1. Introduction
Coagulation and flocculation are important preliminary steps in wastewater and potable water treatment facilities. The processes include the removal of non-dissolved and particulate matter, including algae, pathogens, organic materials, minerals, and others by the addition of materials such as ferric chloride, alum (aluminum sulfate), or organic polymers, which destabilize the colloids resulting in small suspended particles agglomerating into larger settleable flocs [
1]. Poly-diallyl-dimethylammonium chloride (poly-DADMAC, PD, CAS 26062-79-3) is a homopolymer also known as polyquarternium-6, with a chemical formula of (C
8H
16NCl)
n (
Figure 1). In commercial formulations its molecular weight ranges usually between a few to several hundreds of kDa, depending on the number of monomers (each of them with a molecular weight of 161.7 Da) [
2]. PD is the most common polymer for various coagulation processes [
3], including in pulp and paper industry alone [
4] or combined with other polymers [
5]. It was the first cationic polyelectrolyte approved by the Food and Drug Administration of the U.S.A (FDA) for use in potable water treatment [
6]. Recent studies also test its influence when adsorbed on cellulose based products [
7] or for the preparation of specific adsorbing matrices for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances [
8].
The wide use of PD and other organic polymers is attributed to their advantages which encompass their exceptional cationic properties, high charge density resulting in stronger and easy-to-separate flocs, effective bridging capabilities that enable higher solid content in the sludge phase, and minimal impact on pH levels requiring only one adjustment of pH during the process. However, a few disadvantages are associated with the use of PD as a coagulant, mainly regarding the residuals remaining after the process. Remaining polymers of the coagulation/flocculation pretreatment might cause severe fouling for filtration membranes [
9], especially in reverse osmosis, micro- and nanofiltration, even at very low concentrations. Fouling depends on the type, charge, size, and concentration of the polymer, and higher molecule-weight polymers have larger fouling potential [
10,
11]. An additional disadvantage is the reaction of residual PD with disinfection by-products such as chloramine and ozonation, forming carcinogenic nitrosamines [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. Therefore, several American and European standardization organizations have limited the residual amount of PD in drinking water at ≤50μg/L ~ 0.310 µM, which is considered to be also toxic to aquatic organisms [
17].
For those reasons, fast and simple quantification of residual PD is required at relatively low limits of detection (LOD), to control and monitor the optimal coagulant dose with minimal negative effects. Chromatography-based analytical methods for quantification of polymers are usually very sensitive to interferences by other organic molecules [
18]. Indeed, a recent study presents a method based on ion-pair chromatography, that accurately measures residual DADMAC monomers [
19] without measuring the amounts of the polymer. Other accurate methods such as gel permeation chromatography, epoxidation, fluorescent tagging, and co-precipitation required advanced, expensive, and long procedures [
2,
3,
20,
21,
22,
23]. A very sensitive method was developed based on the use of gold nanoparticles [
24], applied in South African treated water [
25] and recently developed to Lovibond color filters [
26], but the preparation of the nanoparticles requires a relatively complicated procedure.
Cationic polyelectrolytes such as PD bind to anionic molecules such as tannic acid, or anionic dyes such as rose Bengal, methyl-orange [
20], Ponceau S [
27], and acid orange [
28] resulting in an insoluble polymer-anion complex that can be precipitated by centrifugation, allowing quantification of the polymer concentration by measuring the remaining dye. A similar method was used for quantification of the cationic biopolymer chitosan, based on complexation with Cibacron Brilliant Red 3B-A [
29]. However, in all those studies LODs were two to three orders of magnitude higher than the requirement.
In this study we present a simple colorimetric quantification method based on addition of fast green (
Figure 1, FG, ethyl-[4-[[4-[ethyl-[(3-sulfophenyl) methyl] aminophenyl]- (4-hydroxy- 2-sulfophenyl) methylidene]-1-cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene]-[(3-sulfophenyl)methyl]azanium), and its complexation with PD. FG is an anionic tri-aryl methane food dye known also as “food green 3”, “green 1724” and “E143”. It is stable in a wide range of pH, and has a brilliant blue-green color with an absorption maximum at 624nm, and two additional smaller absorption bands at 420 and 304 nm [
30]. The very high molar absorptivity (e
624>100000 M
-1cm
-1) enables high sensitivity and yields a procedure suitable for trace quantification of PD with LOD<3 µg L
- 1 (0.018 µM)- one order of magnitude lower than regulation requirements. The primary objective of this research was to establish the proof of concept for the proposed quantification method in a simple, fast, and cost-effective manner, and test it under different conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Analytical polydiallyl dimethylammonium chloride (PD; medium molecular weight, 200.000 to 350.000) and fast green (FG) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Israel). Commercial grade coagulant with 40% PD as an active ingredient manufactured by SNF Ltd. (FLOQUAT® FL-45) was purchased from Amgal-Depotchem Ltd. (Beer Tuvia, Israel). NC24 clay polymer nanocomposites was prepared as described in the literature [
31,
32,
33] using 10 g/L sepiolite S9 provided by Tolsa S.A. (Madrid, Spain), and 45 g/L FL-45. DKG kaolinite clay polymer nanocomposites [
34] were prepared in a similar way, using 10 g/L MPO kaolinite provided by Agat Minerals and Yehu Clays Ltd (Israel) and 45 g/L FL-45.
