Submitted:
28 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Variable Selections and Data Sources
3.2. Sample Analysis and Data Processing
3.3. Model Construction
- (1)
- Improved Tapio Decoupling Model
- (2)
- STIRPAT Model
4. Research Fingdings
4.1. Classification of Carbon Emission Types Based on Tapio Elasticity Coefficient
4.2. Analysis of Regional Characteristics of Carbon Emissions Based on Decoupling Index
4.3. Analysis of Carbon Emission Reduction Paths Based on the STIRPAT Model
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Recommendations
Funding
References
- Liu, J., The spatiotemporal pattern evolution of regional carbon emissions under the background of manufacturing agglomeration: Taking Zhejiang Province as an example. Productivity Research, 2022(8): p. 33-38.[Chinese].
- Xu, L. and X. Shi, Analysis of the Evolution Law and Characteristics of Carbon Emissions in Energy Intensive Regions: Taking Shanxi as an Example. Energy of China, 2018. 40(10): p. 38-41. [Chinese].
- Zhang, J. and S. Wang, Air Pollution Emission Characteristics of Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2017. 9(3): p. 83-88. [Chinese].
- Wang, J., W. Gao, and S. Che, Research on the Driving Mechanism of Carbon Reduction in China from the Perspective of "Dual Carbon" Targets: Evidence from the Energy Mining Industry. Western China, 2023(1): p. 65-81. [Chinese].
- Hu, H., A Study of Coordinative Development Between Economic Growth and Resources and Environmental of the Yangtze River Delta. 2014, Liaoning Normal University. [Chinese].
- Wang, C., S. Ji, and L. Ren, Spatial correlation and influencing factors of energy carbon emissions in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2022. 43(03): p. 8-14. [Chinese]. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L., Q. Wang, and J. Zhang, Inter-industrial Carbon Emission Transfers in China: Economic Effect and Optimization Strategy. Ecological Economics, 2017. 132(FEB.): p. 55-62. [Chinese]. [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P., Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transport Policy, 2005. 12(2): p. 137-151. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Comprehensive Evaluation of Carbon Emission Permits Allocation: Evidence From 30 Provinces in China. in International Conference on Management Science and Engineering. 2018.
- Li, H. and Q. Qin, Challenges for China's carbon emissions peaking in 2030: A decomposition and decoupling analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. and Y. Zhang, Research on Carbon Emission Characteristics and Reduction Pathways of Provinces in China. Ecological Economy, 2022. 38(08): p. 13-19. [Chinese].
- Grand, C. and Mariana, Carbon emission targets and decoupling indicators. Ecological Indicators, 2016. 67: p. 649-656.
- Deutch, J., Decoupling Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions. Joule, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., Research on the Influencing Factors of China's Carbon Emission and the Countermeasures Based on the LMDI Model. Industrial Economy, 2022(20): p. 146-148. [Chinese].
- Ding, S. and Z. Wen, Study on Influential Factors of Carbon Emissions in Yangtze River Delta——Based on IPAT Improved Model. Journal of Technical Economics & Management, 2014(09): p. 106-109. [Chinese].
- Gao, G., et al., Study on Carbon Peak of Urban clusters based on Analysis of Influencing Factors of Carbon Emissions Business and Management Journal, 2023. 45(02): p. 39-58. [Chinese].
- Su, X., Carbon emission growth factor decomposition and carbon tax policy effect simulation based on CGE model in Shanxi Province. 2022, Shanxi University of Finance and Economics. [Chinese].
- Wang, L. and Y. Zhang, Factors Decomposition and Scenario Prediction of Energy-Related CO2 Emissions in China. Electric Power Construction, 2021. 42(09): p. 1-9. [Chinese].
- Zhang, C. and L. Yan, Panel estimation for urbanization, energy consumption and CO2 emissions: A regional analysis in China. Energy Policy, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M., et al., How urbanization affects CO2 emissions in Malaysia? The application of STIRPAT model. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., B. Zhang, and T. Liu, Empirical analysis on the factors influencing national and regional carbon intensity in China. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016. 55: p. 34-42. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., et al., Driving factors of carbon dioxide emissions in China: an empirical study using 2006-2010 provincial data. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2017. 11(1): p. 156-161. [CrossRef]
- Dong, F., et al., Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018. 129: p. 187-201. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., et al., Analysis of China's carbon emission driving factors based on the perspective of eight major economic regions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020(10): p. 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., et al., Synergy and heterogeneity of driving factors of carbon emissions in China's energy-intensive industries. Ecological Indicators, 2022. 142: p. 109161.
- Liu, M., et al., Drivers of China's carbon dioxide emissions: Based on the combination model of structural decomposition analysis and input-output subsystem method. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 2023. 100: p. 107043.
