Submitted:
28 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction


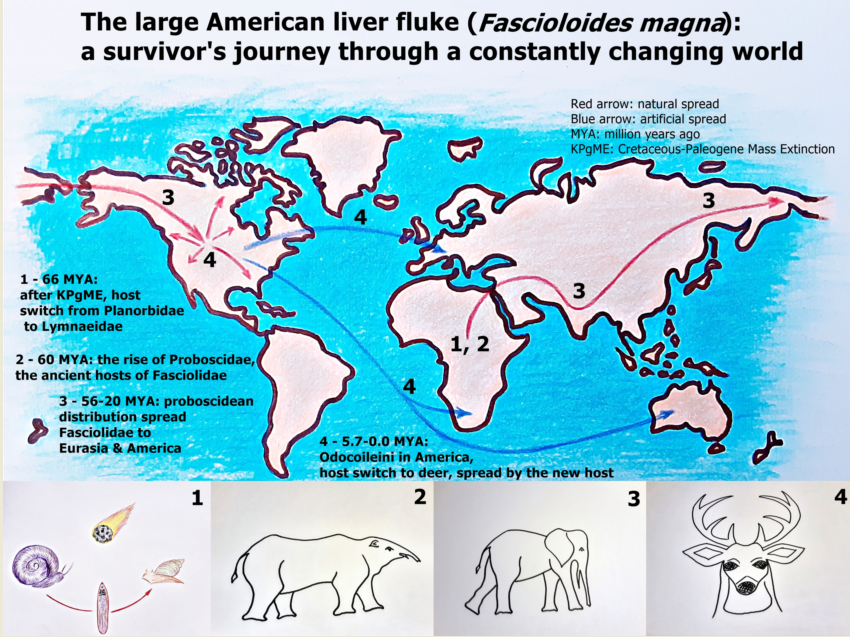
2. Evolutionary history of the large American liver fluke and its relatives
2.1. The Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary
2.2. Distribution by the Proboscidea order
2.3. The fall of the proboscideans and the dawn of the ruminants
2.4. Switch to the cervid host
3. Recent European distribution
4. European final hosts
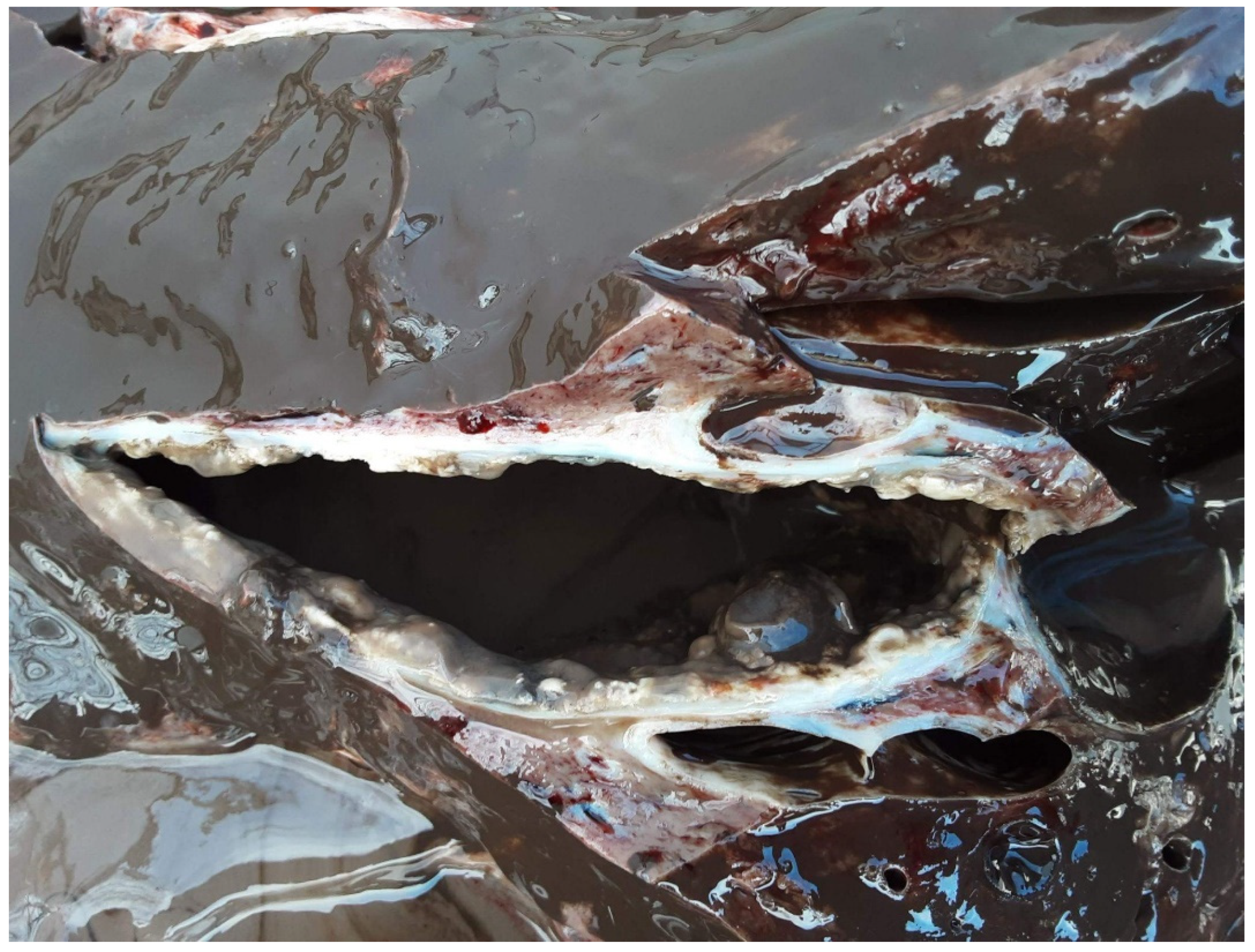
