1. Introduction
Cognitive dysfunction is a frequent and disabling symptom in multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune neuroinflammatory disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) that is also characterized by motor and sensory deficits. Information processing speed deficits are joined over time by difficulties with verbal fluency, verbal episodic memory, visuospatial construction and executive dysfunction [
1,
2]. Treatment for MS-related cognitive dysfunction remains elusive. Current MS disease-modifying therapies (DMT), while highly effective at reducing neuroinflammatory attacks, only modestly benefit MS cognition [
3]. FDA-approved dementia medications donepezil and memantine failed to reduce cognitive dysfunction in MS trials [
4,
5]. Cognitive behavioral therapy can improve processing speed dysfunction in people with MS, but suffers from limited access [
6].
Centella asiatica (
Centella) is a traditional botanical medicine used to support age-related cognitive health. Preclinical studies using a standardized water extract of
Centella (CAW) reveal remarkable cognitive-behavioral enhancing and neuroprotective properties in Alzheimer’s dementia models and aged wild type (WT) animals [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. Proposed mechanisms of CAW in these studies included increases in antioxidant response element (ARE) gene expression and mitochondrial respiration, heightened dendritic arborization in cultured hippocampal neurons, and anti-inflammatory properties. Several clinical trials of
Centella suggest improved memory and reduced anxiety, however these studies are limited by small sample sizes, inadequate descriptions of the investigational products, and in some cases lack of placebo controls [
13].
Because MS pathophysiology includes oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, we hypothesized
Centella would benefit cognition and behavior in MS [
14]. We therefore determined if benefits to behavioral performance, ARE gene expression, and mitochondrial respiratory activity seen in dementia and aging mouse models would also be observed in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CAW Production, Analysis, and Administration
CAW used in this study was produced as previously described [
15]. Briefly
Centella asiatica herb (4kg) was extracted by boiling in water (50 L) for 90 minutes. The extract was filtered to remove solid plant debris and lyophilized in 3 separate runs to yield a dry residue (CAW; total 820g). Voucher samples of the starting plant material (BEN-CA-6) and the CAW batches (BEN-CAW-7, 8 and 9) are stored at OHSU’s BENFRA Botanical Dietary Supplements Research Center. The content of characteristic triterpenes (5.1% w/w) and caffeoylquinic acids (2.6% w/w) in the dried CAW was determined by liquid chromatography coupled to multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry.
For both studies, CAW was dosed at 500mg/kg/day using 2 drops CAW solution (125mg/ml) dissolved in 5% sucrose/phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution. Placebo consisted of an equal volume of 5% sucrose/PBS solution. Placebo and CAW solutions were stored at -20°C until use. A fresh vial of placebo or CAW treatment was thawed for use on each day to avoid repeated freeze-thawing then loaded into individual pipette tips for oral administered.
2.2. Animals
All procedures were conducted in strict accordance with Federal and NIH Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Portland VA Medical Center and Oregon Health & Science University.
Study 1: 8-12-week old female C57BL/6J mice (n=20; Jackson Labs, Sacramento, CA, USA) were divided into 2 cohorts, and housed in mixed-treatment groups of 4 per cage. Mice were maintained in the Animal Resource Facility at the PVAMC on a 12-hour light/dark cycle with access to food and water ad libitum. Each cohort was inoculated on a single day with an emulsion containing 200μg Freund’s complete adjuvant/200μg MOG-35-55 peptide with intraperitoneal booster injections of 75ng and 200ng pertussis toxin on Day 2. Starting at EAE clinical disability score 2, mice received daily treatment with either CAW or placebo in a 1:1 distribution. Saline perfusion followed by euthanasia by cervical dislocation occurred after 14 days of treatment on 2 pre-planned days. Half of the mice underwent immediate brain dissection for harvesting of cerebral cortex (see 2.4) while the other half underwent brain and spinal cord dissection for subsequent fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS).
