Submitted:
24 August 2023
Posted:
25 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
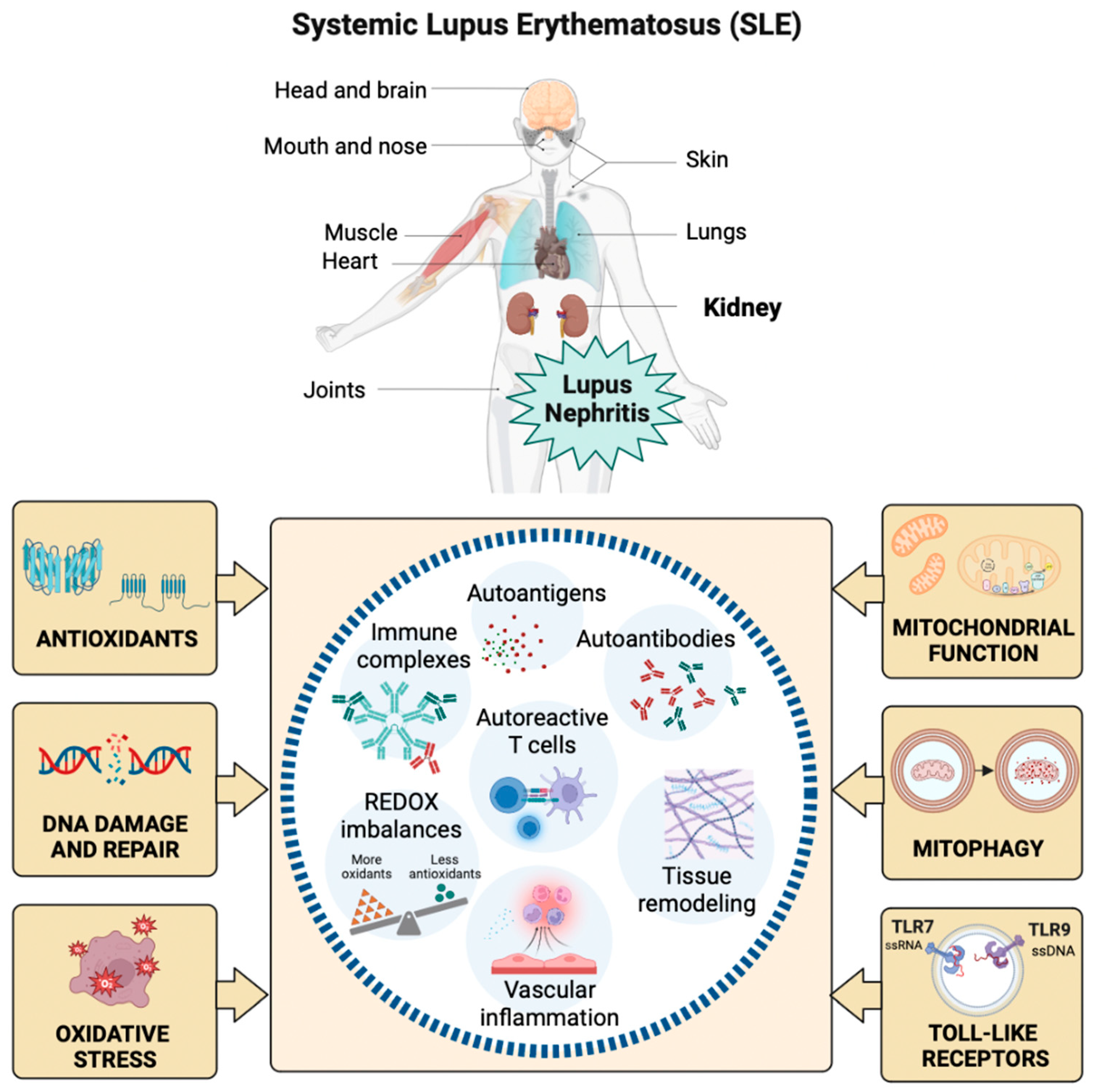
1. Introduction
Oxidative Stress in SLE
DNA Damage and Repair in SLE
Antioxidants in SLE
Mitochondrial Function in SLE
Mitophagy
Toll-like Receptors in SLE
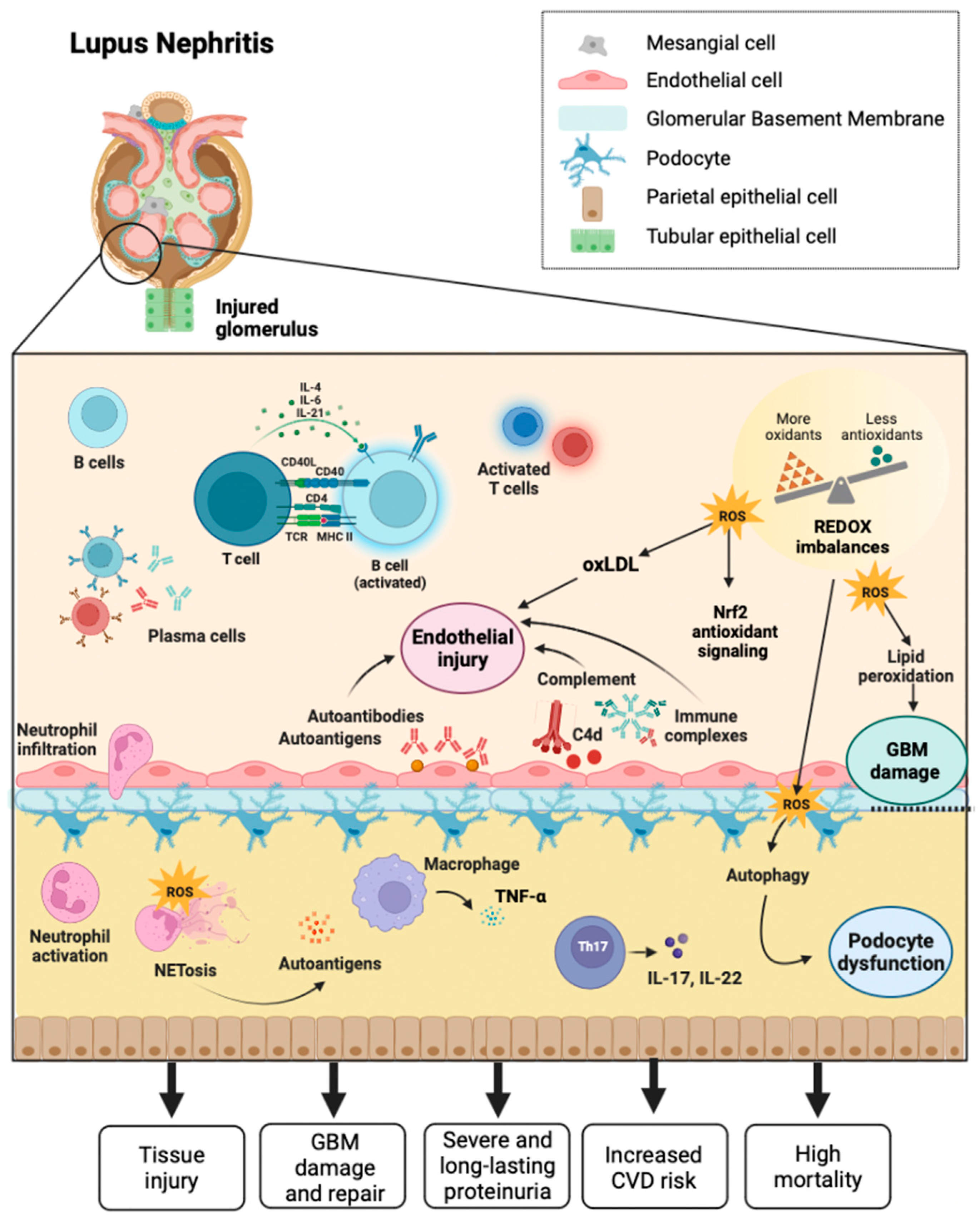
Lupus Nephritis
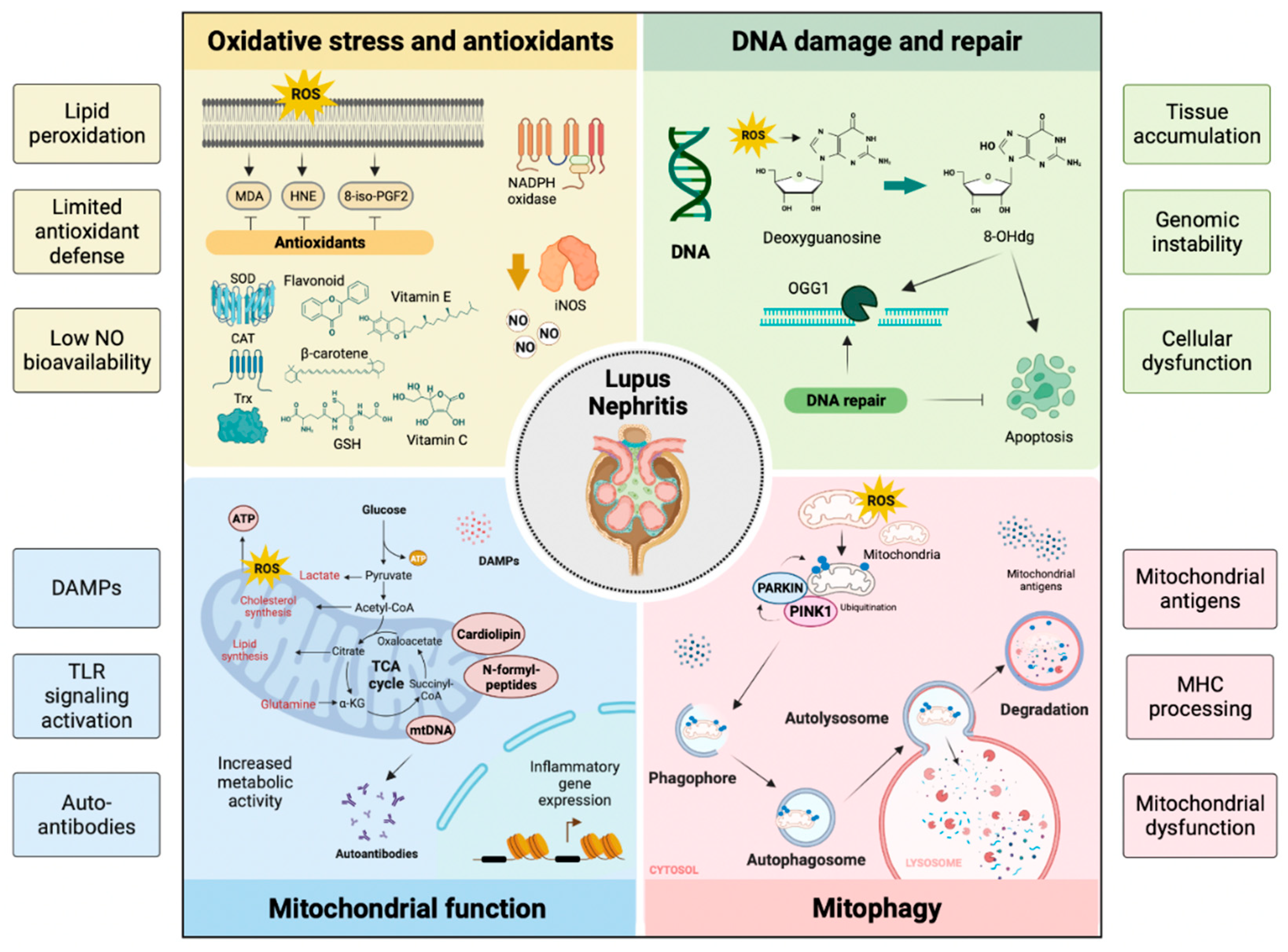
Oxidative Stress in LN
Oxidative Damage to DNA in LN
Antioxidants in LN
Mitochondrial Function in LN
Mitophagy in LN
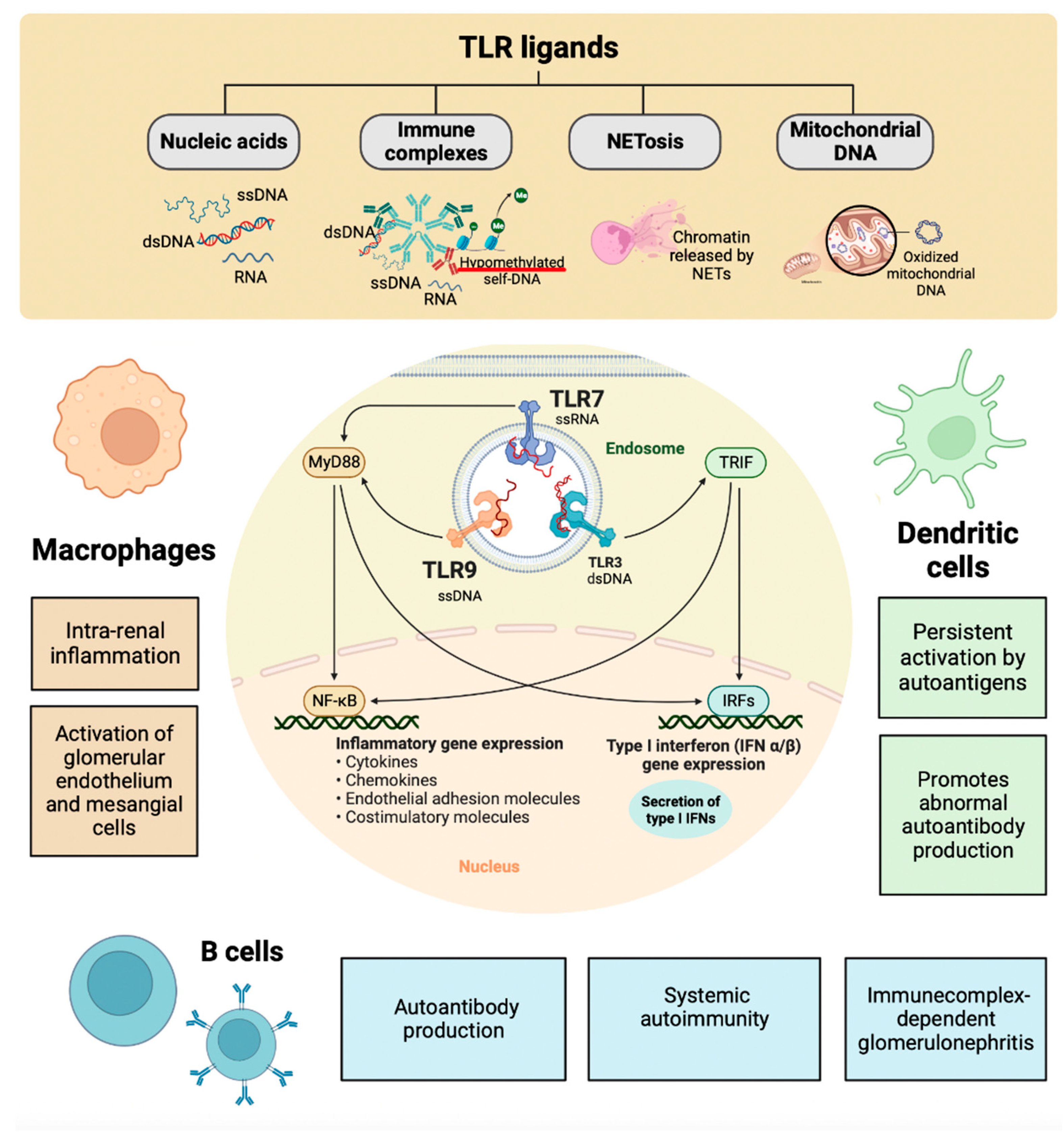
Innate Immunity in LN
Toll-like Receptors in LN
TLR7 in LN
TLR9 in LN
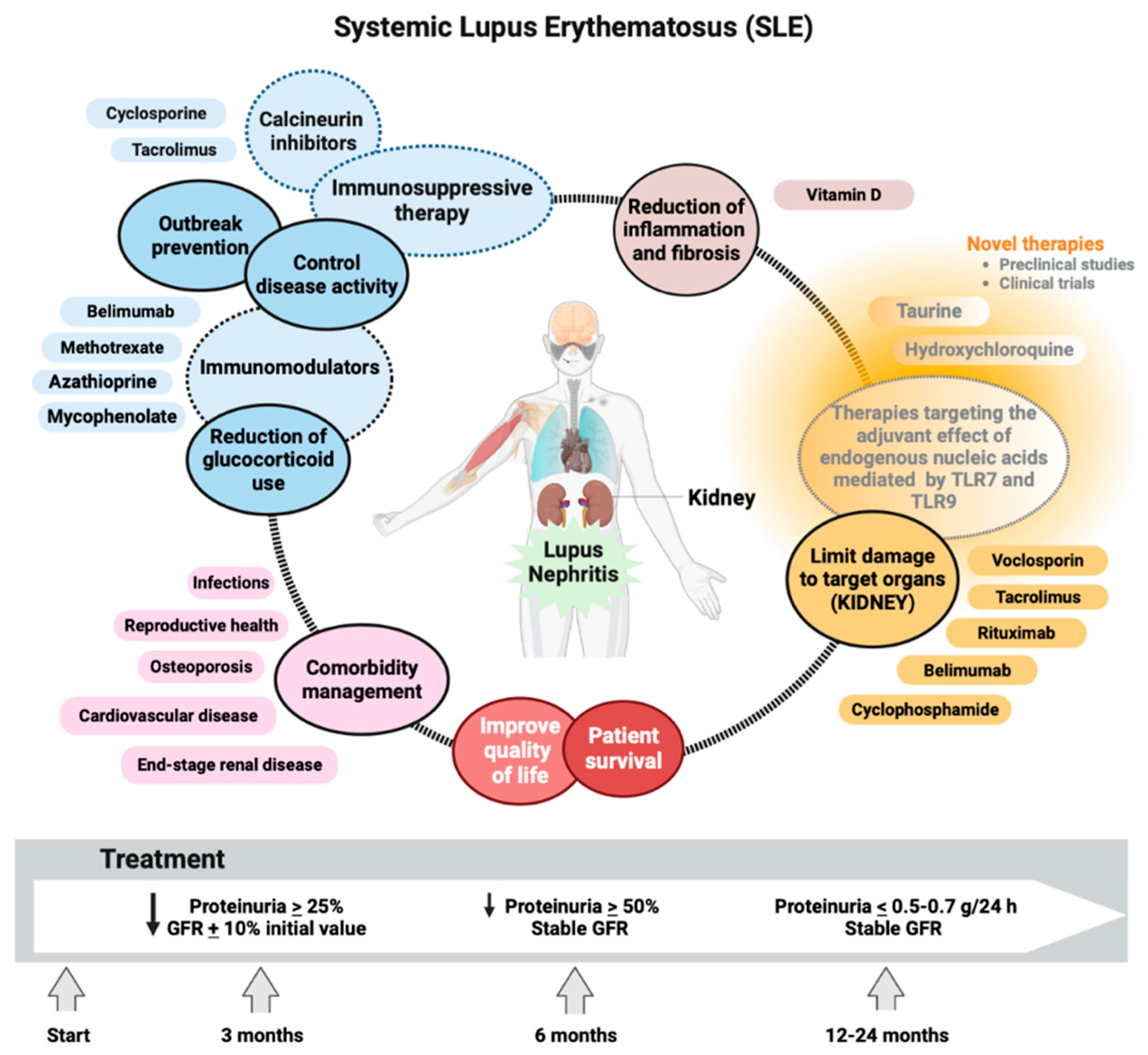
Management of SLE and LN
Conclusions
References
- Smallwood, M.J.; Nissim, A.; Knight, A.R.; Whiteman, M.; Haigh, R.; Winyard, P.G. Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Heshmat, T.S.; Khalil, N.M.; Elhamid, H.A.; Labib, S.; Mahfouz, M. Assessment of premature coronary atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus disease. