Submitted:
17 August 2023
Posted:
21 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
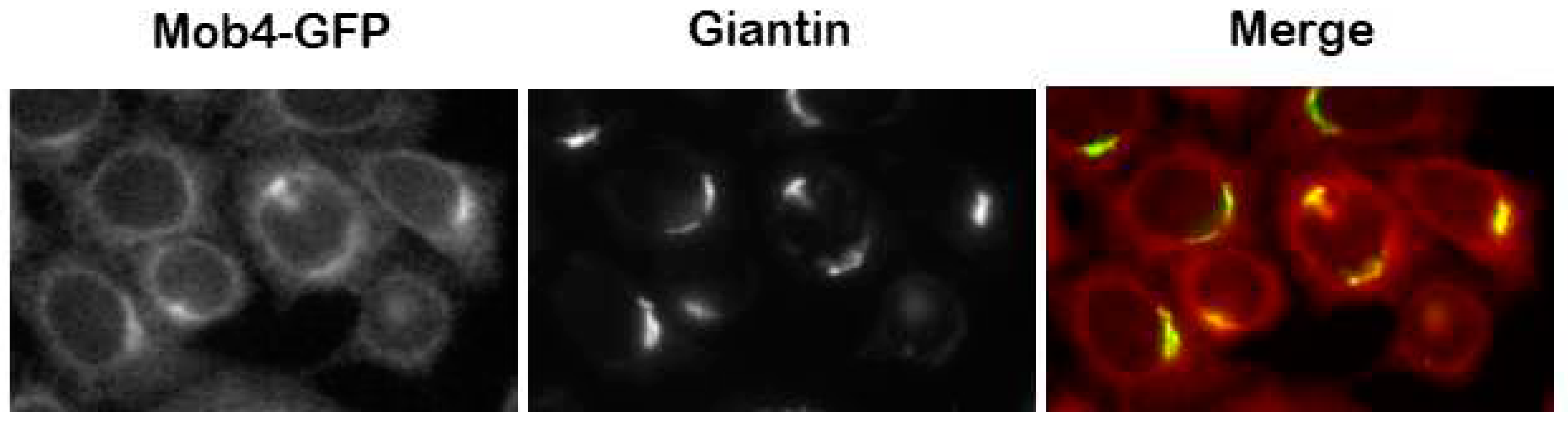
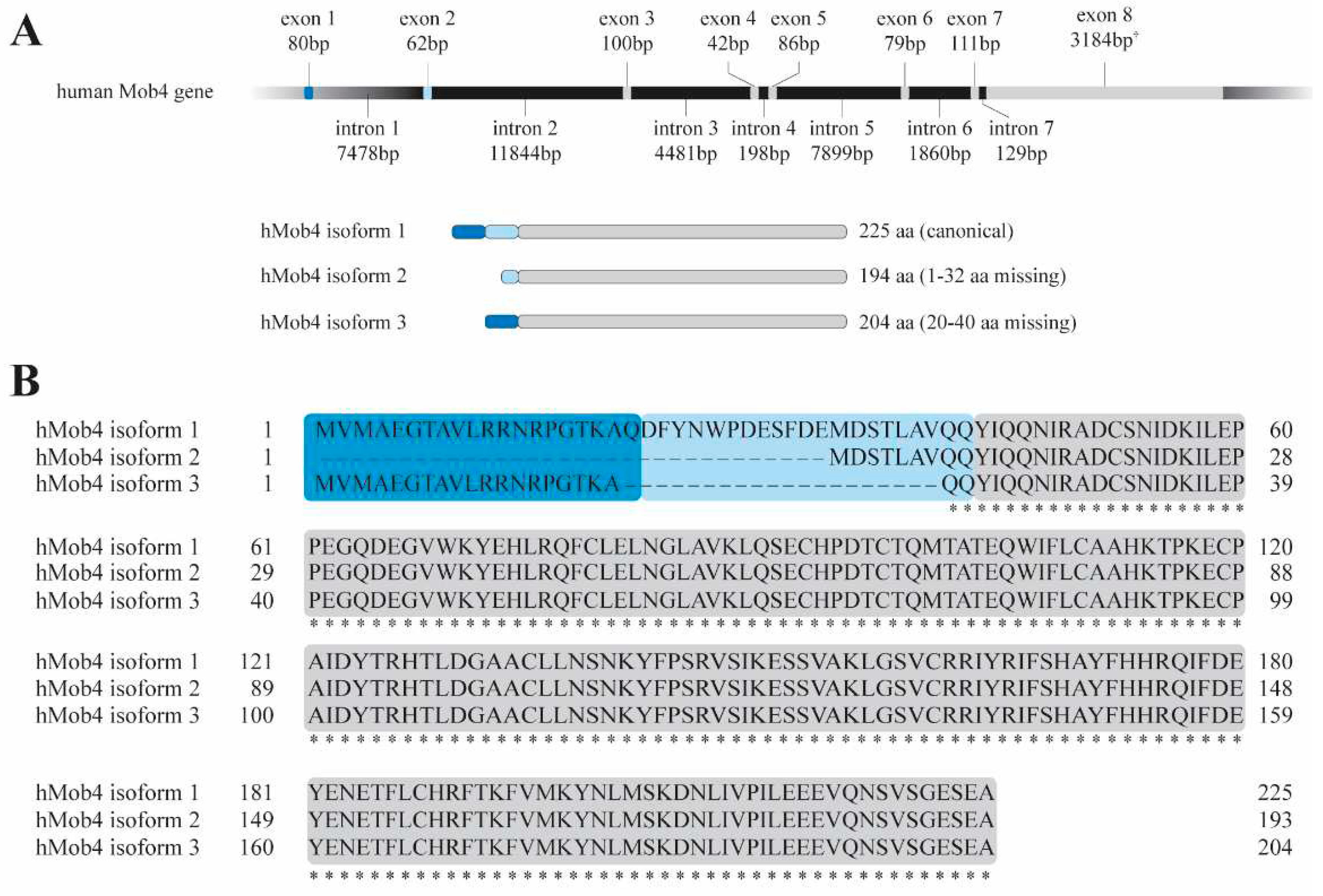
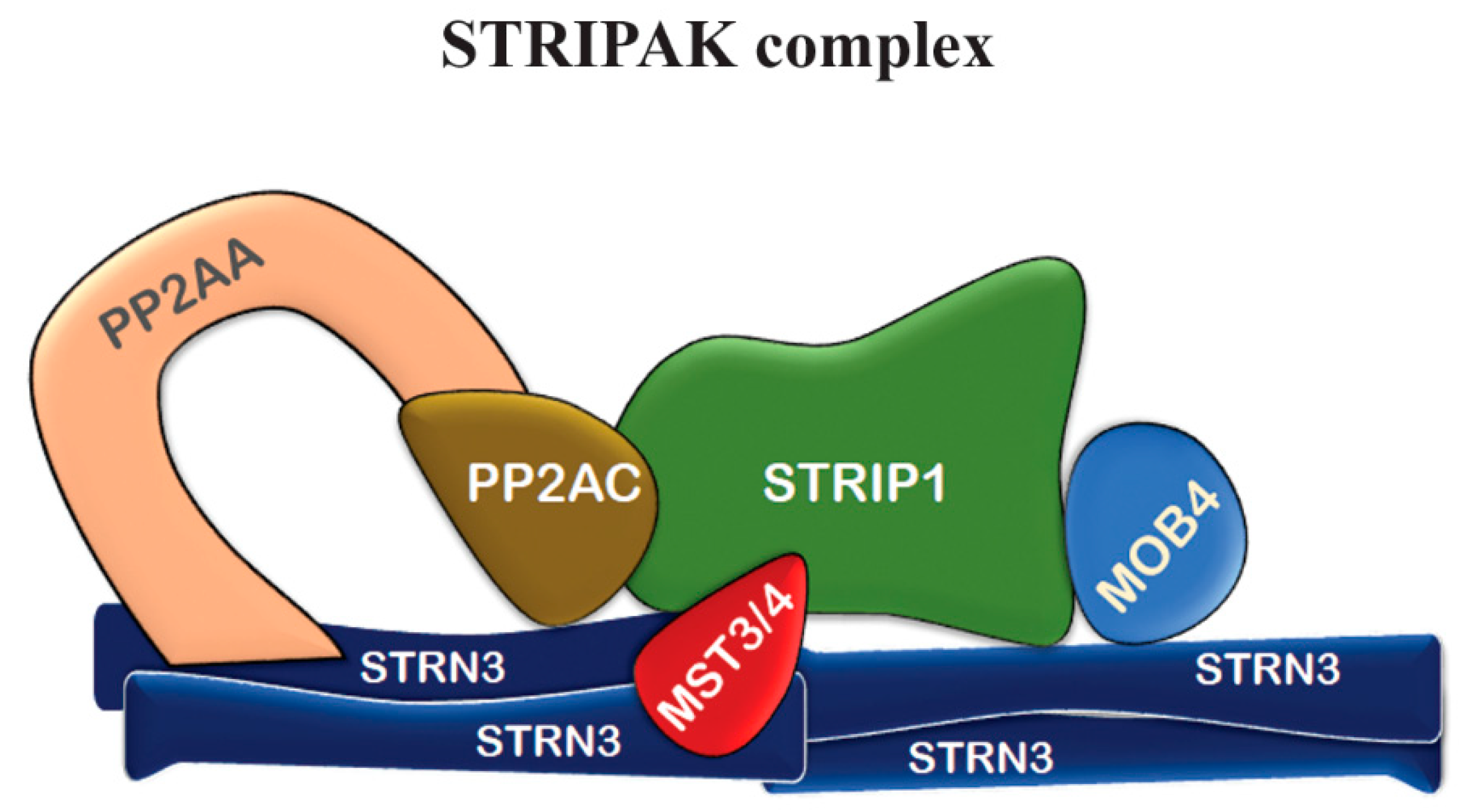
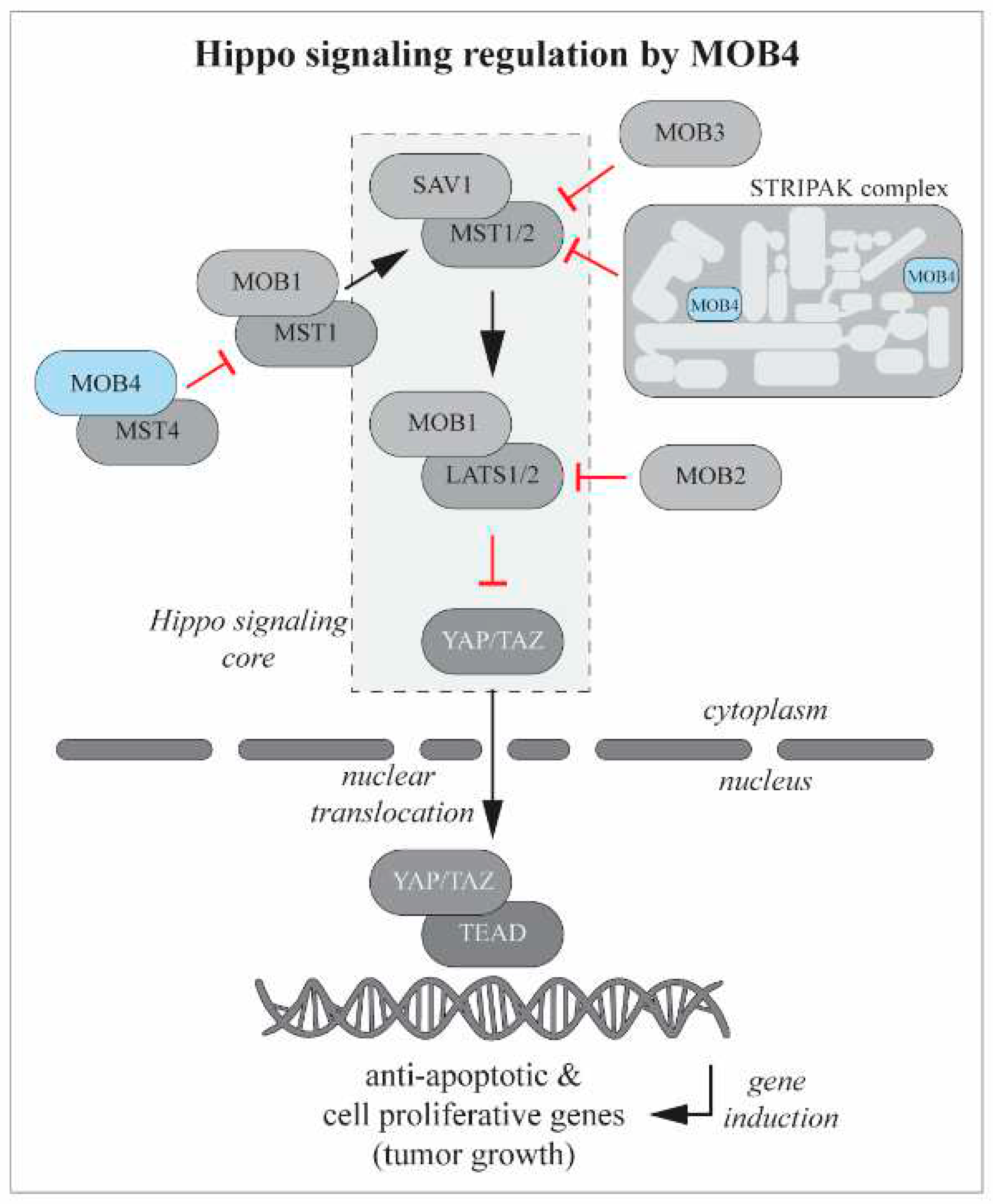
2. MOB4: from the gene to the function
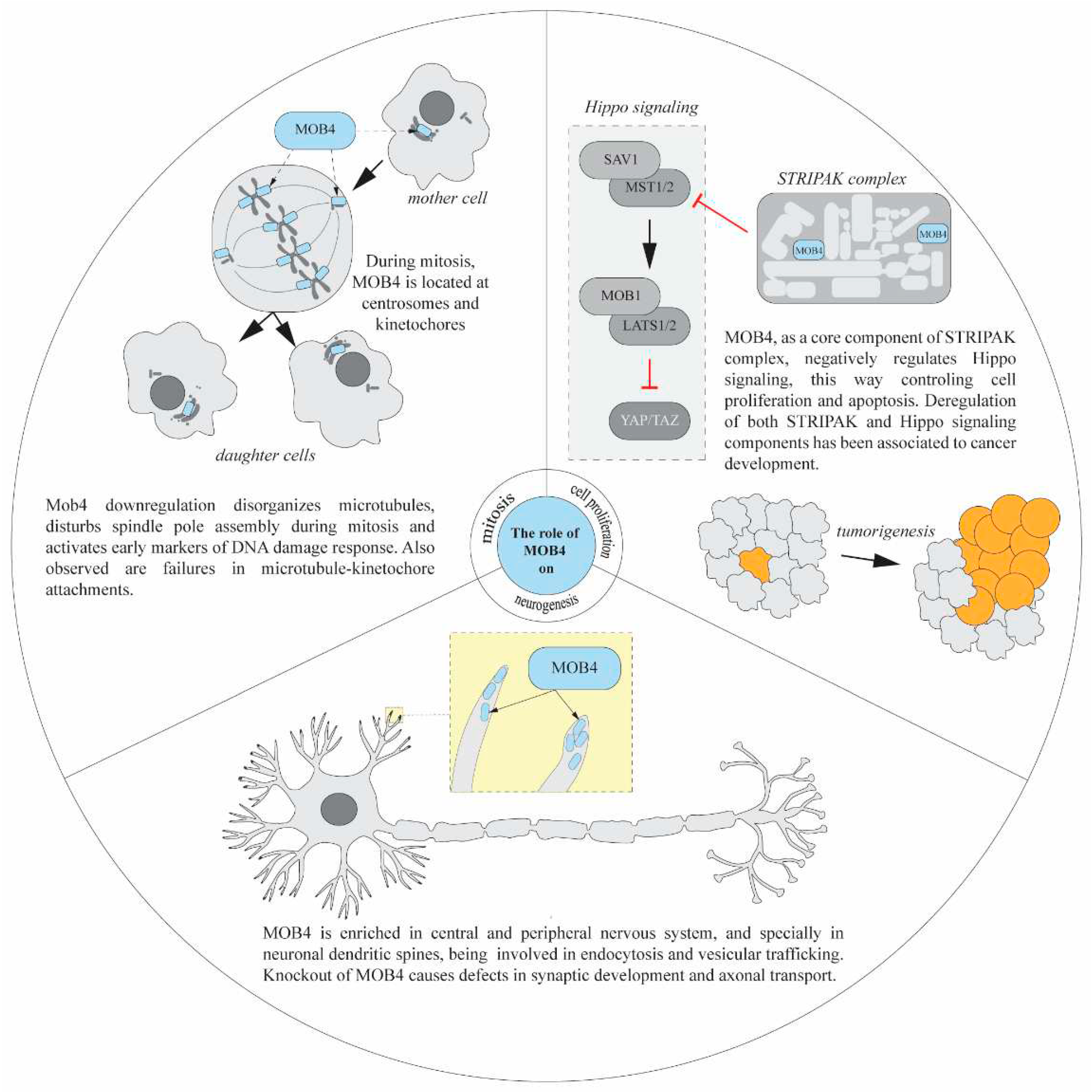
3. Neuronal functions of Mob4
4. Mob4 and cytoskeleton
5. Cell proliferation function of Mob4
6. Mob4 and spermatogenesis
- Other Mob4 functions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado, I.; Carmona, B.; Nolasco, S.; Santos, D.; Leitão, A.; Soares, H. MOB: Pivotal Conserved Proteins in Cytokinesis, Cell Architecture and Tissue Homeostasis. Biology 2020, 9, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhart, J.C.; Raftery, L.A. Mob Family Proteins: Regulatory Partners in Hippo and Hippo-Like Intracellular Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, F.C.; Winey, M. Regulation of Mob1p, an essential budding yeast protein required for completion of mitosis and spindle pole body duplication. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 12A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, F.C.; Winey, M. MOB1, an essential yeast gene required for completion of mitosis and maintenance of ploidy. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Nikolaidis, N.; Nei, M.; Lai, Z. Evolution of the mob Gene Family. The Open Cell Signaling Journal 2009, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitulo, N.; Vezzi, A.; Galla, G.; Citterio, S.; Marino, G.; Ruperti, B.; Zermiani, M.; Albertini, E.; Valle, G.; Barcaccia, G. Characterization and evolution of the cell cycle-associated mob domain-containing proteins in eukaryotes. Evol Bioinform Online 2007, 3, 121–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.C.; Wei, X.; Shimizu, T.; Ramos, E.; Rohrbaugh, M.; Nikolaidis, N.; Ho, L.L.; Li, Y. Control of cell proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, mats. Cell 2005, 120, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D. Hippo signaling in organ size control. Genes and Development. 2007, 21, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, G.; Johnson, R.L. Hippo signaling: Growth control and beyond. Development. 2011, 138, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.L.; Kurischko, C.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.; Drubin, D.G.; Luca, F.C. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mob2p-Cbk1p kinase complex promotes polarized growth and acts with the mitotic exit network to facilitate daughter cell-specific localization of Ace2p transcription factor. J Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, R.S.; Schmitz, D.; Cornils, H.; Hemmings, B.A.; Hergovich, A. Differential NDR/LATS interactions with the human MOB family reveal a negative role for human MOB2 in the regulation of human NDR kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 4507–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xue, G.; Hynx, D.; Wang, Y.; Cron, P.D.; Hundsrucker, C.; Hergovich, A.; Frank, S.; Hemmings, B.A.; Schmitz-Rohmer, D. hMOB3 modulates MST1 apoptotic signaling and supports tumor growth in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3779–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudreault, M.; D'Ambrosio, L.M.; Kean, M.J.; Mullin, M.J.; Larsen, B.G.; Sanchez, A.; Chaudhry, S.; Chen, G.I.; Sicheri, F.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Aebersold, R.; Raught, B.; Gingras, A.C. A PP2A phosphatase high density interaction network identifies a novel striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase complex linked to the cerebral cavernous malformation 3 (CCM3) protein. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009, 8, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatter, T.; Wepf, A.; Aebersold, R.; Gstaiger, M. An integrated workflow for charting the human interaction proteome: Insights into the PP2A system. Mol Syst Biol. 2009, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.S.; Josué, F.; Wepf, A.; Wehr, M.C.; Rinner, O.; Kelly, G.; Tapon, N.; Gstaiger, M. Combined functional genomic and proteomic approaches identify a PP2A complex as a negative regulator of Hippo signaling. Mol Cell. 2010, 39, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Hwang, J.; Carrier, K.J.; Jones, C.A.; Kern, Q.L.; Moreno, C.S.; Karas, R.H.; Pallas, D.C. Protein phosphatase 2a (PP2A) binds within the oligomerization domain of striatin and regulates the phosphorylation and activation of the mammalian Ste20-Like kinase Mst3. BMC Biochem. 2011, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Zhang, B.; Murray, B.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Skrzypek, E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014, mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D512–D520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ranedo, J.; Gonzaga, E.; Jaworek, K.J.; Berger, C.; Bossing, T.; Barros, C.S. STRIPAK Members Orchestrate Hippo and Insulin Receptor Signaling to Promote Neural Stem Cell Reactivation. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Jiao, S.; Zhou, Z. STRIPAK complexes in cell signaling and cancer. Oncogene. 