Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Agiogenesis affects the lung cancer pattern through several mechanisms
3. The epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, their receptors and the downstream
4. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
5. Colony stimulating factors (CSF)
6. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)
7. Fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 (FGF1 and FGF2)
8. Interleukins (IL)
9. Others Growth Factors
10. Conclusion and perspectives
Author’s contribution
Data availability statement
Acknowledgements
Conflict of interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | Protein Kinase B |
| AREG | amphiregulin |
| bFGF | basic Fibroblast Growth Factor |
| BMP | Bone Morphogenetic Protein |
| BTC | beta-cellulin |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CSF | Colony Stimulating Factor |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EPCs | bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells |
| EPGN | Epigene protein |
| EREG | Epiregulin |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FGF (1 and 2) | Fibroblast Growth Factor (1 and 2) |
| FGFR (1 and 2) | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (1 and 2) |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| GLOBOCAN | Global Cancer Observatory |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| HB-EGF | Heparin-Binding EGF-like Growth Factor |
| HER (2 and 3) | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (2 and 3) |
| HGF | Hepatocyte Growth Factor |
| HIF | Hypoxia-Inducible Factors |
| IL | Interleukin |
| MAPK | Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase |
| M-CSF | Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PI3k | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIGF | Phosphatidylinositol-glycan F or Placental Growth Factor |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| SCLC | Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| sNRP1 | Soluble Neuropilin 1 |
| sTie 2 | Soluble Angiopoietin receptor |
| TGF-alpha | Transforming growth factor alpha |
| TGF-beta | Transforming Growth Factor-beta |
| Tie 2 | Angiopoietin receptor |
| TKI | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VEGFR | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor |
References
- Adair TH, Montani JP. Overview of Angiogenesis. In: Angiogenesis. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences; 2010 [cited 2023 May 25]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53238/.
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. 2021 Aug 15 [cited 2023 Jan 10];149(4):778–89. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijc.33588. [CrossRef]
- Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T, Kojiro M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vascular Health and Risk Management. 2006 Aug [cited 2023 May 25];2(3):213–9. Available from: http://www.atypon-link.com/DMP/doi/abs/10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.213.
- Rajabi M, Mousa S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Cancer Treatment. Biomedicines. 2017 Jun 21 [cited 2023 May 25];5(4):34. Available from: http://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/5/2/34. [CrossRef]
- Krishna. Estimation of tumor microvessel density by MRI using a blood pool contrast agent. Int J Oncol. 2009 Sep 1 [cited 2023 Jan 15];35(4). Available from: http://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijo/35/4/797. [CrossRef]
- Folkman J. Tumor Angiogenesis. In: Advances in Cancer Research. Elsevier; 1985 [cited 2023 Jan 15]. p. 175–203. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0065230X0860946X.
- Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T, Kojiro M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vascular Health and Risk Management. 2006 Aug [cited 2023 Jan 15];2(3):213–9. Available from: http://www.atypon-link.com/DMP/doi/abs/10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.213.
- Gupta MK. Mechanism and its regulation of tumor-induced angiogenesis. WJG. 2003 [cited 2023 Jan 15];9(6):1144. Available from: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1144.htm. [CrossRef]
- Shoari A, Khodabakhsh F, Ahangari Cohan R, Salimian M, Karami E. Anti-angiogenic peptides application in cancer therapy; a review. Res Pharma Sci. 2021 [cited 2023 Jan 15];16(6):559. Available from: http://www.rpsjournal.net/text.asp?2021/16/6/559/327503. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee A, Madamsetty VS, Paul MK, Mukherjee S. Recent Advancements of Nanomedicine towards Antiangiogenic Therapy in Cancer. IJMS. 2020 Jan 10 [cited 2023 Jan 15];21(2):455. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/2/455. [CrossRef]
- Irvin MW, Zijlstra A, Wikswo JP, Pozzi A. Techniques and assays for the study of angiogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Nov [cited 2023 Jan 15];239(11):1476–88. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1535370214529386. [CrossRef]
- Roudsari LC, West JL. Studying the influence of angiogenesis in in vitro cancer model systems. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2016 Feb [cited 2023 Jan 15];97:250–9. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0169409X15002604. [CrossRef]
- Ucuzian AA, Gassman AA, East AT, Greisler HP. Molecular Mediators of Angiogenesis. Journal of Burn Care & Research. 2010 Jan [cited 2023 May 25];31(1):158–75. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jbcr/article/31/1/158-175/4602136. [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. 2011 May [cited 2023 May 25];473(7347):298–307. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nature10144. [CrossRef]
- Saman H, Raza SS, Uddin S, Rasul K. Inducing Angiogenesis, a Key Step in Cancer Vascularization, and Treatment Approaches. Cancers. 2020 May 6 [cited 2022 Nov 14];12(5):1172. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/5/1172. [CrossRef]
- Lugano R, Ramachandran M, Dimberg A. Tumor angiogenesis: causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 May [cited 2023 May 26];77(9):1745–70. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00018-019-03351-7. [CrossRef]
- Horn L, Sandler AB. Angiogenesis in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society. 2009 Apr 15 [cited 2023 May 26];6(2):206–17. Available from: http://pats.atsjournals.org/cgi/doi/10.1513/pats.200807-066LC. [CrossRef]
- Niu G, Chen X. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor as an Anti-Angiogenic Target for Cancer Therapy. CDT. 2010 Aug 1 [cited 2023 May 26];11(8):1000–17. Available from: http://www.eurekaselect.com/openurl/content.php?genre=article&issn=1389-4501&volume=11&issue=8&spage=1000. [CrossRef]
- Raica M, Cimpean AM. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)/PDGF Receptors (PDGFR) Axis as Target for Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2010 Mar 11 [cited 2023 May 26];3(3):572–99. Available from: http://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/3/3/572. [CrossRef]
- Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Seminars in Oncology. 2002 Dec [cited 2023 May 26];29(6Q):15–8. Available from: http://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/scripts/om.dll/serve?action=searchDB&searchDBfor=art&artType=abs&id=asonc02906q0015.
