1. Introduction
The chemical components of groundwater are an important part of the hydrogeochemical cycle and are closely related to the surrounding environment[
1], while the changes in the chemical environment of groundwater are closely associated with the ecological stability and water safety[
1,
2,
3]. The research on the chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater is helpful to understand the change process of the groundwater environment and facilitate the scientific and rational protection and development of groundwater resources[
4,
5]. Therefore, exploring the chemical characteristics of groundwater and its controlling factors can not only reveal the influence of various factors on groundwater but also have great significance for the development and utilization of groundwater resources, ecological environment protection, and the construction of ecological civilization .
The chemical characteristics of groundwater are affected by natural factors such as precipitation, evaporation, surface water, and sedimentary environment, as well as human factors such as pollution and mining, which are the product of long-term interaction between groundwater and the surrounding environment[
4,
5]. Scholars have used mathematical statistics, Piper three-line diagram, Gibbs diagram, ion proportional coefficient method, correlation analysis and other analytical methods to study the hydrochemical characteristics of major watersheds in the world and their relationship with regional hydrogeology and rainfall climate conditions, revealing Its formation process and evolution model[
6,
7].
Hainan Island has been conducted as a pilot ecological civilization zone and a pilot free trade zone, and under such a context, the demand for water resources for socio-economic development is increasing, and groundwater supply is becoming more and more important[
8,
9]. The lower reaches of the Changhua River are located in the southwest of Hainan Island,,Shallow groundwater in the lower reaches of the Changhua River is an important source of drinking, agricultural irrigation, and industrial water for residents living at both sides of the river, and it is also an important guarantee for the sustainable development of ecological environment. However, affected by a series of factors such as human activities, climate change, and seawater intrusion, the groundwater environment in this area is facing severe challenges[
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. At the same time, groundwater also reacts chemically with rocks, which leads to great changes in the chemical composition of the water, showing different characteristics[
15]. All of these problems have led to the urgent need to identify the groundwater quality problems, in order to effectively serve the ecological green development of Hainan Island. Therefore, this study comprehensively investigates the chemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the lower reaches of the Changhua River, its formation mechanism, dynamic changes, influencing factors, and solute sources through hydrogeological surveys, water sampling, hydrochemical analysis, and multivariate statistics in the study area. This study aims to provide scientific reference for the protection and rational development of groundwater resources in the lower reaches of the Changhua River[
8].
2. Study Area
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
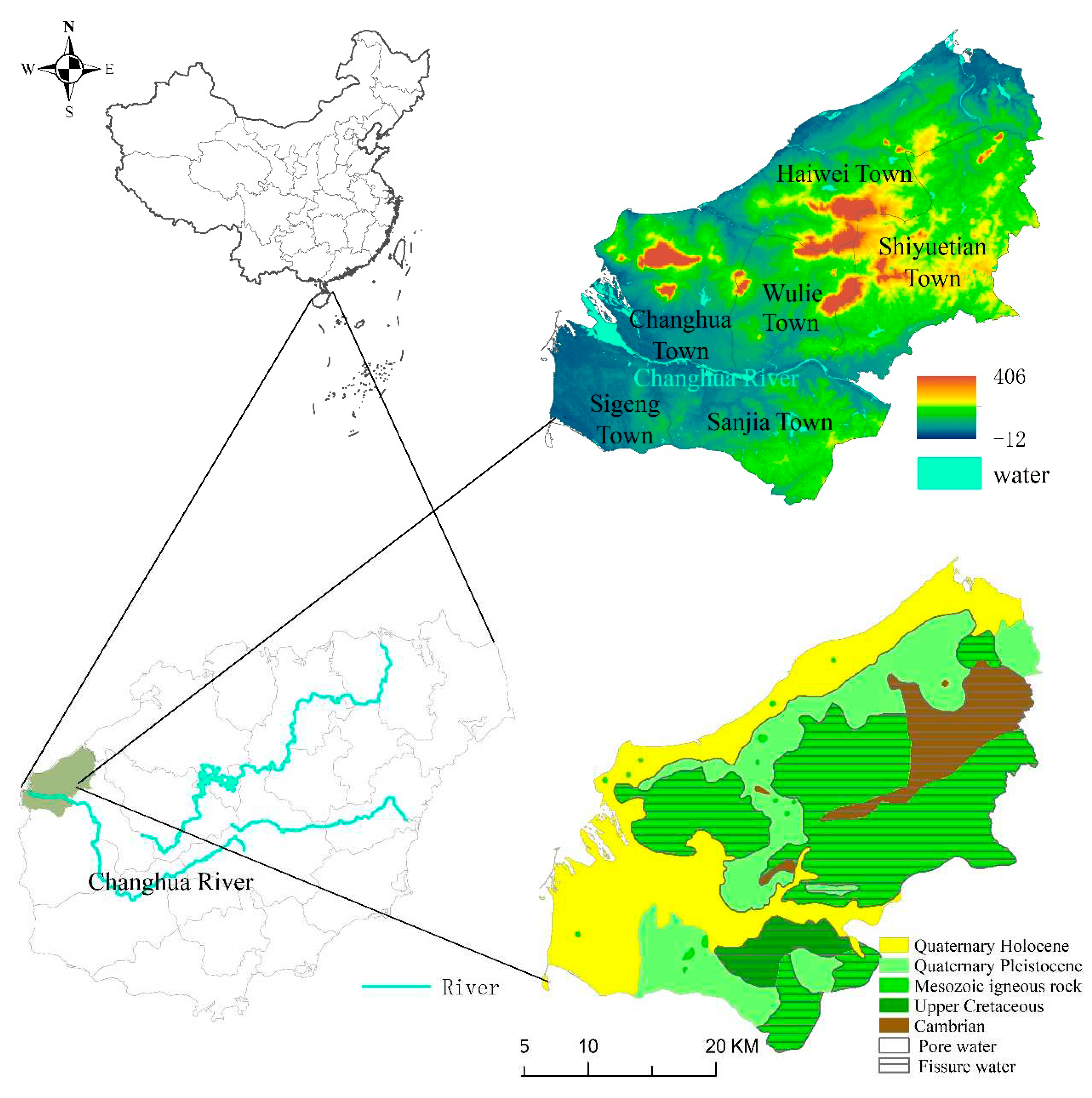
The study area is located in the southwest of Hainan Island, China, and its administrative division covers six towns including Sigeng, Changhua, Haiwei, Shiyuetian, Wulie, and Sanjia. The geographic coordinates are 108°37′~108°59' E and 19°9′~19°30′ N,about 900 km
2.The study area has abundant water resources. The region experiences a distinct tropical monsoon climate. Rainfall distribution is uneven, with more rainfall in the mountainous areas than coastal areas[
16,
17]. The average annual rainfall is 1150mm. There are evident dry and wet seasons throughout the year, with the wet season occurring from May to October, during which rainfall can account for 70%~90% of the annual total. There is a significant spatial variation in evaporation within the region, increasing from the foothills to the coastal areas, with an average annual evaporation of about 2419mm. Additionally, this area is a major production region for tropical cash crops on Hainan Island, which leads to significant water consumption[
16,
17].