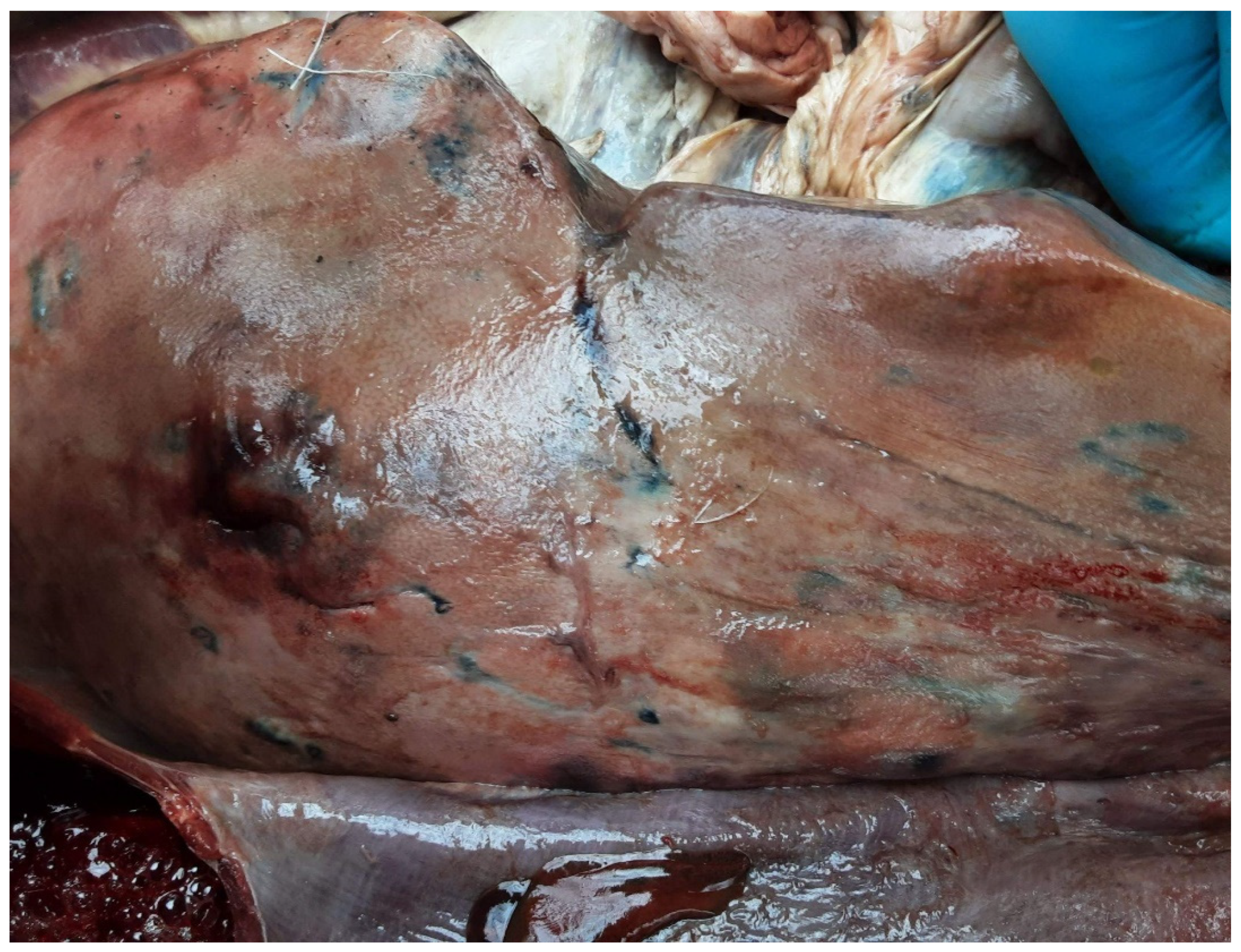

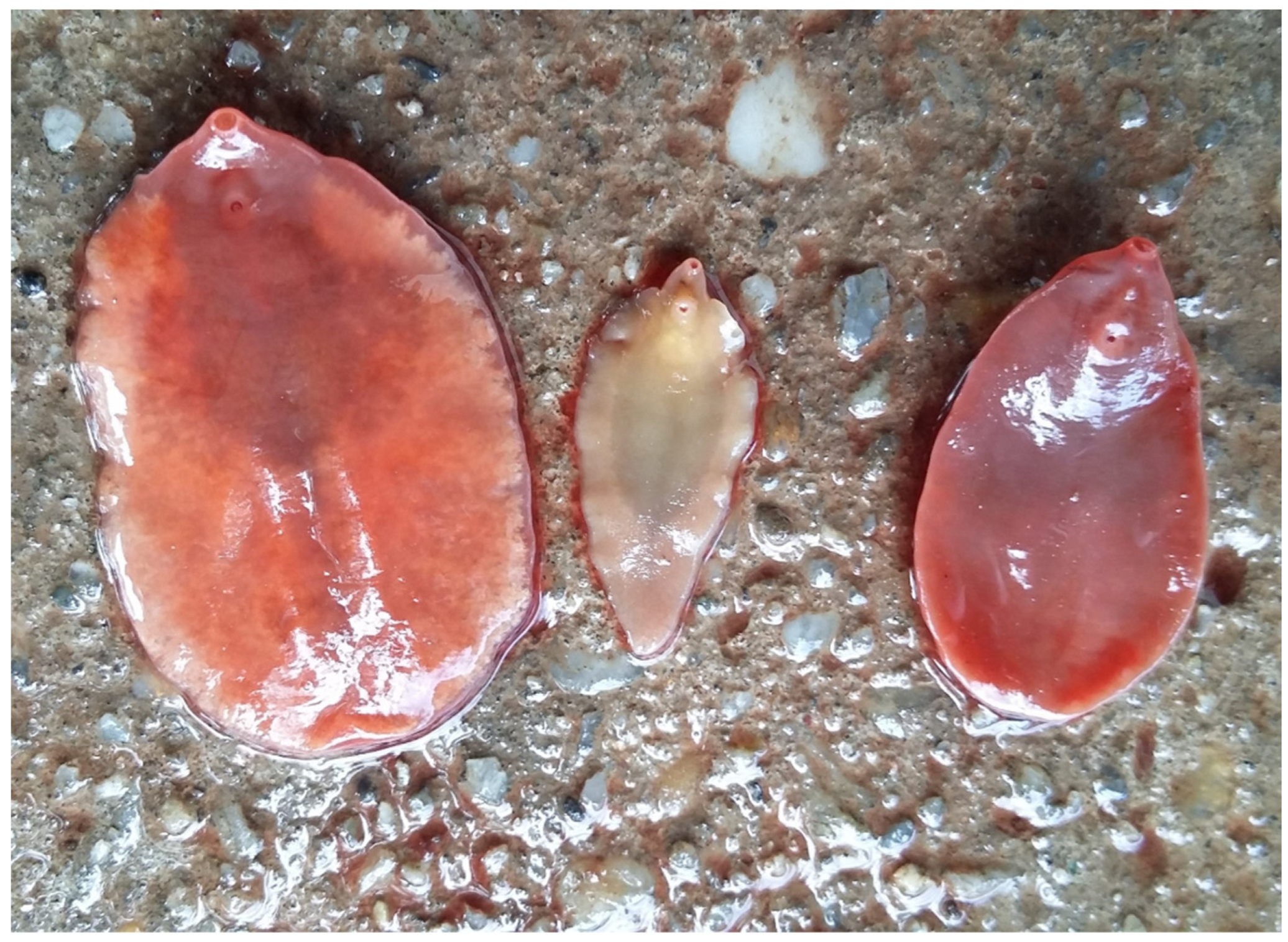
4.1. The special role of roe deer
5. Intermediate hosts of F. magna
5.1. Susceptibility of the intermediate hosts
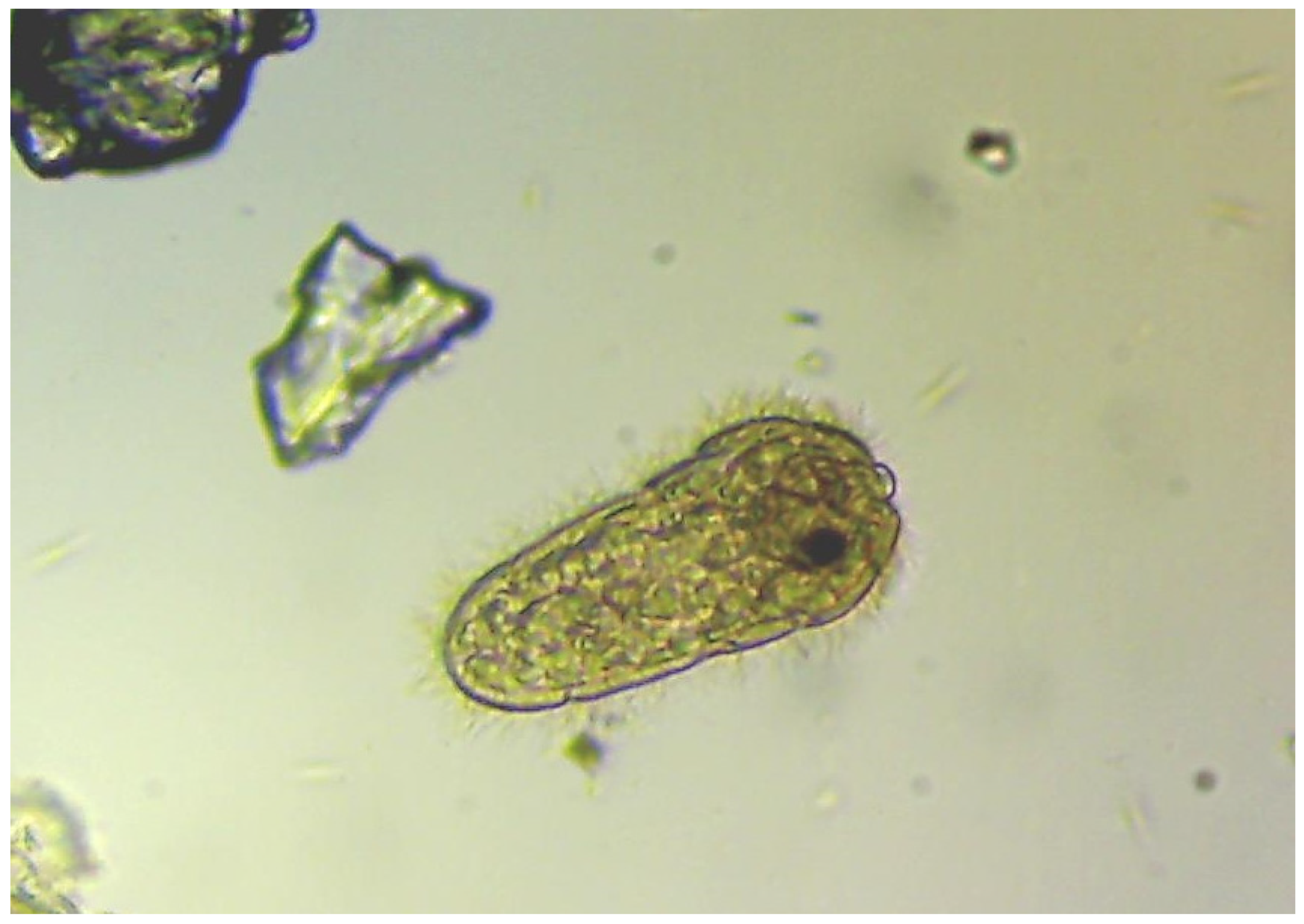
5.2. The course of infection in intermediate hosts
5.3. Self-fertilisation: a trade-off between population persistence and population health
5.4. Environmental demands of snail hosts
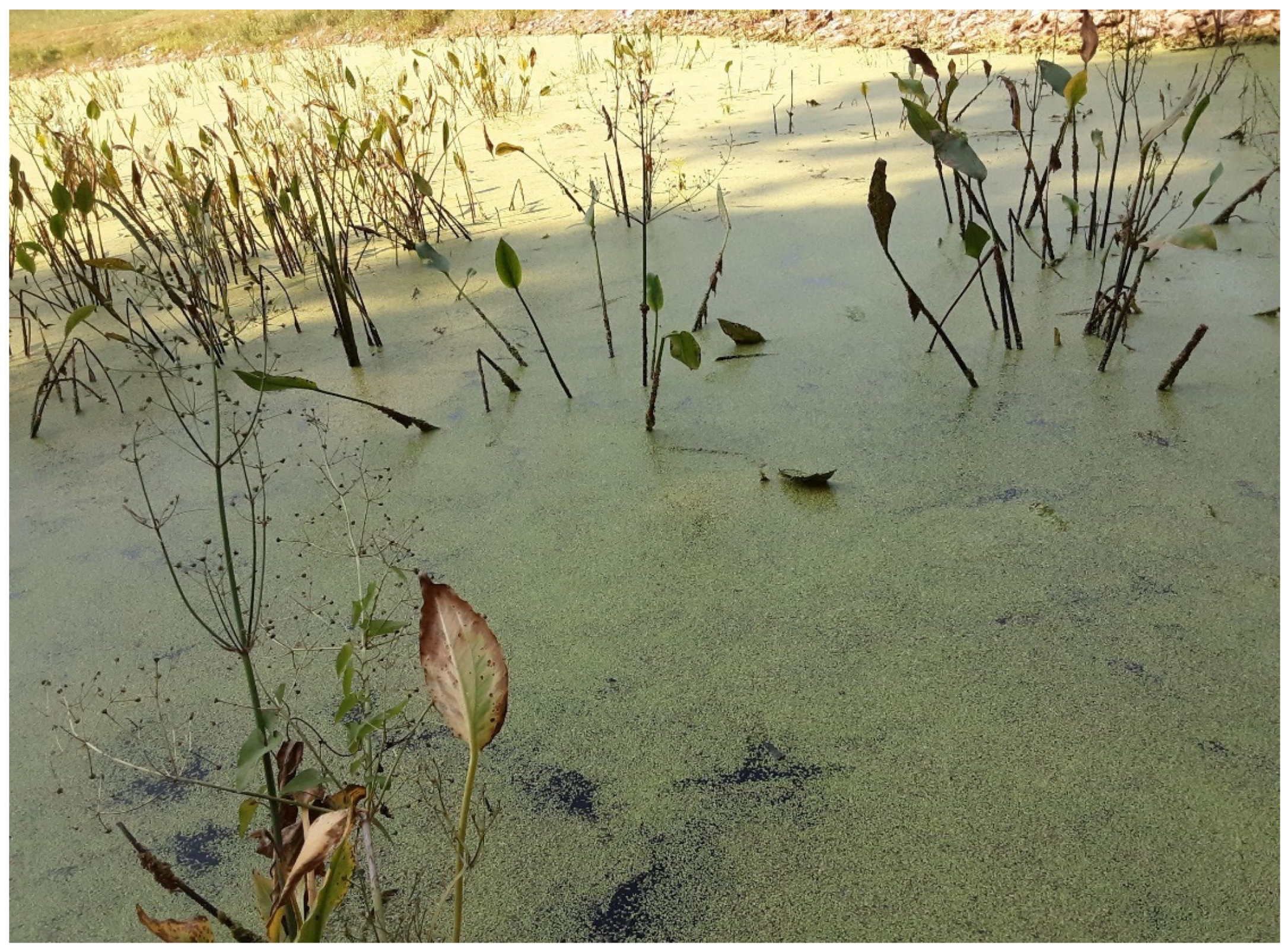



5.5. Human-mediated distribution of epidemiological risk of snails
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotfy, W.M.; Brant, S.V.; DeJong, R.J.; Le, T.H.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.; Rajapakse, R.J.; Perera, V.B.; Laursen, J.R.; Loker, E.S. Evolutionary origins, diversification, and biogeography of liver flukes (Digenea, Fasciolidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 248. [CrossRef]
- Kassai, T. (1999). Digenea. In Veterinary Helminthology. Publisher: Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1999.
