1. Introduction
Forests hold a significant position within the ecological environment, capable of substantially enhancing slope stability and mitigating the emergence of geological calamities, such as debris flows and landslides [
1,
2,
3]. With the development of economic in Northwestern China, the Loess Plateau has become an important base for industrial and agricultural applications [
4,
5]. However, due to the practical engineering in Northwestern China, large amount of the forests in these regions has been significantly disrupted. Consequently, this disturbance has led to the recurrent manifestation of slope-related geological disasters, such as landslides, debris flows, and collapses (
Figure 1). The Loess Plateau covers an area of about 640,000 km
2, accounting for approximately 6.6% of the area of China [
6]. However, due to the unique sedimental environment and the distinctive structural characteristics of loess [
7,
8,
9], its mechanical strength sharply decreases once subjected to engineering disturbances like water infiltration [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. The Loess Plateau is located on the northeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, with strong regional tectonic activity and fragmented rocks. Therefore, the geological and ecological environment of the Loess Plateau is extremely fragile. With the increase in population and over engineering development, soil erosion and desertification have intensified in the loess region. Frequent loess landslides have occurred, seriously impacting livelihoods of people and regional economic development [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
Forests play a vital role in retaining water, which is crucial for stabilizing slopes and reducing the risk of geological disasters like debris flows and landslides, lessening their harm. Recently, more attention has been paid to understanding how forests affect landslides, with studies showing that forests significantly help prevent landslides [
24,
25,
26]. However, due to the collapsibility of loess, landslides triggered by agricultural activities constitute a significant factor in geological disaster of Heifangtai terrace. The irrigation facilities in these regions have led to a substantial rise in the groundwater levels of the loess plateau, resulting in the numerous loess landslides. Extensive research has been conducted on the characteristics of the landslides on the Heifangtai terrace, Gansu Province. Peng et al. (2018) believe that the types of landslides on the Heifangtai terrace include loess landslides and loess-mudstone landslides. They pointed out that loess landslides have the characteristics of high-speed and long-distance movement as well as strong secondary effects. Loess-mudstone landslides exhibit characteristics of low-speed and short-range movement, as well as reactivations [
27]. Xu et al. (2008) systematically classified Heifangtai landslides into categories such as loess mudflow, loess sliding, loess-mudstone contact surface landslide, loess-mudstone inclined layer landslide, and loess-mudstone interbedded landslide [
28]. Through experimental studies, Hou et al. (2018) indicated that loess mudflow landslides exhibit characteristics of fluid movement, with sliding distances exceeding 300 meters. This is the most severe type of landslide in Heifangtai [
29]. In recent years, with the increased attention to the prevention and control of geological disasters in China, extensive research results on Heifangtai landslides have been obtained [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35].
Landslides are natural surface processes that typically begin with localized instability and then expand to affect the entire slope, ultimately leading to the progressive development of large-scale destruction. In terms of the evolution and patterns of landslides, numerous scholars have conducted research on regional or individual landslides, respectively. The evolutionary process of regional landslides can reflect characteristics such as clustering and overlapping of landslides within a region. Understanding the evolution of regional landslides holds significant importance for regional geological hazard prevention and control. Deng et al. (2009) initially focused on the historical evolution of loess landslides and proposed an evolution model for slope deformation and instability based on geological evidence [
36]. Based on the geological conditions of rockslides on both sides of a canyon in France, Stéphane et al. (2012) used numerical simulation to reproduce the process of landslide deformation and evolution [
37]. González et al. (2014) utilizing drone photogrammetry technology, conducted detailed aerial surveys of a 7 km² slope in the Cantabrian Mountains of Spain. Combined with GPS technology, they enhanced the accuracy of image processing results. By comparing historical multi-temporal images, they revealed the variation trend of landslide accumulation over time [
38]. Peng et al. (2019) provided a comprehensive discussion of the application of drone photogrammetry technology in landslide investigations. For regional landslide studies, this technology facilitates the exploration of spatial and temporal distribution patterns as well as developmental features. For individual landslide studies, comparing models over multiple time periods enables a full understanding of the development process [
32]. Xu et al. (2023) used drone photogrammetry to obtain orthophoto images and DEM data. From these data, they extracted information like boundary of landslides, elevation, area, and slope to analyze the evolution process of a landslide on the edge of terrace, validating the results with remote sensing data [
39]. The above research provides a comprehensive investigation on the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of landslides. However, the evolution process of landslides in different locations or even within the same region tends to be gradual. Frequently, assessing the evolution trends of landslides requires dynamic data, and the evolution trends may differ across different locations of a landslide.
Through field investigations and remote sensing interpretation, this study reveals dramatical geomorphological changes in the Heifangtai terrace due to the occurrence of widespread landslides. Taking the evolution of landslides along the edge of the Heifangtai terraces as an example, this study first classified different types of loess landslides. Subsequently, the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of these landslides were analyzed. Finally, utilizing the FLAC3D software, the stability of the loess slopes at the edge of the Heifangtai terrace was examined under the lateral evolution mode. The research findings are significant for assessing loess landslides along the edge of Heifangtai terraces.
2. Geological settings
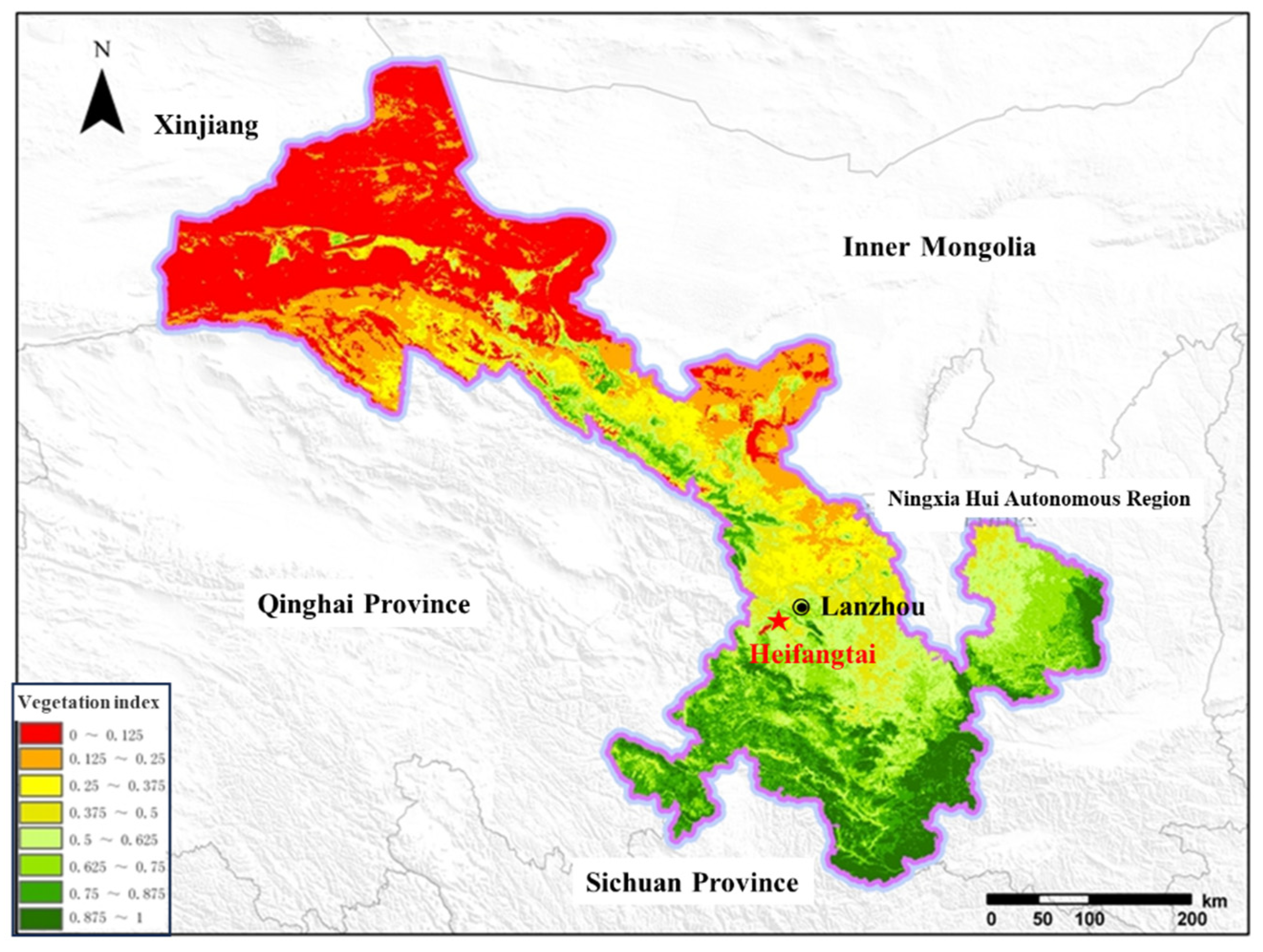
The study area is located 40 km west of Lanzhou City in Gansu Province (
Figure 2). This region comprises two loess plateaus known as Heitai and Fangtai, collectively referred to as Heifangtai. Due to the prevalence of landslide disasters in Heitai, the scope of this study is limited to Heitai region. The vegetation index map in Gansu Province is presented in
Figure 1. The vegetation index serves as a straightforward, efficacious, and empirically grounded measure of surface vegetation conditions. It can be observed that the vegetation index of Heifangtai terrace is between 0.5-0.625, which is intermediate in Gansu Province. Gansu, with its extensive land area, is significantly impacted by natural conditions, resulting in relatively limited forest resources, categorizing it as a province with sparse woodland. According to the findings of the 9th National Forest Resources Inventory of China, the total forest area in Gansu province amounts to 50,973 km², with a forest coverage rate of 11.33%, approximately half of the national average. The forest volume is estimated at 251.89 km³, with an average volume per unit area of 4.942 km³. The significance of forests in the research area impacted by landslides is also notable, especially concerning their influence on water resources and water quality. The excessive moisture content in the loess remains a principal catalyst for slope instability, while steep gradients, fragile soil composition, and landscape features that channel water serve as chief components heightening the susceptibility to landslides. In addition, the extensive agricultural irrigation activities in the Heifangtai terrace have also led to a significant rise in the groundwater level within the research area, consequently triggering a substantial increase in the occurrence of landslides.
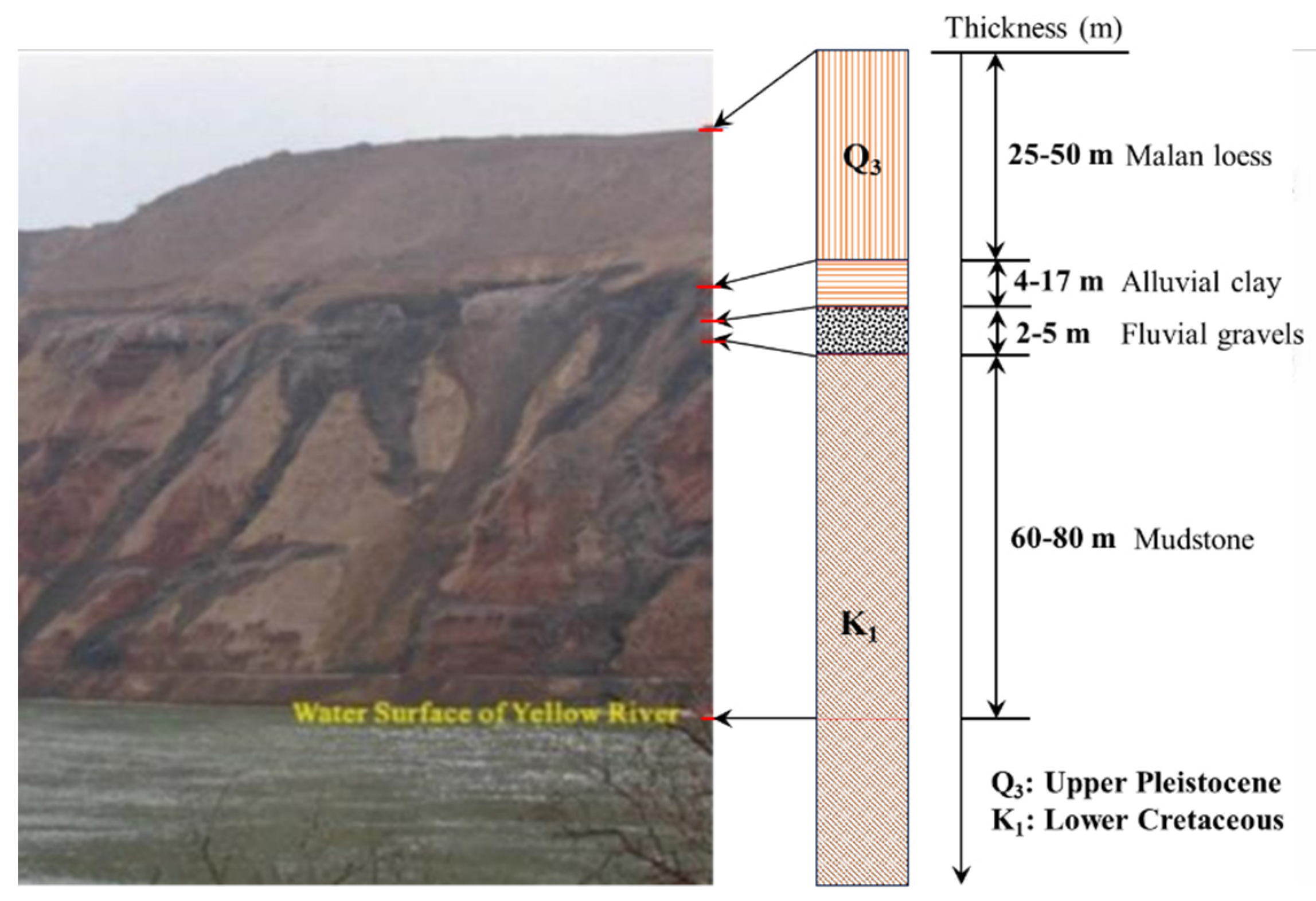
The topography and geomorphology of the study area are relatively simple, mainly characterized by loess platforms, valley, and loess landslide geomorphology. The combined area of Heitai and Fangtai is approximately 15 km
2. Heitai represents a typical loess plateau geomorphology in Northwestern China, covering an area of about 12 km² within the research area. It predominantly forms the 4th-order terrace of the Yellow River. The elevation difference between Heitai and the surface of river is about 100-120 meters. The Heitai extends in an east-west direction, with narrower sections at its eastern and western ends. The lithological profile of Heifangtai is composed of four layers (
Figure 3): (1) the top layer is made up of upper Pleistocene aeolian Malan loess, with a thickness of about 25-50 m; (2) the alluvial clay layer, about 4-17 m thick; (3) the third layer is the fluvial gravel, which is mixed with sands, about 2-5 m in thickness; (4) the bedrocks are composed of lower Cretaceous mudstone, about 60-80 m thick [
16].