2.2. Hydrogeological Conditions of the Study Area
According to
Figure 1, the groundwater in the study area is divided into two main categories: Quaternary loose rock pore water and bedrock fissure water. The loose rock aquifer is primarily distributed in the coastal accumulation layers, river alluvial-proluvial layers, and piedmont denudation accumulation layers. The coastal accumulation layers include sand bar terraces and sea terraces. In the sand bar terraces, the thickness of the rock layers is generally within 20m, and the aquifer thickness is usually 5-15m[
18]. The lithology consists mainly of fine and medium sand with shells, pebbly sandy loam, medium coarse sand, and sandy gravel. The burial depth of water level is generally less than 2m, with a good water abundance. The sea terraces have an aquifer thickness ranging from 2 to 12m. The river alluvial-proluvial terraces are distributed on both sides of the river, and the lithology of the aquifer mainly consists of pebbly sandy loam, pebbly medium coarse sand, medium coarse sand, and sandy gravel. From the outer edge to the inner edge of the terrace, the aquifer thickness increases, sorting becomes better, and the water abundance is improved[
19,
20]. The bedrock fissure water is mainly distributed in the Changhua Daling and Sanjialing mountainous areas, and its water abundance is relatively poor. Atmospheric precipitation is the main recharge source for groundwater in the study area. Due to the loose formation lithology and good permeability, irrigation water is also an important recharge source in some areas. Groundwater runoff and discharge are controlled by the topography. The coastal sand bar terraces and the piedmont alluvial layers have a loose lithology and a certain slope, leading to favorable conditions for groundwater runoff and discharge. However, the river terraces and sea terraces have very small hydraulic gradients, resulting in relatively poor conditions for groundwater runoff and discharge. Groundwater discharge mainly occurs in low-lying areas such as gully or at the edges of terraces, where it is released in the form of springs or sheet flows, eventually flowing into gulley or the sea. In the coastal plain areas, the groundwater level is shallow, and the evaporation is intense, with annual evaporation exceeding rainfall, making evaporation one of the ways for groundwater discharge. In the piedmont areas, the groundwater level is generally higher than the confined water level, and the groundwater laterally recharges the confined water[
19,
20].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
To investigate the hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of the lower Changhua River basin in Hainan Island, this study takes into account the hydrogeological conditions, geological and geomorphic features, as well as land use types in this area. The groundwater samples that can to the greatest extent represent the groundwater characteristics of the lower Changhua River basin in Hainan Island were collected. A total of 100 groundwater samples were collected, including 51 pore groundwater samples and 49 fissure groundwater samples, at the well depths ranging from 5m to 120m. The distribution of sampling points is shown in
Figure 2.
Groundwater samples were collected using water pumps. For actively used groundwater wells, samples were directly collected. However, for abandoned or long-unused domestic wells, they were first cleaned before sampling. Additionally, water samples with turbidity greater than 3NTU were filtered using a 0.45-micron membrane filter. All samples were stored at a low temperature (4°C) and sent to the laboratory for analysis. During the sampling process, detailed data such as coordinates, well depth, and water level were recorded. The collection of samples was conducted under the guidance of experienced laboratory professionals. Before collecting samples, the sample bottles were soaked in dilute nitric acid and then rinsed with deionized water to ensure cleanliness. The sampling process involved rinsing the sample bottles 2-3 times with water samples before filling them with groundwater.
3.2. Sample and Data Processing
In this study, we selected various water sample parameters for analysis, including pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), total dissolved solids (TDS), total hardness (TH), Na
+, K
+, Ca
2+, Mg
2+,
,
, Cl
-,
, etc. The analysis of K
+, Na
+, Ca
2+, and Mg
2+ was conducted using a flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
, Cl
-, and
were measured using an ion chromatograph. TDS was determined by a drying-weighing method, while the
parameter was analyzed through titration. COD (chemical oxygen demand) was measured using a rapid closed-catalytic digestion method, and TH was determined by EDTA titration. The quality control for water sample testing was achieved by means of blank samples, parallel samples, and standard addition samples. The proportion of blank and parallel samples in each batch was 10%~30%, and all blank samples showed no detection, while the parallel samples were within the acceptable range. The recovery rates of standard addition samples were between 86%~113%, which fell within the acceptable range of 80%~120%. The detection limits for each component are listed in
Table 1.
The data processing utilized Origin software for descriptive statistical analysis of the groundwater analysis data in the study area, including mean value, median value, standard deviation, minimum value, maximum value, and coefficient of variation. SPSS was used to analyze the groundwater chemical data with multivariate statistics. ArcGIS software was used to carry out spatial interpolation to investigate the spatial characteristics of the major ions in the shallow groundwater downstream of the Changhua River. Furthermore, the Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram, end-member diagram, and ion ratio diagram were plotted to analyze the chemical characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater in the study area.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Statistical Characteristics of the Main Chemical Indicators of Water
From
Table 2, the overall groundwater pH in the study area ranged from 6.6 to 8.0, indicating its near-neutral to weakly alkaline characteristics. DO ranged between 2.52-7.22mg/L and ORP ranged between 33.5-101.60mV, with the mean values of 3.64mg/L and 71.83mV, respectively, indicating that the groundwater in the study area was generally in an oxidizing environment. The median value of TDS was 281.50mg/L, with a range of 40-958mg/L, indicating that the groundwater in the study area was freshwater and might not have suffered from the impact of seawater intrusion. The TH ranged between 0.22-4.87mmol/L, and the mean value was 1.66mmol/L. The median values of macro cations in the groundwater in the study area were ranked as Ca
2+>Na
+>Mg
2+>K
+, and the median values of macro anions were ranked as
>Cl
->
>
. Among them, the relatively large coefficients of variation for Ca
2+, Mg
2+,
, and
indicated that these four ions have stronger spatial dispersion. It is important to note that
has become a macroscopic component exceeding
in most of the sampling groundwater, indicating that human activities in the study area have a greater impact on groundwater[
21,
22].
