Submitted:
23 August 2023
Posted:
24 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
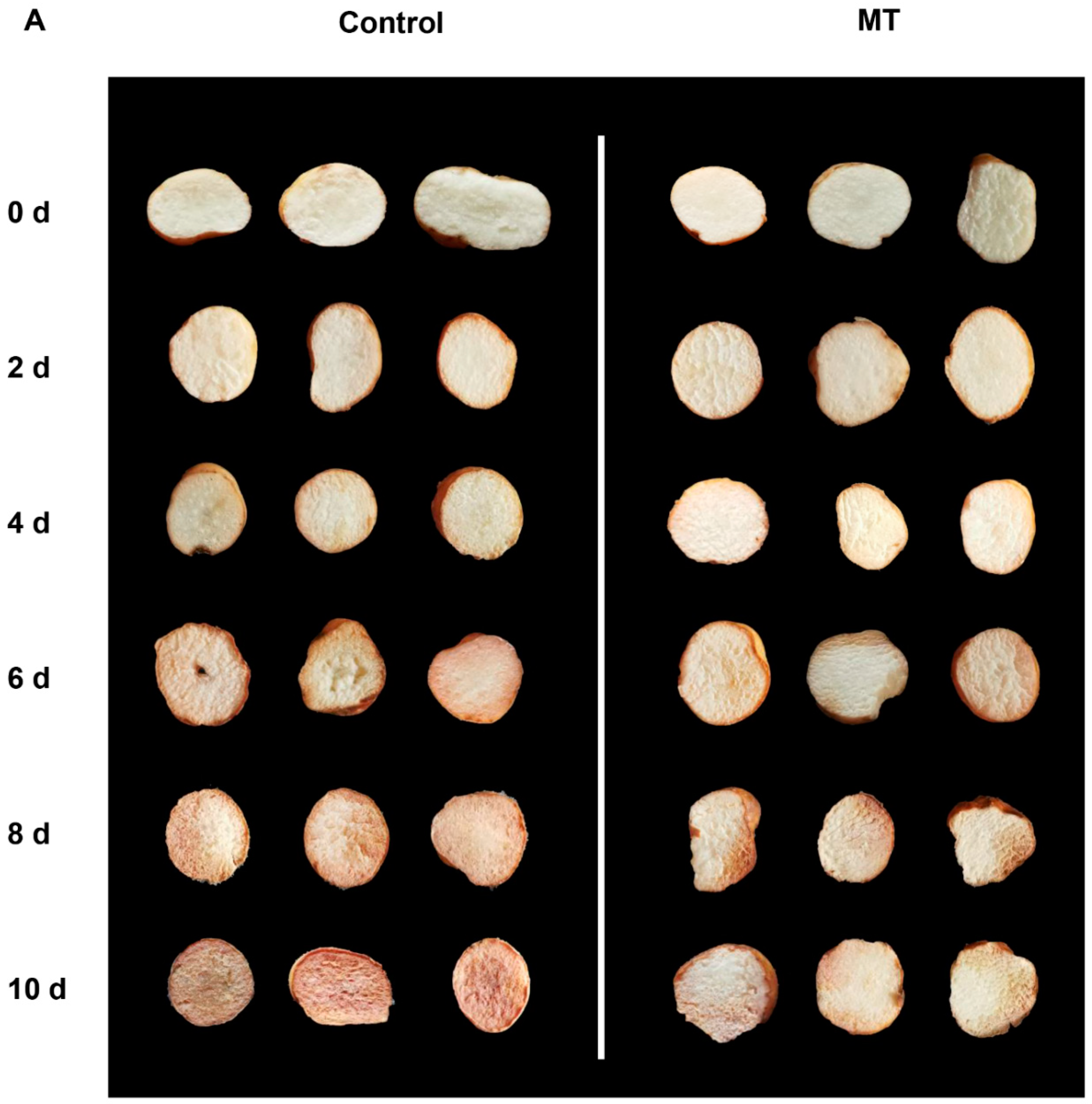
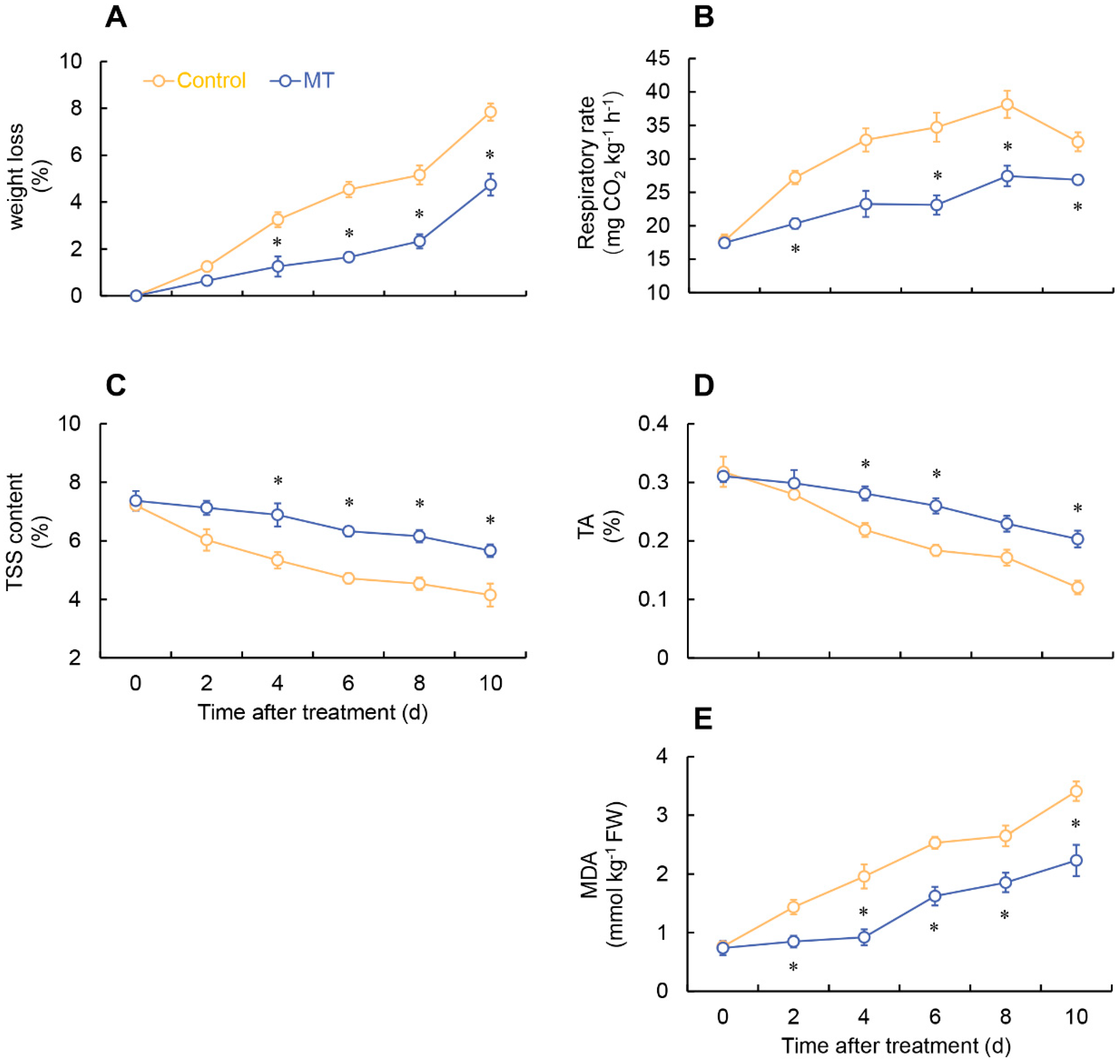
2.1. Effect of MT on phenotypic observation, weight loss, respiratory rate, total soluble solid (TSS), titratable acid (TA) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in fresh-cut G. elata
