1. Introduction
Since the 4th edition of the WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System in 2016, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations have become one of the most important prognostic biomarkers in adult-type infiltrative gliomas.1 IDH mutational status can distinctly separate astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas from more aggressive and deadly glioblastomas, regardless of histopathological features.2 It is well-recognized that astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas harboring IDH mutation demonstrate a better response to chemoradiation therapy, and these patients generally demonstrate better survival outcomes than those with glioblastomas harboring IDH wild-type alleles,3,4 thus emphasizing the importance of non-invasive identification of IDH mutant gliomas.
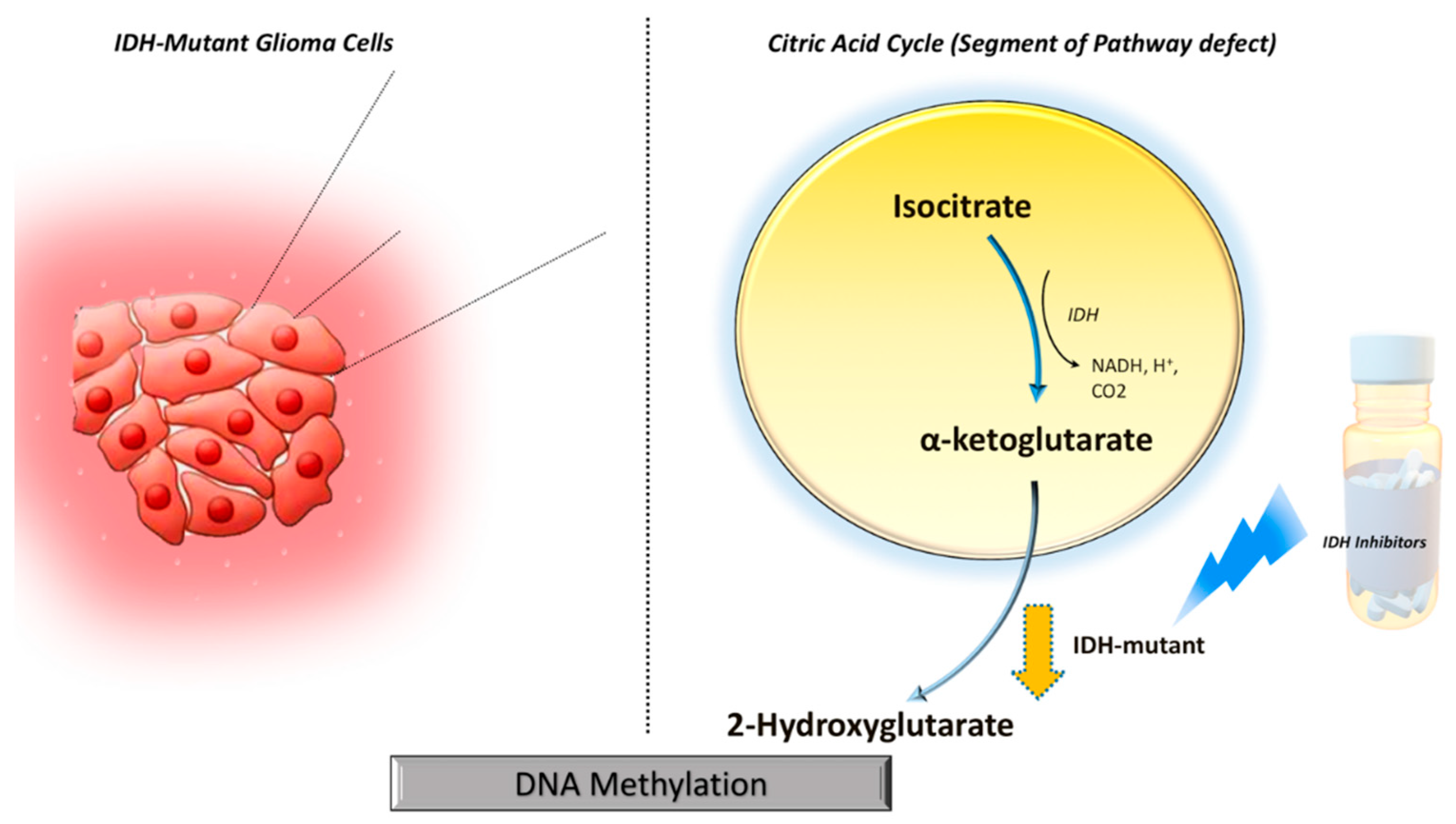
IDH mutations gain neomorphic enzyme activity leading to the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG) to 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG) in the citric acid cycle, resulting in abnormally high levels of 2HG (
Figure 1).
