Submitted:
21 August 2023
Posted:
23 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
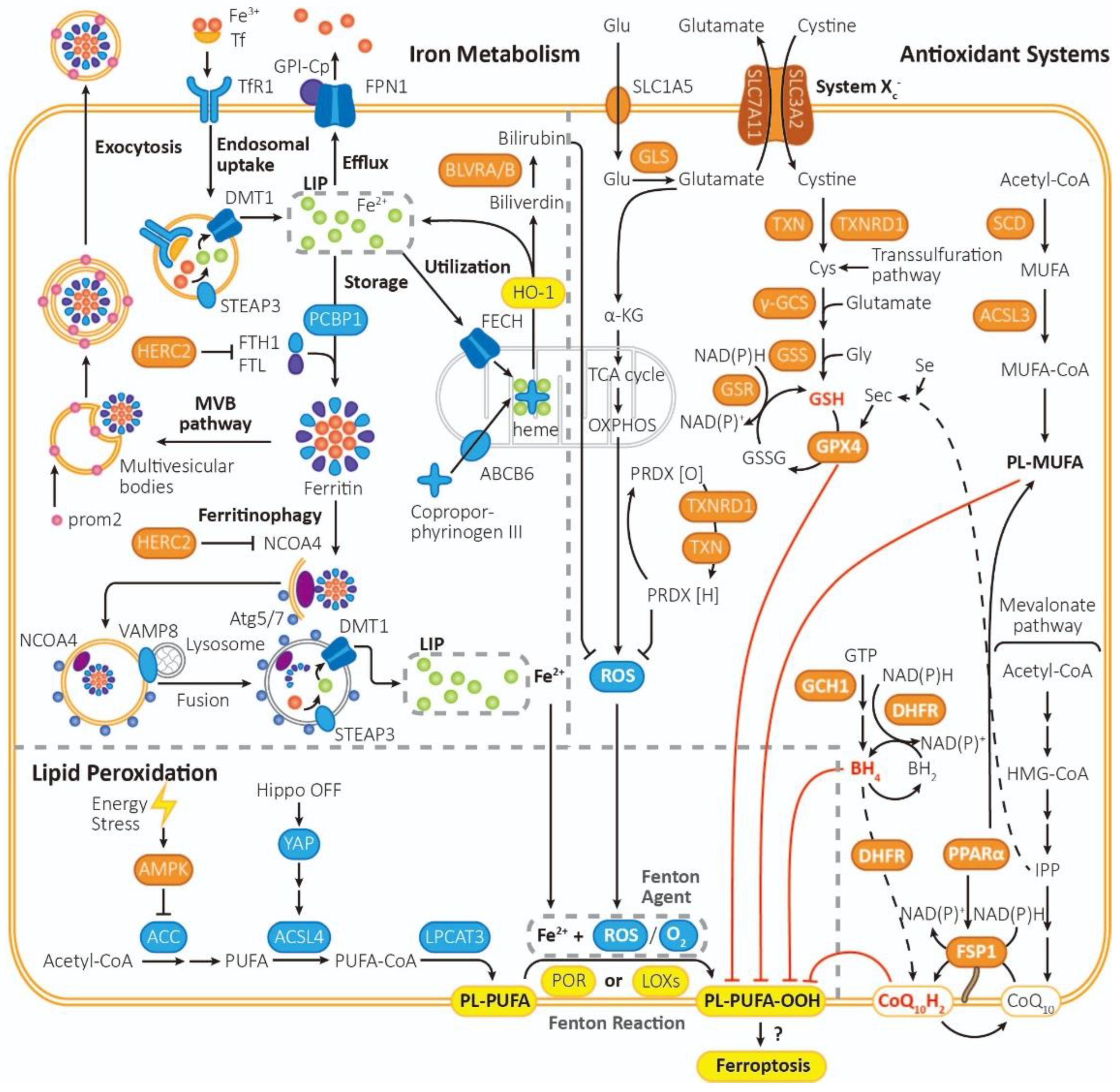
2. Ferroptosis
2.1. Processes that promote ferroptosis
2.1.1. LIP (liable iron pool): Iron drive lipid peroxidation with the aid of ROS
2.1.2. Run-out mitochondrial respiration boosts ROS generation
2.2. Processes that inhibit ferroptosis
2.2.1. Cyst(e)ine/GSH/GPX4 system
2.2.2. FSP1/CoQ10/NAD(P)H system
2.2.3. GCH1/BH4/DHFR system
2.2.4. Lipid metabolism: PL-MUFA inhibits peroxidation of PL-PUFA
3. NRF2 Structure and Function
3.1. NRF2 structure
3.2. NRF2 functions
3.2.1. Antioxidant-dependent function
3.2.2. Antioxidant-independent function