2016, 35, 4549–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillat, G.; Moqrich, A.; Castets, F.; Baude, A.; Bailly, Y.; Benmerah, A.; Monneron, A. Molecular cloning and characterization of phocein, a protein found from the Golgi complex to dendritic spines. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.C.; Bae, S.J.; Ni, L.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C.; Luo, X. Cryo-EM structure of the Hippo signaling integrator human STRIPAK. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021, 28, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, C.S.; Lane, W.S.; Pallas, D.C. A mammalian homolog of yeast MOB1 is both a member and a putative substrate of striatin family-protein phosphatase 2A complexes. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276, 24253–24260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeberlé, A.M.; Castets, F.; Bombarde, G.; Baillat, G.; Bailly, Y. Immunogold localization of MOB4 in dendritic spines. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 495, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, Y.J.; Castets, F. Phocein: A potential actor in vesicular trafficking at Purkinje cell dendritic spines. Cerebellum. 2007, 6, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.; Sepp, K.J.; Jorquera, R.A.; Wu, C.; Song, Y.; Hong, P.; Littleton, J.T. DMob4/Phocein regulates synapse formation, axonal transport, and microtubule organization. J Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5189–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Mimoso, J.M.; Palma, S.L.; Gonçalves, C.; Silvestre, D.; Campinho, M.; Tavares, Á.A. Mob4 is required for neurodevelopment in zebrafish. MicroPubl Biol 2023, micropub.biology.000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Pallas, D.C. STRIPAK complexes: Structure, biological function, and involvement in human diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014, 47, 118–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Musante, V.; Zhou, W.; Picciotto, M.R.; Nairn, A.C. Striatin-1 is a B subunit of protein phosphatase PP2A that regulates dendritic arborization and spine development in striatal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2018, 293, 11179–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trammell, M.A.; Mahoney, N.M.; Agard, D.A.; Vale, R.D. Mob4 plays a role in spindle focusing in Drosophila S2 cells. J Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Berger, S.; Currie, P.D. Mob4-dependent STRIPAK involves the chaperonin TRiC to coordinate myofibril and microtubule network growth. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffe, M.B.; Farr, G.W.; Miklos, D.; Horwich, A.L.; Sternlicht, M.L.; Sternlicht, H. TCP1 complex is a molecular chaperone in tubulin biogenesis. Nature. 