5 The oncometabolite 2HG has been proposed as a surrogate biomarker of IDH mutational status in gliomas. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) allows non-invasive assessment of the metabolic landscape of biological tissue.6–9 Several prior studies have reported the potential utilities of 1H-MRS in diagnosis, planning treatment strategies, and assessing treatment response in gliomas.10–12 However, precise
in vivo detection of 2HG on clinical magnetic field strengths (3T) demands the development of optimized
1H-MRS sequences
due to extensive overlap of 2HG resonances with that of neighboring metabolites such as glutamate, glutamine, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
.12 A spin-echo point-resolved spectroscopy (PRESS) sequence with an optimized echo time (TE) of 97 ms has been proposed to identify a well-defined narrow 2HG peak at 2.25 ppm, resulting in the resolution of overlapping 2HG resonances with greater sensitivity.
13
While immunohistochemical analyses and exomic sequencing are considered gold standards for determining IDH mutational status in gliomas,14,15 tissue heterogeneity, partial sampling of tissue specimens, and the presence of variable amounts of antigens constraint the utility of these methods in reliable detection of IDH mutational status.16 Eloquent locations of these neoplasms may also limit neurosurgical interventions. Therefore, non-invasive identification of IDH mutant gliomas using 1H-MRS plays an important role in patient counseling for therapeutic intervention and prognostication and could be utilized as a pharmacodynamic indicator to monitor treatment response.17,18
We hypothesized that the pathophysiologic changes due to IDH mutations leading to the accumulation of oncometabolite 2HG could also cause variations in the neurochemical profile of other metabolites observed on 1H-MRS. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical potential of 1H-MRS, single voxel (SVS), and single slice multivoxel magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (1H-MRSI) in identifying IDH-mutant gliomas by detecting characteristic resonances of 2HG and its complex interplay with other clinically relevant metabolites.
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Pennsylvania and is compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to the study. A total of 32 patients, comprising 30 suspected newly diagnosed infiltrative gliomas and two suspected neoplastic progression, were recruited based on routine MRI findings for this study.
2.2. Data Acquisition
All Patients underwent anatomical imaging, single voxel (SVS, n=17) and /or single slice multivoxel magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (1H-MRSI, n=15) MRI on a 3T Tim Trio whole-body MR scanner (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with a 12-channel phased array head coil. The anatomical imaging protocol included axial 3D-T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition of gradient echo (MPRAGE) imaging and an axial T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging using standard parameters. The postcontrast T1-weighted images were acquired with the same parameters as the precontrast acquisition after administration of a standard dose (0.14 mmol/Kg) of gadobenate dimeglumine (MultiHance, Bracco Imaging, Milano, Italy) intravenous contrast agent using a power injector (Medrad, Idianola, PA).