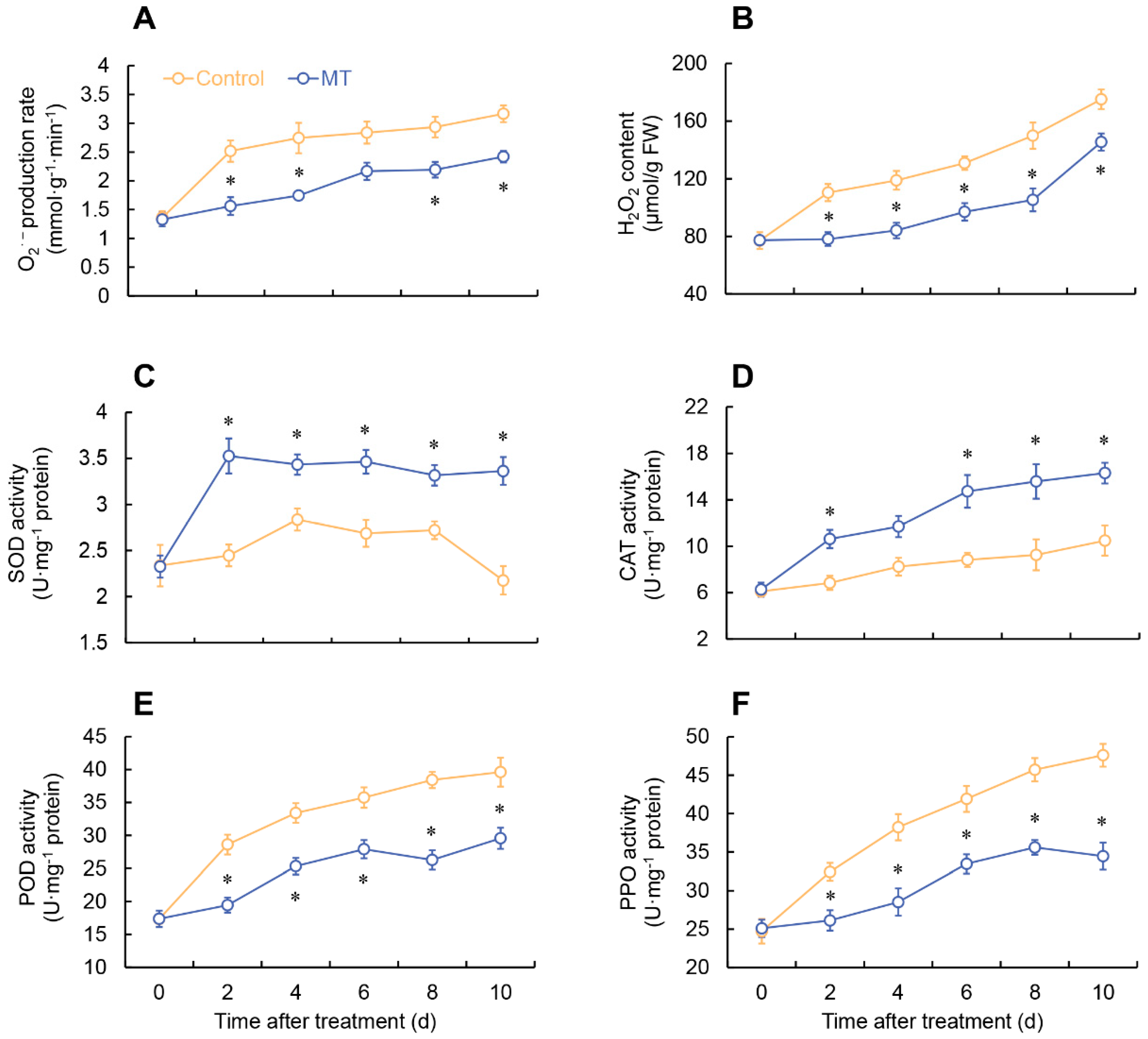
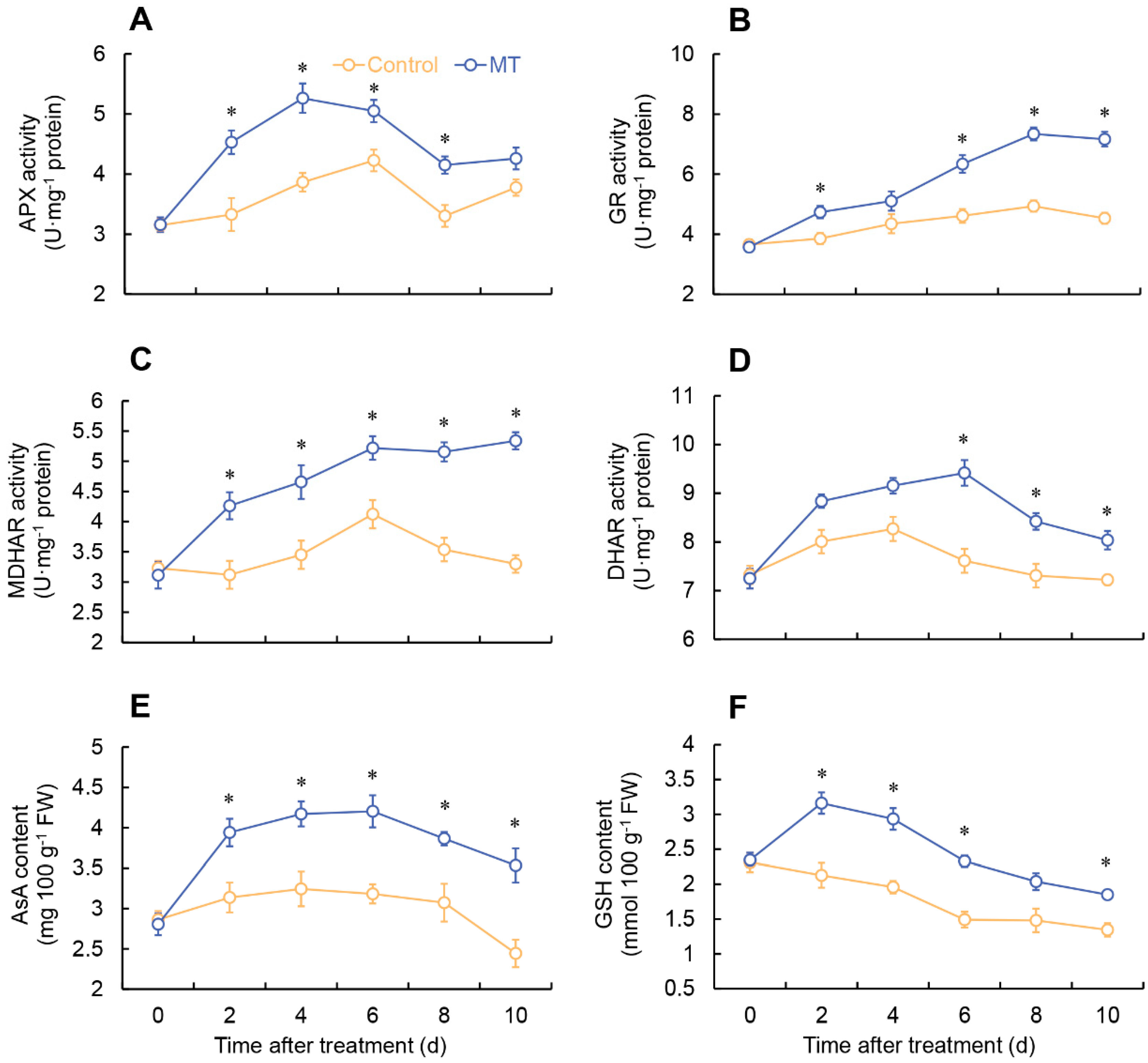
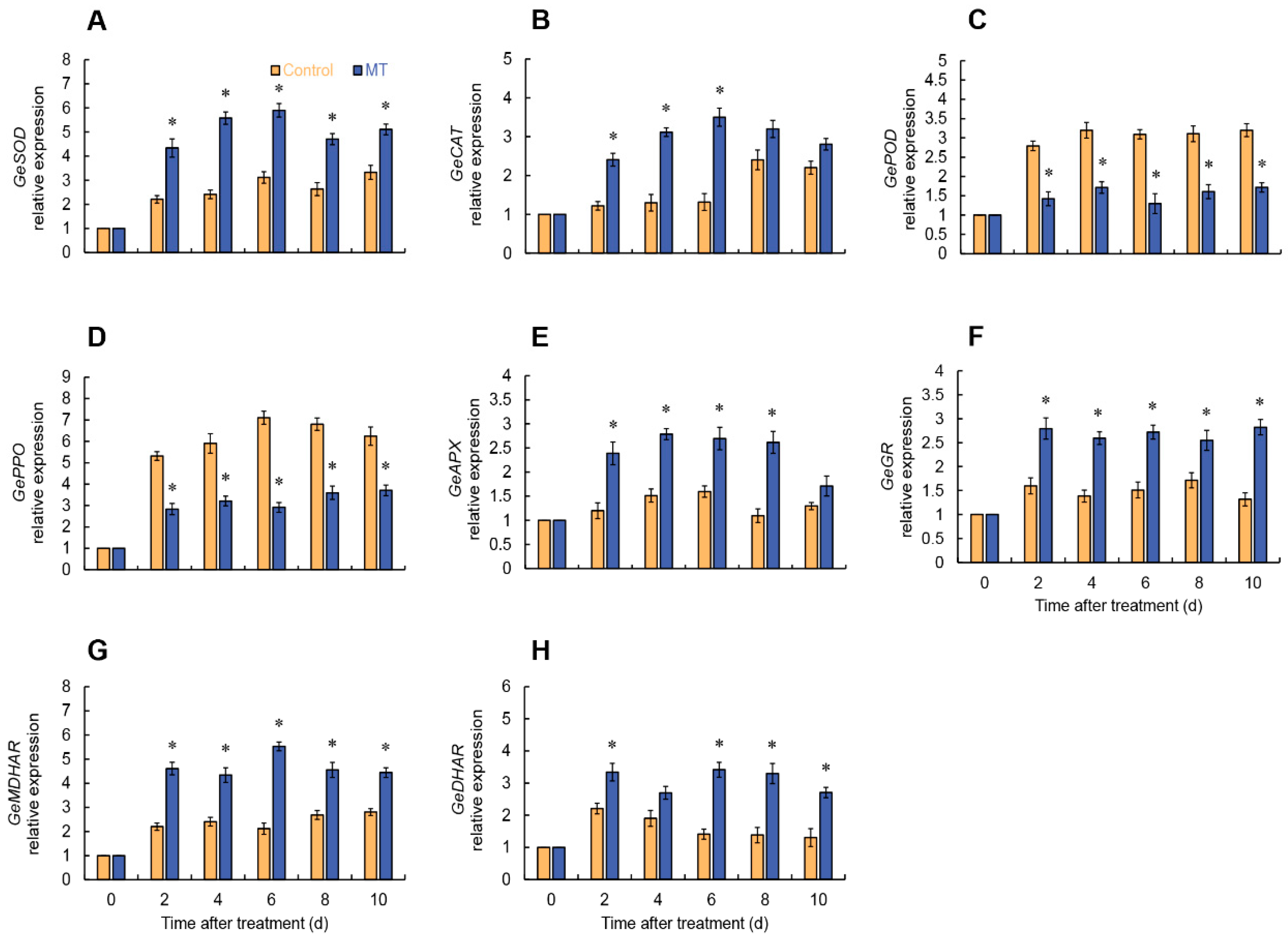
2.2. Effect of MT on ROS metabolism
2.3. Determination of AsA and GSH content
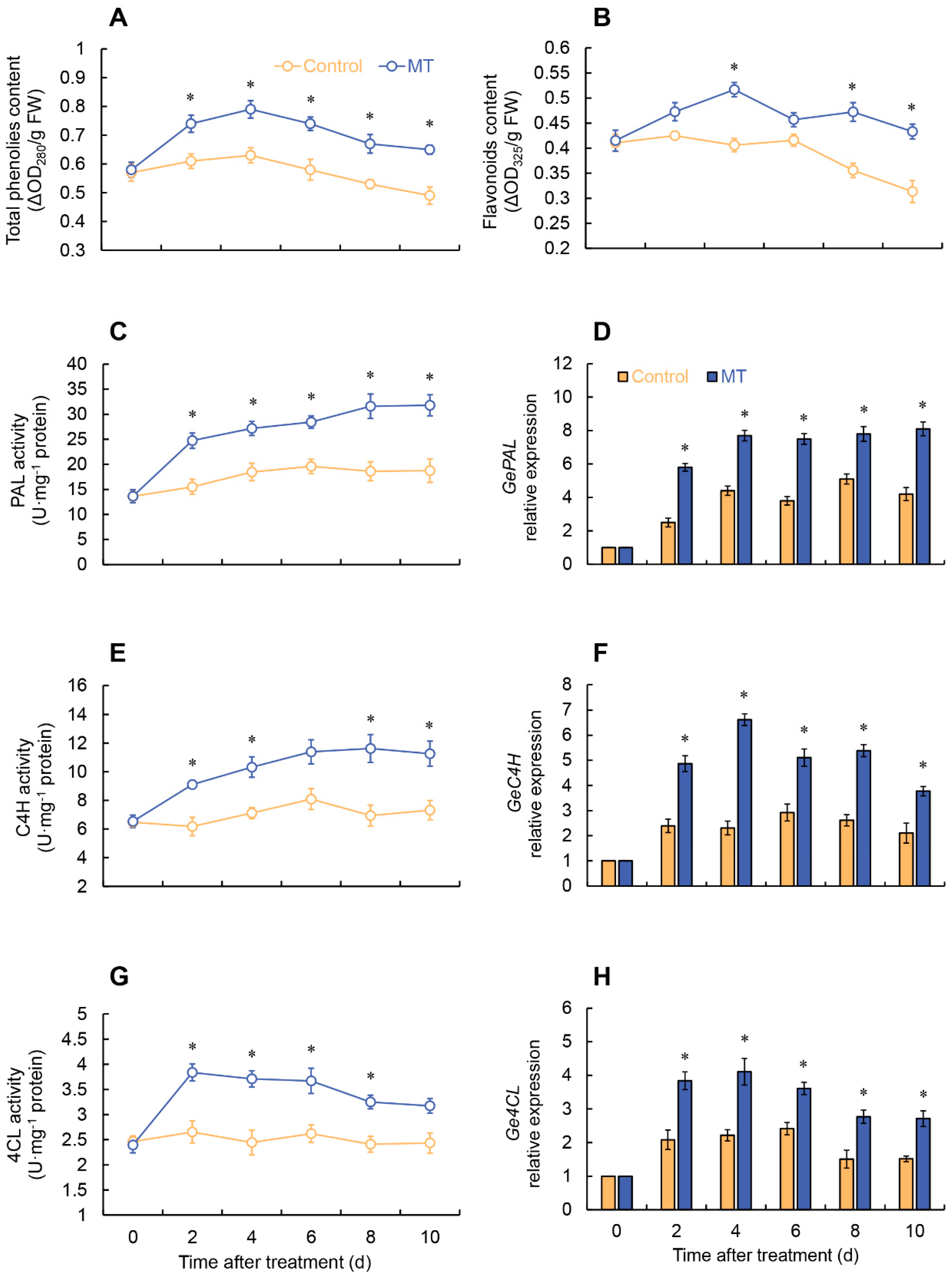
2.4. Effects of MT treatment on total phenolic and flavonoid contents
2.5. Effect of MT on phenylpropanoid pathway
2.6. Gene expressions of ROS metabolism of fresh-cut G. elata
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fruit and treatment
4.2. Determination of weight loss, respiratory rate, TSS, TA and MDA
4.3. Assays for ROS production and the activity of antioxidant scavenging enzymes.
4.4. Activities of POD and PPO
4.5. Determination of AsA and GSH content
4.6. Analysis of the Metabolite Content in the Phenylpropanoid Pathway
4.7. Activities of key enzymes in phenylpropanoid metabolism
4.8. Determination of gene expression
4.9. Data analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding and Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cui, X.; Xiong, Y. Quality evaluation of Gastrodia elata tubers based on HPLC fingerprint analyses and quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker. Molecules 2019, 24, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Cui, X.; Xu, T.; Wan, F.; Yang, Y. Evaluate how steaming and sulfur fumigation change the microstructure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Gastrodia elata Bl. starch. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1087453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Tan, C.; Tang, X.; Chu, Z.; Min, J.; Luo, Y. Study on Quality Influence of Hot Air Drying and Heat pump drying of Xiaocaoba Gastrodia elata. J. Phy. Confere. Ser. 2020, 4, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Lin, X.; Wei, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.N.; Chen, J. Melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence and maintains the organoleptic quality of ‘Newhall’navel orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) by inhibiting respiration and enhancing antioxidant capacity. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 286, 110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Li, C.; Ge, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, J. Exogenous application of melatonin maintains storage quality of jujubes by enhancing anti-oxidative ability and suppressing the activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 127, 109431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, S.; Huber, D.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, X.; Peng, J.; Zhu, S. Melatonin treatment affects wax composition and maintains storage quality in ‘Kongxin’Plum (Prunus salicina L. cv) during postharvest. Foods 2022, 11, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Guo, M.; Liu, J.; Ge, Y. Postharvest melatonin dipping maintains quality of apples by mediating sucrose metabolism. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2022, 174, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, S.; Chen, X. Melatonin alleviates chilling injury and maintains postharvest quality by enhancing antioxidant capacity and inhibiting cell wall degradation in cold-stored eggplant fruit. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2022, 194, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.; Duan, B.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J. Effect of sodium nitroprusside on antioxidative enzymes and the phenylpropanoid pathway in blueberry fruit. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Chen, M.; Lin, M.; Lin, H. Enhanced storability of blueberries by acidic electrolyzed oxidizing water application may be mediated by regulating ROS metabolism. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Ge, Y.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Qin, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. G6PDH regulated NADPH production and reactive oxygen species metabolism to enhance disease resistance against blue mold in apple fruit by acibenzolar-S-methyl. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2019, 148, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wei, M.; Ge, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J. Methyl jasmonate maintained antioxidative ability of ginger rhizomes by regulating antioxidant enzymes and energy metabolism. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Y. Postharvest application of acibenzolar-S-methyl delays the senescence of pear fruit by regulating reactive oxygen species and fatty acid metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4991–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Duan, B.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, M.; Li, J. γ-Aminobutyric acid delays senescence of blueberry fruit by regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, C.; Duan, B.; Li, X.; Wei, M.; Li, J. Acibenzolar-S-methyl treatment enhances antioxidant ability and phenylpropanoid pathway of blueberries during low temperature storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 110, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Fu, X.; Zhao, X.; Min, D.; Zhang, X. Hot air pretreatment alleviates browning of fresh-cut pitaya fruit by regulating phenylpropanoid pathway and ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2022, 190, 111954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, A.; Li, J.; Zong, W. Mild heat treatment inhibits the browning of fresh-cut Agaricus bisporus during cold storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Min, D.; Li, F.; Li, X. Methyl salicylate pretreatment maintains quality and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut pitaya fruit by modulating phenylpropanoid metabolism and antioxidant system. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 309, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Ji, N.; Jin, P.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, F. Cold plasma treatment induces phenolic accumulation and enhances antioxidant activity in fresh-cut pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) fruit. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 115, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Tian, M.; Jiang, A. Ascorbic acid treatment inhibits wound healing of fresh-cut potato strips by controlling phenylpropanoid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2021, 181, 111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wei, M.; Li, C.; Hou, J.; Chen, J. Postharvest sodium nitroprusside treatment maintains storage quality of apple fruit by regulating sucrose metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2019, 154, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.L.; Fan, Z.Q.; Zeng, Z.X.