Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
31 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Research Methodology
3. Results and Analysis
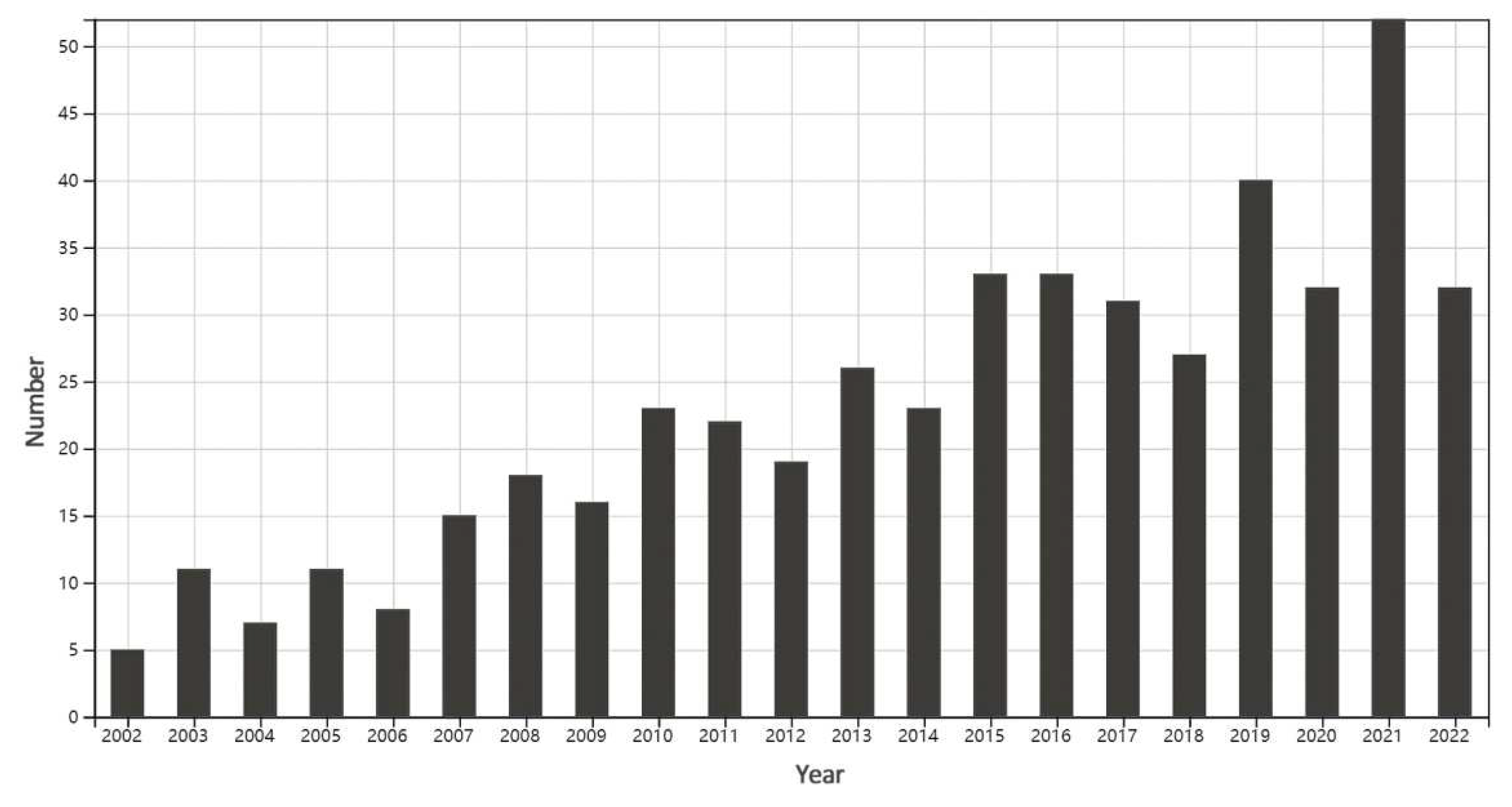
3.1. Analysis of the Literature Published and High Frequency Cited Literature
3.2. Disciplines
3.3. Analysis of the Main Forces of the Study
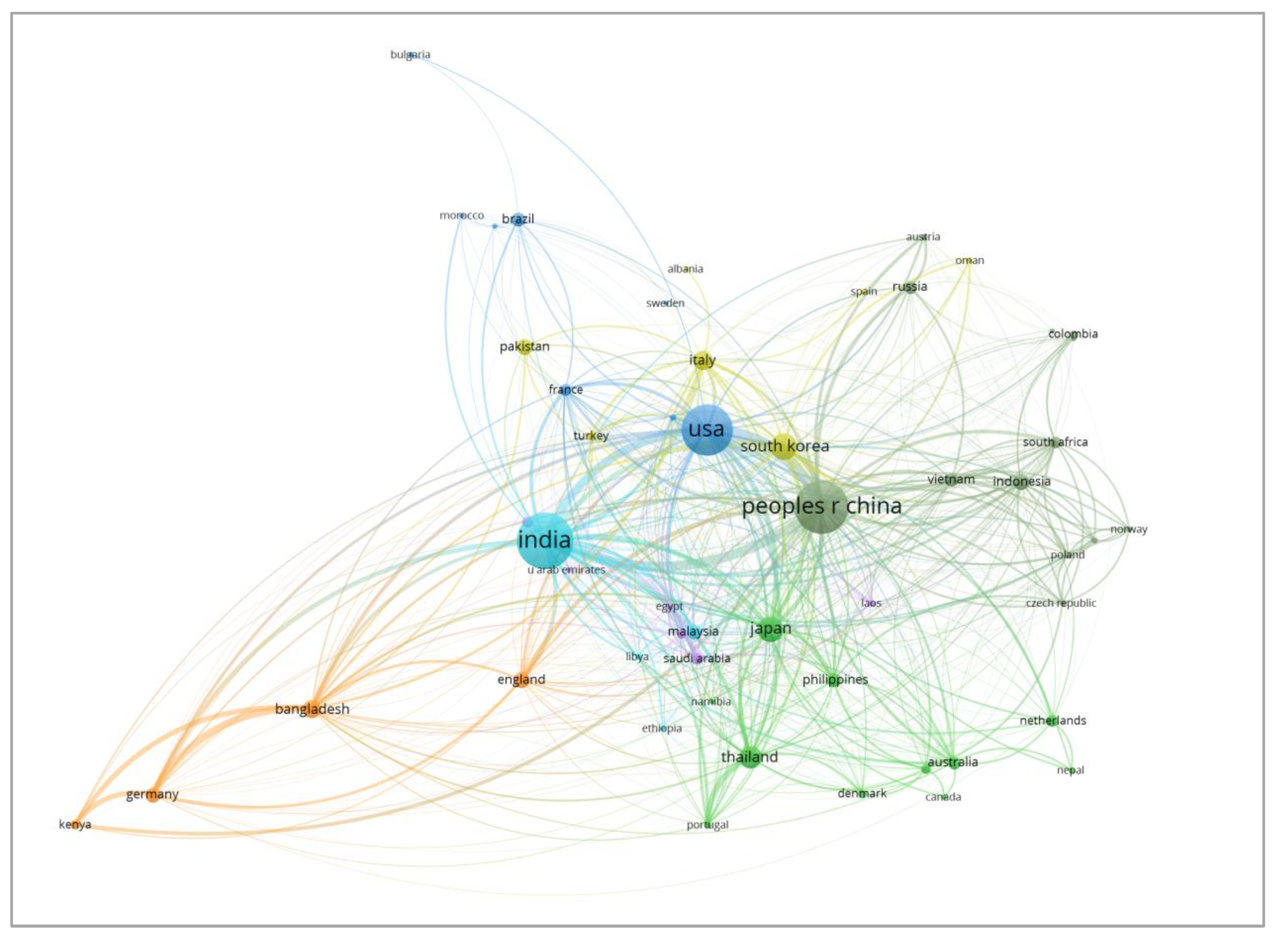
3.3.1. Main Countries Active in This Filed
3.3.2. Analysis of Key Research Institutions
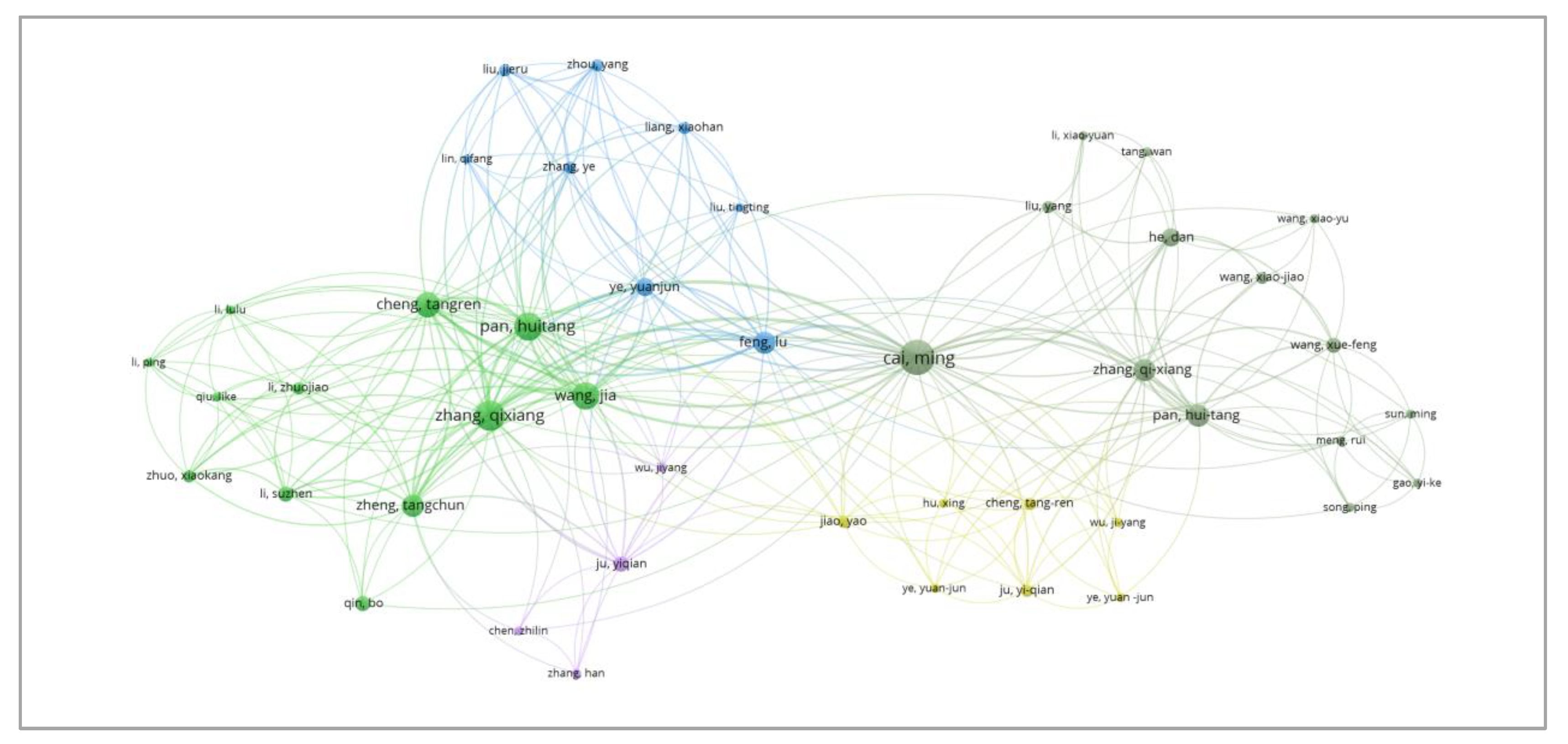
3.3.3. Key Authors and Author Co-Citation Information
3.4. Keyword Visualization Analysis
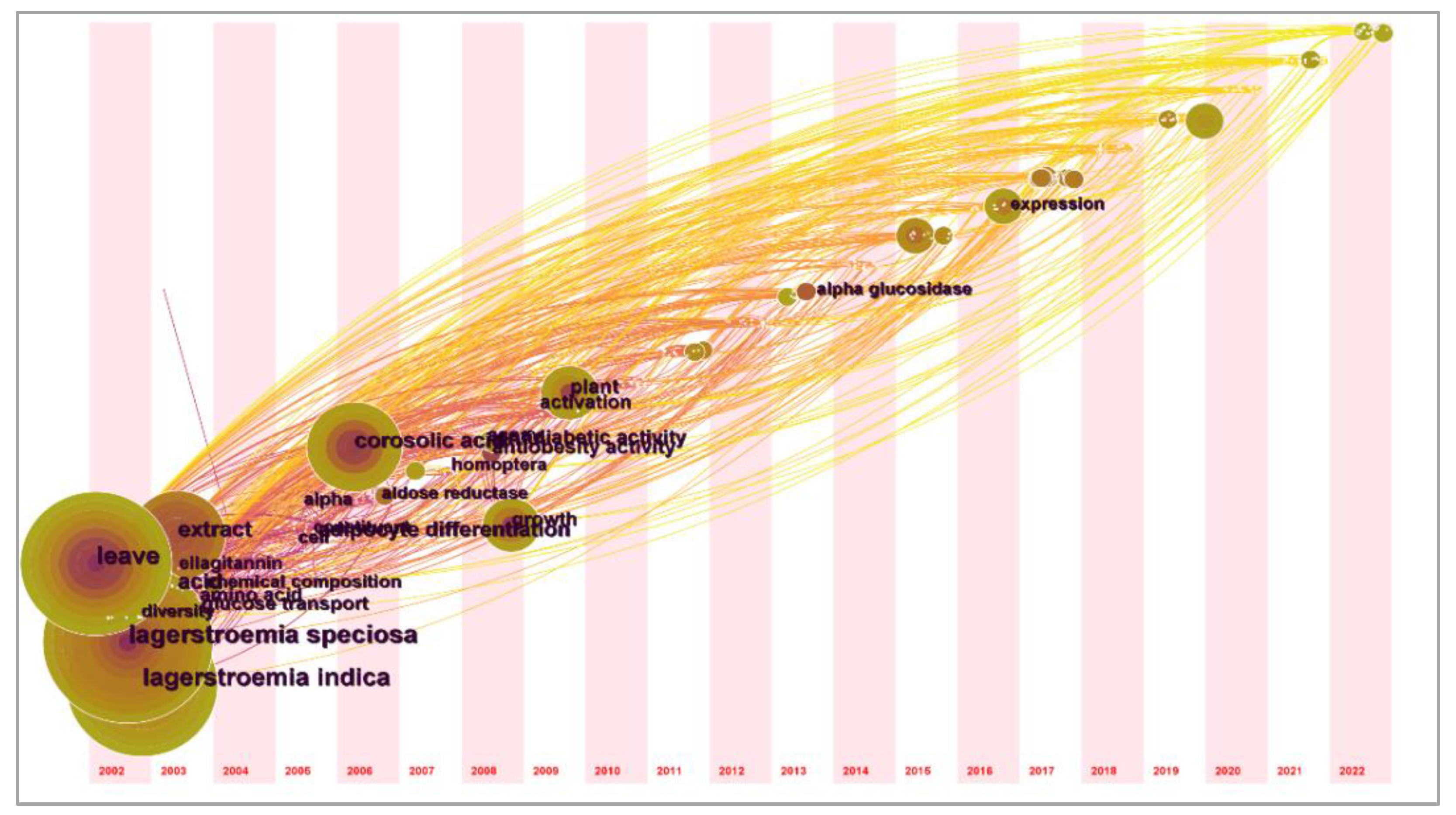
3.4.1. Co-Occurrence of Keywords
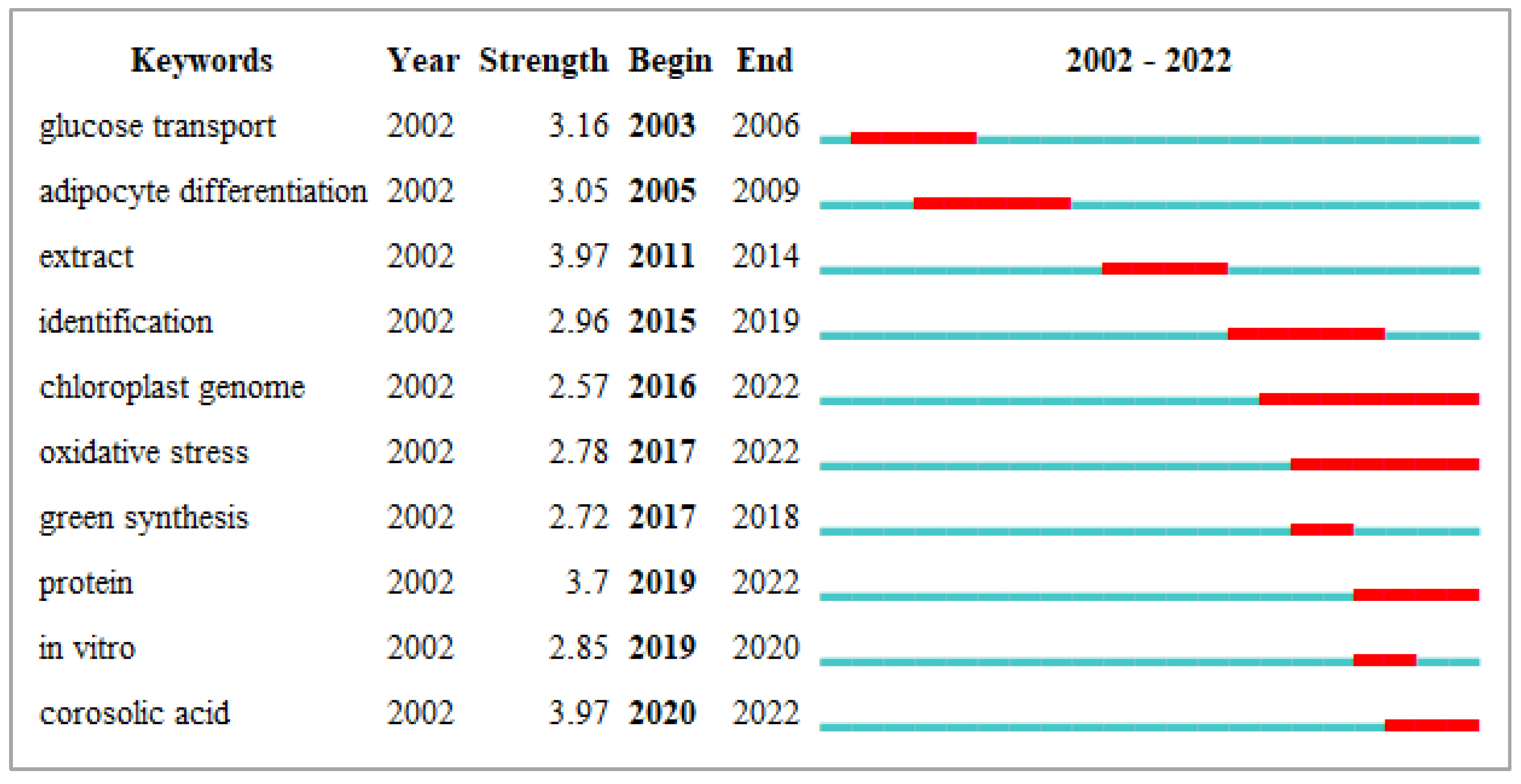
3.4.2. Research Hotspots
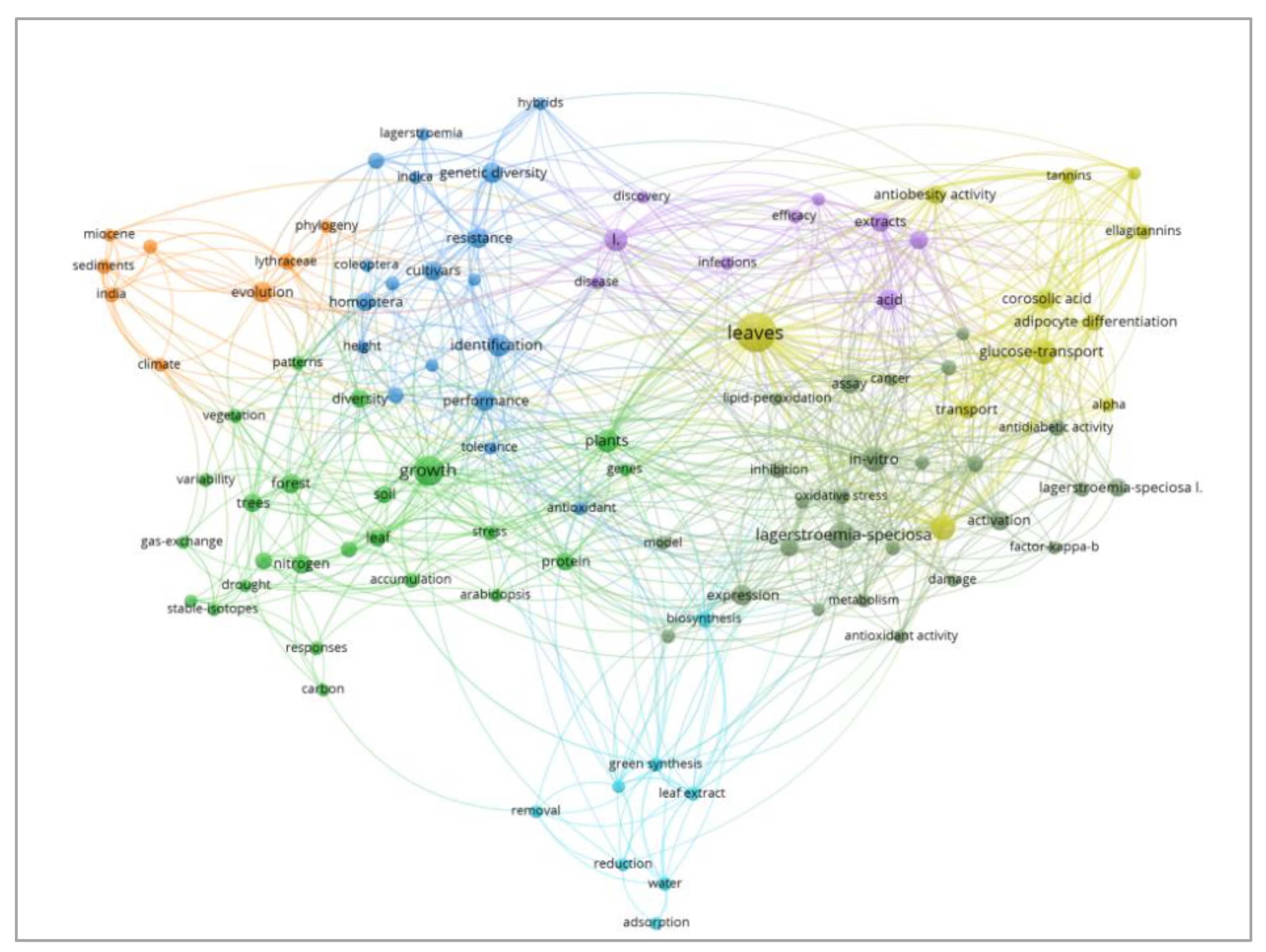
3.4.3. Cluster Analysis of Keywords
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Group, T. A. P. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 161, 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Hogenhout, S.; Al-Sadi, A.; Kuo, C. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Omani Lime (Citrus aurantiifolia) and Comparative Analysis within the Rosids. Plos One 2014, 9, e113049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Taxonomy of Chinese flower varieties; Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, China, 2001; pp. 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wu, T.; Zhe, W.; Ke, H. Research Progress on Plants of Lagerstroemia. Forest Inventory Planning 2005, 30, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K. Research progress of Lagerstroemia. J. Laiyang Agric. College 2002, 19, 276–278. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhen, L.; Jian, L.; Liu, S.; Deng, X. Research Progress in Breeding of Lagerstoemia in China. N. Hortic. 