Study 2: Four-month old female C57BL/6J mice (n=30; Jackson Labs, Sacramento, CA, USA) were divided into 3 equally-sized mixed treatment groups and matched by initial weight. Mice were house at the OHSU animal facility. Control mice received sham inoculation and 2-day booster with saline followed by placebo treatment (5% sucrose in PBS). The remaining 2 groups received EAE induction as described above followed by either placebo treatment (PBO) or CAW (dosed as in Study 1) assigned 1:1 based on weight. Treatments on Day 6 after inoculation each morning for 14 days including the day of euthanasia (Day 20) by cervical dislocation. Animals sometimes required saline due to weight loss. All mice immediately underwent brain and spinal cord dissection with half of all brains harvested for cerebral cortex (see 2.4) while lumbar spinal cords were prepared for immunohistochemistry (IHC).
2.3. Weight, EAE disability and behavioral testing
Weight was recorded at baseline and daily in Study 1 and baseline and starting Day 5 (pretreatment) in Study 2. EAE clinical disability was scored daily by the same technician using a scale from 0 (no disability) to 6 (moribund requiring euthanasia) with a final cumulative disease index (CDI) calculated as the sum of the daily scores over the treatment period as previously described [
16]. A score of 2 indicates moderate hindlimb weakness or mild ataxia.
Behavioral performance was assessed in the open field test as previously described [
17]. The open field consisted of a well-lit square (L 40.6 × W 40.6 × H 40.6 cm) with a central light intensity of 100 lx. Mice were allowed to explore the open field for 10 minutes during two consecutive days. Two adjacent arenas were used simultaneously for testing. The enclosures were cleaned with 0.5% acetic acid between trials. Performance of mice was tracked using Ethovision 15 XT software. Performance measures analyzed were total Distance Moved (general activity), Center Duration (anxiety), Latency to the First Center Entry, and Center Frequency (Study 2 only). Open field testing occurred on the final study day only for Study 1 and on Days 5 (pretreatment), 12 (early disability), and final Day 20 in Study 2. Cognitive tests were not conducted due to the short treatment duration limiting the assessment window, and concern for confounding of test results caused by EAE motor weakness.
2.4. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Inflammation including microglial activation was evaluated from dissected brain and spinal cords in Study 1 via FACS analyses with labelling for mononuclear cells (CD74+) and microglia (CD45loCD11b+ and CD45hiCD11b+) as previously described [
18]. Due to low expected cell counts, tissues from animals within treatment groups were pooled prior to FACS testing.
For IHC and tissue staining, tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, sectioned, and either immunostained with anti-CD3 (BD Pharmigen, 1:300; to label inflammation) or anti-Iba1 (Wako, 1:300; to label activated microglea) antibodies along with Hoechst 3342 (to label cell nuclei) followed by detection with fluorescence-labeled secondary antibodies as previously described [
19]. Myelin was detected using fluoromyelin (ThermoFisher Scientific) as previously described [
20].
2.5. ARE gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity
Gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity were quantified in cortical synaptosomes. Synaptosomes were freshly isolated from one half of the cortical tissue from the left hemisphere using Syn-per reagent (Thermo Scientific #87793) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. Total RNA was collected via Tri-Reagent extraction (Molecular Research Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA) and cDNA produced via reverse transcription using the Superscript III First Strand Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) per manufacturers’ instructions. Relative gene expression was measured using Taqman primers and probes (nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nfe2l2; Nrf2 - Mm00477784_m1), NAD(P)H dehydrogenase-quinone oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1; Mm001253561_m1), glutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (Gclc; Mm00802655_m1), heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1, Ho-1; Mm00516005_m1) and reagents (TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix) from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA, USA) with normalization to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh; hs02758991_g1 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA)) expression. qPCR was performed on a StepOne Plus Machine (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and analyzed using the delta-delta Ct method. All groups were normalized to control mice.
