1. Introduction
Invasive alien plant species (IAPS) are considered a global problem that poses threats to many ecosystems, thereby causing severe ecological, economic, and social impacts [
1]. In the ecological context, IAPS are infamous for disrupting ecosystem processes, altering composition and structure of native plant communities, and outcompeting native plants leading to the decline in indigenous plant diversity [
2,
3]. Meanwhile, on the socio-economic aspect, the presence of IAPS can lead to the reduced agricultural productivity, damaged power lines and buildings, and disturbed cultural heritage and human well-being [
4,
5,
6]. Hence, dictating the importance of implementing control and management strategies to reduce the impacts of invasive plant species on native biodiversity and human well-being.
Swietenia macrophylla or big leaf mahogany is one of the most prominent and aggressive invasive plants introduced to the Philippines as a reforestation species in as early as 1911 [
7]. Back then, its invasive potential remained hidden until it revealed its ability to suppress the growth of other plants under its canopy due to its allelopathic ability [
8]. Efforts has been done to document and assess the population and impacts of
S. macrophylla across the Philippines [
7,
9], thus, declaring it as an invasive species in the country [
10]. Unfortunately, this plant already had established populations in some of the country’s protected areas such as Mt. Makiling Forest Reserve [
11], Ninoy Aquino Parks and Wildlife Center [
12], and Rajah Sikatuna Protected Landscape [
13], among others.
Despite having several studies documenting the presence of
S. macrophylla, there is a scarcity of scientifically accepted information regarding the population and distribution of the species in Mts. Banahaw-San Cristobal Protected Landscape (MBSCPL) including its neighboring zones (e.g., buffer zone). Generally, there are very limited studies about tree species composition and diversity in MBSCPL. Only three studies are publicly available which only focused on biodiversity assessment [