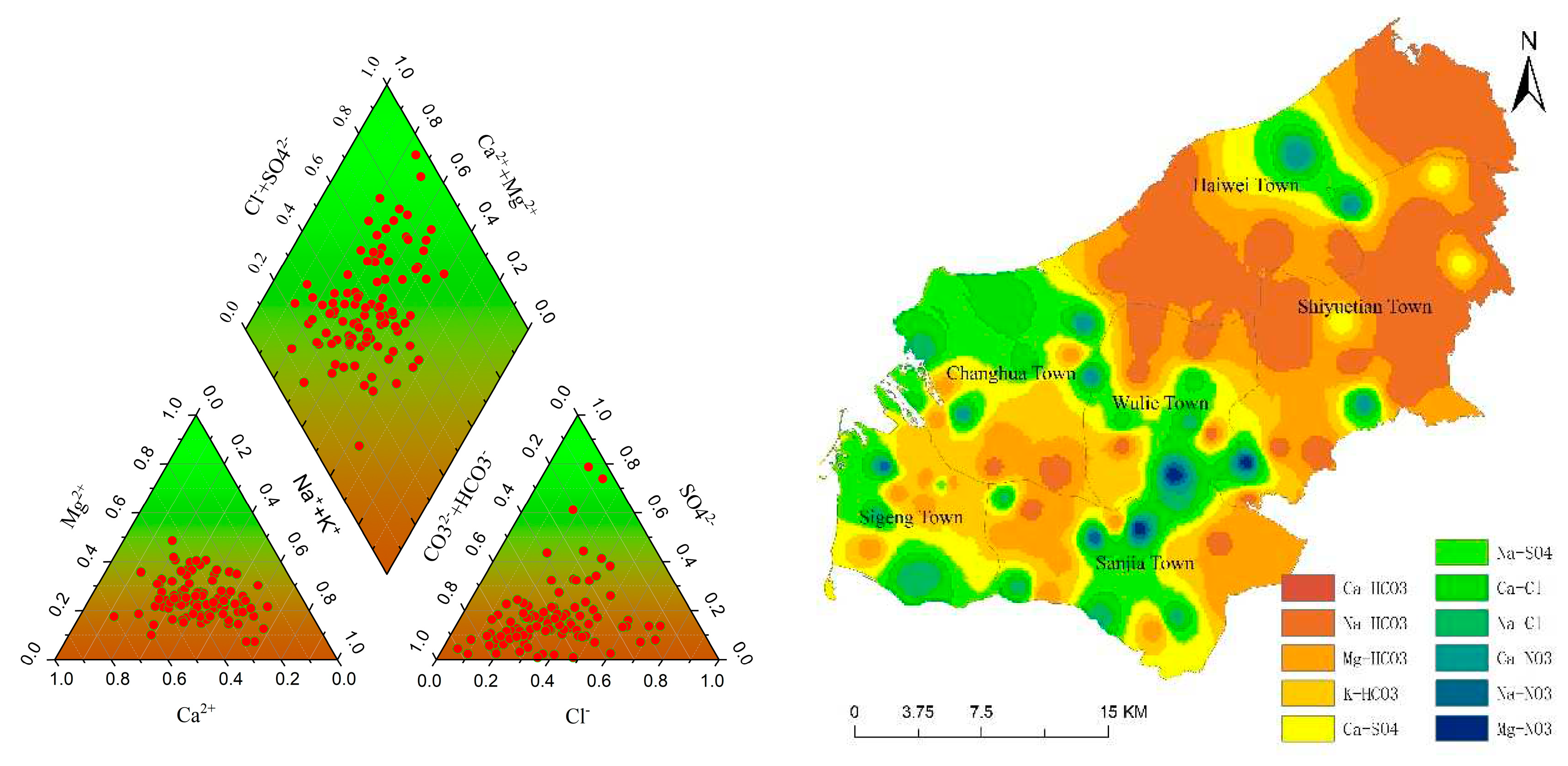
4.2. Chemical Types of Groundwater
The chemical conditions of the groundwater in the study area are complex, with as many as 56 chemical types of groundwater. The Ca•Na-HCO
3 type of water accounted for the largest share of 10%, followed by the Ca-HCO
3 and Na•Ca-HCO
3•Cl types, both accounting for 7%, while the remaining 53 chemical types all accounted for less than 5%. By grouping and simplifying the chemical types and retaining only one of the most dominant cations and anions, the groundwater chemical types were simplified from 56 to 11[
23]. Among them, the Ca-HCO
3 type water dominated with 37%, followed by the Na-HCO
3 type water (21%) and the Na-Cl type water (11%), respectively, and the remaining 8 chemical types were all within 10%. It is worth mentioning that the NO
3 type water accounted for 11%, indicating a more pronounced influence by human activities[
24].
Figure 3.
Chemical types and spatial distribution of groundwater in the study area.
Figure 3.
Chemical types and spatial distribution of groundwater in the study area.
In the study area, the HCO
3 type water accounted for over 60% of the total area and was mainly distributed in Haiwei Town, Shiyuetian Town, and the adjacent area of Changhua, Sigeng, Sanjia Towns. The SO
4 type water ranked the second, accounting for approximately 20% of the area. It was primarily distributed in the northern part of Changhua Town, the adjacent area of Wulie, Sanjia, Shiyuetian Towns, the western and southern parts of Sigeng Town, and the central-eastern part of Haiwei Town. The Cl type water and NO
3 type water each accounted for less than 10% of the area. Specifically, the NO
3 type water was mainly distributed in the urban areas adjacent to Wulie, Sanjia, and Shiyuetian Towns, indicating a close correlation with human activities, such as urbanization, in the study area[
3,
25].
4.3. Analysis of Groundwater Chemical Controlling Factors
4.3.1. Water-Rock Model Analysis
The study area is located in a tropical climate zone and is greatly influenced by seasonal rainfall. Both the infiltration of atmospheric rainfall and the river water runoff contribute to groundwater recharge[
16,
17,
21]. Additionally, reactions between groundwater and the rock formations in the aquifers can also cause chemical changes in groundwater. Therefore, it is essential to explore the groundwater chemical characteristics and the controlling factors in the study area[
26]. Gibbs diagram is commonly used to study the impact of water-rock interactions on groundwater chemistry. It provides a macroscopic understanding of the controlling factors for the major ions in groundwater, including atmospheric precipitation, rock leaching, and evaporation-crystallization[
22,
27,
28].