Mitochondrial bioenergetics were assessed in cortical synaptosomes using the Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer. The total protein concentration of the synaptosomal preparation for each mouse was determined using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. A total of 10ug of synaptosomal protein diluted in 25uL mitochondrial assay solution (MAS; 70mM sucrose, 220mM mannitol, 10mM KH2PO4, 5mM MgCl2, 2mM HEPES, 1mM EGTA, 0.2% BSA) was plated in each well of a polyethylenimine (PEI) coated 96 well Seahorse plate (5-6 replicate wells for each animal) and the plate was centrifuged at 1200g for 1h at 4C. 155 μL of Agilent Seahorse XF DMEM Medium pH 7.4 (Part # 103575-100) supplemented with 1 mM pyruvate, 2 mM glutamine, and 10 mM glucose was plated in each well of the 96 well plate.
Mitochondrial function was then assessed using the MitoStress kit (Agilent #103015-100) as previously described [
21]. Briefly, oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured under varying conditions: basal, following 2μM p-trifluoromethoxy carbonyl cyanide phenyl hydrazone administration (to elicit maximal respiration) and following the addition of 0.5μM rotenone+anitmycin. Spare capacity was calculated by subtracting the basal respiration from the maximal.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
Study 1: Mean change in weights, CDI scores, behavioral tests, and ARE gene expression were compared between groups by t-test at study end. For the Latency to first Center entry, animals that never entered the center were given latency of the full trial length (600 seconds). Mitochondrial function was compared using repeated measures ANOVA across the study profile and by t-tests between groups at basal, maximal, and spare capacity endpoints. Because FACS analyses used pooled tissues (3 mice per treatment group contributed to each sample tested) due to expected low CNS cell numbers, statistical error could not be calculated; Instead, results were qualitatively compared.
Study 2: Mean change in weights were compared between groups by repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis were employed for group differences in daily weights starting Day 5 and cognitive behavioral scores at Days 12, and 20. CDI were compared by t-test between CAW- and placebo- treated mice. ARE gene expression groups were compared using ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc tests for pairwise comparison. For mitochondrial respiration, ANOVA was calculated across the profile and a separate ANOVA was done for each endpoint (i.e., on for basal respiration, another for maximal respiration, etc.) with Tukey’s post-hoc for pairwise comparison. IHC results for CD3 and Iba1 counts were analyzed with T-tests between placebo and CAW- treated EAE mice. Significance for all tests was set at p <0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Safety and tolerability
Of the 20 mice in Study 1, 18 received treatment with CAW or placebo (n=9 each) as 2 animals did not reach clinical disability score of 2 in sufficient time to receive treatment. Because of the pre-planned sacrifice dates, there was an interval of 1-5 days between the 14th day of treatment and sacrifice. One placebo-treated mouse received 12 days of treatment. All 30 mice in Study 2 received 14 days of treatment up to and including day of sacrifice. There was no difference in mean weight change between treatment groups in Study 1 (0.66g SEM 0.44 vs 0.28g SEM 0.38, p=0.26). While there was an effect of group on body weight in Study 2 (F [2,27]=3.350, p=0.050; Tukey’s post hoc Control vs CAW: p=0.040), there was no difference in weight change loss between CAW and placebo cohorts.