14,
15], the conservation status of plants [
16], and the selection of plus and mother trees [
17]. Furthermore, most of these studies were only focused on one side of the mountain located at the province of Quezon. Thus, the portion of the protected area located in Laguna is relatively unexplored as the lack of studies indicate. Nonetheless, local community reports and personal observation of the presence of big leaf mahogany within the area has prompted the author to conduct the study in MBSCPL.
MBCPL is one of the protected areas under the Republic Act No. 7586 or the National Integrated Protected Areas System Act of 1992 (NIPAS Act of 1992) [
18]. It is situated in the provinces of Laguna and Quezon in Southern Luzon, Philippines [
19]. This holds unique keystone organisms such as the endemic
Rafflesia banahaw [
20] and the members of one of the most threatened family, Dipterocarpaceae, including
Shorea contorta and
Parashorea malaanonan [
16]. As a protected zone, the conservation of these biodiversity resources must be the top priority of the concerned institutions.
In line with this, the author aimed to pioneer the documentation of the invasive big leaf mahogany at the edges of Mt. Banahaw de Nagcarlan, the portion of MBSCPL located in Nagcarlan, Laguna. This study can serve as a tool to address the knowledge gap on the presence of the species in the area by locating the populations of big leaf mahogany as well as the existing management practices of the government agencies with regard to
S. macrophylla. Possessing this information can be used to determine key areas for monitoring and control and its impact on the ecosystem, develop targeted management strategies, and inform wise decision-making on the management and control of the species to reduce its negative impact [