- Bielenberg DR, Zetter BR. The Contribution of Angiogenesis to the Process of Metastasis. The Cancer Journal. 2015 Jul [cited 2023 May 26];21(4):267–73. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/00130404-201507000-00007. [CrossRef]
- Jun JC, Rathore A, Younas H, Gilkes D, Polotsky VY. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Cancer. Curr Sleep Medicine Rep. 2017 Mar [cited 2023 May 26];3(1):1–10. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40675-017-0062-7. [CrossRef]
- Lv X, Li J, Zhang C, Hu T, Li S, He S, et al. The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in tumor angiogenesis and cell metabolism. Genes & Diseases. 2017 Mar [cited 2023 May 26];4(1):19–24. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352304216300721. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Cazares D, Chavez-Dominguez R, Carlos-Reyes A, Lopez-Camarillo C, Hernadez De La Cruz ON, Lopez-Gonzalez JS. Contribution of Angiogenesis to Inflammation and Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 12 [cited 2023 May 26];9:1399. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fonc.2019.01399/full. [CrossRef]
- Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Zhang S, Gong Z, et al. The role of microenvironment in tumor angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec [cited 2023 May 26];39(1):204. Available from: https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-020-01709-5. [CrossRef]
- Ribatti D, Crivellato E. Immune cells and angiogenesis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2009 Sep [cited 2023 May 26];13(9a):2822–33. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00810.x. [CrossRef]
- Pekarek L, Torres-Carranza D, Fraile-Martinez O, García-Montero C, Pekarek T, Saez MA, et al. An Overview of the Role of MicroRNAs on Carcinogenesis: A Focus on Cell Cycle, Angiogenesis and Metastasis. IJMS. 2023 Apr 14 [cited 2023 May 26];24(8):7268. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/8/7268. [CrossRef]
- Aspriţoiu VM, Stoica I, Bleotu C, Diaconu CC. Epigenetic Regulation of Angiogenesis in Development and Tumors Progression: Potential Implications for Cancer Treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 6 [cited 2023 May 26];9:689962. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2021.689962/full. [CrossRef]
- Annese T, Tamma R, De Giorgis M, Ribatti D. microRNAs Biogenesis, Functions and Role in Tumor Angiogenesis. Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 27 [cited 2023 May 26];10:581007. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2020.581007/full. [CrossRef]
- Song Y, Fu Y, Xie Q, Zhu B, Wang J, Zhang B. Anti-angiogenic Agents in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Strategy for Cancer Treatment. Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 25 [cited 2023 May 26];11:1956. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01956/full. [CrossRef]
- Lee WS, Yang H, Chon HJ, Kim C. Combination of anti-angiogenic therapy and immune checkpoint blockade normalizes vascular-immune crosstalk to potentiate cancer immunity. Exp Mol Med. 2020 Sep [cited 2023 May 26];52(9):1475–85. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s12276-020-00500-y. [CrossRef]
- Fang L, Zhao W, Ye B, Chen D. Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Brain Metastases From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021 May 4 [cited 2023 May 26];11:670313. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.670313/full. [CrossRef]
- Wieduwilt MJ, Moasser MM. The epidermal growth factor receptor family: Biology driving targeted therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 May [cited 2023 May 26];65(10):1566–84. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00018-008-7440-8. [CrossRef]
- Schneider MR, Wolf E. The epidermal growth factor receptor ligands at a glance. J Cell Physiol. 2009 Mar [cited 2023 May 26];218(3):460–6. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jcp.21635. [CrossRef]
- Stoll SW, Rittié L, Johnson JL, Elder JT. Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Human Keratinocytes. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2012 Sep [cited 2023 May 26];132(9):2148–57. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022202X15358863. [CrossRef]
- Liu TC, Jin X, Wang Y, Wang K. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in lung cancer and targeted therapies. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7(2):187–202.
- Sasaki T, Hiroki K, Yamashita Y. The Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Cancer Metastasis and Microenvironment. BioMed Research International. 2013 [cited 2022 Nov 3];2013:1–8. Available from: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/546318/. [CrossRef]
- Spano JP, Fagard R, Soria JC, Rixe O, Khayat D, Milano G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: preclinical data and therapeutic perspectives. Annals of Oncology. 2005 Feb [cited 2023 May 26];16(2):189–94. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0923753419484147. [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone A, Bova V, Casili G, Repici A, Lanza M, Giuffrida R, et al. Role of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in Cancer: Biological Activity, Targeted Therapies, and Prognostic Value. Cells. 2023 Mar 24 [cited 2023 May 26];12(7):1002. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/12/7/1002. [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhsh F, Merikhian P, Eisavand MR, Farahmand L. Crosstalk between MUC1 and VEGF in angiogenesis and metastasis: a review highlighting roles of the MUC1 with an emphasis on metastatic and angiogenic signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec [cited 2023 May 26];21(1):200. Available from: https://cancerci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12935-021-01899-8. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Yao L, Yang J, Wang Z, Du G. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol Med Report. 2018 Aug 9 [cited 2023 May 26]; Available from: http://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/mmr.2018.9375. [CrossRef]
- Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C. PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene. 2003 Dec 8 [cited 2022 Nov 10];22(56):8983–98. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/1207115. [CrossRef]
- Xu Y, Yuan FE, Chen QX, Liu BH. Molecular mechanisms involved in angiogenesis and potential target of antiangiogenesis in human glioblastomas. Glioma. 2018 [cited 2023 Aug 24];1(2):35. Available from: http://www.jglioma.com/text.asp?2018/1/2/35/231495. [CrossRef]
- Nan X, Xie C, Yu X, Liu J. EGFR TKI as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 26 [cited 2023 May 26];8(43):75712–26. Available from: https://www.oncotarget.com/lookup/doi/10.18632/oncotarget.20095. [CrossRef]
- Ansari MJ, Bokov D, Markov A, Jalil AT, Shalaby MN, Suksatan W, et al. Cancer combination therapies by angiogenesis inhibitors; a comprehensive review. Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Dec [cited 2023 May 26];20(1):49. Available from: https://biosignaling.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12964-022-00838-y. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Gao L, Callies S, Zimmermann A, Walgren R, et al. RELAY, ramucirumab plus erlotinib versus placebo plus erlotinib in untreated EGFR-mutated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: exposure–response relationship. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022 Aug [cited 2023 May 26];90(2):137–48. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00280-022-04447-x. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M, Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2019 Dec [cited 2023 May 26];20(12):1655–69. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1470204519306345.