3.2. Clinical disability, inflammation, and demyelination
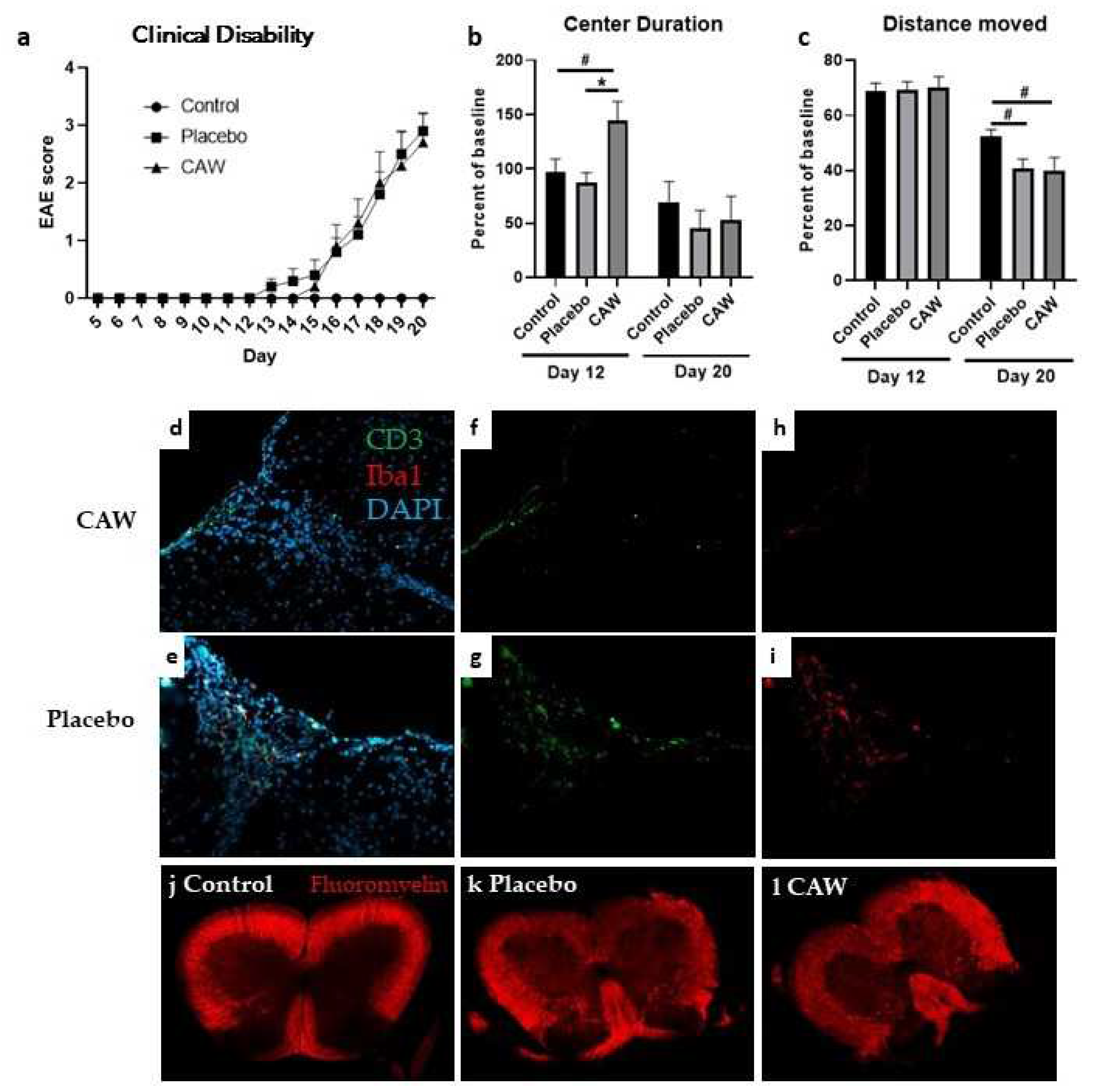
Mean CDI did not differ between CAW and Placebo groups in either study. While mean clinical disability onset in CAW-treated mice in Study 2 occurred 2 days after placebo (Day 15 vs Day 13, Study 2), disability equalized by Day 16 and remained similar to study end (
Figure 1a).
FACS analysis of pooled samples of the 3 CAW-treated mice in Study 1 demonstrated decreased monocyte (CD74+) expression compared to Placebo-treated mice in spinal cords (15% v 19.7%) but similar expression in pooled brain samples. Conversely, a more favorable activated (CD11bCD45hi) to resting (CD11bCD45lo) microglial profile was noted in CAW-treated brains (16.7%/58.3%) vs Placebo (24.9%/54.1%) but not in CAW-treated spinal cords (51.5%/19.0%) vs Placebo (46.6%/17.7%).
IHC of lumbar spinal cords of 9 CAW-treated mice in Study 2 revealed decreased CD3 counts normalized to total cell counts compared to 10 placebo-treated mice in (2.9% STD 1.6% vs 5.0& STD 1.7%, p=0.01,
Figure 1f,g). Normalized Iba1 counts in lumbar spinal cords among 10 CAW-treated mice demonstrated a trend towards reduced microglial activation but was not significantly different from the 9 placebo mice (3.3% STD 2.8% vs 5.2% STD 5.1%, p=0.30,
Figure 1h,i). There was no qualitative difference in myelination between mice treated with CAW or placebo (
Figure 1j,k).