21,
22].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
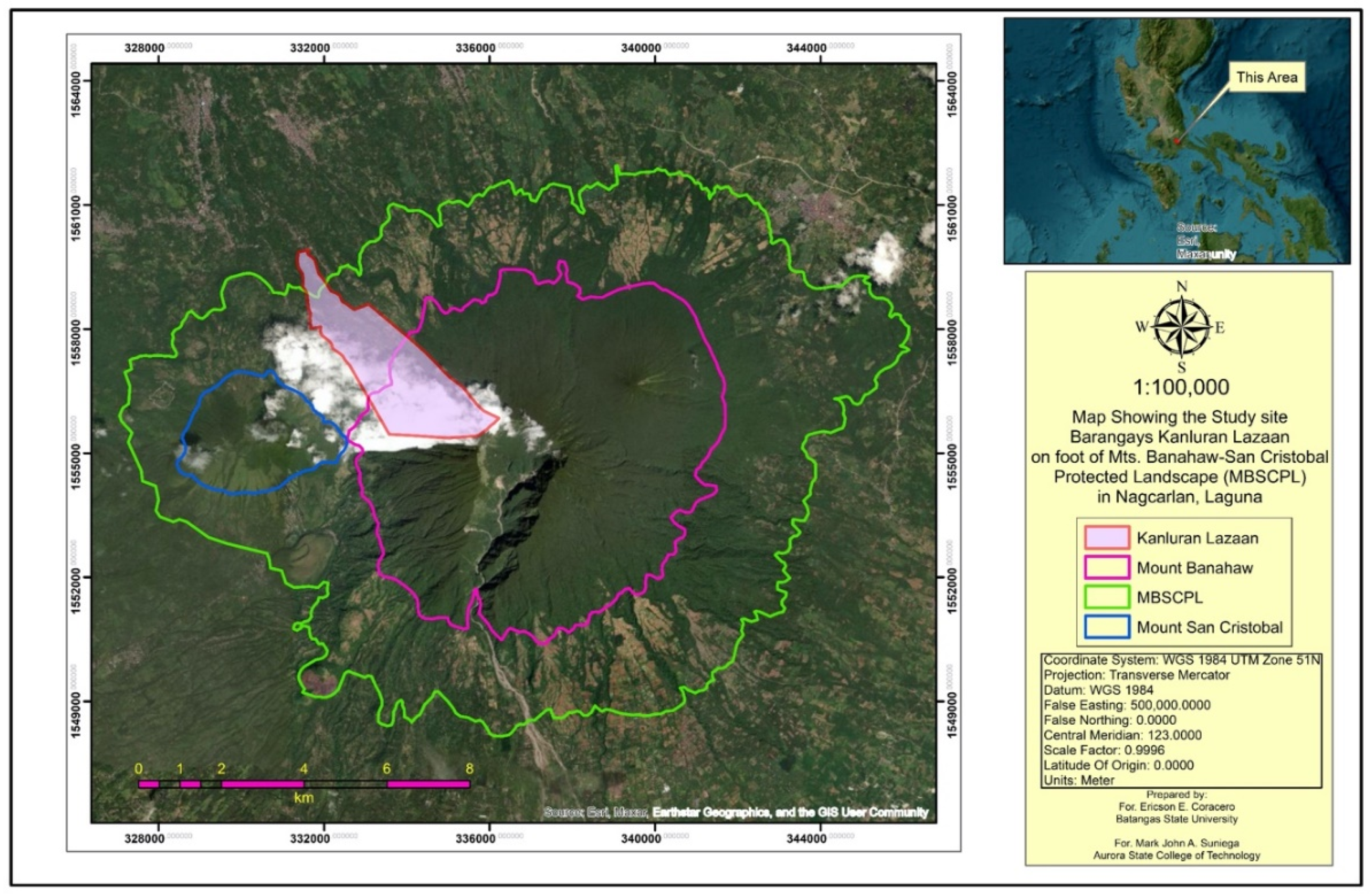
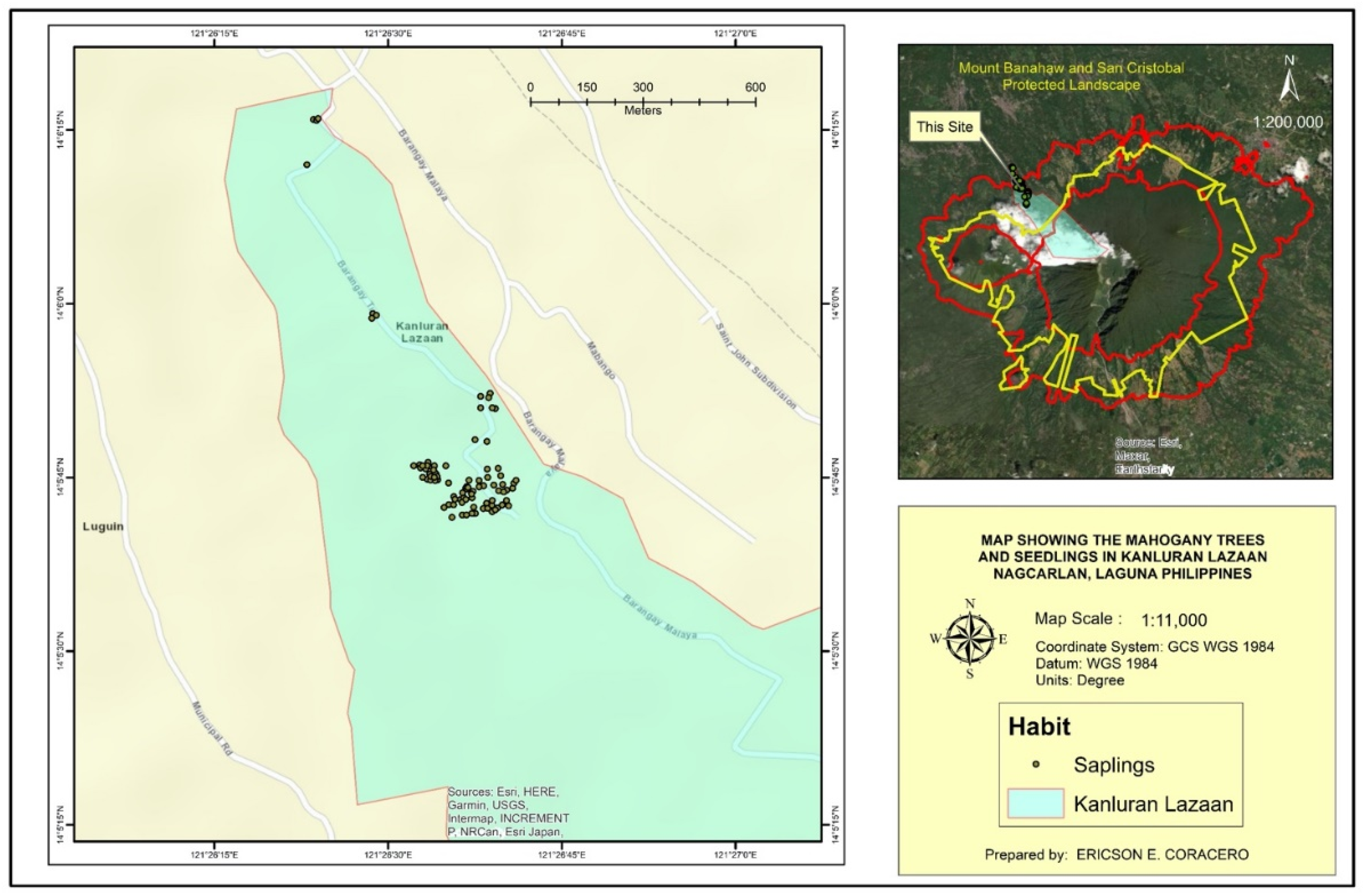
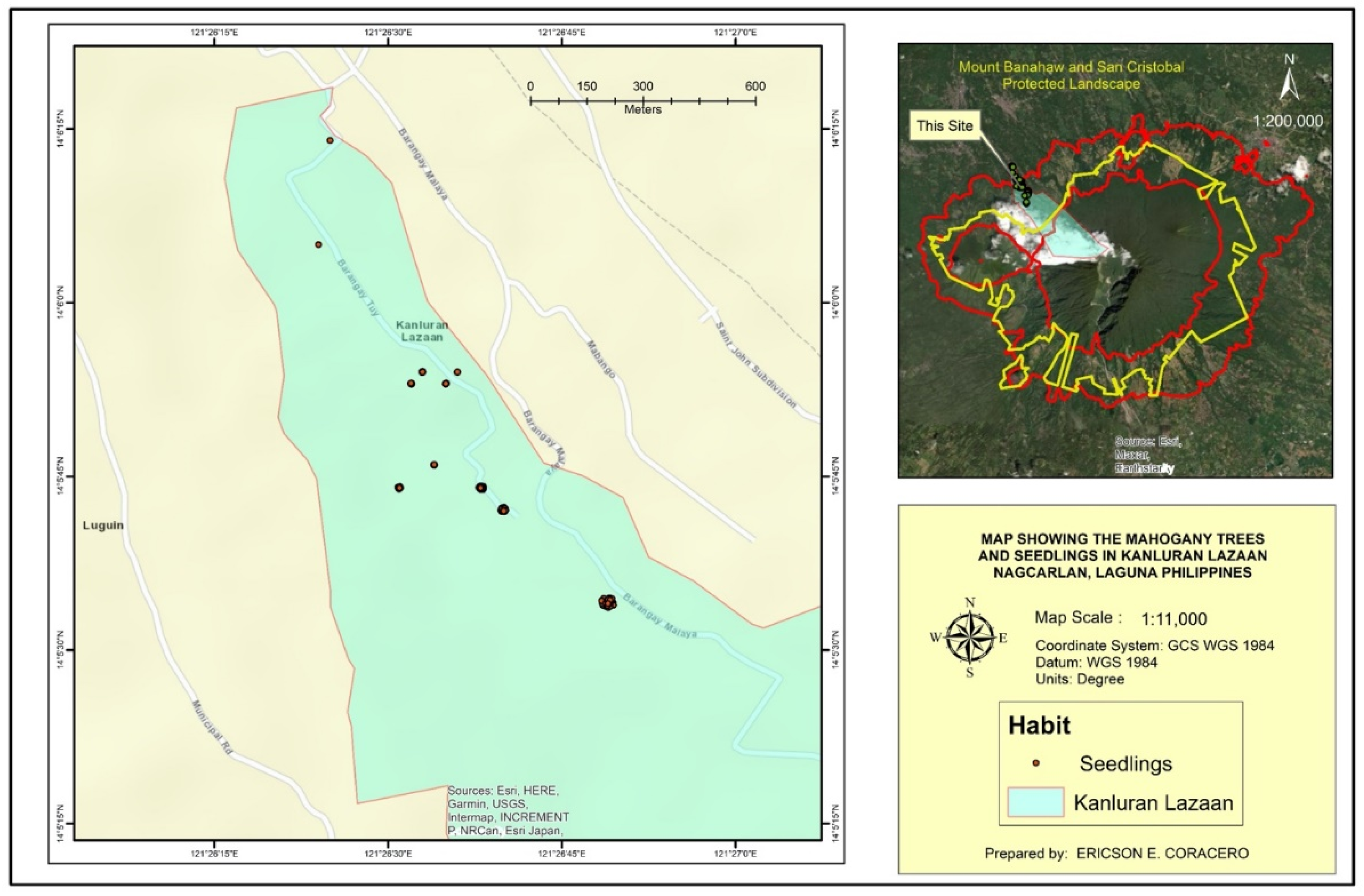
The study was conducted from March to May 2023 at the foot barangay of Mt. Banahaw de Nagcarlan, in Laguna specifically Kanluran Lazaan (
Figure 1). This barangay is within the boundary (forest reservation) of Mts. Banahaw-San Cristobal Protected Landscape (MBSCPL). MBSCPL was declared as a protected landscape under the Mts. Banahaw - San Cristobal Protected Landscape (MBSCPL) Act of 2009. The protected landscape covered around 10,900.59 ha of lowland to submontane forest [
19]. The study was specifically conducted at the foot barangay of the mountain where agriculture and agroforestry were dominant as residential areas. The topography in these areas was moderate to steep. MBSCPL generally belonged to climate type II with a sandy clay loam soil [
23]. The average temperature in Nagcarlan, Laguna could be observed during February with 28°C during the day and 21°C at night [
24]. It typically received 86.95mm of rainfall and experienced about 3 rainy days in the month, and the humidity level was usually around 82%.
2.2. Survey and Mapping of Swietenia macrophylla King
All individuals of S. macrophylla were inventoried and recorded. Data such as diameter, geographical coordinates, tree height, and other notable observations (e.g., fruiting, flowering) were also recorded for each big leaf mahogany individual. Regarding the mapping procedure, the data were encoded in Microsoft excel. The recorded coordinates were converted in the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) format before feeding it to the ArcGIS (v. 10.8) software. Then, location points of each plant individual were plotted in the map.