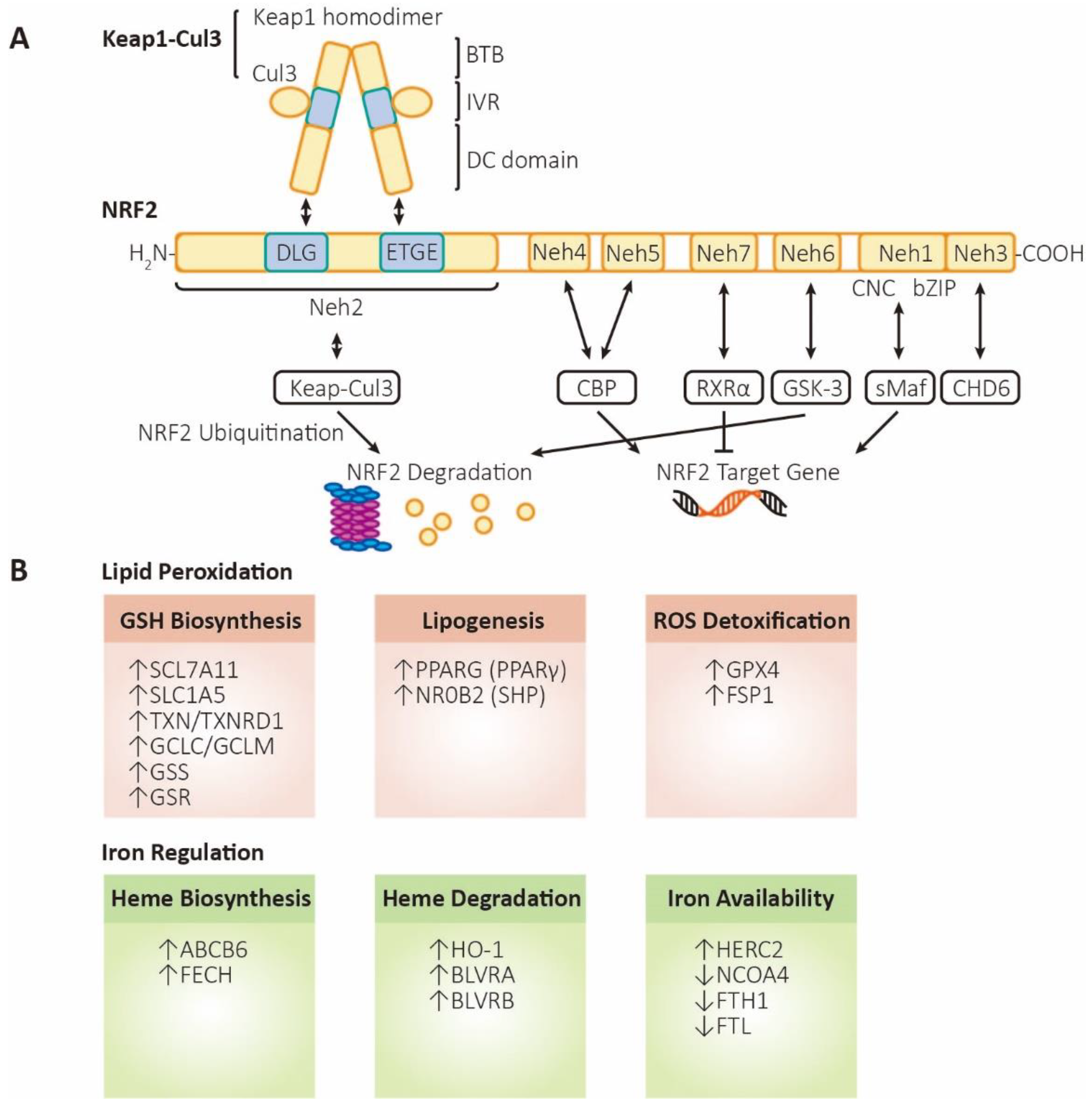
4. NRF2 in Ferroptosis
4.1. Target NRF2 signaling pathway and promote ferroptosis in cancer therapy
4.1.1. Four types of FIN (ferroptosis inducers)
4.1.2. Clinical application of targeting NRF2 and ferroptosis in cancer therapy
4.2. Target NRF2 signaling pathway and inhibit ferroptosis in disease therapy
4.2.1. Diseases associated with ferroptosis
4.2.2. Drugs and clinical experiment
5. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolma, S.; Lessnick, S.L.; Hahn, W.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagoda, N.; von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem Biol 2008, 15, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!!
