Submitted:
22 August 2023
Posted:
22 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- I.
- SARS-COV-2 protease enzyme
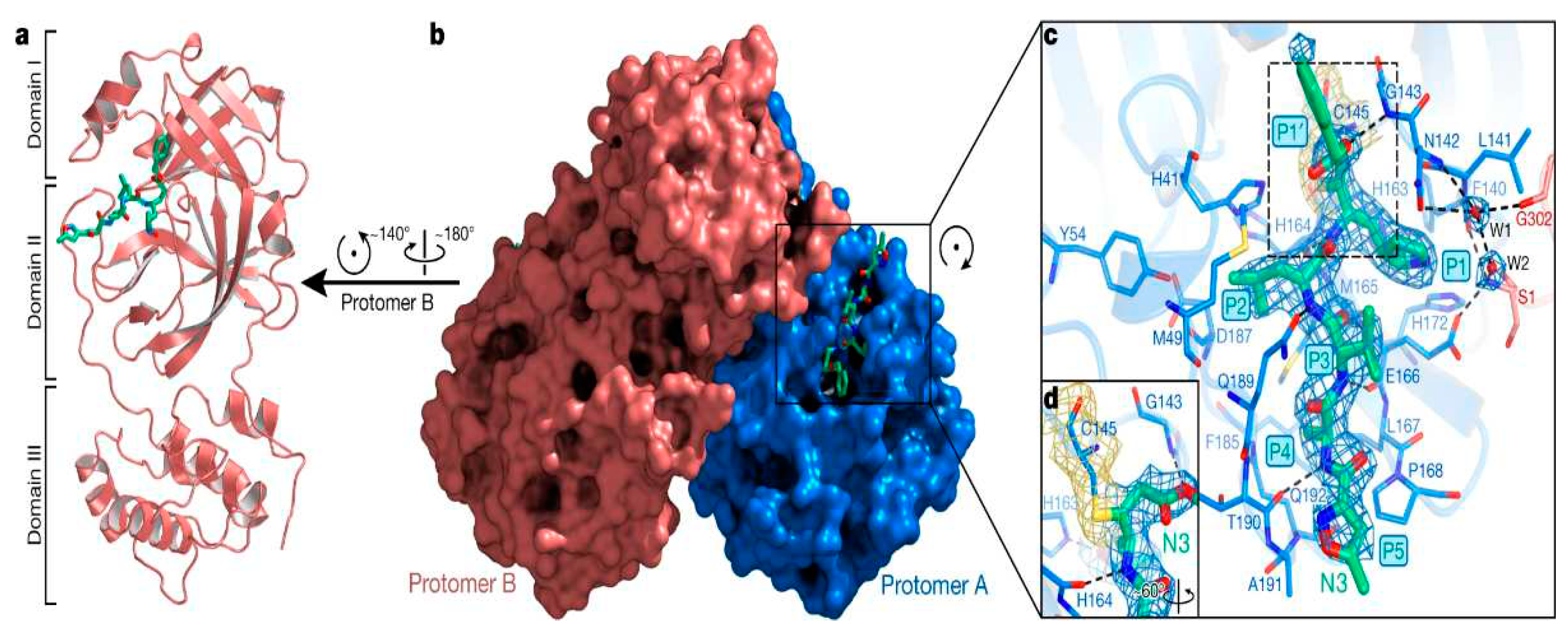
- II.
- General SARS-COV-2 protease enzyme inhibition mechanism
- III.
- Overview of SARS-COV-2 protease enzyme inhibitors properties
- IV.
- Target of SARS-COV-2 protease approach towards drug discovery
- V.
- Computational methods for SARS-COV-2 protease inhibitor identification
- VI.
- Quantitative structure-Activity relationship
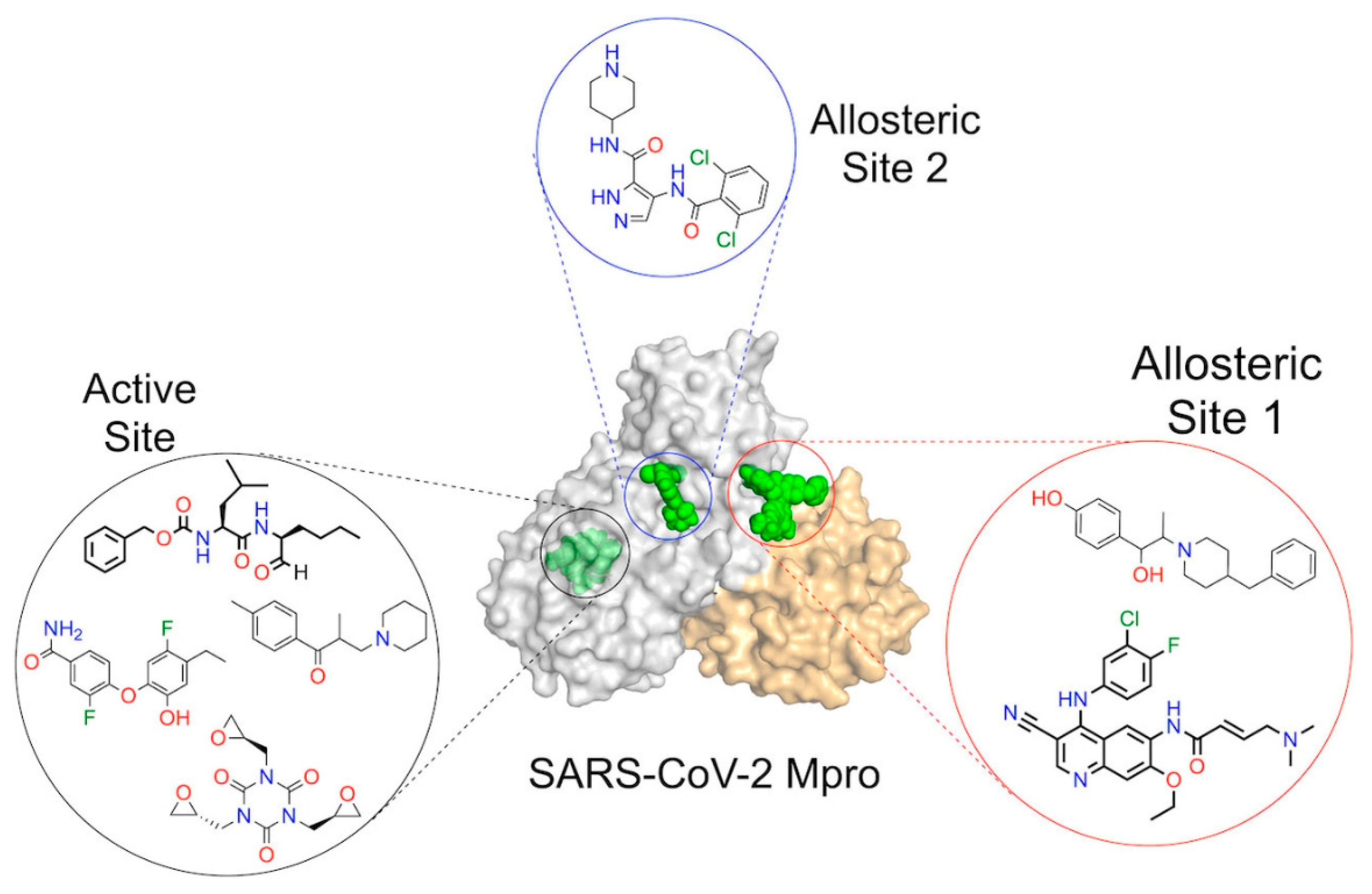
- VII.