- Mehta VB, Besner GE, Mehta VB, Besner GE. HB-EGF promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells via PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Growth Factors. 2007 Jan [cited 2023 May 26];25(4):253–63. Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08977190701773070. [CrossRef]
- Rosell R, Dafni U, Felip E, Curioni-Fontecedro A, Gautschi O, Peters S, et al. Erlotinib and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and activating EGFR mutations (BELIEF): an international, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2017 May [cited 2023 May 26];5(5):435–44. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213260017301297.
- Wang X, Goldstein D, Crowe PJ, Yang JL. Next-generation EGFR/HER tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: a review of the evidence. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:5461–73. [CrossRef]
- Meng Y, Bai R, Cui J. Precision targeted therapy for EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC : Dilemmas and coping strategies. Thoracic Cancer [Internet]. 2023 May [cited 2023 May 26];14(13):1121–34. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1759-7714.14858. [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Home | Beta ClinicalTrials.gov. [cited 2023 Jun 7]. Available from: https://beta.clinicaltrials.gov/.
- European Medicines Agency. Clinical Trials Register. [cited 2023 Jun 7]. Available from: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search.
- Holmes DIR, Zachary I. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: angiogenic factors in health and disease. Genome Biol. 2005;6(2):209. [CrossRef]
- Ye X, Gaucher JF, Vidal M, Broussy S. A Structural Overview of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Pharmacological Ligands: From Macromolecules to Designed Peptidomimetics. Molecules. 2021 Nov 9;26(22):6759. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis: A Crucial Target for Anti- and Pro-Angiogenic Therapies. Genes & Cancer. 2011 Dec 1 [cited 2023 May 31];2(12):1097–105. Available from: http://gan.sagepub.com/lookup/doi/10.1177/1947601911423031. [CrossRef]
- Cébe-Suarez S, Zehnder-Fjällman A, Ballmer-Hofer K. The role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis; complex partnerships. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Mar [cited 2023 May 31];63(5):601. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00018-005-5426-3. [CrossRef]
- Duffy AM, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Harmey JH. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Role in Non-Endothelial Cells: Autocrine Signalling by VEGF. In: Madame Curie Bioscience Database. Landes Bioscience; 2013 [cited 2023 May 31]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6482/.
- Evensen L, Micklem DR, Blois A, Berge SV, Aarsæther N, Littlewood-Evans A, et al. Mural Cell Associated VEGF Is Required for Organotypic Vessel Formation. Cao Y, editor. PLoS ONE. 2009 Jun 4 [cited 2023 May 31];4(6):e5798. Available from: https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005798. [CrossRef]
- Stratman AN, Malotte KM, Mahan RD, Davis MJ, Davis GE. Pericyte recruitment during vasculogenic tube assembly stimulates endothelial basement membrane matrix formation. Blood. 2009 Dec 3 [cited 2023 May 31];114(24):5091–101. Available from: https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/114/24/5091/26627/Pericyte-recruitment-during-vasculogenic-tube. [CrossRef]
- Lind JSW, Smit EF. Angiogenesis inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2009 Sep;1(2):95–107. [CrossRef]
- Horn L, Dahlberg SE, Sandler AB, Dowlati A, Moore DF, Murren JR, et al. Phase II Study of Cisplatin Plus Etoposide and Bevacizumab for Previously Untreated, Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501. JCO. 2009 Dec 10 [cited 2023 May 31];27(35):6006–11. Available from: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7545. [CrossRef]
- Cetean S, Căinap C, Constantin AM, Căinap S, Gherman A, Oprean L, et al. The importance of the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in oncology. Medicine and Pharmacy Reports. 2015 Sep 20 [cited 2023 May 27];88(4):468–72. Available from: https://www.medpharmareports.com/index.php/mpr/article/view/531. [CrossRef]
- Ray A. Cytokines and their Role in Health and Disease: A Brief Overview. MOJI. 2016 Oct 19 [cited 2023 May 27];4(2). Available from: https://medcraveonline.com/MOJI/cytokines-and-their-role-in-health-and-disease-a-brief-overview.html. [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood AJ, Achuthan A, Hamilton JA. Colony Stimulating Factors (CSFs). In: Encyclopedia of Immunobiology. Elsevier; 2016 [cited 2023 May 27]. p. 586–96. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780123742797100153. [CrossRef]
- George AL, Bangalore-Prakash P, Rajoria S, Suriano R, Shanmugam A, Mittelman A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell biology in disease and tissue regeneration. J Hematol Oncol. 2011 Dec [cited 2023 May 27];4(1):24. Available from: https://jhoonline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1756-8722-4-24. [CrossRef]
- Gao D, Nolan D, McDonnell K, Vahdat L, Benezra R, Altorki N, et al. Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells contribute to the angiogenic switch in tumor growth and metastatic progression. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 2009 Aug [cited 2023 May 27];1796(1):33–40. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304419X09000286. [CrossRef]
- Aapro M, Crawford J, Kamioner D. Prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia with granulocyte colony-stimulating factors: where are we now? Support Care Cancer. 2010 May [cited 2023 Jun 6];18(5):529–41. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00520-010-0816-y. [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis I, Salataj E, Said Abu Egal E, Beswick EJ. G-CSF in tumors: Aggressiveness, tumor microenvironment and immune cell regulation. Cytokine. 2021 Jun [cited 2023 May 27];142:155479. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1043466621000594. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Fang C, Chen R, Yuan S, Chen L, Qiu X, et al. rhG-CSF is associated with an increased risk of metastasis in NSCLC patients following postoperative chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec [cited 2023 May 27];22(1):741. Available from: https://bmccancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12885-022-09850-4. [CrossRef]