3.3. Behavioral performance
Overall, CAW did not impact behavioral performance in Study 1 including Distance Moved, Center Duration, and Latency to First Center Entry. In Study 2, Center Duration times on day 12 (early symptomatic) were longer in CAW-treated mice (ANOVA
F[2,27]=5.229,
p=0.012; Tukey’s post-hoc: p=0.014 CAW vs placebo, 0.050 CAW vs control) a finding not seen at study end (
Figure 1c). There was an effect of group on Distance Moved at study end (ANOVA
F[2,27]=3.433,
p=0.047), however this was driven by EAE (
Figure 1d). Tukey’s post-hoc pairwise comparisons did not reach significance for control vs CAW (p=0.064) or control vs placebo (p=0.097). There were no effects of group for Latency to First Center Entry and Center Frequency.
3.4. ARE gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity
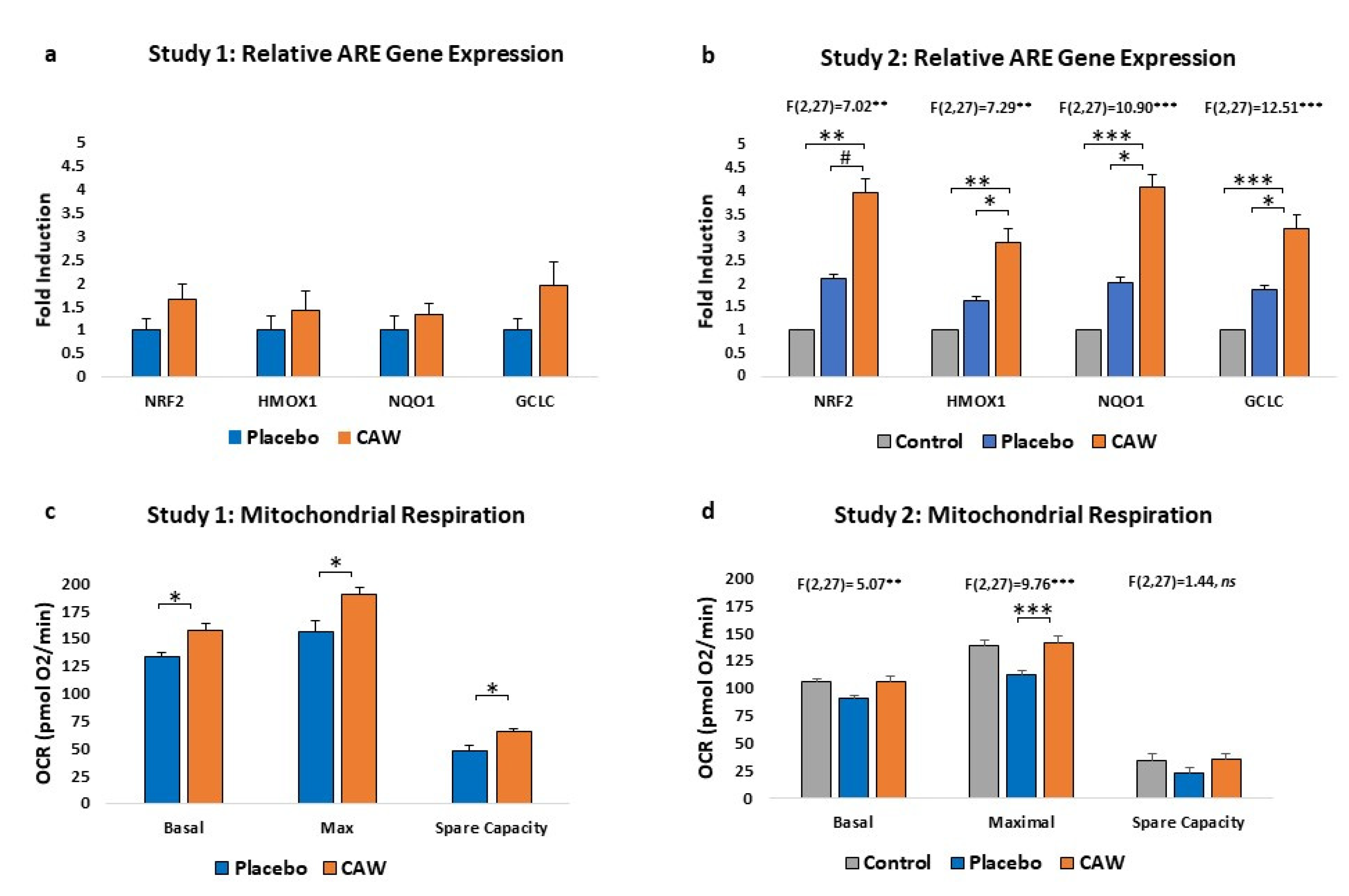
CAW-treated mice demonstrated a non-significant trend towards increased ARE gene expression in cerebral cortex over placebo-treated mice (n=4 per group) in Study 1. However, in Study 2, ARE gene expression was significantly impacted by treatment group, elevated compared to both placebo-treated animals and healthy controls (n=10 per group,
Figure 2a and 2b). Notably, placebo gene expression was greater than control reflecting the expected increase in ARE expression as a response to EAE.
CAW-treated mice also demonstrated significantly greater cortical mitochondrial respiratory activity than placebo-treated animals in Study 1 across the study profile (F(1,2)=42.64, p<0.001) and between study endpoints (
Figure 2c). Mitochondrial respiratory activity was also significantly influenced by group in Study 2 (F[2,27]=3.601, p=0.041), with Tukey’s post-hoc CAW vs placebo nearing significance (p=0.065). Oxygen consumption rates in CAW-treated animals were restored to those of healthy control mice (
Figure 2d).
4. Discussion
In two independent studies, we found that treatment with CAW, a water extract of the botanical Centella asiatica significantly increased ARE gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity, and reduced inflammation in the spinal cords in EAE mice. The effects of CAW specifically on microglial activation were equivocal, and, besides reduced measures of anxiety on day 12, there were no effects on behavioral performance or clinical disability or demyelination.