3. The characteristics of landslides in the Heifangtai terrace
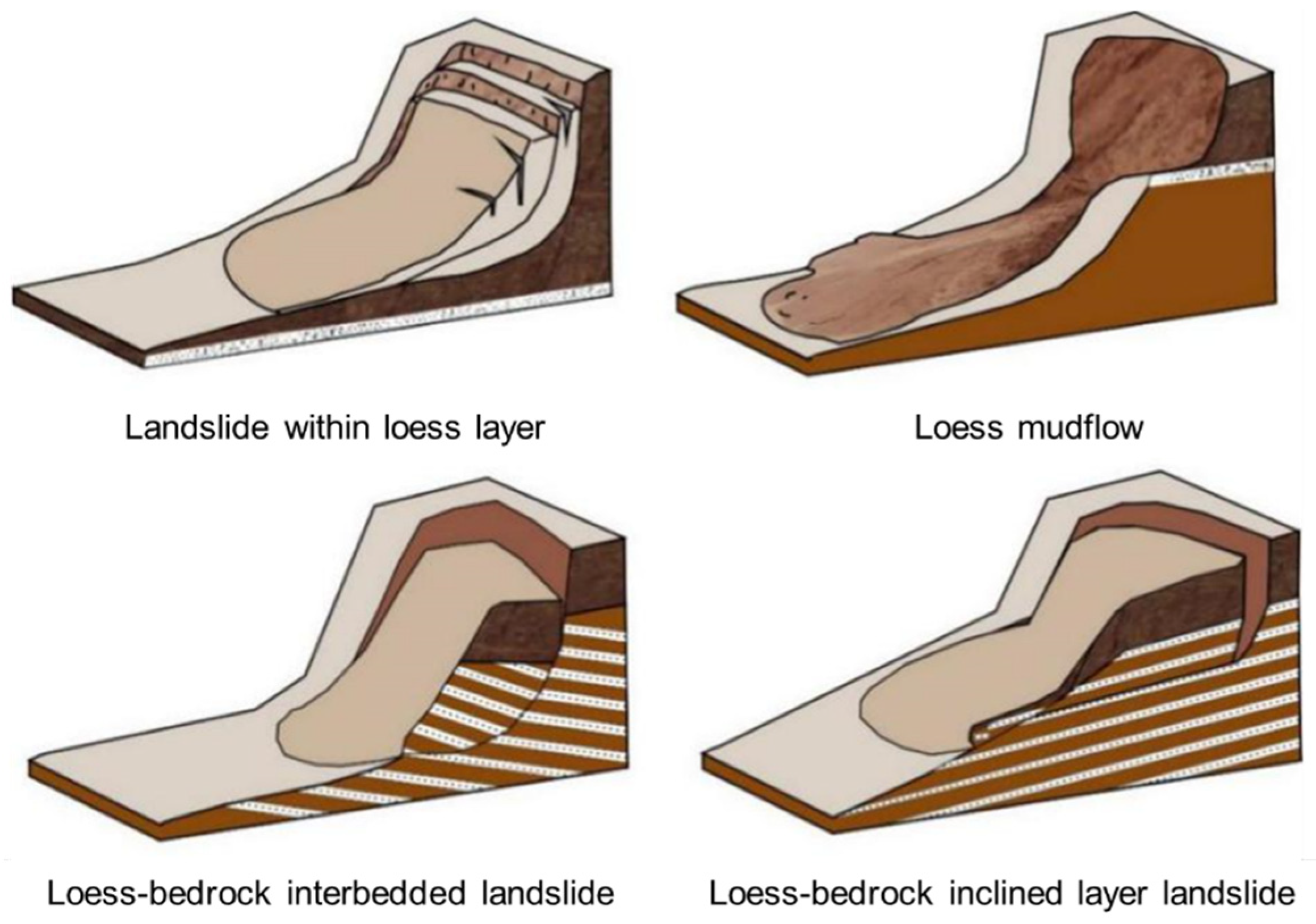
There are various types of landslides in the Heifangtai terrace. Based on field investigation and the typical classification scheme for loess landslides, the landslides in Heitai terrace can be categorized as loess-bedrock landslides and landslides within loess layer. Loess-bedrock landslides further subdivide into loess-bedrock contact surface landslides, loess-bedrock inclined layer landslides, and loess-bedrock interbedded landslides. Landslides within loess layer can be further classified as loess collapse and loess mudflow. The schematic diagram of different types of loess landslide in the study area is presented below (
Figure 4).
3.1. Classifications of Landslides in the Heifangtai terrace
In recent years, there have been several landslide disasters in the Heifangtai terrace. Based on in-situ investigations of landslides and remote sensing image interpretation, a total of 36 landslides have been identified in the Heifangtai terrace (
Table 1). Some of these landslides have evolved into larger landslides over multiple occurrences. Such cases are treated as composite landslides, resulting in a difference between the number of landslides indicated on the landslide distribution map and the cumulative landslide in
Table 1.
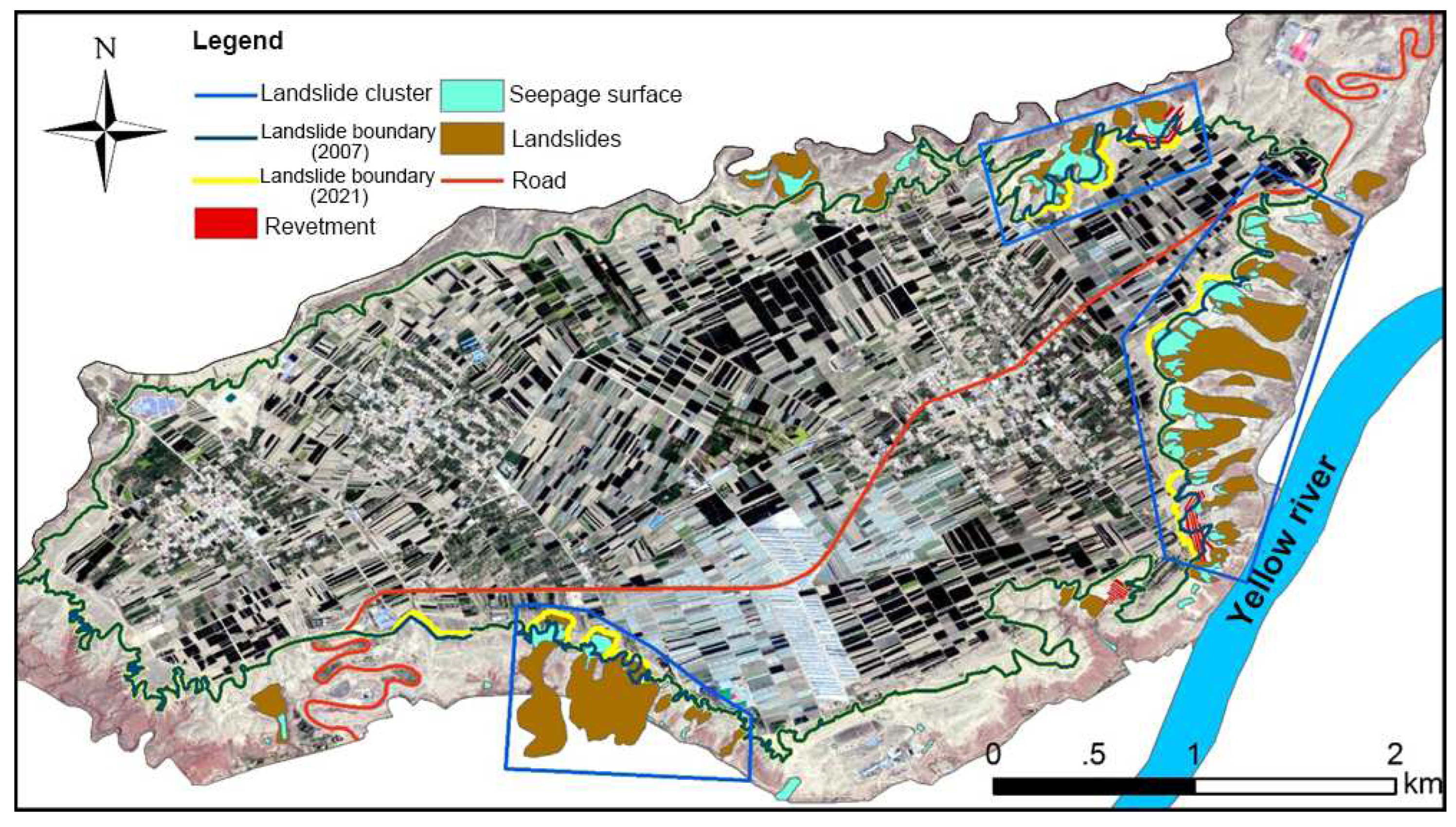
Figure 5 presents the distribution of loess landslides in the Heifangtai terrace. As shown in the figure, loess landslides are primarily concentrated in the eastern part of the study area, forming distinct clusters with clear grouping characteristics.
3.1.1. Loess Mudflow
This type of landslide exhibits typical flow characteristics, with the shear outlet located at the bottom of the Q3 loess layer. Under the influence of groundwater, the loess undergoes liquefaction, leading to a reduction in strength and triggering landslides. Mudflow-type landslides are characterized by high-speed and long-distance movement. Loess mudflows in the study area have relatively long sliding distances, proposing the greatest threat to agriculture and roads in the lower part of the plateau. The No. 1 Dangchuan landslide that occurred on April 29, 2015, is a typical example of loess mudflow (
Figure 6). The occurrence of this landslide can be divided into two stages. Initially, a landslide mass of approximately 5 × 10
4 m
3 slid from Heitai terrace to the second-level terrace of Yellow River. About three hours later, a faster-moving landslide mass of around 35 × 10
4 m
3 rapidly moved downstream. The final deposit of the landslide accumulation reached a thickness of up to 17 m.