Both SVS and 1H-MRSI were acquired using a standard spin-echo point-resolved spectroscopy (PRESS) sequence. Sequences parameters for SVS included: repetition time (TR)/echo time (TE)/number of excitations (NEX)=2000/97ms/128, bandwidth = 1,200 Hz. Voxel size varied from 10 x 10 x 10 mm3 (volume: 1 cm3) – 20 x 20 x 20 mm3 (volume: 8 cm3). Sequences parameters for 1H-MRSI included: TR/TE/NEX=2000/97ms/3, bandwidth = 1,200 Hz, field of view = 16 × 16 cm2-20 × 20 cm2, slice thickness = 15-20 mm, matrix size = 16 × 16. The typical voxel size varied from 10 × 10 × 15 mm3 (volume: 1.5 cm3) to 10 × 12.5 × 20 mm3 (volume: 2.5 cm3) depending upon the dimensions of the neoplasms. For 1H-MRSI, the volume of interest (VOI) was selected to include neoplasm visible as a hyperintense mass on T2-FLAIR images and contralateral normal brain parenchyma, avoiding scalp, skull base, or sinuses. Eight outer volume saturation slabs were placed outside VOI to suppress lipid signals from the scalp. The data set was acquired using elliptical-K-space sampling with weighted phase encoding. Manual shimming was performed to achieve an optimal fullwidth at half maximum value (<20 Hz) of magnitude water signal. Both water-suppressed and unsuppressed spectra were acquired, and the unsuppressed water signal was used for computing metabolite concentrations.
2.3. Data Processing
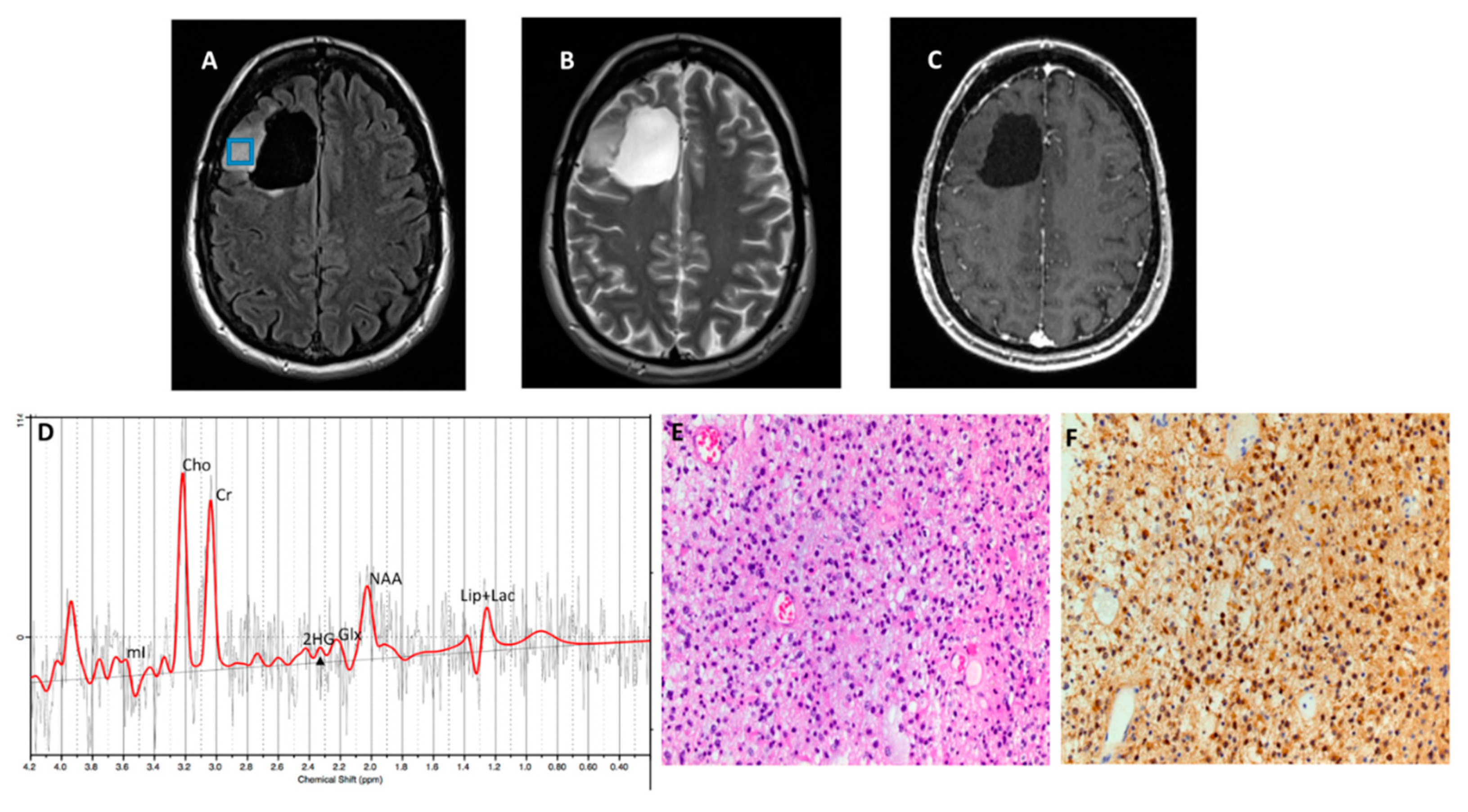
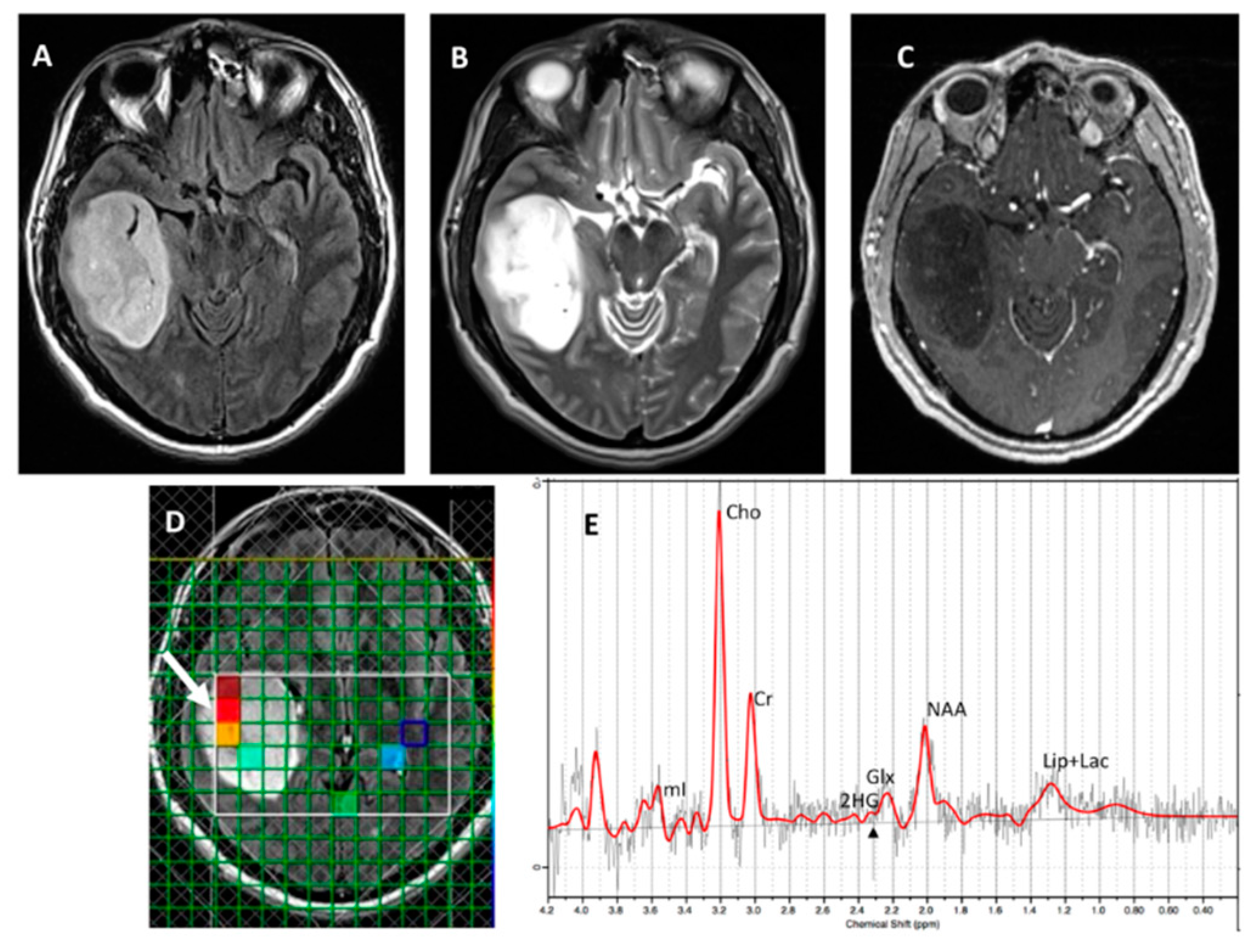