- Pharmacophore development and validation
- VIII.
- ADMET
- IX.
- Virtual screening
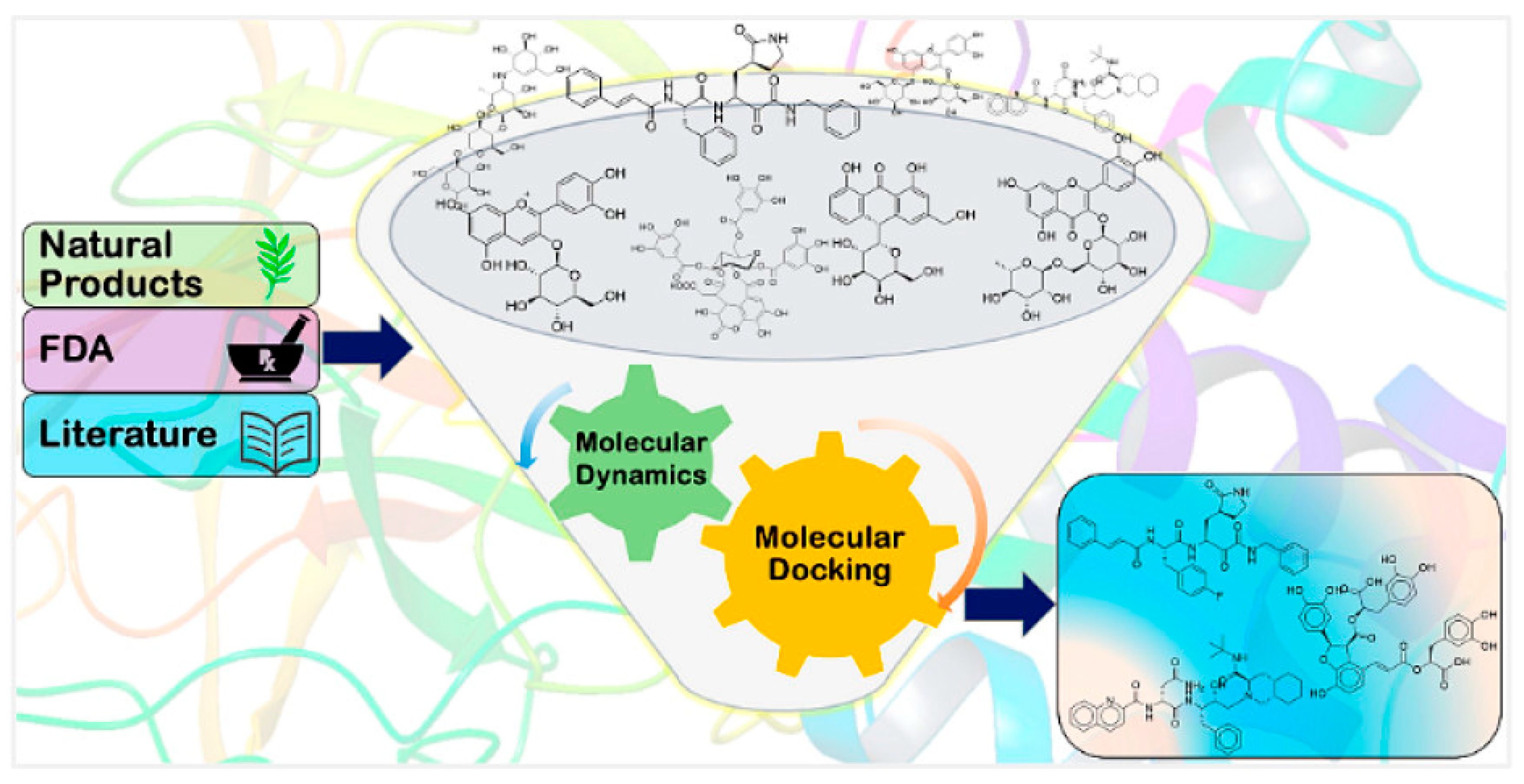
- X.
- Molecular Docking
| Inhibitor | Type | Simulation Method | Target Protein | Time Scale | Binding Free Energy (ΔG) | Key Interactions | References |
PF-07321332/ Nirmatrelvir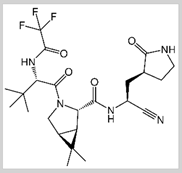
|
Covalent | Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 250 ns | -63.2 kcal/mol | Covalent bond with Cys145 | Wang, Yeng-Tseng, et al., (2022): |
N3/
|
Covalent | Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 100 ns | -62.2 kcal/mol | Covalent bond with Cys145 | Gogoi, B., Chowdhury, P., Goswami, N., et al., 2021. |
GC376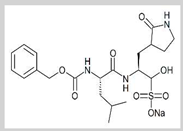
|
Covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 300 ns | -43.5 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Gln189 and Thr190 | Gangadharan, S., Ambrose, J.M., Rajajagadeesan, A., Kullappan, M., Patil, S., Gandhamaneni, S.H., Veeraraghavan, V.P., et al., 2022. |
Ritonavir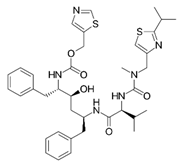
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 200 ns | -20.3 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Glu166, Gln189, and His41 | Ahmad, B., Batool, M., Ain, Q.U., Kim, M.S. and Choi, S., 2021 |
Darunavir
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 500 ns | -36.8 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Glu166, Gln189, and His41 | Bolcato, G., Bissaro, M., Pavan, M., Sturlese, M. and Moro, S., 2020. |
Remdesivir
|
Non-covalent | QM/MM simulations | SARS-CoV-2 RdRp | 5.5 ns | -21.9 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Asn691 and Thr790 | Surti, M., Patel, M., Adnan, M., Moin, A., Ashraf, S.A., Siddiqui, A.J., Snoussi, M., Deshpande, S. and Reddy, M.N., 2020. |
Favipiravir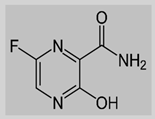
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 RdRp | 200 ns | -43.3 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Gln552 and Gln556 | Surti, M., Patel, M., Adnan, M., Moin, A., Ashraf, S.A., Siddiqui, A.J., Snoussi, M., Deshpande, S. and Reddy, M.N., 2020. Mujwar, S., Sun, L. and Fidan, O., 2022. |
Molnupiravir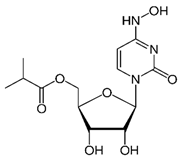
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 RdRp | 500 ns | -43.4 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Asp623 and Ser682 | Gangadharan, S., Ambrose, J.M., Rajajagadeesan, A., Kullappan, et al., 2022. |
Camostat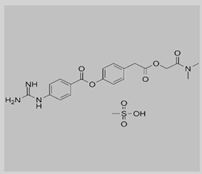
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | 100 ns | -27.3 kcal/mol | Hydrogen bonds with Ser884 and Thr859 | Rahman, N., Basharat, Z., Yousuf, M., Castaldo, G., Rastrelli, L. and Khan, H., 2020. |
Ebselen
|
Non-covalent | MD simulations | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro | 200 ns | -26.8 kcal/mol | Covalent bond with Cys145 and hydrogen bond with His41 | Durdagi, S., Aksoydan, B., Dogan, B., Sahin, K., Shahraki, A. and Birgül-İyison, N., 2020. |
- XI.