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2015, 37, S43–S47. [CrossRef]
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell 1996;8:843-851.
- Fujii J, Kurahashi T, Konno T, Homma T, Iuchi Y. Oxidative stress as a potential causal factor for autoimmune hemolytic anemia and systemic lupus erythematosus. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(2):213-222.
- Shruthi, S.; Thabah, M.M.; Zachariah, B.; Negi, V.S. Association of Oxidative Stress with Disease Activity and Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross Sectional Study from a Tertiary Care Centre in Southern India. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 36, 185–193. [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, P.; Gęgotek, A.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Oxidative Stress and Lipid Mediators Modulate Immune Cell Functions in Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 723. [CrossRef]
- Perl, A. Oxidative stress in the pathology and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 674–686. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ahsan, H. Singlet oxygen species and systemic lupus erythematosus: a brief review. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2019, 40, 343–349. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, W.; Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Fang, S.; Yu, B. Mitochondria-derived methylmalonic acid, a surrogate biomarker of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101741. [CrossRef]
- Costa JH, Mohanapriya G, Bharadwaj R, Noceda C, Thiers KLL, Aziz S, et al. ROS/RNS balancing, aerobic fermentation regulation and cell cycle control - a complex early trait (‘CoV-MAC-TED’) for combating SARS-CoV-2-induced cell reprogramming. Front Immunol. 2021;12:673692.
- Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Lu, L.; Xie, G.; Luo, W.; Du, Y.; Xie, Z.; Han, X.; et al. Oxidative stress-induced aberrant lipid metabolism is an important causal factor for dysfunction of immunocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 163, 210–219. [CrossRef]
- Bona, N.; Pezzarini, E.; Balbi, B.; Daniele, S.M.; Rossi, M.F.; Monje, A.L.; Basiglio, C.; Pelusa, H.F.; Arriaga, S.M.M. Oxidative stress, inflammation and disease activity biomarkers in lupus nephropathy. Lupus 2020, 29, 311–323. [CrossRef]
- Mitran, M.I.; Nicolae, I.; Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.I.; Ene, C.D.; Matei, C.; Georgescu, S.R.; Popa, M.I. Reactive Carbonyl Species as Potential Pro-Oxidant Factors Involved in Lichen Planus Pathogenesis. Metabolites 2019, 9, 213. [CrossRef]
- Tampa, M.; Nicolae, I.; Ene, C.D.; Sarbu, I.; Matei, C.; Georgescu, S.R. Vitamin C and Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) in Psoriasis Vulgaris Related to Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI). Rev. de Chim. 2017, 68, 43–47. [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.D.; Awad, J.A.; Boss, H.J.; Blair, I.A.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd. Non-cyclooxygenase-derived prostanoids (F2-isoprostanes) are formed in situ on phospholipids.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10721–10725. [CrossRef]
- Praticò, D.; Rokach, J.; Lawson, J.; FitzGerald, G.A. F2-isoprostanes as indices of lipid peroxidation in inflammatory diseases. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2004, 128, 165–171. [CrossRef]
- Leitinger N. The role of phospholipid oxidation products in inflammatory and autoimmune disease: evidence from animal models and in humans. Subcell Biochem 2008;49:325-350.
- Ames, P.R.; Alves, J.; Murat, I.; Isenberg, D.A.; Nourooz-Zadeh, J. Oxidative stress in systemic lupus erythematosus and allied conditions with vascular involvement. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 529–534. [CrossRef]
- 3: 2021;70(1), 2021.
- Zavadskiy, S.; Sologova, S.; Moldogazieva, N. Oxidative distress in aging and age-related diseases: Spatiotemporal dysregulation of protein oxidation and degradation. Biochimie 2022, 195, 114–134. [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.; Russo, V.; Mello, T.; Galli, A. Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage in Chronic Disease and Environmental Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6936. [CrossRef]
- Ntouros PA, Vlachogiannis NI, Pappa M, Nezos A, Mavragani CP, Tektonidou MG, et al. Effective DNA damage response after acute but not chronic immune challenge: SARS-CoV-2 vaccine versus systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2021;229:108765.
- Tumurkhuu, G.; Chen, S.; Montano, E.N.; Laguna, D.E.; Santos, G.D.L.; Yu, J.M.; Lane, M.; Yamashita, M.; Markman, J.L.; Blanco, L.P.; et al. Oxidative DNA Damage Accelerates Skin Inflammation in Pristane-Induced Lupus Model. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Yang, W.; Karplus, M.; Verdine, G.L. Structure of a repair enzyme interrogating undamaged DNA elucidates recognition of damaged DNA. Nature 2005, 434, 612–618. [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot, Y.L.; Blanco, L.P.; Kaplan, M.J. Metabolic abnormalities and oxidative stress in lupus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 442–449. [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species in living systems: Source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S14–S22. [CrossRef]
- Zhang VX, Sze KM, Chan LK, Ho DW, Tsui YM, Chiu YT, et al. Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):217.
- Sies, H. Role of reactive oxygen species in biological processes. Klin Wochenschr 1991, 69, 965–968. [CrossRef]
- Schafer, F.Q.; Buettner, G.R. Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1191–1212. [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Sah, S.; Wanchu, A.; Wu, M.X.; Bhatnagar, A. Altered redox state and apoptosis in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 620–627. [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, W. The ratio of superoxide dismutase to standard deviation of erythrocyte distribution width as a predictor of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23230. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, F.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; et al. Confirmation of C4 gene copy number variation and the association with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese Han population. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 3047–3053. [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. The trail to superoxide dismutase. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 2688–2690. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Oberley, L.W.; Li, Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase.. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 497–500. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lin, C.; Lee, C.; Tsai, C.; Wei, Y. Increased 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in plasma and decreased mRNA expression of human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1, anti-oxidant enzymes, mitochondrial biogenesis-related proteins and glycolytic enzymes in leucocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 66–77. [CrossRef]
- D'Souza, A.; Kurien, B.T.; Rodgers, R.; Shenoi, J.; Kurono, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Hensley, K.; Nath, S.K.; Scofield, R.H. Detection of Catalase as a major protein target of the lipid peroxidation product 4-HNE and the lack of its genetic association as a risk factor in SLE. BMC Med Genet. 2008, 9, 62. [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Pétrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006, 440, 237–241. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, F.; Iribarren, C.; Gross, M.D.; Comstock, G.W.; Cutler, R.G. Uric acid and serum antioxidant capacity: a reaction to atherosclerosis?. Atherosclerosis 2000, 148, 131–139. [CrossRef]
- Drulović J, Dujmović I, Stojsavljević N, Mesaros S, Andjelković S, Miljković D, et al. Uric acid levels in sera from patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2001;248:121-126.
- Collins AR, Horvathova E. Oxidative DNA damage, antioxidants and DNA repair: applications of the comet assay. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29:337-341.