2.2. Complexation/calibration experiments description
In order to prepare calibration curves and demonstrate the method’s applicability, several complexation experiments were conducted, including a wide range of analytic poly-DADMAC with fast green dye. Three separate experiments were performed for low, medium, and high analytic PD concentrations. The low, medium, and high PD ranges included 0.01-1, 1-30, and 10-200 µM (0.01617-0.1617, 0.1617-4.851 and 1.617-32.34 mg L-1) PD solutions respectively, dissolved in double-distilled water. To each PD range, 0.8, 20, and 100 µM of FG were added to the solutions in the low, medium, and high series respectively. After the addition of FG, pH values were adjusted to 3-3.5 by adding 20 µl of 1 mM HCl (see section 2.4), and all samples were kept at room temperature (23 ± 1 °C) on an orbital shaker (200 rpm) for 1 h. FG spectra were measured using a 1 cm cuvette in a Cary 60 UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and absorbance was determined using the absorption bands at 624 and 420nm with a molar absorptivity of 103500 and 11600 M-1cm-1 respectively. To increase the sensitivity, the low range FG absorbances were measured at 624 nm using 5cm cuvette.
2.3. Implementation in water with commercial PD
Commercial PD samples were examined in medium-range concentrations of 2-50 µM (0.323-8.085 mg L-1) PD dissolved in double-distilled water with the addition of 20 µM FG. FG spectra were measured in the UV–Vis spectrophotometer using a 1 cm cuvette as described in section 2.2.
2.4. Influence of pH
To test the influence of pH on FG chromophore and monitor changes in its spectrum, a series of 10 µM fast green solutions were prepared and the pH of each solution was adjusted by adding negligible volumes of high concentration HCl or NaOH. The final pH values varied from 2.24 to 9.13 and all the samples were scanned in the UV–Vis spectrophotometer as described in section 2.2.
2.5. Quantification of poly-DADMAC in coagulation water treatment samples
To evaluate the efficiency of the quantification method in "real" water samples, two coago-flocculation experiments were performed, in cyanobacteria polluted water, and in cowshed effluents. Experiments included testing commercial PD formulation, and clay-PD nanocomposites developed in our research group [
32,
33,
34]
The first coagulation experiment was performed on cyanobacteria culture suspension using concentrations of two poly-DADMAC-based coagulants: industrial PD and kaolinite-PD nanocomposites (DKG). The cyanobacteria suspension contained Microcystis family isolated from Lake Kinneret and grown in batch cultures in BG11 medium [
35] The experiments were carried out in 300 ml glass beakers and included two sets of PD and DKG coagulants. Each set contained five different coagulant concentrations: 14, 28, 42, 53, and 71µM PD present either in its free form or adsorbed onto kaolinite clay particles (as DKG coagulant). The coagulants were added to 250 ml cyanobacteria suspensions. After the addition, the suspensions were stirred thoroughly for 1 min and left to settle for 1 h.
The second coagulation experiment was performed on cowshed effluents. The wastewater was taken from Kfar Blum industrial cowshed (Upper Galilee, Israel) during July 2023. To determine the required amount of coagulant needed for neutalization [
36] the electrokinetic colloidal charge of the wastewater was measured in a particle charge detector (PCD) (BTG Mütek, PCD-05, Eclépens, Switzerland). Three poly-DADMAC-based coagulants were tested: commercial PD, kaolinite-PD nanocomposite (DKG), and sepiolite-PD nanocomposite (NC). The doses were equivalent to 100% of the requirement to neutralize the colloids (4.3 mM charges). The experiments were carried out in 300 ml glass beakers each treatment included 3 replicates. After the addition, the suspensions were stirred thoroughly for 1 min and left to settle for 1 h.
In both experiments, turbidity was measured with a LaMotte 2020i turbidimeter before and after the treatment to estimate the clarification and coagulation efficiency. The residual PD concentrations were quantified using the complexation method as described section 2.2: 10 ml supernatant were sample, pH values were adjusted to 3-3.5 by adding 20 µl of 1 mM HCl. Subsequently, suitable volumes of FG from a 1000 µM stock solution were added to each samples yielding FG concentration of 20 µM. Test tubes were kept on an orbital shaker (200 rpm) for 1 h, and samples measured in the spectrophotometer as described in section 2.2.
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of analytical poly-DADMAC concentrations
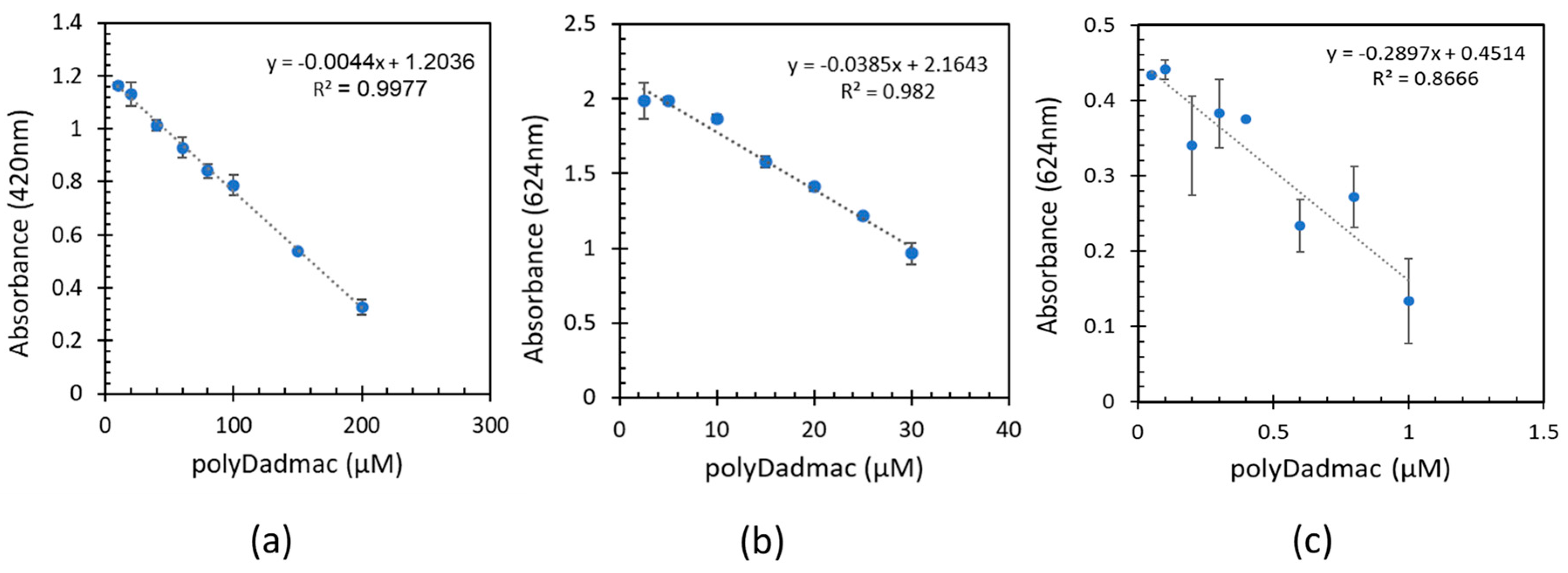
As mentioned in section 2.2., three separate calibration experiments were conducted to quantify PD at different concentration levels: low, medium, and high. Each range included addition of different FG concentrations. The quantification method is based on the measurement of free fast-green molecules in the solution, according to its distinct absorption bands at wavelengths 420 and 624 nm.
