1. Introduction
Radiation therapy (RT) is a primary treatment for various cancers, often in combination with surgery or chemotherapy. Classical RT fractionation can stimulate an immune response, however studies suggest that hypofractionated RT can stimulate an even stronger immune response [
1,
2]. Unfortunately, hypofractionation also triggers various immune suppressive signals that can limit the anti-cancer immune response which provide a potential role for use of immune modulators [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Combining radiation with immunotherapy would allow for enhancement of the radiation effect without increasing the radiation dose.
One such immunotherapy option is an immune checkpoint inhibitor. Immune checkpoint therapies have demonstrated dramatic but varied success in the past decade, with programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/associated ligand (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) being the most frequently used and researched [
5,
6]. PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade prevent T-cell suppression, thus potentiating the anti-tumor response. These therapies have demonstrated promise alone and in combination with radiation, but their effects are highly variable [
6,
7]. There is recent evidence that the lack of PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade efficacy can occur through upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints [
8]. Several other immune checkpoints have been recently identified, including VISTA (V-domain Ig Suppressor of T cell Activation) [
9]. VISTA is expressed on hematopoietic and myeloid derived cells, tumor cells, as well as various T cell populations [
10,
11,
12,
13]. The presence of VISTA on both antigen presenting cells and regulatory T cells appears to be most important for limiting cytotoxic T cell activity and function [
14]. VISTA has both receptor and ligand functions that act by suppressing and negatively regulating activation and function of T cells, while also promoting immune suppression through expression on myeloid derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells [
15,
16]. Anti-VISTA has shown immune stimulatory and tumor control promise when used alone, and in combination with anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA4 [
17,
18].
In this study we hypothesize that combining VISTA inhibition with RT will result in an enhanced T-cell mediated apoptosis response and overall improved treatment efficacy in B16F10 melanoma and MC38 adenocarcinoma murine flank tumor models. In separate studies, we utilize VISTA knock-out (KO) mice and anti-VISTA antibodies to achieve VISTA blockade and combined this a single dose of 15 Gy radiation. 15 Gy is a frequently employed dose in radiation research and has been shown to be relevant for the assessment of RT and immune modulation studies. Although several promising combined radiation and immune checkpoint inhibition studies have been published, we believe this to be the first comparison of two VISTA-blockading methods (antibody inhibition and genetic knockout) in combination with RT. Furthermore, this study is unique in its validations used to assess two cancer types previously unexamined in the context of VISTA-enhanced RT.
2. Results
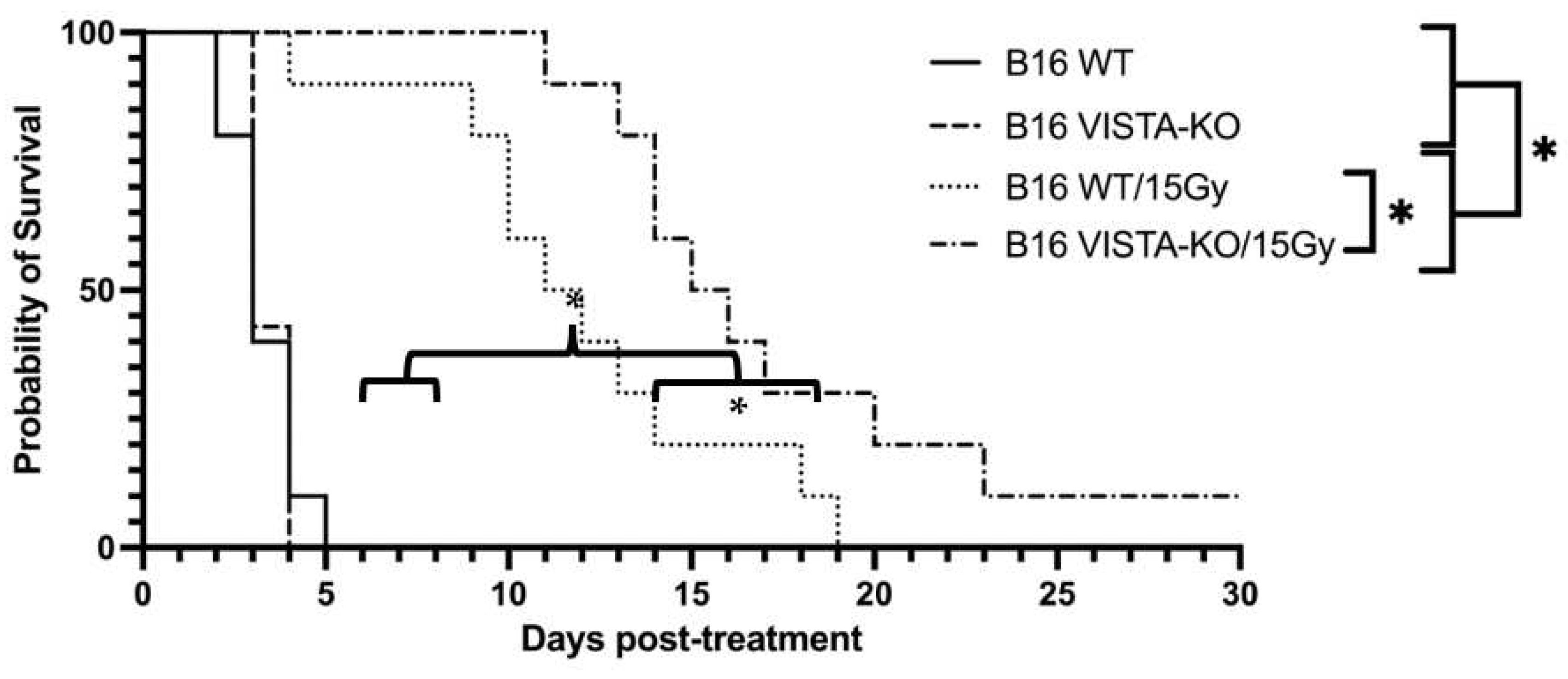
2.1. VISTA-KO + RT leads to improved tumor control in the murine B16F10 flank tumor model