- MD Simulations
- XII.
- Hybrid quantum mechanics/Molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods
- XIII.
- Advanced MD simulations
- XIV
- Authors insight on the topic
- XV
- Conclusion and future perspectives
References
- Ukhurebor, K.E., Singh, K.R., Nayak, V. and Gladys, U.E., 2021. Influence of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a review from the climate change perspective. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 23(8), pp.1060-1078. [CrossRef]
- Acter, T., Uddin, N., Das, J., Akhter, A., Choudhury, T.R. and Kim, S., 2020. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Science of the Total Environment, 730, p.138996. [CrossRef]
- Acter, T., Uddin, N., Das, J., Akhter, A., Choudhury, T.R. and Kim, S., 2020. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Science of the Total Environment, 730, p.138996. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.K. and Das Mukhopadhyay, C., 2021. Ayurvedic metal nanoparticles could be novel antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2. International Nano Letters, pp.1-7. [CrossRef]
- Ma, C., Sacco, M.D., Hurst, B., Townsend, J.A., Hu, Y., Szeto, T., Zhang, X., Tarbet, B., Marty, M.T., Chen, Y. and Wang, J., 2020. Boceprevir, GC-376, and calpain inhibitors II, XII inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral replication by targeting the viral main protease. Cell research, 30(8), pp.678-692. [CrossRef]
- La Monica, G., Bono, A., Lauria, A. and Martorana, A., 2022. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease for treatment of COVID-19: covalent inhibitors structure–activity relationship insights and evolution perspectives. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 65(19), pp.12500-12534. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, W.B. and Mendanha, S.A., 2021. Molecular dynamics simulation of docking structures of SARS-CoV-2 main protease and HIV protease inhibitors. Journal of molecular structure, 1225, p.129143. [CrossRef]
- Badavath, V.N., Kumar, A., Samanta, P.K., Maji, S., Das, A., Blum, G., Jha, A. and Sen, A., 2022. Determination of potential inhibitors based on isatin derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (mpro): a molecular docking, molecular dynamics and structure-activity relationship studies. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(7), pp.3110-3128.. [CrossRef]
- Elgohary, A.M., Elfiky, A.A., Pereira, F., Abd El-Aziz, T.M., Sobeh, M., Arafa, R.K. and El-Demerdash, A., 2022. Investigating the structure-activity relationship of marine polycyclic batzelladine alkaloids as promising inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Computers in Biology and Medicine, 147, p.105738.
- Chowdhury, P., 2021. In silico investigation of phytoconstituents from Indian medicinal herb ‘Tinospora cordifolia (giloy)’against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by molecular dynamics approach. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(17), pp.6792-6809. [CrossRef]
- Rao, P., Shukla, A., Parmar, P., Rawal, R.M., Patel, B., Saraf, M. and Goswami, D., 2020. Reckoning a fungal metabolite, Pyranonigrin A as a potential Main protease (Mpro) inhibitor of novel SARS-CoV-2 virus identified using docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Biophysical Chemistry, 264, p.106425. [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S., Lee, K.E., Dwivedi, V.D. and Kang, S.G., 2020. Computational insights into tetracyclines as inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro via combinatorial molecular simulation calculations. Life Sciences, 257, p.118080.
- Ghosh, R., Chakraborty, A., Biswas, A. and Chowdhuri, S., 2021. Evaluation of green tea polyphenols as novel corona virus (SARS CoV-2) main protease (Mpro) inhibitors–an in silico docking and molecular dynamics simulation study. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(12), pp.4362-4374. [CrossRef]
- Peele, K.A., Durthi, C.P., Srihansa, T., Krupanidhi, S., Ayyagari, V.S., Babu, D.J., Indira, M., Reddy, A.R. and Venkateswarulu, T.C., 2020. Molecular docking and dynamic simulations for antiviral compounds against SARS-CoV-2: A computational study. Informatics in medicine unlocked, 19, p.100345.
- Muteeb, G., Alshoaibi, A., Aatif, M., Rehman, M.T. and Qayyum, M.Z., 2020. Screening marine algae metabolites as high-affinity inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro): an in silico analysis to identify novel drug candidates to combat COVID-19 pandemic. Applied biological chemistry, 63, pp.1-12. [CrossRef]
- Salman, S., Shah, F.H., Idrees, J., Idrees, F., Velagala, S., Ali, J. and Khan, A.A., 2020. Virtual screening of immunomodulatory medicinal compounds as promising anti-SARS-COV-2 inhibitors. Future Virology, 15(5), pp.267-275.
- Batool, F., Mughal, E.U., Zia, K., Sadiq, A., Naeem, N., Javid, A., Ul-Haq, Z. and Saeed, M., 2022. Synthetic flavonoids as potential antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(8), pp.3777-3788. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.S., Jagdale, S.S., Bansode, S.B., Shankar, S.S., Tellis, M.B., Pandya, V.K., Chugh, A., Giri, A.P. and Kulkarni, M.J., 2021. Discovery of potential multi-target-directed ligands by targeting host-specific SARS-CoV-2 structurally conserved main protease. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(9), pp.3099-3114. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. and Rao, Z., 2021. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19(11), pp.685-700.
- Steuten, K., Kim, H., Widen, J.C., Babin, B.M., Onguka, O., Lovell, S., Bolgi, O., Cerikan, B., Neufeldt, C.J., Cortese, M. and Muir, R.K., 2021. Challenges for targeting SARS-CoV-2 proteases as a therapeutic strategy for COVID-19. ACS infectious diseases, 7(6), pp.1457-1468.