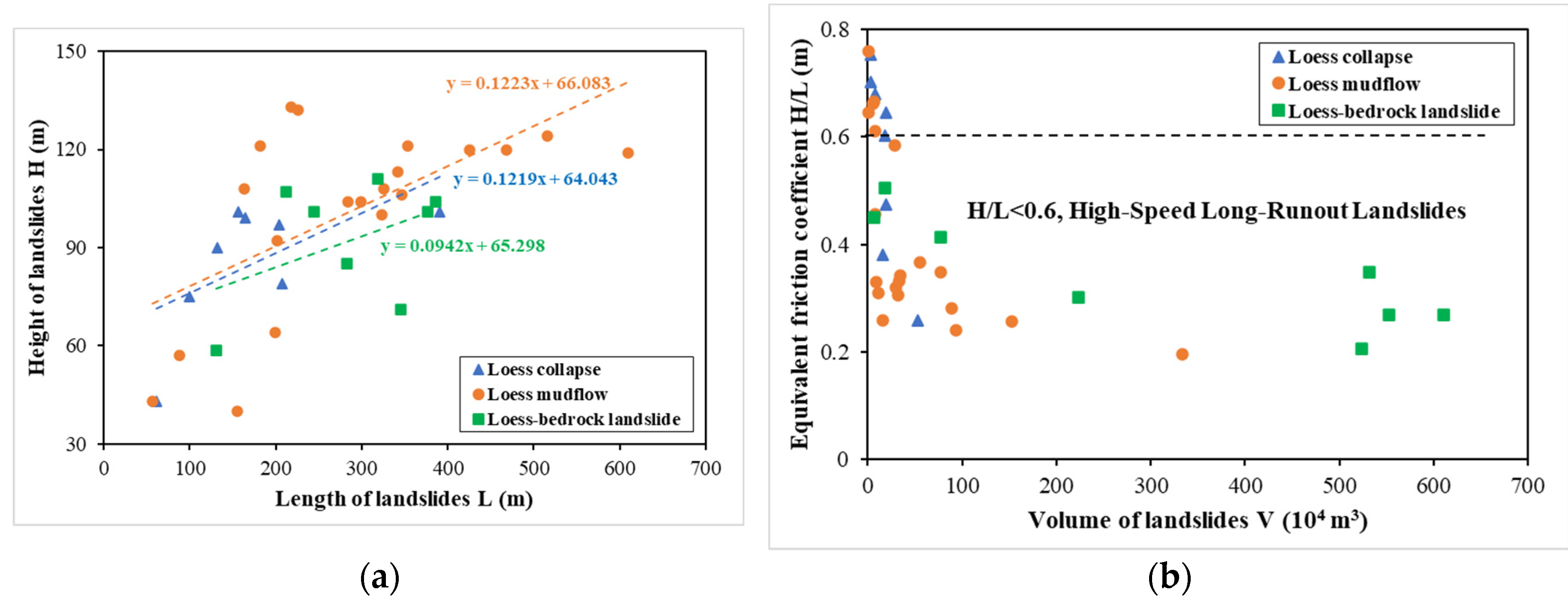
The equivalent friction coefficient indicates the mobility of the landslide, defined as the ratio (H/L) of the height (H) and the length (L) of the landslide.
Figure 7(a) shows the relationship between H and L for the 36 landslides collected in the study area. The average ratio H/L for collapse and mudflow are nearly the same, equals to about 0.12. For loess-bedrock landslides, the ratio H/L is smaller than the other two types of loess, equals 0.09, which implies that the height is relatively smaller than the length for the bedrock landslides. The relationship between H/L and the volume (V) for the 36 landslides is presented in
Figure 7(b). The equivalent friction coefficient and V exhibit a clear mathematical relationship. The equivalent friction coefficient decreases from 0.75 to below 0.20 as the volume of the landslide increases. According to the research of Wang et al. (2014), when the equivalent friction coefficient is below 0.60, the landslide is high-speed and long-runout [
40]. It can be seen in
Figure 7(b) that for all the loess-bedrock landslides, the ratio H/L is smaller than 0.60. Large amount of loess mudflow is also classified as high-speed long-runout landslides.
3.1.2. Loess Collapse
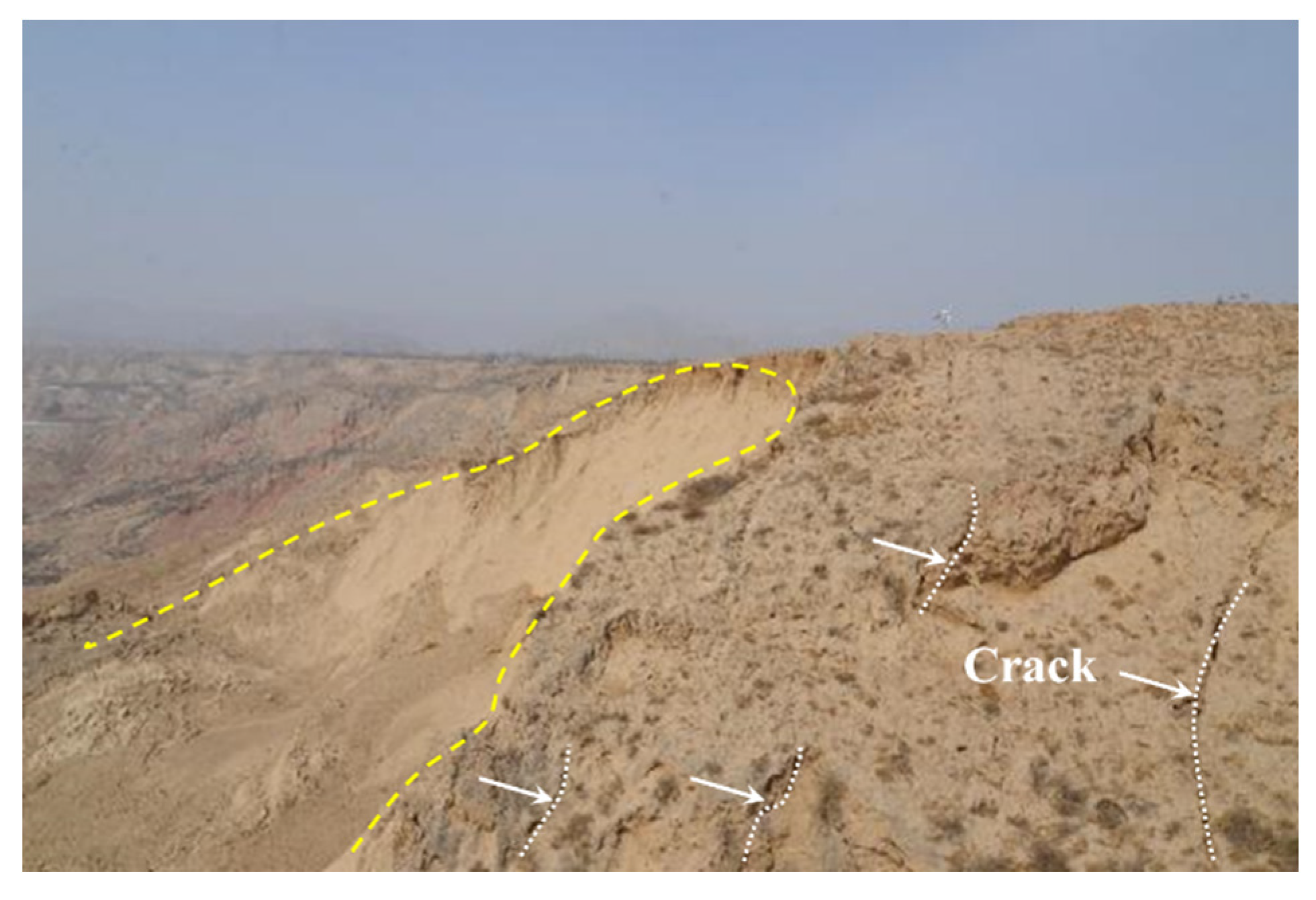
Loess collapses are widely distributed in the study area, primarily controlled by the cracks near the edge of the terrace (
Figure 8). Loess collapse occur within the unsaturated Q3 loess layer. Their scale has been gradually increasing, posing an escalating threat. The occurrence of loess collapse is mainly triggered by the infiltration of irrigation water and rainfall along the cracks near the edge of the terrace. This process induces the softening of the structure of the unsaturated loess layer and reduces the matrix suction in loess. In recent years, they have also been infrequently observed in the Dangchuan and Huangci region. Although the scale and impact of landslide collapse are smaller compared to loess mudflow, ongoing collapses often lead to the formation of large through cracks at the rear of the landslide. Along these cracks, the influence of groundwater can trigger subsequent landslides.
3.1.3. Loess-Mudstone Landslide
Landslides caused by the contact surface of loess and mudstone are less common in the study area. Their source material is mainly the loess on the slopes. The movement direction of the landslides is consistent with the slope direction of the underlying bedrock.
- 2.
Loess-Mudstone inclined layer landslides;
Landslides caused by loess-mudstone interlayer are also relatively scarce in the Heitai terrace, often being older landslides that have subsequently experienced continuous occurrences of subsequent landslides. The topography and geomorphology have undergone continuous changes, and only a few intact inclined layers landslides remain.
- 3.
Loess-Mudstone interbedded landslides;
Landslides caused by loess-Mudstone interbedded layers are the most widespread type of landslide in the research area. For this type of landslide, the main sliding surface is located on the surface of the bedrock, and the landslide mass moves along the bedrock surface in a direction consistent with the inclination of the bedrock layers. The mechanism behind the occurrence of this type of landslide involves the infiltration of groundwater, which reduces the strength of the mudstone, leading to deformation and failure. Therefore, these landslides are characterized by a long incubation period, large-scale occurrences, and relatively short sliding distances. The Huangci landslide in the study area is an example of this type of landslide (
Figure 9).
3.1.4. Statistics of Different Types of Landslides
Combining remote sensing interpretation data with on-site investigations, a total of 36 landslide disasters have occurred in Heifangtai terrace (
Table 1). Due to the relatively long history of landslide disaster in the research area, newly formed landslides often cause damage to previously identified landslide sites, or several initially separate landslides evolve over time into a larger composite landslide. Therefore, within this landslide investigation data, some landslides are a result of multiple smaller landslides coalescing into a larger one.
According to the survey data, there are four types of landslides in the study area: loess collapses account for 4%, loess landslides comprise 26%, loess mudflows constitute 42% of the total landslide occurrences, and loess-mudstone inclined and loess-bedrock interlayer landslides together make up 30% of the landslide disasters. Among these, loess-bedrock interlayer landslides are the least distributed type in the study area, while loess mudflow are the most prevalent.
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Landslides in the Study Area
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Landslides
The spatial distribution of landslides in the Heifangtai terrace is influenced by various factors such as the terrain, geomorphology, lithology, and stratigraphy of the study area. Analyzing and understanding the spatial distribution patterns of landslides holds significant importance for the research of this study, as well as for the prevention and management of landslides in the area. To better illustrate the patterns of spatial distribution, landslides are categorized into two main types based on their material composition. The first category is loess landslides, which include loess collapses and loess mudflows. The second category is loess-bedrock landslides, comprising loess-mudstone contact surface landslides, loess-mudstone inclined landslides, and loess-bedrock interlayer landslides.
Based on on-site investigation data, there are 28 occurrences of loess collapses in the Heitai terrace, accounting for approximately 73% of the landslide disasters in the study area. Among the types of loess landslides, those characterized by high-speed and long-distance sliding, referred to as high-speed long-range landslides, are predominant. They are mainly distributed in the area behind Village cliffs.
- 2.
Loess-Bedrock Landslides;
Distribution of Loess-bedrock Landslides is mainly concentrated in the area from Yehu Gully to Hulang Gully, spanning a length of about 4.3 km along the escarpment. There are a total of 10 bedrock landslides in this section, accounting for 21% of the investigated landslides, with a density of 4.88 slides/km. The topography trends in an east-west direction, with a broader Huanghe River Level II terrace in front.
3.2.2. Temporal Distribution of Landslides
The precise occurrence time of landslides cannot be obtained through in-situ surveys. However, due to the extensive landslides in Heifangtai terrace, reports and studies on landslides in this area have always been a hot topic. Therefore, it is possible to obtain the occurrence time of landslide disasters in the study area through the collection of a large amount of literature, thus analyzing landslide distribution patterns on a temporal scale.