1992, 358, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Berger, S.; Li, M.; Jacoby, A.S.; Arner, A.; Bavi, N.; et al. In Vivo Function of the Chaperonin TRiC in alpha-Actin Folding during Sarcomere Assembly. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghozlan, H.; Cox, A.; Nierenberg, D.; King, S.; Khaled, A.R. The TRiCky Business of Protein Folding in Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022, 10, 906530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegusa, K.; Sato, M.; Sato, K.; Nakajima-Shimada, J.; Harada, A.; Sato, K. Caenorhabditis elegans chaperonin CCT/TRiC is required for actin and tubulin biogenesis and microvillus formation in intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014, 25, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabirova, E.; Moloney, A.; Marciniak, S.J.; Williams, J.; Lomas, D.A.; Oliver, S.G.; et al. The TRiC/CCT chaperone is implicated in Alzheimer’s disease based on patient GWAS and an RNAi screen in Abeta-expressing Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, E.G.; Petersen, C.P. STRIPAK Limits Stem Cell Differentiation of a WNT Signaling Center to Control Planarian Axis Scaling. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.E.; Wang, I.E.; Reddien, P.W. Clonogenic neoblasts are pluripotent adult stem cells that underlie planarian regeneration. Science. 2011, 332, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddien, P.W. The Cellular and Molecular Basis for Planarian Regeneration. Cell 2018, 175, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Loh, K.M.; Nusse, R. Stem cell signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration: Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science. 2014, 346, 1248012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurley, K.A.; Rink, J.C.; Sanchez Alvarado, A. Beta-catenin defines head versus tail identity during planarian regeneration and homeostasis. Science 2008, 319, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.P.; Reddien, P.W. Smed-betacatenin-1 is required for anteroposterior blastema polarity in planarian regeneration. Science. 2008, 319, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sileo, P.; Simonin, C.; Melnyk, P.; Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Cotelle, P. Crosstalk between the Hippo Pathway and the Wnt Pathway in Huntington's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells. 2022, 11, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, A.; Gonçalves, J.; Florindo, C.; Tavares, A.A.; Soares, H. Mob1, defining