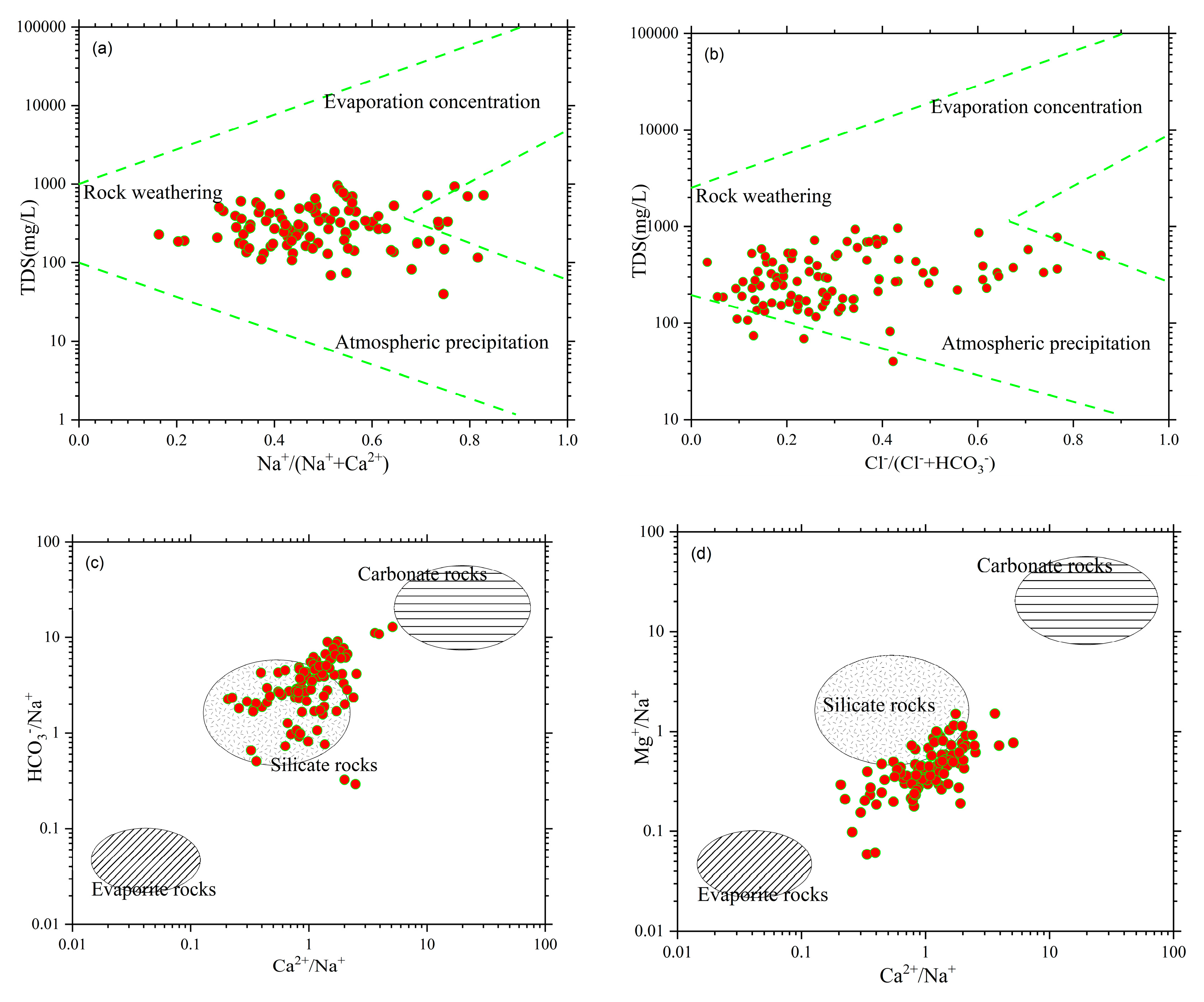
As shown in
Figure 4a,b, the ratio of cation mass concentration Na
+/(Na
++Ca
2+) ranges from 0.20 to 0.80, and the ratio of anion mass concentration Cl
-/(Cl
-+
) ranges from 0.10 to 0.80. Water samples with moderate total dissolved solids and low ratios are located in the rock weathering control area, i.e., the middle-left part of the graph, indicating the rock weathering effect. This suggests that water-rock interactions dominate the hydrogeochemical processes in the study area. Some water samples fall within the region influenced by evaporation concentration, indicating a certain degree of impact from evaporation concentration. No water samples are located in the bottom-right region of the graph, which represents the area influenced by atmospheric precipitation. This suggests that atmospheric precipitation may have an influence, but its effect is not significant.
The Na
+ end-member method was used to further explore the influence of rock weathering on the groundwater hydrochemical evolution process in the study area. According to the concentration ratio of (Ca
2+/Na
+)/(
/Na
+) and (Ca
2+/Na
+)/(Mg
2+/Na
+), the main weathering sources of groundwater ions are divided into three types, namely carbonate rock, silicate rock, and evaporite rock[
29,
30]. It can be seen from
Figure 4c,d that the shallow groundwater samples from the Changhua River Basin are mainly concentrated in the middle of the silicate rock end-member, and a small number are biased toward the carbonate rocks and evaporite rocks control end-members, indicating that the groundwater in this area is mainly affected by silicate rocks weathering, followed by the carbonate rocks and evaporite rocks weathering.
4.3.2. Analysis of Ion Ratio Relationship and Source of Main Components
Previous research commonly used correlation analysis between various chemical components of groundwater to reveal their sources[
31,
32]. Based on the correlation analysis results of various chemical components in
Table 3, TDS shows a significant positive correlation with K
+, Na
+, Ca
2+, Mg
2+, Cl
-,
,
, and
(P < 0.01). This indicates that these chemical components have a significant contribution to the TDS. Among them, the correlations between TDS and Na
+, Ca
2+, Mg
2+, and Cl
- are the most significant, with correlation coefficients of 0.797, 0.842, 0.802, and 0.837, respectively. This suggests that these four components are the primary factors influencing the TDS[
33].
shows significant correlations with Na
+, Ca
2+, and Mg
2+, indicating that
shares a common source with Na
+, Ca
2+, and Mg
2+, possibly originating from the weathering and dissolution of silicate rocks or carbonate rocks. The significant correlation of Na
+ with Cl
- and
suggests the presence of weathering and dissolution of sodium-bearing silicate minerals like sodium feldspar, which could also come from atmospheric precipitation and the dissolution of evaporite rocks. The correlation coefficient of 0.83 between Na
+ and Cl
- indicates a common source for both ions. The study area is close to the ocean, whereas the average Cl
-/Na
+ (mEq/L) ratio of 0.85 is lower than the world average seawater ratio (Cl
-/Na
+=1.16), suggesting that their chemical components may not be significantly influenced by seawater intrusion[
31,
34]. Furthermore, the correlation coefficient between K
+ and Cl
- is 0.169, 0.421 between K
+ and
, and 0.136 between Cl
- and
, respectively. Potassium chloride (KCl) is a common source of K
+ and Cl
-, and potassium nitrate (KNO
3) is a common source of K
+ and
, suggesting that a portion of K
+, Cl
-, and
could come from agricultural activities such as fertilizer usage and the discharge of domestic wastewater[
35].