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorino, M.; Conrad, M.; Ursini, F. GPx4, Lipid Peroxidation, and Cell Death: Discoveries, Rediscoveries, and Open Issues. Antioxid Redox Signal 2018, 29, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingold, I.; Berndt, C.; Schmitt, S.; Doll, S.; Poschmann, G.; Buday, K.; Roveri, A.; Peng, X.; Porto Freitas, F.; Seibt, T.; et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell 2018, 172, 409–422.e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, P.; Chan, K.; Asunis, I.; Cao, A.; Kan, Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Sato, H.; Kuriyama-Matsumura, K.; Sato, K.; Maebara, K.; Wang, H.; Tamba, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Bannai, S. Electrophile response element-mediated induction of the cystine/glutamate exchange transporter gene expression. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 44765–44771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Calkins, M.J.; Chan, K.; Kan, Y.W.; Johnson, J.A. Identification of the NF-E2-related factor-2-dependent genes conferring protection against oxidative stress in primary cortical astrocytes using oligonucleotide microarray analysis. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 12029–12038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.C.; Cui, J.Y.; Klaassen, C.D. Beneficial role of Nrf2 in regulating NADPH generation and consumption. Toxicol Sci 2011, 123, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerins, M.J.; Ooi, A. The Roles of NRF2 in Modulating Cellular Iron Homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal 2018, 29, 1756–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.A.; Caldwell, S.E.; Mills, K.A. Mechanisms of free radical oxidation of unsaturated lipids. Lipids 1995, 30, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Li, H.; Graham, E.T.; Deik, A.A.; Eaton, J.K.; Wang, W.; Sandoval-Gomez, G.; Clish, C.B.; Doench, J.G.; Schreiber, S.L. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase contributes to phospholipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 2020, 16, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H.; Banthiya, S.; van Leyen, K. Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1851, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.; Doll, S.; Croix, C.S.; Dar, H.H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 2017, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Freitas, F.P.; Shah, R.; Aldrovandi, M.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingold, I.; Goya Grocin, A.; Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Panzilius, E.; Scheel, C.H.; et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2019, 575, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zandkarimi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meena, J.K.; Kim, J.; Zhuang, L.; Tyagi, S.; Ma, L.; Westbrook, T.F.; Steinberg, G.R.; et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2020, 22, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Kaplan, A.; Yang, W.S.; Hayano, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Brown, L.M.; Valenzuela, C.A.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Stockwell, B.R. Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 2016, 12, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küch, E.M.; Vellaramkalayil, R.; Zhang, I.; Lehnen, D.; Brügger, B.; Sreemmel, W.; Ehehalt, R.; Poppelreuther, M.; Füllekrug, J. Differentially localized acyl-CoA synthetase 4 isoenzymes mediate the metabolic channeling of fatty acids towards phosphatidylinositol. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1841, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindou, H.; Shimizu, T. Acyl-CoA:lysophospholipid acyltransferases. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Minikes, A.M.; Gao, M.; Bian, H.; Li, Y.; Stockwell, B.R.; Chen, Z.N.; Jiang, X. Intercellular interaction dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature 2019, 572, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, D.M.; Anderson, G.J. The regulation of iron transport. Biofactors 2014, 40, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgami, R.S.; Campagna, D.R.; Greer, E.L.; Antiochos, B.; McDonald, A.; Chen, J.; Sharp, J.J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Barker, J.E.; Fleming, M.D. Identification of a ferrireductase required for efficient transferrin-dependent iron uptake in erythroid cells. Nat Genet 2005, 37, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.D.; Romano, M.A.; Su, M.A.; Garrick, L.M.; Garrick, M.D.; Andrews, N.C. Nramp2 is mutated in the anemic Belgrade (b) rat: evidence of a role for Nramp2 in endosomal iron transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.J.; Frey, A.G.; Palenchar, D.J.; Achar, S.; Bullough, K.Z.; Vashisht, A.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Philpott, C.C. A PCBP1-BolA2 chaperone complex delivers iron for cytosolic [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.J.; Vulpe, C.D. Mammalian iron transport. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009, 66, 3241–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, A.R.; Miyazawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Tsuji, Y. Regulators of Iron Homeostasis: New Players in Metabolism, Cell Death, and Disease. Trends Biochem Sci 2016, 41, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.R.; Karaca, M.; Adamski, K.N.; Chorley, B.N.; Wang, X.; Bell, D.A. Novel hematopoietic target genes in the NRF2-mediated transcriptional pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013, 2013, 120305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, A.S.; Chaerkady, R.; Shaw, P.G.; Davidson, N.E.; Visvanathan, K.; Pandey, A.; Kensler, T.W. Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of KEAP1 disrupted and sulforaphane-treated human breast epithelial cells reveals common expression profiles. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012, 132, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Katsuoka, F.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Nishida, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2-MafG heterodimers contribute globally to antioxidant and metabolic networks. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 10228–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassannia, B.; Wiernicki, B.; Ingold, I.; Qu, F.; Van Herck, S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayır, H.; Abhari, B.A.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Choi, S.M.; et al. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Xie, E.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Gu, S.; Gao, F.; Zhu, N.; Yin, X.; et al. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, O.; Boddu, R.; Traylor, A.; Lever, J.M.; Bolisetty, S.; George, J.F.; Agarwal, A. Heme oxygenase-1 mitigates ferroptosis in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2018, 314, F702–f714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.L.