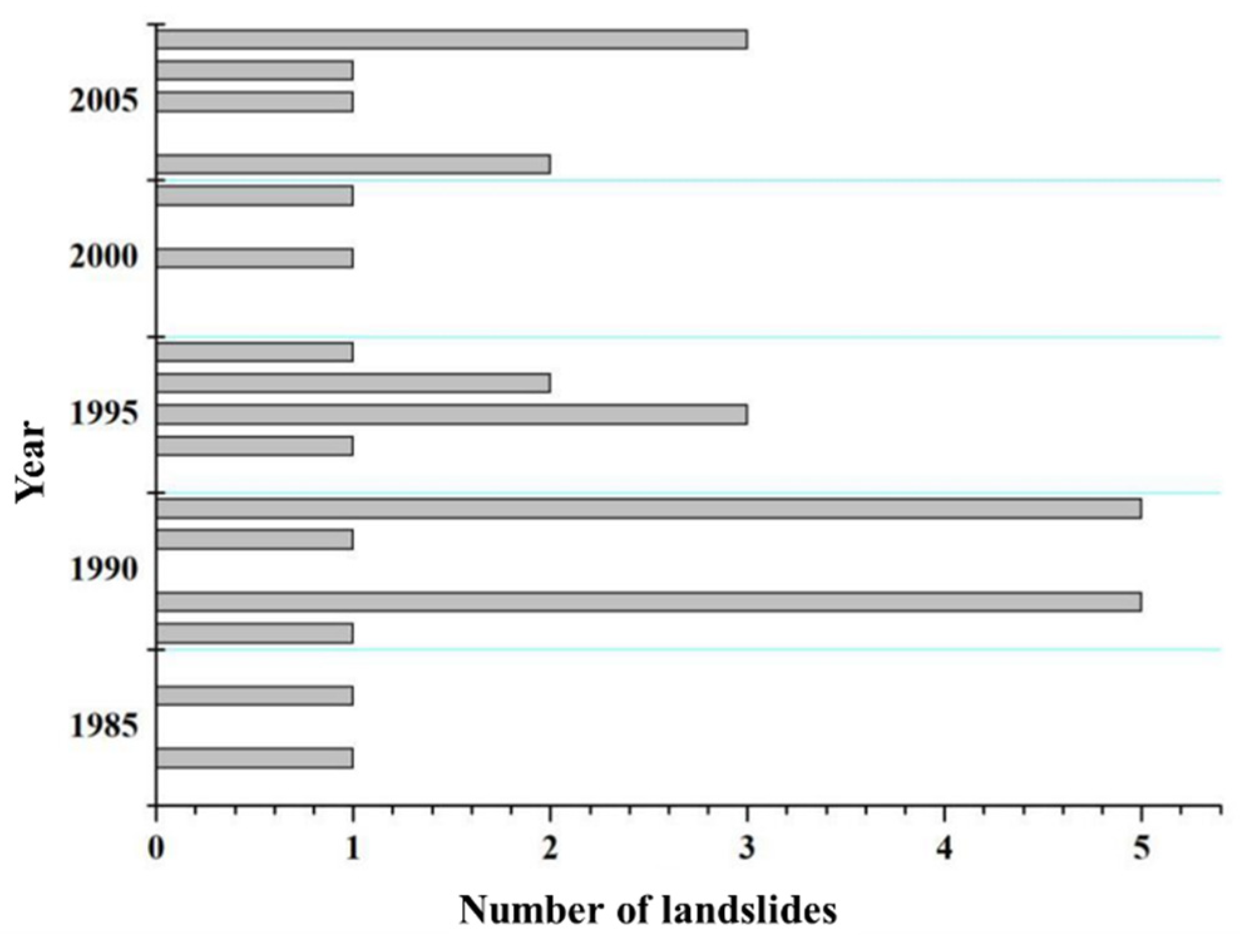
Under unchanged geological conditions, the occurrence of landslides exhibits certain regularity in annual frequency. From the 1960s to the present day, landslides have shown an overall increasing trend with localized decreases on an annual span. This regularity is related to the annual variations in factors such as rainfall, temperature, and geological activity in the research area (
Figure 10).
- 2.
Monthly distribution of landslides;
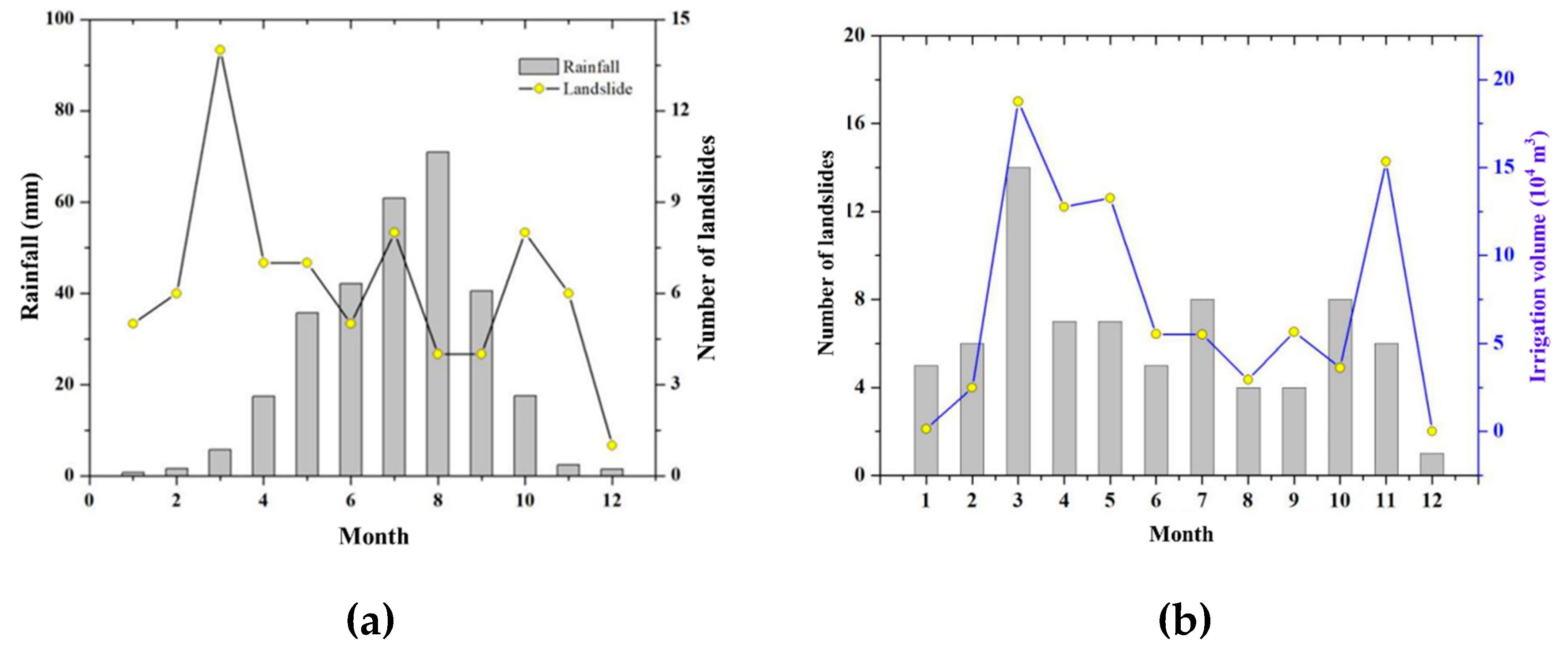
The cause of landslides in Heifangtai terrace is largely attributed to extensive agricultural irrigation. Agricultural irrigation is a seasonal production auxiliary activity that exhibits clear regularity. As a result, the occurrence of landslides within the year also demonstrates noticeable regularity. Based on the collected data, the following
Figure 11(a) can be obtained. There is no clear correlation between the occurrence of landslides and the monthly frequency of rainfall. Rainfall in the Heifangtai terrace is concentrated in the summer of June to September. However, during these months, there is no significant increase in the occurrence of landslide disasters. In fact, there seems to be a decreasing trend compared to other months. The main reason is that the research area is located in Northwestern China with a semi-arid continental climate. The annual rainfall is relatively low, and the limited amount of rainfall, combined with the thick loess layer in the area, prevents water on the surface layer from effectively infiltrating and replenishing groundwater. As a result, rainfall does not trigger large-scale landslides.
Figure 11(b) shows the relationship between the occurrence of landslides and agricultural irrigation in the Heifangtai terrace. It can be observed that the most intensive agricultural irrigation happens in March each year, with the highest irrigation volume. The occurrence of landslides also shows a peak.
Figure 11(b) indicates a clear correlation between the number of landslides and the volume of irrigation. Research by Xu et al. (2019) and others suggests that for agricultural irrigation in March, it needs to pass through the saturated zone of loess with a permeability coefficient of 5×10
-6 m/s at the surface [
13]. Taking the average thickness of the loess layer in the research area as 20 m, it would take about 46 days of infiltration for surface water to replenish the groundwater system. This indicates that the occurrence of landslides and the impact of irrigation on groundwater exhibit a significant lag effect. Therefore, the trend shown in
Figure 11 does not necessarily imply a clear regularity between the formation of landslides and the distribution of irrigation volume.
Yang et al. (2022) and Kong et al. (2023) proposed the theory of the seasonal "freeze-thaw-induced sliding effect" for the mechanism of landslide [
41,
42]. They believe that the seasonal freeze-thaw of groundwater in loess areas has a significant impact on the stability of slopes. The rise of groundwater caused by agricultural irrigation is discharged in the form of springs at the edge of the plateau. During the winter, the surface water at the drainage channel of the plateau freezes, causing a reduced discharge, which leads to an increase in groundwater level. The rise of groundwater significantly reduces the strength and stability of the slope soil, creating hydrostatic pressure. After the thaw in spring, the permeation of groundwater increases significantly, and the larger hydraulic head difference generates a greater hydraulic force.
4. Analysis of Geomorphologic Evolution Patterns of Loess Landslides
With the continuous occurrence of landslides, it is observed that loess landslides usually occur on the back of early landslides, exhibiting the characteristics of geomorphologic evolution. Compared to the lateral edges of the slope body formed after the landslide, the concave terrain formed by the landslide has a higher initial risk. Shallow groundwater in the loess plateau tends to accumulate in these concave areas, leading to a faster increase in water level at the back of the landslide body than at the edges. The hydrological response caused by landslide occurrence differs from the overall groundwater system within the loess plateau. Based on field survey and remote sensing interpretations, the development and evolution of landslides in the Heifangtai terrace have been categorized into two types: longitudinal evolution and lateral evolution patterns.
4.1. Longitudinal Evolution Patterns of Landslides
The longitudinal evolution pattern of landslides is always considered in relation to individual landslide. Under factors like agricultural irrigation, small landslides begin to occur on the slopes of the loess tableland. After a landslide occurs, the accumulated landslide debris liquefies under the influence of groundwater, and the liquefied debris gradually flows downslope. Cracks appear in the slope behind the landslide accumulation, and the unstable back wall of the landslide continuously generates new landslides. Over time, numerous small landslides lead to the expansion of the erosion area, transforming the initially small landslides into a larger one. As the landslide evolves through stages, it gradually moves towards a stable state. This type of landslide is widely distributed in the Heifangtai terrace, mainly characterized by loess mudflows.
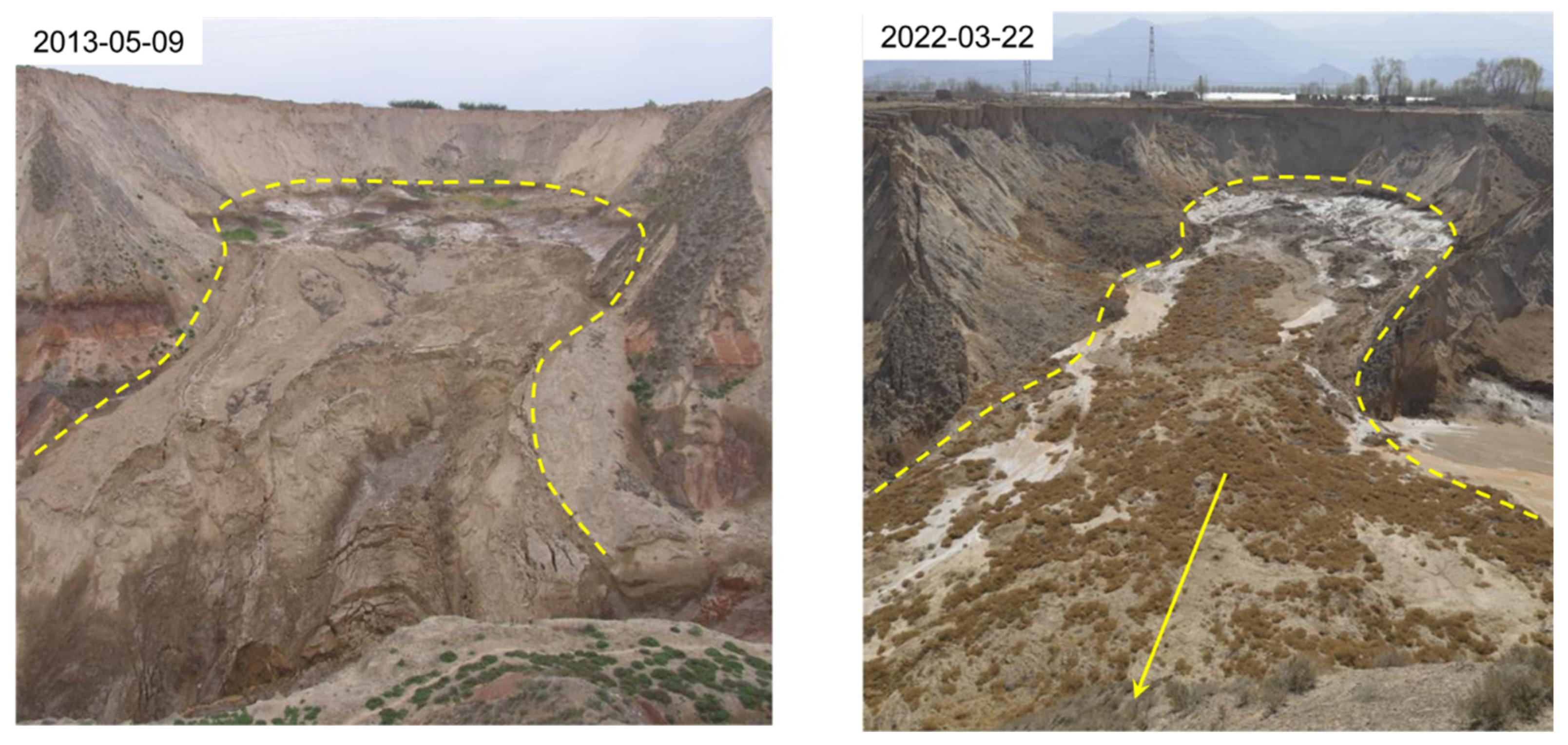
Figure 12 shows the Moshigou landslide. Over a span of nine years from 2013 to 2022, small collapses and landslides have continuously formed along the back edge of the concave terrain. The accumulated debris flows in a fluid state into the Moshi Gou due to the influence of groundwater, while the back wall of the landslide undergoes erosion, leading to the gradual enlargement of the concave terrain.