- Zhang, Y. and Tang, L.V., 2020. Overview of targets and potential drugs of SARS-CoV-2 according to the viral replication. Journal of proteome research, 20(1), pp.49-59. [CrossRef]
- Umar, H.I., Josiah, S.S., Saliu, T.P., Jimoh, T.O., Ajayi, A. and Danjuma, J.B., 2021. In-silico analysis of the inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease by some active compounds from selected African plants. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, 16(2), pp.162-176.
- Arshia, A.H., Shadravan, S., Solhjoo, A., Sakhteman, A. and Sami, A., 2021. De novo design of novel protease inhibitor candidates in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 using deep learning, docking, and molecular dynamic simulations. Computers in biology and medicine, 139, p.104967. [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.X. and Reiter, R.J., 2022. Mechanisms and clinical evidence to support melatonin's use in severe COVID-19 patients to lower mortality. Life Sciences, p.120368.
- Kaur, H., Sarma, P., Bhattacharyya, A., Sharma, S., Chhimpa, N., Prajapat, M., Prakash, A., Kumar, S., Singh, A., Singh, R. and Avti, P., 2021. Efficacy and safety of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors “leflunomide” and “teriflunomide” in Covid-19: A narrative review. European journal of pharmacology, 906, p.174233. [CrossRef]
- Salluh, J.I.F.; Arabi, Y.M.; Binnie, A. COVID-19 research in critical care: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Intensiv. Care Med. 2021, 47, 470–472. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Srivastava, A. A review of modern technologies for tackling COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 569–573. [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, S., Kottekad, S., Crasta, I., Sreevathsan, S., Usharani, D., Perumal, M.K. and Mudliar, S.N., 2021. Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease through active phytocompounds of ayurvedic medicinal plants–Emblica officinalis (Amla), Phyllanthus niruri Linn.(Bhumi Amla) and Tinospora cordifolia (Giloy)–A molecular docking and simulation study. Computers in biology and medicine, 136, p.104683.
- Ullrich, S. and Nitsche, C., 2020. The SARS-CoV-2 main protease as drug target. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 30(17), p.127377.
- Lobo-Galo, N., Terrazas-López, M., Martínez-Martínez, A. and Díaz-Sánchez, Á.G., 2021. FDA-approved thiol-reacting drugs that potentially bind into the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, essential for viral replication. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(9), pp.3419-3427. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C., Fadl, S., Villanueva, A.J. and Rabeh, W.M., 2021. Catalytic dyad residues His41 and Cys145 impact the catalytic activity and overall conformational fold of the main SARS-CoV-2 protease 3-chymotrypsin-like protease. Frontiers in Chemistry, 9, p.692168.
- Silvestrini, L., Belhaj, N., Comez, L., Gerelli, Y., Lauria, A., Libera, V., Mariani, P., Marzullo, P., Ortore, M.G., Palumbo Piccionello, A. and Petrillo, C., 2021. The dimer-monomer equilibrium of SARS-CoV-2 main protease is affected by small molecule inhibitors. Scientific Reports, 11(1), p.9283.
- Pillaiyar, T., Flury, P., Krüger, N., Su, H., Schäkel, L., Barbosa Da Silva, E., Eppler, O., Kronenberger, T., Nie, T., Luedtke, S. and Rocha, C., 2022. Small-molecule thioesters as SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors: enzyme inhibition, structure–activity relationships, antiviral activity, and X-ray structure determination. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 65(13), pp.9376-9395. [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.M.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Sirwi, A.; El-Araby, A.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Koshak, A.E.; Asfour, H.Z.; Awan, Z.A.; Elfaky, M.A. Repurposing of Some Natural Product Isolates as SARS-COV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors via In Vitro Cell Free and Cell-Based Antiviral Assessments and Molecular Modeling Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 213. [CrossRef]
- La Monica, Gabriele, Alessia Bono, Antonino Lauria, and Annamaria Martorana. "Targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease for treatment of COVID-19: covalent inhibitors structure–activity relationship insights and evolution perspectives." Journal of medicinal chemistry 65, no. 19 (2022): 12500-12534.
- Pradhan, R. and Sahu, P.K., 2023. In-silico approaches towards development of model irreversible HIV-1 protease inhibitors.
- Feitosa, E.L., Júnior, F.T.D.S., Neto, J.A.D.O.N., Matos, L.F., Matheus, H.D.S., Rosales, T.O. and De Freitas, G.B.L., 2020. COVID-19: Rational discovery of the therapeutic potential of Melatonin as a SARS-CoV-2 main Protease Inhibitor. International journal of medical sciences, 17(14), p.2133.
- Li, Z., Li, X., Huang, Y.Y., Wu, Y., Liu, R., Zhou, L., Lin, Y., Wu, D., Zhang, L., Liu, H. and Xu, X., 2020. Identify potent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors via accelerated free energy perturbation-based virtual screening of existing drugs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(44), pp.27381-27387. [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, N., Sacco, M.D., Ma, C., Hu, Y., Townsend, J.A., Meng, X., Zhang, F., Zhang, X., Ba, M., Szeto, T. and Kukuljac, A., 2021. Expedited approach toward the rational design of noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 65(4), pp.2848-2865.
- Aljoundi, A.; Bjij, I.; El Rashedy, A.; Soliman, M.E.S. Covalent Versus Non-covalent Enzyme Inhibition: Which Route Should We Take? A Justification of the Good and Bad from Molecular Modelling Perspective. Protein J. 2020, 39, 97–105. [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, H., Moore, G.J., Mavromoustakos, T., Tsiodras, S., Ligielli, I., Kelaidonis, K., Chasapis, C.T., Gadanec, L.K., Zulli, A., Apostolopoulos, V. and Petty, R., 2022. Discovery of a new generation of angiotensin receptor blocking drugs: Receptor mechanisms and in silico binding to enzymes relevant to SARS-CoV-2. Computational and structural biotechnology journal, 20, pp.2091-2111. [CrossRef]
- Ashour, N.A., Abo Elmaaty, A., Sarhan, A.A., Elkaeed, E.B., Moussa, A.M., Erfan, I.A. and Al-Karmalawy, A.A., 2022. A systematic review of the global intervention for SARS-CoV-2 combating: from drugs repurposing to molnupiravir approval. Drug design, development and therapy, pp.685-715.
- Banerjee, R., Perera, L. and Tillekeratne, L.V., 2021. Potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Drug Discovery Today, 26(3), pp.804-816.