- Malcicka, M. Life history and biology of Fascioloides magna (Trematoda) and its native and exotic hosts. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1381-1397. [CrossRef]
- Juhász, A; Stothard, J.R. The giant liver fluke in Europe: A review of Fascioloides magna within cervids and livestock with considerations on an expanding snail-fluke transmission risk. Adv. Parasit. 2022, 119, 223-257. [CrossRef]
- Králová-Hromadová, I.; Juhásová, L.; Bazsalovicsová, E. The giant liver fluke, Fascioloides magna: past, present and future research. Springer International Publishing: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Marinković, D.; Kukolj, V.; Aleksić-Kovačević, S.; Jovanović, M.; Knežević, M.The role of hepatic myofibroblasts in liver cirrhosis in fallow deer (Dama dama) naturally infected with giant liver fluke (Fascioloides magna). BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Šimonji, K.; Konjević, D.; Bujanić, M.; Rubić, I.; Farkaš, V.; Beletić, A.; Grbavac, L.; Kuleš, J. Liver proteome alterations in red deer (Cervus elaphus) infected by the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1503. [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.F.; Drdlicek, J.; Müller, M.; Thelemann, A.; Just, F.T. Fascioloides magna and other liver parasites in cloven-hoofed game from northeastern Bavaria, Germany: occurrence and pathological findings with special emphasis on red deer (Cervus elaphus). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2022, 68, 73. [CrossRef]
- Pankrác, J.; Novobilský, A.; Rondelaud, D.; Leontovyč, R.; Syrovátka, V.; Rajský, D.; Horák, P.; Kašný, M. Effect of Fascioloides magna (Digenea) on fecundity, shell height, and survival rate of Pseudosuccinea columella (Lymnaeidae). Parasit. Res. 2016, 115, 3119-3125. [CrossRef]
- Rondelaud, D.; Novobilský, A.; Höglund, J.; Kašný, M.; Pankrác, J.; Vignoles, P.; Dreyfuss, G. Growth rate of the intermediate snail host Galba truncatula influences redial development of the trematode Fascioloides magna. J. Helmint. 2014, 88, 427-433. [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, A.E.; Jones, C.S.; Noble, L.R.; Rollinson, D. Trematodes and snails: an intimate association. Can. J. Zool. 2004, 82, 251-269. [CrossRef]
- Sattmann, H.; Hörweg, C.; Gaub, L.; Feix, A.S.; Haider, M.; Walochnik, J.; Rabitsch, W.; Prosl, H. Wherefrom and whereabouts of an alien: the American liver fluke Fascioloides magna in Austria: an overview. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2014, 126, 23. [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.J.; Park, A.W.; Cressler, C.E.; Dallas, T.; Huang, S.; Mideo, N.; Morales-Castilla, I.; Davies, T. J.; Stephens, P. The ghost of hosts past: impacts of host extinction on parasite specificity. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 2021, 376, 20200351. [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.R.; Rogers, K.A.C.; Bagley, B.C.; Goodin, J.J.; Hartman, J.H.; Thole, J.T.; Zatoń, M. Pushing the record of trematode parasitism of bivalves upstream and back to the Cretaceous. Geology 2018, 46, 431-434. [CrossRef]
- Barrios-de Pedro, S.; Osuna, A.; Buscalioni, Á. D. Helminth eggs from early cretaceous faeces. Sci. Rep. UK 2020, 10, 18747. [CrossRef]
- Poinar, G.; Boucot, A.J. Evidence of intestinal parasites of dinosaurs. Parasitology 2006, 133, 245-249. [CrossRef]
- Kaiho, K.; Oshima, N.; Adachi, K.; Adachi, Y.; Mizukami, T.; Fujibayashi, M.; Saito, R. Global climate change driven by soot at the K-Pg boundary as the cause of the mass extinction. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 28427. [CrossRef]
- Chiarenza, A.A.; Farnsworth, A.; Mannion, P.D.; Lunt, D.J.; Valdes, P.J.;; Morgan, J.V.; Allison, P.A. Asteroid impact, not volcanism, caused the end-Cretaceous dinosaur extinction. Proc. National Acad. of Sci. 2020, 117, 17084-17093. [CrossRef]
- de Moya, R.S.; Allen, J.M.; Sweet, A.D.; Walden, K.K.; Palma, R.L.; Smith, V.S.; Cameron, S.L.; Valim, M.P.; Galloway, T.D.; Weckstein, J.D.; Johnson, K.P. Extensive host-switching of avian feather lice following the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction event. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 445. [CrossRef]
- Renne, P.R.; Sprain, C.J.; Richards, M.A.; Self, S.; Vanderkluysen, L.; Pande, K. State shift in Deccan volcanism at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary, possibly induced by impact. Science 2015, 350, 76-78. [CrossRef]
- Sprain, C.J.; Renne, P.R.; Vanderkluysen, L.; Pande, K.; Self, S.; Mittal, T. The eruptive tempo of Deccan volcanism in relation to the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Science, 2019, 363, 866-870. [CrossRef]
- Hull, P.M.; Bornemann, A.; Penman, D.E.; Henehan, M.J.; Norris, R.D.; Wilson, P.A.; Blum, P.; Alegret, L.; Batenburg, S.J.; Zachos, J. C. +26 authors. On impact and volcanism across the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Science 2020, 367, 266-272. [CrossRef]
- Turner, S. K. Constraints on the onset duration of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. Philos. T. Roy. Soc. A 2018, 376, 20170082. [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv. Parasit. 2009, 69, 41-146. [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Fontenla, S.; Fischer, P.U.; Le, T.H.; Costábile, A.; Blair, D.; Brindley P.J.; Tort, J. F.; Cabada, M. M.; Mitreva, M. Adaptive radiation of the flukes of the family Fasciolidae inferred from genome-wide comparisons of key species. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 84-99. [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.C.; Escobar, J.S. Durand, P.; Renaud, F.; David, P.; Jarne, P.; Pointier J.-P.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. Bridging gaps in the molecular phylogeny of the Lymnaeidae (Gastropoda: Pulmonata), vectors of fascioliasis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.G.; Seiffert, E.R.; Simons, E.L. Stable isotope evidence for an amphibious phase in early proboscidean evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008, 105, 5786-5791. [CrossRef]
- Los Huertos, M. Coevolution of biota, geology, and climate. In Ecology and Management of Inland Waters: A Californian Perspective with Global Applications. Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lounnas, M.; Correa, A.C.; Vázquez, A.A.; Dia, A.; Escobar, J.S.; Nicot, A.; Arenas, J.; Ayaqui, R.; Dubois, M.P.; Gimenez, T.; Gutierrez, A.; Gonzalez-Ramirez, C.; Noya, O.; Prepelitchi., L.; Uribe, N.; Wisnivesky-Colli, C.; Yong, M.; David, P.; Loker, E.S.; Jarne, P.; Pointier, J.P.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. Self-fertilization, long-distance flash invasion and biogeography shape the population structure of Pseudosuccinea columella at the worldwide scale. Molec. Ecol. 2017, 26, 887-903. [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, T.A.; Georgopoulou, E. Extinction risk is linked to lifestyle in freshwater gastropods. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 2357-2368. [CrossRef]
- Palasio, R.G.S.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F.; Tuan, R. Distribution of genetic diversity of neotropical Biomphalaria (Preston 1910) (Basommatophora: Planorbidae) intermediate hosts for schistosomiasis in Southeast Brazil. Front. Trop. Dis. 2023, 4, 1143186. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Neubauer, T.A.; Jochum, A. First freshwater gastropod preserved in amber suggests long-distance dispersal during the Cretaceous Period. Geological Magazine, 2021, 158(7), 1327-1334. [CrossRef]
- Juhász, A.; Majoros, G. A proposed ectochory of Galba truncatula snails between wallow sites enhances transmission of Fascioloides magna at Gemenc, in Hungary. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 21, 2019-223. [CrossRef]
- Hurtrez-Boussès, S.; Hurtrez, J.E.; Turpin, H.; Durand, C.; Durand, P.; De Meeüs, T.; Meunier, C.; Renaud, F. Hydrographic network structure and population genetic differentiation in a vector of fasciolosis, Galba truncatula. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10(2), 178-183. [CrossRef]
- McCabe, D.J. Rivers and streams: life in flowing water. Nature Education Knowledge. 2010, 3(10), 19.