Using the previously described tumor growth endpoint (days to tripling volume), WT and VISTA-KO animals remained on study an average of 3.3 days (SEM=0.3) and 3.43 days (SEM=0.2) respectively. The WT/15Gy and VISTA-KO/15Gy animals remained on study an average of 12 days (SEM=1.39) and 17.5 days (SEM=1.95) respectively. Using a two-way ANOVA, we determined there was no significant difference between the WT and VISTA-KO control cohorts. However, both radiation cohorts were significantly different from controls (p< 0.037). Most importantly, the VISTA-KO/15GY radiation cohort significantly outperformed the WT/15GY radiation cohort (p< 0.02). This data is summarized in
Figure 1.
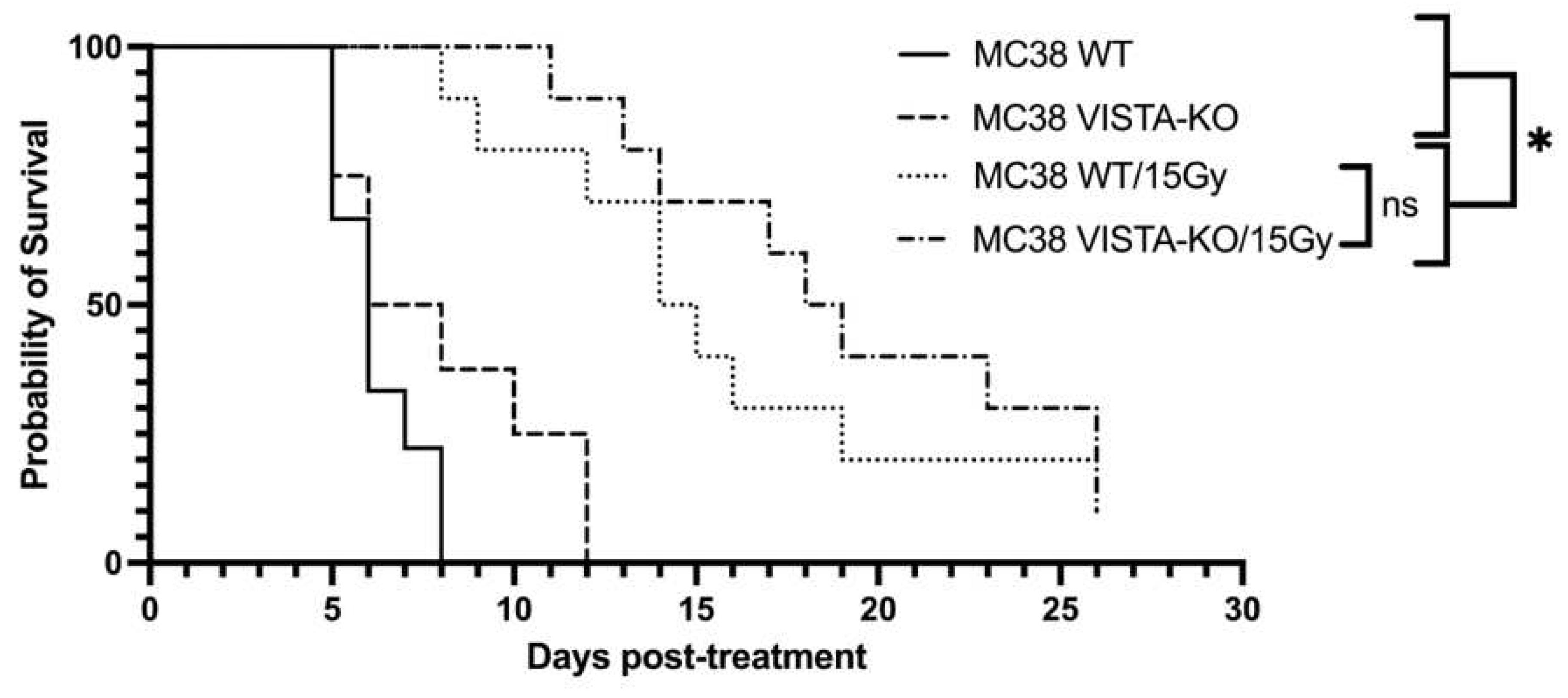
To confirm this effect, we repeated the VISTA-KO study using a murine colon adenocarcinoma MC38 cell line. The Kaplan-Meier treatment efficacy data is shown in
Figure 2. Similar to the B16F10 model, there was no significant difference between the WT and VISTA-KO control arms with average survival of 6.5 days (SEM=0.41) and 8.13 days (SEM=1.06) respectively. Comparatively, the WT/15Gy group remained on study an average of 16 days (SEM=1.93) and the VISTA-KO/15Gy group an average of 19.3 days (SEM=1.8). Although these cohorts are not statistically different a trend toward significance is present. Additionally, tumor growth rates for each treatment were determined to gain a better understanding into the differences and effects between cohorts. As expected, the growth rate of all irradiated tumors was slower than unirradiated control, however there was minimal differences between the WT and KO radiation cohorts. In this model, it appeared that radiation was equally effective at tumor control with or without VISTA KO blockade.
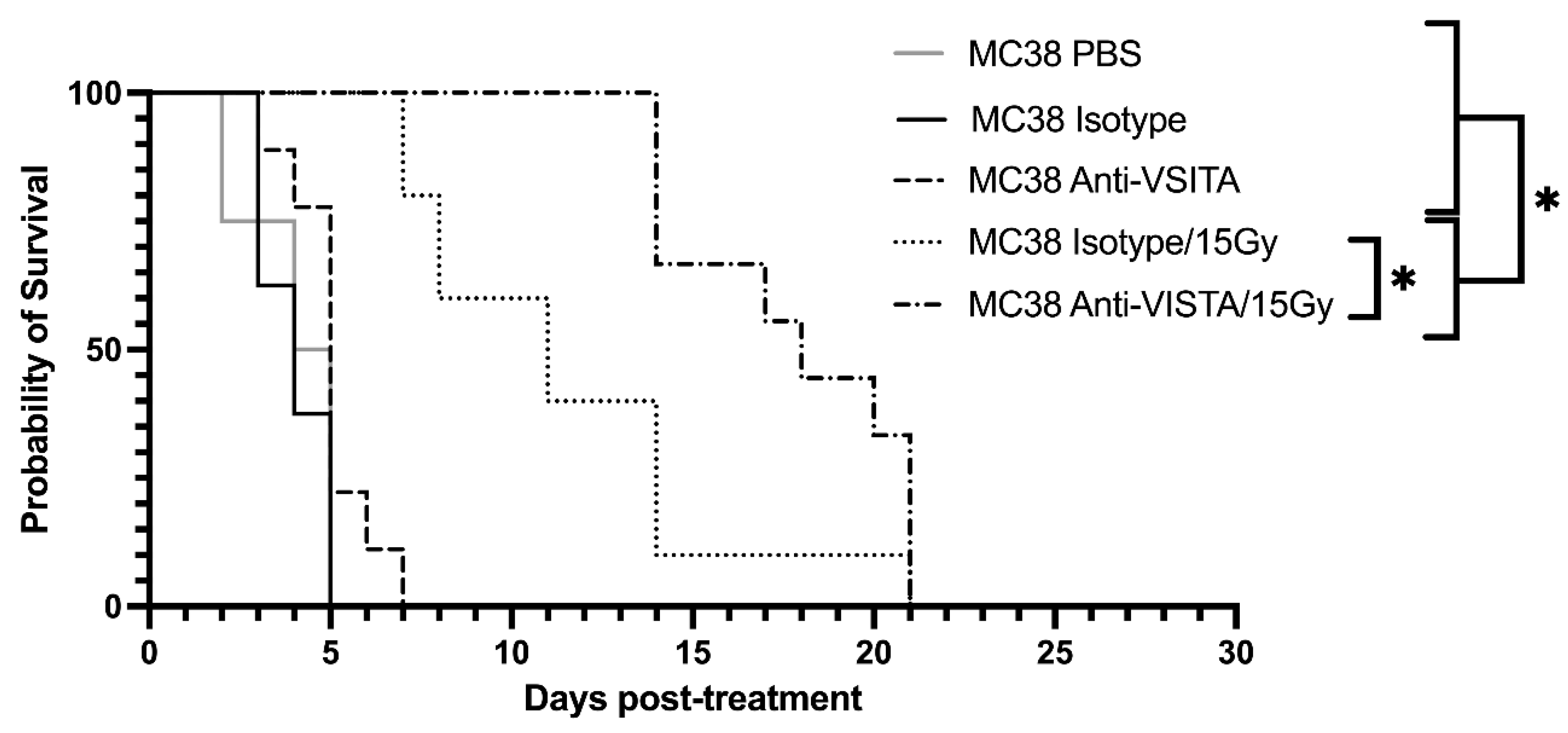