2021, 490, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Li, L. Analysis of Soil Lead Pollution Around the World Based on Bibliometrics. J. Anhui Sci. Technol. Univ. 2020, 34, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Qi, Q.; Niu, L. Current status and hotspot of Lonicera Japonica Flos research based on bibliometrics. Drug Eval. Res. 2022, 45, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Ilan, J. Which h-index? — A comparison of WoS, Scopus and Google Scholar. Scientometrics 2008, 74, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, N. J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer: A Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2009, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.; Xiao, X. Comparative Study of Science Mapping Software Tools VOS and NWB Tool. Inf. Sci. 2015, 33, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Tec. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sei. USA, 101(suppl), 5303-5310. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. Usa. 2004, 101, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yuanhao, L.; Cui, H.; Jun, S. Remolding the Policy Text Data through Documents Quantitative Research: The Formation,Transformation and Method Innovation of Policy Documents Quantitative Research. J. Public Manag. 2015, 159, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. Z.; Shen, L. Bibliometric analysis on research progress of four footprint methodologies in China. J. Nat. Resources 2016, 31, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, Z.; Nan, S.; Yang, H.; Fang, X. Knowledge mapping of research on international E-government during 2000-2010 based on Citespace and VOSviewer. J. Intell-Basel 2012, 31, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bornmann, L.; Mutz, R. Growth rates of modern science: A bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Tech. 2015, 66, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q. Bibliometric-based analysis of advances in research on Elymus. Pratacultural Sci. 2021, 38, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Research Progress of Lagerstroemia Plants. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Houghton, P. J. Soumyanath A. alpha-Amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Kim, J.; Himmeldirk, K.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X. Antidiabetes and Anti-obesity Activity of Lagerstroemia speciosa. Evid-Based Compl. Alt. 2007, 4, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S. J.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G. R. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L. ) and corosolic acid. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kim, J. K.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, X. Tannic acid stimulates glucose transport and inhibits adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, T.; Sakane, I.; Masumizu, T.; Kohno, M.; Kakuda, T. Antioxidative Activity of Water Extracts of Lagerstroemia speciosa Leaves. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 1997, 61, 1772–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M. T.; Lampronti, I.; Martello, D.; Bianchi, N.; Jabbar, S.; Choudhuri, M. S.; Datta, B. K.; Gambari, R. Identification of pyrogallol as an antiproliferative compound present in extracts from the medicinal plant Emblica officinalis: effects on in vitro cell growth of human