- Sturm, R. Aquatic molluscs in high mountain lakes of the Eastern Alps (Austria): Species-environment relationships and specific colonization behaviour. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30(1), 59. [CrossRef]
- Bargues, M.D.; Artigas, P.; Khoubbane, M.; Ortiz, P.; Naquira, C.; Mas-Coma, S. Molecular characterisation of Galba truncatula, Lymnaea neotropica and L. schirazensis from Cajamarca, Peru and their potential role in transmission of human and animal fascioliasis. Parasites Vectors, 2012, 5, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Alba, A.; Vázquez, A.A.; Sánchez, J.; Lounnas, M.; Pointier, J.P.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S.; Gourbal, B. Patterns of distribution, population genetics and ecological requirements of field-occurring resistant and susceptible Pseudosuccinea columella snails to Fasciola hepatica in Cuba. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9(1), 14359. [CrossRef]
- Ngcamphalala, P.I.; Malatji, M.P.; Mukaratirwa, S. Geography and ecology of invasive Pseudosuccinea columella (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) and implications in the transmission of Fasciola species (Digenea: Fasciolidae)–a review. J. Helminthol. 2022, 96, e1. [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; Mohamed, F.A.; Nachev, M.; Meabed, E.M.; Sabry, A.H.A.; Sures, B. Invasion biology meets parasitology: a case study of parasite spill-back with Egyptian Fasciola gigantica in the invasive snail Pseudosuccinea columella. PloS One, 2014, 9(2), e88537. [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, J. The palaeontology of browsing and grazing. In The Ecology of Browsing and Grazing II, 1st ed.; Gordon, I. J.; Prins, H. H. T, Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland AG, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gheerbrant, E. Paleocene emergence of elephant relatives and the rapid radiation of African ungulates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009, 106(26), 10717-10721. [CrossRef]
- Baleka, S.; Varela, L.; Tambusso, P.S.; Paijmans, J.L.; Mothé, D.; Stafford, T.W.; Farina, R.A.; Hofreiter, M. Revisiting proboscidean phylogeny and evolution through total evidence and palaeogenetic analyses including Notiomastodon ancient DNA. iScience, 2022, 25(1), 103559. [CrossRef]
- Tabuce, R.; Sarr, R.;, Adnet, S.; Lebrun, R.; Lihoreau, F.; Martin, J.E.; Sambou, B.; Thiam, M.; Hautier, L. Filling a gap in the proboscidean fossil record: a new genus from the Lutetian of Senegal. J. Paleontol. 2020, 94(3), 580-588. [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, J.L.; Sanisidro, O.; Zhang, H.; Alberdi, M.T.; Prado, J.L.; Blanco, F.; Saarinen, J. The rise and fall of proboscidean ecological diversity. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5(9), 1266-1272. [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Pham, K.L.T.; Doan, H.T.T.; Le, T.X.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lawton, S.P. Description and phylogenetic analyses of ribosomal transcription units from species of Fasciolidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea). J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e136. [CrossRef]
- Heneberg, P. Phylogenetic data suggest the reclassification of Fasciola jacksoni (Digenea: Fasciolidae) as Fascioloides jacksoni comb. nov. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1679-1689. [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, R.P.V.J.; Pham, K.L.T.; Karunathilake, K.K.; Lawton, S.P.; Le, T.H. Characterization and phylogenetic properties of the complete mitochondrial genome of Fascioloides jacksoni (syn. Fasciola jacksoni) support the suggested intergeneric change from Fasciola to Fascioloides (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Plagiorchiida). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 82, 104281. [CrossRef]
- Reblánová, M.;Špakulová, M.; Orosová, M.; Bazsalovicsová, E.; Rajský, D. A description of karyotype of the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna (Trematoda, Platyhelminthes) and a review of Fasciolidae cytogenetics. Helminthologia, 2010, 47, 69-75. [CrossRef]
- Bargues, M.D.; Halajian, A.; Artigas, P.; Luus-Powell, W.J.; Valero, M.A.; Mas-Coma, S. Paleobiogeographical origins of Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica in light of new DNA sequence characteristics of F. nyanzae from hippopotamus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 990872. [CrossRef]
- Mennecart, B.; Dziomber, L.; Aiglstorfer, M.; Bibi, F.; DeMiguel, D.; Fujita, M.; Kubo, M.O.; Laurens, F.; Meng, J.; Métais, G.; Müller, B.; Ríos, M.; Rössner, G. E.; Sánchez, I. M.; Schulz, G.; Wang, S.; Costeur, L. Ruminant inner ear shape records 35 million years of neutral evolution. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13(1), 7222. [CrossRef]
- Codron, D. Evolution of large mammal herbivores in savannas. In Savanna Woody Plants and Large Herbivores, 1st ed.; Scogings, P. F.; Sankaran, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Sheil, D. Dangerous giants?—Large herbivores, forest feedbacks and climate tipping points. Russ. j. ecosyst. ecol. 2020, 5(3), 1-33. [CrossRef]
- Ao, H.; Rohling, E.J.; Zhang, R.; Roberts, A.P.; Holbourn, A.E.; Ladant, J.B.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Kuhnt, W.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Dekkers, M.J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Poulsen, C.J.; Licht, A.; Sun, Q.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Ma, C.; Zhou, W.; Jin, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Peng, X.; Qiang, X.; An, Z. Global warming-induced Asian hydrological climate transition across the Miocene–Pliocene boundary. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12(1), 6935. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Crespo, V.A.; Prado, J.L.; Alberdi, M.T.; Arroyo-Cabrales, J.; Johnson, E. Feeding ecology of the gomphotheres (Proboscidea, Gomphotheriidae) of America. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 229, 106126. [CrossRef]
- Ameen, M.; Khan, A.M.; Ahmad, R.M.; Ijaz, M.U.; Imran, M. Tooth marker of ecological abnormality: The interpretation of stress in extinct mega herbivores (proboscideans) of the Siwaliks of Pakistan. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9432. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Ropiquet, A.; Hassanin, A. Mitochondrial and nuclear phylogenies of Cervidae (Mammalia, Ruminantia): systematics, morphology, and biogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40(1), 101-117. [CrossRef]
- Polziehn, R.O.; Strobeck, C. Phylogeny of wapiti, red deer, sika deer, and other North American cervids as determined from mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1998, 10(2), 249-258. [CrossRef]
- Pybus, M.J. Liver flukes. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Mammals; Samuel, W.M., Pybus, M.J., Kocan, A.A., Eds.; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2021; pp. 121–149. [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; David, A.A. Genetic characterization of the giant liver fluke, Fascioloides magna (Platyhelminthes: Fasciolidae) from the Adirondack Region of Northern New York. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 259-263. [CrossRef]
- Králová-Hromadová, I.; Bazsalovicsová, E.; Štefka, J.; Špakulová, M.; Vávrová, S.; Szemes, T.; Tkach, V.; Trudgett, A.; Pybus, M. Multiple origins of European populations of the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna (Trematoda: Fasciolidae), a liver parasite of ruminants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41(3-4), 373-383. [CrossRef]
- Engelstädter, J.; Fortuna, N. Z. The dynamics of preferential host switching: Host phylogeny as a key predictor of parasite distribution. Evolution, 2019, 73(7), 1330-1340. [CrossRef]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Kuligowska, I.; Pyziel, A.M.; Lachowicz, J.; Kowalczyk, R. Extension of occurrence area of the American fluke Fascioloides magna in south-western Poland. Ann. Parasitol. 2015, 61(2), 93-96.