2.2. Anti-VISTA antibody blockade and RT improve tumor control in a B16 melanoma model
Following assessment in VISTA-KO model, a similar study was designed using an anti-VISTA antibody blockade and +/- RT model. PBS, isotype antibody control, and anti-VISTA blockade were used with or without radiation in the B16 melanoma model. Kaplan-Meier data is shown in
Figure 3. The unirradiated PBS, isotype, and VISTA blockade averaged 4 (SEM=0.47), 4 (SEM=0.33), and 5 (SEM=0.37) days on study, respectively. The radiated groups survived significantly longer, with isotype/15Gy and Anti-VISTA/15Gy remaining on study an average of 11.5 days (SEM=1.39) and 17.8 (SEM=1.05) days, respectively. Using a two-way ANOVA of survival, PBS and unirradiated isotype and anti-VISTA cohorts were not statistically different from each other. Both 15 Gy cohorts (isotype and anti-VISTA) survived significantly longer than unirradiated groups (p<0.05). The isotype/15Gy and VISTA blockade/15Gy groups did not differ in survival from each other (p<0.0003).
2.3. Anti-VISTA antibody leads to anti-tumor mRNA expression changes
For the anti-VISTA antibody study, we used NanoString technologies quantification analytics to assess changes in RNA expression in B16 melanoma tumor. Unless otherwise specified, the comparative anti-VISTA genetic changes noted below are compared to an isotype antibody control.
Following anti-VISTA antibody treatment, two genes in the immune cell adhesion/migration and cell signaling/metastasis pathways changed significantly (defined as greater than a 2-fold change and p <0.05): genes Clec4e (C-type lectin domain family 4 member E, cell adhesion molecule) and Ptger4 (Prostaglandin EP4 receptor, T-cell signaling).