2.3. Identification of Management Strategies
For the management strategies of various government institutions such as the Department of Environment and Natural Resources – Protected Area Management Office (DENR-PAMO), Municipal Environment and Natural Resources Office (MENRO), Sangguniang Bayan Committee on Natural Resources and Environmental Protection, and Sangguniang Barangay of Kanluran Lazaan, exhaustive interviews were done with the office heads to determine the detailed management strategies being employed in invasive alien plant species (with emphasis on big leaf mahogany) in the barangay, in MBSCPL and in other areas under their jurisdiction. The interviews were unstructured to really exhaust the information from them regarding the management strategies of IAPS. Unstructured interviews are believed to produce new insights and ideas that are flexible and free from error and misinterpretations [
25].
2.4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
2.4.1. Distribution Maps
The distribution of population was presented in the form of a maps showing their size classes based on DBH. For the DBH, several literatures about size classes were read by the researcher. The studies of Norghauer et al. [
26] on
Swietenia macrophylla King and Itoh et al. [
27] on trees in the tropical rainforest were selected based on their agreed classification of tree size classes and specially that the first study focused on S. macrophylla which is the focal species of the current undertaking (
Table 1).
2.4.2. Content Analysis of Management Strategies
The interview responses of the government agency respondents were assessed via content analysis. The method of Hermann [
28] in performing content analysis was followed. The steps indicated in this literature are presented in
Table 2 with its corresponding equivalent in the present study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. S. macrophylla and its Spatial Distribution
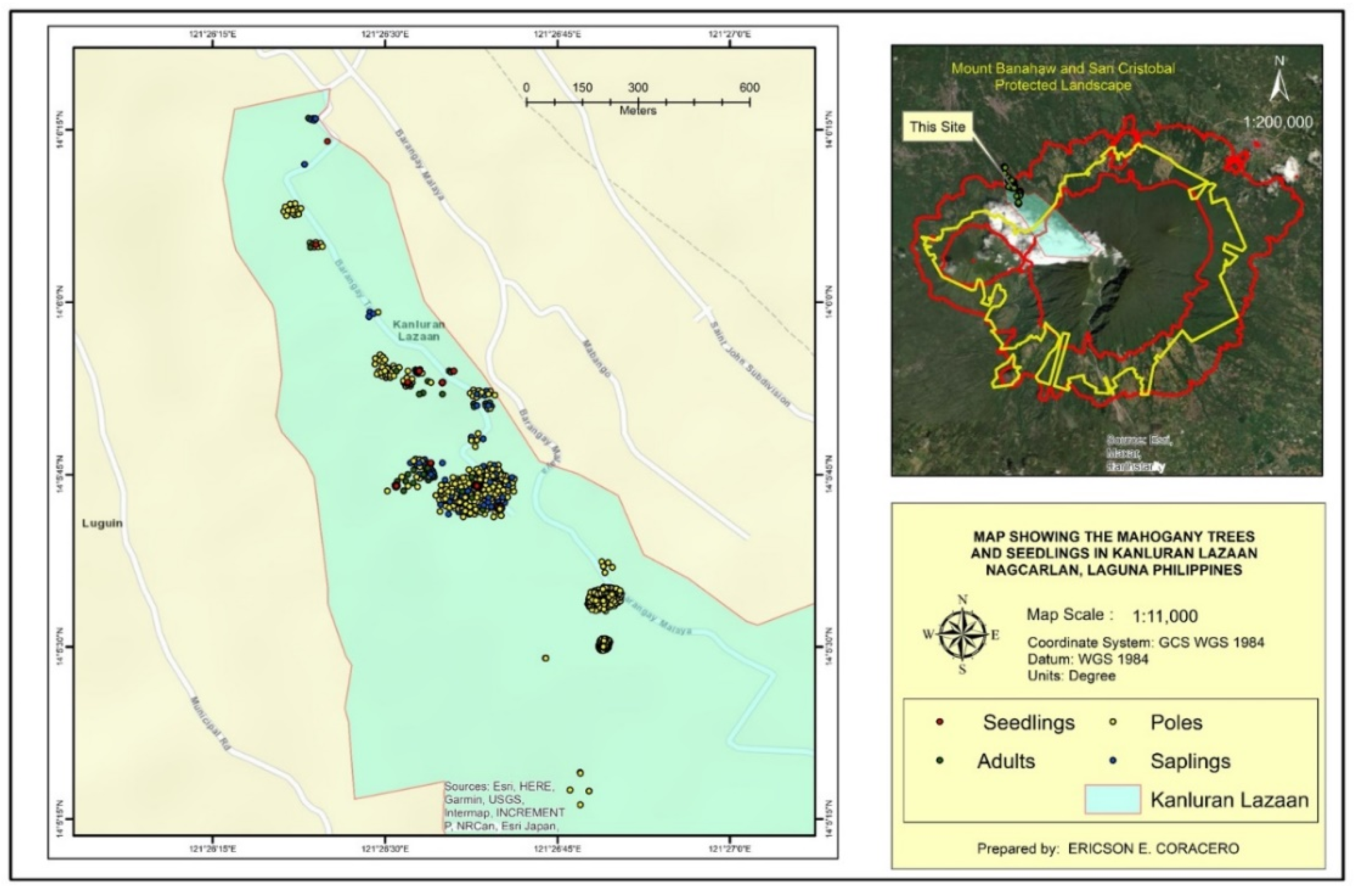
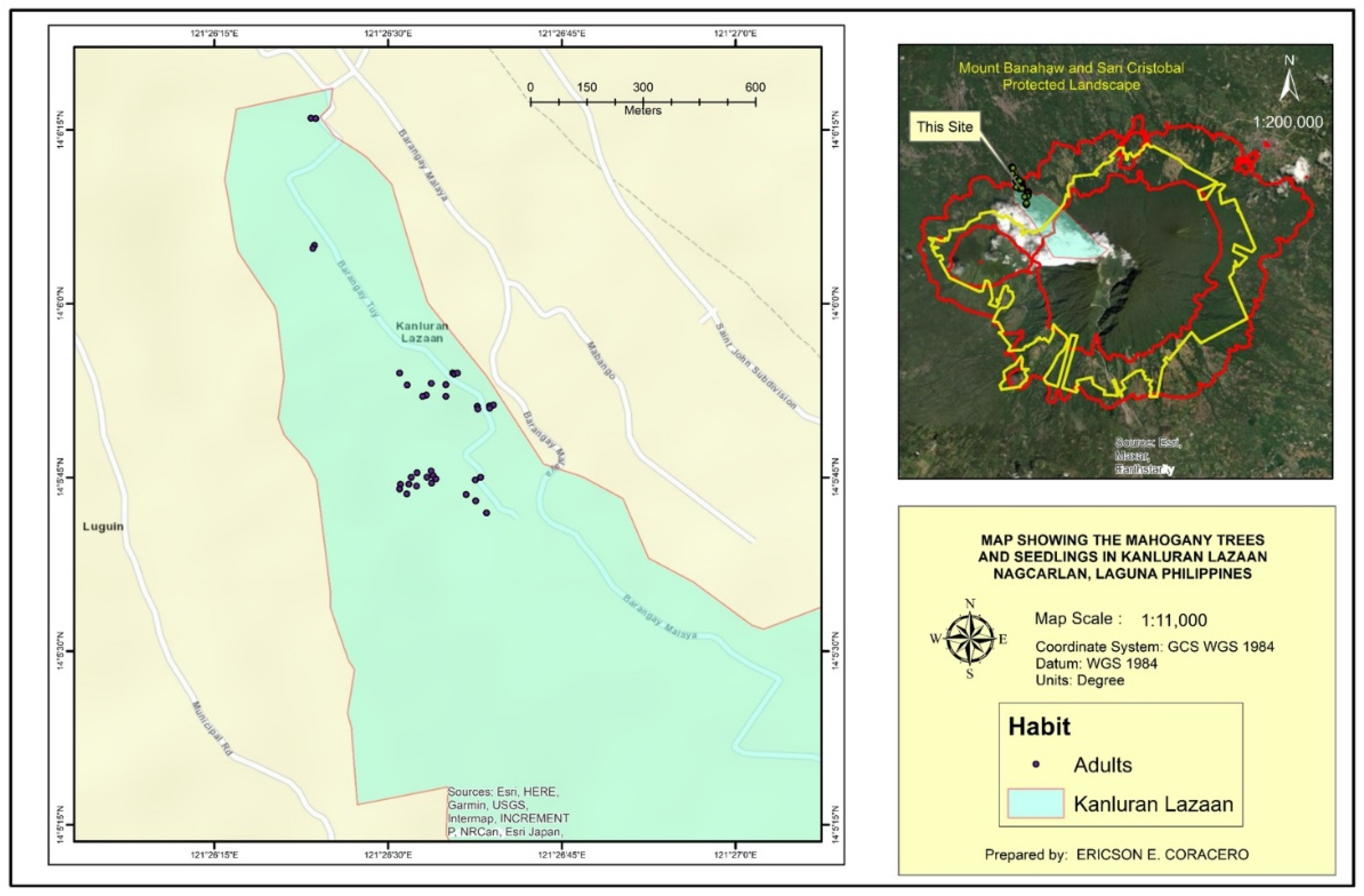
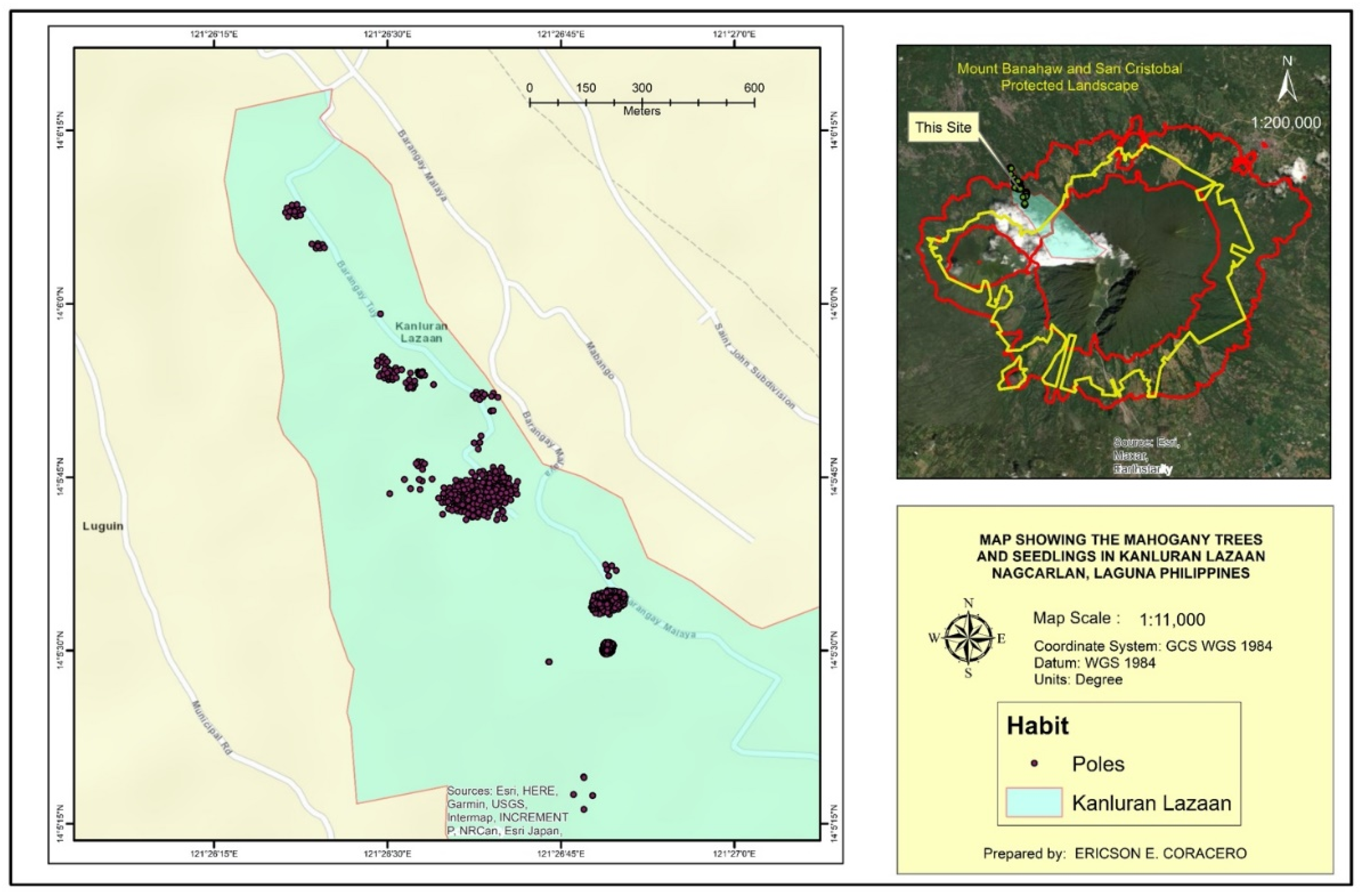
A total of 1591 individuals of Mahogany plants were recorded (