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.F.; Lu, W.J.; Zhao, Y.T. Exogenous melatonin maintains leaf quality of postharvest Chinese flowering cabbage by modulating respiratory metabolism and energy status. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2021, 177, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nawaz, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, T.; Xu, T. Exogenous melatonin attenuates post-harvest decay by increasing antioxidant activity in wax apple (Syzygium samarangense). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 569779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, H.; Shi, J.; Neethirajan, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y. Effects of a novel chitosan formulation treatment on quality attributes and storage behavior of harvested litchi fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Du, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X. Exogenous nitric oxide improves chilling tolerance of Chinese cabbage seedlings by affecting antioxidant enzymes in leaves. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2014, 55, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Younas, S.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, L. Melatonin immersion affects the quality of fresh-cut broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) during cold storage: Focus on the antioxidant system. J. Food Process. Pres. 2020, 44, e14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Q. Exogenous melatonin delays postharvest fruit senescence and maintains the quality of sweet cherries. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Pareek, S.; Mani, S.; Domínguez-Avila, J.A.; González-Aguilar, G.A. A melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence, maintains quality, reduces chilling injury, and regulates antioxidant metabolism in mango fruit. J. Food Quality, 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Torres, C.; Feriche-Linares, R.; Rodríguez-Ruíz, M.; Palma, J.M.; Corpas, F.J. Arsenic-induced stress activates sulfur metabolism in different organs of garlic (Allium sativum L.) plants accompanied by a general decline of the NADPH-generating systems in roots. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 211, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cang, J.; Lu, Q.; Fan, B.; Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, X. ABA enhanced cold tolerance of wheat ‘dn1’via increasing ROS scavenging system. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1780403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.S.; Moradi, M.; Razavi, F.; Rabiei, V. Exogenous phenylalanine application promotes chilling tolerance in tomato fruits during cold storage by ensuring supply of NADPH for activation of ROS scavenging systems. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.S.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; Jannatizadeh, A.; Fard, J.R.; Pirzad, F. Melatonin treatment maintains nutraceutical properties of pomegranate fruits during cold storage. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Kitazawa, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, S. Melatonin retards senescence via regulation of the electron leakage of postharvest white mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, M.; Zhu, J.; Ge, Y.; Sun, T. Postharvest application of acibenzolar-S-methyl delays the senescence of pears by mediating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xiong, T.; Lei, Q.; Tan, Q.; Cai, J.; Song, Z.; Zhu, X. Melatonin treatment improves postharvest preservation and resistance of guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.). Foods 2022, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Li, Q.; Feng, S.; Lei, Q.; Abbas, F.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, X. Melatonin maintains fruit quality and reduces anthracnose in postharvest papaya via enhancement of antioxidants and inhibition of pathogen development. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z. Ozone treatment promotes physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut red pitaya based on phenolic metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1016607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Antolí, A; Martínez-Romero, D.; Guillén, F.; Zapata, P.J.; Serrano, M.; Valero, D. Melatonin pre-harvest treatments leads to maintenance of sweet cherry quality during storage by increasing antioxidant systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shen, S.