Submitted:
31 August 2023
Posted:
01 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study object and data for system calibration
- Supporting structure
- Lower chamber for sewage or rainwater
- Pump set for transporting sewage or rainwater
- Plastic straps
- Sewage pipes of various diameters
- Mounting brackets for sewage pipes
- Power supply system
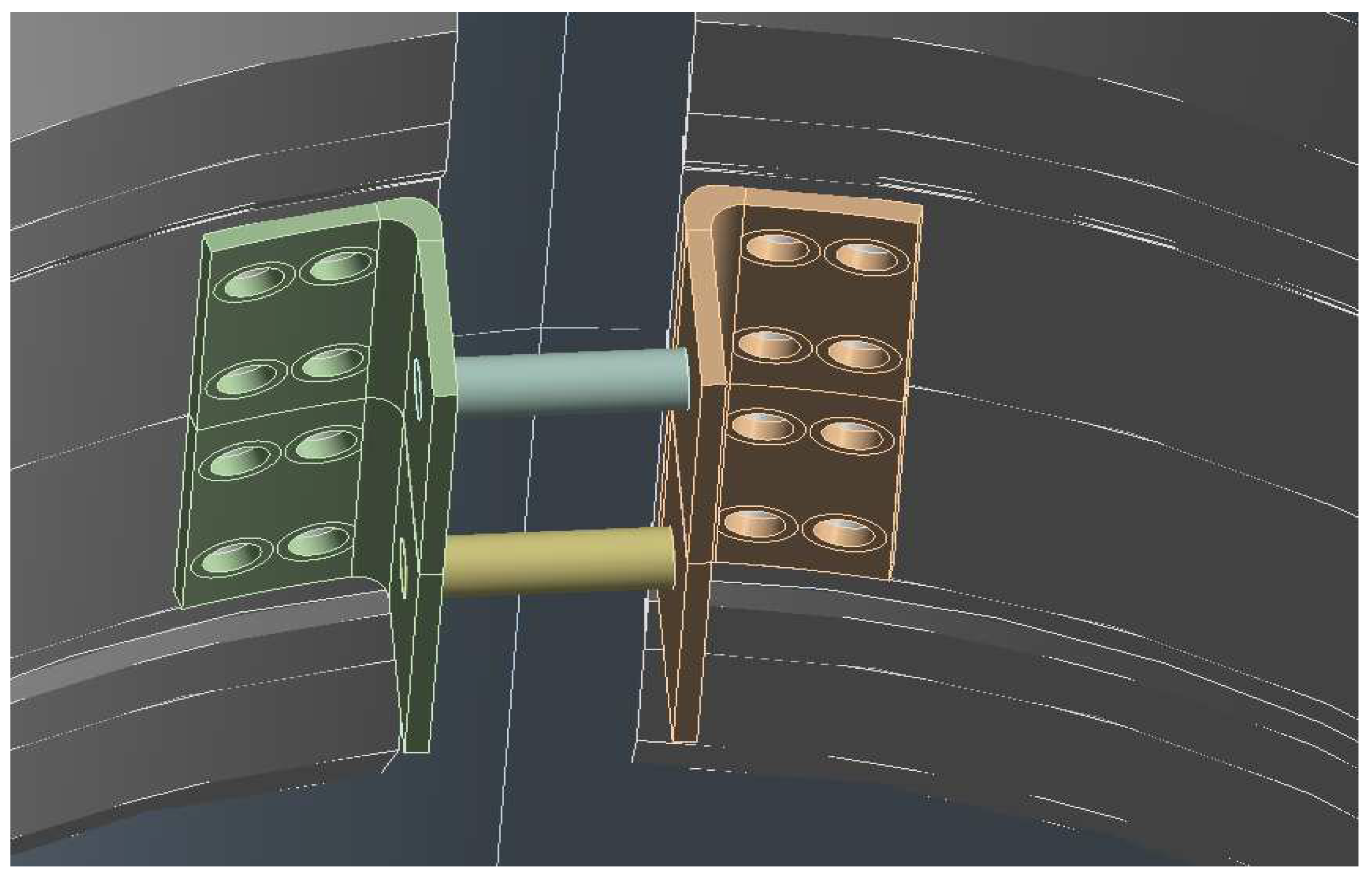
2.2. Investigation of Material Selection for the Plastic Enclosure of the Measurement Strap
2.3. Problem of shrinkage in 3D printing of armlet with wet circuit measurement
2.4. Experimental procedures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
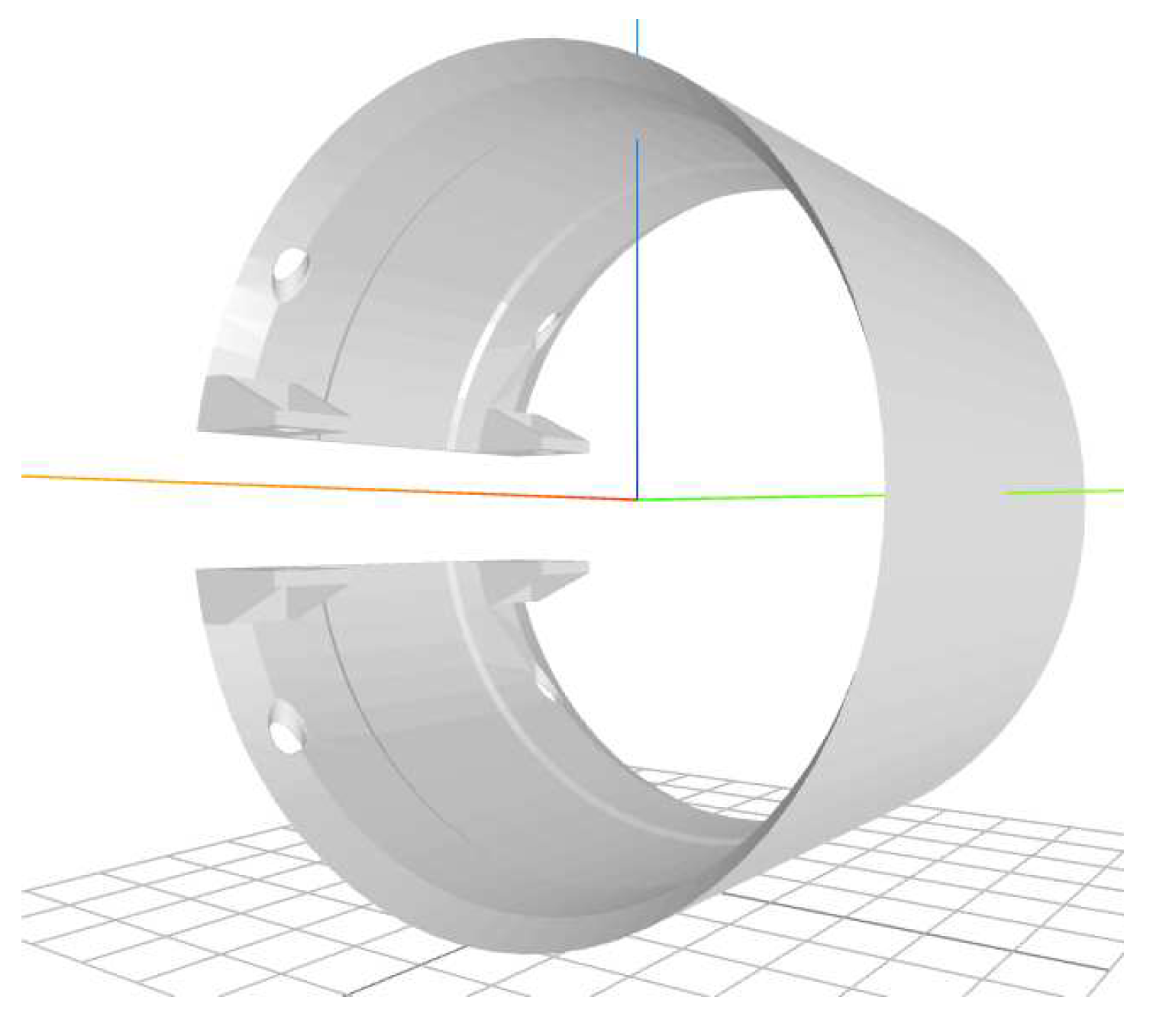
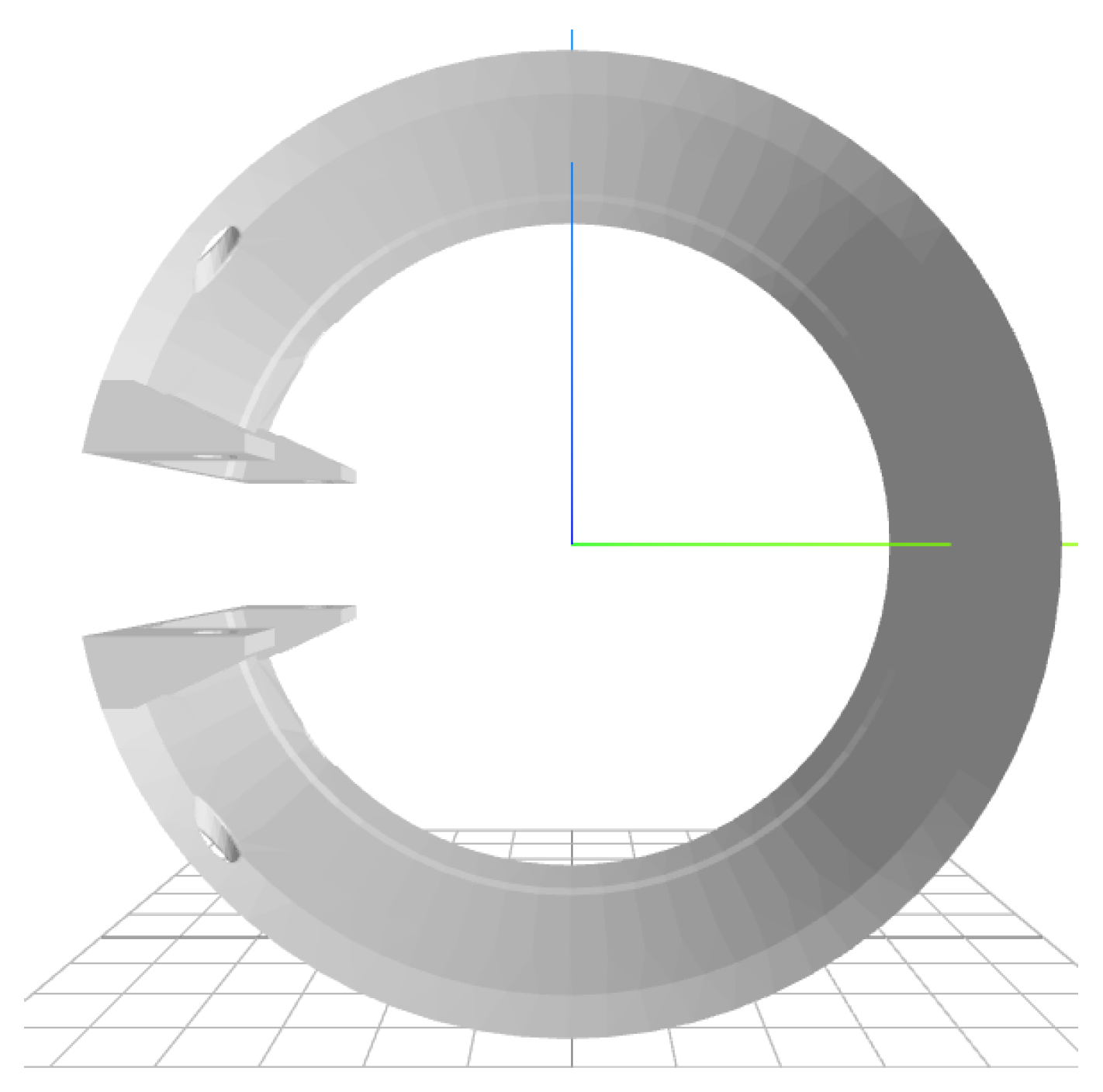
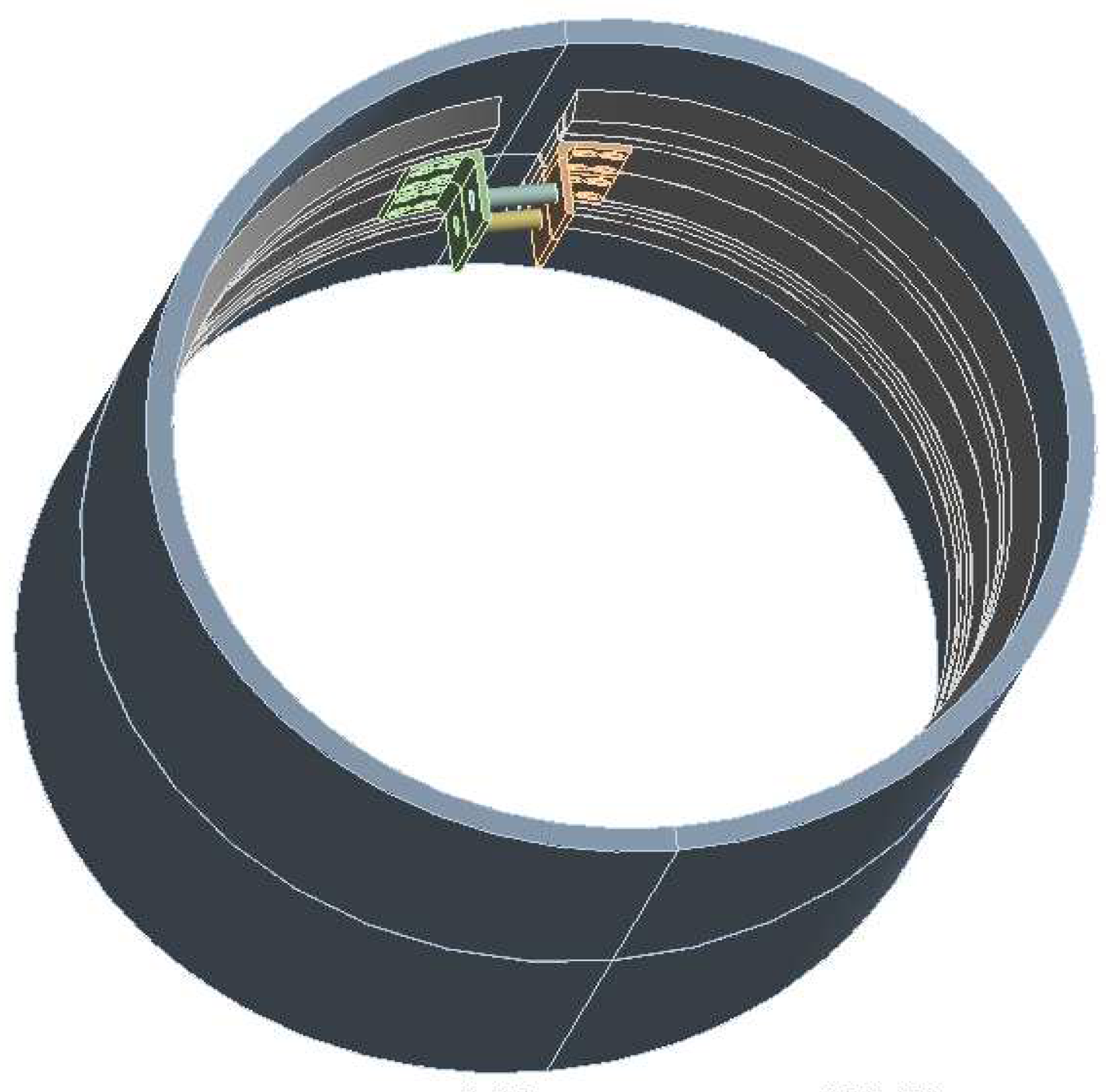
3.1. Optimal armlet shape for wet circuit measurement system: Key findings
3.2. Results of laboratory measurements of water/wastewater flow through the armlet with wet circuit system (housing of measurement straps)