cell polarity for proper cell division. J Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Perdigão, J.; Fesquet, D.; Schiebel, E.; Pines, J.; Tavares, A.A. Human Mob1 proteins are required for cytokinesis by controlling microtubule stability. J Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroli, M.E.; Blanchette, J.O.; Jabbarzadeh, E. Polarity as a physiological modulator of cell function. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019, 24, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhards, Y.; Pöggeler, S. The phocein homologue SmMOB3 is essential for vegetative cell fusion and sexual development in the filamentous ascomycete Sordaria macrospora. Curr Genet. 2011, 57, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.; Iwasa, H.; Kuroyanagi, H.; Hata, Y. Loss of Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of human MOB4 compromises life span, health life span and thermotolerance. Genes Cells. 2021, 26, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, H.; Maimaiti, S.; Kuroyanagi, H.; Kawano, S.; Inami, K.; Timalsina, S.; Ikeda, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Hata, Y. Yes-associated protein homolog, YAP-1, is involved in the thermotolerance and aging in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp Cell Res. 2013, 319, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Xu, Q.; Guan, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhou, Z. The MST4-MOB4 complex disrupts the MST1-MOB1 complex in the Hippo-YAP pathway and plays a pro-oncogenic role in pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2018, 293, 14455–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kück, U.; Radchenko, D.; Teichert, I. STRIPAK, a highly conserved signaling complex, controls multiple eukaryotic cellular and developmental processes and is linked with human diseases. Biol Chem. 2019, 400, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, I.M. Growth factor genes as oncogenes. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1989, 10, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.S.; Miller, L.D. RAS Mutations and Oncogenesis: Not all RAS Mutations are Created Equally. Front Genet. 2012, 2, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrish, F.; Neretti, N.; Sedivy, J.M.; Hockenbery, D.M. The oncogene c-Myc coordinates regulation of metabolic networks to enable rapid cell cycle entry. Cell Cycle. 2008, 7, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, D.W. The retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor gene, the exception that proves the rule. Oncogene. 