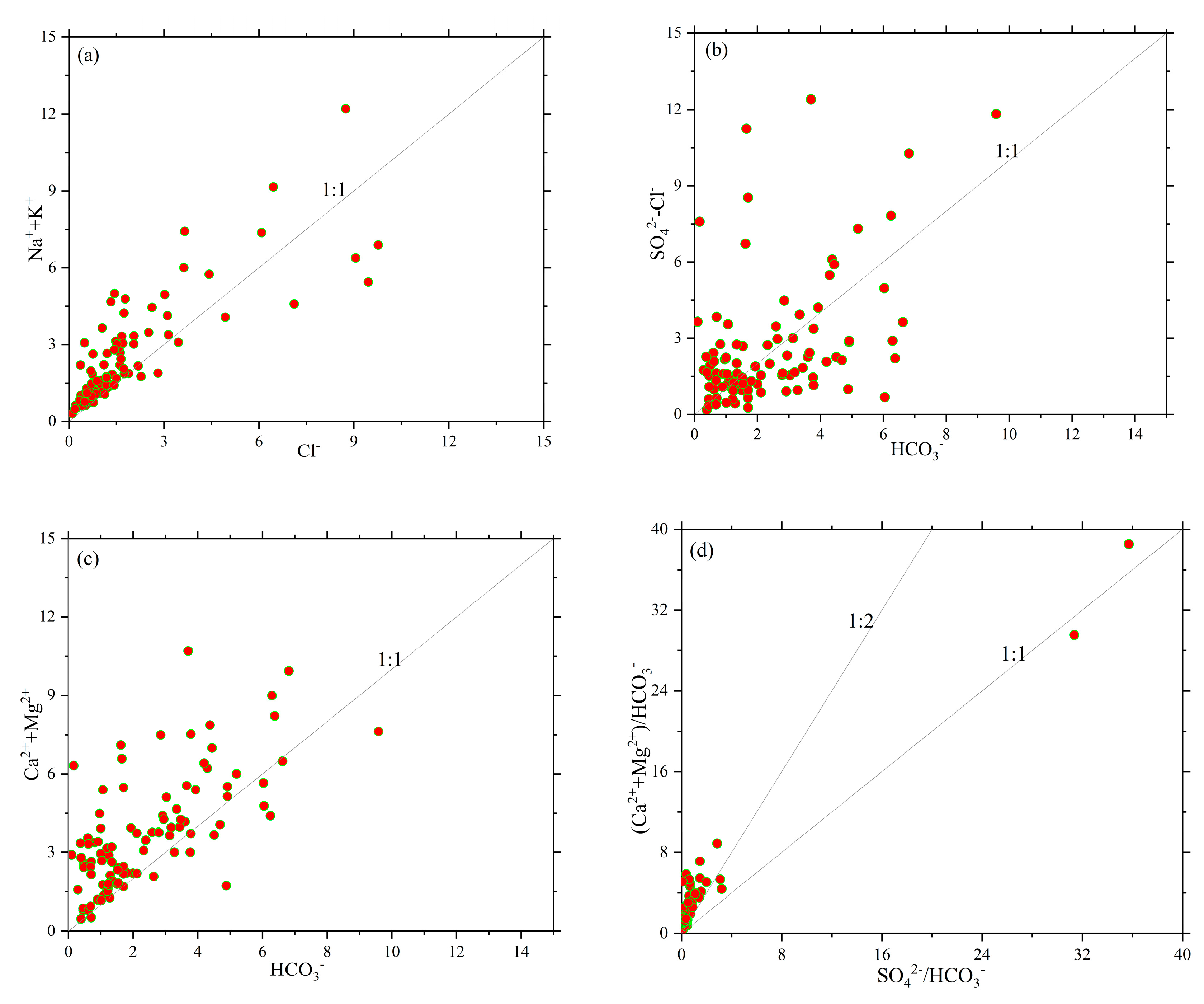
In this section, we further investigate the controlling factors of the chemical characteristics of the shallow aquifers downstream of the Changhua River. Due to the reaction between groundwater and aqueous media, the proportional relationship of various ions in groundwater is conducive to clarify the sources of major ions and hydrogeochemical processes. Therefore, a comparison of the main indicators of the 100 groundwater samples in the study area was conducted using milliequivalent ratios, as shown in
Figure 6.
In general, the relationship between n(Na
++K
+) and n(Cl
-) in a groundwater system can provide insights into the sources of Na
++K
+ and Cl
-. For example, a ratio of n(Na
++K
+)/n(Cl
-) = 1 suggests dissolution from evaporite rocks, while a ratio of n(Na
++K
+)/n(Cl
-) > 1 indicates weathering from silicate rocks[
4,
36]. From
Figure 5(a), it can be observed that the majority of groundwater sampling points at downstream of the Changhua River are located above the 1:1 line, indicating that the main source of Na
+ and K
+ in this area is likely from the leaching of silicate rocks. Meanwhile, some points are distributed below the 1:1 line, confirming that groundwater chemical composition is influenced by the leaching of carbonate rocks. The ratio of n(
+Cl
-)/n(
) reflects the dissolution of carbonate rocks in the study area. When n(
+Cl
-)/n(
) > 1, it suggests that
and Cl
- are derived from the weathering of evaporite rocks. Conversely, if n(
+Cl
-)/n(
) < 1, it indicates that
is sourced from the weathering of carbonate rocks[
37,
38]. In
Figure 5b, all the water sampling points are located above the 1:1 line, and some samples have much higher concentrations of (
+Cl
-) compared to
, indicating that the groundwater is mainly influenced by the weathering of evaporite rocks such as gypsum, rock salt, and mirabilite.
The sources of Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ can be determined based on the milliequivalent concentration ratio of (Ca
2++Mg
2+)/
. When this ratio is greater than 1, it indicates that Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ are primarily sourced from the dissolution of carbonate rocks. Conversely, if the ratio is less than 1, it suggests that Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ are mainly derived from the dissolution of silicate rocks and evaporite rocks[
39,
40]. As shown in
Figure 5c, most groundwater sampling points in the study area are located above the ratio line of 1 and only a small portion is located below, indicating that Ca
2+ and Mg2+ in the groundwater primarily come from the dissolution of carbonate rocks. From the milliequivalent concentration ratios of (Ca
2++Mg
2+)/
and (
/
), we can further analyze the involvement of carbonic acid and sulfuric acid in the dissolution of carbonate rocks. When the ratio is 2, it suggests that sulfuric acid participates in the dissolution process of carbonate minerals. When the ratio is 1:1, it indicates that carbonic acid is involved in the dissolution of carbonate minerals[
39,
40]. From
Figure 5d, it can be observed that most water sampling points are located near the ratio line of 1:2 and the upper left corner, indicating that both carbonic acid and sulfuric acid in the water are involved in the dissolution of carbonate minerals, but the carbonic acid contributes significantly more than the sulfuric acid.