- Padhi, S., Masi, M., Chourasia, R., Rajashekar, Y., Rai, A.K. and Evidente, A., 2021. ADMET profile and virtual screening of plant and microbial natural metabolites as SARS-CoV-2 S1 glycoprotein receptor binding domain and main protease inhibitors. European journal of pharmacology, 890, p.173648.. [CrossRef]
- Tan, H., Hu, Y., Jadhav, P., Tan, B. and Wang, J., 2022. Progress and challenges in targeting the SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 65(11), pp.7561-7580.
- Liu, H., Iketani, S., Zask, A., Khanizeman, N., Bednarova, E., Forouhar, F., Fowler, B., Hong, S.J., Mohri, H., Nair, M.S. and Huang, Y., 2022. Development of optimized drug-like small molecule inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease for treatment of COVID-19. Nature Communications, 13(1), p.1891.. [CrossRef]
- Alagu Lakshmi, S., Shafreen, R.M.B., Priya, A. and Shunmugiah, K.P., 2021. Ethnomedicines of Indian origin for combating COVID-19 infection by hampering the viral replication: using structure-based drug discovery approach. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(13), pp.4594-4609.
- Vázquez-Mendoza, L.H., Mendoza-Figueroa, H.L., García-Vázquez, J.B., Correa-Basurto, J. and García-Machorro, J., 2022. In silico drug repositioning to target the SARS-CoV-2 main protease as covalent inhibitors employing a combined structure-based virtual screening strategy of pharmacophore models and covalent docking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), p.3987.
- Abuo-Rahma, Gamal El-Din A., Mamdouh FA Mohamed, Tarek S. Ibrahim, Mai E. Shoman, Ebtihal Samir, and Rehab M. Abd El-Baky. "Potential repurposed SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection drugs." RSC advances 10, no. 45 (2020): 26895-26916. [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Almes, F.J., 2020. Repurposing approved drugs as potential inhibitors of 3CL-protease of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening and structure based drug design. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 88, p.107351.
- Li, Q. and Kang, C., 2020. Progress in developing inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease. Microorganisms, 8(8), p.1250.
- Ahmed, M.Z., Zia, Q., Haque, A., Alqahtani, A.S., Almarfadi, O.M., Banawas, S., Alqahtani, M.S., Ameta, K.L. and Haque, S., 2021. Aminoglycosides as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: an in silico drug repurposing study on FDA-approved antiviral and anti-infection agents. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 14(5), pp.611-619.. [CrossRef]
- Attiq, N., Arshad, U., Brogi, S., Shafiq, N., Imtiaz, F., Parveen, S., Rashid, M. and Noor, N., 2022. Exploring the anti-SARS-CoV-2 main protease potential of FDA approved marine drugs using integrated machine learning templates as predictive tools. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 220, pp.1415-1428.
- Murugan, N.A., Pandian, C.J. and Jeyakanthan, J., 2021. Computational investigation on Andrographis paniculata phytochemicals to evaluate their potency against SARS-CoV-2 in comparison to known antiviral compounds in drug trials. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(12), pp.4415-4426.. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Song, W.; Huang, H.; Sun, Q. Pharmacological Therapeutics Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase, Proteinase and Spike Protein: From Mechanistic Studies to Clinical Trials for COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1131. [CrossRef]
- Awadasseid, A., Wu, Y., Tanaka, Y. and Zhang, W., 2021. SARS-CoV-2 variants evolved during the early stage of the pandemic and effects of mutations on adaptation in Wuhan populations. International journal of biological sciences, 17(1), p.97.
- Muratov, E.N., Amaro, R., Andrade, C.H., Brown, N., Ekins, S., Fourches, D., Isayev, O., Kozakov, D., Medina-Franco, J.L., Merz, K.M. and Oprea, T.I., 2021. A critical overview of computational approaches employed for COVID-19 drug discovery. Chemical Society Reviews, 50(16), pp.9121-9151.
- Shree, P., Mishra, P., Selvaraj, C., Singh, S.K., Chaube, R., Garg, N. and Tripathi, Y.B., 2022. Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease through active phytochemicals of ayurvedic medicinal plants–Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Tinospora cordifolia (Giloy) and Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi)–a molecular docking study. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(1), pp.190-203. [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.N., Goswami, D., Jaiswal, D.G., Parmar, R.M., Solanki, H.A. and Pandya, H.A., 2021. Pinpointing the potential hits for hindering interaction of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein with ACE2 from the pool of antiviral phytochemicals utilizing molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 105, p.107874.
- Abdalla, M.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Sarangi, A.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Eltayb, W.A.; Alam, M.; El-Arabey, A.A.; Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Seidel, V.; et al. In silico studies on phytochemicals to combat the emerging COVID-19 infection. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101367–101367. [CrossRef]
- Esam, Z., Akhavan, M., Lotfi, M. and Bekhradnia, A., 2022. Synthesis and In Silico Investigation of Isatin-Based Schiff Bases as Potential Inhibitors for Promising Targets against SARS-CoV-2. ChemistrySelect, 7(46), p.e202201983.
- Abdusalam, A.A. and Ben-Hander, G.M., 2022. Identification of Potential Natural Bioactive Compounds from Glycyrrhiza glabra as Sars-CoV-2 Main Protease (MPRO) Inhibitors: In-Silico Approach. Al-Mukhtar Journal of Sciences, 37(2), pp.150-161.
- Boufissiou, A., Abdalla, M., Sharaf, M., Al-Resayes, S.I., Imededdine, K., Alam, M., Yagi, S., Azam, M. and Yousfi, M., 2022. In-silico investigation of phenolic compounds from leaves of Phillyrea angustifolia L. as a potential inhibitor against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro PDB ID: 5R83) using a virtual screening method. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 26(3), p.101473.
- Nazir, M., Tousif, M.I., Khalid, M., Parveen, S., Akhter, N., Farooq, N., Khan, M.U., Mehmood, R.F., Mahomoodally, M.F., Muhammad, S. and Alarfaji, S.S., 2022. Isolation of Thioinosine and Butenolides from a Terrestrial Actinomycetes sp. GSCW-51 and Their in Silico Studies for Potential against SARS-CoV-2. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 19(4), p.e202100843. [CrossRef]
- Abel, R., Paredes Ramos, M., Chen, Q., Pérez-Sánchez, H., Coluzzi, F., Rocco, M., Marchetti, P., Mura, C., Simmaco, M., Bourne, P.E. and Preissner, R., 2020. Computational prediction of potential inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in chemistry, p.1162.
- Yadav, P., Rana, M. and Chowdhury, P., 2021. DFT and MD simulation investigation of favipiravir as an emerging antiviral option against viral protease (3CLpro) of SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1246, p.131253.. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. and Kang, C., 2020. Progress in developing inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease. Microorganisms, 8(8), p.1250.
- Kalasariya, H.S., Patel, N.B., Gacem, A., Alsufyani, T., Reece, L.M., Yadav, V.K., Awwad, N.S., Ibrahium, H.A., Ahn, Y., Yadav, K.K. and Jeon, B.H., 2022. Marine Alga Ulva fasciata-Derived Molecules for the Potential Treatment of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Approach. Marine Drugs, 20(9), p.586.