- Rajský, D.; Patus, A.; Bukovjan, K. Prvýnález Fascioloides magna Bassi, 1875 na Slovensku (in Slovakian). Slov. Vet. Čas. 1994, 19, 29–30.
- Majoros, G.; Sztojkov, V. Appearance of the large American liver fluke Fascioloides magna (Bassi, 1875) (Trematoda: Fasciolata) in Hungary. Parasitologia Hungarica 1994, 27, 27-38.
- Houszka, M.; Piekarska, J.; Podkowik, M.; Gorczykowski, M.; Bania, J. Morphology and molecular study of Fascioloides magna–a growing threat to cervids (Cervidae) in Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 60(4), 435-439. [CrossRef]
- Juhásová, L.; Králová-Hromadová, I.; Zeleňáková, M.; Blišťan, P.; Bazsalovicsová, E. Transmission risk assessment of invasive fluke Fascioloides magna using GIS-modelling and multicriteria analysis methods. Helminthologia, 2017, 54(2), 119-131. [CrossRef]
- Marinculić, A.; Džakula, N.; Janicki, Z.; Hardy, Z.; Lučinger, S.; Živičnjak, T. Appearance of American liver fluke (Fascioloides magna, Bassi, 1875) in Croatia. Vet. Arh. 2002, 72(6), 319-325.
- Slavica, A.; Florijančić, T.; Janicki, Z.; Konjević, D.; Severin, K.; Marinculić, A.; Pintur, K. Treatment of fascioloidosis (Fascioloides magna, Bassi, 1875) in free ranging and captive red deer (Cervus elaphus L.) at eastern Croatia. Vet. Arh. 2006, 76(Suppl.), 9-18.
- Konjević, D.; Janicki, Z.; Calmels, P.; Jan, D.S.; Marinculić, A.; Šimunović, M.; Pavlak, M.; Krapinec, K.; Poljak, Z. Evaluation of factors affecting the efficacy of treatment against Fascioloides magna in wild red deer population. Vet Ital, 54(1), 2018, 33-39. [CrossRef]
- Trailović, S.M.; Marinković, D.; & Kulišić, Z. Diagnosis and therapy of liver fluke (Fascioloides magna) infection in fallow deer (Dama dama) in Serbia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52(2), 319-326. [CrossRef]
- Mirčeta, J.; Pelić, M.; Božić, B.; Petrović, J.; Urošević, M.; Stankov, B.; Bugarski, D. (2018). Prevalence of the giant liver fluke (Fascioloides magna, Bassi, 1875) in red deer (Cervus elaphus) in the region of floodplain forests of northern Serbia. Arch. Vet. Med. 2018, 11(1), 17-26. [CrossRef]
- Plötz, C.; Rehbein, S.; Bamler, H.; Reindl, H.; Pfister, K.; Scheuerle, M. C. Fascioloides magna–epizootiology in a deer farm in Germany. Berl. Munch. Tierärzt. Wochensch. 2015, 128(5/6), 111-182.
- Konjević, D.; Bujanić, M.; Beck, A.; Beck, R.; Martinković, F.; Janicki, Z. First record of chronic Fascioloides magna infection in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 15, 173-176. [CrossRef]
- Halász, T.; Tari, T.; Nagy, E;, Nagy, G; Csivincsik, Á. (2023). Hatchability of Fascioloides magna eggs in cervids. Pathogens, 2023, 12(5), 741. [CrossRef]
- Králová-Hromadová, I.; Špakulová, M.; Horáčková, E.; Turčeková, L.; Novobilský, A.; Beck, R.; Koudela, B.; Marinculic, A.; Rajský, D.; Pybus, M. Sequence analysis of ribosomal and mitochondrial genes of the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna (Trematoda: Fasciolidae): intraspecific variation and differentiation from Fasciola hepatica. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94(1), 58-67. [CrossRef]
- Leontovyč, R.; Košťáková, M.; Siegelová, V.; Melounová, K.; Pankrác, J.; Vrbová, K.; Horák, P.; Kašný, M. (2014). Highland cattle and Radix labiata, the hosts of Fascioloides magna. BMC Vet. Res, 2014, 10, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Konjević, D.; Bujanić, M.; Erman, V.; Kurilj, A.G.; Živičnjak, T.; Severin, K.; Tomić, S.; Martinković, F. New data on wild boar (Sus scrofa L.) a dead-end host for large American liver fluke (Fascioloides magna). Helminthologia, 2017, 54(1), 77-80. [CrossRef]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Kowalczyk, R.; Filip, K.J.; Pyziel, A. M. Fascioloides magna: a parasite of roe deer in Bory Zielonogórskie (in Polish). Med. Weter. 2018, 74(4), 257-260. [CrossRef]
- Filip-Hutsch, K.; Pyziel-Serafin, A.M.; Hutsch, T.; Bulak, K.; Czopowicz, M.; Merta, D.; Kobielski, J.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W. The occurrence of Fascioloides magna (Bassi, 1875) in the wild cervid population in the Lower Silesian Wilderness–epidemiological and pathological aspects. J. Vet. Res. 66(3), 381-387. [CrossRef]
- Shury, T.K.; Pybus, M.J.; Nation, N.; Cool, N.L.; & Rettie, W.J. Fascioloides magna in moose (Alces alces) from Elk Island National Park, Alberta. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56(3), 476-485. [CrossRef]
- Živković, D.; John, S.; Verin, M.; Stephan, W.; Tellier, A. Neutral genomic signatures of host-parasite coevolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19(1), 230. [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, L.J.; Ashby, B. Coevolutionary theory of hosts and parasites. J. Evol. Biol. 2022, 35, 205–224.