- Ahsan, H.; Ali, A.; Ali, R. Oxygen free radicals and systemic autoimmunity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 398–404. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Wei, Y.-H. Mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial DNA maintenance of mammalian cells under oxidative stress. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 822–834. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Dang, C.V. Multifaceted roles of glycolytic enzymes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 142–150. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Semenza, G.L.; Dang, C.V. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 177–185. [CrossRef]
- Chávez, M.D.; Tse, H.M. Targeting Mitochondrial-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species in T Cell-Mediated Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Pickles, S.; Vigié, P.; Youle, R.J. Mitophagy and Quality Control Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R170–R185. [CrossRef]
- Yurasov, S.; Wardemann, H.; Hammersen, J.; Tsuiji, M.; Meffre, E.; Pascual, V.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Defective B cell tolerance checkpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 703–711. [CrossRef]
- van Loosdregt, J.; Spreafico, R.; Rossetti, M.; Prakken, B.J.; Lotz, M.; Albani, S. Hydroxychloroquine preferentially induces apoptosis of CD45RO+ effector T cells by inhibiting autophagy: A possible mechanism for therapeutic modulation of T cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1443–1446.e1. [CrossRef]
- Lind, N.A.; Rael, V.E.; Pestal, K.; Liu, B.; Barton, G.M. Regulation of the nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 224–235. [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Hoehlig, K.; Roch, T.; Neves, P.; Gómez, E.C.; Sweenie, C.H.; Hao, Y.; Freitas, A.A.; Steinhoff, U.; Anderton, S.M.; et al. TLR-Activated B Cells Suppress T Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity. J Immunol. 2008, 180, 4763–4773. [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.J.; Cañete, P.F.; Wang, H.; Medhavy, A.; Bones, J.; Roco, J.A.; He, Y.; Qin, Y.; Cappello, J.; Ellyard, J.I.; et al. TLR7 gain-of-function genetic variation causes human lupus. Nature 2022, 605, 349–356. [CrossRef]
- Fillatreau, S.; Manfroi, B.; Dörner, T. Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells during systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 98–108. [CrossRef]
- Souyris, M.; Cenac, C.; Azar, P.; Daviaud, D.; Canivet, A.; Grunenwald, S.; Pienkowski, C.; Chaumeil, J.; Mejía, J.E.; Guéry, J.-C. TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3. [CrossRef]
- Margery-Muir, A.A.; Bundell, C.; Nelson, D.; Groth, D.M.; Wetherall, J.D. Gender balance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 258–268. [CrossRef]
- Scofield, R.H.; Bruner, G.R.; Namjou, B.; Kimberly, R.P.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Petri, M.; Reveille, J.D.; Alarcón, G.S.; Vilá, L.M.; Reid, J.; et al. Klinefelter's syndrome (47,XXY) in male systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Support for the notion of a gene-dose effect from the X chromosome. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2511–2517. [CrossRef]
- Hanna Kazazian, N.; Wang, Y.; Roussel-Queval, A.; Marcadet, L.; Chasson, L.; Laprie, C.; Desnues, B.; Charaix, J.; Irla, M.; Alexopoulou, L. Lupus Autoimmunity and Metabolic Parameters Are Exacerbated Upon High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Due to TLR7 Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian-Ding IB, Wagner M, Hornung V, Giese T, Schnurr M, Endres S, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells control TLR7 sensitivity of naive B cells via type I IFN. J Immunol. 2005;174:40434050.
- Berland R, Fernandez L, Kari E, Han JH, Lomakin I, Akira S, et al. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knock-in mice. Immunity. 2006;25:429-440.
- Diebold, S.S.; Kaisho, T.; Hemmi, H.; Akira, S.; Reis E Sousa, C. Innate Antiviral Responses by Means of TLR7-Mediated Recognition of Single-Stranded RNA. Science 2004, 303, 1529–1531. [CrossRef]
- Caielli, S.; Veiga, D.T.; Balasubramanian, P.; Athale, S.; Domic, B.; Murat, E.; Banchereau, R.; Xu, Z.; Chandra, M.; Chung, C.-H.; et al. A CD4+ T cell population expanded in lupus blood provides B cell help through interleukin-10 and succinate. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 75–81. [CrossRef]
- Nündel, K.; Green, N.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Moody, K.L.; Busto, P.; Eilat, D.; Miyake, K.; Oropallo, M.A.; Cancro, M.P.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Cell-Intrinsic Expression of TLR9 in Autoreactive B Cells Constrains BCR/TLR7-Dependent Responses. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2504–2512. [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K. Nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors: Beyond ligand search. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 782–785. [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; John, S.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Kashgarian, M.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell–intrinsic TLR9 expression is protective in murine lupus. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3172–3187. [CrossRef]
- Fukui, R.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Kanno, A.; Onji, M.; Shibata, T.; Ito, A.; Onji, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Akira, S.; Yoshida, N.; et al. Unc93B1 Restricts Systemic Lethal Inflammation by Orchestrating Toll-like Receptor 7 and 9 Trafficking. Immunity 2011, 35, 69–81. [CrossRef]
- 7: 2020;6(1), 2020.
- Doria, A.; Gatto, M.; Zen, M.; Iaccarino, L.; Punzi, L. Optimizing outcome in SLE: treating-to-target and definition of treatment goals. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 770–777. [CrossRef]
- Hajji, M.; Harzallah, A.; Kaaroud, H.; Barbouch, S.; Ben Hamida, F.; Ben Abdallah, T. Factors associated with relapse of lupus nephritis: A single center study of 249 cases. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2017, 28, 1349–1355. [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, I.; Birmingham, D.; Rovin, B.; Hebert, L. Commentary on the Current Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Lupus Nephritis Flare. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 12. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, I.; Hamano, T.; Tomida, K.; Inoue, K.; Takabatake, Y.; Nagasawa, Y.; Kawada, N.; Ito, T.; Kawachi, H.; Rakugi, H.; et al. Active vitamin D and its analogue, 22-oxacalcitriol, ameliorate puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrosis in rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2354–2361. [CrossRef]
- Shankland, S. The podocyte's response to injury: Role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 2131–2147. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-J.; Cheng, F.-J.; Hou, P.; Ren, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-X.; Zhao, M.-H.; Yang, L.; Martinez, J.; Zhang, H. Increased autophagy is cytoprotective against podocyte injury induced by antibody and interferon-α in lupus nephritis. Rheumatol. 2018, 77, 1799–1809. [CrossRef]
- Ene, C.D.; Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Matei, C.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Penescu, M.N.; Nicolae, I. Cellular Response against Oxidative Stress, a Novel Insight into Lupus Nephritis Pathogenesis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 693. [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Lupus aortitis: A fatal, inflammatory cardiovascular complication in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2020, 29, 1652–1654. [CrossRef]
- Martin N, ¿Tu X, Egan AJ, Stover C. Complement activation on endothelial cell-derived microparticles-A key determinant for cardiovascular risk in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus? Medicina. 2020;56(10):533.
- Giannelou, M.; Mavragani, C.P. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive update. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 82, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrera, C.; Barbarroja, N.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Aguirre, M.A.; Cuadrado, M.J. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of atherothrombosis associated with anti-phospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: new therapeutic approaches. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2096–2108. [CrossRef]
- Lozovoy MA, Simão AN, Morimoto HK, Iryioda TM, Panis C, Reiche EM, et al. Hypertension is associated with serologically active disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: role of increased Th1/Th2 ratio and oxidative stress. Scand J Rheumatol. 2014;43(1):59-62.
- Yan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Y. Oxidative Stress Contributes to Inflammatory and Cellular Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Cellular Markers and Molecular Mechanism. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 453–465. [CrossRef]
- Li D, Shi G, Wang J, Zhang D, Pan Y, Dou H, et al. Baicalein ameliorates pristane-induced lupus nephritis via activating Nrf2/HO-1 in myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):105.
- Yang SM, Chan YL, Hua KF, Chang JM, Chen HL, Tsai YJ, et al. Osthole improves an accelerated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis model in the early stage by activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and subsequently inhibiting NF-kappaB-mediated COX-2 expression and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;73:260-269.
- Li Y, Li W, Liu C, Yan M, Raman I, Du Y, et al. Delivering Oxidation Resistance-1 (OXR1) to Mouse Kidney by Genetic Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibited Enhanced Protection against Nephrotoxic Serum Induced Renal Injury and Lupus Nephritis. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;4(9):231.