All spectroscopy data were analyzed using a user-independent spectral fit program [linear combination (LC) model, (http://s-provencher.com/lcmodel.shtml)].19 The region between 0.2 and 4.2 ppm of the spectrum was analyzed, and the following metabolites were evaluated: Lipids + Lactate (1.3 ppm); N-acetylaspartate (NAA), 2.02 ppm; creatine (Cr), 3.02 ppm; choline (Cho), 3.22 ppm; glutamate+glutamine (Glx), 2.24 to 2.34 ppm; myoinositol (mI), 3.56 ppm and 2HG, (2.25 ppm). The resonance of Cr at 3.02 ppm was used as an internal chemical shift reference for computing metabolite ratios. The quality of spectral fitting was evaluated by analyzing the difference spectrum (fitted spectrum subtracted from the original spectrum) and by using Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) values, with less than 40% considered acceptable for detecting 2HG20 and less than 20% for all other metabolites.21,22 The number of voxels analyzed in the cases of 1H-MRSI varied from 2 to 41, and at least two neighboring voxels with CRLB values < 40% for 2HG were required to classify the cases as 2HG positive. Histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses for glioma-grade and IDH mutational status were subsequently performed from resected tumor specimens, and the findings were compared with the results from spectral data. Metabolic ratios for NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, Glx/Cr, mI/Cr, and Lipids + Lactate/Cr from the selected voxels were computed from each patient. Additionally,
the absolute concentration of 2HG and metabolite ratio of 2HG/Cr were computed from true positive IDH mutant gliomas.
2.4. Determination of IDH Status by Immunohistochemistry
Tissue specimens received by pathology were fixed in formalin and processed for paraffin embedding. Hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry were conducted on 5-micron thick formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections mounted on Leica Surgipath slides followed by drying for 60 minutes at 70°C. Immunohistochemistry with the anti-IDH1-R132H antibody (Monoclonal Mouse Anti-human IDH1 (R132H), Dianova, DIA Clone H09) and DAB chromogen were performed on a Leica Bond III instrument using Bond Polymer Refine Detection System (Leica Microsystems AR9800) following a 20-min heat-induced epitope retrieval with Epitope Retrieval 2, EDTA, pH 9.0.23
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using a statistical package, SPSS for Windows (v. 18.0; Chicago, IL). Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests were used to determine the nature of data distribution. As the data showed a departure from Gaussian distribution, non-parametric Mann-Whitney U tests were performed to assess differences in metabolite levels between IDH-mutant and IDH-wild-type gliomas. The chi-square test was used to assess differences in categorical variables. A probability (p) value of less than 0.05 was considered significant. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were determined. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analyses were also performed for the metabolites exhibiting significant differences between two groups (IDH-mutant and IDH-wild-type gliomas).