- Kowanetz M, Wu X, Lee J, Tan M, Hagenbeek T, Qu X, et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor promotes lung metastasis through mobilization of Ly6G+Ly6C+ granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010 Dec 14 [cited 2023 May 27];107(50):21248–55. Available from: https://pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.1015855107. [CrossRef]
- Terceiro LEL, Edechi CA, Ikeogu NM, Nickel BE, Hombach-Klonisch S, Sharif T, et al. The Breast Tumor Microenvironment: A Key Player in Metastatic Spread. Cancers. 2021 Sep 25 [cited 2023 May 27];13(19):4798. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/19/4798. [CrossRef]
- Dentelli P, Rosso A, Olgasi C, Camussi G, Brizzi MF. IL-3 is a novel target to interfere with tumor vasculature. Oncogene. 2011 Dec 15 [cited 2023 May 27];30(50):4930–40. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/onc2011204. [CrossRef]
- Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M, Peabody M, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes & Diseases. 2014 Sep [cited 2023 May 28];1(1):87–105. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352304214000105. [CrossRef]
- Dyer LA, Pi X, Patterson C. The role of BMPs in endothelial cell function and dysfunction. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2014 Sep [cited 2023 May 28];25(9):472–80. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S104327601400085X. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki Y, Montagne K, Nishihara A, Watabe T, Miyazono K. BMPs Promote Proliferation and Migration of Endothelial Cells via Stimulation of VEGF-A/VEGFR2 and Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 Signalling. Journal of Biochemistry. 2008 Feb 1 [cited 2023 May 28];143(2):199–206. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jb/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/jb/mvm215. [CrossRef]
- Chen WC, Chung CH, Lu YC, Wu MH, Chou PH, Yen JY, et al. BMP-2 induces angiogenesis by provoking integrin α6 expression in human endothelial progenitor cells. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2018 Apr [cited 2023 May 28];150:256–66. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006295218300789. [CrossRef]
- Carreira AC, Lojudice FH, Halcsik E, Navarro RD, Sogayar MC, Granjeiro JM. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Facts, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. J Dent Res. 2014 Apr [cited 2023 May 28];93(4):335–45. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0022034513518561. [CrossRef]
- Scharpfenecker M, Van Dinther M, Liu Z, Van Bezooijen RL, Zhao Q, Pukac L, et al. BMP-9 signals via ALK1 and inhibits bFGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis. Journal of Cell Science. 2007 Mar 15 [cited 2023 May 28];120(6):964–72. Available from: https://journals.biologists.com/jcs/article/120/6/964/29968/BMP-9-signals-via-ALK1-and-inhibits-bFGF-induced. [CrossRef]
- Meng W, Xiao H, Zhao R, Li D, Li K, Meng Y, et al. The Prognostic Value of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Their Receptors in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 22 [cited 2023 May 28];11:608239. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.608239/full. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, Pang H, Xin B, Duan L, Liu L, Zhang H. Biological effects of BMP7 on small-cell lung cancer cells and its bone metastasis. Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul 4 [cited 2023 May 28]; Available from: http://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ijo.2018.4469. [CrossRef]
- Ehata S, Miyazono K. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling in Cancer; Some Topics in the Recent 10 Years. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 25 [cited 2023 May 28];10:883523. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2022.883523/full. [CrossRef]
- Katagiri T, Watabe T. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Jun [cited 2023 May 28];8(6):a021899. Available from: http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/cshperspect.a021899. [CrossRef]
- Farooq M, Khan AW, Kim MS, Choi S. The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Signaling in Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Cells. 2021 Nov 19 [cited 2023 May 28];10(11):3242. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/10/11/3242. [CrossRef]
- Ornitz DM, Itoh N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. WIREs Developmental Biology. 2015 May [cited 2023 May 28];4(3):215–66. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/wdev.176. [CrossRef]
- Korc M, Friesel R. The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factors in Tumor Growth. CCDT. 2009 Aug 1 [cited 2022 Nov 16];9(5):639–51. Available from: http://www.eurekaselect.com/openurl/content.php?genre=article&issn=1568-0096&volume=9&issue=5&spage=639. [CrossRef]
- Pardo OE, Wellbrock C, Khanzada UK, Aubert M, Arozarena I, Davidson S, et al. FGF-2 protects small cell lung cancer cells from apoptosis through a complex involving PKCɛ, B-Raf and S6K2. EMBO J. 2006 Jul 12 [cited 2023 May 28];25(13):3078–88. Available from: http://emboj.embopress.org/cgi/doi/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601198. [CrossRef]
- Behrens C, Lin HY, Lee JJ, Raso MG, Hong WK, Wistuba II, et al. Immunohistochemical Expression of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor and Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in the Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2008 Oct 1 [cited 2023 May 28];14(19):6014–22. Available from: https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/14/19/6014/73027/Immunohistochemical-Expression-of-Basic-Fibroblast.
