Submitted:
26 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
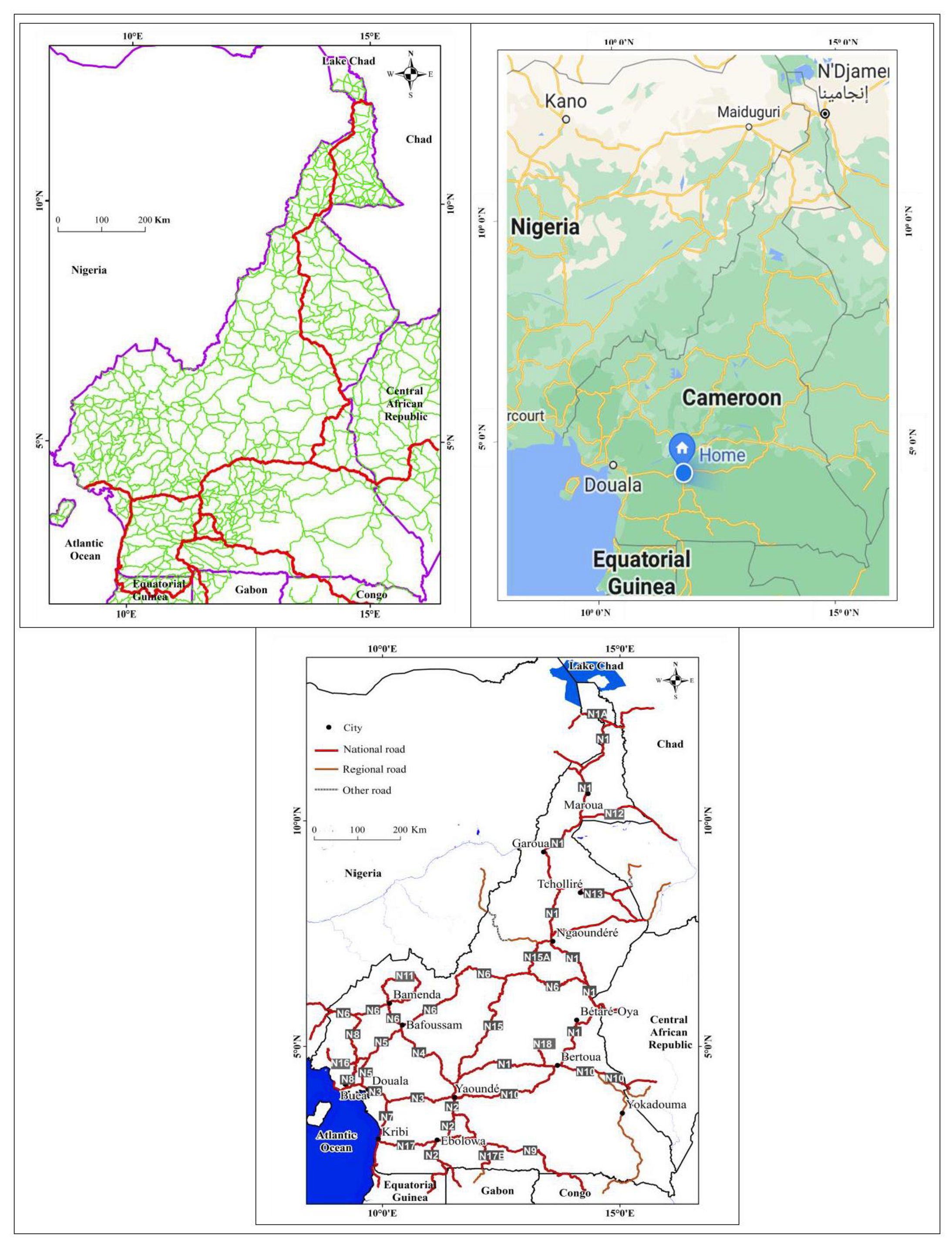
2. Study area
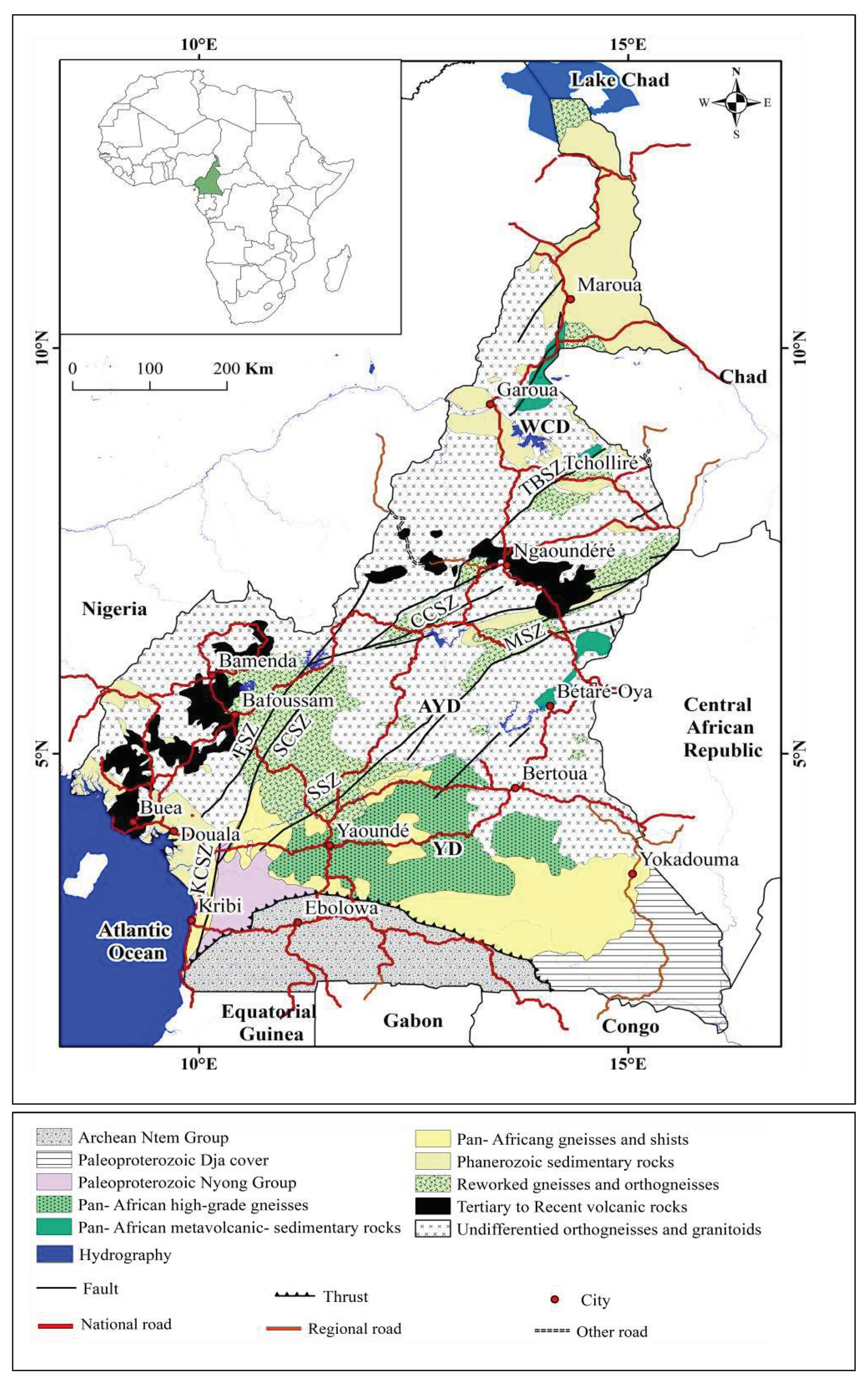
2.1. Geological setting
- (1)
- The southern domain is a huge allochthonous nappe unit bounded to the south by the Congo Craton, to the west by the Kribi-Campo fault and extending eastwards into the Central African Republic in the Bolé and Gbaya series [35]. It comprises high-grade metamorphic and igneous rock units, low to medium grade shales of sedimentary origin and metamorphosed Neoproterozoic metasediments under high pressure metamorphism [36]; (2) the central domain, which is bounded by the Sanaga Fault in the south and the Tcholliré-Banyo Fault in the north, includes the Adamaoua Fault and other anastomosing faults, constituting the N70E central Cameroonian shear zone system [37].