- de Souza, A.S., de Souza, R.F. and Guzzo, C.R., 2022. Quantitative structure-activity relationships, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations reveal drug repurposing candidates as potent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(21), pp.11339-11356. [CrossRef]
- Mekni, N., Coronnello, C., Langer, T., Rosa, M.D. and Perricone, U., 2021. Support Vector Machine as a Supervised Learning for the Prioritization of Novel Potential SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), p.7714.
- Amin, S.A., Banerjee, S., Singh, S., Qureshi, I.A., Gayen, S. and Jha, T., 2021. First structure–activity relationship analysis of SARS-CoV-2 virus main protease (Mpro) inhibitors: an endeavor on COVID-19 drug discovery. Molecular diversity, pp.1-12.
- Islam, R., Parves, M.R., Paul, A.S., Uddin, N., Rahman, M.S., Mamun, A.A., Hossain, M.N., Ali, M.A. and Halim, M.A., 2021. A molecular modeling approach to identify effective antiviral phytochemicals against the main protease of SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(9), pp.3213-3224.
- Liu, Z.; Roberts, R.A.; Lal-Nag, M.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Tong, W. AI-based language models powering drug discovery and development. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2593–2607. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K. and Aggarwal, R., 2021. Repurposing potential of FDA-approved and investigational drugs for COVID-19 targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike and main protease and validation by machine learning algorithm. Chemical biology & drug design, 97(4), pp.836-853.
- Musa, A., Abulkhair, H.S., Aljuhani, A., Rezki, N., Abdelgawad, M.A., Shalaby, K., El-Ghorab, A.H. and Aouad, M.R., 2023. Phenylpyrazolone-1, 2, 3-triazole Hybrids as Potent Antiviral Agents with Promising SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibition Potential. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), p.463. [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.T., Gentile, F., Hsing, M., Ban, F. and Cherkasov, A., 2020. Rapid identification of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by deep docking of 1.3 billion compounds. Molecular informatics, 39(8), p.2000028.
- Kumar, V., Kar, S., De, P., Roy, K. and Leszczynski, J., 2022. Identification of potential antivirals against 3CLpro enzyme for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2: A multi-step virtual screening study. SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research, 33(5), pp.357-386.
- Prajapati, J., Patel, R., Rao, P., Saraf, M., Rawal, R. and Goswami, D., 2022. Perceiving SARS-CoV-2 Mpro and PLpro dual inhibitors from pool of recognized antiviral compounds of endophytic microbes: an in silico simulation study. Structural Chemistry, 33(5), pp.1619-1643. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.O., Adegboyega, A.E., Ojo, O.A., Yusuf, A.J., Iwaloye, O., Ugwah-Oguejiofor, C.J., Asomadu, R.O., Chukwuma, I.F., Ejembi, S.A., Ugwuja, E.I. and Alotaibi, S.S., 2022. A computational approach to elucidate the interactions of chemicals from Artemisia annua targeted toward SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition for COVID-19 treatment. Frontiers in medicine, 9.
- Ghosh, A., Chakraborty, M., Chandra, A. and Alam, M.P., 2021. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) and molecular dynamics study of withaferin-A fragment derivatives as potential therapeutic lead against main protease (M pro) of SARS-CoV-2. Journal of molecular modeling, 27, pp.1-17.
- Gentile, D., Patamia, V., Scala, A., Sciortino, M.T., Piperno, A. and Rescifina, A., 2020. Putative inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease from a library of marine natural products: A virtual screening and molecular modeling study. Marine drugs, 18(4), p.225. [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.A., Ashour, A., Elhady, S.S., Darwish, K.M. and Al-Karmalawy, A.A., 2022. Calendulaglycoside A showing potential activity against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: Molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and SAR studies. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine, 12(1), pp.16-34.
- Houchi, S. and Messasma, Z., 2022. Exploring the inhibitory potential of Saussurea costus and Saussurea involucrata phytoconstituents against the Spike glycoprotein receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B. 1.617. 2) variant and the main protease (Mpro) as therapeutic candidates, using Molecular docking, DFT, and ADME/Tox studies. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1263, p.133032.
- Domínguez-Villa, F.X., Durán-Iturbide, N.A. and Ávila-Zárraga, J.G., 2021. Synthesis, molecular docking, and in silico ADME/Tox profiling studies of new 1-aryl-5-(3-azidopropyl) indol-4-ones: Potential inhibitors of SARS CoV-2 main protease. Bioorganic chemistry, 106, p.104497. [CrossRef]
- Markovic, M.; Deodhar, S.; Machhi, J.; Yeapuri, P.; Saleh, M.; Edagwa, B.J.; Mosley, R.L.; Gendelman, H.E. Prodrug Therapies for Infectious and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 518. [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, J., Patel, R., Goswami, D., Saraf, M. and Rawal, R.M., 2021. Sterenin M as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease identified from MeFSAT database using molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy calculation. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 135, p.104568.
- Johnson, T.O., Adegboyega, A.E., Ojo, O.A., Yusuf, A.J., Iwaloye, O., Ugwah-Oguejiofor, C.J., Asomadu, R.O., Chukwuma, I.F., Ejembi, S.A., Ugwuja, E.I. and Alotaibi, S.S., 2022. A computational approach to elucidate the interactions of chemicals from Artemisia annua targeted toward SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition for COVID-19 treatment. Frontiers in medicine, 9.
- Bakowski, M.A.; Beutler, N.; Wolff, K.C.; Kirkpatrick, M.G.; Chen, E.; Nguyen, T.-T.H.; Riva, L.; Shaabani, N.; Parren, M.; Ricketts, J.; et al. Drug repurposing screens identify chemical entities for the development of COVID-19 interventions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3309. [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, B.S., Rathi, B., Singh, J. and Poonam, F.N.U., 2020. Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 disease COVID-19: Infection, prevention and clinical advances of the prospective chemical drug therapeutics: Array. Chemical Biology Letters, 7(1), pp.63-72.
- Nasir, A.M., Awang, N., Hubadillah, S.K., Jaafar, J., Othman, M.H.D., Salleh, W.N.W. and Ismail, A.F., 2021. A review on the potential of photocatalysis in combatting SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 42, p.102111. [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Hernández, J.E., Rodas-Zuluaga, L.I., López-Pacheco, I.Y., Melchor-Martínez, E.M., Aghalari, Z., Limón, D.S., Iqbal, H.M. and Parra-Saldívar, R., 2021. Sources of antibiotics pollutants in the aquatic environment under SARS-CoV-2 pandemic situation. Case studies in chemical and environmental engineering, 4, p.100127.