- Mitran, M.I.; Nicolae, I.; Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.I.; Ene, C.D.; Matei, C.; Georgescu, S.R.; Popa, M.I. Reactive Carbonyl Species as Potential Pro-Oxidant Factors Involved in Lichen Planus Pathogenesis. Metabolites 2019, 9, 213. [CrossRef]
- Shah D, Mahajan N Sah S., Nath SK, Paudial B. Oxidative stress and its biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Sci. 2014;21:23.
- Ene CD, Ceausu E, Nicolae I, Tampa M, Matei C, Georgescu SR. Ultraviolet radiation, Vitamin D and autoimmune disorders. Rev Chim Buc. 2015;66:1068-1073.
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Giustarini, D.; Colombo, R.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A. Protein carbonylation in human diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 169–176. [CrossRef]
- Beal, M. Oxidatively modified proteins in aging and disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 797–803. [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N.; Chandra, M.; Tuteja, R.; Misra, M.K. Nitric Oxide as a Unique Bioactive Signaling Messenger in Physiology and Pathophysiology. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2004, 2004, 227–237. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Nitric Oxide in the Kidney : Its Physiological Role and Pathophysiological Implications. Electrolytes Blood Press. 2008, 6, 27–34. [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Garvin, J.L. Recent Advances in the Regulation of Nitric Oxide in the Kidney. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1062–1067. [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, B.B.; Abdulmahdi, W.; Pawar, R.; Wolin, M.S. Oxidant Mechanisms in Renal Injury and Disease. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 119–146. [CrossRef]
- Semenikhina, M.; Stefanenko, M.; Spires, D.R.; Ilatovskaya, D.V.; Palygin, O. Nitric-Oxide-Mediated Signaling in Podocyte Pathophysiology. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 745. [CrossRef]
- Wanchu, A.; Khullar, M.; Deodhar, S.D.; Bambery, P.; Sud, A. Nitric oxide synthesis is increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.. Rheumatol. Int. 1998, 18, 41–43. [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.C.; Ruizb, P.; Alexanderc, A.; Pippen, A.M.; Gilkeson, G.S. Effect of Late Modulation of Nitric Oxide Production on Murine Lupus. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 83, 86–92. [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, K.H.; Sigar, I.M.; Rana, S.V.; Gupta, J.; Holland, S.M.; Byrne, G.I.; Morrow, J.D. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Regulates Production of Isoprostanes In Vivo during Chlamydial Genital Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 7183–7187. [CrossRef]
- Dinu L, Ene CD, Nicolae I, Tampa M, Matei C, Georgescu SR. The serum levels of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine under the chemicals influence. Rev Chim. 2014;65:1319-1326.
- Wang, K.; Maayah, M.; Sweasy, J.B.; Alnajjar, K.S. The role of cysteines in the structure and function of OGG1. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 296, 100093. [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Kang, J.H.; Karlson, E.W. Antioxidant Intake and Risks of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Women. Am. J. Epidemiology 2010, 172, 205–216. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Lane, J.H.; Zurier, R.B.; A Lawrence, D.; Lawrence, D.A. Analysis of the thiol status of peripheral blood leukocytes in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 934–941. [CrossRef]
- Tewthanom K, Janwityanuchit S, Totemchockchyakarn K, Panomvana D. Correlation of lipid peroxidation and glutathione levels with severity of systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study from single center. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2008;11:30-4.
- Morgan, P.E.; Sturgess, A.D.; Hennessy, A.; Davies, M.J. Serum protein oxidation and apolipoprotein CIII levels in people with systemic lupus erythematosus with and without nephritis. Free. Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 1301–1312. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, W.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X. Early-stage lupus nephritis treated with N-acetylcysteine: A report of two cases. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 689–692. [CrossRef]
- Schieke, S.M.; Phillips, D.; McCoy, J.P.; Aponte, A.M.; Shen, R.-F.; Balaban, R.S.; Finkel, T. The Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway Regulates Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption and Oxidative Capacity. J Biol Chem. 2006, 281, 27643–27652. [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.L.; Kornbluth, S. The Tangled Circuitry of Metabolism and Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 399–410. [CrossRef]
- Friedman JR, Nunnari J. Mitochondrial form and function. Nature. 2014;505:335-43.
- Barshad, G.; Marom, S.; Cohen, T.; Mishmar, D. Mitochondrial DNA Transcription and Its Regulation: An Evolutionary Perspective. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 682–692. [CrossRef]
- Pfanner, N.; Warscheid, B.; Wiedemann, N. Mitochondrial proteins: from biogenesis to functional networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 267–284. [CrossRef]
- Murphy MP, Hartley RC. Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for common pathologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:865-886.
- Lee, S.; Min, K.-T. The Interface Between ER and Mitochondria: Molecular Compositions and Functions. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 1000–1007. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, P.; Mai, J.; Choi, E.T.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.-F. Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 19–19. [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 158–167. [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Agostinis, P.; Krysko, O.; Garg, A.D.; Bachert, C.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Vandenabeele, P. Emerging role of damage-associated molecular patterns derived from mitochondria in inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 157–164. [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondria in the Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Immunity 2015, 42, 406–417. [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y.; Marcoux, G.; Allaeys, I.; Julien, A.-S.; Loignon, R.-C.; Benk-Fortin, H.; Rollet-Labelle, E.; Rauch, J.; Fortin, P.R.; Boilard, E. Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Target Mitochondrial RNA. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1026. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Gu, Y.; Ye, S. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Mitochondrial DNA and Its Autoantibody in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Proof-of-Concept Trial of Metformin. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3190–3200. [CrossRef]
- Basso, P.J.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S. Targeting immune cell metabolism in kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 465–480. [CrossRef]
- Kingsmore, K.M.; Bachali, P.; Catalina, M.D.; Daamen, A.R.; Heuer, S.E.; Robl, R.D.; Grammer, A.C.; Lipsky, P.E. Altered expression of genes controlling metabolism characterizes the tissue response to immune injury in lupus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, P.; Ko, Y.-A.; Han, S.H.; Chinga, F.; Park, A.S.D.; Tao, J.; Sharma, K.; Pullman, J.; et al. Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 37–46. [CrossRef]
- Grayson PC, Eddy S, Taroni JN, Lightfoot YL, Mariani L, Parikh H, et al. Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium, the European Renal cDNA Bank cohort, and the Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network. Metabolic pathways and immunometabolism in rare kidney diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018, 77, 1226–1233. [CrossRef]
- MacIver, N.J.; Michalek, R.D.; Rathmell, J.C. Metabolic Regulation of T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 259–283. [CrossRef]
- Shi LZ, Wang R, Huang G, Vogel P, Neale G, Green DR, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells. J Exp Med. 2011;208(7):1367-76.
- Jacobs SR, Herman CE, Maciver NJ, Wofford JA, Wieman HL, Hammen JJ, et al. Glucose uptake is limiting in T cell activation and requires CD28-mediated Akt-dependent and independent pathways. J Immunol. 2008;180(7):4476-86.