Table 3). Seedlings had the highest individual count with 835 (52.48%) while adults had the least with 40 individuals (2.51%). These individuals were found only in two types of locations, roadside and in mixed land use areas (anthurium and vegetable plantations). Only 25 (1.57%) plants were along the side of the road while 1566 (98.42%) were in the mixed land use areas.
The spatial distribution of the S. macrophylla population in the study site in relation to the protected area is primarily found in the buffer zones of the MBSCPL. Fortunately, no individuals of the species were found thriving beyond the buffer zone towards Mt. Banahaw de Nagcarlan proper. However, this close location of existence of the species still poses threats to the protected area and its native natural resources.
Regarding elevation, the populations were found along elevations of 490 to 570 masl. This elevation range satisfies the current known distribution patterns of big leaf mahogany in terms of elevation as reports says that it can be found in areas with elevation of 0 to 1500 masl aside from its ability to tolerate a very wide range of soils and environmental conditions [
29]. Since
S. macrophylla was introduced under unique conditions, it is impossible to compare its degree of invasiveness across elevations. It should be mentioned that the Mahogany found in the locations with the greatest concentration of people was probably planted on purpose by humans. There may have been a human-driven factor in the higher density of
S. macrophylla in those specific regions. Because of this, comparing the degree of invasiveness based purely on elevation may not give a true reflection of the species' capacity for invasiveness in other habitats or its natural range.
While direct comparisons of the level of invasiveness across different available environmental conditions, what can be deduced is that big leaf mahogany exhibits invasive qualities in the area. This conclusion is backed by the finding that six mother S. macrophylla trees were able to generate at least 627 offspring in a very small area of mixed land use, measuring around 500 square meters, during a period of 25 years. Big leaf mahogany has the capacity to spread and establish itself outside of its original planting places due to its prolific reproduction and quick population increase. This implies that the species has invasive traits and emphasizes the significance of tracking and controlling its spread to avoid ecological effects on indigenous ecosystems.