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, X. Melatonin treatment inhibits gray mold and induces disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit during postharvest. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2019, 157, 110962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, C.; Deng, H.; Hu, L.; Dong, B. Effect of postharvest acibenzolar-S-methyl dipping on phenylpropanoid pathway metabolism in muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 168, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Wu, W.; Ba, L.; Ma, C.; Ji, N.; Cao, S. Melatonin enhances the postharvest disease resistance of blueberries fruit by modulating the jasmonic acid signaling pathway and phenylpropanoid metabolites. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 957581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; Hu, M.; Yun, Z.; Duan, X.; Jiang, G. Inhibition of downy blight and enhancement of resistance in litchi fruit by postharvest application of melatonin. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafi, Y.; Aghdam, M.S.; Luo, Z.; Jannatizadeh, A.; Razavi, F.; Fard, J.R.; Farmani, B. Melatonin treatment promotes endogenous melatonin accumulation and triggers GABA shunt pathway activity in tomato fruits during cold storage. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 254, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Cao, M.; Cao, W. Melatonin treatment reduces chilling injury in peach fruit through its regulation of membrane fatty acid contents and phenolic metabolism. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, F.; Xiao, S.; Duan, X. BTH treatment delays the senescence of postharvest pitaya fruit in relation to enhancing antioxidant system and phenylpropanoid pathway. Foods 2021, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhu, D.; Yao, Q.; Tang, H.; Ding, X. Hydrogen-rich water treatment maintains the quality of Rosa sterilis fruit by regulating antioxidant capacity and energy metabolism. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 161, 113361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



