolation of the ProLectin-I data shows what its effect could be at a higher concentration. These ‘in vitro’ studies demonstrated that ProLectin-I and ProLectin-M may have broad spectrum antiviral activity (broadly acting antivirals). Furthermore, most broad-spectrum antiviral medications have a variety of antiviral activity depending on the virus. As a result, research into drug combinations to reduce drug resistance development and boost antiviral activity is also required. Both the test products can be tested further for variety of viral infection and further pre-clinical research is warranted based on the anti-viral reports and ‘in vitro’ studies in different viral strains.
Conclusion
Both ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I demonstrated their broad spectrum antiviral activity on different concentrations. The outcome of ‘in vitro’ studies on different virus strains concluded that, ProLectin-M found to be a profound antiviral entry inhibitor with broad spectrum antiviral activity. Further pre-clinical research is required to assess detailed broad spectrum anti-viral pharmacology and toxicokinetics of ProLectin-M and ProLectin-I.
Funding
This study was funded by Bioxytran Inc.
Acknowledgments
We thank Genesys Scientific for manuscript writing services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu,J.D., Meng,W., Wang,X.J. and Wang,H.C.R. (2015) Broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Front. Microbiol, 6, 517. [CrossRef]
- Ianevski,A., Zusinaite,E., Kuivanen,S., Strand,M., Lysvand,H., Teppor,M., Kakkola,L., Paavilainen,H., Laajala,M., Kallio-Kokko,H. et al. (2018) Novel activities of safe-in-human broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Antivir. Res., 154, 174–182. [CrossRef]
- Bekerman E, Einav S. Infectious disease. Combating emerging viral threats. Science 2015;348:282–3.
- Andersen, Petter I., et al. “Discovery and Development of Safe-in-Man Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents.” International Journal of Infectious Diseases: IJID: Official Publication of the International Society for Infectious Diseases, vol. 93, Apr. 2020, pp. 268–76. [CrossRef]
- Nainwal, Nidhi. “Treatment of Respiratory Viral Infections through Inhalation Therapeutics: Challenges and Opportunities.” Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, vol. 77, Dec. 2022, p. 102170. [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, Mohammad Amin, and Victor H. Leyva-Grado. “Overview of Current Therapeutics and Novel Candidates Against Influenza, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infections.” Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 10, 2019. [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data.
- Sigamani, Alben, et al. Galectin Antagonist Use in Mild Cases of SARS-CoV-2; Pilot Feasibility Randomised, Open Label, Controlled Trial. medRxiv, 9 Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Alvarez, L. & Ortega, E. The Many Roles of Galectin-3, a Multifaceted Molecule, in Innate Immune Responses against Pathogens. Mediators Inflamm, 2017.
- Sigamani, Alben, et al. “An Oral Galectin Inhibitor in COVID-19—A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial.” Vaccines, vol. 11, no. 4, Apr. 2023, p. 731. [CrossRef]
- Brinchmann, Monica Fengsrud, et al. “The Role of Galectins as Modulators of Metabolism and Inflammation.” Mediators of Inflammation, vol. 2018, May 2018, 18, p. e9186940. [CrossRef]
- Amarelle, L. , Lecuona, E., and Sznajder, J. I. (2017). Anti-influenza treatment: drugs currently used and under development. Arch. Bronconeumol. 53, 19–26. [CrossRef]
- Yip, T. F. , Selim, A. S. M., Lian, I., and Lee, S. M. (2018). Advancements in host-based interventions for influenza treatment. Front. Immunol. 9:1547. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).