Figure 2 show the measured absorbance values in specific wavelengths as a function of the known PD concentrations. To increase sensitivity at the medium and low PD range, the selected wavelength was 624nm. To avoid the need of dilutions at the high range the 420nm
(with lower molar absorptivity
) was selected. Linear regression calculations between the absorbance and the PD concentrations were performed for all three ranges (see
Figure 2), and excellent correlation (R
2>0.982) was observed for the high and medium range (1-200 µM, 0.1617-32.4 mg L
-1). According to the results, the absorbance values decrease as the PD concentration increase, indicating the formation of a PD-fast green complex that decreases the available fast green molecules in solution. This inverse relationship between dye absorbance and PD concentration forms the basis for the quantitative analysis of PD using the complexation with the FG dye, similarly to the effect seen in the chitosan quantification method [
29]. The relatively low R
2 (R
2=0.866) for the 0.01-1 µM PD range is ascribed to the increase to measurement noise and experimental variability at such low concentration levels.
As a confirmation step the need for removing the PD-fast green complex from the solution by centrifugation was tested: Centrifugation of the samples was performed at 3000 rpm for 20min, followed by spectrophotometer measurements. According to the results, centrifugation of the mixture solution after complexation did not affect the absorbance values (data not shown).
3.2. Influence of pH
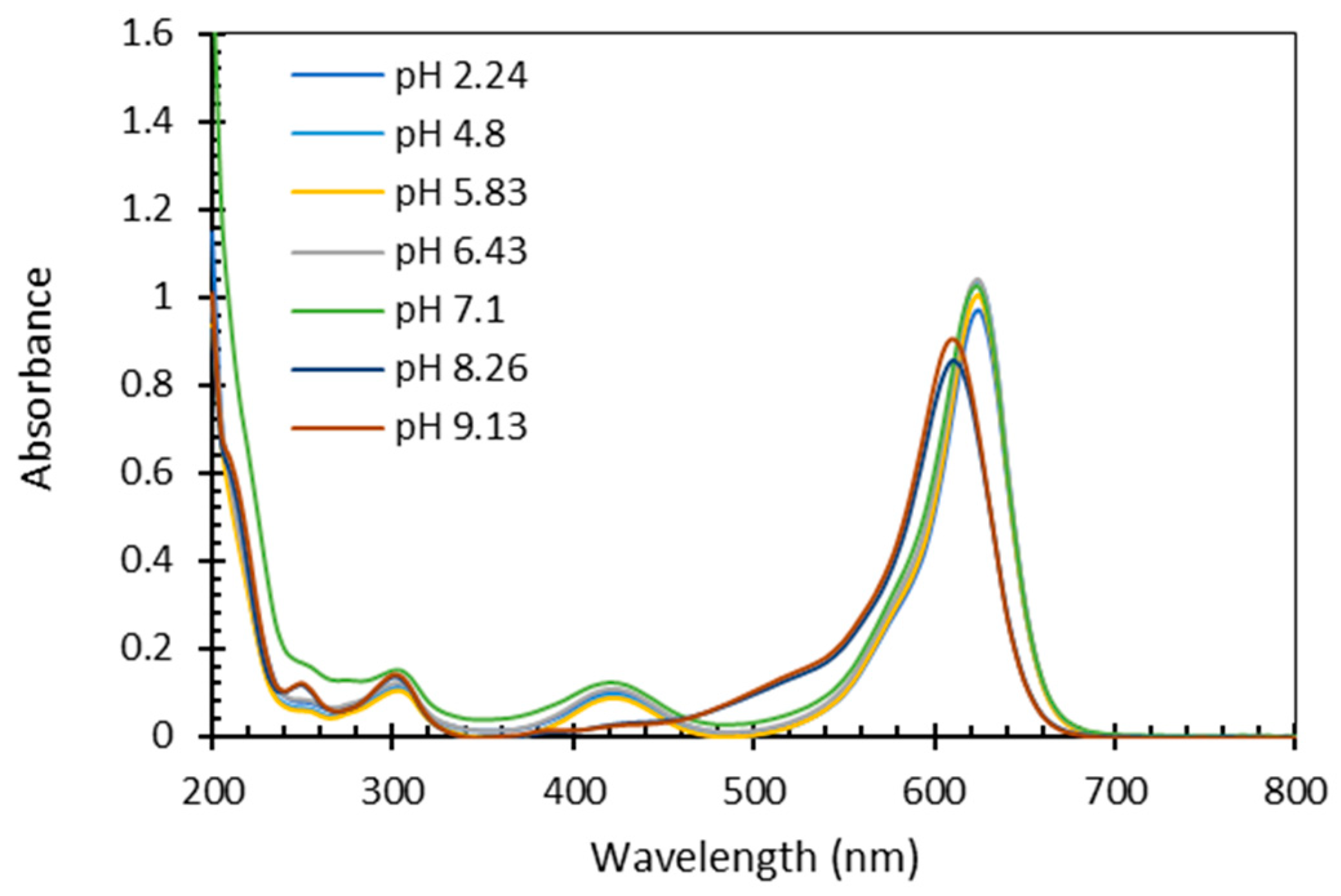
Considering accuracy of spectroscopy measurements depends on the stability of the spectrum measured, we tested the influence of pH on FG spectra. Absorbance spectrum of FG was measured at different pH values ranging from 2 to 9.1 (
Figure 3). According to the results, within pH range of 2 to 7, the spectrum of FG remained constant, with no changes in the molar absorptivity at any wavelength, indicating no significant changes in the chromophore along these acidic to neutral pH levels. However, as the pH increased above 7, the spectrum demonstrated a clear deviation. from the constant trend observed in the acidic to neutral pH range: The large absorption band at 624 nm shifts hypsochromically (to lower wavelenghts), and molar absorptivity slightly increases, while the absorption band at 420 nm dissappears. These findings are crucial to determine the pH requirements and limitations relevant when applying the quantification method presented hereby, and highlight the importance of pH control to a range of 2-7 during the analysis process. In our study, in all samples before measuring the spectrum, pH was adjusted to 3-3.5 by adding very small volumes of HCl.
3.3. Quantification of commercial poly-DADMAC
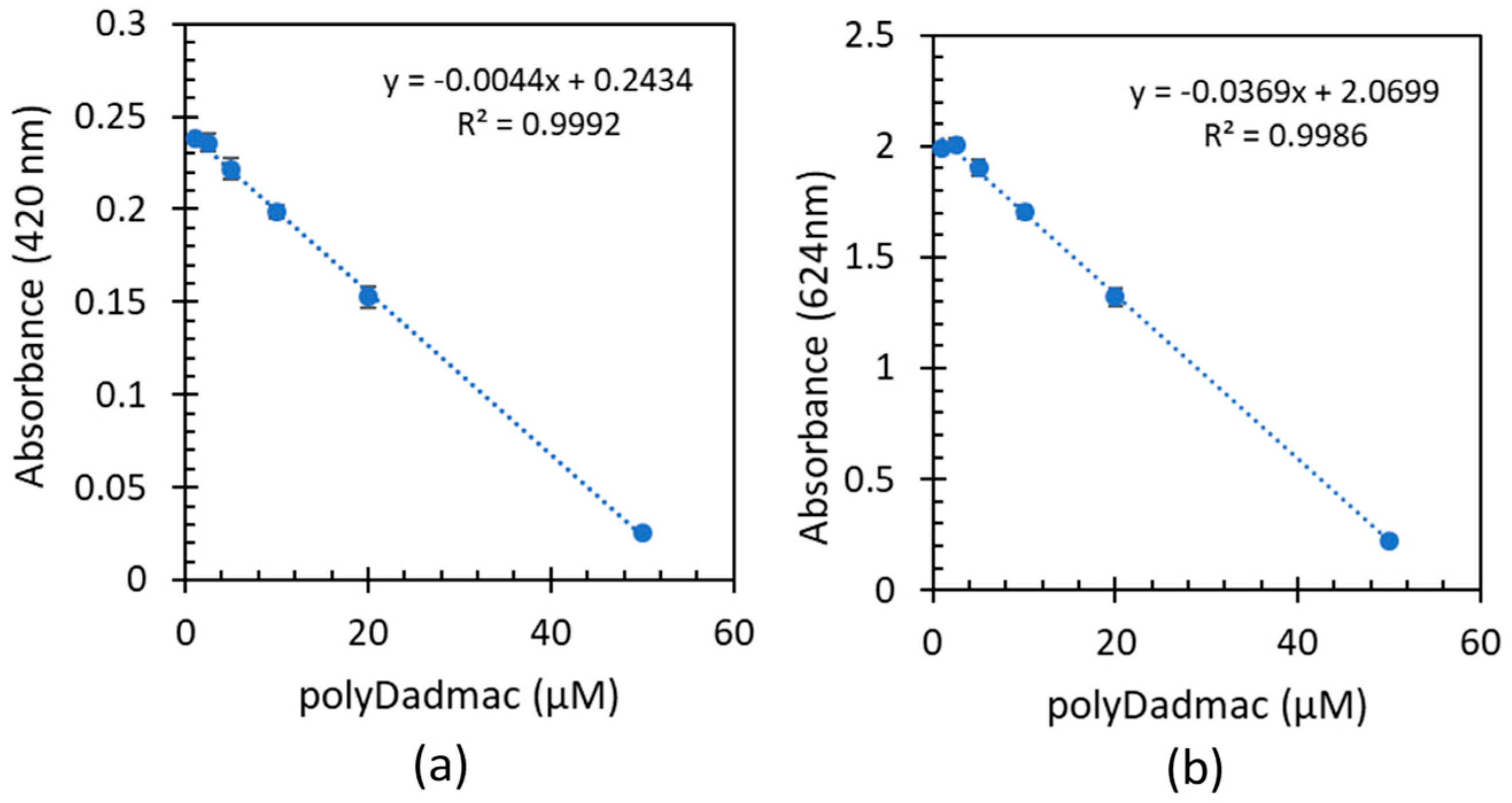
Complexation experiments were conducted with commercial PD in a range of 1-50 µM polymer concentrations, with the addition of 20 µM FG according to the medium range presented in section 3.1.