4.2. The Lateral Evolution Pattern of Landslides
The lateral evolution pattern is another characteristic of landslide in the Heifangtai terrace. The lateral evolution history of landslides is a feature of landslide clusters. When a landslide occurs, not only does the rear slope of the landslide become unstable, but the side slopes of the landslide mass also become unstable. The formation of new landslides on the side slopes causes the landslide to extend continuously to both sides, transforming a small landslide into a landslide cluster.
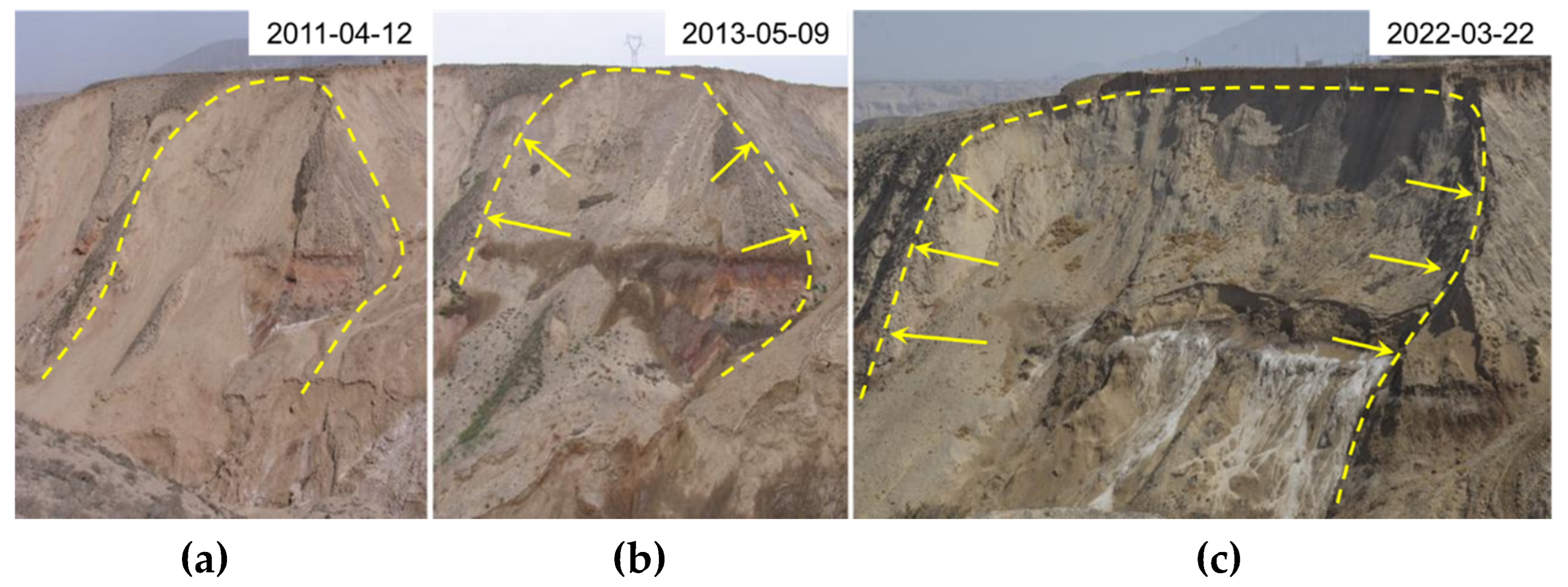
In
Figure 13(a), the left side of the landslide developed shallow slumping bodies as shown in
Figure 13(b) in 2013. However, with the rise of the water level, the slumping body continuously extended to both sides, creating a larger lateral sliding surface. This differs significantly from the landslide pattern shown in
Figure 13(c).
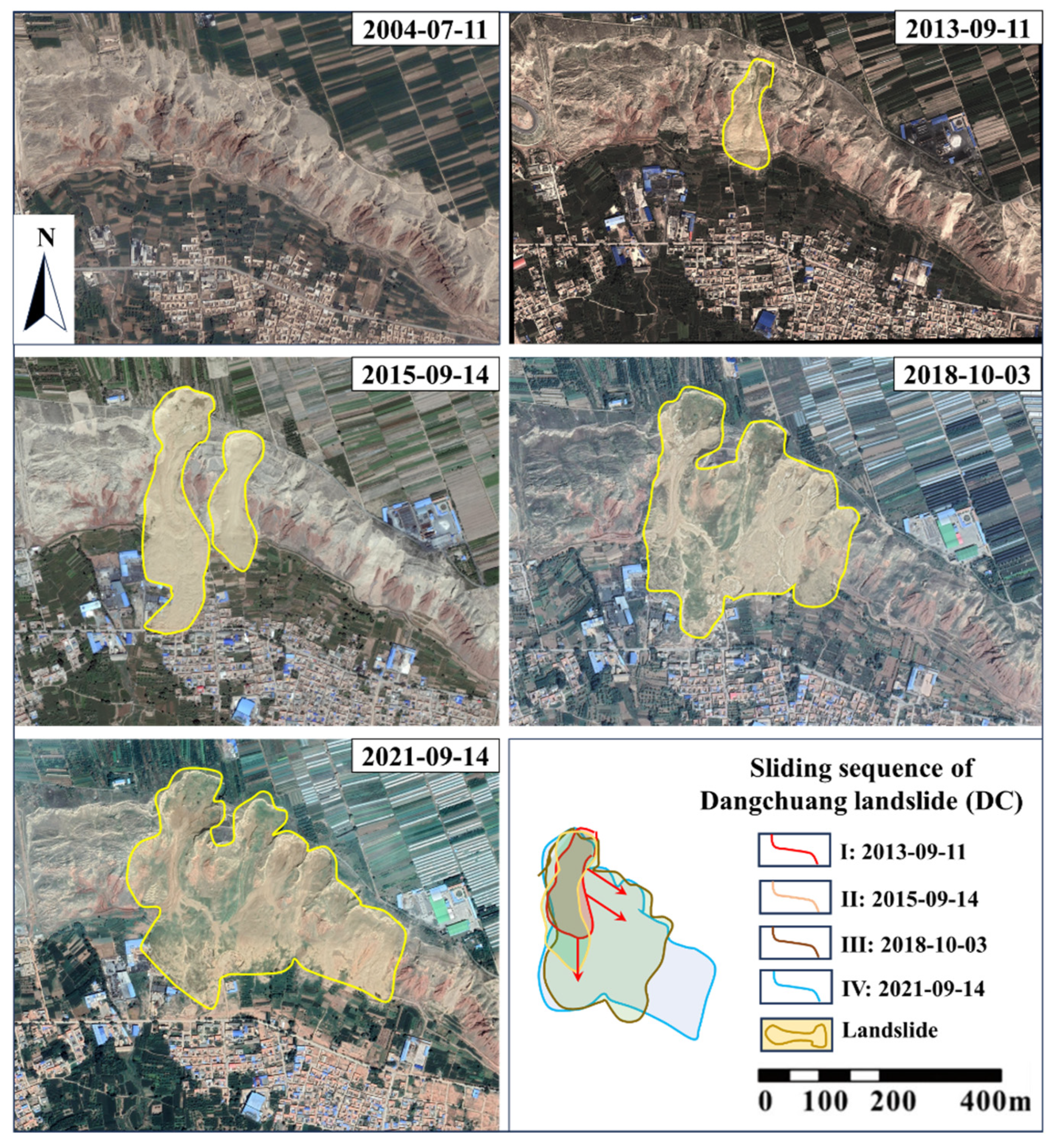
Figure 14 displays the remote sensing images of a landslide clusters in Dangchuan region, Heifangtai terrace, from 2004 to 2021. Before 2004, there was no new landslide in this area, mostly consisting of landslides from the previous century. During that period, the landslide bodies were in a stable state. It is evident that since 2013, new landslide has occurred. In 2015, it was observed that the existed landslide expanded longitudinally and more new landslides appeared. After that, the adjacent landslides continue to expand gradually on the basis of longitudinal landslides, leading to the development of larger landslide clusters. This phenomenon of landslide cluster evolution is most pronounced on the Heifangtai terrace, giving rise to the most famous landslide cluster: the Dangchuan Landslide Cluster. The lateral evolution pattern is evident in the case of Dangchuan Landslide Cluster, where different sliding sequence can be identified clearly.
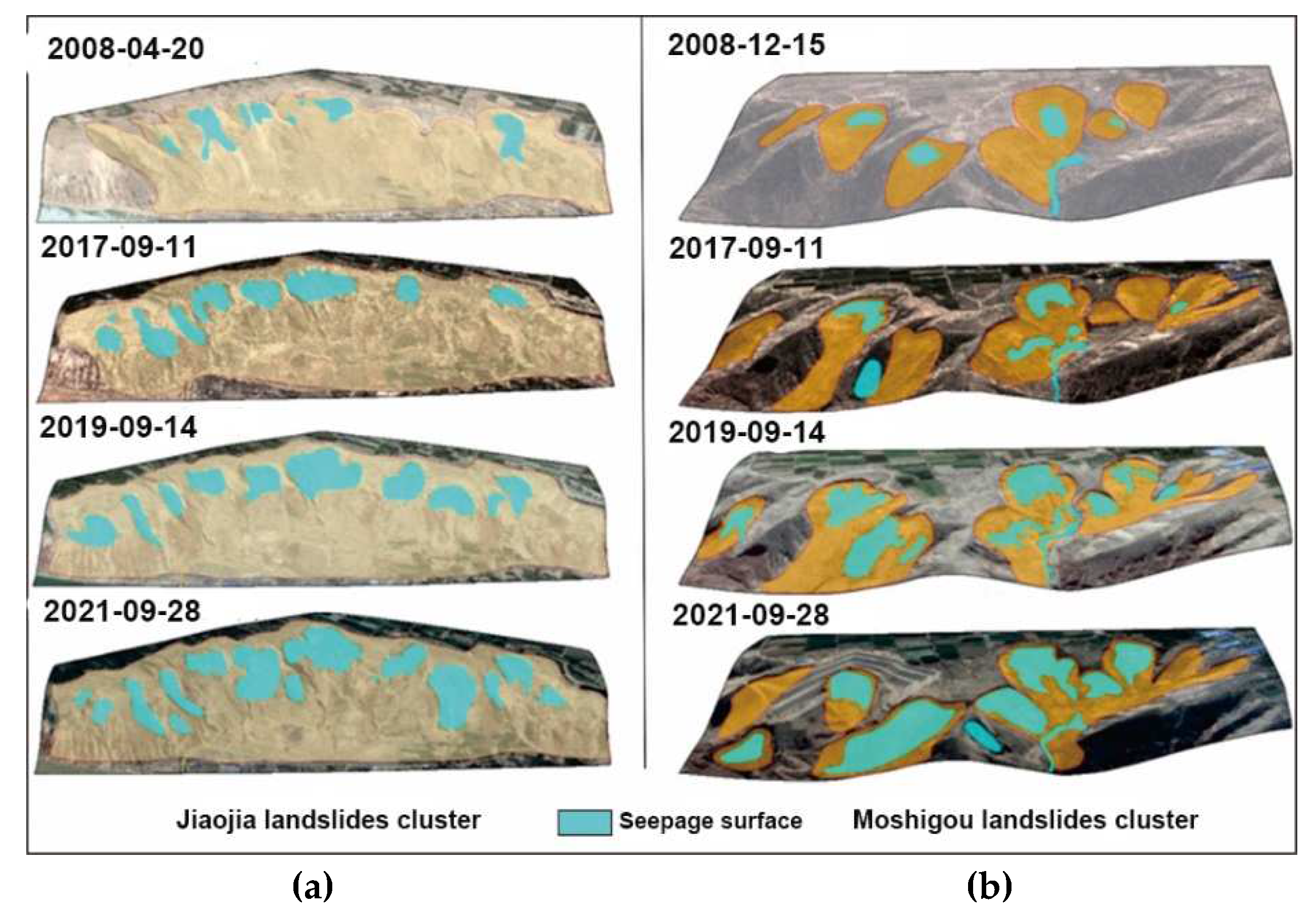
The remote sensing images of two landslide clusters on the Heifangtai terrace: Jiaojia and Moshigou landslide clusters, are presented in
Figure 15. Before 2008, there were few instances of new landslides occurring in this area. Be similar to the Dangchuan landslide cluster before 2004, these landslide bodies were also stable. In
Figure 15(b), it is evident that since 2017, new landslides have occurred every year in the Moshigou landslide cluster. Adjacent landslides continue to expand gradually on the basis of longitudinal evolution, leading to the development of larger landslide clusters.