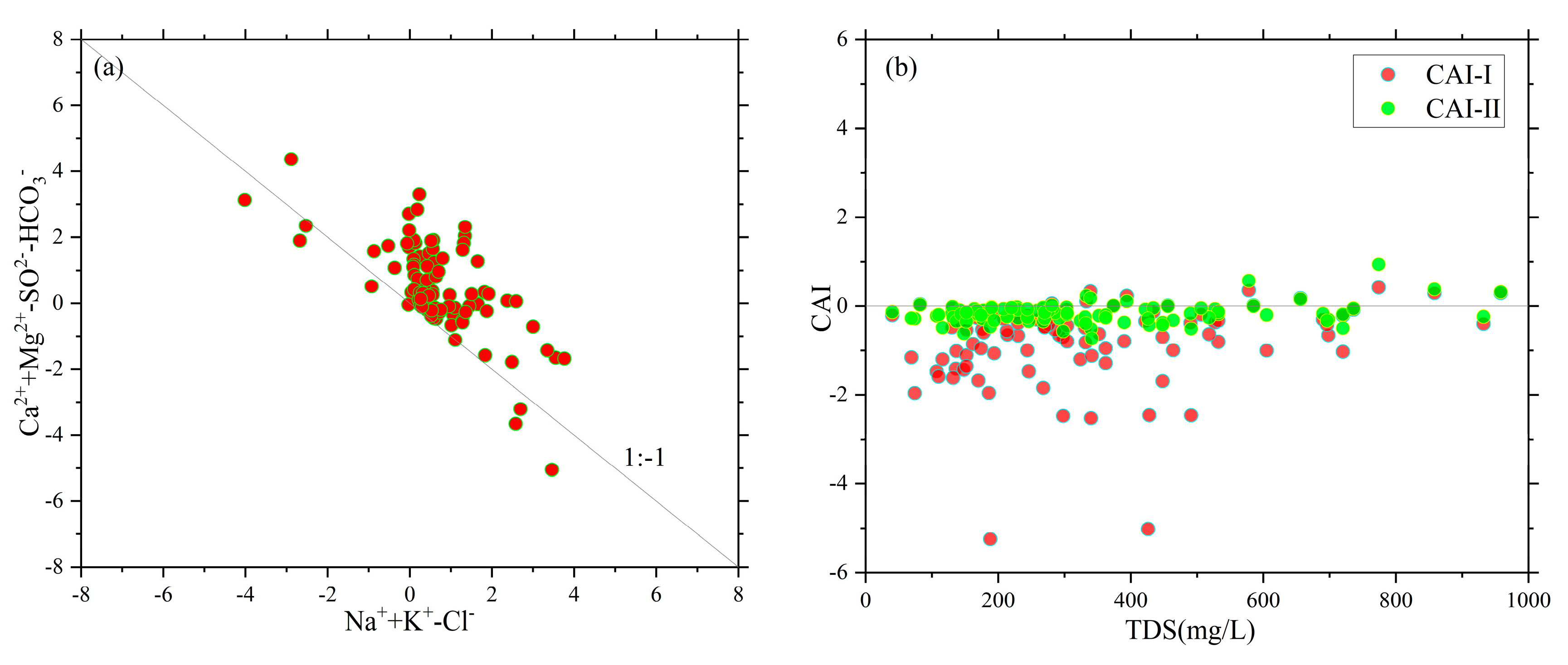
4.3.3. Analysis of Cationic Exchange Adsorption
Under certain conditions, the exchange of certain cations adsorbed on the rock and soil surfaces with the cations in groundwater is referred to as cationic exchange adsorption. It is commonly represented by the ratio of n(Ca
2++Mg
2+)/n(Na
++K
+−Cl
-), where if cationic exchange occurs, the ratio of n(Ca
2++Mg
2+)/n(Na
++K
+−Cl
-) is approximately equal to -1[
15,
28]. In the case of the shallow groundwater in the lower reaches of Changhua River, there is a strong correlation between n(Ca
2++Mg
2+) and n(Na
++K
+−Cl
-), and the ratio is around -1 (
Figure 6a), indicating that cationic exchange is occurring in the study area.
The direction and strength of cationic exchange can be further represented by the Chloro-Alkali Index (CAI)[
5,
23]. Typically, when the Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in groundwater undergo cationic exchange with the Na
+ and K
+ adsorbed on the surface of the aquifer particles, both CAI-Ⅰ and CAI-Ⅱ are negative values. Conversely, if there is an anionic exchange process, CAI-Ⅰ and CAI-Ⅱ will be positive values.
Figure 6.
Cationic exchange adsorption.
Figure 6.
Cationic exchange adsorption.
From the relationship between CAI and TDS (
Figure 6b), it can be observed that 81% of the water sampling points have negative CAI values. This indicates that the shallow groundwater in the study area primarily undergoes cationic exchange, where Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in the pore water exchange with Na
+ and K
+ in the aquifer minerals, leading to a reduction in Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ concentrations and an increase in Na
+ and K
+ concentrations in the water.
4.3.4. Analysis of the Impact of Human Activities
In this study, the downstream area of the Changhua River in Hainan Island is the main tropical crop planting region with a wide rural area. Agricultural fertilization, and untreated domestic sewage and waste can generate a large number of pollutants, such as chloride ions and nitrates, which can enter the shallow groundwater with rainwater or surface water, thereby affecting the hydrochemical evolution of the groundwater[
8,
9].