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, H.; Shin, D. Nrf2 inhibition reverses the resistance of cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cells to artesunate-induced ferroptosis. Redox Biol 2017, 11, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ou, Z.; Chen, R.; Niu, X.; Chen, D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2016, 63, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Amante, J.J.; Chhoy, P.; Elaimy, A.L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.J.; Baer, C.E.; Dixon, S.J.; Mercurio, A.M. Prominin2 Drives Ferroptosis Resistance by Stimulating Iron Export. Dev Cell 2019, 51, 575–586.e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhan, A.; Dodson, M.; Shakya, A.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, K.; et al. NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci Adv 2023, 9, eade9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhan, A.; Dodson, M.; Schmidlin, C.J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, D.D. Breakdown of an Ironclad Defense System: The Critical Role of NRF2 in Mediating Ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol 2020, 27, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; García-Yagüe Á, J.; Escoll, M.; de Ceballos, M.L.; Van Leuven, F.; Rábano, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Cuadrado, A. Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yi, J.; Zhu, J.; Minikes, A.M.; Monian, P.; Thompson, C.B.; Jiang, X. Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Mol Cell 2019, 73, 354–363.e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.I.; Katoh, Y.; Kusunoki, H.; Itoh, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 recruits Neh2 through binding to ETGE and DLG motifs: characterization of the two-site molecular recognition model. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 2887–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayano, M.; Yang, W.S.; Corn, C.K.; Pagano, N.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Loss of cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) induces the transsulfuration pathway and inhibits ferroptosis induced by cystine deprivation. Cell Death Differ 2016, 23, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibt, T.M.; Proneth, B.; Conrad, M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 133, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, H.J.; Karlenius, T.C.; Tonissen, K.F. Regulation of the human thioredoxin gene promoter and its key substrates: a study of functional and putative regulatory elements. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1840, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, D.; Portales-Casamar, E.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, S.; Arenillas, D.; Happel, C.; Shyr, C.; Wakabayashi, N.; Kensler, T.W.; Wasserman, W.W.; et al. Global mapping of binding sites for Nrf2 identifies novel targets in cell survival response through ChIP-Seq profiling and network analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 5718–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hickman, J.H.; Wang, S.J.; Gu, W. Dynamic roles of p53-mediated metabolic activities in ROS-induced stress responses. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2881–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Conrad, M. Selenium and GPX4, a vital symbiosis. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 127, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.M.; Bandeiras, T.M.; Teixeira, M. New insights into type II NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2004, 68, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, G.J.; Berry, M.J.; Moustafa, M.E.; Carlson, B.A.; Hatfield, D.L.; Faust, J.R. Inhibition of selenoprotein synthesis by selenocysteine tRNA [Ser]Sec lacking isopentenyladenosine. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 28110–28119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, D.; O'Brien, N.A.; Zandkarimi, F.; Tong, D.R.; Stokes, M.E.; Dunn, D.E.; Kengmana, E.S.; Aron, A.T.; Klein, A.M.; Csuka, J.M.; et al. MDM2 and MDMX promote ferroptosis by PPARα-mediated lipid remodeling. Genes Dev 2020, 34, 526–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, V.A.N.; Bezjian, C.T.; Pfeiffer, S.; Ringelstetter, L.; Müller, C.; Zandkarimi, F.; Merl-Pham, J.; Bao, X.; Anastasov, N.; Kössl, J.; et al. GTP Cyclohydrolase 1/Tetrahydrobiopterin Counteract Ferroptosis through Lipid Remodeling. ACS Cent Sci 2020, 6, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, C.M.; Ntambi, J.M. Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009, 297, E28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magtanong, L.; Ko, P.J.; To, M.; Cao, J.Y.; Forcina, G.C.; Tarangelo, A.; Ward, C.C.; Cho, K.; Patti, G.J.; Nomura, D.K.; et al. Exogenous Monounsaturated Fatty Acids Promote a Ferroptosis-Resistant Cell State. Cell Chem Biol 2019, 26, 420–432.e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Itoh, K.; Yoshida, E.; Miyagishi, M.; Fukamizu, A.; Yamamoto, M. Two domains of Nrf2 cooperatively bind CBP, a CREB binding protein, and synergistically activate transcription. Genes to Cells 2001, 6, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuoka, F.; Motohashi, H.; Ishii, T.; Aburatani, H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Genetic evidence that small Maf proteins are essential for the activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2005, 25, 8044–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Itoh, K.; Suzuki, T.; Osanai, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Katoh, Y.; Takagi, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Identification of the interactive interface and phylogenic conservation of the Nrf2-Keap1 system. Genes to Cells 2002, 7, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Keap1-dependent proteasomal degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 contributes to the negative regulation of antioxidant response element-driven gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003, 278, 21592–21600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioi, P.; Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. The carboxy-terminal Neh3 domain of Nrf2 is required for transcriptional activation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2005, 25, 10895–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.; Berger, N.D.; Luijsterburg, M.S.; Piett, C.G.; Stanley, F.K.T.; Schräder, C.U.; Fang, S.; Chan, J.A.; Schriemer, D.C.; Nagel, Z.D.; et al. The CHD6 chromatin remodeler is an oxidative DNA damage response factor. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Velasco, D.; de Sagarra, R.M.; Cuadrado, A. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 14841–14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, L.B.; Keum, Y.S. Binding partners of NRF2: Functions and regulatory mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys 2019, 678, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A. Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by glycogen synthase kinase 3/beta-TrCP. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2015, 88, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Hayes, J.D.