Figure 4 shows absorbance of the remaining dye as a function of commercial PD concentrations, after the formation of the complexes at 420 (
Figure 4a) and 624 nm (
Figure 4b). All samples were acidified with 20 µl of 1mM HCl to ensure spectrum is not shifted due to high pH (as described in section 3.2). Full spectra of commercial PD samples after complexation with FG is shown in
Figure S1 in the Supplementary Material. To verify the similarity of the measured spectra to that of FG, Pearson's correlation of all spectra with FG in the range 300-800 nm was evaluated using CORREL function in Excel©, yielding R>0.993.
As in the results with analytical PD (
Figure 2), a consistent decreasing linear behavior between the absorbance and PD concentration with very high R
2 values for both wavelengths (0.9992 and 0.9986 for 420 and 624nm respectively) is observed. It is interesting to notice from the linear regression equations in
Figure 2b &
Figure 4b, that both intercept and slopes are very similar. Furthermore, the slope in
Figure 2a and
Figure 4a are identical, although intercept differs due to the different FG concentrations. These findings highlight the applicability of the complexation method in quantifying commercial PD concentrations.
3.4. Quantification of poly-DADMAC in coagulation treatment samples
The applicability of the quantification method in "field conditions" was tested by estimating the residual PD concentrations in coagulation and clarification treatment for cyanobacteria-contaminated water and cowshed effluents.
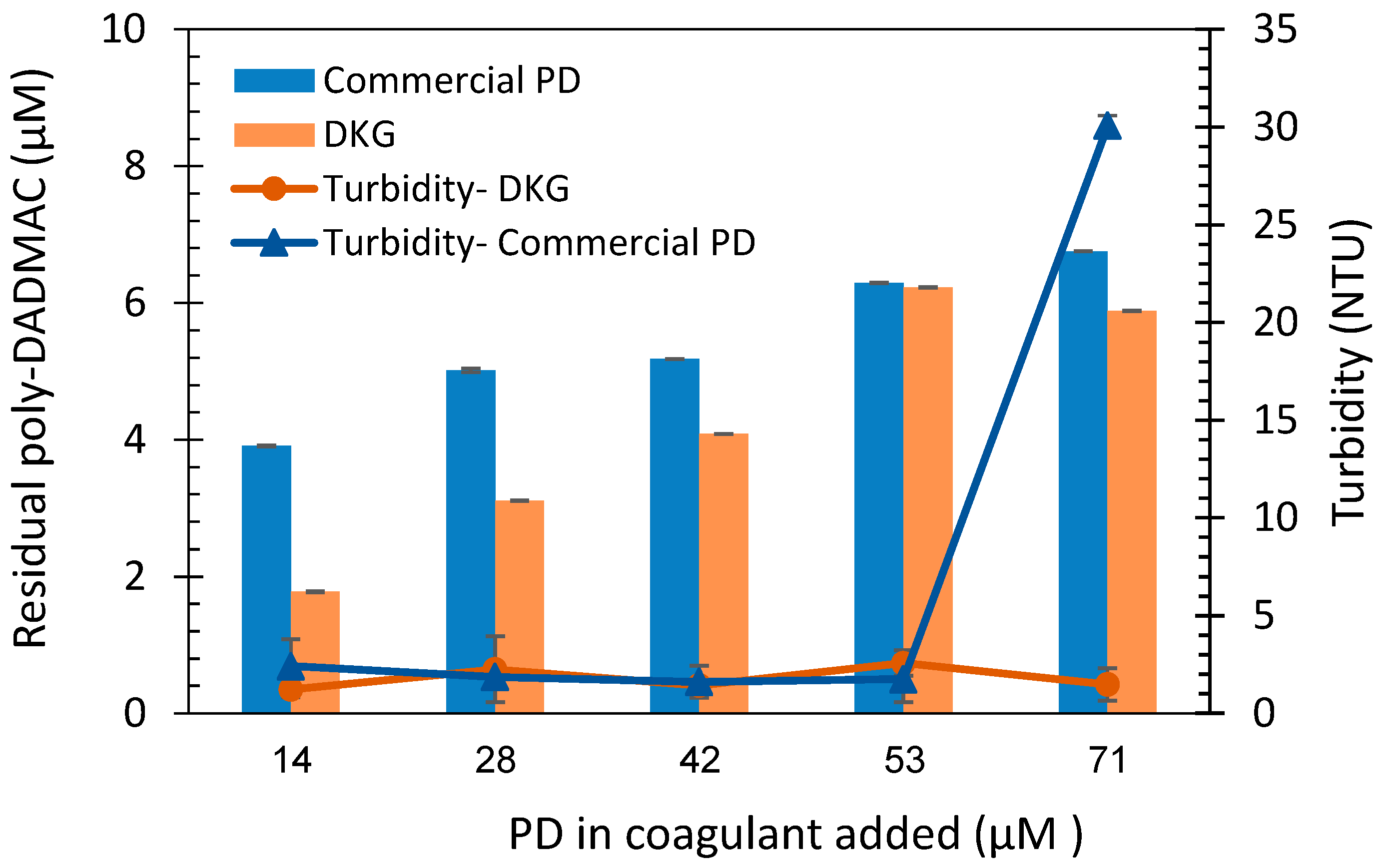
The cyanobacteria water samples were treated with commercial PD and kaolinite-PD nanocomposites (DKG). As mentioned in section 2.5, coagulants were added in amounts equivalent to the following PD concentrations: 14, 28, 42, 53, and 71µM (either in free form or adsorbed onto kaolinite clay particles). The initial turbidity value for the cyanobacteria suspension was 98.2± 3.67 NTU. After the addition of coagulants as described in section 2.5, the supernatants were sampled to 10 ml test tubes, acidified, and FG concentrated solution was added yielding an FG concentration of 20 µM was added. The absorbance was measured at 420nm, and residual PD concentration was evaluated using the calibration curve established in the previous section (