- Haibe Y, Kreidieh M, El Hajj H, Khalifeh I, Mukherji D, Temraz S, et al. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-angiogenic Therapies in Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 27 [cited 2023 May 28];10:221. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fonc.2020.00221/full. [CrossRef]
- Zahra FT, Sajib MdS, Mikelis CM. Role of bFGF in Acquired Resistance upon Anti-VEGF Therapy in Cancer. Cancers. 2021 Mar 20 [cited 2023 May 28];13(6):1422. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/6/1422. [CrossRef]
- Terai H, Soejima K, Yasuda H, Nakayama S, Hamamoto J, Arai D, et al. Activation of the FGF2-FGFR1 Autocrine Pathway: A Novel Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Gefitinib in NSCLC. Molecular Cancer Research. 2013 Jul 1 [cited 2023 May 28];11(7):759–67. Available from: https://aacrjournals.org/mcr/article/11/7/759/89344/Activation-of-the-FGF2-FGFR1-Autocrine-Pathway-A.
- Gacche RN. Compensatory angiogenesis and tumor refractoriness. Oncogenesis. 2015 Jun 1 [cited 2023 Jun 7];4(6):e153–e153. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/oncsis201514. [CrossRef]
- Chae, Young Kwang, Pai, Sachin G., Sun, Peng, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) as a therapeutic target in lung and head and neck cancer. Am J Hematol Oncol. 2016;12(3):13–9. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sachin-Pai/publication/301290574_Fibroblast_Growth_Factor_Receptor_FGFR_as_a_Therapeutic_Target_in_Lung_and_Head_and_Neck_Cancer/links/570fbb7908ae170055bdea7f/Fibroblast-Growth-Factor-Receptor-FGFR-as-a-Therapeutic-Target-in-Lung-and-Head-and-Neck-Cancer.pdf.
- Zheng J, Zhang W, Li L, He Y, Wei Y, Dang Y, et al. Signaling Pathway and Small-Molecule Drug Discovery of FGFR: A Comprehensive Review. Front Chem. 2022 Apr 14 [cited 2023 May 28];10:860985. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2022.860985/full. [CrossRef]
- Kubick N, Klimovich P, Flournoy PH, Bieńkowska I, Łazarczyk M, Sacharczuk M, et al. Interleukins and Interleukin Receptors Evolutionary History and Origin in Relation to CD4+ T Cell Evolution. Genes. 2021 May 26 [cited 2023 May 29];12(6):813. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/12/6/813. [CrossRef]
- L. Ferreira V, H.L. Borba H, De F. Bonetti A, P. Leonart L, Pontarolo R. Cytokines and Interferons: Types and Functions. In: Ali Khan W, editor. Autoantibodies and Cytokines. IntechOpen; 2019 [cited 2023 May 29]. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/autoantibodies-and-cytokines/cytokines-and-interferons-types-and-functions. [CrossRef]
- Chen JJW, Yao PL, Yuan A, Hong TM, Shun CT, Kuo ML, et al. Up-regulation of tumor interleukin-8 expression by infiltrating macrophages: its correlation with tumor angiogenesis and patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Feb;9(2):729–37.