- Liu, Z., et al., Efficient distribution of carbon emissions reduction targets at the city level: A case of Yangtze River Delta region. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017. 172(pt.2): p. 1711-1721. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., Convergence of carbon intensity in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Habitat International, 2017. 60: p. 58-68. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W., et al., Coordinated carbon reduction mechanism and policy design to achieve carbon peak and neutrality goals in the Yangtze River Delta. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2023. 56: p. 103113. [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T. and E.A. Rosa, Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, Affluence and technology. 1994.

| Variable Type | Variable name | Mark | Unit | Variable description | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained Variable | Carbon dioxide emission | TC | 10000 ton |
The effectiveness of emission reduction | China Carbon Accounting Database |
| explanatory variable | Gross domestic product | GDP | 0.1 billion yuan |
economic development level |
provincial statistical yearbooks |
| Population | P | 10000 people |
The number of permanent residents | provincial statistical yearbooks | |
| Low Carbon Technology | LCT | One item | The number of green technologies | CSMAR database | |
| Industry structure | IS | % | The ratio of industrial-added value to regional GDP | China Economic Data website | |
| Foreign Direct Investment | FDI | % | The ratio of foreign direct investment to regional GDP, the Exchange rate is 0.153 | China Economic Data website | |
| Energy Intensity | EI | % | The growth rate of energy consumption per unit of GDP | China Economic Data website, Provincial Report on the Implementation of the National Economic and Social Development Plan | |