2.2. Roads
3. Material and methods
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS
3.1.2. SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)
3.1.3. Field data
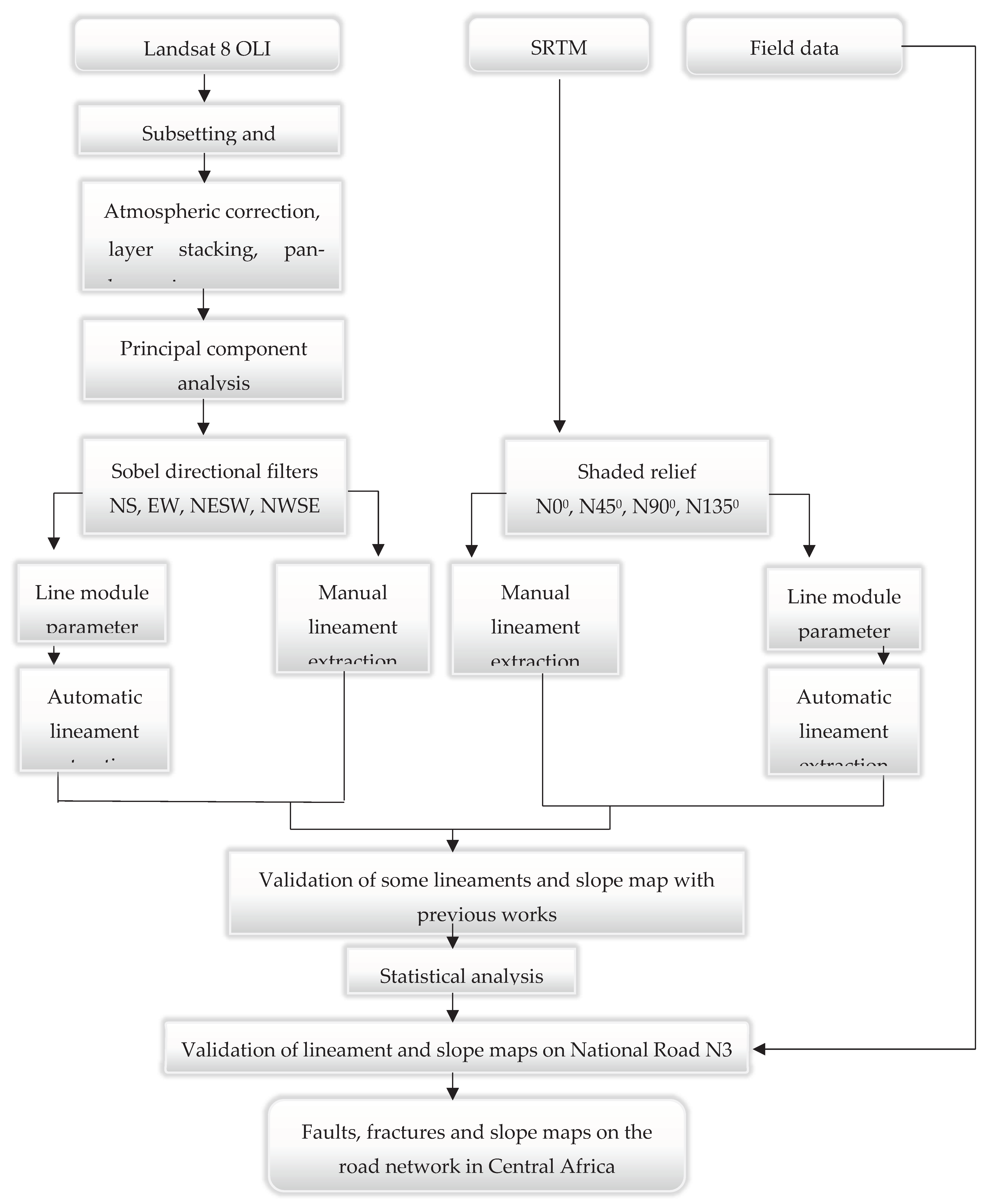
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Preprocessing
3.2.2. Processing
- Principal component analysis (PCA)
- Directional filtering
- Shaded relief
- Manual and automatic lineament extraction
- Rose diagram
- Slope
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Results
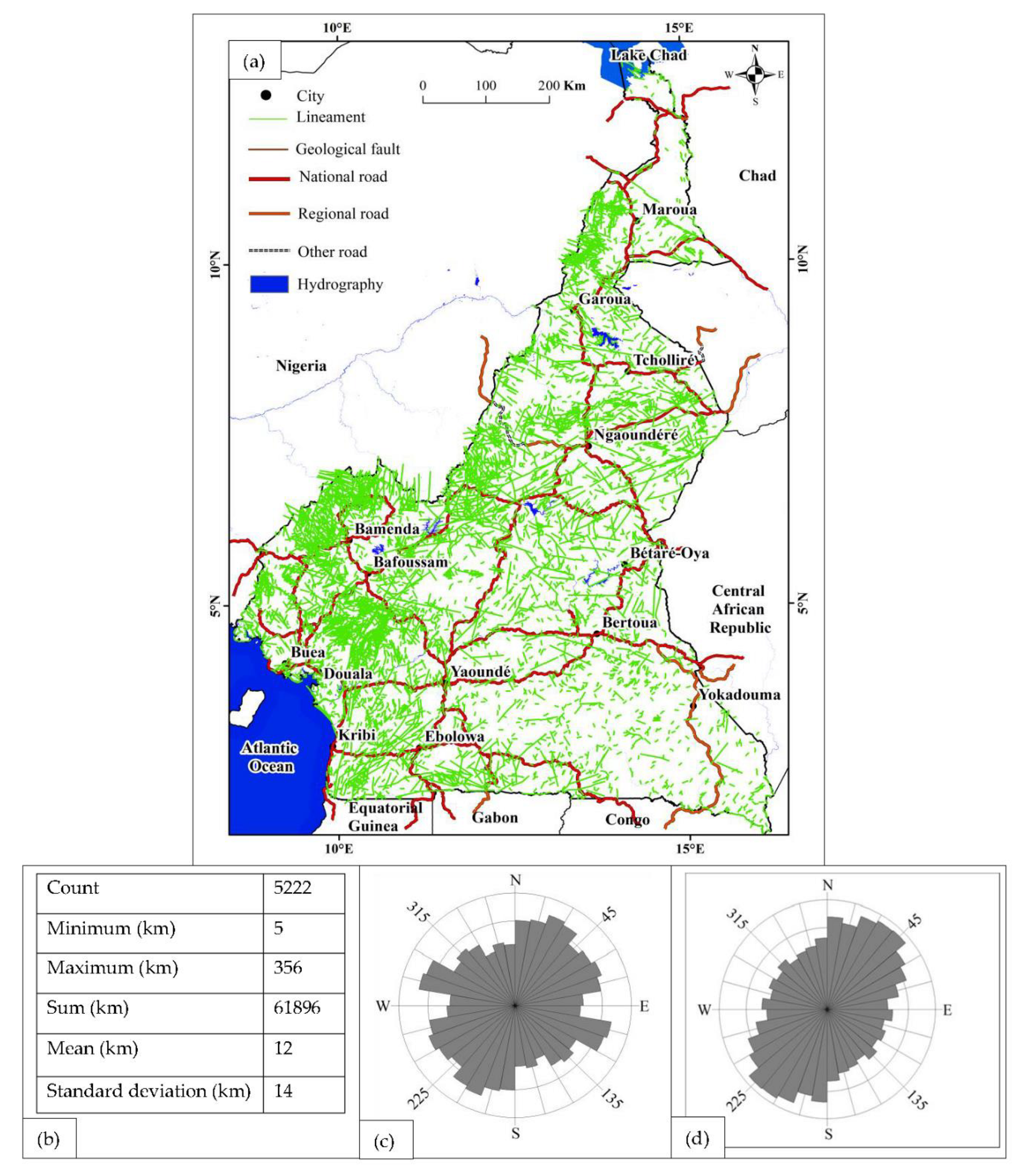
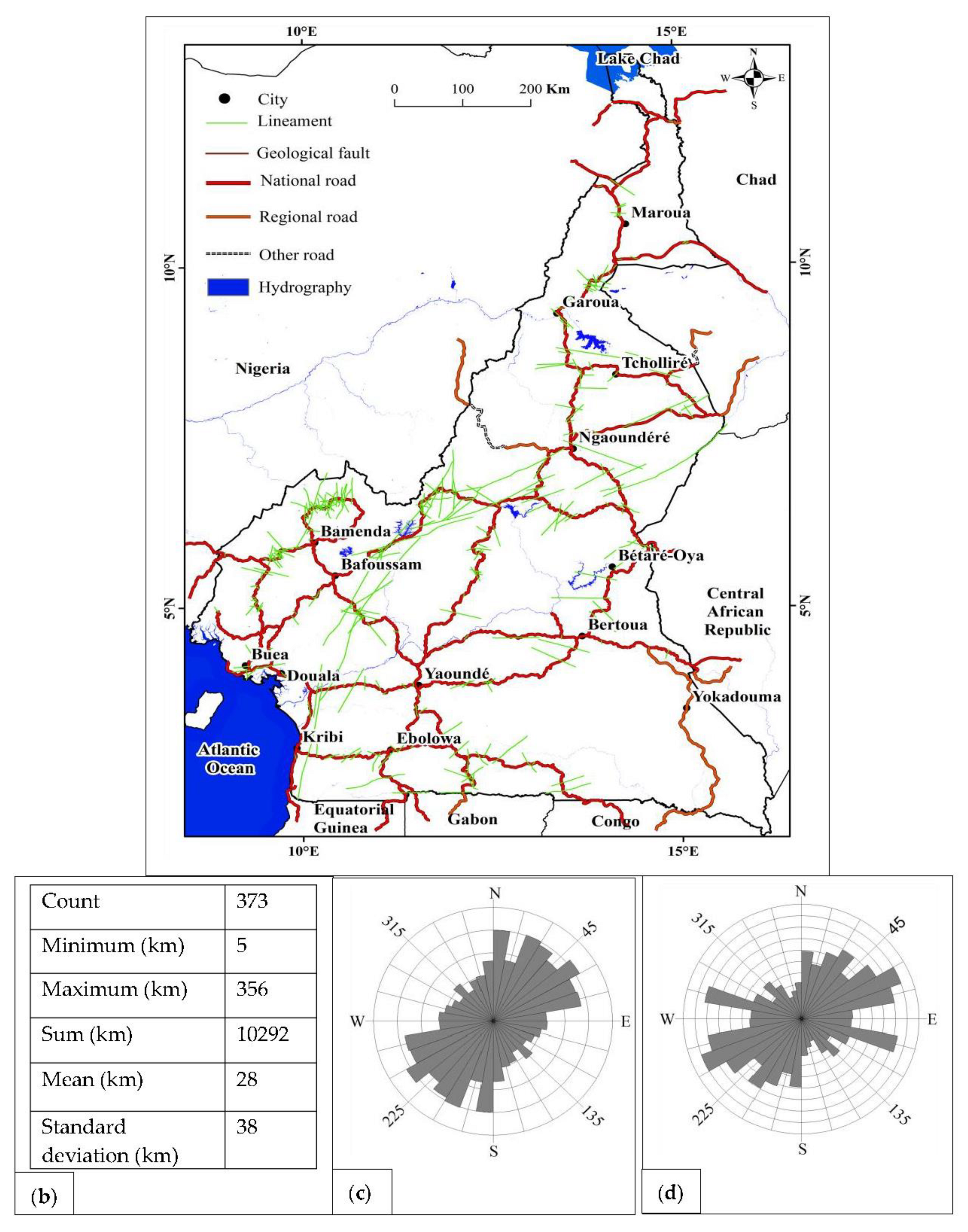
4.1.1. Lineaments obtained
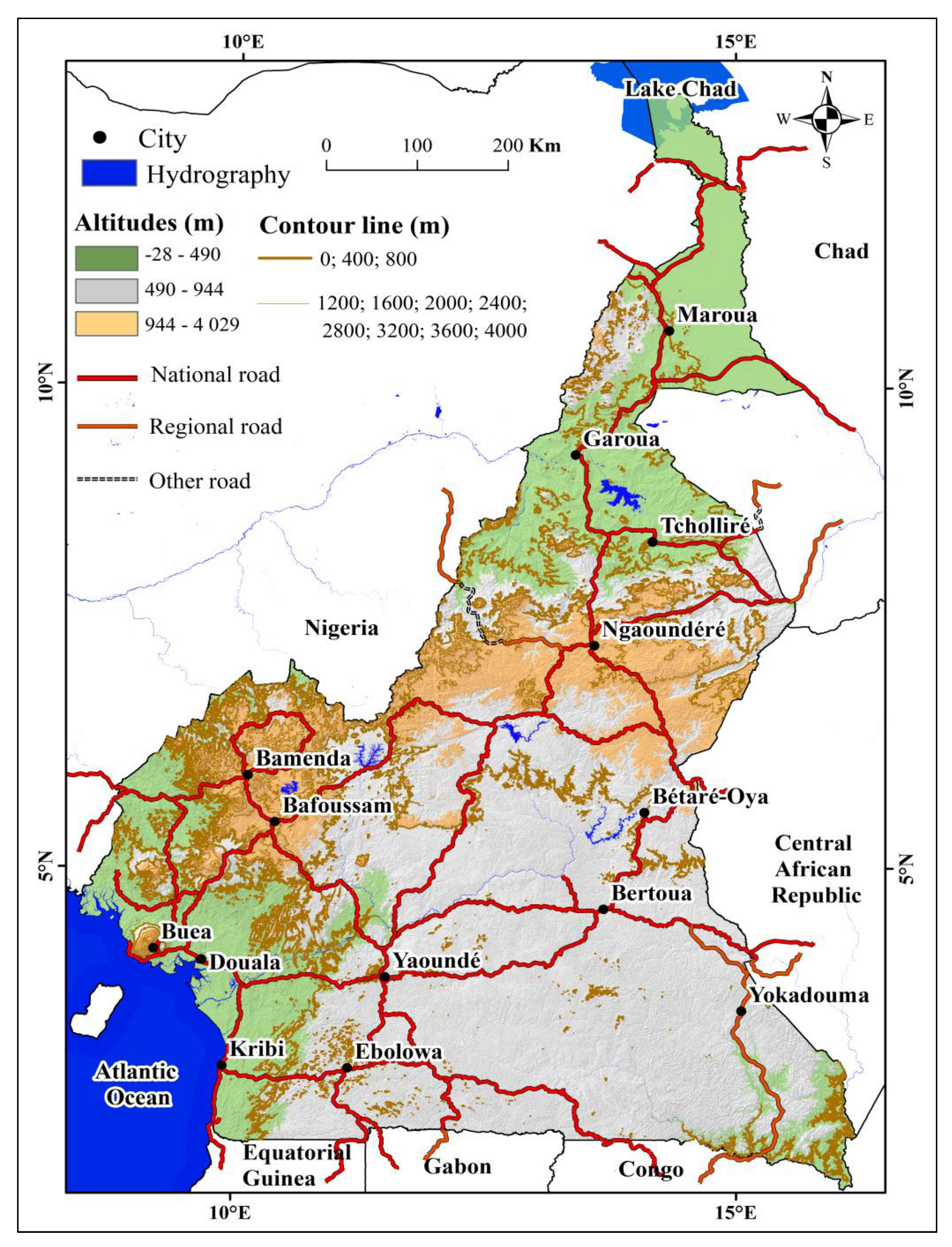
4.1.2. Altimetry
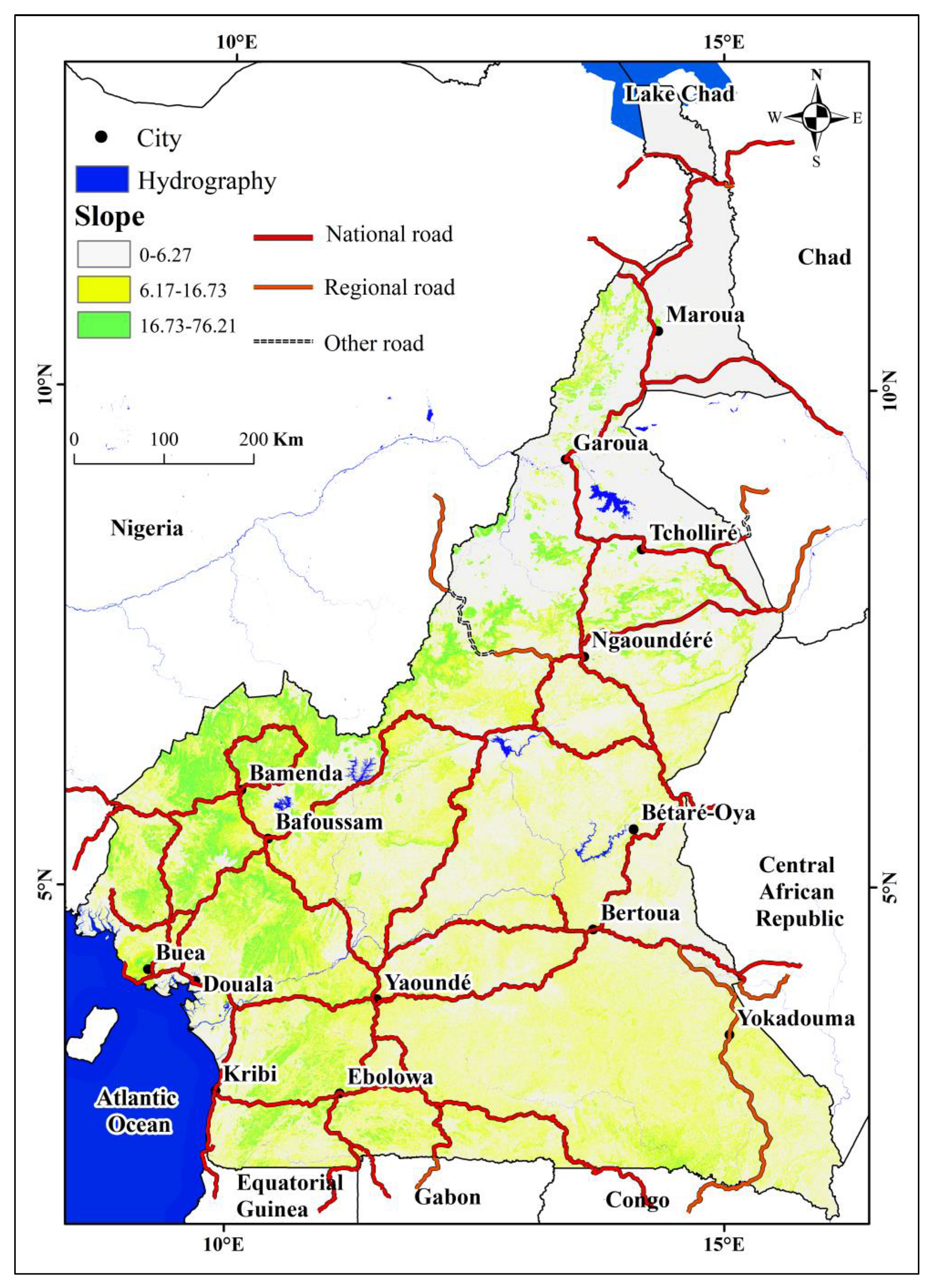
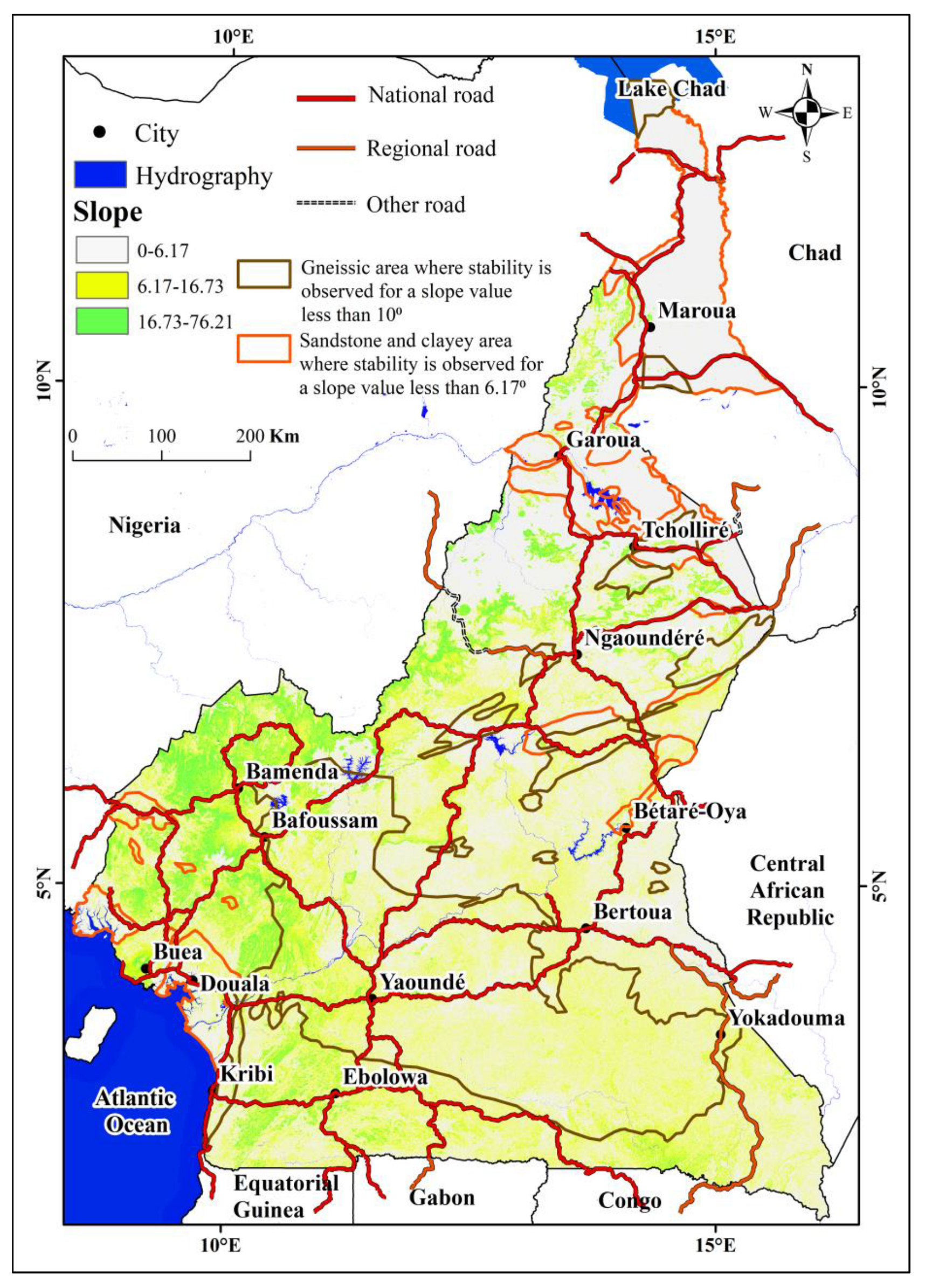
4.1.3. Slope
4.2. Discussion
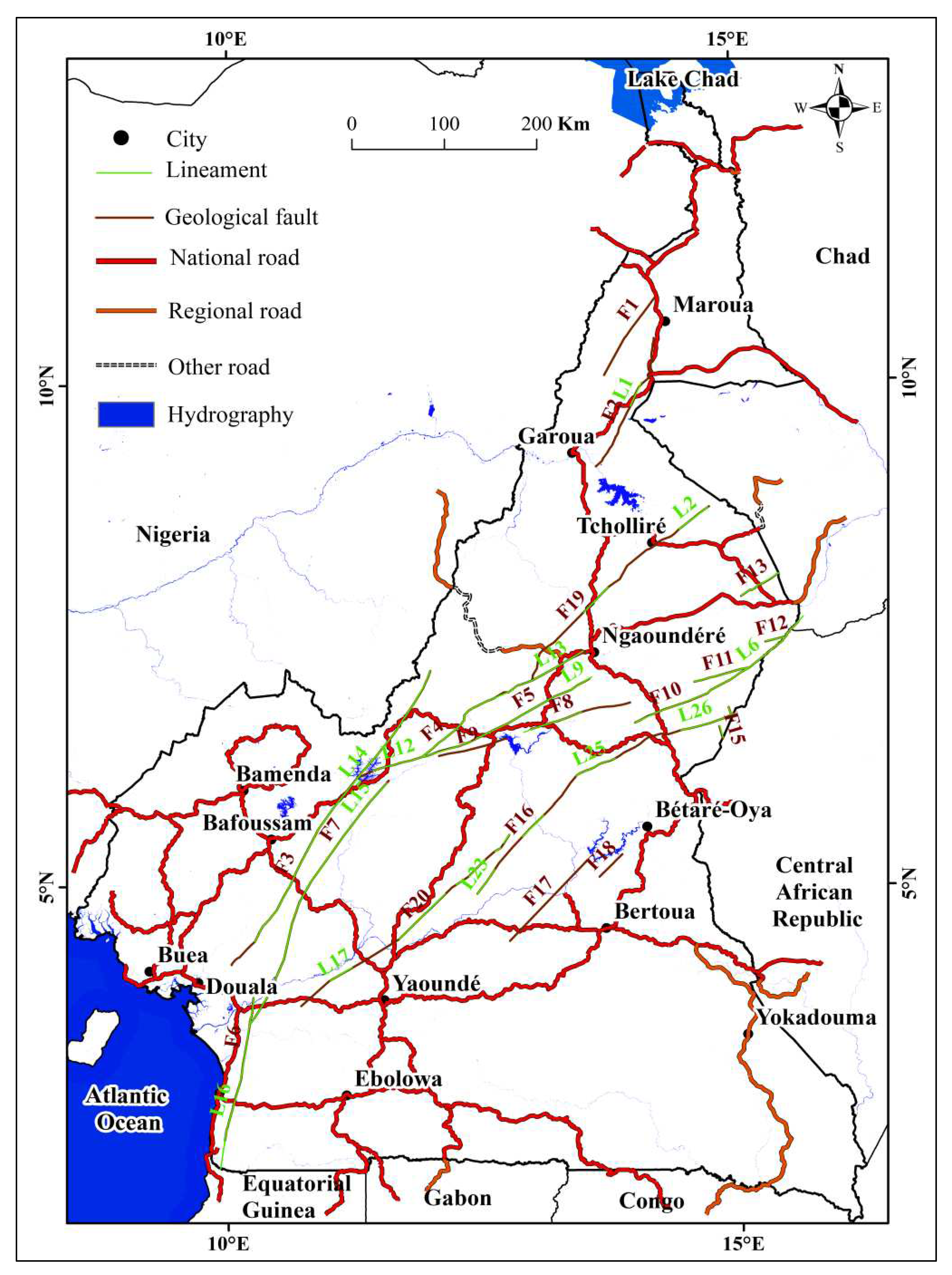
4.2.2. Correlation of lineaments with the geological map
4.2.3. Correlation of the lineaments with some previous geophysical work
4.2.4. Correlation of the lineaments with the elevation map
4.2.5. Correlation of lineaments with the slope map
4.2.6. Correlation of the slope map with the geological map
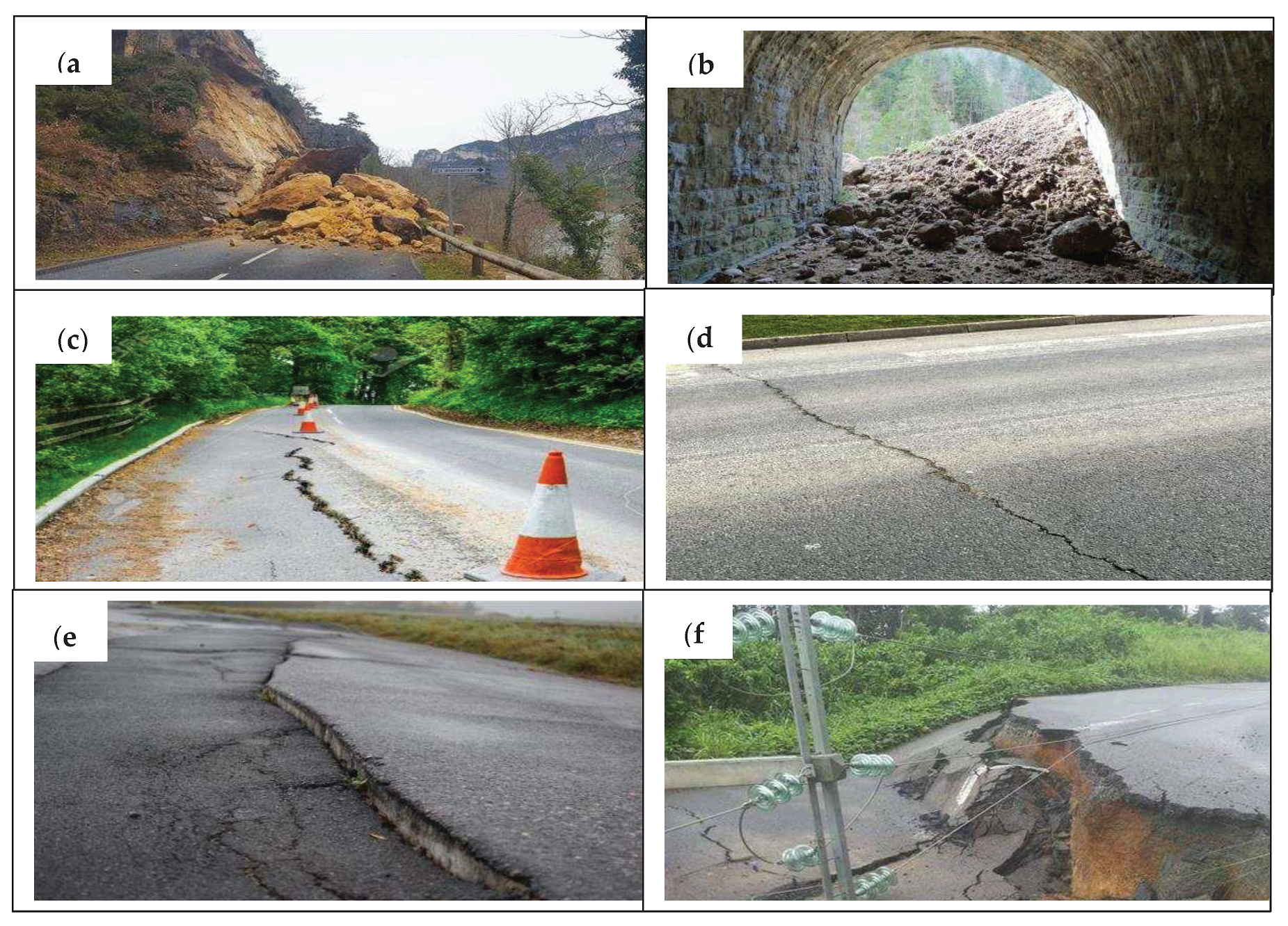
4.2.7. Correlation of the slope map with the road network
4.2.8. Correlation of lineaments with the road network
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Coûts unitaires des projets d’infrastructure en Afrique subsaharienne. 2008. Available online: https://www.eu-africa-infrastructure-tf.net/attachments/library/aicd-background-paper-11-unit-costs-summary-fr.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Coût de la route au kilomètre : Le Gabon affole les statistiques. 2016. Available online: http://news.alibreville.com/h/55354 (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Gabon : Entre 1 et 3 milliards de francs CFA, le km de route le plus cher d’Afrique. 2021. Available online: https://www.gabonreview.com/gabon-entre-1-et-3-milliards-de-francs-cfa-le-km-de-route-le-plus-cher-dafrique/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Le coût du km de route bitumée au Cameroun est le double du prix moyen en Afrique. 2013. 1709. Available online: https://www.investiraucameroun.com/btp/1709-4597-le-cout-du-km-de-route-bitumee-au-cameroun-est-le-double-du-prix-moyen-en-afrique (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Lin, Y.; Zong, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Across-fault ground motions and their effects on some bridges in the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake. Advances in Bridge Engineering 2021, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Hou, L.; Xu, S. A Review of Digital Twin Applications in Civil and Infrastructure Emergency Management. Buildings 2023, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Mero, P.; Briones-Bitar, J.; Morante-Carballo, F.; Stay-Coello, D.; Blanco-Torrens, R.; Berrezueta, E. Evaluation of Slope Stability in an Urban Area as a Basis for Territorial Planning: A Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretouyap, Z.; Kemgang, F. E. G.; Domra, J. K.; Bisso, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; D., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Njandjock, P. N. Understanding the occurrences of fault and landslide in the region of West-Cameroon using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Natural Hazards 2021, 109, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R. N.; Islam, M.; Islam, M. N. Modeling on management strategies of slope stability and susceptibility to landslides catastrophe at hilly region in Bangladesh. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2017, 3, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbouombouo, I. N.; Meli’i, J. L.; Gweth, M. M. A.; Pokam, B. P. G.; Koffi, Y. P.; Njock, M. C.; Nkoma, M. A. P.; Nouck, P. N. Analysis of safety factors for roads slopes in central Africa. Engineering Failure Analysis 2022, 138, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweth, M. M. A.; Nkoungou, H. E.; Meli’i, J. L.; Gouet, D. H.; Nouck, P. N. Fractures models comparison using GIS data around crater lakes in Cameroon volcanic line environment. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science 24, 419–429. [CrossRef]
- Nguemhe Fils, S. C.; Mongo, C. H. B.; Nkouathio, D. G.; Mimba, M. E.; Etouna, J.; Nouck, P. N.; Nyeck, B. Radarsat-1 image processing for regional-scale geological mapping with mining vocation under dense vegetation and equatorial climate environment, Southwestern Cameroon. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science 2018, 21, S43–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, R.; Singh, B. Landslide hazard and risk assessment mapping of mountainous terrains—a case study from Kumaun Himalaya, India. Engineering Geology 1996, 43, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.-N.; Vu, M.-N.; Pham, D.-T.; Nguyen-Sy, T.; Nguyen, Q.-B.; Dang, V.-D. A Multi-Layer Blowout Model for the Tunneling Face Stability Analysis. Buildings 2023, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; RoY, A.; Kumar, R. V.; Mukherjee, A.; KhirE, M. Landslide hazard susceptibility mapping based on terrain and climatic factors for tropical monsoon regions. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 2000, 58, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, B.; Mohammed, M.; Korme, T. Natural hazard assessment using GIS and remote sensing methods, with particular reference to the landslides in the Wondogenet area, Ethiopia. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part C: Solar, Terrestrial & Planetary Science 2001, 26, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Gupta, R.; Arora, M. GIS-based landslide hazard zonation in the Bhagirathi(Ganga) valley, Himalayas. International journal of remote sensing 2002, 23, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Tung, C.C. A GIS-based potential analysis of the landslides induced by the Chi-Chi earthquake. Engineering Geology 2004, 71, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soesilo, I.; Hoppin, R. Evaluation of digitally processed Landsat imagery and SIR-A imagery for geological analysis of West Java region, Indonesia. Remote sensing for ressources development and environmental management. International symposium 1986, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, J.; Jha, V.K.; Rawat, G.S. Application of binary logistic regression analysis and its validation for landslide susceptibility mapping in part of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2257–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.J. Detecting landslide location using KOMPSAT 1 and its application to landslide-susceptibility mapping at the Gangneung area, Korea. Advances in Space Research 2006, 38, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Akhir, J. M.; Abdullah, I. Automatic mapping of lineaments using shaded relief images derived from digital elevation model (DEMs) in the Maran–Sungi Lembing area, Malaysia. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 2010, 15, 949–958. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, B.M; Thompson, T.J. Lineament Analysis of Mineral Areas of Interest in Afghanistan: Automatically delineated lineaments using 30-m TM imagery. 2012. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2012/1048/pdf/ofr2012-1048.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Thannoun, R. G. Automatic extraction and geospatial analysis of lineaments and their tectonic significance in some areas of Northern Iraq using remote sensing techniques and GIS. International Journal of Enhanced Research In Science Technology & Engineering Bulletin 2013, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ramli, M.; Yusof, N.; Yusoff, M.; Juahir, H.; Shafri, H. Lineament mapping and its application in landslide hazard assessment: a review. Bulletin of engineering Geology and the Environment 2010, 69, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dossary, S.; Marfurt, K. J. Lineament-preserving filtering. Geophysics 2007, 72, P1–P8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.; Haas, R.; Schell, J.; Deering, D. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with ERTS Third ERTS Symposium (pp. 309–317). Washington, DC: NASA. 1973. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19740022614/downloads/19740022614.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Gazel, J.; Guiraudie, C. Notice Explicative sur la Région Abong-Mbang Ouest de la Carte Géologique de Reconnaissance à l’échelle du 1/500.000. 1965. Direction des Mines et Géologie, Yaoundé, 29 p. Available online: https://books.google.com/books/about/Notice_explicative_sur_la_feuille_Abong.html?id=kaAPswEACAAJ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Vicat, J.-P.; Pouclet, A.; Nsifa, E. Les dolérites du groupe du Ntem (Sud Cameroun) et des régions voisines (Centrafrique, Gabon, Congo, Bas Zaïre) : Caractéristiques géochimiques et place dans l’évolution du craton du Congo au Protérozoïque. 1998. In: J. P. Vicat, and P. Bilong, Eds., Géologie et environnements au Cameroun. Collection GEOCAM: 305-324. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jean_Paul_Vicat/publication/281612596_Les-dolerites-du-complexe-du-Ntem-Sud-Cameroun-comparaison-avec-les-dolerites-du-Nord-Ouest-du-craton-du-Congo-et-evolution-geodynamique-du-Paleoproterozoique-et-du-Neoproterozoique.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Gong, P.; Yu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Liang, L.; Li, X.; Ji, L.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Z. A new research paradigm for global land cover mapping. Annals of GIS 2016, 22, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D. P.; Saepuloh, A.; Meer, F. V. D. Land cover classification in the tropics, solving the problem of cloud covered areas using topographic parameters. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 77, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toteu, S.F.; Van Schmus, W.R.; Penaye, J.; Nyobe, J.B. U/Pb and Sm/ Nd edvidence for Eburnian and Pan-African high-grade metamorphism in cratonic rocks of southern Cameroon. Precambrian Res. 1994, 67, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchameni, R.; Pouclet, A.; Penaye, J.; Ganwa, A.A.; Toteu, S.F. Petrography and geochemistry of the Ngaoundere Pan-African granitoids in Central North Cameroon: Implications for their sources and geological setting. J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 2006, 44, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toteu, S. F.; PenayE, J.; Djomani, Y. P. Geodynamic evolution of the Pan-African belt in central Africa with special reference to Cameroon. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 2004, 41, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, C.; Poidevin, J.L. U-Pb zircon evidence for a pan-african granulite facies metamorphism in the Central African Republic. A new interpretation of the high-grade series of the northern border of the congo craton. Precambrian Res. 1987, 36, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzenti, J.; Barbey, P.; MacaudierE, J.; Soba, D. Origin and evolution of the late Precambrian high-grade Yaounde gneisses (Cameroon). Precambrian research 1988, 38, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njanko, T.; Nédélec, A.; Affaton, P. Synkinematic high-K calc-alkaline plutons associated with the Pan-African Central Cameroon shear zone (W-Tibati area): petrology and geodynamic significance. Journal of African Earth Sciences 2006, 44, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eboulement spectaculaire sur la route des gorges du Tarn. 2017. Available online: https://www.journaldemillau.fr/2017/03/08/un-eboulement-spectaculaire-sur-la-route-des-gorges-du-tarn/ (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Haute-Savoie : spectaculaire éboulement sur la départementale 22 à Vinzier, dans le Chablais. 2018. Available online: https://images.app.goo.gl/ci97cQee8MZbyWqL6 (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Road works on cracked Tarmac from subsidence. 2016. Available online: https://images.app.goo.gl/7pWM2E9HkamWFunS7 (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Colmaroute spécialiste du traitement fissures de chaussée. 2014. Available online: https://images.app.goo.gl/25gtcYSrZkgdeSqA8 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Une route fissurée et déformée qui exaspère le maire et les habitants. 2017. Available online: https://images.app.goo.gl/mJUdXYF8Kmqv15t4A (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Effondremant de la route à Bifoun : le gouveernement se mobilise pour rétablir la situation. 2018. Available online: https://courierdesjournalistes.com/societe/effondrement-de-la-rote-a-bifoun-le-gouvernement-se-mobilise (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Nzenti, J.; Barbey, P.; Bertrand, J.; Macaudière, J. La chaîne panafricaine au Cameroun : cherchons suture et modèle. 1994. Abstracts 15eme RST, Nancy, Société Géologique France, édition Paris, 99.
- Nzolang, C.; Kagami, H.; Nzenti, J. P.; Holtz, F. Geochemistry and preliminary Sr-Nd isotopic data on the Neoproterozoic granitoids from the Bantoum area, west Cameroon: evidence for a derivation from a Paleoproterozoic to Archaean crust. Polar Geosci. 2003, 16, 196–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njiosseu, E. L. T.; Nzenti, J.-P.; Njanko, T.; Kapajika, B.; Nédélec, A. New UPb zircon ages from Tonga (Cameroon): coexisting Eburnean–Transamazonian (2. 1 Ga) and Pan-African (0.6 Ga) imprints. Comptes Rendus Geoscience 2005, 337, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toteu, S.; Michard, A.; Bertrand, J.; Rocci, G. U/Pb dating of Precambrian rocks from Northern Cameroon, orogenic evolution and chronology of the Pan-African belt of Central Africa. Precambrian Research 1987, 37, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaye, J.; Toteu, S. F.; Michard, A.; Bertrand, J.