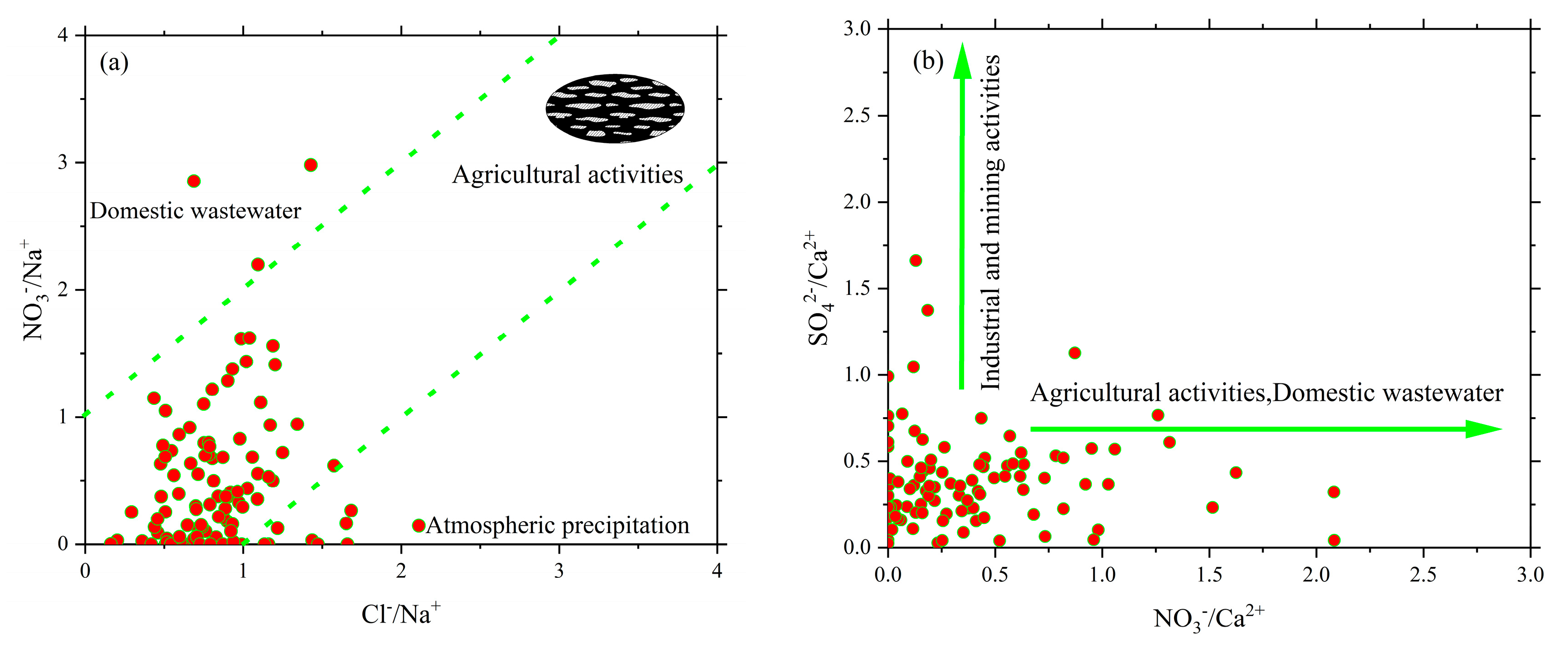
The higher the ratios of Cl
-/Na
+ and
/Na
+ in groundwater, the more significant the impact of human activities[
41]. From
Figure 7a, we can observe that the both ratios are relatively high, and some samples are close to or fall within the agricultural pollution end-member, indicating that shallow groundwater has been influenced to some extent by agricultural pollution. The relationship between
/Ca
2+ and
/Ca
2+ is commonly used to analyze the influence of human activities on the main ions in groundwater. When
/Ca
2+ >
/Ca
2+, it indicates a greater impact from industrial and mining activities, whereas the opposite suggests a greater influence from agricultural activities and domestic sewage,
Figure 7b.
5. Conclusions and Outlook
This study comprehensively analyzed the hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the downstream area of the Changhua River using multiple methods. The results showed that the overall pH of the groundwater in the study area ranged from 6.6 to 8.0, indicating a near-neutral to weak alkaline nature. The dissolved oxygen (DO) content ranged from 2.52 to 7.22mg/L, with an average of 3.64mg/L, and the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) ranged from 33.5 to 101.60mV, with an average of 71.83mV, indicating an overall slightly oxidizing environment for the groundwater in the study area. The groundwater in the study area was classified as freshwater, suggesting that it might not be affected by seawater intrusion.
By using the Piper diagram and the Shukalev classification method, the chemical types of groundwater in the study area were classified into 56 types. The most abundant types were the Ca•Na-HCO3 type, the Ca-HCO3 type, and the Na•Ca-HCO3•Cl type. The NO3 type water was mainly distributed in the urban areas adjacent to the Wulie, Sanjia, and Shiyuetian Towns, indicating a close relationship between the distribution of NO3 type water and urbanization and other human activities in the study area. Furthermore, in the majority of the sampled groundwater, the concentration of exceeded that of , indicating a strong impact of human activities (such as untreated sewage, industrial wastewater, and agricultural fertilizers and pesticides) on the groundwater chemicals in the study area.
Analysis of the Gibbs diagram indicated that the groundwater chemical characteristics in the study area were mainly influenced by water-rock interactions. The water-rock interaction was dominantly affected by silicate weathering, and less affected by the weathering of carbonate rocks and evaporite rocks. Additionally, there was evidence of significant cationic exchange, leading to a decrease in Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations and an increase in Na+ and K+ concentrations in the water. The ion ratio analysis showed that Na+ and K+ mainly originated from the leaching of silicate rocks, while Ca2+ and Mg2+ primarily came from the dissolution of carbonate rocks. The presence of was primarily related to human activities, particularly associated with agricultural activities and untreated domestic wastewater, rather than industrial activities. Considering these findings on groundwater pollution, appropriate prevention and remediation measures should be implemented in the study area.
The hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater are not only influenced by water-rock interactions but also undergo significant changes due to intensified human activities and the development of natural resources. To better understand the impact of human activities on the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the study area, a comprehensive investigation should be conducted from various perspectives, such as spatial and temporal distributions and human-induced activities. This will provide reliable information for the development and sustainable utilization of groundwater resources in the study area.