2006, 25, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; Robin, T.P.; Ford, H.L. Molecular pathways: Targeting the TGF-β pathway for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4514–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.I.; Harkin, D.P. BRCA1, a ‘complex’ protein involved in the maintenance of genomic stability. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, F.; Collavin, L.; Del Sal, G. Mutant p53 as a guardian of the cancer cell. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Hamada, K.; Kawahara, K.; Sasaki, M.; Noguchi, F.; Chiba, S.; Mizuno, K.; Suzuki, S.O.; Dong, Y.; Tokuda, M.; Morikawa, T.; Hikasa, H.; Eggenschwiler, J.; Yabuta, N.; Nojima, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Hata, Y.; Nishina, H.; Mimori, K.; Mori, M.; Sasaki, T.; Mak, T.W.; Nakano, T.; Itami, S.; Suzuki, A. Cancer susceptibility and embryonic lethality in Mob1a/1b double-mutant mice. J Clin Invest. 2012, 122, 4505–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St John, M.A.; Tao, W.; Fei, X.; Fukumoto, R.; Carcangiu, M.L.; Brownstein, D.G.; Parlow, A.F.; McGrath, J.; Xu, T. Mice deficient of Lats1 develop soft-tissue sarcomas, ovarian tumours and pituitary dysfunction. Nat Genet. 1999, 21, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Conrad, C.; Xia, F.; Park, J.S.; Payer, B.; Yin, Y.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Thasler, W.; Lee, J.T.; Avruch, J.; Bardeesy, N. Mst1 and Mst2 maintain hepatocyte quiescence and suppress hepatocellular carcinoma development through inactivation of the Yap1 oncogene. Cancer Cell. 2009, 16, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.P.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, T.H.; Park, H.D.; Byun, J.S.; Kim, M.C.; Jeong, W.I.; Calvisi, D.F.; Kim, J.M.; Lim, D.S. The Hippo-Salvador pathway restrains hepatic oval cell proliferation, liver size, and liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010, 107, 8248–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Yao, G.; Hu, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, D.; Shen, D.; Zhang, G.; Meng, S.; Piao, H. MOB2 suppresses GBM cell migration and invasion via regulation of FAK/Akt and cAMP/PKA signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.B.; Wainman, A.; Garrido-Maraver, J.; Pires, V.; Riparbelli, M.G.; Kovács, L.; Callaini, G.; Glover, D.M.; Tavares, Á.A. Mob4 is essential for spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, A.; Elgort, M.G.; Brandman, O.; Ives, C.; Collins, S.R.; Miller-Vedam, L.; Weibezahn, J.; Hein, M.Y.; Poser, I.; Mann, M.; Hyman, A.A.; Weissman, J.S. Functional repurposing revealed by comparing S. pombe and S. cerevisiae genetic interactions. Cell. 2012, 149, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, R.D.; Soni, D.V.; Wollman, R.; Hahn, A.T.; Yee, M.C.; Guan, A.; Hesley, J.A.; Miller, S.C.; Cromwell, E.F.