When the VISTA blockade was combined with 15 Gy radiation, genes associated with the following pathways were affected: antigen processing & presentation (both MHC I and MHC II), T cell receptor signaling (including CD28, CD3, and CD247), and leukocyte trans-endothelial migration (including ITGAL, ITGB2, ICAM1, VCAM1, and PECAM1). Although many immune and cytotoxic pathways were expressed higher by both radiation groups (anti-VISTA/15Gy and isotype control/15G), several notable genes were enhanced with the addition of anti-VISTA antibody (Ccl2, Cxcl12, Siglec1, and Tnfsf13). Expression level details are presented in
Table 1.
Table 1. Differential Expression. Differential expression data (as average linear fold change) for each treatment cohort, as compared to isotype control for notable genes as mentioned in the text. While anti-VISTA did not change many genes, it did affect Clec4e, Tnsfsf13, Ptger4, and Siglec1 significantly. Additionally, there were several genes that anti-VISTA/15Gy increased more than isotype/15Gy, such as CD247, and FasL.
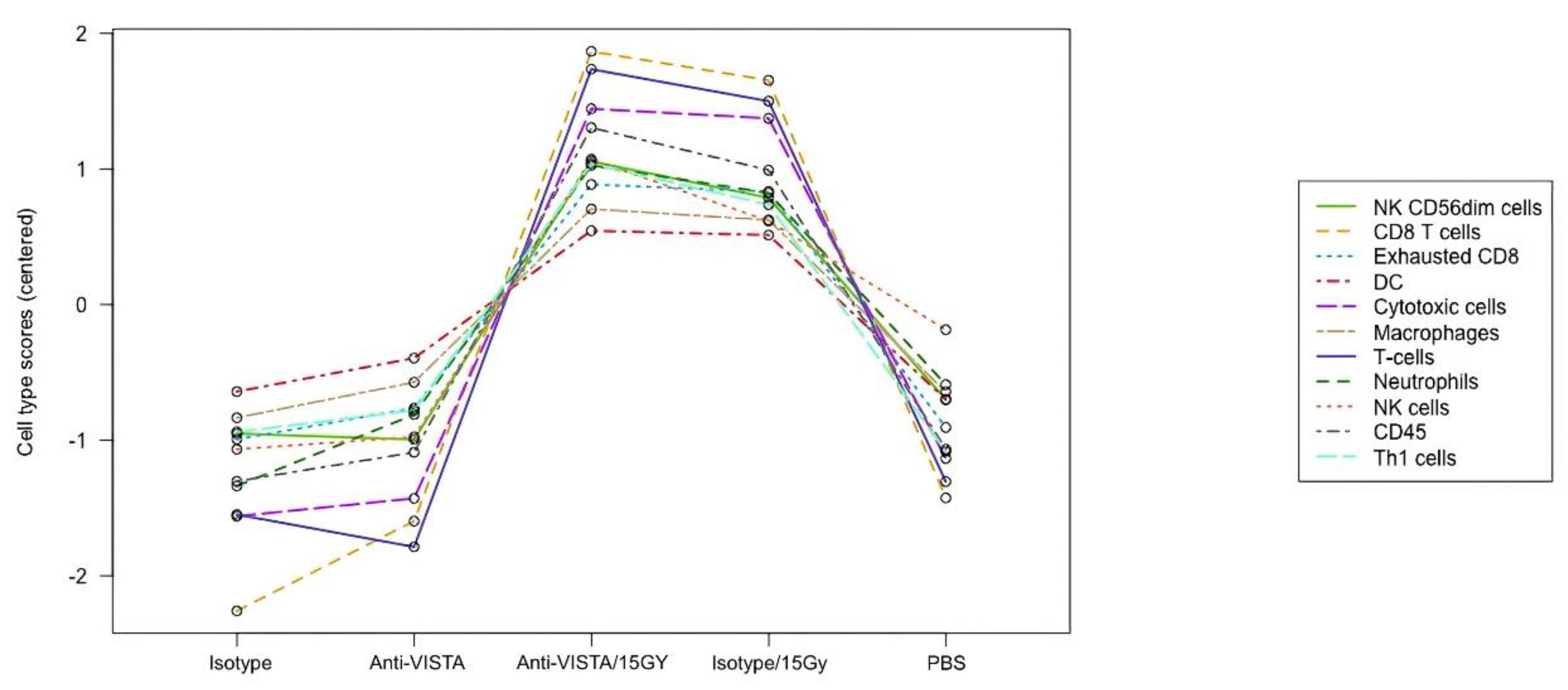
2.4. Immune infiltration based on mRNA expression
The RNA data also demonstrates that VISTA blockade with radiation leads to increased cytotoxic immune cell presence. The NanoString program has a cell type profiling analysis and allows for a qualitative comparison of relative cell abundance in B16 melanoma tumor between different treatment types (
Figure 4). The data suggests a combination of 15 Gy/VISTA blockade leads to a slightly higher tumor level of cytotoxic immune cells such as CD8 T cells and Natural Killer cells, as compared to 15 Gy/isotype control. Additionally, 15 Gy/VISTA blockade demonstrated a higher ratio of functional CD8+ cells to exhausted CD8+ cells.