4. Discussion
4.1. Rainwater ingress detection device for enhanced wastewater management:
4.2. Advancing measurement technology for monitoring wet circuits in closed channels
4.3. Innovations for urban wastewater management: Advancing sewage transformation strategies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matheri, A. N.; Mohamed, B.; Ntuli, F.; Nabadda, E.; Ngila, J. C. Sustainable circularity and intelligent data-driven operations and control of the wastewater treatment plant. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2022, 126, 103152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Selvakumar, P.; Kumar, P. S.; Satheeskumar, V.; Vijaysunder, M. G.; Hariharan, S.; Antony, K. Recent advances in electrochemical sensor developments for detecting emerging pollutant in water environment. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasiuk, O.; Hedström, A.; Marsalek, J.; Ashley, R. M.; Viklander, M. Contamination of stormwater by wastewater: A review of detection methods. J. Environ. Manage. 2015, 152, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. M.; Hong, C. S. Internet of things for secure surveillance for sewage wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasiuk, O.; Hedström, A.; Marsalek, J.; Ashley, R. M.; Viklander, M. Contamination of stormwater by wastewater: A review of detection methods. J. Environ. Manage. 2015, 152, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, V.; Cerny, M.; Lim, M.; Gledson, B.; Lockley, S.; Woodward, J. A smart sewer asset information model to enable an ‘Internet of Things’ for operational wastewater management. Autom. Constr. 2018, 91, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Verma, N.; Lugani, Y.; Kumar, S.; Asadnia, M. Conventional and advanced techniques of wastewater monitoring and treatment. In Green sustainable process for chemical and environmental engineering and science; Elsevier, 2021; 1-48.