tumor cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2002, 21, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Dong, W. P.; Li, W. Q.; Lu, Y. Z.; Xie, X. M.; Jin,X. B.; Shi, J. P.; He, K. H.; Suo, Z. L. Comparative Analysis of Six Lagerstroemia Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Ma, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes from 22 Lythraceae species: inferences for phylogenetic relationships and genome evolution within Myrtales. Bmc. Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, Z.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Reference gene selection for qRT-PCR analysis of flower development in Lagerstroemia indica and L. speciosa. Plos One. 2018, 13, e0195004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, R.; Du, J.; Xin, H.; Ling, C. Corosolic acid induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and caspase activation in human cervix adenocarcinoma HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 284, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. D. Corosolic acid induces apoptotic cell death in HCT116 human colon cancer cells through a caspase-dependent pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 943–949. [Google Scholar]
- Uto, T.; Sakamoto, A.; Tung, N.; Fujiki, T.; Kishihara, K.; Oiso, S.; Kariyazono, H.; Morinaga, O.; Shoyama, Y. Anti-Proliferative Activities and Apoptosis Induction by Triterpenes Derived from Eriobotrya japonica in Human Leukemia Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4106–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, H.; Tong, D.; Tan, Z.; Han, D.; Ji, F.; Hu, W. Corosolic acid triggers mitochondria and caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Seo, S.; Min, K. J.; Im, S. S.; Nam, J. O.; Chang, J. S.; Kim, S.; Park, J. W.; Kwon, T. K. Corosolic Acid Induces Non-Apoptotic Cell Death through Generation of Lipid Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Human Renal Carcinoma Caki Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amresh, G.; Agrawal, V.; Rao, C. V. Self microemulsifying formulation of Lagerstroemia speciosa against chemically induced hepatotoxicity. J. Tradit. Compl. Med. 2018, 8, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, B. K.; Dutta, S.; Dey, P.; Hossain, M.; Kumar, A.; Bihani, S.; Nanda, A. K.; Chaudhuri, T. K.; Chakraborty, R. Radical Scavenging Activities of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L. ) Pers. Petal Extracts and its hepato-protection in CCl 4 -intoxicated mice. Bmc. Complem. Altern. M. 2017, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SaiSaraswathi, V.; Saravanan, D.; Santhakumar, K. Isolation of quercetin from the methanolic extract of Lagerstroemia speciosa by HPLC technique, its cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells and photocatalyticactivity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2017, 171, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T. R.; Ezhilarasan, D. Ethanolic extract of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L. ) Pers., induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R. S.; Devaraj, E. Lagerstroemia speciosa (L. ) Pers. triggers oxidative stress mediated apoptosis via intrinsic mitochondrial pathway in HepG2 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, B. T. D.; Staerk, D.; Jager, A. K. Screening for potential alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase inhibitory constituents from selected Vietnamese plants used to treat type 2 diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 186, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S. J.; Badmaev, V. A Review of Natural Stimulant and Non-stimulant Thermogenic Agents. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathi, V. S.; Tatsugi, J.; Shin, P. K.; Santhakumar, K. Facile biosynthesis, characterization, and solar assisted photocatalytic effect of ZnO nanoparticles mediated by leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa. J. Photoch. Photobio. B. 2017, 167, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B. C.; Paul, D.; Gupta, T.; Tetgure, S. R.; Garole, V. J.; Borse, A. U.; Garole, D. J. Photocatalytic reduction of organic pollutant under visible light by green route synthesized gold nanoparticles. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshrestha, S.; Qayyum, S.; Khan, A. U. Antibiofilm efficacy of green synthesized graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite using Lagerstroemia speciosa floral extract: A comparative study on inhibition of gram-positive and gram-negative biofilms. Microb. Pathogenesis 2017, 103, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusbu, B.; Pallabi, D.; Kumar, D. S.; Mala, T.; Mukesh, S.; Avik, M.; Santosh, K. Lagerstroemia speciosa fruit-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its application as filler in agar based nanocomposite films for antimicrobial food packaging. Food Packaging Shelf 2018, 17, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, L.; Singh, J. Synthesis of novel biochar from waste plant litter biomass for the removal of Arsenic (III and V) from aqueous solution: A mechanism characterization, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 248, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Aishan, T.; Halik, Ü.; Wei, Z.; Wumaier, M. A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Research Progress and Trends on Decay and Cavity Trees in Forest Ecosystem over 20 Years: An Application of the CiteSpace Software. Forests 2022, 13, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, S.; Ho, Y. S. A bibliometric analysis of world volatile organic compounds research trends. Scientometrics 2010, 83, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Huang, Y. Global trend in aquatic ecosystem research from 1992 to 2011. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. L.; Ding, G.; Feng, N.; Wang, M. H.; Ho, Y. S. Global stem cell research trend: Bibliometric analysis as a tool for mapping of trends from 1991 to 2006. Scientometrics 2009, 80, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ranking | Title | First author | First organization | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Alpha-amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus | Ali H | Kings Coll London | 443 |
| Ⅱ | Synthesis, biology and clinical significance of pentacyclic triterpenes: a multi-target approach to prevention and treatment of metabolic and vascular diseases | Sheng HM | Purdue University | 220 |
| Ⅲ | Tannic acid stimulates glucose transport and inhibits adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells | Liu XQ | Ohio Univ | 144 |
| Ⅳ | Triterpene Acids Isolated from Lagerstroemia speciosa Leaves as alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors | Hou WL | Dezhou University | 138 |
| Ⅴ | Adverse effects of herbal medicines: an overview of systematic reviews | Posadzki P | Nanyang Technological University | 135 |