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; Meyer, T.; Cimprich, K.A. A genome-wide siRNA screen reveals diverse cellular processes and pathways that mediate genome stability. Mol Cell. 2009, 35, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, L.J.; El-Osta, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. γH2AX: A sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia. 2010, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.H.; Lee, T.Y.; Liang, H.K.; Huang, C.M.; Wang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Chu, C.H.; Huang, H.D.; Ko, M.T.; Hwang, J.K. KinasePhos 2.0, a web server for identifying protein kinase-specific phosphorylation sites based on sequences and coupling patterns. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W588–W594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, T.; Enomoto, A.; Miyagawa, K. Serine-Threonine Kinase 38 regulates CDC25A stability and the DNA damage-induced G2/M checkpoint. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, M.K.; Yuan, Z.; Boag, P.R.; Yang, Y.; Villén, J.; Becker, E.B.; DiBacco, S.; de la Iglesia, N.; Gygi, S.; Blackwell, T.K.; Bonni, A. A conserved MST-FOXO signaling pathway mediates oxidative-stress responses and extends life span. Cell. 2006, 125, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanphui, P.; Biswas, S.C. FoxO3a is activated and executes neuron death via Bim in response to β-amyloid. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valis, K.; Prochazka, L.; Boura, E.; Chladova, J.; Obsil, T.; Rohlena, J.; Truksa, J.; Dong, L.F.; Ralph, S.J.; Neuzil, J. Hippo/Mst1 stimulates transcription of the proapoptotic mediator NOXA in a FoxO1-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, N.; Nagai, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Kurata, T.; Takehisa, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Okazawa, H.; Abe, K. Progressive decrease in the level of YAPdeltaCs, prosurvival isoforms of YAP, in the spinal cord of transgenic mouse carrying a mutant SOD1 gene. J Neurosci Res. 2009, 87, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Emoto, K.; Fang, X.; Ren, N.; Tian, X.; Jan, Y.N.; Adler, P.N. Drosophila Mob family proteins interact with the related tricornered (Trc) and warts (Wts) kinases. Mol Biol Cell. 2005, 16, 4139–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, K.; He, Y.; Ye, B.; Grueber, W.B.; Adler, P.N.