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R. Identification of retinoic acid as an inhibitor of transcription factor Nrf2 through activation of retinoic acid receptor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 19589–19594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Geng, M.; Gao, P.; Wu, X.; Hai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Hayes, J.D.; et al. RXRα inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the Neh7 domain of NRF2. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Enhanced expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 by cancer chemopreventive agents: role of antioxidant response element-like sequences in the nrf2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Itoh, K.; Takahashi, S.; Sato, H.; Yanagawa, T.; Katoh, Y.; Bannai, S.; Yamamoto, M. Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 16023–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Magilnick, N.; Lee, C.; Kalmaz, D.; Ou, X.; Chan, J.Y.; Lu, S.C. Nrf1 and Nrf2 regulate rat glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit transcription indirectly via NF-kappaB and AP-1. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25, 5933–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.; Kwong, M. Impaired expression of glutathione synthetic enzyme genes in mice with targeted deletion of the Nrf2 basic-leucine zipper protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000, 1517, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Rangasamy, T.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Osburn, W.O.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M.; Biswal, S. Glutathione peroxidase 2, the major cigarette smoke-inducible isoform of GPX in lungs, is regulated by Nrf2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006, 35, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobbagy, S.; Vitturi, D.A.; Salvatore, S.R.; Turell, L.; Pires, M.F.; Kansanen, E.; Batthyany, C.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr.; Freeman, B.A.; Schopfer, F.J. Electrophiles modulate glutathione reductase activity via alkylation and upregulation of glutathione biosynthesis. Redox Biol 2019, 21, 101050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Bai, Y. Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword. Cancer Med 2019, 8, 2252–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.H.; Rizzi, E.S.; Alves-Lopes, R.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Tostes, R.C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Antioxidant and antihypertensive responses to oral nitrite involves activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 141, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlenius, T.C.; Tonissen, K.F. Thioredoxin and Cancer: A Role for Thioredoxin in all States of Tumor Oxygenation. Cancers (Basel) 2010, 2, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsera, M.; Buchanan, B.B. Evolution of the thioredoxin system as a step enabling adaptation to oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 140, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Stewart, D.; Touchard, C.; Boinapally, S.; Choi, A.M.; Cook, J.L. Nrf2, a Cap'n'Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 26071–26078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorley, B.N.; Campbell, M.R.; Wang, X.; Karaca, M.; Sambandan, D.; Bangura, F.; Xue, P.; Pi, J.; Kleeberger, S.R.; Bell, D.A. Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: influence on retinoid X receptor alpha. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 7416–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, R.H.; Schwartz, J.D.; De Bishnu, P.; Ferris, B.; Omberg, L.; Mezey, J.G.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G. Coordinate control of expression of Nrf2-modulated genes in the human small airway epithelium is highly responsive to cigarette smoking. Mol Med 2009, 15, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Shibata, T.; Nukiwa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.C.; Hay, N. The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 2014, 39, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.S.; Metallo, C.M. Mitochondria as biosynthetic factories for cancer proliferation. Cancer Metab 2015, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, P.K.; Seiler, A.; Perisic, T.; Kölle, P.; Banjac Canak, A.; Förster, H.; Weiss, N.; Kremmer, E.; Lieberman, M.W.; Bannai, S.; et al. System x(c)- and thioredoxin reductase 1 cooperatively rescue glutathione deficiency. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 22244–22253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soula, M.; Weber, R.A.; Zilka, O.; Alwaseem, H.; La, K.; Yen, F.; Molina, H.; Garcia-Bermudez, J.; Pratt, D.A.; Birsoy, K. Metabolic determinants of cancer cell sensitivity to canonical ferroptosis inducers. Nat Chem Biol 2020, 16, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Gladwell, W.; Wang, X.; Chorley, B.; Bell, D.; Reddy, S.P.; Kleeberger, S.R. Nrf2-regulated PPAR{gamma} expression is critical to protection against acute lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010, 182, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Tabbi-Anneni, I.; Gunda, V.; Wang, L. Transcription factor Nrf2 regulates SHP and lipogenic gene expression in hepatic lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010, 299, G1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewerenz, J.; Hewett, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Lambros, M.; Gout, P.W.; Kalivas, P.W.; Massie, A.; Smolders, I.; Methner, A.; Pergande, M.; et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 2013, 18, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Antonucci, L.; Karin, M. NRF2 as a regulator of cell metabolism and inflammation in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Sayin, V.I.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Singh, S.X.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Karakousi, T.R.; Ellis, D.C.; Bhutkar, A.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; et al. Keap1 loss promotes Kras-driven lung cancer and results in dependence on glutaminolysis. Nat Med 2017, 23, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, C.; Liu, S.; Xiao, D.; Huang, J.; Tao, Y. Emerging mechanisms and targeted therapy of ferroptosis in cancer. Mol Ther 2021, 29, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouta, R.; Dixon, S.J.; Wang, J.; Dunn, D.E.; Orman, M.; Shimada, K.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Lo, D.C.; Weinberg, J.M.; Linkermann, A.; et al. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc 2014, 136, 4551–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cao, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, M.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The ferroptosis inducer erastin enhances sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Cell Oncol 2015, 2, e1054549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; An, P.; Jin, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.; et al. Auranofin mitigates systemic iron overload and induces ferroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.N.