The increases in ARE gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity in our studies are consistent with those found in dementia and aging mouse models. CAW-induced increases in ARE gene expression were observed in frontal cortex and hippocampi of 5xFAD Aβ-amyloid mice, and in 18-month (old) C57BL/6J mice [
11]. Interestingly, while young (6 week) C57BL/6J mice treated with CAW also increased ARE gene expression, cognitive improvements were primarily observed in the old mice suggesting compensatory mechanisms in younger animals [
9]. Mitochondrial respiratory activity improved in 5xFAD mice but not in WT suggesting a ceiling effect for this biomarker [
11]. Indeed, CAW-treated EAE mice in our Study 2 demonstrated restoration that met, but did not exceed, the bioenergetic profile of control mice.
Conclusions regarding CAW effects on neuroinflammation and microglial activation based on our study are limited due to the different evaluation methods used in Studies 1 and 2, and other factors. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are postulated to be both a cause and result of inappropriate microglial activation in MS, although tissue damage caused by EAE inflammation limits evaluation of these pathologies [
22]. Newer models may circumvent this issue and could be considered for future evaluations of CAW in EAE [
23].
The lack of behavioral changes, aside from reduced measures of anxiety on day 12, in response to CAW in our studies has several possible explanations. While the EAE model of MS is reported to display behavioral alterations, a common concern is that EAE motor disability obstructs assessment of behavioral performance [
24]. However, given that, aside from 1 measure, behavioral performance did not differ between early symptomatic and final testing, motor weakness is less likely to have confounded our results. Other explanations include the relatively young age of mice tested as discussed above, the choice of the behavioral tests, the short treatment duration, and a small sample size. Finally, it’s possible that CAW does not affect behavioral performance in EAE which may be attributed to differences in pathologies between different disease models.