| No. | Subject areas | Frequency | Subject category | Subject gradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plant Sciences | 91 | Science | Technological science |
| 2 | Pharmacology & Pharmacy | 68 | Medicine | Technological science |
| 3 | Agriculture | 64 | Agronomy | Fundamental science |
| 4 | Environmental Sciences & Ecology | 59 | Engineering | Engineering science |
| 5 | Chemistry | 40 | Science | Technological science |
| 6 | Biochemistry & Molecular Biology | 37 | Science | Technological science |
| 7 | Entomology | 35 | Agronomy | Fundamental science |
| 8 | Forestry | 28 | Agronomy | Fundamental science |
| 9 | Integrative & Complementary Medicine | 26 | Medicine | Technological science |
| 10 | Science & Technology Other Topics | 26 | Science | Technological science |
| Institution | Country | Publications | Total citation | Average citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing Forestry University | China | 26 | 253 | 9. 73 |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | China | 24 | 468 | 19. 5 |
| Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeobtany | India | 20 | 239 | 11. 95 |
| Department of Science Technology India | India | 20 | 239 | 11. 95 |
| Texas A&M University System | The United States | 20 | 134 | 6. 7 |
| State University System of Florida | The United States | 19 | 308 | 16. 21 |
| United States Department of Agriculture | The United States | 17 | 274 | 16. 12 |
| University of Florida | The United States | 17 | 191 | 11. 24 |
| Texas A&M University College station | The United States | 14 | 35 | 2. 5 |
| Zhejiang A&F University | China | 14 | 94 | 6. 71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