- Saadi, A.J.; Davison, A.; Wade, C.M. Molecular phylogeny of freshwater snails and limpets (Panpulmonata: Hygrophila). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 190(2), 518-531. [CrossRef]
- Hörweg, C.; Prosl, H.; Wille-Piazzai, W.; Joachim, A.; Sattmann, H. Prevalence of Fascioloides magna in Galba truncatula in the Danube backwater area east of Vienna, Austria. Wien Tierarztl Monat, 2011, 98, 261-7.
- Haider, M.; Hörweg, C.; Liesinger, K.; Sattmann, H.; & Walochnik, J. Recovery of Fascioloides magna (Digenea) population in spite of treatment programme? Screening of Galba truncatula (Gastropoda, Lymnaeidae) from Lower Austria. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187(3-4), 445-451. [CrossRef]
- Schniebs, K.; Peter, G.; Vinarski, M.V.; Hundsdoerfer, A.K. Intraspecific morphological and genetic variability in the European freshwater snail Radix labiata (Rossmaessler, 1835)(Gastropoda: Basommatophora: Lymnaeidae). Contrib. Zool. 2013, 82(1), 55-68. [CrossRef]
- Salgado, S.Q.; Soriano, J.L.; Glöer, P. First report of Radix labiata (Rossmässler, 1835)(Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) in Aragon (NE Spain). J. Conchol, 2016, 40, 657-678.
- Garbar, А.; Komіushіn, А.V.. Karyotypes of European species of Radix (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Lymnaeidae) and their relevance to species distinction in the genus. Malacologia, 2003, 45(1), 141-148.
- Alda, P.; Lounnas, M.; Vázquez, A.A.; Ayaqui, R.; Calvopiña, M.; Celi-Erazo, M.; Dillon, R.T.; Jr, Jarne, P.; Loker, E.S.; Muñiz Pareja, F.C.; Muzzio-Aroca, J.; Nárvaez, A.O.; Noya, O.; Robles, L.M.; Rodríguez-Hidalgo, R.; Uribe, N.; David, P.; Pointier, J.P.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. A new multiplex PCR assay to distinguish among three cryptic Galba species, intermediate hosts of Fasciola hepatica. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 251, 101-105. [CrossRef]
- Bargues, M.D.; Mas-Coma, S. Phylogenetic analysis of lymnaeid snails based on 18S rDNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14(5), 569-577. [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.N.; Tyson, F.; Cutress, D.; Davies, E.;, Jones, D.L.; Brophy, P.M.; Prescott, A.; Rose, M.T.; Williams, M.; Williams, H.W.; Jones, R.A. Rapid detection of Galba truncatula in water sources on pasture-land using loop-mediated isothermal amplification for control of trematode infections. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Caron, Y.; Righi, S.; Lempereur, L.; Saegerman, C.; Losson, B. An optimized DNA extraction and multiplex PCR for the detection of Fasciola sp. in lymnaeid snails. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178(1-2), 93-99. [CrossRef]
- Caron, Y.; Lasri, S.; Losson, B. Fasciola hepatica: an assessment on the vectorial capacity of Radix labiata and R. balthica commonly found in Belgium. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149(1-2), 95-103. [CrossRef]
- Novobilský, A.; Kašný, M.; Beran, L.; Rondelaud, D.; Höglund, J. Lymnaea palustris and Lymnaea fuscus are potential but uncommon intermediate hosts of Fasciola hepatica in Sweden. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Kasny, M.; Beran, L.; Siegelova, V.; Siegel, T.; Leontovyc, R.; Berankova, K.; Pankrac, J.; Kostakova M.; Horak, P. (2012). Geographical distribution of the giant liver fluke (Fascioloides magna) in the Czech Republic and potential risk of its further spread. Vet. Med. (Praha) 2012, 57(2), 101-109. [CrossRef]
- Sindou, P.; Rondelaud, D.; Barthe, D. Fasciola hepatica L.: comparative studies of tissue lesions in seven lymnaeid species submitted to individual monomiracidial exposures at hatching. Bull. de la Soc. Zool. de France 1990, 115(4), 331-340.
- Georgieva, K.; Georgieva, L.; Mizinska-Boevska, Y.; Stoitsova, S.R. Study of surface carbohydrates in Galba truncatula tissues before and after infection with Fasciola hepatica. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2016, 111, 475-483. [CrossRef]
- Krull, W.H. The intermediate hosts of Fasciola hepatica and Fascioloides magna in the United States. North American Veterinarian 1934, 15(12), 13-17.
- Correa, A.C.; De Meeûs, T.; Dreyfuss, G.; Rondelaud, D.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. Galba truncatula and Fasciola hepatica: Genetic costructures and interactions with intermediate host dispersal. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 186-194. [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, E.; Trouve, S.; Facon, B.; Degen, L.; Goudet, J. High quantitative and no molecular differentiation of a freshwater snail (Galba truncatula) between temporary and permanent water habitats. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16(16), 3484-3496. [CrossRef]
- Alda, P.; Lounnas, M.; Vázquez, A.A., Ayaqui, R.; Calvopiña, M.; Celi-Erazo, M.; Dillon R.T.; Jr, González Ramírez, L.C.; Loker, E.S.; Muzzio-Aroca, J.; Nárvaez, A.O.; Noya, O.; Pereira, A.E.; Robles, L.M.; Rodríguez-Hidalgo, R.; Uribe, N.; David, P.; Jarne, P.; Pointier, J.P.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. Systematics and geographical distribution of Galba species, a group of cryptic and worldwide freshwater snails. Mol. Phylogenetics Evolut. 2021, 157, 107035. [CrossRef]
- Ebbs, E.T.; Loker, E.S.; Brant, S.V. Phylogeography and genetics of the globally invasive snail Physa acuta Draparnaud 1805, and its potential to serve as an intermediate host to larval digenetic trematodes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18(1), 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Kengne-Fokam, A.C.; Nana-Djeunga, H.C.; Djuikwo-Teukeng, F.F.; Njiokou, F. Analysis of mating system, fecundity, hatching and survival rates in two Schistosoma mansoni intermediate hosts (Biomphalaria pfeifferi and Biomphalaria camerunensis) in Cameroon. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Burgarella, C.; Gayral, P.; Ballenghien, M.; Bernard, A.; David, P.; Jarne, P.; Correa, A.; Hurtrez-Bousses, S.; Escobar, J.; Galtier, N.; Glémin, S. Molecular evolution of freshwater snails with contrasting mating systems. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32(9), 2403-2416. [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, A.A.; Alba, A.; Alda, P.; Vittecoq, M.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S. On the arrival of fasciolosis in the Americas. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38(3), 195-204. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.;, Noble, L.R.; Rollinson, D.; Southgate, V.R.; Webster, J.P.; Jones, C.S. Low genetic diversity in a snail intermediate host (Biomphalaria pfeifferi Krass, 1848) and schistosomiasis transmission in the Senegal River Basin. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19(2), 241-256. [CrossRef]