3. Discussion
Radiation therapy (RT) is an effective cancer therapy. However, due to a variety of patient and normal tissue complications and its stimulation of both pro- and anti-tumor signaling, it is often not curative. Immune checkpoints are among the pro-tumor signals associated with RT. For this reason, we evaluated whether combining radiation with the anti-VISTA checkpoint inhibitor could enhance the therapeutic effect of RT. To assess this hypothesis, flank tumors were grown in mice using two well studied syngenetic murine tumor lines (B16F10 and MC38), and VISTA blockade was achieved using either the genetically modified VISTA-KO mice or anti-VISTA antibody in WT mice.
The VISTA-KO and anti-VISTA blockade experiments resulted in strong evidence that RT efficacy can be significantly enhanced by eliminating or blocking VISTA. The studies also suggest that the blockade of VISTA enhances the anti-tumor effect of radiation in a synergistic manner. If the effect were additive rather than synergistic, there would be a marked difference in the cohorts without radiation. The single dose of radiation combined with a systemic administration of VISTA antibody blockade demonstrated a significant enhancement in tumor control, indicating that VISTA blockade can be used safely and effectively.
Although the mechanism underlying the enhancement of RT by VISTA blockade is being investigated, our mRNA and immune infiltration data strongly suggests that the enhancement is associated with cell-mediated apoptosis. For the VISTA antibody blockade alone, the most impressive mRNA changes were Clec4e, and Ptger4. The function of Clec4e has been debated, with respect to its pro-inflammatory/immune and immune regulatory functions [
22,
23]. Its role could either support pro-immune activation through the innate pathway, or it could indicate new pathways of immune regulation following a VISTA block. This evasion characteristic has been seen with other immune checkpoint inhibitors, as reported in previous studies [
9,
24]. On the other hand, Ptger4, a subtype of the prostaglandin E receptor, has been shown to be involved in the metastasis pathway. Studies utilizing antagonists and KO models have demonstrated a decrease in metastatic potential and decreased tumor growth [
25,
26]. This suggests that a decrease in Ptger4 following VISTA blockade could result in a longer-term anti-tumor effect. As expected, the combination of VISTA blockade with radiation stimulated many mRNA expressions changes in various immune and cytotoxic pathways. There were several notable trends and differences between the two radiation cohorts that could indicate an enhanced effect at the genetic or immune cell infiltration level. CD247 and CD3 had higher expression changes with the addition of VISTA antibody blockade to RT than did the isotype control, indicating increased T cell stimulation and activation. Additionally, cytotoxic genes, such as Fas Ligand and Granzyme B, had higher expression changes, further implicating immune cell mediated cytotoxicity.
Together, these mRNA changes provide evidence that VISTA blockade, especially with 15 Gy radiation, is capable of initiating significant anti-tumor genetic change. It is worth noting that anti-VISTA antibody, as well as other checkpoint inhibitors, act at the protein level to prevent the immune checkpoint/regulatory function associated with VISTA. Any changes would seem to indicate that the treatment had enough effect on a cell structure or process that translated to alteration of RNA expression levels.