Limitations of this study were the different designs of Studies 1 and 2 preventing combining data for analyses. Cognition was not assessed in this study which precludes conclusions about CAW effects on EAE cognition and comparison with other disease model results. Other limitations of behavioral testing and evaluation of neuroinflammation were discussed previously.
In conclusion, the EAE model of MS repeats the CAW-induced increases in ARE gene expression and mitochondrial respiratory activity seen in aging and dementia models. Further exploration will determine the clinical correlates to the striking improvements in these potential MS biomarkers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.; methodology, N.G, J.R, A.V., A.S. and L.S.S.; formal analysis, P.K., K.Y. and N.E.G.; investigation, P.K., K.Y., A.H., M.S.B., J.A.Z., C.J.N., S.H., K.K., S.M. and H.O.; data curation, C.W..; writing—original draft preparation, R.S. and C.W.; writing—review and editing, A.V., A.S., L.S.S., J.R., N.E.G. and R.I.S.; visualization, P.K., K.Y., C.W. and N.E.G.; project administration, C.W.; funding acquisition, R.I.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National MS Society, grant number CA 1073-A-4. Additional support was provided by the Department of Veterans Affairs (R.I.S.), NIH P51 OD011092 (L.S.S), National MS Society RG-1702-27047 (K.Y.), T32 AG055378 (P.K.), T32 ES007060 (P.K.), RF1 AG059088 (J.R.), R21 AG065914 (J.R.), R21 AG079158-01A1 (J.R.), National MS Society RG-2206-39711 (J.R.), NIH NCCIH U19 AT010829 (A.S., N.E.G., J.R., C.J.N., M.S.B.).
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ashley Headrick for her participation conducting EAE experiments in Study 1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Brissart, H.; Morele, E.; Baumann, C.; Perf, M.L.; Leininger, M.; Taillemite, L.; Dillier, C.; Pittion, S.; Spitz, E.; Debouverie, M. Cognitive impairment among different clinical courses of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Res. 2013, 35, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planche, V.; Gibelin, M.; Cregut, D.; Pereira, B.; Clavelou, P. Cognitive impairment in a population-based study of patients with multiple sclerosis: differences between late relapsing-remitting, secondary progressive and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2016, 23, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmeyer, N.C.; Bürkner, P.C.; Wiendl, H.; Landmeyer, N.C.; Bürkner, P.C.; Wiendl, H. Disease-modifying treatments and cognition in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 94, e2373–e2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupp, L.B.; Christodoulou, C.; Melville, P.; Scherl, W.F.; Pai, L.Y.; Muenz, L.R.; He, D.; Benedict, R.H.; Goodman, A.; Rizvi, S.; et al. Multicenter randomized clinical trial of donepezil for memory impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2011, 76, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsafi, Z.; Tafakhori, A.; Agah, E.; Mojarrad, M.; Dehghani, R.; Ghaffarpour, M.; Aghamollaii, V.; Mousavi, S.V.; Fouladi, Z.; Pourghaz, B.; Balali, P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of memantine for multiple sclerosis-related fatigue: A pilot randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Neurol Sci. 2020, 414, 116844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Costa, S.L.; Moore, N.B.; Costanza, K.; DeLuca, J. The efficacy of speed of processing training for improving processing speed in individuals with multiple sclerosis: a randomized clinical trial. J Neurol. 2022, 269, 3614–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumyanath, A.; Zhong, Y.P.; Henson, E.; Wadsworth, T.; Bishop, J.; Gold, B.G.; Quinn, J.F. Centella asiatica extract improves behavioral deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: Investigation of a possible mechanism of action. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 2012, 381974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, R.; Aminyavari, S.; Hosseini, M.; Hassanzadeh-Taheri, M.; Foadoddini, M.; Saebipour, M.R. The Ameliorative Impact of Centella asiatica on the Working Memory Deficit in Streptozotocin-induced Rat Model of Alzheimer Disease. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2022, 13, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.E.; Harris, C.J.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica modulates antioxidant and mitochondrial pathways and improves cognitive function in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.E.; Sampath, H.; Zweig, J.A.