Figure 4). Residual PD concentrations and turbidity values are shown in
Figure 5. According to the measured results, very low turbidity is observed in all the range of added PD-kaolinite, and up to 53 µM of commercial PD, with a significant clear phase (about 90% of the volume) at the top of the vessels. However, increasing residual PD is clearly observed as the added amounts of coagulant increase. Furthermore, significant differences between the remaining PD concentrations were observed between the two coagulants, with lowest amounts of 1.9 and 4.1 PD µM for the nanocomposites and commercial PD, respectively. The relatively lower residual PD values remains for DKG samples are likely associated with the attachment of PD to the kaolinite clay particles, and the higher density of the clays, leading to increased precipitation of excessive coagulant materials. As the coagulant concentrations increased, no significant changes were observed in the turbidity values. However, higher turbidity was observed in the addition of 71 µM commercial PD indicating coagulant over-dose that disrupts the neutralization of the colloidal charge of the suspension [
36].
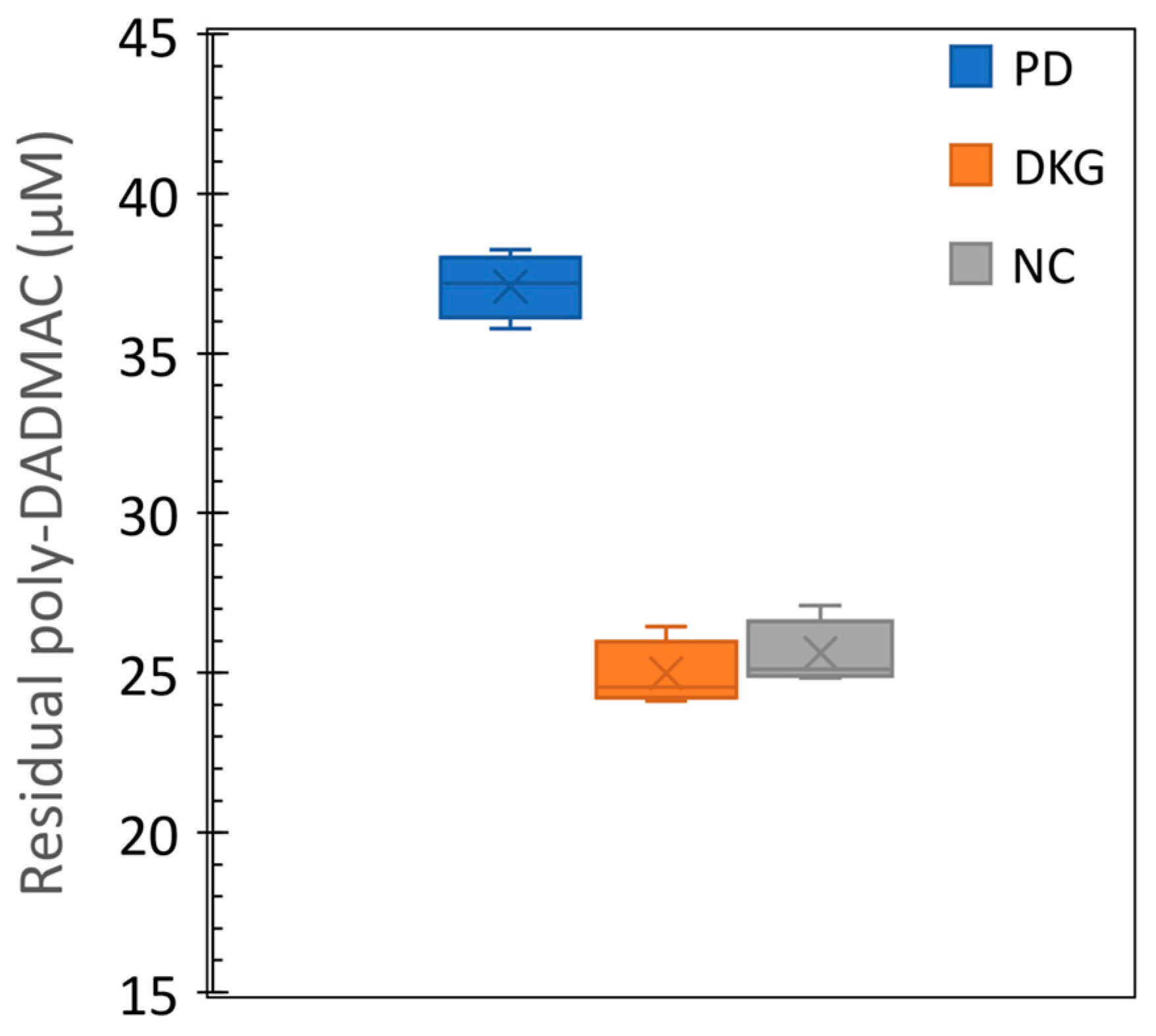
As an additional test for the method, clarification and coagulation was performed in cowshed effluents. Such effluents are heavily polluted with total suspended solid (TSS) values that may reach 10 g L
-1, and turbidity >4000 NTU [
37]. TSS removal is required as pretreatment, since wastewater treatment plants limit the maximum inflow value to <0.4 g L
-1 [
38]. In the samples collected at Kfar Blum cowshed during July 2023, the initial turbidity of the effluents was 3355 ±226 NTU. Optimal coagulant doses were determined by measuring the colloidal particle charge as described in section 2.5. After the coagulation process turbidity decreased to 1.2-4.5% of the initial values (77, 152, and 43 NTU in the kaolinite-PD, sepiolite-PD, and commercial PD coagulant treatments, respectively). The residual PD concentrations in the three treatments are presented in
Figure 6. As in the cyanobacteria-polluted effluents, residual PD was considerably lower in the clay-PD coagulants (~25 µM= ~4.04 mg L
-1) than in the commercial PD (37 µM= 5.98 mg L
-1), probably due to the high density of the clays and precipitation of excess coagulants.