The assessment of tumor immune cell infiltration through mRNA expression of characteristic genes demonstrated several potentially important anti-tumor signals. One important example is that VISTA blockade alone or combined with radiation led to increased tumor cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. In addition, there was an enhanced ratio of CD8 T cells to exhausted T cells, indicating an enhanced cytotoxic immune presence within the tumor. This finding further supports an increase in immune mediated apoptosis, and better overall tumor control.
In our study, radiation therapy alone showed significant tumor control for all study models. However, as expected, the response to radiation was tumor-model specific, with MC38 tumors being slightly more resistant to radiation. However, VISTA blockade significantly improved survival in irradiated groups across both B16 and MC38 tumor models.
An interesting feature of the VISTA/radiation treatment is the heterogeneity of the individual response. In our study, we saw evidence that some animals who received VISTA blockade and RT showed a marked tumor control response, whereas others showed a lesser or minimal response. This distinction between “responders” and “non-responders” is characteristic of existing immune therapies and is observed with VISTA blockade as well. We therefore hypothesize that the treatment combination may be especially beneficial to responders compared to non-responders. As such, the identification of responders at early stage of cancer may dramatically improve the outcome.
In conclusion, these experiments have demonstrated VISTA blockade significantly enhances the therapeutic effect of radiation in two murine tumor models. Although many mechanistic and confirmatory concepts remain to be determined and proven, this foundational study demonstrates the VISTA enhancement of RT is through increased immune mediated pathways, such as T-cell induced apoptosis.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Flank Tumor models
In this study, we grew flank tumors in mice using two different cell lines, B16F10 murine melanoma and MC38 murine colon adenocarcinoma, obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) in Manassas, VA. The B16F10 cells were cultured in RPMI media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, and 1% antibiotics until inoculation. The MC38 cells were cultured in DMEM media with 10% fetal bovine serum, and 1% antibiotics until inoculation. For VISTA knock out (KO) experiments, tumors were implanted in male C57BL/6 WT and C57BL/6 VISTA-KO mice. For the anti-VISTA antibody experiments tumors were implanted in female WT C57BL/6 mice. Knock out mice and anti-VISTA antibody were acquired from Dr. Noelle’s laboratory at the Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine and Immunext Corp, and wild type mice were acquired from Charles River Corp (Wilmington, MA).
Tumors were implanted by injecting B16F10 cells or MC38 cells (2 x 106) intradermally into the right flank. Radiation and immunotherapy treatments were initiated when a tumor reached 110 (+/-20) mm3. Mice were randomly placed in treatment groups, and tumors were measured daily by investigators blinded to treatment condition. Tumor length (l), width (w), and depth (d) were measured using calipers and tumor volume calculation followed the common ellipsoid approach where:
Experimental VISTA-KO groups consisted of both B16 and MC38 tumor models and included: WT control, KO control, WT/15Gy, and VISTA-KO/15Gy. Experimental antibody groups consisted of only the B16 tumor model and included: PBS control, isotype control, anti-VISTA antibody, isotype/15Gy, and anti-VISTA/15Gy.
4.2. RT Delivery
Following a computerized treatment and delivery plan, a Varian 2100 CD Linear Accelerator was used to deliver a uniform 6 MeV tumor dose of 15 Gy (SSD=100 cm). The treatment encompassed the entire tumor and a 2 mm peritumor region. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane for treatment and positioned using conventional radiation oncology laser beam location techniques.
4.3. Isotype control antibody & anti-VISTA antibody
The isotype control antibody (PIP monoclonal antibody, inVivoMAB Armenian hamster IgG isotype control, anti-glutathione S-transferase) was acquired from Bxcell (BE0260). This control antibody was selected due to the absence of glutathione S-transferase expression in mammals. Both isotype control antibody and anti-VISTA antibody (13F3, Immunext Corp., USA) treatments were given 3 times on consecutive days at 300ug/dose (diluted in PBS, injected in 300uL IP). Antibody injection began immediately after a 15Gy radiation dose was delivered.
4.4. In Vivo Endpoints
Two cohorts of mice were used for each treatment group, with the first being sacrificed at 6 days post-treatment for mRNA analysis (n=5). The second group was sacrificed when the tumor reached 3 times its treatment volume for assessment of tumor growth delay (n=8-10). Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed with “survival” values calculated using time to tumor volume tripling.