- Pan, Y.; Mao, K.; Hui, Q.; Wang, B.; Cooper, J.; Yang, Z. Based devices for rapid diagnosis and wastewater surveillance. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenoyanis, A.; Raad, R.; Wady, I.; Krogh, C. Implementation of an IoT based radar sensor network for wastewater management. Sensors 2019, 19(2), 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C. W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Swain, N.; Reid, K.; Saint, C. P. Development of smart data analytics tools to support wastewater treatment plant operation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 177, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejeian, F.; Etedali, P.; Mansouri-Tehrani, H. A.; Soozanipour, A.; Low, Z. X.; Asadnia, M.; Razmjou, A. Biosensors for wastewater monitoring: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeer, S.; Pandey, R. P.; Rehman, B.; Safdar, T.; Ahmad, I.; Hasan, S. W.; Ullah, A. A review of artificial intelligence in water purification and wastewater treatment: Recent advancements. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N. A.; Ramli, S.; Mamat, N. H.; Khan, S.; Gomes, C. Chemical and biosensor technologies for wastewater quality management. Int. J. Adv. Res. Publ. 2017, 1(6), 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Karn, A. L.; Pandya, S.; Mehbodniya, A.; Arslan, F.; Sharma, D. K.; Phasinam, K.; Sengan, S. An integrated approach for sustainable development of wastewater treatment and management system using IoT in smart cities. Soft Comput. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jońca, J.; Pawnuk, M.; Arsen, A.; Sówka, I. Electronic noses and their applications for sensory and analytical measurements in the waste management plants—A review. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Crittenden, J.; Huang, N.; Ahmad, U. M. Technology status and trends of industrial wastewater treatment: A patent analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, R.; Vela, N.; El Aatik, A.; Murray, E.; Roche, P.; Navarro, J. M. On the use of an IoT integrated system for water quality monitoring and management in wastewater treatment plants. Water 2020, 12(4), 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, A. K.; Dhingra, N.; Gupta, M.; Bhati, N.; Kumari, P. Machine learning and IoT-based waste management model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Mittal, Y.; Gupta, S.; Abbassi, R.; Garaniya, V. Recent progress in biosensors for wastewater monitoring and surveillance. In Artificial Intelligence and Data Science in Environmental Sensing; 2022; pp 245-267.
- Abbassi, P. R.; Srivastava, V. Y. G. M.; Gupta, S. Recent progress in biosensors for wastewater monitoring and surveillance. In Artificial Intelligence and Data Science in Environmental Sensing; 2022; p 245.
- Newhart, K. B.; Holloway, R. W.; Hering, A. S.; Cath, T. Y. Data-driven performance analyses of wastewater treatment plants: A review. Water Res. 2019, 157, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, M. L.; Mendieta-Pino, C. A.; Brito-Espino, S.; Ramos-Martín, A. Climate Change Mitigation Tool Implemented through an Integrated and Resilient System to Measure and Monitor Operating Variables, Applied to Natural Wastewater Treatment Systems (NTSW) in Livestock Farms. Water 2022, 14(18), 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S. V.; Singh, R.; Gehlot, A.; Rashid, M.; AlGhamdi, A. S.; Alshamrani, S. S.; Prashar, D. Role of wireless aided technologies in the solid waste management: A comprehensive review. Sustainability 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H. W.; Yoo, S. S.; Lee, B. J.; Koo, D. D.; Kang, J. H. Measurement of wastewater discharge in sewer pipes using image analysis. Water 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muga, H. E.; Mihelcic, J. R. Sustainability of wastewater treatment technologies. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 88, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, C.; Schütze, M. Real-time control of sewer systems using turbidity measurements. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63(11), 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apperl, B.; Pressl, A.; Schulz, K. Feasibility of locating leakages in sewage pressure pipes using the distributed temperature sensing technology. Water, Air, & Soil Pollut.
- Qi-yu, Z.; Zeng-jin, L.; Lai-sheng, L.; Na, L. Research on comprehensive evaluation model of rural domestic sewage treatment technology based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and analytic hierarchy process method. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16(2), 452–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, M.; Zimmermann, M. Improving sewage sludge treatment and utilisation in China: a German perspective on barriers to and measures for the dissemination of innovative technologies. H2Open J. 2023, 6(2), 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuval, H.; Adin, A.; Fattal, B.; Rawitz, E.; Yekutiel, P. Integrated Resource Recovery: Wastewater Irrigation in Developing Countries: Health Effects and Technical Solutions. Disclosure 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhale, S.; Graham, J. A. A new development in locating leaks in sanitary sewers. Tunnelling Undergr. Space Technol. 2004, 19(1), 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, H.; Messmann, S.; Giga, A.; Grüning, H. Options and limits of quantitative and qualitative online-monitoring of industrial discharges into municipal sewage systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, L.; Li, P. Water consumption and wastewater discharge in China’s steel industry. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45(10), 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggelke, K.; Löwe, R.; Beeneken, T.; Fuchs, L. Implementation of an integrated real-time control system of sewer system and waste water treatment plant in the city of Wilhelmshaven. Urban Water J. 2013, 10(5), 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Pinho, J. L.; Faria, R.; Vieira, J. M. P.; Costa, C. Improving operational management of wastewater systems. A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80(1), 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utepov, Y.; Neftissov, A.; Mkilima, T.; Mukhamejanova, A.; Zharassov, S.; Kazkeyev, A.; Biloshchytskyi, A. prototyping an integrated iot-based real-time sewer monitoring system using low-power sensors. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol.