Author Contributions
D.W., original draft preparation, methodology, writing; L.Z.Z., L.X.P. and X.W.L., review and project administration; Y.M.Y., and Z.H.C., investigation; Z.H.C. and L.D.L., visualization and formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the China Geological Survey Program, Land-sea coordination of basic geological survey results integration and expression of key technologies(DD20230416) and Ecological Restoration Support Survey Project of Changhua River Basin of Hainan Island(ZD20220209).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khan, A.F.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Gopinath, S.; Saravanan, K.; Vinnarasi, F.; Babu, C.; Rabina, C.; Prakash, R. Human health risk assessment for fluoride and nitrate contamination in the groundwater: a case study from the east coast of Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, India. Environmental Earth Sciences 2021, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Meister, R.; Prudhomme, C. Modelling the effects of climate change and its uncertainty on UK Chalk groundwater resources from an ensemble of global climate model projections. Journal of Hydrology 2011, 399, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Groundwater is important for the geochemical cycling of phosphorus in rapidly urbanized areas: a case study in the Pearl River Delta. Environmental Pollution 2020, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Imran, M.; Natasha, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Rahman, G.; Miandad, M.; Shahid, M.; Murtaza, B. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment, and public perception of groundwater in Bahawalnagar, Punjab, Pakistan: a multivariate analysis. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Gaillardet, J.; Allègre, C. Geochemistry of dissolved and suspended loads of the Seine River, France: anthropogenic impact, carbonate and silicate weathering. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta 1999, 63, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V. Assessment of TDS, Total Hardness and Nitrate in Groundwater of North-West Rajasthan, India. International Journal of Plant Research 2013, 26, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolabi, A.; Bonyadi, Z.; Paydar, M.; Najafpoor, A.A.; Ramavandi, B. Spatial distribution, occurrence, and health risk assessment of nitrate, fluoride, and arsenic in Bam groundwater resource, Iran. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2020, 12, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, M.B.; Mohammad, R.; Md. ,R. Improved Sustainability of Water Supply Options in Areas with Arsenic-Impacted Groundwater. Water 2013, 5, 1941–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, Y.; Beek, L.P.H.V.; Kempen, C.M.V.; Reckman, J.W.T.M.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophysical Research Letters 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.S.A.J.D.A.W.S.M.A.S.L.A.J. An examination of groundwater discharge and the associated nutrient fluxes into the estuaries of eastern Hainan Island, China using 226Ra. Science of the Total Environment 2011.
- Yuguo, Z.; Ganlin, Z.; Zitong, G. SOTER-Based Soil Water Erosion Simulation in Hainan Island. Pedosphere 2003, 13, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zu-guang, Z. Appraisal of service function value of Hainan Island water ecosystem. Journal of Economics of Water Resources.
- Jie, L.W. Agricultural Use of Hainan Water Resourses and Countermeasures to the Development of Water-saving Agriculture. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Jeffery, C.; Peter, D. The Economics of Groundwater Replenishment for Reliable Urban Water Supply. Water 2014, 6, 1662–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Xinyan, L.; Hao, W.; Hui, Q.; Yanyan, G. Groundwater Chemistry Regulated by Hydrochemical Processes and Geological Structures: A Case Study in Tongchuan, China. Water 2018, 10, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Pei, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y. Water resource utilization characteristics and driving factors in the Hainan Island. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering 2023, 11, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui-lin, C.; Cui-ling, W.U. Climate Resources of Hainan Island and Their Utilization. Journal of Qiongzhou University 2003.
- Dsikowitzky, J.L. Land–sea interactions at the east coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea: A synthesis. Continental Shelf Research 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chunrong, C. Distribution Pattern of Silica Concentration in Major Rivers and Their Ground Water in Hainan Province. Journal of South China University of Tropical Agriculture 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jingsheng, C. A STUDY ON STABLE ISOTOPES OF HYDROGEN AND OXYGEN IN RAIN WATER, RIVER WATER AND GROUNDWATER FROM HAINAN ISLAND OF CHINA. Scientia Geographica Sinica 1993. [Google Scholar]
- A,H. L.;B,X.Z.A.;A,Y.Z.;A,M.W.;A,M.T.;A,K.H.;A,M.Y.;A,D.H. Hydrochemical characteristics of travertine-depositing hot springs in western of Yunnan, China. Quaternary International 2020, 547, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui-fang, Z.; Hong-bing, T.; Xi-ying, Z. Recharge source,hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Nantong,Jiangsu Province. Geochimica 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation of the Madeng Hot Spring in Yunnan, China. Geofluids 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bouri, S.; Nsiri, M.; Brahim, F.B.; Khlifi, M. Assessment of the effects of anthropogenic activities on the El Arich groundwater using hydrogeochemistry, GIS and multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the semi-arid Kasserine region, Tunisia. Environmental Quality Management 2022, 31, 261–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Ding, D.; Zhao, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and groundwater quality appraisal for irrigation uses in the Lan-gan region, Northern Anhui Province, East China. Water Science & Technology: Water Supply 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Tao, F.X.; Liu, B.J.; Tao, Z.H.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L.H. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Pengcheng;Jiao;Ying;Bo;Chenglin;Liu. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors for waters' chemical composition in the Tarim Basin, Western China. Geochemistry: Interdisciplinary Journal for Chemical Problems of the Geosciences and Geoecology 2013, 73, 343–356. [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.E.; Ke, P.; Pan, X.; Center, W.; Survey, C.G. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Groundwater in Xianning Area. Resources Environment & Engineering 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gugulothu, S.; Subbarao, N.; Das, R.; Dhakate, R. Geochemical evaluation of groundwater and suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in an agricultural region of South India. Applied Water Science 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.; Li, L. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Science of the Total Environment 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umarani, P.; Ramu, A.; Kumar, V. Hydrochemical and statistical evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal aquifers in Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Earth Sciences 2019, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiatos, I. Nitrate source identification in groundwater of multiple land-use areas by combining isotopes and multivariate statistical analysis: A case study of Asopos basin (Central Greece). Science of the Total Environment 2016, 541, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfi, S.; Zouari, K.; Feki, S.; Mami, E. Study of variation in groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer in north-eastern Tunisia using multivariate factor analysis. Quaternary International 2013, 302, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Science of the Total Environment 2013, s463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel;Arias-estévez;And;Eugenio;López-periago;And;Elena;Martínez-carballo;And;Jesús. The mobility and degradation of pesticides in soils and the pollution of groundwater resources. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2008, 123, 247–260.
- Zhu, G.F.; Pan, H.X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Xiang, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and control factors of acid anion in Shiyang River Basin. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/china Environmental Science 2018, 38, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Li, X. The distribution characteristics and geological control factors of shallow high-arsenic groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia, from the perspective of Late Pleistocene–Holocene depositional environments. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2023, 30, 63305–63321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gibson, C.E. Mechanisms controlling the water chemistry of small lakes in Northern Ireland. Water Research 1996, 30, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, T.; Rishi, M.S.; Naik, P.K.; Sharma, P. Elucidating hydrochemical properties of groundwater for drinking and agriculture in parts of Punjab, India. Environmental Earth Sciences 2016, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, L. Temporal Evolution of Groundwater Composition in an Alluvial Aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by Principal Component Analysis. Water Research 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megan, M.; Joshua, V.; Josué, M.; Thomas, H. Economic Feasibility of Irrigated Agricultural Land Use Buffers to Reduce Groundwater Nitrate in Rural Drinking Water Sources. Water 2014, 7, 12–37. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).