4.5. RNA collection and analysis
RNA isolation was performed using the Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit. Normalized RNA samples were prepared, followed by mRNA expression quantification using the NanoString PanCancer IO 360 (murine) panel. This panel includes genes involved in the tumor biology, the tumor microenvironment, and the immune response. Expression values were then analyzed with nSolver Analysis software (v. 4.0) and Advanced Analysis Software (v. 2.0).
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Genetic/RNA (NanoString) assessment with nSolver Advanced Analysis utilizes XQuartz and R statistical software. ANOVA (in MATLAB) was used to analyze the Kaplan-Meier survival curve and tumor growth. Tumor growth data are displayed on a log scale and were fit with a mixed model, with p-value reported [
19,
20]. This advanced methodology accounts for the heterogeneity of individual response to treatment with the rate of tumor growth as the endpoint of the treatment effect. Unlike the traditional mean +/-SEM display, we show individual growth curves that allows assessment of the individual treatment response. Additionally, synergy was tested to determine if the survival/tumor growth for two treatments act antagonistically or synergistically [
21].
Funding
This research was supported by the Dartmouth Cancer Center CCSG: 5P30CA023108-37(Irradiation and Imaging Shared Resource, Genetic Shared Resource, Pathology Shared Resource). NIH/NCI grant: U01CA260446.
Acknowledgments
Radiation resources were provided by Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Department of Radiation Oncology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yoshimoto, Y.; Kono, K.; Suzuki, Y. YANTI-TUMORIMMUNERESPONSESINDUCEDBYRADIOTHERAPY : AREVIEWANTI-TUMORIMMUNERESPONSESINDUCEDBYRADIOTHERAPYFukushima. J. Med Sci. 2015, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Simon, S.S.; Moody, T.D.; Garnett-Benson, C. Immunomodulatory effects of radiation: What is next for cancer therapy? Future Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.J. Awakening the immune system with radiation: Optimal dose and fractionation. Cancer Lett. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, I.; Grosu, A.L.; Niedermann, G.; Duda, D.G. Immune modulation by hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy: Therapeutic implications. Radiother Oncol. 2016, 120, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basudan, A.M. The Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Clin Pract. 2022, 13, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaab, H.O. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S. Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElTanbouly, M.A.; Zhao, Y.; Schaafsma, E.; et al. VISTA: A Target to Manage the Innate Cytokine Storm. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 595950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lines, J.L. VISTA is an immune checkpoint molecule for human T cells. Cancer Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. VISTA, a novel mouse Ig superfamily ligand that negatively regulates T cell responses. J Exp Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lines, J.L.; Sempere, L.F.; Broughton, T.; Wang, L.; Noelle, R. VISTA Is a Novel Broad-Spectrum Negative Checkpoint Regulator for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulati, K. VISTA expressed in tumour cells regulates T cell function. Br J Cancer. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mercier, I. VISTA regulates the development of protective antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.; Sim, D.Y.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Immune functions as a ligand or a receptor, cancer prognosis potential, clinical implication of VISTA in cancer immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, E.C. Immunoregulatory functions of VISTA. Immunol Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y. Differential contribution of three immune checkpoint (VISTA, CTLA-4, PD-1) pathways to antitumor responses against squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.S. Immune-checkpoint proteins VISTA and PD-1 nonredundantly regulate murine T-cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, E. Three endpoints of in vivo tumour radiobiology and their statistical estimation. Int J Radiat Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, E. Mixed models: Theory and applications with R: Second edition. Mixed Models: Theory and Applications with R 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, E.; Miller, T.W. Statistical determination of synergy based on Bliss definition of drugs independence. PLoS One. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, M.; Saenz, J.; Chiffoleau, E. C-Type Lectin-Like Receptors: Head or Tail in Cell Death Immunity. Frontiers in Immunology 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patin, E.C.; Orr, S.J.; Schaible, U.E. Macrophage inducible C-type lectin as a multifunctional player in immunity. Frontiers in Immunology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; et al. VISTA is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that is increased after ipilimumab therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, M.; et al. Direct melanoma cell contact induces stromal cell autocrine prostaglandin E2-EP4 receptor signaling that drives tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simper, M.S.; et al. The tumor promoting activity of the EP4 receptor for prostaglandin E2 in murine skin. Mol. Oncol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).