- Soldánová, M.; Selbach, C.; Sures, B.; Kostadinova, A.; Pérez-del-Olmo, A. Larval trematode communities in Radix auricularia and Lymnaea stagnalis in a reservoir system of the Ruhr River. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Selbach, C.; Soldánová, M.; Feld, C.K.; Kostadinova, A.; Sures, B. Hidden parasite diversity in a European freshwater system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10(1), 2694. [CrossRef]
- Roldán, C.; Begovoeva, M.; López-Olvera. J.R.; Velarde, R.; Cabezón, Ó.; Molinar Min, A.R.; Pizzato, F.; Pasquetti, M.; Fernández Aguilar, X.; Mentaberre, G.; Serrano, E.;, Puig Ribas, M.; Espunyes, J.; Castillo-Contreras, R.; Estruch, J.; Rossi, L. Endemic occurrence of Fasciola hepatica in an alpine ecosystem, Pyrenees, Northeastern Spain. Transbound.Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68(4), 2589-2594. [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska-Ochmann, K.; Cuber, P.; Lewin, I. The first record and occurrence of Stagnicola turricula (Held, 1836)(Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Lymnaeidae) in Upper Silesia (Southern Poland) in relation to different environmental factors. Zoo. Anz. J. Comp. Zool. 2012, 251(4), 357-363. [CrossRef]
- Outa, J.O.; Sattmann, H.; Köhsler, M.; Walochnik, J.; Jirsa, F. Diversity of digenean trematode larvae in snails from Lake Victoria, Kenya: First reports and bioindicative aspects. Acta Trop. 2020, 206, 105437. [CrossRef]
- Sokolow, S.H.; Jones, I.J.; Jocque, M.; La, D.; Cords, O.; Knight, A.; Lund, A.; Wood, C.L.; Lafferty, K.D.; Hoover, C.M.; Collender, P.A.; Remais, J V.; Lopez-Carr, D.; Fisk, J.; Kuris, A.M.; De Leo, G.A. Nearly 400 million people are at higher risk of schistosomiasis because dams block the migration of snail-eating river prawns. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, Biol. Sci. 2017, 372(1722), 20160127. [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.M. Epidemiology of schistosomiasis in Egypt: travel through time. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4(5), 425-432. [CrossRef]
- Hrivnák, R.; Medvecká, J;, Baláži, P.; Bubíková, K.; Oťaheľová, H.; Svitok, M. Alien aquatic plants in Slovakia over 130 years: historical overview, current distribution and future perspectives. NeoBiota 2019, 49, 37–56. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Murillo, P. Hydrocharis laevigata in Europe. Plants, 2023, 12(4), 701. [CrossRef]
- Abe, E.M.; Guan, W.; Guo, Y.H.; Kassegne, K., Qin, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; CHen, J.-H.; Ekpo, U.F.; Li, S.-Z.; Zhou, X.N. Differentiating snail intermediate hosts of Schistosoma spp. using molecular approaches: fundamental to successful integrated control mechanism in Africa. Infect. Dis. Poverty, 2018, 7(02), 6-18. [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M.L. Impact of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) on snail hosts of schistosomiasis in Lake Victoria, East Africa. EcoHealth, 2005, 2, 81-86. [CrossRef]
- Hussner, A.. Alien aquatic plant species in European countries. Weed Res. 2012, 52(4), 297-306. [CrossRef]
- Preston, D L.; Crone, E.R.; Miller-ter Kuile, A.; Lewis, C.D.; Sauer, E.L.; Trovillion, D.C. Non-native freshwater snails: a global synthesis of invasion status, mechanisms of introduction, and interactions with natural enemies. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67(2), 227-239. [CrossRef]
- Vignoles, P., Dreyfuss, G.; Rondelaud, D. Consequences of invasion by Pseudosuccinea columella on the dynamics of native lymnaeids living on the acid soils of central France. Molluscan Res. 2018, 38(4), 287-295.
- Schols, R.; Carolus, H.; Hammoud, C.; Muzarabani, K.C;, Barson, M.; Huyse, T. Invasive snails, parasite spillback, and potential parasite spillover drive parasitic diseases of Hippopotamus amphibius in artificial lakes of Zimbabwe. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Pointier, J.P. Coustau, C. Rondelaud, D. Theron, A. Pseudosuccinea columella (Say 1817) (Gastropoda, Lymnaeidae), snail host of Fasciola hepatica: first record for France in the wild. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101(5), 1389-1392. [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.; Lőkkös, A. (2021) Mollusc fauna of the Lake Hévíz (in Hungarian). .Soosiana 2021, 35, 3-18.
- Njiokou, F.; Mouafo, J.B.; Teukeng, F.; Njine, T.; Ekobo, A.S.; Jarne, P. The influence of self-fertilization and pairing on life-history traits in the freshwater snail Bulinus forskalii (Gastropoda, Planorbidae). Acta Trop. 2000, 76(2), 159-167. [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, G.; Vignoles, P.; Rondelaud, D. Relationships between the distribution of Galba truncatula (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) climatic conditions and the altitude of municipalities in Haute Vienne (France). In Ann. Limnol. 2018, 54, 19-28). [CrossRef]
- Crone, E.R.; Sauer, E.L.; Preston, D.L.. Non-native fish facilitate non-native snails and alter food web structure in experimental pond communities. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37(4), 947-958. [CrossRef]
- Beesley, N.J.; Williams, D.J.; Paterson, S.; Hodgkinson, J. Fasciola hepatica demonstrates high levels of genetic diversity, a lack of population structure and high gene flow: Possible implications for drug resistance. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 11–20. [CrossRef]
- Turner, W C.; Kamath, P.L.; Van Heerden, H.; Huang, Y.H.; Barandongo, Z.R.; Bruce, S.A.; Kausrud, K. The roles of environmental variation and parasite survival in virulence–transmission relationships. Royal Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8(6), 210088. [CrossRef]
- Morran, L.T;, Schmidt, O.G.; Gelarden, I A.; Parrish, R.C.; Lively, C.M. Running with the Red Queen: host-parasite coevolution selects for biparental sex. Science, 2011, 333(6039), 216-218. [CrossRef]
- Arakelyan, M.; Harutyunyan, T.; Aghayan, S.A.; Carretero, M.A.. Infection of parthenogenetic lizards by blood parasites does not support the “Red Queen hypothesis” but reveals the costs of sex. Zoology, 2019, 136, 125709. [CrossRef]
- Majewska, A.A.; Sims, S.; Schneider, A.; Altizer, S.; Hall, R.J. Multiple transmission routes sustain high prevalence of a virulent parasite in a butterfly host. Proc. R. Soc. B, 2019, 286(1910), 20191630. [CrossRef]
- White, P.S.; Choi, A.; Pandey, R.; Menezes, A.; Penley, M.; Gibson, A.K.; de Roode, J.; Morran, L. Host heterogeneity mitigates virulence evolution. Biol. Lett. 2020, 16, 20190744. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