The distribution map of
S. macrophylla population in Kanluran Lazaan revealed high density especially in one area as seen in
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. This specific area was where the existing pioneer Mahogany trees were located. According to some key informants, big leaf mahogany was introduced in the barangay in 1998 by the Department of Forestry and Natural Resources to be planted along the roadsides. One of the barangay officials during that time planted six individuals in his land around 10 meters away from the road. The individuals planted in the roadsides were already cut while six individuals planted by the barangay official was left. As observed, these six individuals became mother trees and was able to produce 627 Mahogany plants within 25 years of which majority are seedlings (~350 individuals). It was also said that some of the individuals were already transplanted to other locations. This number of individuals may be brought by the fact that a big leaf mahogany fruit can bear around 62 seeds and may be dispersed 20 to 40 m from the mother tree [
7]. Also, according to the key informants, a
S. macrophylla tree can bear fruits even before it reaches 10 years.
3.2. Existing Management Strategies of Invasive Alien Plant Species
The interview for the management of invasive alien plant species were done with the barangay officials of Kanluran Lazaan, head of the Protected Area Management Board (PAMB) of MBSCPL, MENR officer of Nagcarlan, and Sangguniang Bayan (SB) Committee on Natural Resources head and Environmental Protection (CNREP). Unfortunately, only the MENR officer and the SB head of CNREP were implementing strategies to manage invasive alien species.
The head of SB-CNREP mentioned that their strategies in managing invasive alien species include delivering talks about the importance of native plants and the harm of introduced and invasive plants in the ecosystem. Also, they aid in providing seedlings of native plants to those organizations that wish to conduct tree planting activities. The committee also facilitates tree planting activities in Landing Point, an ecotourism site that is within the MBSCPL, wherein native plants are planted.