-M.; Dautel, D. 1989. Reliques granulitiques d’âge protérozoïque inférieur dans la zone mobile panafricaine d’Afrique centrale au Cameroun; géochronologie U-Pb sur zircons. CR Acad. Sci. Paris 2003, 309, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Toteu, S.; Van Schmus, W.; Penaye, J.; Michard, A. New U–Pb and Sm–Nd data from north-central Cameroon and its bearing on the pre-Pan African history of central Africa. Precambrian Research 2001, 108, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngako, V.; Affaton, P.; Njonfang, E. Pan-African tectonics in northwestern Cameroon: implication for the history of western Gondwana. Gondwana research 2008, 14, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankeu, B.; Greiling, R.O.; Nzenti, J.P.; Ganno, S.; Danguene, P.Y.E.; Bassahak, J.; Hell, J.V. Contrasting Pan-African structural styles at the NW margin of the Congo Shield in Cameroon. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 146, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C. K.; Satir, M.; Siebel, W. TTG magmatism in the Congo craton; a view from major and trace element geochemistry, Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd systematic: case of Sangmelima region, Ntem complex, southern Cameroon. Journal of African Earth Sciences 2004, 40, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouclet, A.; Tchameni, R.; Mezger, K.; Vidal, M.; Nsifa, N. E.; Penaye, P. Archaean crustal accretion at the northern border of the Congo Craton (South Cameroon). The charnockite-TTG link. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2007, 178, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Takam, T.; Arima, M.; Kokonyangi, J.; Dunkley, D. J.; Nsifa, E. N. Paleoarchaean charnockites in the Ntem complex, Congo craton, Cameroon: insights from SHRIMP zircon U–Pb ages. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2009, 104, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchameni, R.; Lerouge, C.; Penaye, J.; Cocherie, A.; Milesi, J. P.; Toteu, S. F.; Nsifa, E. N. Mineralogical constraint for metamorphic conditions in a shear zone affecting the Archean Ngoulemakong tonalite, Congo craton (southern Cameroon) and retentivity of U–Pb SHRIMP zircon dates. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerouge, C.; Cocherie, A.; Toteu, S.F.; Penaye., J; Milesi, J.P., Tchameni; Fanning, C. M.; Deloule, E. Shrimp U–Pb zircon age evidence for Paleoproterozoic sedimentation and 2.05 Ga syntectonic plutonism in the Nyong Group, South-Western Cameroon: consequences for the Eburnean–Transamazonian belt of NE Brazil and Central Africa. Journal of African Earth Sciences 2006, 44, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C. K.; Satir, M.; Nsifa, E. N.; Liegeois, J. P.; Siebel, W.; Taubald, H. Archaean high K granitoids produced by remelting of the earlier Tonalite–Trondhjemite–Granodiorite (TTG) in the Sangmelima region of the Ntem complex of the Congo craton, southern Cameroon. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 817–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carte routière du Cameroun. 2023. Available online: https://www.club-des-voyages.com (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Tchato, S.C.; Manguelle-Dicoum, E.; Njandjock, P.N. Notice explicative des routes principales en Afrique Centrale. Université de Yaoundé 1, Faculté de sciences, 2022.