- Pan B, Shen J, Cao J, Zhou Y, Shang L, Jin S, et al. Author Correction: Interleukin-17 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells via the STAT3/GIV signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2020 May 27 [cited 2023 May 29];10(1):8808. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-65650-5. [CrossRef]
- Huang Q, Duan L, Qian X, Fan J, Lv Z, Zhang X, et al. IL-17 Promotes Angiogenic Factors IL-6, IL-8, and Vegf Production via Stat1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 7 [cited 2023 May 29];6(1):36551. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep36551. [CrossRef]
- Leung JH, Ng B, Lim WW. Interleukin-11: A Potential Biomarker and Molecular Therapeutic Target in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells. 2022 Jul 21 [cited 2023 May 29];11(14):2257. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/14/2257. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Veeramachaneni N. Targeting interleukin-1β and inflammation in lung cancer. Biomark Res. 2022 Dec [cited 2023 May 29];10(1):5. Available from: https://biomarkerres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40364-021-00341-5. [CrossRef]
- Song L, Smith MA, Doshi P, Sasser K, Fulp W, Altiok S, et al. Antitumor Efficacy of the Anti-Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Antibody Siltuximab in Mouse Xenograft Models of Lung Cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 2014 Jul [cited 2023 Jun 7];9(7):974–82. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1556086415303312. [CrossRef]
- Ray K, Ujvari B, Ramana V, Donald J. Cross-talk between EGFR and IL-6 drives oncogenic signaling and offers therapeutic opportunities in cancer. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 2018 Jun [cited 2023 Aug 24];41:18–27. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S135961011830042X. [CrossRef]
- Yan X, Han L, Zhao R, Fatima S, Zhao L, Gao F. Prognosis value of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β in serum of patients with lung cancer: A fresh look at interleukins as a biomarker. Heliyon. 2022 Aug [cited 2023 May 29];8(8):e09953. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405844022012415. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura T, Mizuno S. The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(6):588–610. [CrossRef]
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004 Jul [cited 2023 May 30];4(7):540–50. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrc1388. [CrossRef]
- Stabile LP, Rothstein ME, Keohavong P, Jin J, Yin J, Land SR, et al. Therapeutic targeting of human hepatocyte growth factor with a single neutralizing monoclonal antibody reduces lung tumorigenesis. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2008 Jul 1 [cited 2023 May 30];7(7):1913–22. Available from: https://aacrjournals.org/mct/article/7/7/1913/93201/Therapeutic-targeting-of-human-hepatocyte-growth. [CrossRef]