The MENR officer also had somewhat similar strategies in managing invasive and introduced species. According to the MENR Officer, when she or her staff are invited to deliver talks in environmental events and seminars, they made sure to tackle this topic especially about Mahogany being an allelopathic and a very aggressive plants that can suppress the growth of the native plants. Also, they assist clienteles in requesting seedlings of native trees from the DENR as part of their advocacy to promote native forest and fruit trees rather than introduced and invasive plants.
Based on the strategies implemented by the government, they are on the right track. The involvement of government highlights the significance of local governance in addressing environmental concerns. Their initiatives, including delivering talks and facilitating tree planting activities, showcase a proactive approach to raising awareness and promoting native plant species which is acknowledged as an effective strategy to address not only IAPS but other environmental issues [
30]. However, these strategies alone cannot solve the issue. The municipality may opt to prioritize policy establishment and enforcement as well as monitoring and assessment of the situation of IAPS which are crucial in addressing biological invasions [
31,
32].
Though there were involvement from MENRO and SB-CNREP, it is important to address the absence of involvement from other key stakeholders such as sangguniang barangay and PAMB to maximize the effectiveness of the efforts being exerted to address IAPS which is a benefit of collaborative approaches [
33]. In the case of this study, since the barangay officials did not have any strategies, it may have contributed to the community’s lack of knowledge and desirable perception of IAPS.
5. Conclusions
This study formally confirmed the presence and rapid proliferation of S. macrophylla along the edges of Mt. Banahaw de Nagcarlan in Kanluran Lazaan which highlights its invasive potential. The study found a total of 1591 individuals of S. macrophylla primarily distributed in mixed land use areas and roadside locations, with a concentration in a specific area where mother trees were originally planted. Thus, posing significant threats to the MBSCPL proper calling for an urgent need to implement effective management strategies. While local government units exert efforts to raise awareness and promote native plants, it is crucial to foster a stronger collaboration among key stakeholders to develop and enforce comprehensive management strategies in connection with the presence of IASP. In conclusion, the present study emphasizes the urgent need to address the invasive nature of S. macrophylla in the area. Documenting its population distribution is a crucial step towards informed decision-making and planning of effective management strategies to secure the conservation and protection of the ecosystems in the area holding unique biodiversity resources.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author is sincerely thankful to the participation of the government agencies (PAMB of MBSCPL, Sangguniang Barangay of Kanluran Lazaan, MENRO, and Municipal Government of Nagcarlan, Laguna) in the interview that helped in the completion of the study. Sincere gratitude is also expressed to the author’s family, partner (Jasent Gonzales Abadayan), and students (Divine, Princess Nicole, Christian, Maria Juana, Prince, Darwin, Kenneth, Loi, Cris Jude) for giving full support in the conduct of the study. Finally, the author is thankful to his mentors Dr. RB Gallego, For. Michelle Resueño, For. Mary Jane Aragon-Marigmen, For. Maria Cristina Cañada, For. Afed Daiwey, and Dr. Jay Amon for the guidance.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Richardson, D. M., & Rejmánek, M. Trees and shrubs as invasive alien species–a global review. Diversity and distributions 2011, 17(5), 788-809. [CrossRef]
- Foxcroft LC., Pyšek P, Richardson DM, Genovesi P, MacFadyen S. Plant invasion science in protected areas: progress and priorities. Biological Invasions 2017; 19: 1353-1378. [CrossRef]
- Mavimbela LZ, Sieben EJ, & Procheş Ş. Invasive alien plant species, fragmentation and scale effects on urban forest community composition in Durban, South Africa. New Zealand Journal of Forestry Science 2018; 48: 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Crowl TA, Crist TO, Parmenter RR, Belovsky G, Lugo AE. The spread of invasive species and infectious disease as drivers of ecosystem change. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 2008; 6(5): 238-246. [CrossRef]
- Booy O, Cornwell L, Parrott D, Sutton-Croft M, Williams F. Impact of biological invasions on infrastructure. In: Vilà M, Hulme P, editors. Impact of biological invasions on ecosystem services. Cham: Springer; 2017. p. 235-247. [CrossRef]
- Potgieter LJ, Gaertner M, O'Farrell PJ, Richardson DM. Perceptions of impact: invasive alien plants in the urban environment. Journal of environmental management 2019; 229: 76-87. [CrossRef]
- Baguinon NT, Quimado MO, Francisco GJ. Country report on forest invasive species in the Philippines. Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Forest Invasive Conference; 17-23 Aug 2003; Kunming: China; 2005.
- Mukaromah AS, Purwestri YA, Fujii Y.Determination of allelopathic potential in Mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) leaf litter using sandwich method. Indonesian Journal of Biotechnology 2016; 21(2): 93-101. [CrossRef]
- Lee YK, Lee DK, Woo SY, Abraham ERG, Carandang WM, Yeo US, Park C. Differences of tree species composition and microclimate between a mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) plantation and a secondary forest in Mt. Makiling, Philippines. Forest Science and Technology, 2006; 2(1): 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R. C. (2006). Invasive alien species (IAS): concerns and status in the Philippines. Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Development of Database (APASD) for Biological Invasion; 18-22 Sep 2006; FFTC, Taichung, Taiwan: China; 2006.
- Han A, Sohng J, Barile JR, Lee Y, Woo S, Lee D, Park P. Comparison of soil seed banks in canopy gap and closed canopy areas between a secondary natural forest and a big leaf mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) plantation in the Mt. Makiling Forest Reserve, the Philippines. Journal of Environmental Science and Management 2012; 15(Special Issue 1): 47-59.