- Farr, T.G.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission produces a wealth of data. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union 2000, 81, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Earth explorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Gabr, S.; Ghulam, A.; Kusky, T. Detecting areas of high-potential gold mineralization using ASTER data. Ore Geology Reviews 2010, 38, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiri, Z.; El Harti, A.; Jellouli, A.; Maacha, L.; Bachaoui, E. M. Lithological mapping using Landsat 8 OLI and Terra ASTER multispectral data in the Bas Drâa inlier, Moroccan Anti Atlas. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2016, 10, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, R.; Kusky, T.; El Mezayen, A. Remote sensing detection of gold related alteration zones in Um Rus area, Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. Advances in Space Research 2012, 49, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pazner, M.; Duke, N. Lithologic and mineral information extraction for gold exploration using ASTER data in the south Chocolate Mountains (California). ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2007, 62, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bousquet, P. A statistical and geometrical edge detector for SAR images. IEEE Transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 1988, 26, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezry, E.; Lopes, A.; Touzi, R. Detection of structural and textural features for SAR images filtering. IGARSS’91; Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Espoo, Finland. New York, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., p. 2169-2172. 1991. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/575470 (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Lopes, A.; Nezry, E.; Touzi, R.; Laur, H. Structure detection and statistical adaptive speckle filtering in SAR images. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1993, 14, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binam, E. P. M.; Bidjeck, L. M. B.; Wambo, J. D. T.; Taku JR, A.; Betsi, T. B.; Ipan, A. S.; Nfada, L. T.; Dieudonné, L. B. Lithologic and structural mapping of the Abiete–Toko gold district in southern Cameroon, using Landsat 7 ETM+/SRTM. Comptes Rendus Geoscience 2018, 350, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenea, N. Improved geological mapping using Landsat TM data, Southern Red Sea Hills, Sudan: PC and IHS decorrelation stretching. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1997, 18, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzen, M.; Toprak, V. Filtering of satellite images in geological lineament analyses: an application to a fault zone in Central Turkey. International journal of remote sensing 1998, 19, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallast, U.; Gloaguen, R.; Geyer, S.; Rödiger, T.; Siebert, C. Derivation of groundwater flow-paths based on semi-automatic extraction of lineaments from remote sensing data. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2011, 15, 2665–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelouhed, F.; Algouti, A.; Algouti, A.; Mlouk, M. A.; Ifkirne, M. Lithological mapping using Landsat 8 Oli multispectral data in Boumalne, Imider, and Sidi Ali Oubork, High Central Atlas, Morocco. E3S Web of Conferences 2021, 234, 00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.; Koike, K. Arid land salinization detected by remotely-sensed landcover changes: A case study in the Siwa region, NW Egypt. Journal of arid environments 2006, 66, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Arya, A. K.; Agarwal, K. K. Landslide Occurrences Along Lineaments on NH-154A, Chamba, Himachal Pradesh; Extracted from Satellite Data Landsat 8, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing 2020, 48, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.K.; Oya, Y.M.S.; Olivier, F.; Assoma, V. Extraction de linéaments structuraux à partir d’images satellitaires, et estimation des biais induits, en milieu de socle précambrien métamorphisé. Revue Teledetection 2012, 10, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, B. B. S.; Gupta, R. P. Applied hydrogeology of fractured rocks, Springer Science & Business Media. 2010. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-90-481-8799-7 (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Li, N. Textural and rule-based lithological classification of remote sensing data, and geological mapping in Southwestern Prieska sub-basin. Transvaal Supergroup, South Africa. lmu. 2010, 60, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkono, C.; FéméniaS, O.; Lesne, A.; Mercier, J.-C.; Demaiffe, D. Fractal Analysis of lineaments in Equatorial Africa: insights on lithospheric structure. Open Journal of Geology 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actualités IRGM : Séisme dans plusieurs localités du Cameroun. 2019. Available online: https://www.irgm-cameroun.org/actualites (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Manguelle, E.D.; Bokosah, A.S.; Kwende-Mbanwi, T.E. Geophysical evidence for a major Precambrian schist-granite boundary in southern Cameroon. Tectonophysics 1992, 205, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweth, M.M.A.; Meli’i, J.L.; Oyoa, V.; Diab, A.D.; Gouet, D.H.; Jean, M.; Njandjock, P.N. Fracture network mapping using remote sensing in three crater lakes environments of the Cameroon volcanic line (central Africa). Arabian Journal of Geosciences 14, 422. [CrossRef]
- Cheunteu, C. A. F.; Adiang, C. M.; Pemi, M. M.; Tokam, A. P. K.; Nouayou, R.; Nguiya, S. Mapping of major tectonic lineaments across Cameroon using potential field data. Earth, Planets and Space 2022, 74, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguimbous-Kouoh, J.J.; Manguelle-Dicoum, E. Contribution of topographic and penetrometric measurements to a site characterization, case of the Kekem landslide, National road N⁰5 (western Cameroon). Earth Sci. Res. 2010, 14, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pouyon, D. E.; Ganno, S.; Tabod, C. T. Geophysical and Geotechnical Investigations of a Landslide in Kekem Area, Western Cameroon. International Journal of Geosciences 2012, 3, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Scenes | Row | Path | Acquisition date | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 58 | 182 | 01/05/2020 | 1 |