- Fuzimoto, A.D., 2021. An overview of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties of Artemisia annua, its antiviral action, protein-associated mechanisms, and repurposing for COVID-19 treatment. Journal of integrative medicine, 19(5), pp.375-388.
- Jang, W.D.; Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, S.; Shahraki, B.T.; Rameh, F.; Nazarabi, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Akhavan, O.; Rabiee, M.; Mostafavi, E.; Lima, E.C.; Saeb, M.R.; et al. A review on computer-aided chemogenomics and drug repositioning for rational COVID -19 drug discovery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 699–721. [CrossRef]
- Estrada, E., 2020. COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2. Modeling the present, looking at the future. Physics Reports, 869, pp.1-51.
- Chowdhury, K.H., Chowdhury, M.R., Mahmud, S., Tareq, A.M., Hanif, N.B., Banu, N., Reza, A.A., Emran, T.B. and Simal-Gandara, J., 2020. Drug repurposing approach against novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) through virtual screening targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Biology, 10(1), p.2.
- Federico, L.B., Silva, G.M., da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I., Gomes, S.Q., Barcelos, M.P., Galindo Francischini, I.A. and Tomich de Paula da Silva, C.H., 2021. Identification of known drugs as potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors using ligand-and structure-based virtual screening. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 13(16), pp.1353-1366. [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, K., Rubavathy, S.E., Prakash, M., Thilagavathi, R., Hosseini-Zare, M.S. and Selvam, C., 2022. Antiviral activities of natural compounds and ionic liquids to inhibit the Mpro of SARS-CoV-2: a computational approach. RSC advances, 12(6), pp.3687-3695.
- Jang, W.D.; Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Luttens, A., Gullberg, H., Abdurakhmanov, E., Vo, D.D., Akaberi, D., Talibov, V.O., Nekhotiaeva, N., Vangeel, L., De Jonghe, S., Jochmans, D. and Krambrich, J., 2022. Ultralarge virtual screening identifies SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with broad-spectrum activity against coronaviruses. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 144(7), pp.2905-2920.
- Laref, S.; Harrou, F.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Laref, A.; Laleg-Kirati, T.-M.; Gojobori, T.; Gao, X. Synergy of Small Antiviral Molecules on a Black-Phosphorus Nanocarrier: Machine Learning and Quantum Chemical Simulation Insights. Molecules 2023, 28, 3521. [CrossRef]
- Staszak, M.; Staszak, K.; Wieszczycka, K.; Bajek, A.; Roszkowski, K.; Tylkowski, B. Machine learning in drug design: Use of artificial intelligence to explore the chemical structure–biological activity relationship. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2021, 12, e1568. [CrossRef]
- Zohora, F.T., Azam, A.T.M., Ahmed, S., Rahman, K.M., Halim, M.A., Anwar, M., Sohrab, M., Tabassum, F., Hasan, C.M. and Ahsan, M., 2022. Isolation and In Silico Prediction of Potential Drug-like Compounds with a New Dimeric Prenylated Quinolone Alkaloid from Zanthoxylum rhetsa (Roxb.) Root Extracts Targeted against SARS-CoV-2 (Mpro). Molecules, 27(23), p.8191.
- Abdalla, M.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Sarangi, A.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Eltayb, W.A.; Alam, M.; El-Arabey, A.A.; Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Seidel, V.; et al. In silico studies on phytochemicals to combat the emerging COVID-19 infection. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101367–101367. [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, A., Haldar, S., Singh, H., Roy, P. and Varshney, A., 2021. Coronil, a tri-herbal formulation, attenuates spike-protein-mediated SARS-CoV-2 viral entry into human alveolar epithelial cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines production by inhibiting spike protein-ACE-2 interaction. Journal of Inflammation Research, 14, p.869.
- da Silva, F.M.A., da Silva, K.P.A., de Oliveira, L.P.M., Costa, E.V., Koolen, H.H., Pinheiro, M.L.B., de Souza, A.Q.L. and de Souza, A.D.L., 2020. Flavonoid glycosides and their putative human metabolites as potential inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 115.
- DasGupta, D., Chan, W.K. and Carlson, H.A., 2022. Computational identification of possible allosteric sites and modulators of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 62(3), pp.618-626.. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.K., Singh, R., Das, P. and Purohit, R., 2021. Evaluation of acridinedione analogs as potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors and their comparison with repurposed anti-viral drugs. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 128, p.104117.
- Qaisar, M., Muhammad, S., Iqbal, J., Khera, R.A., Al-Sehemi, A.G., Alarfaji, S.S., Khalid, M. and Hussain, F., 2022. Identification of marine fungi-based antiviral agents as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 by molecular docking, ADMET and molecular dynamic study. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry, 21(02), pp.139-153.
- Majeed, A., Hussain, W., Yasmin, F., Akhtar, A. and Rasool, N., 2021. Virtual screening of phytochemicals by targeting HR1 domain of SARS-CoV-2 S protein: molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and DFT studies. BioMed Research International, 2021, pp.1-19.
- Parihar, A., Sonia, Z.F., Akter, F., Ali, M.A., Hakim, F.T. and Hossain, M.S., 2022. Phytochemicals-based targeting RdRp and main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using docking and steered molecular dynamic simulation: A promising therapeutic approach for Tackling COVID-19. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 145, p.105468. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K., Mahanta, S., Tanti, B., Tag, H. and Hui, P.K., 2022. Identification of phytocompounds from Houttuynia cordata Thunb. as potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 replication proteins through GC–MS/LC–MS characterization, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Molecular Diversity, 26(1), pp.365-388.
- Abdalla, M.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Sarangi, A.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Eltayb, W.A.; Alam, M.; El-Arabey, A.A.; Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Seidel, V.; et al. In silico studies on phytochemicals to combat the emerging COVID-19 infection. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101367–101367. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, C. Fragment tailoring strategy to design novel chemical entities as potential binders of novel corona virus main protease. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 3733–3746. [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, S.V., Stoddard, S.D., Oelkers, B.K., Fitts, K., Whalum, K., Whalum, K., Hemphill, A.D., Manikonda, J., Martinez, L.M., Riley, E.G. and Roof, C.M., 2020. Optimization rules for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro antivirals: Ensemble docking and exploration of the coronavirus protease active site. Viruses, 12(9), p.942.
- 116.
- El-Demerdash, A., Al-Karmalawy, A.A., Abdel-Aziz, T.M., Elhady, S.S., Darwish, K.M. and Hassan, A.H., 2021. Investigating the structure–activity relationship of marine natural polyketides as promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. RSC advances, 11(50), pp.31339-31363.