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.D.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.E.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. Elife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, B.; Han, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xia, Y.; Gong, C.; Dai, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, G. Ferroptosis: A Novel Anti-tumor Action for Cisplatin. Cancer Res Treat 2018, 50, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarnicola, M.; Altomare, D.F.; Correale, M.; Ruggieri, E.; D'Attoma, B.; Mastrosimini, A.; Guerra, V.; Caruso, M.G. Serum lipid profile in colorectal cancer patients with and without synchronous distant metastases. Oncology 2005, 68, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021, 18, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.; Castro-Portuguez, R.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol 2019, 23, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, E.R.; Truesdale, A.T.; McDonald, O.B.; Yuan, D.; Hassell, A.; Dickerson, S.H.; Ellis, B.; Pennisi, C.; Horne, E.; Lackey, K.; et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 6652–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Cheu, K.W.; N'Da, D.; Coghi, P.; Monti, D. Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin antimalarials: part 1--the 'carbon radical' and 'heme' hypotheses. Infect Disord Drug Targets 2013, 13, 217–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Moriguchi, T.; Takai, J.; Ebina, M.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2 prevents initiation but accelerates progression through the Kras signaling pathway during lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 4158–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Rojo de la Vega, M.; Chapman, E.; Ooi, A.; Zhang, D.D. The effects of NRF2 modulation on the initiation and progression of chemically and genetically induced lung cancer. Mol Carcinog 2018, 57, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Long, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Q.; et al. NRF2 activation by antioxidant antidiabetic agents accelerates tumor metastasis. Sci Transl Med 2016, 8, 334ra351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, B.; Tong, K.I.; Ohta, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Scharlock, M.; Ohtsuji, M.; Kang, M.I.; Kobayashi, A.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamamoto, M. Structural basis for defects of Keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol Cell 2006, 21, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, V.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Ames, S.; Hoque, M.O.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Sidransky, D.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS Med 2006, 3, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2018, 69, 182–236. [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Schorpp, K.; Jin, J.; Yozwiak, C.E.; Hoffstrom, B.G.; Decker, A.M.; Rajbhandari, P.; Stokes, M.E.; Bender, H.G.; Csuka, J.M.; et al. Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker. Cell Rep 2020, 30, 3411–3423.e3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, R.; Ding, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, C.; Xu, Q.; Cai, J. KAT6A is associated with sorafenib resistance and contributes to progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting YAP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021, 585, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, W. Combination of Metformin and Sorafenib Induces Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. J Cancer 2022, 13, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Dai, H.Q.; Huang, X.W.; Feng, J.; Deng, J.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.H.; et al. Artesunate synergizes with sorafenib to induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2021, 42, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ke, Z.P. Apigenin sensitizes BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin through inhibiting miR-101/Nrf2 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82085–82091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Bai, J. MicroRNA-532 and microRNA-3064 inhibit cell proliferation and invasion by acting as direct regulators of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in ovarian cancer. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Bole, D.; Eaton, J.K.; Matov, A.; Galeas, J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Berens, M.E.; Schreiber, S.L.; et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature 2017, 551, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xie, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ju, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhuo, W.; et al. Fascin enhances the vulnerability of breast cancer to erastin-induced ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Dielschneider, R.F.; Henson, E.S.; Xiao, W.; Choquette, T.R.; Blankstein, A.R.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, S.B. Ferroptosis and autophagy induced cell death occur independently after siramesine and lapatinib treatment in breast cancer cells. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0182921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Henson, E.S.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, S.B. Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2016, 7, e2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lee, S. Levistolide A Induces Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated ER Stress Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017, 42, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Mo, Y.; Liu, D.; Duan, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. Levistilide a Induces Ferroptosis by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 2022, 16, 2981–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Chen, W. Epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Thorac Cancer 2019, 10, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.; Mao, C.Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Combating the drug resistance of cisplatin using a platinum prodrug based delivery system. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2012, 51, 6742–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, H.; Duan, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, W.; Mei, Z.; Luo, L.; Yan, P. Isoorientin reverses lung cancer drug resistance by promoting ferroptosis via the SIRT6/Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2023, 954, 175853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review. Environ Sci Technol 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Tratnyek, P.G. Reduction of azo dyes with zero-valent iron. Water Research 2000, 34, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hsieh, H.C.; Shih, F.S.; Wang, P.W.; Yang, L.X.; Shieh, D.B.; Wang, Y.C. An innovative NRF2 nano-modulator induces lung cancer ferroptosis and elicits an immunostimulatory tumor microenvironment. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7072–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Hu, X.R.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.G.; Meng, X.M.; Qi, X.M. Wogonin protects glomerular podocytes by targeting Bcl-2-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in diabetic kidney disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022, 43, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Cen, S.; Yang, C.; Ma, Z.; Shi, X. Wogonin induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting the Nrf2/GPX4 axis. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1129662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gout, P.W.; Buckley, A.R.; Simms, C.R.; Bruchovsky, N. Sulfasalazine, a potent suppressor of lymphoma growth by inhibition of the x(c)- cystine transporter: a new action for an old drug. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, C.; Liptay, S.; Adler, G.; Schmid, R.M. Sulfasalazine: a potent and specific inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest 1998, 101, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Lo, M.; Dockery, P.; Mahon, S.; Karp, C.M.; Buckley, A.R.; Lam, S.; Gout, P.W.; Wang, Y.Z. The xc- cystine/glutamate antiporter as a potential therapeutic target for small-cell lung cancer: use of sulfasalazine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009, 64, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Shintani, S.; Hirata, Y.; Suina, K.; Semba, T.; Yamasaki, J.; Umene, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Saya, H.; Nagano, O. Synthetic lethality of the ALDH3A1 inhibitor dyclonine and xCT inhibitors in glutathione deficiency-resistant cancer cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33832–33843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranti, I.; Wahyuningsih, M.S.H.; Wirohadidjojo, Y.W. The antifibrotic effect of isolate tagitinin C from tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) A. Gray on keloid fibroblast cell. Pan Afr Med J 2018, 30, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.H.; Lin, W.C.; Wen, H.C.; Pu, H.F. Tithonia diversifolia and its main active component tagitinin C induce survivin inhibition and G2/M arrest in human malignant glioblastoma cells. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. Anti-TMV activity and functional mechanisms of two sesquiterpenoids isolated from Tithonia diversifolia. Pestic Biochem Physiol 2017, 140, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves-Santos, E.; Vilas-Boas, D.F.; Diniz, L.F.; Veloso, M.P.; Mazzeti, A.L.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Oliveira, C.M.; Fernandes, V.H.C.; Novaes, R.D.; Chagas-Paula, D.A.; et al. Sesquiterpene lactone potentiates the immunomodulatory, antiparasitic and cardioprotective effects on anti-Trypanosoma cruzi specific chemotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2019, 77, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fei, J.; Hao, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci 2021, 17, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarskis, E.J.; Tandon, L.; Lovell, M.A.; Ehmann, W.D. Aluminum, calcium, and iron in the spinal cord of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using laser microprobe mass spectroscopy: a preliminary study. J Neurol Sci 1995, 130, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Yantiri, F.; Rajagopalan, S.; Kumar, J.; Mo, J.Q.; Boonplueang, R.; Viswanath, V.; Jacobs, R.; Yang, L.; Beal, M.F.; et al. Genetic or pharmacological iron chelation prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: a novel therapy for Parkinson's disease. Neuron 2003, 37, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xie, W.; Pan, T.; Xu, P.; Fridkin, M.; Zheng, H.; Jankovic, J.; Youdim, M.B.; Le, W. Prevention and restoration of lactacystin-induced nigrostriatal dopamine neuron degeneration by novel brain-permeable iron chelators. Faseb j 2007, 21, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, M.; Doan, N.T.; van Rooden, S.; Versluis, M.J.; van Lew, B.; Milles, J.; van der Grond, J.; van Buchem, M.A. In vivo assessment of iron content of the cerebral cortex in healthy aging using 7-Tesla T2*-weighted phase imaging. Neurobiol Aging 2017, 53, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Ayton, S.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Spoerri, L.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Wright, D.K.; Wong, B.X.; Adlard, P.A.; Cherny, R.A.; Lam, L.Q.; et al. Tau deficiency induces parkinsonism with dementia by impairing APP-mediated iron export. Nat Med 2012, 18, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.B.; Chai, R.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, H.L.; Fan, Y.G.; Guo, C. Iron Exposure and the Cellular Mechanisms Linked to Neuron Degeneration in Adult Mice. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.R.; Menzies, S.L.; St Martin, S.M.; Mufson, E.J. A histochemical study of iron, transferrin, and ferritin in Alzheimer's diseased brains. J Neurosci Res 1992, 31, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotorno, N.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Stomrud, E.; Lampinen, B.; Strandberg, O.T.; van Westen, D.; Hansson, O. Relationship between cortical iron and tau aggregation in Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2020, 143, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerril-Ortega, J.; Bordji, K.; Fréret, T.; Rush, T.; Buisson, A. Iron overload accelerates neuronal amyloid-β production and cognitive impairment in transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2014, 35, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, D.W.; Xu, S.F.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; Guo, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Redox Biol 2018, 14, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayton, S.; Lei, P.; Duce, J.A.; Wong, B.X.; Sedjahtera, A.; Adlard, P.A.; Bush, A.I.; Finkelstein, D.I. Ceruloplasmin dysfunction and therapeutic potential for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 2013, 73, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexter, D.T.; Wells, F.R.; Lees, A.J.; Agid, F.; Agid, Y.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 1989, 52, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.M.; Hare, D.J.; Cottam, V.; Chen, N.; Hilgers, L.; Halliday, G.; Mercer, J.F.; Double, K.L. Localization of copper and copper transporters in the human brain. Metallomics 2013, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, R.K.; Owen, A.; Daniel, S.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Alterations in the distribution of glutathione in the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 1997, 104, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.; Krishnan, K.J.; Morris, C.M.; Taylor, G.A.; Reeve, A.K.; Perry, R.H.; Jaros, E.; Hersheson, J.S.; Betts, J.; Klopstock, T.; et al. High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease. Nat Genet 2006, 38, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, D.; Moreau, C.; Devedjian, J.C.; Kluza, J.; Petrault, M.; Laloux, C.; Jonneaux, A.; Ryckewaert, G.; Garçon, G.; Rouaix, N.; et al. Targeting chelatable iron as a therapeutic modality in Parkinson's disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 21, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, K.J.; Han, B.S.; et al. Quantitative proteomic analyses reveal that GPX4 downregulation during myocardial infarction contributes to ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Xuan, J.; Ge, Z. Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol 2021, 37, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, R.; Cui, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, J.; Geng, B.; Chen, Z. Ferroptosis due to Cystathionine γ Lyase/Hydrogen Sulfide Downregulation Under High Hydrostatic Pressure Exacerbates VSMC Dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 829316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, W.; Hu, A.; Lin, J.; Xia, Z.; Yang, C.F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Dexmedetomidine alleviated sepsis-induced myocardial ferroptosis and septic heart injury. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Kong, B.; Qin, T.; Xiao, Z.; Fang, J.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Fu, H.; Meng, H.; et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis reduces susceptibility to frequent excessive alcohol consumption-induced atrial fibrillation. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.V.; Liu, J.; Tsai, H.P.; Zeng, L.; Yang, S.; Asnani, A.; Kim, J. Excess heme upregulates heme oxygenase 1 and promotes cardiac ferroptosis in mice with sickle cell disease. Blood 2022, 139, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2020, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.N.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, L.; Yu, D.X.; Xu, D.X.; Xu, S. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species are involved in renal cell ferroptosis during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 107, 108687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A.; Foerder, C.A. Effects of inorganic iron and myoglobin on in vitro proximal tubular lipid peroxidation and cytotoxicity. J Clin Invest 1992, 89, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Sanchez, D.; Ruiz-Andres, O.; Poveda, J.; Carrasco, S.; Cannata-Ortiz, P.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ruiz Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Linkermann, A.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Ferroptosis, but Not Necroptosis, Is Important in Nephrotoxic Folic Acid-Induced AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 2017, 28, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paller, M.S. Hemoglobin- and myoglobin-induced acute renal failure in rats: role of iron in nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol 1988, 255, F539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrdova, E.; Giovannoni, G.; Gold, R.; Fox, R.J.; Kappos, L.; Phillips, J.T.; Okwuokenye, M.; Marantz, J.L. Effect of delayed-release dimethyl fumarate on no evidence of disease activity in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: integrated analysis of the phase III DEFINE and CONFIRM studies. Eur J Neurol 2017, 24, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio; Cuadrado. NRF2 in neurodegenerative diseases. Current Opinion in Toxicology 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Takaya, K.; Suzuki, T.; Motohashi, H.; Onodera, K.; Satomi, S.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M. Validation of the multiple sensor mechanism of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med 2012, 53, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, M.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yi, W.; Yang, J.; Yi, D.; et al. Honokiol Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Type 1 Diabetic Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through Activating the SIRT1-Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018, 3159801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Gao, X.; Wei, W. The crosstalk between Sirt1 and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE anti-oxidative pathway forms a positive feedback loop to inhibit FN and TGF-β1 expressions in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Cell Res 2017, 361, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lu, Z.; Lin, V.; May, A.; Shaw, D.H.; Wang, Z.; Che, B.; Tran, K.; Du, H.; Shaw, P.X. MicroRNA miR-24-3p Reduces Apoptosis and Regulates Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway in Mouse Cardiomyocytes Responding to Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018, 7042105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Wan, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, D.; Lin, N.; Zhou, H.; Zhong, J. miR-503 Is Involved in the Protective Effect of Phase II Enzyme Inducer (CPDT) in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017, 9167450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, J.Z.; He, Q.; Wang, C.Q. miR-155 modulates high glucose-induced cardiac fibrosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 4003–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhao, X. Inhibiting microRNA-144 abates oxidative stress and reduces apoptosis in hearts of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Pathol 2015, 24, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, W.; Fan, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Xiong, M.; Ma, C.; Yang, J. MicroRNA-24 inhibits the oxidative stress induced by vascular injury by activating the Nrf2/Ho-1 signaling pathway. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Park, H.P.; Kim, E.; Lee, H.; Hwang, J.W.; Jeon, Y.T.; Lim, Y.J. The antioxidant effect of preischemic dexmedetomidine in a rat model: increased expression of Nrf2/HO-1 via the PKC pathway. Braz J Anesthesiol 2023, 73, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Zuo, T.; Deng, L.; Chen, S.; Yu, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Dong, Z. β-Caryophyllene suppresses ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Bao, S.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Hu, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yan, S. Xiaojianzhong decoction attenuates gastric mucosal injury by activating the p62/Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway to inhibit ferroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 155, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.H.; Jin, S.G.; Fei, D.S.; Kang, K.; Jiang, L.; Lian, Z.Y.; Pan, S.H.; Zhao, M.R.; Zhao, M.Y. Artesunate Protects Against Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury Via Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulation. Inflammation 2016, 39, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civantos, E.; Bosch, E.; Ramirez, E.; Zhenyukh, O.; Egido, J.; Lorenzo, O.; Mas, S. Sitagliptin ameliorates oxidative stress in experimental diabetic nephropathy by diminishing the miR-200a/Keap-1/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2017, 10, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