| 2 | 59 | 182 | 01/05/2020 | 1 |
| 3 | 55 | 183 | 13/02/2020 | 1 |
| 4 | 57 | 183 | 13/02/2020 | 1 |
| 5 | 58 | 183 | 28/01/2020 | 1 |
| 6 | 51 | 184 | 20/02/2020 | 1 |
| 7 | 52 | 184 | 04/02/2020 | 1 |
| 8 | 53 | 184 | 04/02/2020 | 1 |
| 9 | 54 | 184 | 20/02/2020 | 1 |
| 10 | 55 | 184 | 20/02/2020 | 1 |
| 11 | 56 | 184 | 18/11/2020 | 1 |
| 12 | 57 | 184 | 18/11/2020 | 1 |
| 13 | 58 | 184 | 23/12/2015 | 1 |
| 14 | 51 | 185 | 27/02/2020 | 1 |
| 15 | 52 | 185 | 11/02/2020 | 1 |
| 16 | 53 | 185 | 11/02/2020 | 1 |
| 17 | 54 | 185 | 11/02/2020 | 1 |
| 18 | 55 | 185 | 11/02/2020 | 1 |
| 19 | 56 | 185 | 11/02/2020 | 1 |
| 20 | 57 | 185 | 26/01/2020 | 1 |
| 21 | 58 | 185 | 26/01/2020 | 1 |
| 22 | 55 | 186 | 18/02/2020 | 1 |
| 23 | 56 | 186 | 05/03/2020 | 1 |
| 24 | 57 | 186 | 06/01/2016 | 1 |
| 25 | 58 | 186 | 29/03/2017 | 1 |
| 26 | 55 | 187 | 25/02/2020 | 1 |
| 27 | 56 | 187 | 24/01/2020 | 1 |
| 28 | 57 | 187 | 29/01/2016 | 1 |
| Threshold parameters and units | default values | Selected values |
|---|---|---|
| RADI (In pixels) | 10 | 10 |
| GTHR (In range, 0–255) | 100 | 80 |
| LTHR (In pixels) | 30 | 30 |
| FTHR (In pixels) | 3 | 3 |
| ATHR (In degrees) | 30 | 20 |
| DTHR (In pixels) | 20 | 20 |
| N0 | Lineaments | Geological faults | Corresponding road |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | / | F1 | / |
| 2 | L1 | F2 | N1 |
| 3 | L14 | F3 (FSZ) | N4, N6 |
| 4 | L13 | F4 | N6, N15A |
| 5 | L9, L10, L11, L12 | F5 (CCSZ) | N6, N15A |
| 6 | L16 | F6 (KCSZ) | N3, N17 |
| 7 | L15 | F7 (SCSZ) | N3, N4 |
| 8 | L8 | F8 | N6 |
| 9 | / | F9 | N15 |
| 10 | L6 | F10 | N1 |
| 11 | L7 | F11 | / |
| 12 | L5 | F12 | / |
| 13 | L4 | F13 | N13 |
| 14 | L27 | F14 | / |
| 15 | L28 | F15 | / |
| 16 | L23, L24, L25, L26 | F16 (MSZ) | N1, N6 |
| 17 | / | F17 | N1 |
| 18 | / | F18 | / |
| 19 | L2, L3 | F19 (TBSZ) | N1, N13 |
| 20 | L17, L18, L19, L20, L21, L22 | F20 (SCZ) | N3, N4, N15 |
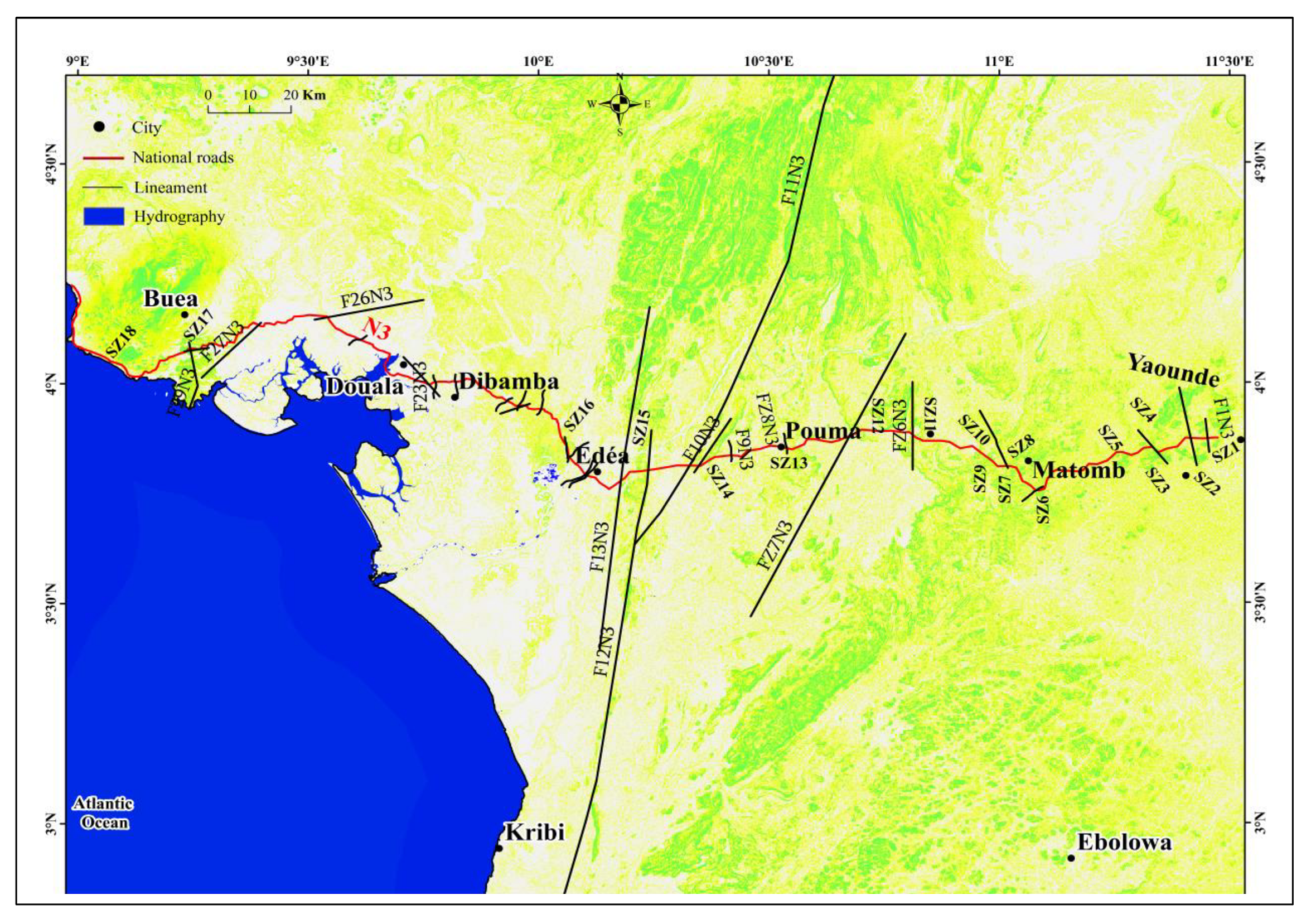
| Lineament | Slope | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1N3 | 11⁰26’55,5"E | 3⁰52’30,8"N | SZ1 | 11⁰28’16,2"E | 3⁰52’6,6"N |
| F2N3 | 11⁰24’40,7"E | 3⁰52’45,"N | SZ2 | 11⁰22’53,7"E | 3⁰51’0,5"N |
| F3N3 | 11⁰19’59,3"E | 3⁰51’0,2"N | SZ3 | 11⁰19’11,5"E | 3⁰50’58,3"N |
| F4N3 | 11⁰4’39,4"E | 3°45’18,1"N | SZ4 | 11⁰20’34,7"E | 3⁰50’30,2"N |
| FZ5N3 | 11⁰0’53,6"E | 3⁰48’38,4"N | SZ5 | 11⁰16’30,2"E | 3⁰50’8,5"N |
| FZ6N3 | 10⁰48’35,6"E | 3⁰52’57,3"N | SZ6 | 11⁰2’39,1"E | 3⁰47’23,2"N |
| FZ7N3 | 10⁰40’24"E | 3⁰52’51,4"N | SZ7 | 11⁰2’35,8"E | 3⁰47’15"N |
| FZ8N3 | 10⁰32’12,1"E | 3⁰51’22,8"N | SZ8 | 11⁰2’3,1"E | 3⁰48’24,7"N |
| F9N3 | 10⁰20’45,7"E | 3⁰48’45,4"N | SZ9 | 10⁰57’14,4"E | 3⁰50’36,5"N |
| F10N3 | 10⁰24’59,7"E | 3⁰50’16,9"N | SZ10 | 10⁰58’26,5"E | 3⁰49’43,3"N |
| F11N3 | 10⁰19’41,7"E | 3⁰48’54,7"N | SZ11 | 10⁰49’37"E | 3⁰52’15,1"N |
| F12N3 | 10⁰14’14,6"E | 3⁰48’9,3"N | SZ12 | 10⁰44’52,8"E | 3⁰53’28,4"N |
| F13N3 | 10⁰10’39,5"E | 3⁰46’42,3"N | SZ13 | 10⁰33’41"E | 3⁰51’11"N |
| F14N3 | 10⁰6’16,5"E | 3⁰47’24"N | SZ114 | 10⁰22’25,3"E | 3⁰49’37"N |
| F15N3 | 10⁰5’58,2"E | 3⁰47’35,5"N | SZ15 | 10⁰12’60"E | 3⁰48’5,1"N |
| F16N3 | 10⁰3’59,5"E | 3⁰49’55,8"N | SZ16 | 10⁰3’38,4"E | 3⁰51’31,5"N |
| F17N3 | 10⁰3’29,9"E | 3⁰51’30"N | SZ17 | 9⁰14’17,9"E | 4⁰4’36,7"N |
| F18N3 | 10⁰0’18,1"E | 3⁰56’26,6"N | SZ18 | 9⁰11’14,3"E | 4⁰3’15,8"N |
| F19N3 | 9⁰58’10"E | 3⁰57’1,2"N | |||
| F20N3 | 9⁰57’22"E | 3⁰56’59"N | |||
| F21N3 | 9⁰55’50,5"E | 3⁰57’40,5"N | |||
| F22N3 | 9⁰49’8"E | 4⁰0’19,4"N | |||
| F23N3 | 9⁰46’32,4"E | 4⁰0’12,7"N | |||
| F24N3 | 9⁰45’42"E | 3⁰59’52,1"N | |||
| F25N3 | 9⁰36’37,8"E | 4⁰6’0,2"N | |||
| F26N3 | 9⁰32’28,5"E | 4⁰9’4,2"N | |||
| F27N3 | 9⁰23’32,9"E | 4⁰7’55,5"N | |||
| F28N3 | 9⁰14’12,2"E | 4⁰4’26,7"N | |||
| F29N3 | 9⁰14’39,6"E | 4⁰4’45"N | |||
| N⁰ | Road Name | Accident type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone of possible landslides | Possible collapse zone | Possible shear zone | ||||
| Transverse | Longitudinal | Transverse | Longitudinal | |||
| 1 | N1 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 65 | 7 |
| 2 | N1A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | N2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 4 | N2A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | N3 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 19 | 1 |
| 6 | N4 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 17 | 1 |
| 7 | N5 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 8 | N6 | 7 | 23 | 0 | 56 | 1 |
| 9 | N6A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | N7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
| 11 | N8 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 1 |
| 12 | N9 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| 13 | N10 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| 14 | N11 | 19 | 17 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
| 15 | N12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| 16 | N13 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 17 | N13A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 18 | N14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 19 | N15 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| 20 | N15A | 4 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 1 |
| 21 | N16 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 22 | N17 | 13 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 23 | N17A | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 | N17B | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 25 | N18 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 113 | 117 | 2 | 271 | 15 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).