- El-Demerdash, A., Al-Karmalawy, A.A., Abdel-Aziz, T.M., Elhady, S.S., Darwish, K.M. and Hassan, A.H., 2021. Investigating the structure–activity relationship of marine natural polyketides as promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. RSC advances, 11(50), pp.31339-31363. [CrossRef]
- Bouback, T.A., Pokhrel, S., Albeshri, A., Aljohani, A.M., Samad, A., Alam, R., Hossen, M.S., Al-Ghamdi, K., Talukder, M.E.K., Ahammad, F. and Qadri, I., 2021. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening, quantum mechanics calculations, and molecular dynamics simulation approaches identified potential natural antiviral drug candidates against MERS-CoV S1-NTD. Molecules, 26(16), p.4961.
- Giudetti, G., Polyakov, I., Grigorenko, B.L., Faraji, S., Nemukhin, A.V. and Krylov, A.I., 2022. How Reproducible Are QM/MM Simulations? Lessons from Computational Studies of the Covalent Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Carmofur. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 18(8), pp.5056-5067.
- widerek, K. and Moliner, V., 2020. Revealing the molecular mechanisms of proteolysis of SARS-CoV-2 M pro by QM/MM computational methods. Chemical Science, 11(39), pp.10626-10630. [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L.; Frishcosy, J.; Huzumi, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Schluckbier, T.; Wei, X.; Wei, G.-W. Methodology-Centered Review of Molecular Modeling, Simulation, and Prediction of SARS-CoV-2. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11287–11368. [CrossRef]
- Arafet, K., Serrano-Aparicio, N., Lodola, A., Mulholland, A.J., González, F.V., Świderek, K. and Moliner, V., 2021. Mechanism of inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 M pro by N3 peptidyl Michael acceptor explained by QM/MM simulations and design of new derivatives with tunable chemical reactivity. Chemical Science, 12(4), pp.1433-1444.
- Algar-Lizana, S.; Bonache, M..; González-Muñiz, R. SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors: What is moving in the field of peptides and peptidomimetics?. J. Pept. Sci. 2022, 29, e3467. [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.A.; Kumar, S.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srivastava, V. Searching for target-specific and multi-targeting organics for Covid-19 in the Drugbank database with a double scoring approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J., Worrall, L.J., Vuckovic, M., Rosell, F.I., Gentile, F., Ton, A.T., Caveney, N.A., Ban, F., Cherkasov, A., Paetzel, M. and Strynadka, N.C., 2020. Crystallographic structure of wild-type SARS-CoV-2 main protease acyl-enzyme intermediate with physiological C-terminal autoprocessing site. Nature communications, 11(1), p.5877.
- Rudrapal, M., Issahaku, A.R., Agoni, C., Bendale, A.R., Nagar, A., Soliman, M.E. and Lokwani, D., 2022. In silico screening of phytopolyphenolics for the identification of bioactive compounds as novel protease inhibitors effective against SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(20), pp.10437-10453. [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.S., Okimoto, N., Koyama, Y.M., Hirano, Y., Morimoto, G., Ohno, Y. and Taiji, M., 2020. Drug binding dynamics of the dimeric SARS-CoV-2 main protease, determined by molecular dynamics simulation. Scientific reports, 10(1), p.16986.
- Pipitò, L.; Rujan, R.; Reynolds, C.A.; Deganutti, G. Molecular dynamics studies reveal structural and functional features of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. BioEssays 2022, 44, e2200060. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.B.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, D.; Khanna, P.; Mansi; Khanna, L.; Kumar, V.; Kumari, K.; Gupta, A.; Chaudhary, P.; et al. An understanding of coronavirus and exploring the molecular dynamics simulations to find promising candidates against the Mpro of nCoV to combat the COVID-19: A systematic review. J. Infect. Public Heal. 2022, 15, 1326–1349. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.K., Singh, R., Das, P. and Purohit, R., 2021. Evaluation of acridinedione analogs as potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors and their comparison with repurposed anti-viral drugs. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 128, p.104117.
- Khan, S., Fakhar, Z., Hussain, A., Ahmad, A., Jairajpuri, D.S., Alajmi, M.F. and Hassan, M.I., 2022. Structure-based identification of potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(8), pp.3595-3608.
- Menéndez, C.A., Byléhn, F., Perez-Lemus, G.R., Alvarado, W. and de Pablo, J.J., 2020. Molecular characterization of ebselen binding activity to SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Science Advances, 6(37), p.eabd0345.
- Gossen, J., Albani, S., Hanke, A., Joseph, B.P., Bergh, C., Kuzikov, M., Costanzi, E., Manelfi, C., Storici, P., Gribbon, P. and Beccari, A.R., 2021. A blueprint for high affinity SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors from activity-based compound library screening guided by analysis of protein dynamics. ACS pharmacology & translational science, 4(3), pp.1079-1095. [CrossRef]
- Arshia, A.H., Shadravan, S., Solhjoo, A., Sakhteman, A. and Sami, A., 2021. De novo design of novel protease inhibitor candidates in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 using deep learning, docking, and molecular dynamic simulations. Computers in biology and medicine, 139, p.104967.
- Gurung, A.B., Ali, M.A., Lee, J., Farah, M.A. and Al-Anazi, K.M., 2020. Unravelling lead antiviral phytochemicals for the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro enzyme through in silico approach. Life sciences, 255, p.117831.
- Kulkarni, S.A. and Ingale, K., 2022. In Silico Approaches for Drug Repurposing for SARS-CoV-2 Infection.
- Yan, G., Li, D., Lin, Y., Fu, Z., Qi, H., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Si, S. and Chen, Y., 2021. Development of a simple and miniaturized sandwich-like fluorescence polarization assay for rapid screening of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Cell & Bioscience, 11(1), pp.1-14. [CrossRef]
- Krishnaprasad, B., Maity, S., Mehta, C., Suresh, A., Nayak, U.Y. and Nayak, Y., 2020. In silico drug repurposing of penicillins to target main protease Mpro of SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceutical Sciences, 26(Covid-19), pp.S52-S62.
- Ton, A.T., Gentile, F., Hsing, M., Ban, F. and Cherkasov, A., 2020. Rapid identification of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by deep docking of 1.3 billion compounds. Molecular informatics, 39(8), p.2000028.
- Amin, S.A.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, K.; Gayen, S.; Jha, T. Protease targeted COVID-19 drug discovery and its challenges: Insight into viral main protease (Mpro) and papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 29, 115860. [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.D.; Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Bzówka, M., Mitusińska, K., Raczyńska, A., Samol, A., Tuszyński, J.A. and Góra, A., 2020. Structural and evolutionary analysis indicate that the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro is a challenging target for small-molecule inhibitor design. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), p.3099. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.M., Baric, R.S., Saphire, E.O. and Ulmer, J.B., 2022. Stopping pandemics before they start: lessons learned from SARS-CoV-2. Science, 375(6585), pp.1133-1139. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