- Alexopoulos, E.; Seron, D.; Hartley, R.B.; Cameron, J.S. Lupus nephritis: Correlation of interstitial cells with glomerular function. Kidney Int. 1990, 37, 100–109. [CrossRef]
- Couzi, L.; Merville, P.; Deminière, C.; Moreau, J.-F.; Combe, C.; Pellegrin, J.-L.; Viallard, J.-F.; Blanco, P. Predominance of CD8+ T lymphocytes among periglomerular infiltrating cells and link to the prognosis of class III and class IV lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2362–2370. [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Avery, L.; Menk, A.V.; Gordon, R.A.; Smita, S.; Kane, L.P.; Chikina, M.; Delgoffe, G.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Kidney-infiltrating T cells in murine lupus nephritis are metabolically and functionally exhausted. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4884–4897. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lai, Y.; Chen, B.; Guo, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Zhang, H. NAMPT is a metabolic checkpoint of IFNγ-producing CD4+ T cells in lupus nephritis. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 193–210. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Choi, S.-C.; Xu, Z.; Perry, D.J.; Seay, H.; Croker, B.P.; Sobel, E.S.; Brusko, T.M.; Morel, L. Normalization of CD4 + T cell metabolism reverses lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 274ra18–274ra18. [CrossRef]
- Pickles, S.; Vigié, P.; Youle, R.J. Mitophagy and Quality Control Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R170–R185. [CrossRef]
- Palikaras, K.; Lionaki, E.; Tavernarakis, N. Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1013–1022. [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Duvezin-Caubet, S.; Koob, S.; Occhipinti, A.; Jagasia, R.; Petcherski, A.; Ruonala, M.O.; Priault, M.; Salin, B.; Reichert, A.S. Mitophagy is triggered by mild oxidative stress in a mitochondrial fission dependent manner. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 2297–2310. [CrossRef]
- Kubli DA, Gustafsson AB. Mitochondria and mitophagy: The yin and yang of cell death control. Circ Res. 2012;111:1208-1221.
- Sun, N.; Yun, J.; Liu, J.; Malide, D.; Liu, C.; Rovira, I.I.; Holmström, K.M.; Fergusson, M.M.; Yoo, Y.H.; Combs, C.A.; et al. Measuring In Vivo Mitophagy. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 685–696. [CrossRef]
- Matheoud, D.; Sugiura, A.; Bellemare-Pelletier, A.; Laplante, A.; Rondeau, C.; Chemali, M.; Fazel, A.; Bergeron, J.J.; Trudeau, L.-E.; Burelle, Y.; et al. Parkinson’s Disease-Related Proteins PINK1 and Parkin Repress Mitochondrial Antigen Presentation. Cell 2016, 166, 314–327. [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, O.; Kousios, A.; Hadjisavvas, A.; Lauwerys, B.; Sokratous, K.; Kyriacou, K. Biomarkers of systemic lupus erythematosus identified using mass spectrometry-based proteomics: a systematic review. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 993–1012. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Mitophagy in Acute Kidney Injury and Kidney Repair. Cells 2020, 9, 338. [CrossRef]
- Lui, S.L.; Tsang, R.; Chan, K.W.; Zhang, F.; Tam, S.; Yung, S.; Chan, T.M. Rapamycin attenuates the severity of established nephritis in lupus-prone NZB/W F1 mice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2768–2776. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.R.; Crow, M.K. CD8 T cells and mTOR: new concepts and targets for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2018, 391, 1126–1127. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, Y. A novel pathway regulating the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1071–1077. [CrossRef]
- Oaks, Z.; Winans, T.; Caza, T.; Fernandez, D.; Liu, Y.; Landas, S.K.; Banki, K.; Perl, A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Liver and Antiphospholipid Antibody Production Precede Disease Onset and Respond to Rapamycin in Lupus-Prone Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2728–2739. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Law, H.K.W. Immune Complexes Impaired Glomerular Endothelial Cell Functions in Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5281. [CrossRef]
- Flür, K.; Allam, R.; Zecher, D.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Lichtnekert, J.; Schwarz, M.; Beutler, B.; Vielhauer, V.; Anders, H.-J. Viral RNA Induces Type I Interferon-Dependent Cytokine Release and Cell Death in Mesangial Cells via Melanoma-Differentiation-Associated Gene-5: Implications for Viral Infection-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2014–2022. [CrossRef]
- Lech, M.; Anders, H.-J. The Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1357–1366. [CrossRef]
- Hof, D.; Raats, J.M.; Pruijn, G.J. Apoptotic modifications affect the autoreactivity of the U1 snRNP autoantigen. Autoimmun. Rev. 2005, 4, 380–388. [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Ni, H.; Capodici, J.; Lamphier, M.; Weissman, D. mRNA Is an Endogenous Ligand for Toll-like Receptor 3. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 12542–12550. [CrossRef]
- Chan, O.T.; Hannum, L.G.; Haberman, A.M.; Madaio, M.P.; Shlomchik, M.J. A Novel Mouse with B Cells but Lacking Serum Antibody Reveals an Antibody-independent Role for B Cells in Murine Lupus. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1639–1648. [CrossRef]
- Guiducci, C.; Gong, M.; Xu, Z.; Gill, M.; Chaussabel, D.; Meeker, T.; Chan, J.H.; Wright, T.; Punaro, M.; Bolland, S.; et al. TLR recognition of self nucleic acids hampers glucocorticoid activity in lupus. Nature 2010, 465, 937–941. [CrossRef]
- Allam, R.; Lichtnekert, J.; Moll, A.G.; Taubitz, A.; Vielhauer, V.; Anders, H.-J. Viral RNA and DNA Trigger Common Antiviral Responses in Mesangial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1986–1996. [CrossRef]
- 5: 2004;18, 2004.
- Rich, S.A. Human Lupus Inclusions and Interferon. Science 1981, 213, 772–775. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ito, S.; Chino, Y.; Goto, D.; Matsumoto, I.; Murata, H.; Tsutsumi, A.; Hayashi, T.; Uchida, K.; Usui, J.; et al. Laser microdissection-based analysis of cytokine balance in the kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 159, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J. Pseudoviral immunity – a novel concept for lupus. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 553–561. [CrossRef]
- Barrat, F.J.; Coffman, R.L. Development of TLR inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 223, 271–283. [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.; Mashmoushi, A.; Shaftman, S.; Gilkeson, G. NADPH oxidase and nitric oxide synthase-dependent superoxide production is increased in proliferative lupus nephritis. Lupus 2013, 22, 1361–1370. [CrossRef]
- Allam, R.; Anders, H.-J. The role of innate immunity in autoimmune tissue injury. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2008, 20, 538–544. [CrossRef]
- Lorenz G, Anders HJ. Neutrophils, dendritic cells, toll-like receptors, and interferon-alpha in lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35:410-426.
- Rönnblom, L.; Pascual, V. The innate immune system in SLE: type I interferons and dendritic cells. Lupus 2008, 17, 394–399. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pla, A.; Patel, P.; Maecker, H.T.; Rossello-Urgell, J.; Baldwin, N.; Bennett, L.; Cantrell, V.; Baisch, J.; Punaro, M.; Gotte, A.; et al. IFN Priming Is Necessary but Not Sufficient To Turn on a Migratory Dendritic Cell Program in Lupus Monocytes. J Immunol. 2014, 192, 5586–5598. [CrossRef]
- Patole PS, Zecher D, Pawar RD, Grone HJ, Schlondorff D, Anders HJ. G-rich DNA suppresses systemic lupus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3273–3280. [CrossRef]
- Lee TP, Huang JC, Liu CJ, Chen HJ, Chen YH, Tsai YT, et al. Interactions of surface-expressed TLR-4 and endosomal TLR-9 accelerate lupus progression in anti-dsDNA antibody transgenic mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2014;239:715-723.