Normalized spectra of cyanobacteria and cowshed water samples after treatment compared to spectrum of FG with commercial PD in clear water is presented in
Figure S2 of the Supplementary Material. FG spectrum in cyanobacteria sample is almost identical to clear water (Pearson's correlation in the range 300-800 nm= 0.999). On the other hand, FG in the cowshed effluents differs from clear water, (Pearson's correlation=0.938) due to remaining color and turbidity. However, limiting the range to 600-800 nm increases Pearson's correlation to 0.977 indicating that the differences do not interfere measuring absorbance at 624nm.
The results of both demonstration experiments emphasize the applicability of the method at real conditions, providing essential information regarding the optimal coagulation treatment in an easy, simple, and low-cost manner.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a colorimetric quantification method for poly-DADMAC through complexation with fast green dye was developed and evaluated.
The method exhibited high sensitivity with a detection limit of 0.02 µM (0.0032 mg L-1), meeting regulatory demands according to the world standard limitations.
Quantification experiments of analytical PD concentrations including low, medium, and high ranges demonstrated a linear correlation between the absorbance and PD concentrations.
The influence of pH on the quantification process was tested, revealing that the absorbance spectrum of FG remains unchanged within the pH range of 2 to 7, exhibiting an hypsochromic and hyperchromic shift at higher pH. Thus, acidification (or adequate pH measurements) step is necessary before quantification, to ensure FG spectrum is in the required range.
The quantification method's feasibility was demonstrated in coagulation experiments, estimating remaining PD concentrations in treated water samples.
The method's feasibility in estimating PD concentrations under "real" coagulation conditions highlights its potential for efficient monitoring and control of coagulation processes, offering a rapid, cost-effective, and sensitive tool for accurate measurement of PD concentrations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Spectra of an initial 20 µM FG upon complexation with the increasing concentrations of commercial PD; Figure S2: Normalized spectra of an initial 20 µM FG upon complexation with commercial PD in distilled water, cyanobacteria polluted water and cowshed effluents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.R.; methodology, G.R., I.L., B.C, and I.M.; software, I.L. and Y.K.; validation, G.R., I.L., and Y.K.; formal analysis, I.L.; investigation, G.R., I.L., B.C, and I.M.; resources, G.R.; data curation, I.L. and G.R..; writing—original draft preparation, G.R., I.L., and B.C..; writing—review and editing, I.L. and G.R.; visualization, I.L. and Y.K.; supervision, G.R.; project administration, G.R.; funding acquisition, G.R. All authors (except I.M. that deceased) have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by CSO-MOH (Israeli Ministry of Health), in the frame of the collaborative international consortium (REWA) financed under the 2020 AquaticPollutants Joint call of the AquaticPollutants ERA-NET Cofund (GA Nº 869178).
Data Availability Statement
All raw data are available from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to dedicate this manuscript to the memory of the late Ido Maor. The authors would like to thank the European Commission and AKA (Finland), CSO-MOH (Israel), IFD (Denmark) and WRC (South Africa) for funding in the frame REWA international consortium (additional details in “funding” paragraph). REWA is an integral part of the activities developed by the Water, Oceans and AMR JPIs. The authors are also thankful to the Mr. Yehezkel Zwecher for growing the cyanobacteria suspension, the whole team of the Hydrogeology and Examination of Soil Fertility Lab at MIGAL Research Institute.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Amuda, O.S.; Amoo, I.A. Coagulation/flocculation process and sludge conditioning in beverage industrial wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Görnitz, E.; Jaeger, W. Synthesis and characterization of poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) in a broad range of molecular weight. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1998, 199, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.S.; Bennett, D.; Bolto, B.; Dixon, D.; Eldridge, R.; Le, N.; Rye, C. Detection of polyelectrolytes at trace levels in water by fluorescent tagging. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 60, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.A.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, M.S.B.; Ariffin, A. Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater with various molecular weight of polyDADMAC induced flocculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, A.; Razali, M.A.A.; Ahmad, Z. PolyDADMAC and polyacrylamide as a hybrid flocculation system in the treatment of pulp and paper mills waste water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 179, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, M.J.A.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Forward osmosis for water recovery using polyelectrolyte PolyDADMAC and DADMAC draw solutions as a low pressure energy saving process. Desalination 2019, 453, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampl, C.; Schaubeder, J.; Hirn, U.; Spirk, S. Interplay of electrolyte concentration and molecular weight of polyDADMAC on cellulose surface adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.; Singh Kalra, S.; Johnson, N.W.; Khor, C.M.; Borthakur, A.; Cranmer, B.; Dooley, G.; Mohanty, S.K.; Jassby, D.; Blotevogel, J.; et al. Enhanced removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in complex matrices by polyDADMAC-coated regenerable granular activated carbon. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelich, C.J.; Ishida, K.P.; Bold, R.M. Testing of water treatment copolymers for compatibility with polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. Environ. Prog. 2005, 24, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Fouling of microfiltration membranes by organic polymer coagulants and flocculants: Controlling factors and mechanisms. Water Res. 2011, 45, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, H.; Shen, Y.; Liu, G.; Shi, W. Comparative analysis of membrane fouling mechanisms induced by colloidal polymer: Effects of sodium and calcium ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, H.; Kim, D.; Karanfil, T. Removal of wastewater and polymer derived N-nitrosodimethylamine precursors with integrated use of chlorine and chlorine dioxide. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Padhye, L.P.; Wang, P.; Cho, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Huang, C.-H. N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) formation potential of amine-based water treatment polymers: Effects of in situ chloramination, breakpoint chlorination, and pre-oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Wei, S.; Mizaikoff, B.; Taylor, A.E.; Favero, C.; Huang, C.H. Degradation of amine-based water treatment polymers during chloramination as N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Padhye, L.P.; Park, S.H. PolyDADMAC and dimethylamine as precursors of N-nitrosodimethylamine during ozonation. Water Qual. Technol. Conf. Expo. 2011 2011, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, A.J.; Fischer, N.; Donovan, S.; Bartlett, J.; Alrehaili, O.; Sinha, S.; Kommineni, S.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Purification and removal of the low molecular weight fraction of polyDADMAC reduces N -nitrosodimethylamine formation during water treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2492–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T Manickum Occurrence, Fate and Preliminary Environmental Risk Assessment of Residual Poly-Diallyldimethyl Ammonium Chloride, and Some Disinfection By-Products, in Treated (Potable), and Environmental, Waters in the Umgeni Water Catchment in Kwazulu-Natal. SM J. Public Heal. Epidemiol. 2017, 3.
- Al Momani, F.A.; Örmeci, B. Measurement of polyacrylamide polymers in water and wastewater using an in-line UV-vis spectrophotometer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gaudio, F.; Barreca, S.; Orecchio, S. Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride (DADMAC) in Water Treated with Poly-Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride (PDADMAC) by Reversed-Phase Ion-Pair Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2023, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, W. Synthesis, properties and analysis of polydadmac for water purification. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mwangi, I.W.; Ngila, J.C.; Ndungu, P.; Msagati, T.A.M. Method Development for the Determination of Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride at Trace Levels by Epoxidation Process. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, I.W.; Catherine Ngila, J.; Ndungu, P.; Msagati, T. Preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of polyDADMAC in treated water by in situ co-precipitation with naphthalene. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2014, 72–75, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, I.; Ngila, J.; Ndungu, P. A new spectrophotometric method for determination of residual polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride flocculant in treated water based on a diazotization-coupled ion pair. Water SA 2012, 38, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, B.; Ngila, J.C.; Ndungu, P.G. Gold nanoparticles for the quantification of very low levels of poly-diallyldimethylammonium chloride in river water. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickum, T.; John, W.; Toolsee, N.; Rajagopaul, R. Preliminary Performance Evaluation of the Gold Nanoparticle Method for Quantification of Residual Poly-(Diallyldimethyl Ammonium Chloride) in Treated Waters in the Umgeni Water Catchment, Kwazulu-Natal (South Africa). Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2015, 06. [Google Scholar]
- Magubane, S.E.; Ntlhoro, S.; Sabela, M.; Kanchi, S.; Mlambo, M.; Onwubu, S.C.; Mdluli, P.S.; Inamuddin; Asiri, A.M. Novel on-site residual screening of poly-diallyldimethylammonium chloride in treated potable water using gold nanoparticle based lovibond color filters. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 101, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majam, S.; Thompson, P.A. Polyelectrolyte determination in drinking water. Water SA 2006, 32, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilak Kumar, R.; Umamaheswari, S. FTIR, FTR and UV-Vis analysis of carbamazepine. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelovits, A.; Prat, T.; Gonen, Y.; Rytwo, G.; Rytwoa, G. Improved colorimetric determination of chitosan concentrations by dye binding. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, N.; Murugadoss, G.; Mohamed, A.A.A.; Kumar, M.R.; Peera, S.G.; Sakthivel, P. A Novel Nanocomposite Based on Triazine Based Covalent Organic Polymer Blended with Porous g-C3N4 for Photo Catalytic Dye Degradation of Rose Bengal and Fast Green. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Lavi, R.; Rytwo, Y.; Monchase, H.; Dultz, S.; König, T.N. Clarification of olive mill and winery wastewater by means of clay-polymer nanocomposites. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytwo, G. The Use of Clay-Polymer Nanocomposites in Wastewater Pretreatment. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytwo, G. Hybrid Clay-Polymer Nanocomposites for the Clarification of Water and Effluents. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 11, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytwo, G. US20190152813 Method for production of potable water 2019.
- Sukenik, A.; Beardall, J.; Hadas, O. Photosynthetic characterization of developing and mature akinetes of Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanoprokaryota). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Lavi, R.; König, T.N.; Avidan, L. Direct Relationship Between Electrokinetic Surface-charge Measurement of Effluents and Coagulant Type and Dose. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2014, 1, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Malka, H. A pilot plant for the treatment of cowshed efflFuents. Water Irrig. 2013, 530, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Inbar, Y. New Standards for Treated Wastewater Reuse in Israel. In Proceedings of the Wastewater Reuse--Risk Assessment, Decision-Making and Environmental Security; Zaidi, M.K., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2007; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).