- Valle PBS. Comparison of species composition, species diversity, and structural distribution of urban trees in three types of urban greenspaces. Ecosystems and Development Journal 2018; 8(2): 28-40.
- Jose RP, Aspe NM, Aureo WA, Parba RY, Capunhag CD, Narido CI. Earthworm diversity and populations in different habitats of Rajah Sikatuna Protected Landscape, Bohol, Philippines. Philippine Journal of Systematic Biology 2021; 15(1): 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Gascon CN, Garcia RC, Beltran FN, Faller WC, Agudilla MAR. Biodiversity assessment of Mt. Banahaw de Dolores. Asian Journal of Biodiversity 2013; 4(1): 23-45.
- Gestiada EC, Gestiada AS, Castillo ML, Bantayan NC, Balatibat JB. Tree Vegetation Diversity, Distribution and Structure across the Elevation Gradients and Habitat Types of Mt. Banahaw de Majayjay, Philippines. Ecosystems and Development Journal 2016; 6(1): 15-26.
- Santiago JO, Buot IE. Conservation Status of Selected Plants of Mount Banahaw-San Cristobal Protected Landscape, Quezon Province, Philippines. IAMURE International Journal of Ecology and Conservation 2015; 16: 64-79. [CrossRef]
- Engay-Gutierrez K, Dimailig E, Yacon J. Plus and Mother Trees in Mt. Banahaw de Lucban, Quezon, Philippines. Journal of Environmental Science and Management 2022; 25(2): 35-50.
- Ureta JCP, Abueg LC, Inocencio AB. Towards Establishment of a Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) in Protected Areas: The Case of Mounts Banahaw and San Cristobal in Quezon Province, Philippines. DLSU Business & Economics Review 2021; 31(1): 1-15.
- Foundation for the Philippine Environment. Mt. Banahaw-San Cristobal Protected Landscape, Laguna/Quezon [Internet]. 2023 [cited 23 May 2023]. Available from: https://fpe.ph/conservation_site/location_details/mt.-banahaw-san-cristobal-protected-landscape-lagunaquezon.
- Barcelona JF, Pelser PB, Cajano MO. Rafflesia banahaw (Rafflesiaceae), a new species from Luzon, Philippines. Blumea-Biodiversity, Evolution and Biogeography of Plants 2007; 52(2): 345-350. [CrossRef]
- Rollins LA, Woolnough AP, Wilton AN, Sinclair R, Sherwin WB. Invasive species can't cover their tracks: using microsatellites to assist management of starling (Sturnus vulgaris) populations in Western Australia. Molecular Ecology 2009; 18(8): 1560-1573. [CrossRef]
- Büyüktahtakın İE, Kıbış EY, Cobuloglu HI, Houseman GR, Lampe JT. An age-structured bio-economic model of invasive species management: insights and strategies for optimal control. Biological invasions 2015; 17(9): 2545-2563. [CrossRef]
- Banaticla MCN, Buot IE. Altitudinal zonation of pteridophytes on Mt. Banahaw de lucban, luzon Island, Philippines. Plant Ecology 2005; 180: 135-151. [CrossRef]
- World Weather Online. Nagcarlan Annual Weather Averages [Internet]. 2023 [cited 15 Mar 2023]. Available from: https://www.worldweatheronline.com/nagcarlan-weather-averages/laguna/ph.aspx.
- Bihu R. Using unstructured interviews in educational and social science research: The process, opportunity and difficulty. GSJ 2020; 8(10): 1-10.
- Norghauer JM, Malcolm JR, Zimmerman BL. Juvenile mortality and attacks by a specialist herbivore increase with conspecific adult basal area of Amazonian Swietenia macrophylla (Meliaceae). Journal of Tropical Ecology 2006; 22(4): 451-460. [CrossRef]
- Itoh A, Yamakura T, Ogino K, Seng Lee H, Ashton PS. Spatial distribution patterns of two predominant emergent trees in a tropical rainforest in Sarawak, Malaysia. Plant Ecology 1997; 132: 121-136. [CrossRef]
- Hermann MG. Content Analysis. In: Klotz A, Prakash D, editors. Qualitative Methods in International Relations. London: Springer; 2008 p. 151-167.
- Krisnawati H, Kallio MH, Kanninen M.Swietenia macrophylla King: ecology, silviculture and productivity. Indonesia: CIFOR; 2011. [CrossRef]
- Yen MD. Status and Management of Invasive Alien Species (IAS) in Vietnam. In: Pullaiah T, Ielmini MR, editors. Invasive Alien Species: Observations and Issues from Around the World. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2021. p. 226-243.
- Genovesi P, Monaco A. Guidelines for addressing invasive species in protected areas. In: Foxcroft L, Pyšek P, Richardson D, Genovesi P, editors. Plant invasions in protected areas: patterns, problems and challenges. London: Springer; 2013. p. 487-506.
- Reaser JK, Burgiel SW, Kirkey J, Brantley KA, Veatch SD., Burgos-Rodríguez J. The early detection of and rapid response (EDRR) to invasive species: a conceptual framework and federal capacities assessment. Biological Invasions 2020; 22: 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Graham S, Metcalf AL, Gill N, Niemiec R, Moreno C, Bach T, Ikutegbe V, Hallstrom L, Ma Z, Lubeck A. Opportunities for better use of collective action theory in research and governance for invasive species management. Conservation Biology 2019; 33(2): 275-287. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).