5. Numerical modeling of Lateral Evolution Slope Stability
Based on field investigations and remote sensing image interpretation, it can be observed that landslides on the Heifangtai terrace have evolved into two major landslide clusters, with the lateral evolution pattern dominating. Therefore, in this section, FLAC3D software is used to simulate the mechanical response mechanism of the longitudinal evolution mode of slopes, as well as the stability state of the lateral slope after landslide occurs, in order to reveal the mechanism of lateral evolution pattern of landslide.
5.1. Three-dimensional Model and Parameters
A three-dimensional model is created using FLAC3D software. The model has the dimensions of 300 m × 100 m × 100 m. The entire computational model is divided into 37,500 grid cells and 40,716 nodes. The simulation used the Mohr-Coulomb model, considering only the deformation caused by the self-weight stress of the slope while neglecting the influence of structural stress on stability. Apart from the slope surfaces, the boundaries and bottom of the model are set as unidirectional constraint boundaries. The calculation is conducted from the natural state to equilibrium state, and then the displacement velocity constraints are set to the initial state for further stability calculations after increasing the groundwater level. The calculation parameters of the model are listed in
Table 2, obtained from triaxial tests.
5.2. Analysis of Simulation Results
Under the influence of irrigation water, the loess undergoes sub-erosion. Due to the prolonged presence of sub-erosion, the shear strength of the loess gradually decreases, forming plastic and weak zone. As sub-erosion further develops, cracks in the escarpment connect with loess joints, forming an arc-shaped sliding surface. The slope will then experience shear failure. The excavated area represents the portion of the slope that has slid and eroded. After the slope instability and sliding, an arc-shaped groove forms in the sliding area, creating a new free surface. The concave terrain facilitates the collection of groundwater, and the concentrated collection and discharge of groundwater lead to the bottom of the material source of the new landslide remaining in a saturated state. Consequently, the loess at the bottom of this area remains saturated for a long time, making it susceptible to landslide.
Additionally, after the initial landslide occurs, the accumulation effect at the foot of the slope causes the groundwater level to rise, leading to the slope being in a saturated state for an extended period. The initial landslide disrupts the equilibrium state of the slope, generating W-shaped cracks at the rear edge. With the development of these cracks, they provide pathways for surface water infiltration, prompting the development of vertical discontinuities. The simulation results of the landslide are analyzed in the following results: the shear strain distribution, lateral displacement along X axis, longitudinal displacement along Y axis, plastic zone distribution, and vertical stress distribution.
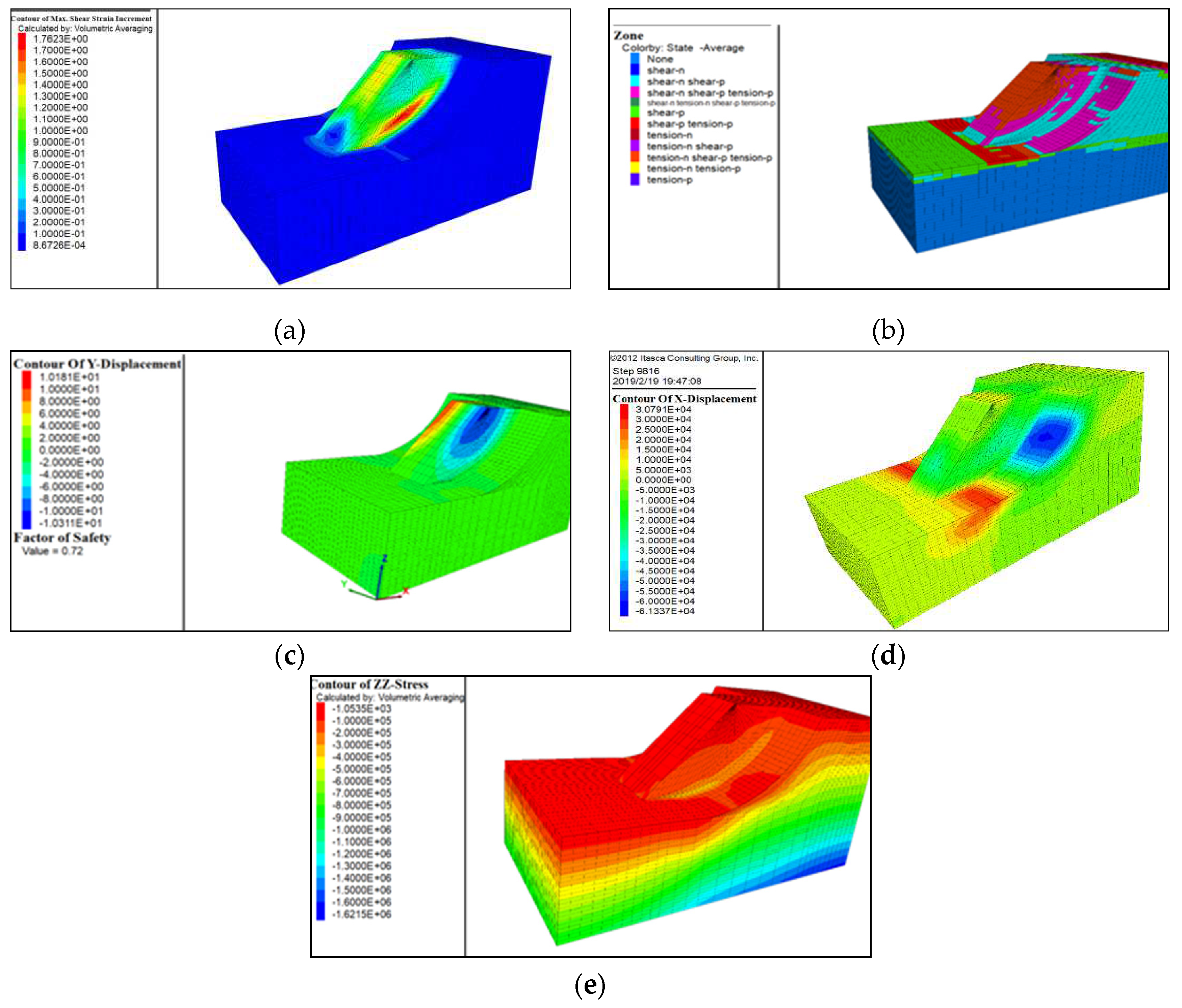
5.2.1. The Shear Strain Distribution
The shear strain distribution map is shown in
Figure 16(a). It displays the position, characteristics, and distribution range of the sliding surface. The sliding surface is always located in areas with larger shear strains. This is also the region where the deformation and failure occur during landslides. The portion of shear strain variation extends from the foot of the slope upward, revealing potential sliding surfaces and exhibiting significant localized shear deformation. The contour of shear strains can be used to visualize the distribution position and range of the sliding surface. The maximum value of shear strain corresponds to the location of the sliding surface, which presents the region of deformation and movement of the landslide. Larger values near the front edge of the landslide indicate a greater possibility of deformation and movement occurring.
5.2.2. Plastic Zones Analysis
Figure 16(b) shows the scattered distribution of plastic zones in the normal condition (before excavation) of the slope. Most of them are located at the foot of the slope and at the rear of the slope surface, indicating an already unstable state. Under the influence of rising groundwater levels, the area of the plastic zones expands further. The plastic zones extend from the base to the top of the slope, indicating significant shear failure. The plastic zones at the lower part of the sliding mass and along the slope contact surface represent the sliding zone.
5.2.3. Longitudinal Displacement along Y axis
After the landslides occurred on both sides, there is a noticeable unloading rebound on either side of the convex body (
Figure 16(c)). Field investigations have revealed that numerous cracks form on the convex body generated by lateral evolution.
5.2.4. Lateral Displacement along X axis
The displacement along the negative X-direction of the slope gradually increases, with the displacement growing from the toe of the slope towards the crest (
Figure 16(d)). This signifies an increase in the destructive strength of the landslide, indicating heightened instability. The significant variations of displacements along X axis suggest that the slope has already experienced sliding.
5.2.5. Vertical Stress Distribution
In the original slope, under the influence of self-weight stress, the vertical pressure increases significantly with depth (
Figure 16(e)). When sliding occurs on both sides, the sudden absence of horizontal compressive stress due to the slope orientation leads to pronounced compressive stress at the base of the convex-shaped slope on both sides.
By using FLAC3D to analyze the stability of landslides under different triggering conditions, it has been demonstrated that the lateral evolution of landslides is more pronounced. Under the lateral evolution mode, landslides exhibit a stronger inhibition on groundwater infiltration, which is more conducive to slope stability.
Figure 16.
Numerical modeling stability results of slope with lateral evolution pattern: (a) Shear strain distribution; (b) Distribution of plastic zones; (c) Longitudinal displacement distribution; (d) Lateral displacement distribution; (e) Vertical stress distribution.
Figure 16.
Numerical modeling stability results of slope with lateral evolution pattern: (a) Shear strain distribution; (b) Distribution of plastic zones; (c) Longitudinal displacement distribution; (d) Lateral displacement distribution; (e) Vertical stress distribution.
6. Conclusions
Based on a thorough investigation of landslides, this study comprehensively analyzed factors such as landslide types, topography, geomorphology, hydrogeological conditions, rainfall, and agricultural irrigation in the Heifangtai terrace. Different types of loess landslides are classified. In addition, the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of landslides are analyzed. Utilizing the numerical simulation software FLAC3D, the stability of slopes under the lateral evolution mode of landslides is analyzed, leading to the following conclusions:
- (1)
Landslides are widely distributed in the Heifangtai terrace, exhibiting various forms, including all typical types of loess landslides: landslides within loess layer and loess-bedrock slides. Landslides within loess layer can be further categorized into loess mudflows and loess collapse. Loess-bedrock slides include the loess-bedrock contact surface landslides, loess-bedrock inclined layer landslides, and loess-bedrock interbedded landslides. Among these, the most widespread and hazardous landslide type in the study area is the loess mudflow, with a friction coefficient less than 1.17.
- (2)
The development pattern of landslides in the study area exhibits both longitudinal evolution and lateral expansion patterns. Through field investigations, it's evident that lateral evolution is more widespread in the Heifangtai terrace. The initial stages of landslide often demonstrate characteristics of longitudinal evolution, with continual occurrence of smaller landslides along the rear edge of the landslide. However, when the longitudinal sliding reaches a certain extent, significant cracks develop along the rear edge of the the landslide, leading to lateral expansion. Lateral expansion has a more pronounced impact on the water level changes in Heifangtai terrace, and under this lateral evolution pattern, landslides in the Heifangtai terrace tend to achieve equilibrium more rapidly.
- (3)
The simulation results with FLAC3D indicate that when neighboring landslides occur in the study area, convex landforms without lateral support experience unloading rebound, leading to the formation of cracks on the convex body. Under the influence of self-weight stress, plastic deformation occurs within the slope body, resulting in instability and failure of slopes.