- Marmor MD, Skaria KB, Yarden Y. Signal transduction and oncogenesis by ErbB/HER receptors. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics. 2004 Mar [cited 2023 May 30];58(3):903–13. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0360301603020972. [CrossRef]
- Riudavets M, Sullivan I, Abdayem P, Planchard D. Targeting HER2 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a glimpse of hope? An updated review on therapeutic strategies in NSCLC harbouring HER2 alterations. ESMO Open. 2021 Oct [cited 2023 May 30];6(5):100260. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2059702921002222. [CrossRef]
- Uy NF, Merkhofer CM, Baik CS. HER2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review of Emerging Therapies. Cancers. 2022 Aug 27 [cited 2023 May 30];14(17):4155. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/17/4155. [CrossRef]
- Farooqi AA, Siddik ZH. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signalling in cancer: rapidly emerging signalling landscape: PDGF-induced Signalling Cascades. Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Jul [cited 2023 May 30];33(5):257–65. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbf.3120. [CrossRef]
- Paluri R, Madan A, Li P, Jones B, Saleh M, Jerome M, et al. Phase 1b trial of nintedanib in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 5 [cited 2023 May 30];83(3):551–9. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00280-018-3761-y. [CrossRef]
- Makinde T, Agrawal DK. Intra and extravascular transmembrane signalling of angiopoietin-1-Tie2 receptor in health and disease. J Cellular Mol Med. 2008 Jun [cited 2023 May 30];12(3):810–28. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00254.x. [CrossRef]
- Khan KA, Wu FT, Cruz-Munoz W, Kerbel RS. Ang2 inhibitors and Tie2 activators: potential therapeutics in perioperative treatment of early stage cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Jul 7 [cited 2023 May 30];13(7):e08253. Available from: https://www.embopress.org/doi/10.15252/emmm.201708253. [CrossRef]
- Mehta V, Fields L, Evans IM, Yamaji M, Pellet-Many C, Jones T, et al. VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Induces NRP1 (Neuropilin-1) Cleavage via ADAMs (a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase) 9 and 10 to Generate Novel Carboxy-Terminal NRP1 Fragments That Regulate Angiogenic Signaling. ATVB. 2018 Aug [cited 2023 May 30];38(8):1845–58. Available from: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311118. [CrossRef]
- Hong TM, Chen YL, Wu YY, Yuan A, Chao YC, Chung YC, et al. Targeting neuropilin 1 as an antitumor strategy in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 15;13(16):4759–68. [CrossRef]