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica Attenuates Amyloid-β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.E.; Zweig, J.A.; Caruso, M.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wright, K.M.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica attenuates hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction and improves memory and executive function in β-amyloid overexpressing mice. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X. Asiaticoside Mitigates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology by Attenuating Inflammation and Enhancing Synaptic Function. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.E.; Alcazar Magana, A.; Lak, P.; Wright, K.M.; Quinn, J.; Stevens, J.F.; Maier, C.S.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica - Phytochemistry and mechanisms of neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement. Phytochem Rev. 2018, 17, 161–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, L.; Simeonidou, C.; Steinberger, G.; Hametner, S.; Grigoriadis, N.; Deretzi, G.; Kovacs, G.G.; Kutzelnigg, A.; Lassmann, H.; Frischer, J.M. Multiple sclerosis deep grey matter: the relation between demyelination, neurodegeneration, inflammation and iron. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014, 85, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Marney, L.; Magana, A.A.; Choi, J.; Wright, K.; Mcferrin, J.; Gray, N.E.; Soumyanath, A.; Stevens, J.F.; Maier, C.S. Quantification of caffeoylquinic acids and triterpenes as targeted bioactive compounds of Centella Asiatica in extracts and formulations by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2023, 4, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbark, A.A.; Meza-Romero, R.; Wiedrick, J.; Gerstner, G.; Seifert, H.; Kent, G.; Piechycna, M.; Benedek, G.; Bucala, R.; Offner, H. “Near Cure” treatment of severe acute EAE in MIF-1-deficient female and male mice with a bifunctional MHCII-derived molecular construct. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 378, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Torres, E.R.S.; Stagaman, K.; Kasschau, K.; Okhovat, M.; Holden, S.; Ward, S.; Nevonen, K.A.; Davis, B.A.; Saito, T.; et al. Integrated analysis of behavioral, epigenetic, and gut microbiome analyses in AppNL-G-F, AppNL-F, and wild type mice. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, G.; Zhang, J.; Bodhankar, S.; Nguyen, H.; Kent, G.; Jordan, K.; Manning, D.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Offner, H. Estrogen induces multiple regulatory B cell subtypes and promotes M2 microglia and neuroprotection during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2016, 293, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, C.W.; Foster, S.C.; Matsumoto, S.G.; Preston, M.A.; Xing, R.; Bebo, B.F.; Banine, F.; Berny-Lang, M.A.; Itakura, A.; McCarty, O.J.; et al. Hyaluronan anchored to activated CD44 on central nervous system vascular endothelial cells promotes lymphocyte extravasation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Biol Chem. 2012, 28, 33237–33251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, C.W.; Foster, S.C.; Itakura, A.; Matsumoto, S.G.; Asari, A.; McCarty, O.J.; Sherman, L.S. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides perturb lymphocyte slow rolling on brain vascular endothelial cells: implications for inflammatory demyelinating disease. Matrix Biol 2013, 32, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Neilson, A.; Swift, A.L.; Moran, R.; Tamagnine, J.; Parslow, D.; Armistead, S.; Lemire, K.; Orrell, J.; Teich, J.; et al. Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link between attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C125–C136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.T.; Wimmer, I.; Höftberger, R.; Gerlach, S.; Haider, L.; Zrzavy, T.; Hametner, S.; Mahad, D.; Binder, C.J.; Krumbholz, M.; et al. Disease-specific molecular events in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain. 2013, 136 Pt 6, 1799–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudler, J.; Ecott, T.; Ivan, D.C.; Bouillet, E.; Walthert, S.; Berve, K.; Dick, T.P.; Engelhardt, B.; Locatelli, G. Autoimmune neuroinflammation triggers mitochondrial oxidation in oligodendrocytes. Glia. 2022, 70, 2045–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharjee, S.; Nayani, N.; Tsutsui, M.; Hill, M.N.; Ousman, S.S.; Pittman, Q.J. Altered cognitive-emotional behavior in early experimental autoimmune encephalitis--cytokine and hormonal correlates. Brain Behav Immun. 2013, 33, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).