- (4)
Forests play a pivotal role within the ecological milieu, with alterations to forested areas not only impacting the local environment but also serving as a significant contributing factor to the occurrence of landslide disasters. However, the significance of forests in connection with deep seated landslides is diminished. Loess landslide disasters in Heifangtai terrace remains severe. The continuous geomorphologic evolution of landslide will ultimately lead to a reduction in the area of the plateau surface. This will have significant impacts on the production and livelihoods of local people. Therefore, efforts to prevent and mitigate landslide disasters in this area should continue to be strengthened.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Y.; methodology, X.W.; software, D.Y.; validation, D.Y., P. M. and X.W.; investigation, D.Y., P. M. and X.W.; resources, X.W.; data curation, D.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.W.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, X.W.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of Youth, grant number 42007278 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number xhj032021017-02.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
Ling. X. of School of Human Settlements and Civil Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University provided the experimental devices and aided with the field investigation. The authors would like to extend their deepest gratitude to him.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alcántara-Ayala, I. Geomorphology, natural hazards, vulnerability and prevention of natural hazards in developing countries. Geomorphology 2002, 47, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaranthus, M.; Rice, R.; Barr, N.R.; Ziemer, R.R. Logging and forest roads related to increased debris slides in southwestern Oregon. J. Forest. 1985, 83, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bischetti, G.B.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Epis, T.; Morlotti, E. Root cohesion of forest species in the Italian Alps. Plant Soil 2009, 324, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, F.C.; Tham, L.G.; Tu, X.B.; Jin, Y.L. Landslides in the transitional slope between a platformand river terrace, Northwest China. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2011, 17, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Li, T.L.; Xing, X.L.; Zou, Y. Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an, NW China. Environmental. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7933–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.S.; Ding, Z.L.; Guo, Z.T. Loess, Environment and Global Change; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Xie, W.L.; Pak, R.Y.S.; Vanapalli, S.K. Microstructural evolution of loess soils from the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2019, 173, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.Y.; Dong, H.; Liao, H.J.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.B.; Zhang, J.W. Effects of in-situ wetting-drying cycles on the mechanical behaviour of an intact loess. Can. Geotech. J. 2022, 59, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, C.Y.; Zuo, L.; Liu, K.; Li, L.W. The critical states of saturated loess soils. Eng. Geol. 2022, 307, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, L.; Mcgown, A.; Collins, K. The collapse mechanism in partly saturated soil. Eng. Geol. 1973, 7, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Wang, G.H.; Luo, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. A rapid losses flow slide triggered by irrigation in China. Landslides 2009, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.J.; Hu, H.J.; Liu, F. Summary of collapsible behaviour of artificially structured loess in oedometer and triaxial wetting tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garakani, A.A.; Haeri, S.M.; Khosravi, A.; Habibagahi, G. Hydro-mechanical behavior of undisturbed collapsible loessial soils under different stress state conditions. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.M.; Xu, Q.; Scaringi, G.V.; Li, S.; Peng, D.L. A chemo-mechanical insight into the failure mechanism of frequently occurred landslides in the loess plateau, Gansu Province, China. Eng. Geol. 2017, 228, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.K.; Vanapalli, S.K.; Li, T.L. Water infiltration characteristics in loess associated with irrigation activities and its influence on the slope stability in Heifangtai loess highland, China. Eng. Geol. 2018, 234, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, D.D. The groundwater responses to loess flowslides in the Heifangtai platform. B. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4931–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.A.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Hong, B.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.Q. Characterization of the mechanisms underlying loess collapsibility for land~creation project in Shaanxi Province, China-a study from a micro perspective. Eng. Geol. 2019, 249, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.L.; Qiang, X.; Liu, F.Z.; He, Y.S.; Zhang, S.; Qi, X.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Distribution and failure modes of the landslides in Heitai terrace, China. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.Q.; Peng, J.B.; Wang, G.H.; Javed, I.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: A case study in Shaanxi province. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentes, G. The role of recent tectonics and hydrological processes in the evolution of recurring landslides on the Danube’s high bank in Dunaföldvár, Hungary. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirus, B.B.; Smith, J.B.; Baum, R.L. Hydrologic impacts of landslide disturbances: Implications for remobilization and hazard persistence. Water. Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 8250–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithana, S.B.; Nakamura, S.; Gibo, S. Yoshinaga, A. Kimura, S. Correlation of large displacement drained shear strength of landslide soils measured by direct shear and ring shear devices. Landslides 2012, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Wan, L.; Wang, P. Initiation mechanism of mudflow-like loess landslide induced by the combined effect of 486 earthquakes and rainfall. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 3079–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammeraat, E.; Beek, R.V.; Kooijman, A. Vegetation Succession and its Consequences for Slope Stability in SE Spain. Plant Soil 2005, 278, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorren, L.K.A.; Berger, F.; le Hir, C.; Mermin, E.; Tardif, P. Mechanisms, effects and management implications of rockfall in forests. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2005, 215, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genet, M.; Stokes, A.; Fourcaud, T.; Norris, J. The influence of plant diversity on slope stability in a moist evergreen deciduous forest. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.B.; Ma, P.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, F.Y.; Tong, X.; Huang, W.L. Interaction between landsliding materials and the underlying erodible bed in a loess flowslide. Eng. Geol. 2018, 234, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, F.C.; Kwong, A.K.L. Types and characteristics of loess landslides at Heifangtai loess plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci-Engl. 2008, 26, 364–371, (in Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.K.; Vanapalli, S.K.; Li, T.L. Water infiltration characteristics in loess associated with irrigation activities and its influence on the slope stability in Heifangtai loess highland, China. Eng. Geol. 2018, 234, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, F.C.; Tham, L.G.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wu, C.X. Investigating landslide-related cracks along the edge of two loess platforms in Northwest China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Zhu, L.F.; Hu, W. Geological environment changes and loess disater caused by irrigation: A case study of Heifangtai Irrigation District in Gansu Province; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Xing, H.L.; Zhang, S.; Kang, K.; Qi, X.; Ju, Y.Z.; Zhao, K.Y. Hydrological response of loess slopes with reference to widespread landslide events in the Heifangtai terrace, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Peng, D.L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; He, C.Y.; Qi, X.; Zhao, K.Y.; Xiu, D.H.; Ju, N.P. Successful implementations of a real-time and intelligent early warning system for loess landslides on the Heifangtai terrace, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 278, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Qiu, H.J.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Y.R.; Cui, Y.F.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.J.; Pei, Y.Q.; Cao, M.M. Spatiotemporal distribution and evolution characteristics of successive landslides on the Heifangtai tableland of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geomorphology 2021, 378, 107619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, B.Q.; Wang, X.G.; Zhan, H.B.; Wang, J.D.; Peng, J.B.; Gu, T.F.; Zhu, R.S. Creep mechanical and microstructural insights into the failure mechanism of loess landslides induced by dry-wet cyclres in the Heifangtai platform, China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 300, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, X. Mass rock creep and landsliding on the Huangtupo slope in the reservoir area of the Three Gorges Project, Yangtze River, China. Eng. Geol. 2009, 58, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stéphane, B.; Darnault, R.; Chemenda, A.; Rolland, Y. Evolution of gravity-driven rock slope failure and associated fracturing: Geological analysis and numerical modeling. Tectonophysics 2012, 526–529, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- González-Díez, A.; Fernández-Maroto, G.; Doughty, M.W.; Díaz de Terán, J.R.; Bruschi, V.; Cardenal, J.; Pérez, J.L.; Mata, E.; Delgado, J. Development of a methodological approach for the accurate measurement of slope changes due to landslides, using digital photogrammetry. Landslides 2014, 11, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, B.; Dai, K.R.; Dong, X.J.; Li, W.L.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.H.; Xiao, X.X.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, H.Y.; Deng, B.; Ge, D.Q. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: A progress report from China. Eng. Geol. 2023, 321, 107156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Suemine, A.; Zhang, F.Y.; Hata, Y.; Fukuoka, H.; Kamai, T. Some fluidized landslides triggered by the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake (Mw 9.0), Japan. Geomorphology 2014, 208, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Wu, G.L.; Jiao, J.Y.; Dyck, M.; He, H.L. Freeze-thaw induced landslides on grasslands in cold regions. Catena 2022, 219, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.X.; Zhuang, J.Q.; Peng, J.B.; Ma, P.H.; Zhan, J.W.; Mu, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, J.; Fu, Y.T.; Wang, S.B.; Du, C.H. Failure mechanism and movement process of three loess landslides due to freeze-thaw cycle in the Fangtai village, Yongjing County, Chinese Loess Plateau. Eng. Geol. 2023, 315, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
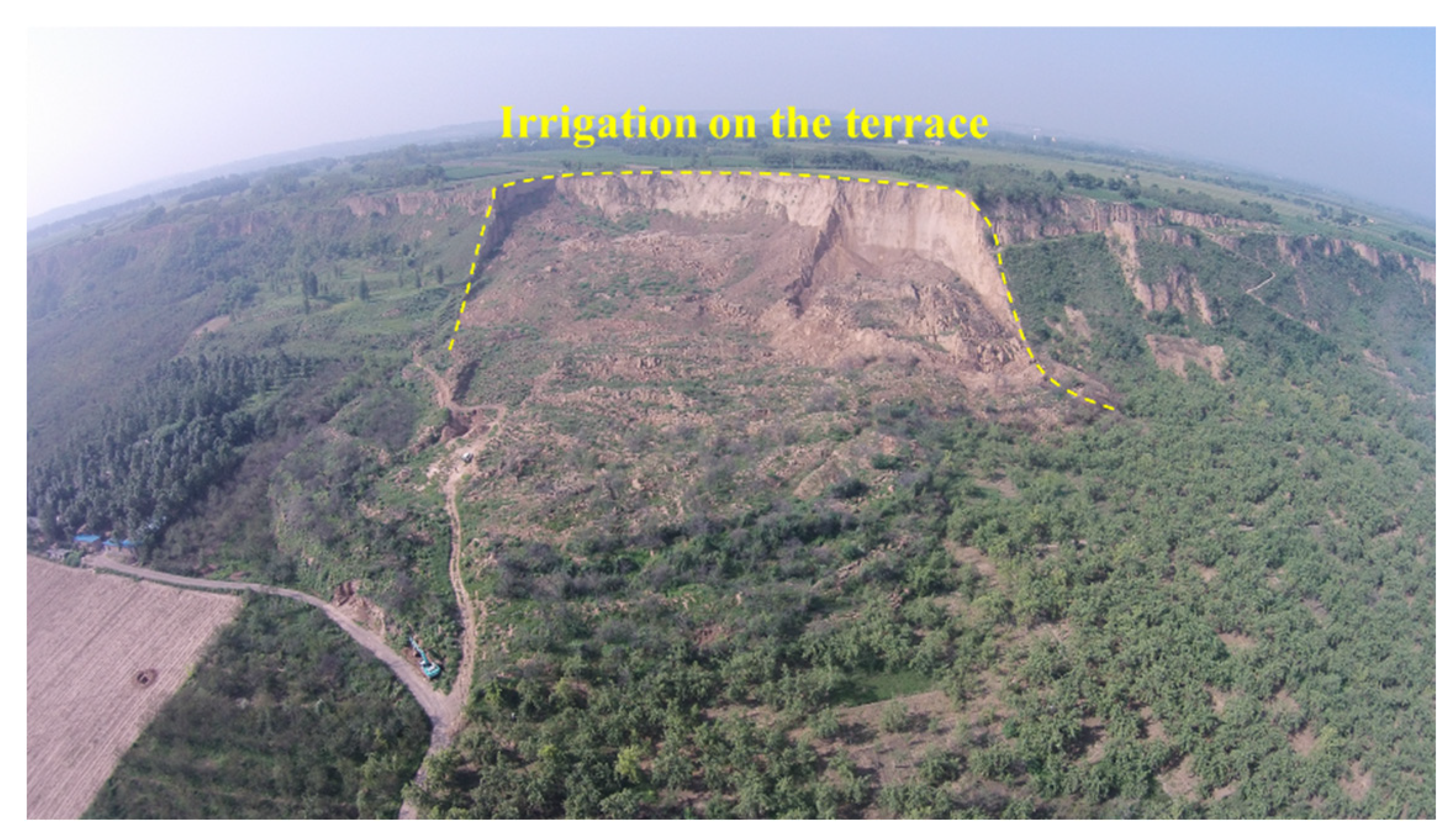
Figure 1.
Photo of a typical landslide on the Heifangtai terrace due to irrigation, Gansu Province, China.
Figure 1.
Photo of a typical landslide on the Heifangtai terrace due to irrigation, Gansu Province, China.
Figure 2.
The vegetation index map of Gansu Province.
Figure 2.
The vegetation index map of Gansu Province.
Figure 3.
The lithological profile of the Heifangtai terrace.
Figure 3.
The lithological profile of the Heifangtai terrace.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of different types of loess landslides in Heifangtai terrace.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of different types of loess landslides in Heifangtai terrace.