| Urbanization | UR | % | The ratio of the urban population to the total population | China Economic Data website |
| Decoupling types | Indicator | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | |||
| Strong decoupling | <0 | >0 | (-∞,0) |
| Weak decoupling | >0 | >0 | (0,0.8) |
| Expansive negative decoupling | >0 | >0 | (0.8,∞) |
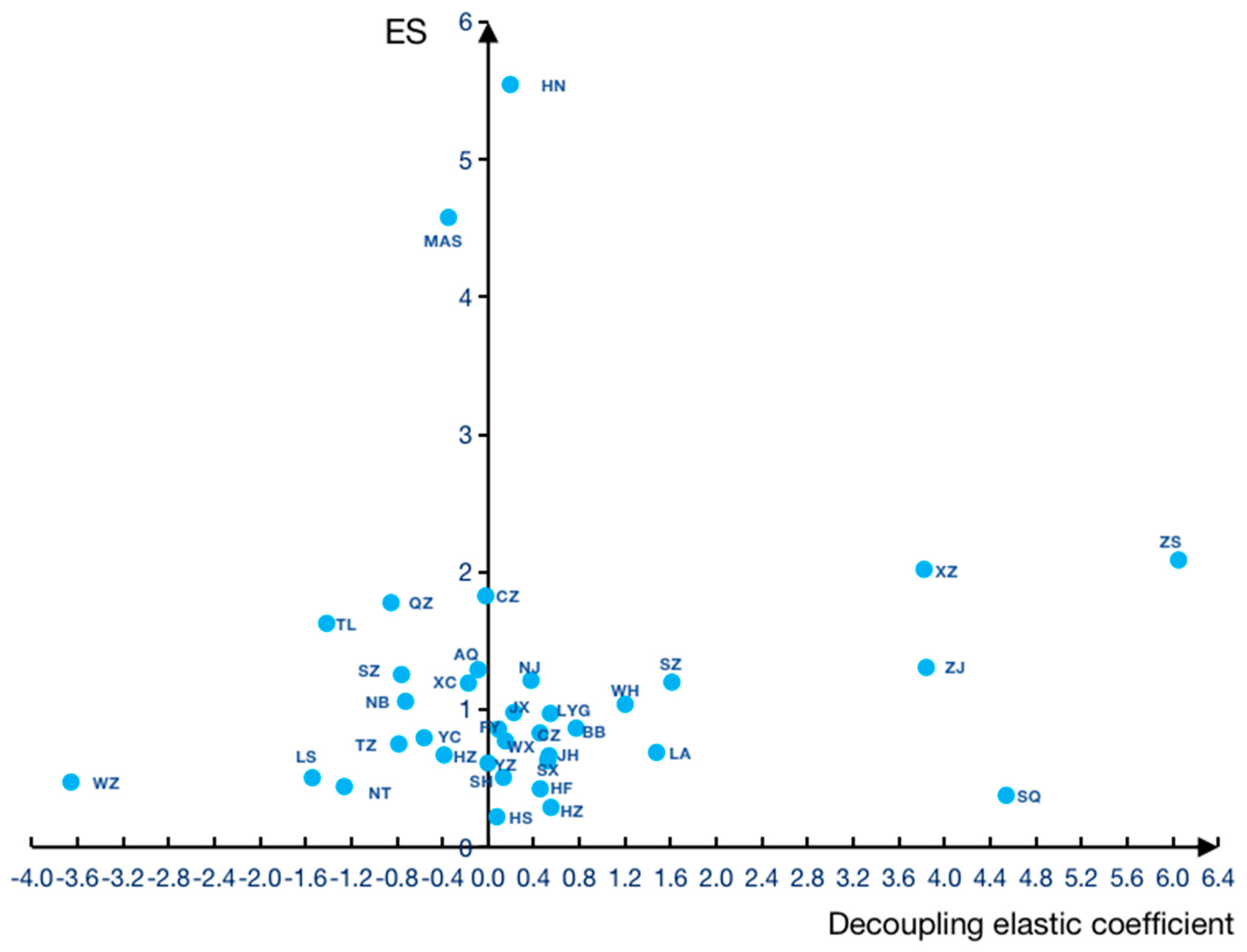
| Decoupling types | City |
|---|---|
| Strong decoupling | Huzhou, Lishui, Ningbo, Quzhou, Taizhou, Wenzhou, Nantong, Yancheng, Yangzhou, Anqing, Chizhou, Ma'anshan, Suzhou, Xuancheng, Tongling |
| Weak decoupling | Shanghai, Hangzhou, Jiaxing, Jinhua, Shaoxing, Changzhou, Lianyungang, Nanjing, Wuxi, Bengbu, Fuyang, Hefei, Huainan, Huangshan |
| Expansive negative decoupling | Zhoushan, Suzhou, Suqian, Xuzhou, Zhenjiang, Lu'an, Wuhu |
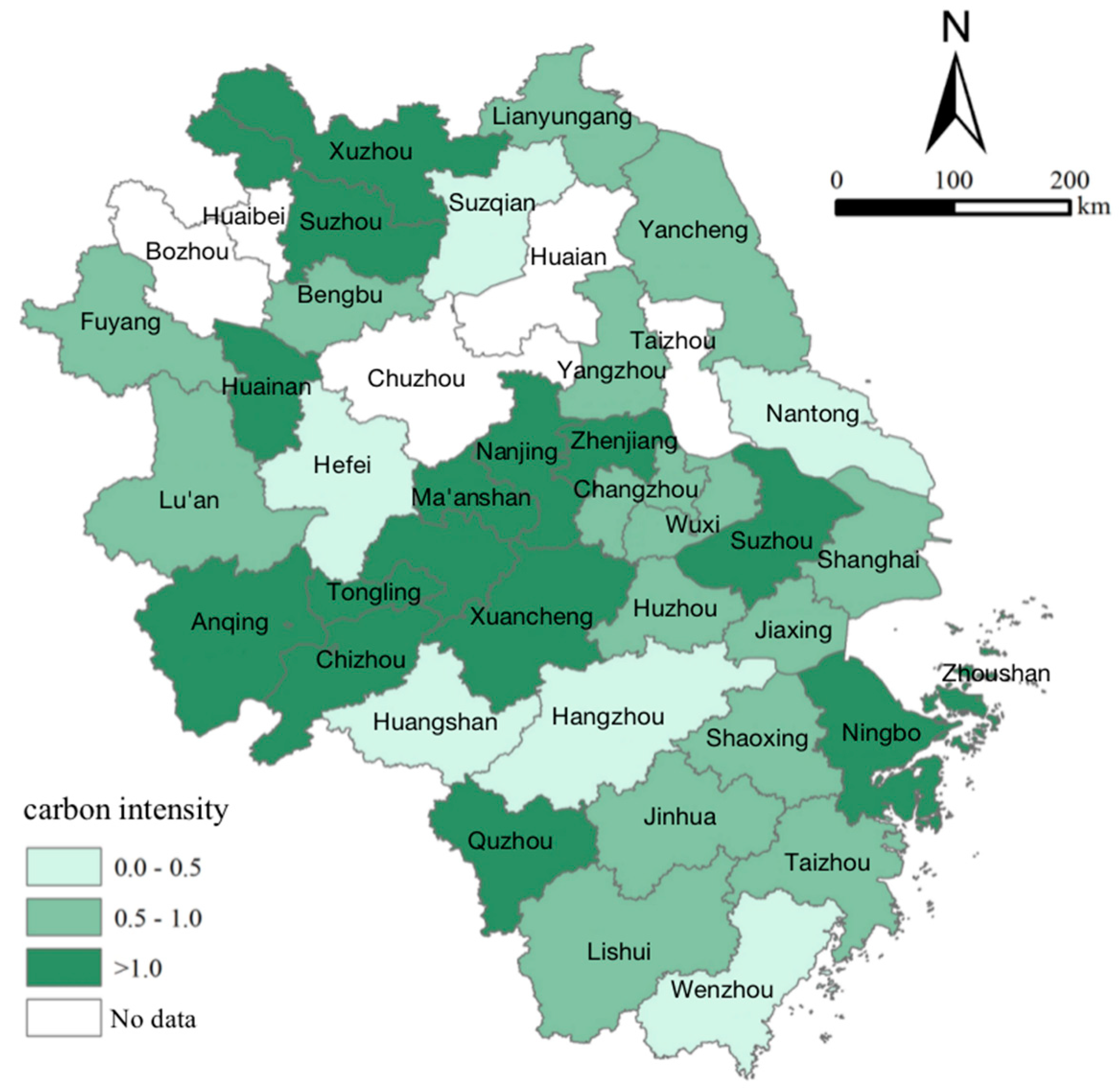
| Types of Carbon emission intensity | City |
|---|---|
| High carbon emission intensity (ES>1) | Ningbo, Quzhou, Zhoushan, Nanjing, Suzhou, Xuzhou, Zhenjiang, Anqing, Chizhou, Huainan, Ma'anshan, Suzhou, Wuhu, Xuancheng, Tongling |
| Low carbon emission intensity (0<ES<1) | Shanghai, Hangzhou, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Lishui, Jinhua, Shaoxing, Taizhou, Wenzhou, Changzhou, Lianyungang, Nantong, Suqian, Wuxi, Yancheng, Yangzhou, Bengbu, Fuyang, Hefei, Huangshan, Lu'an |
| Indicators | Tapio decoupling coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <0 | <0.8 | >0.8 | |
| High carbon emission intensity (ES>1) | Type IV(High-carbon, negative growth) | Type V(High-carbon , low growth ) | Type VI(High-carbon, high growth) |
| Low carbon emission intensity (0<ES<1) | Type I(Low-carbon, negative growth) | Type II(Low-carbon , low growth ) | Type III(Low-carbon , high growth ) |
| Variable | LLC test | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | P-value | ||