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Control of dendritic branching and tiling by the Tricornered-kinase/Furry signaling pathway in Drosophila sensory neurons. Cell. 2004, 119, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norkett, R.; Del Castillo, U.; Lu, W.; Gelfand, V.I. Ser/Thr kinase Trc controls neurite outgrowth in Drosophila by modulating microtubule-microtubule sliding. Elife. 2020, 9, e52009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Baker, N.E. Salvador-Warts-Hippo pathway regulates sensory organ development via caspase-dependent nonapoptotic signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Hsieh, M.; Fan, S.S. The promotion of neurite formation in Neuro2A cells by mouse Mob2 protein. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Ganetzky, B. Identification of Mob2, a novel regulator of larval neuromuscular junction morphology, in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2013, 195, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, A.C.; Kyrousi, C.; Einsiedler, M.; Burtscher, I.; Drukker, M.; Markie, D.M.; Kirk, E.P.; Götz, M.; Robertson, S.P.; Cappello, S. Mob2 Insufficiency Disrupts Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cortex. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondius, D.C.; Eigenhuis, K.N.; Morrema, T.H.J.; van der Schors, R.C.; van Nierop, P.; Bugiani, M.; Li, K.W.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Smit, A.B.; Rozemuller, A.J.M. Proteomics analysis identifies new markers associated with capillary cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, J.; Kawana, N.; Yamamoto, Y. Pathway Analysis of ChIP-Seq-Based NRF1 Target Genes Suggests a Logical Hypothesis of their Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2013, 7, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, J. Insights on altered mitochondrial function and dynamics in the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration. Transl Neurodegener. 2013, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, J.; Vincze, O.; Virók, D.; Simon, D.; Bozsó, Z.; Tõkési, N.; Horváth, I.; Hlavanda, E.; Kovács, J.; Magyar, A.; Szũcs, M.; Orosz, F.; Penke, B.; Ovádi, J. Interactions of pathological hallmark proteins: Tubulin polymerization promoting protein/p25, beta-amyloid, and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286, 34088–34100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, A.; ffrench-Constant, C. The control of cell number during central nervous system development in flies and mice. Mech Dev. 2003, 120, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