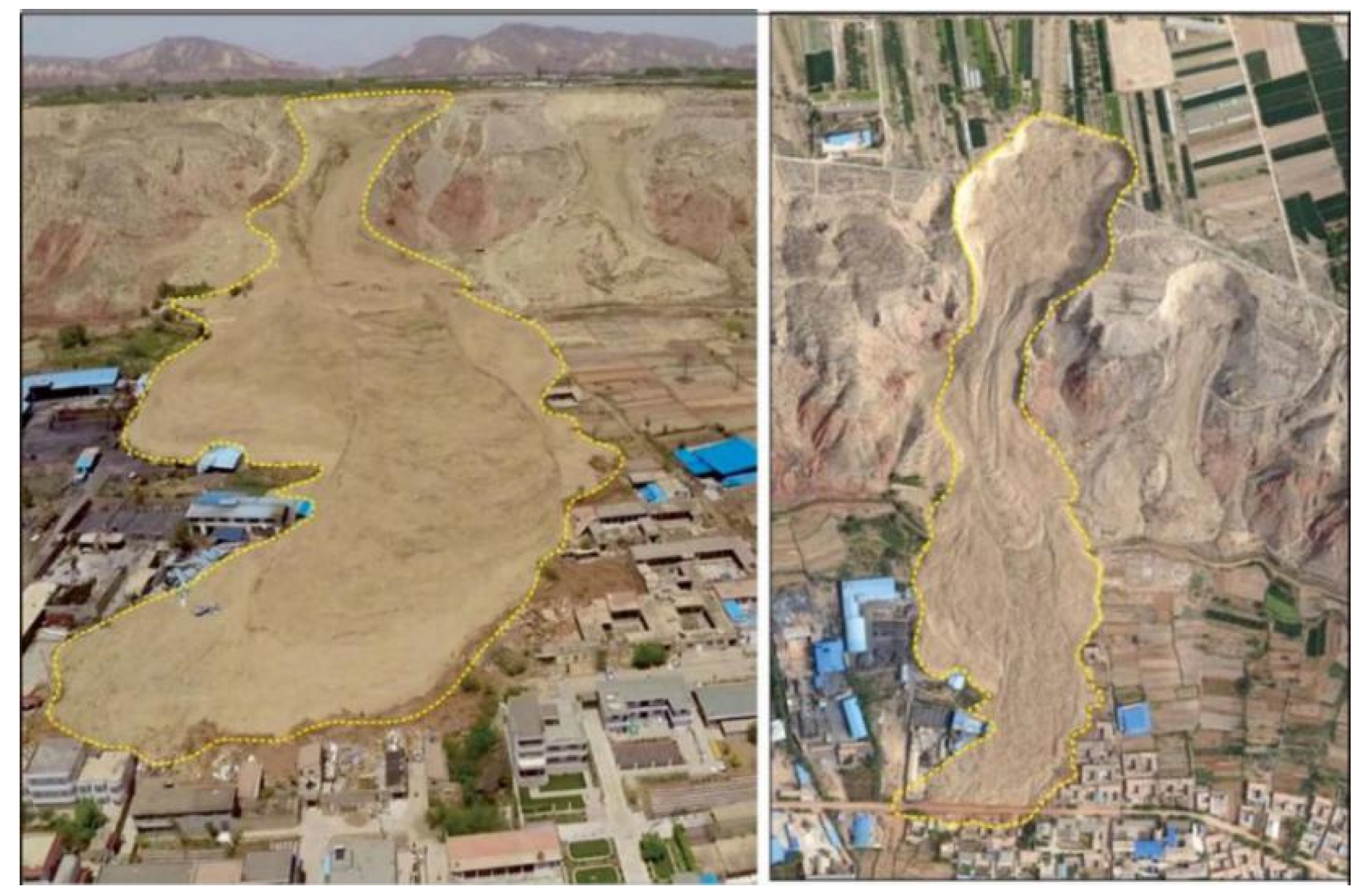
Figure 5.
Interpretation of remote sensing images from Heifangtai terrace.
Figure 5.
Interpretation of remote sensing images from Heifangtai terrace.
Figure 6.
Photos of loess mudflow in Dangchuan region.
Figure 6.
Photos of loess mudflow in Dangchuan region.
Figure 7.
Parameters of Dangchuan loess mudflow: (a) Equivalent friction coefficient (H/L); (b) relationship between H/L and the volume (V) of loess mudflow.
Figure 7.
Parameters of Dangchuan loess mudflow: (a) Equivalent friction coefficient (H/L); (b) relationship between H/L and the volume (V) of loess mudflow.
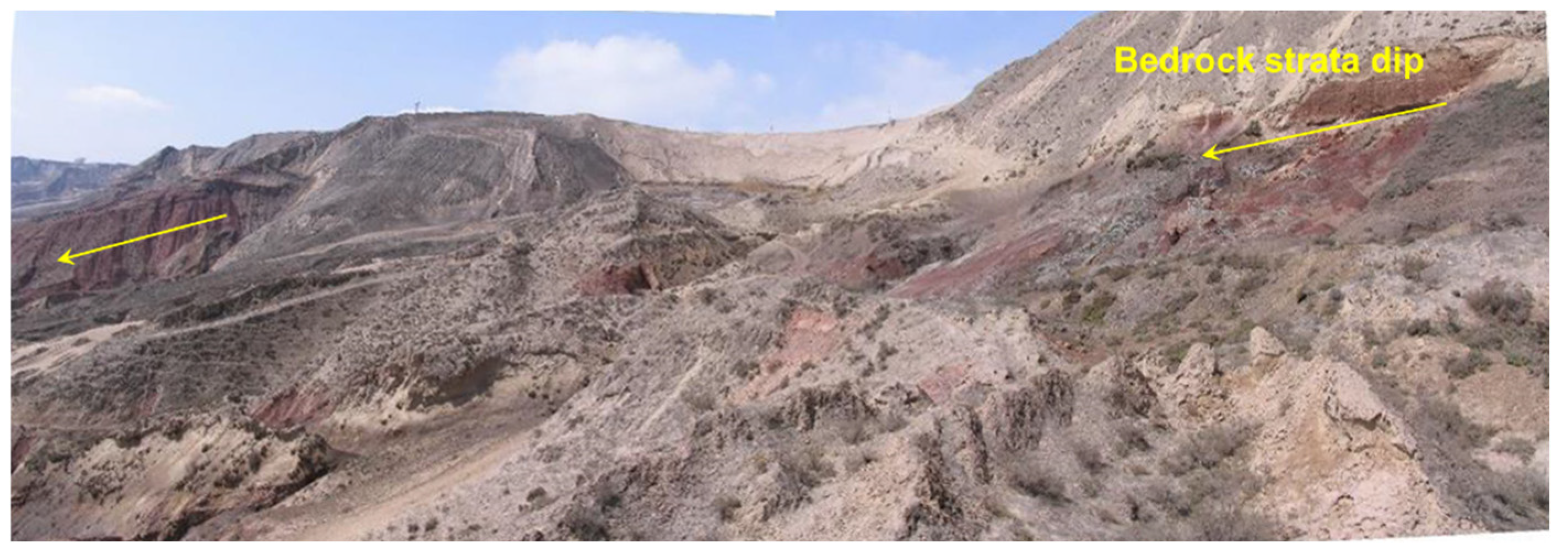
Figure 8.
Photo of loess collapses in Dangchuan region.
Figure 8.
Photo of loess collapses in Dangchuan region.
Figure 9.
Photo of landslides caused by loess-Mudstone interbedded layers, Huangci region.
Figure 9.
Photo of landslides caused by loess-Mudstone interbedded layers, Huangci region.
Figure 10.
Annual distribution of landslides (from 1980 to 2010).
Figure 10.
Annual distribution of landslides (from 1980 to 2010).
Figure 11.
Monthly distribution of landslides: (a) Monthly distribution of landslides considering rainfall; (b) Relationship between irrigation volume and landslide frequency.
Figure 11.
Monthly distribution of landslides: (a) Monthly distribution of landslides considering rainfall; (b) Relationship between irrigation volume and landslide frequency.
Figure 12.
Photos of the Moshigou landslide in 2013 and 2022.
Figure 12.
Photos of the Moshigou landslide in 2013 and 2022.
Figure 13.
The lateral evolution pattern of landslide in Dangchuan region.
Figure 13.
The lateral evolution pattern of landslide in Dangchuan region.
Figure 14.
Remote sensing image interpretation of typical loess landslide clusters in Dangchuan, Heifangtai Terrace.
Figure 14.
Remote sensing image interpretation of typical loess landslide clusters in Dangchuan, Heifangtai Terrace.
Figure 15.
Remote sensing image interpretation of typical loess landslide clusters in Heifangtai: (a) Jiaojia landslide cluster; (b) Moshigou landslide cluster.
Figure 15.
Remote sensing image interpretation of typical loess landslide clusters in Heifangtai: (a) Jiaojia landslide cluster; (b) Moshigou landslide cluster.
Table 1.
Information and classification of loess landslides in Heifangtai terrace.
Table 1.
Information and classification of loess landslides in Heifangtai terrace.
| Num. |
Location |
Length/m |
Height/m |
Width/m |
Volume/(104 m3) |
Type of landslides |
| 1 |
103°18'15"E,36°05'37"N |
282.75 |
85 |
499 |
223.73 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 2 |
103°17'41"E,36°05'29"N |
345.55 |
71 |
673 |
523.68 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 3 |
103°18'25"E,36°05'39"N |
318.9 |
111 |
159 |
531.61 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 4 |
103°18'32"E,36°05'37"N |
346.09 |
106 |
164 |
32.03 |
Loess mudflow |
| 5 |
103°18'34"E,36°05'34"N |
298.48 |
104 |
72 |
77.32 |
Loess mudflow |
| 6 |
103°18'38"E,36°05'32"N |
99.48 |
75 |
95 |
3.11 |
Loess collapse |
| 7 |
103°18'41"E,36°05'30"N |
61.14 |
43 |
65 |
2.73 |
Loess collapse |
| 8 |
103°18'41"E,36°05'30"N |
156.37 |
101 |
80.2 |
19.15 |
Loess collapse |
| 9 |
103°18'48"E,36°05'26"N |
204.03 |
97 |
87.6 |
19.11 |
Loess collapse |
| 10 |
103°18'56"E,36°05'23"N |
132.26 |
90 |
51 |
7.9 |
Loess collapse |
| 11 |
103°19'03"E,36°05'18"N |
244.32 |
101 |
\ |
77.04 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 12 |
103°19'14"E,36°05'21"N |
386.18 |
104 |
451 |
553.05 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 13 |
103°19'32"E,36°05'29"N |
376.44 |
101 |
406 |
610.36 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 14 |
103°19'49"E,36°05'32"N |
130.4 |
58.7 |
\ |
6.2 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 15 |
103°19'53"E,36°05'39"N |
212.16 |
107 |
\ |
18.24 |
Loess-bedrock landslide |
| 16 |
103°20'05"E,36°05'44"N |
226.15 |
132 |
144 |
28.68 |
Loess mudflow |
| 17 |
103°20'08"E,36°05'46"N |
181.41 |
121 |
81 |
7.05 |
Loess mudflow |
| 18 |
103°20'11"E,36°05'52"N |
217.7 |
133 |
74 |
8.16 |
Loess mudflow |
| 19 |
103°20'13"E,36°05'52"N |
163.31 |
108 |
26 |
5.26 |
Loess mudflow |
| 20 |
103°20'13"E,36°05'55"N |
201.36 |
92 |
117 |
7.32 |
Loess mudflow |
| 21 |
103°20'10"E,36°05'59"N |
342.2 |
113 |
61 |
8.69 |
Loess mudflow |
| 22 |
103°20'12"E,36°06'00"N |
56.58 |
43 |
31 |
0.41 |
Loess mudflow |
| 23 |
103°20'13"E,36°06'02"N |
88.26 |
57 |
49 |
0.94 |
Loess mudflow |
| 24 |
103°20'09"E,36°06'04"N |
353.43 |
121 |
81 |
34.38 |
Loess mudflow |
| 25 |
103°20'05"E,36°06'09"N |
425.66 |
120 |
212 |
88.99 |
Loess mudflow |
| 26 |
103°20'06"E,36°06'16"N |
515.48 |
124 |
192 |
92.88 |
Loess mudflow |
| 27 |
103°20'06"E,36°06'24"N |
609.55 |
119 |
334 |
333.81 |
Loess mudflow |
| 28 |
103°20'12"E,36°06'33"N |
468.73 |
120 |
174 |
152.65 |
Loess mudflow |
| 29 |
103°20'18"E,36°06'37"N |
326.17 |
108 |
195 |
33.2 |
Loess mudflow |
| 30 |
103°20'20"E,36°06'42"N |
322.83 |
100 |
83 |
10.55 |
Loess mudflow |
| 31 |
103°20'18"E,36°06'45"N |
390.97 |
101 |
137 |
52.86 |
Loess collapse |
| 32 |
103°20'04"E,36°07'01"N |
283.86 |
104 |
104 |
55.65 |
Loess mudflow |
| 33 |
103°19'53"E,36°06'58"N |
164.11 |
99 |
33 |
17.75 |
Loess collapse |
| 34 |
103°19'48"E,36°06'53"N |
207.58 |
79 |
116 |
15.77 |
Loess collapse |
| 35 |
103°19'53"E,36°06'54"N |
199.53 |
64 |
157 |
29.92 |
Loess mudflow |
| 36 |
103°19'46"E,36°06'50"N |
154.97 |
40 |
133 |
15.91 |
Loess mudflow |
Table 2.
The calculation parameters of the model.
Table 2.
The calculation parameters of the model.
| Type of soil |
K/Pa |
G/Pa |
c/kPa |
φ/° |
ρ/kg.m-3
|
| Natural unsaturated loess |
3.9×106
|
8×106
|
21 |
30.7 |
1480 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).