- Pawar, R.D.; Patole, P.S.; Wörnle, M.; Anders, H.-J. Microbial nucleic acids pay a Toll in kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 291, F509–F516. [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.; Krug, A.; Pawar, R.D. Molecular mimicry in innate immunity? The viral RNA recognition receptor TLR7 accelerates murine lupus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1795–1799. [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.-Q.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Cen, H.; Wang, D.-G.; Feng, C.-C.; Li, R.-J.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F. The TLR7 7926A>G polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 105–110. [CrossRef]
- Horton, C.G.; Farris, A.D. Toll-like Receptors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.D.; Roths, J.B. A y chromosome associated factor in strain bxsb producing accelerated autoimmunity and lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheum. 1979, 22, 1188–1194. [CrossRef]
- Deane, J.A.; Pisitkun, P.; Barrett, R.S.; Feigenbaum, L.; Town, T.; Ward, J.M.; Flavell, R.A.; Bolland, S. Control of Toll-like Receptor 7 Expression Is Essential to Restrict Autoimmunity and Dendritic Cell Proliferation. Immunity 2007, 27, 801–810. [CrossRef]
- Lee PY, Kumagai Y, Li Y, Takeuchi O, Yoshida H, Weinstein J, et al. TLR7-dependent and FcgammaR-independent production of type I interferon in experimental mouse lupus. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2008;205:2995-300.
- Yokogawa, M.; Takaishi, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kamijima, R.; Fujimoto, C.; Kataoka, S.; Terada, Y.; Sano, S. Epicutaneous Application of Toll-like Receptor 7 Agonists Leads to Systemic Autoimmunity in Wild-Type Mice: A New Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 694–706. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bethunaickan, R.; Huang, W.; Lodhi, U.; Solano, I.; Madaio, M.P.; Davidson, A. Interferon-α accelerates murine systemic lupus erythematosus in a T cell-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 219–229. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Jacob, N.; Carreras, E.; Bajana, S.; Putterman, C.; Turner, S.; Neas, B.; Mathian, A.; Koss, M.N.; Stohl, W.; et al. Deficiency of Type I IFN Receptor in Lupus-Prone New Zealand Mixed 2328 Mice Decreases Dendritic Cell Numbers and Activation and Protects from Disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6021–6029. [CrossRef]
- Celhar, T.; Hopkins, R.; Thornhill, S.I.; De Magalhaes, R.; Hwang, S.-H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Yasuga, H.; Jones, L.A.; Casco, J.; Lee, B.; et al. RNA sensing by conventional dendritic cells is central to the development of lupus nephritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, E6195–E6204. [CrossRef]
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science. 2003;300(5625):1524-1525.
- Soni, C.; Wong, E.B.; Domeier, P.P.; Khan, T.N.; Satoh, T.; Akira, S.; Rahman, Z.S.M. B Cell–Intrinsic TLR7 Signaling Is Essential for the Development of Spontaneous Germinal Centers. J Immunol. 2014, 193, 4400–4414. [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.D. Toll-like receptors in kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 189–196. [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; John, S.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Kashgarian, M.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell–intrinsic TLR9 expression is protective in murine lupus. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3172–3187. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.M.; Majidi, J.; Baradaran, B.; Yousefi, M. Toll-Like Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 605–614. [CrossRef]
- Giles JR, Kashgarian M, Koni PA, Shlomchik MJ. B cell-specific MHC class II deletion reveals multiple nonredundant roles for B cell antigen presentation in murine lupus. J Immunol. 2015;195(6):2571-2579.
- Iribarren, K.; Bloy, N.; Buqué, A.; Cremer, I.; Eggermont, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Fucikova, J.; Galon, J.; Špíšek, R.; Zitvogel, L.; et al. Trial Watch: Immunostimulation with Toll-like receptor agonists in cancer therapy. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e108863. [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; John, S.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Kashgarian, M.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell–intrinsic TLR9 expression is protective in murine lupus. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3172–3187. [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Alunno, A.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; Gordon, C.; Govoni, M.; et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:736-45. [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update οn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Gatto, M.; Tamborini, F.; Quaglini, S.; Radice, F.; Saccon, F.; Frontini, G.; Alberici, F.; Sacchi, L.; Binda, V.; et al. Lack of EULAR/ERA-EDTA response at 1 year predicts poor long-term renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020, 79, 1077–1083. [CrossRef]
- Pons-Estel, G.J.; Alarcón, G.S.; McGwin, G.; Danila, M.I.; Zhang, J.; Bastian, H.M.; Reveille, J.D.; Vilá, L.M.; Lumina Study Group Protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on renal damage in patients with lupus nephritis: LXV, data from a multiethnic US cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 830–839. [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature. 2002;416:603-607.
- Takeuchi, T.; Wakasugi, N.; Uno, S.; Makino, H. Long-term Safety and Effectiveness of Tacrolimus in Patients With Lupus Nephritis: 5-year Interim Postmarketing Surveillance Study in Japan (TRUST). J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 74–81. [CrossRef]
- Dall'Era, M.; Bruce, I.N.; Gordon, C.; Manzi, S.; McCaffrey, J.; E Lipsky, P. Current challenges in the development of new treatments for lupus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 729–735. [CrossRef]
- Navarra SV, Guzmán RM, Gallacher AE, Hall S, Levy RA, Jimenez RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011;377:721-731. [CrossRef]
- Barrat, F.J.; Meeker, T.; Chan, J.H.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L. Treatment of lupus-prone mice with a dual inhibitor of TLR7 and TLR9 leads to reduction of autoantibody production and amelioration of disease symptoms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3582–3586. [CrossRef]
- Zen, M.; Iaccarino, L.; Gatto, M.; Saccon, F.; Larosa, M.; Ghirardello, A.; Punzi, L.; Doria, A. Lupus low disease activity state is associated with a decrease in damage progression in Caucasian patients with SLE, but overlaps with remission. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 104–110. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Cantorna, M.T. The vitamin D receptor is required for iNKT cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5207–5212. [CrossRef]
- Luo H, Geng CJ, Miao SM, Wang LH, Li Q. Taurine attenuates the damage of lupus nephritis mouse via inactivation of the NF-κB pathway. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(1):137-147.
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Ouyang, C.; Shi, G. Identification of the tubulointerstitial infiltrating immune cell landscape and immune marker related molecular patterns in lupus nephritis using bioinformatics analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1596. [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Yi, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.; Ji, J.; Xu, L. Luteolin attenuates lupus nephritis by regulating macrophage oxidative stress via HIF-1α pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 953, 175823. [CrossRef]
- Popp, H.D.; Kohl, V.; Naumann, N.; Flach, J.; Brendel, S.; Kleiner, H.; Weiss, C.; Seifarth, W.; Saussele, S.; Hofmann, W.-K.; et al. DNA Damage and DNA Damage Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1177. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