| lnTC | -6.84324 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnP | -33.8807 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnPGDP | -10.9294 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnLCT | -10.6621 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnIS | -5.74237 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnFDI | -6.18488 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| lnUR | -5.22267 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| EI | -11.0908 | 0.0000 | Stationary |
| ADF | t-Statistic | Prob. |
| -7.370456 | 0.0000 | |
| Residual variance | 0.071730 | |
| HAC variance | 0.052136 |
| Variable | lnTC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | Type V | Type VI | |
| lnP | 0.538*** | 0.942*** | 2.544 | 0.667*** | 1.028 | 0.894*** |
| (0.102) | (0.109) | (7.836) | (0.095) | (0.638) | (0.088) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.819*** | 1.113*** | 1.708 | 1.318*** | 1.380*** | 0.516 |
| (0.200) | (0.197) | (1.027) | (0.383) | (0.460) | (0.351) | |
| lnLCT | 0.343*** | 0.081* | -0.175 | 0.023 | -0.472** | 0.094 |
| (0.108) | (0.190) | (0.197) | (0.084) | (0.218) | (0.071) | |
| lnIS | 0.501 | 0.152 | -1.354 | 0.316 | -0.645 | 0.645*** |
| (0.351) | (0.147) | (2.262) | (0.286) | (0.882) | (0.175) | |
| lnFDI | -0.037 | 0.093** | -0.040 | -0.037 | 0.811*** | -0.210*** |
| (0.056) | (0.046) | (3.363) | (0.054) | (0.276) | (0.063) | |
| lnUR | 0.875 | -0.452 | 0.499 | -0.049 | -0.104 | 1.135* |
| (0.872) | (0.378) | (2.765) | (0.864) | (1.663) | (1.020) | |
| EI | 0.048*** | 0.027*** | 0.042 | 0.019 | -0.039 | 0.029** |
| (0.013) | (0.012) | (0.041) | (0.017) | (0.043) | (0.015) | |
| Constant | -13.113*** | -10.889* | -23.438 | -12.626*** | -9.120 | -11.545*** |
| (3.861) | (1.888) | (40.709) | (2.185) | (5.450) | (2.030) | |
| FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| TE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 84 | 144 | 24 | 96 | 24 | 60 |
| 0.868 | 0.924 | 0.910 | 0.861 | 0.965 | 0.959 | |
| DW | 1.316 | 0.811 | 1.897 | 0.784 | 1.697 | 1.940 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