- Kang, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Oh, J. Time series prediction of wastewater flow rate by bidirectional LSTM deep learning. Int. J. Control, Autom. Syst, 3023; 18. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Sheng, J.; Jin, Z. Remote Sensing Detection and Resource Utilisation of Urban Sewage Sludge Based on Mobile Edge Computing. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2023, 30(2), 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chunhong, Z.; Qianglin, L. Development and application of random forest regression soft sensor model for treating domestic wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, D.; Sandhya, K.; Shruthi, K.; Latha, T. S. S. IoT based automation in sewage treatment plant. Acta Technica Corviniensis-Bull. Eng. 2023, 16, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, P.; Bao, X.; Meng, F.; Lu, R. Multi-objective Pigeon-inspired Optimized feature enhancement soft-sensing model of Wastewater Treatment Process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.; Eddaif, L.; Telegdi, J. Sensors for water and wastewater monitoring. In Advanced Sensor Technology; Elsevier, 2023; pp 517-563.
- Zidaoui, I.; Wemmert, C.; Dufresne, M.; Joannis, C.; Isel, S.; Wertel, J.; Vazquez, J. Validation of wastewater data using artificial intelligence tools and the evaluation of their performance regarding annotator agreement. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87(12), 2957–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Oshita, K.; Takaoka, M.; Kusakabe, T. Real-time measurement of the moisture contents of dewatered sewage sludge during thermal drying using a low-cost ECH2O EC-5 soil moisture sensor. Drying Technol. 2023, 41, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiplagat, R. K.; Mutuku, M. Artificial Intelligence Inclusion and Performance of Sensor Management System in Nairobi-City Water and Sewerage Company, Kenya. J. Bus. 2023, 11(3), 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utepov, Y.; Neftissov, A.; Mkilima, T.; Mukhamejanova, A.; Zharassov, S.; Kazkeyev, A.; Biloshchytskyi, A. prototyping an integrated IOT-based real-time sewer monitoring system using low-power sensors. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2023, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chunhong, Z.; Qianglin, L. Development and application of random forest regression soft sensor model for treating domestic wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, M.; Akbarian, H.; Gheibi, M.; Akrami, M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A. M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Tian, G. A soft-sensor for sustainable operation of coagulation and flocculation units. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselink, L.; Vahdatikhaki, F.; Harmsen, Y.; Voordijk, H. Usability analysis of virtual-reality-enabled digital twin for the inspection of sewage pumping stations. Int. J. Constr. Manage. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomperi, J.; Rossi, P. M.; Ruusunen, M. Estimation of wastewater flowrate in a gravitational sewer line based on a low-cost distance sensor. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, (pt2022171), wpt2022171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiqi, M. M.; Zhao, W.; Cotterill, S.; Dereli, R. K. Smart management of combined sewer overflows: From an ancient technology to artificial intelligence. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2023, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Yang, F.; Yan, R. Design and Implementation of Three-Channel Drainage Pipeline Ground Penetrating Radar Device. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Mao, D. Truth Discovery Technology for Mobile Crowd Sensing in Water Quality Monitoring. Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput. 2023.
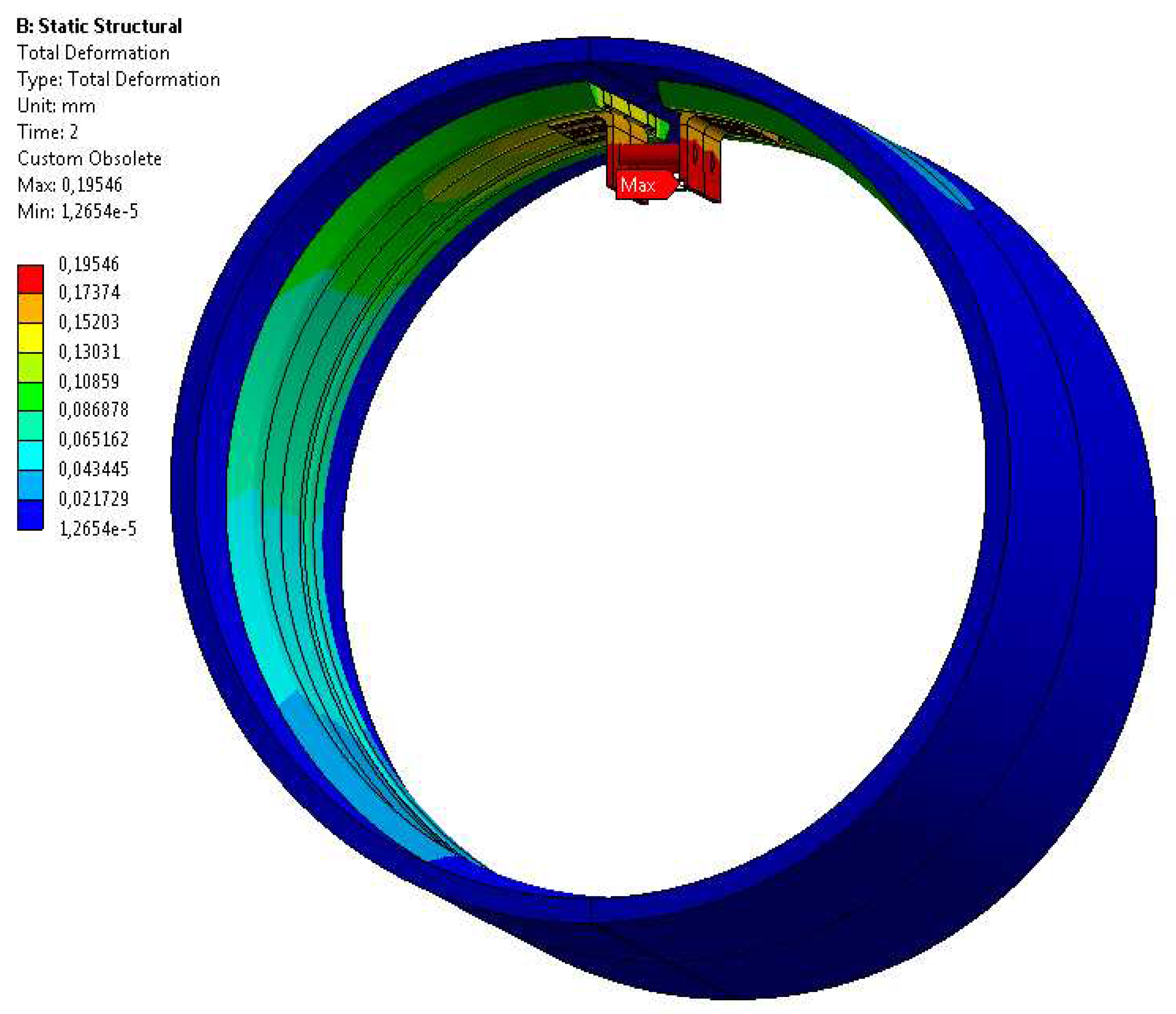
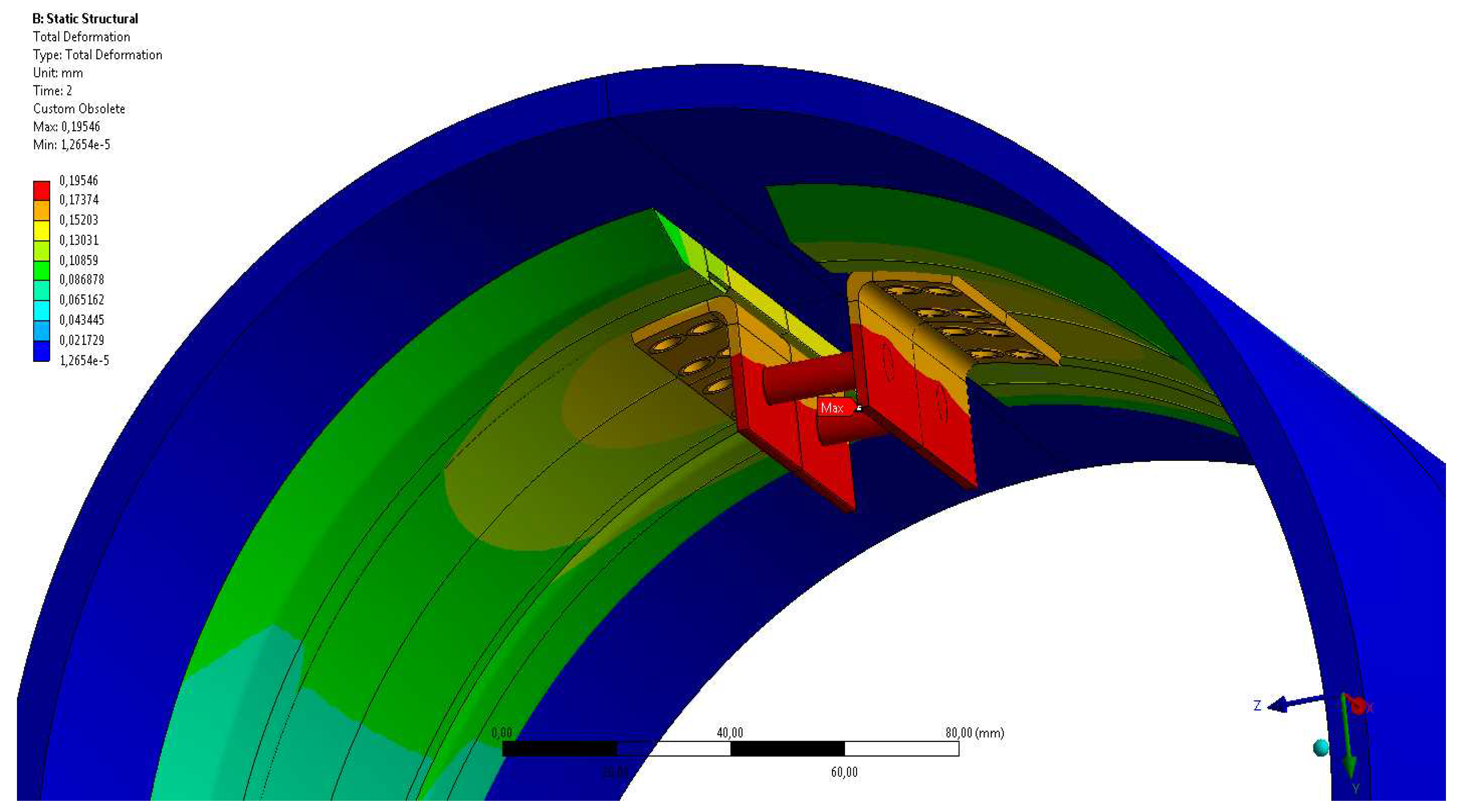
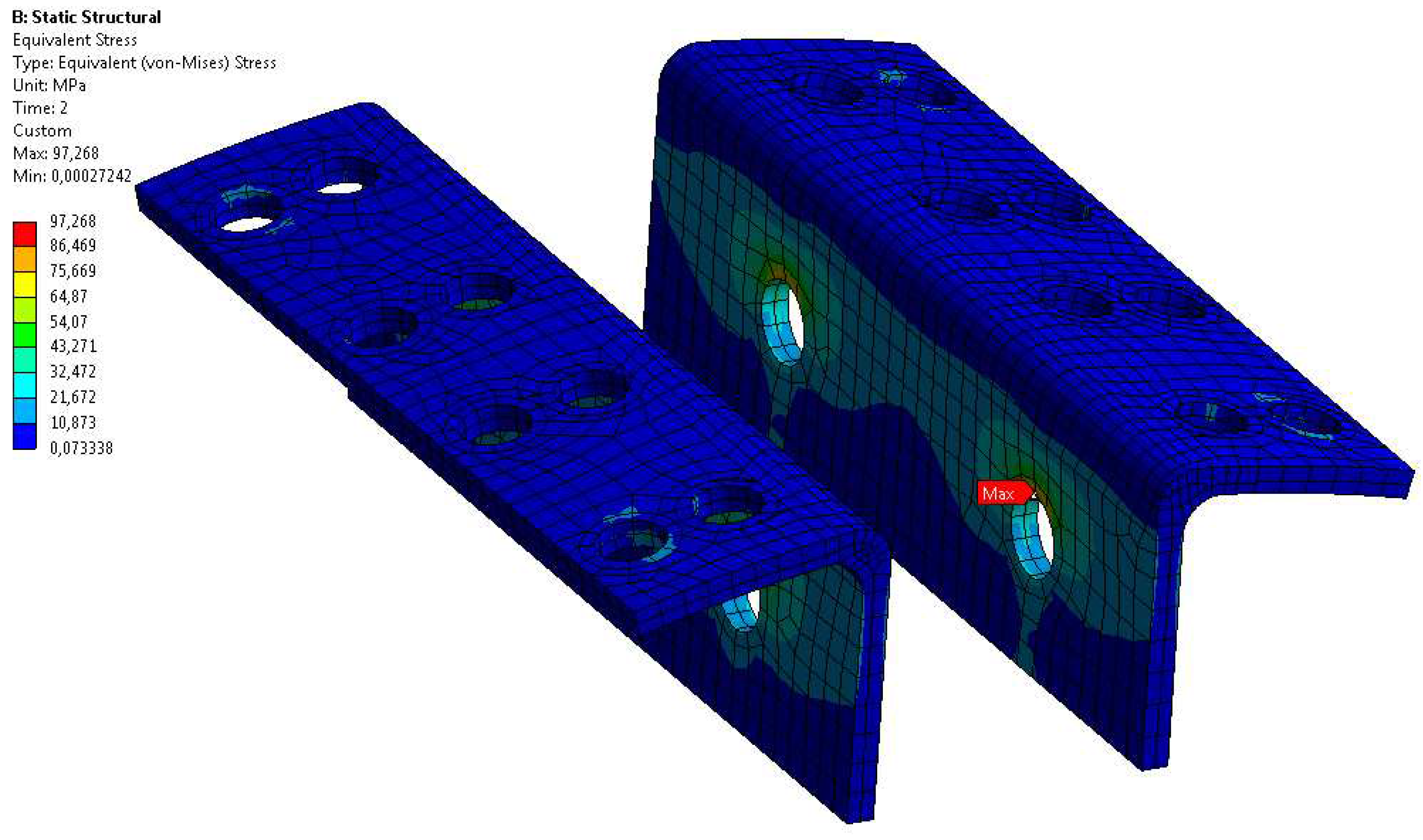
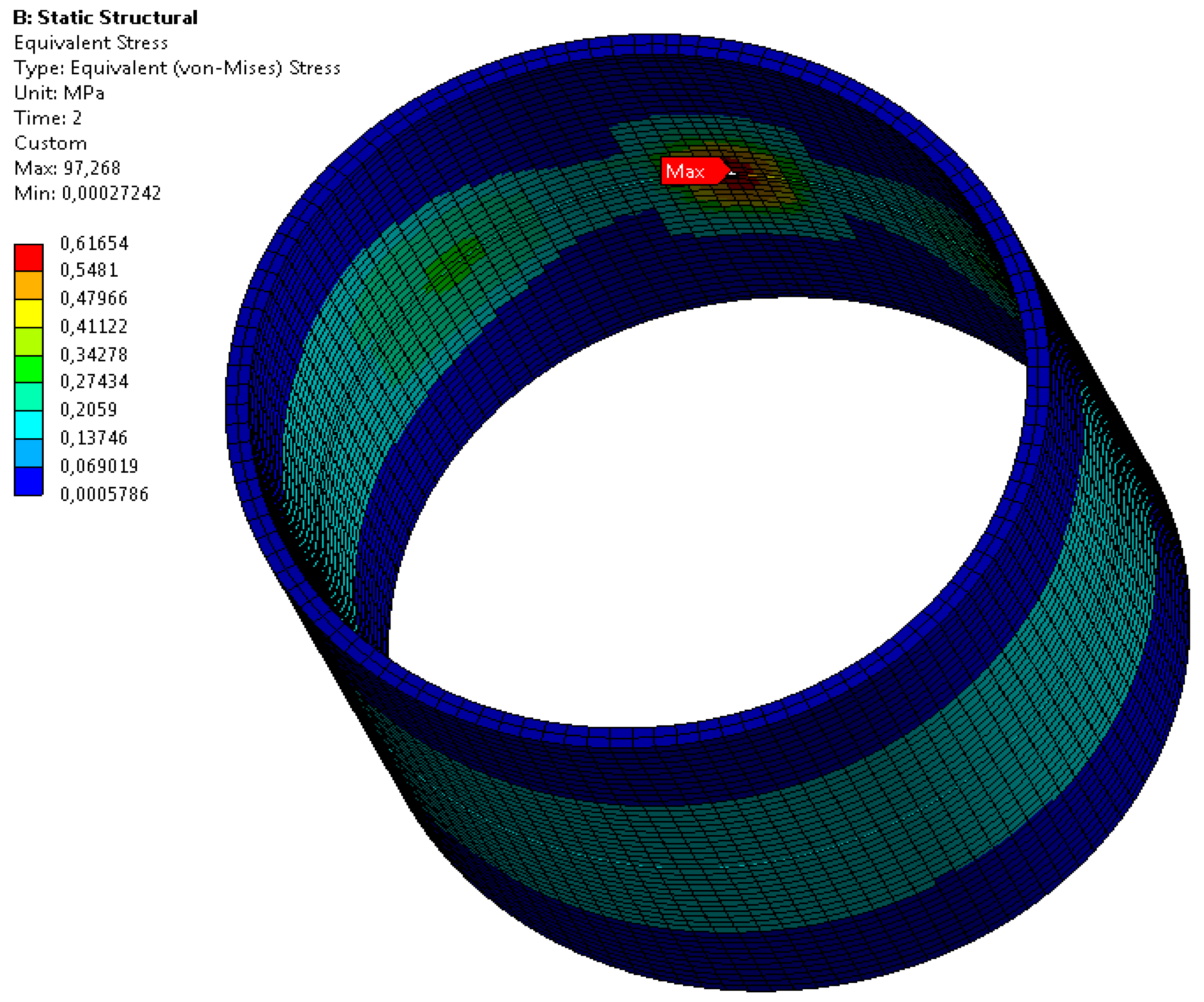
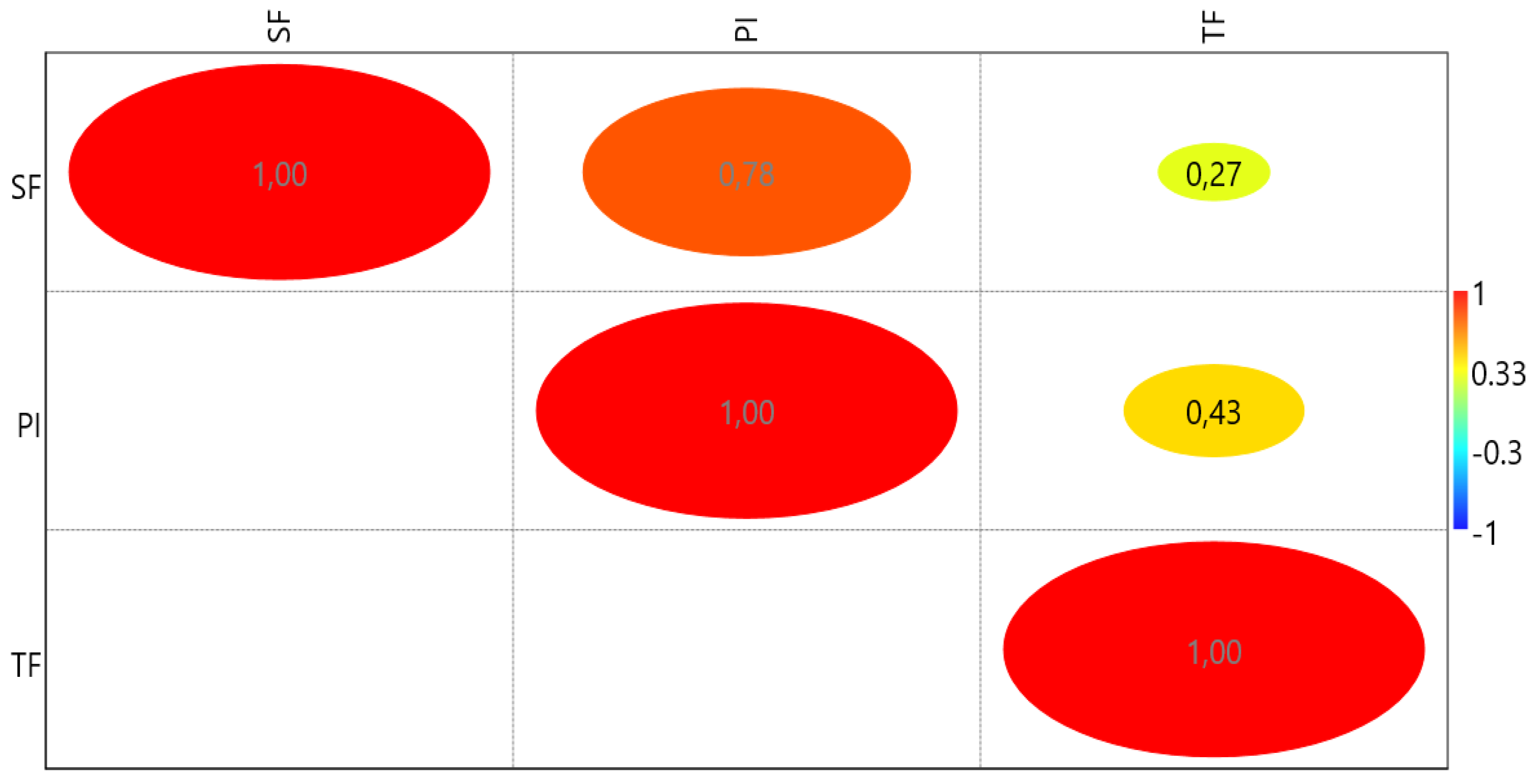
| Samples | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| Samples | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| Samples | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| Sample | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| Sample | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | medium | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | medium | 0 | 5 |
| Lp. | Pipe slope - inclination[‰] | Water/sewage flow [dm3/h] | Splashing of water/sewage | Displacement[mm] | Duration of water/sewage flow [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 20 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 100 | 3600 | low | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | 50 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 100 | 7200 | low | 0 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