- Liu SD, Zhong LP, He J, Zhao YX. Targeting neuropilin-1 interactions is a promising anti-tumor strategy. Chinese Medical Journal. 2021 Mar 5 [cited 2023 May 30];134(5):508–17. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/CM9.0000000000001200. [CrossRef]
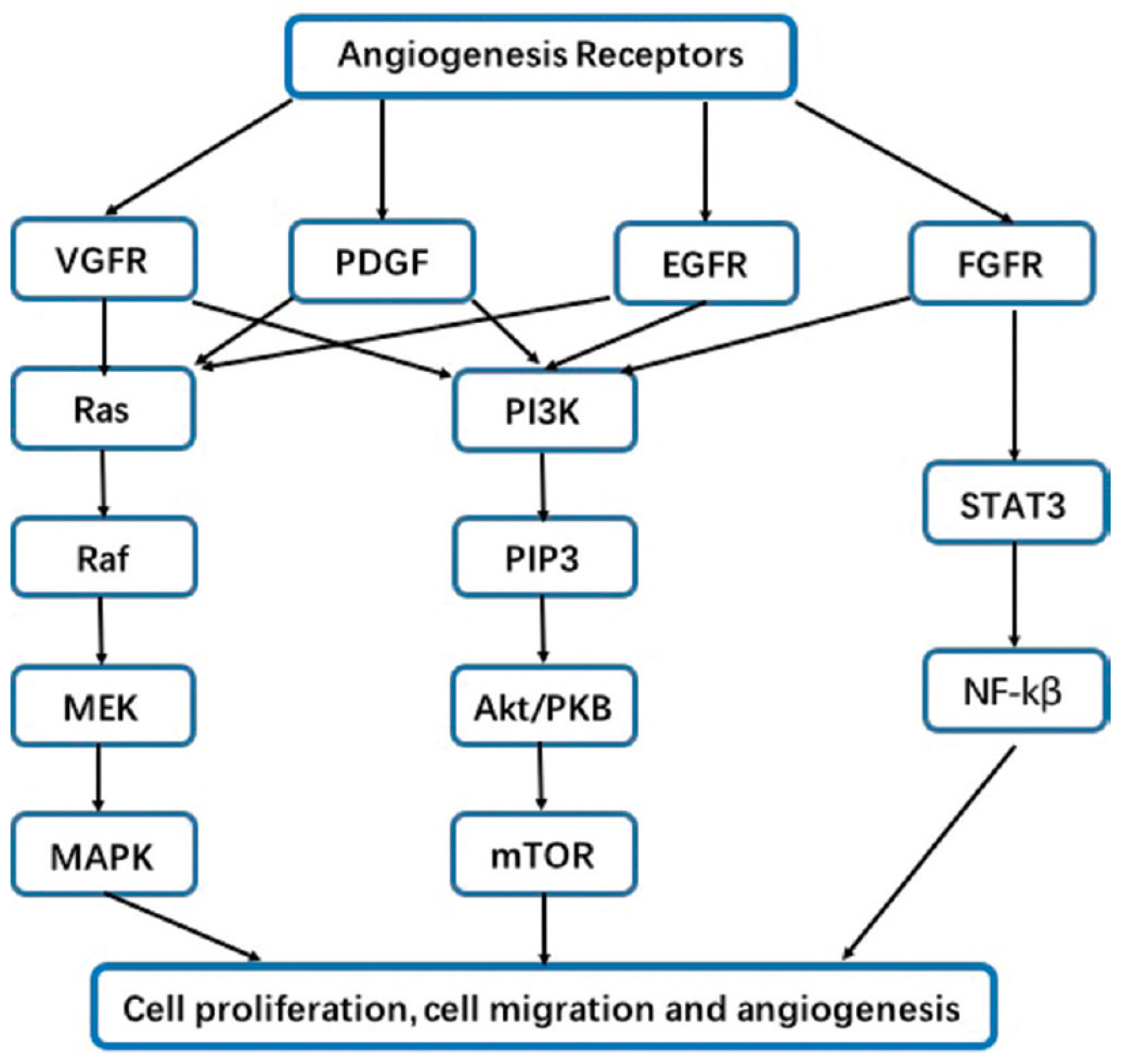
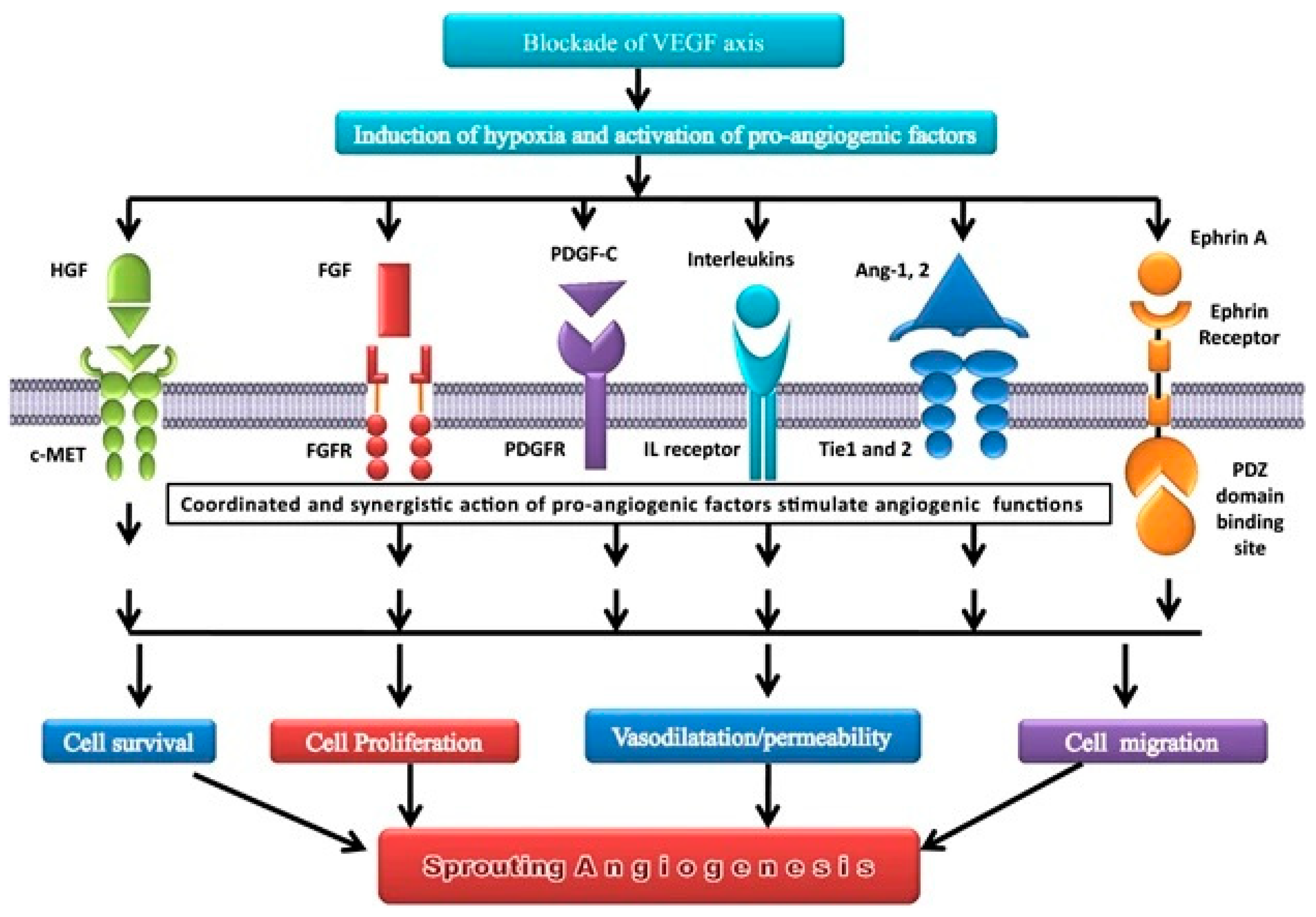
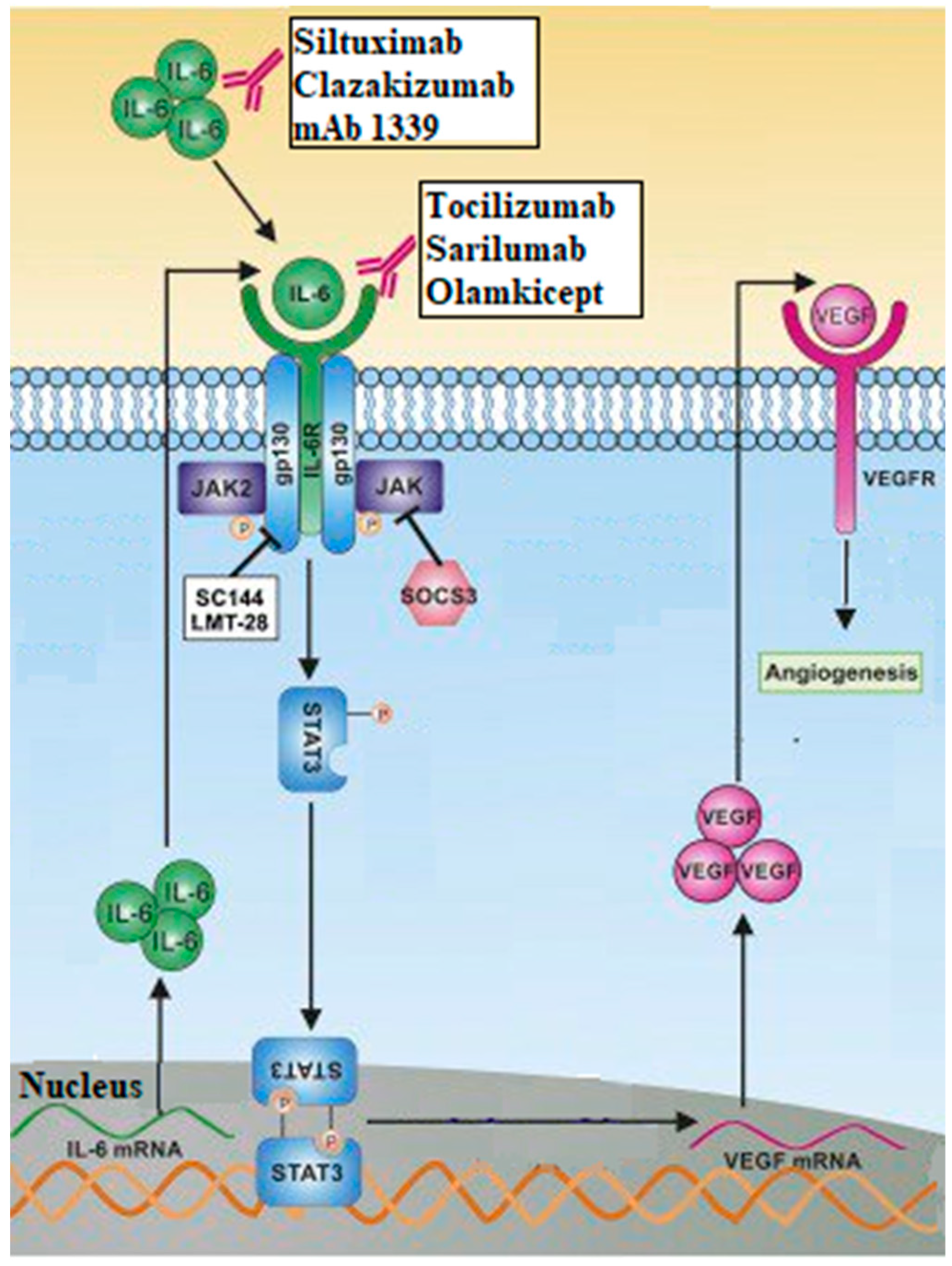
| Last update | Location and Study identifier | Study title | Condition | Intervention | Status | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
May 2023 |
United Kingdom NCT04179890 |
The Study observes how long patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) benefit from treatment with epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) when given either for uncommon mutations or for common mutations in the sequence afatinib followed by osimertinib (UpSwinG) | Non-squamous, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, NB: This study is observational, retrospective and non-interventional |
Observation of EGFR-TKI: -Afatinib -Erlotinib -Gefitinib -Osimertinib |
Complete | treatment with EGFR-TKI should be considered as standard for most patients with uncommon mutations |
| February 2023 |
USA NCT05062980 |
Quaratusugene Ozeplasmid (Reqorsa) in combination with Pembrolizumab in previously treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Acclaim-2) Phase I/II |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | A: Quaratusugene ozeplasmid (pan-TKI: EGFR and Akt inhibitor) + Pembrolizumab (VEGFR downstream inhibitor: PD1 inhibitor) B: Docetaxel (microtubule inhibitor) + ramucirumab (VEGFR inhibitor) + 3rd molecule proposed by physician |
On going | / |
| May 2019 |
United Kingdom NCT02109016 |
A single arm, open-label, phase II study to assess the efficacy of the dual VEGFR-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Lucitanib, given orally as a single agent to patients with FGFR1-driven lung cancer. | Advance stage of Small and Non-small cell lung cancer with adenomatous, squamous, and large cell histologies, as well as FGF, VEGF, or PDGF genetic alterations. |
Lucitanib, a VEGFR-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Terminated | Interim analysis was either impossible (due to short time data collection) or showed low probability of clinically significant result |
| January 2013 |
USA NCT00862134 |
Randomized, Multi-center, Open-label, Study of PR104 Versus PR104/Docetaxel in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Phase II |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | A: Docetaxel (microtubule inhibitor) B: Docetaxel + PR104 (hypoxia-activated prodrug) + G-CSF for prophylaxis |
Terminated | Interim analysis indicated low probability of clinically significant result |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