3. Results
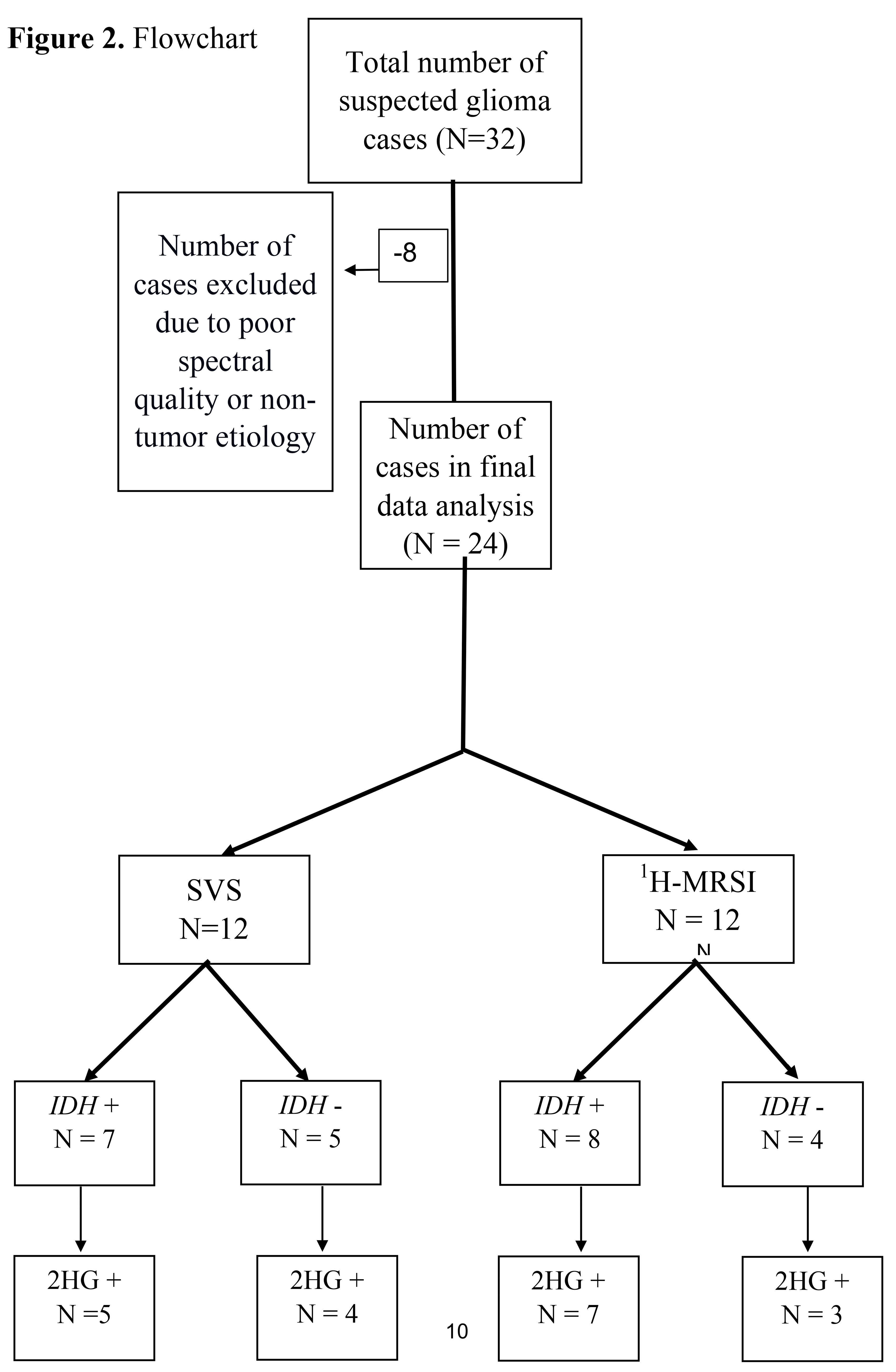
Of these 32 patients, eight were excluded as five patients had sub-optimal spectral quality due to inadequate water suppression for reliable detection and quantification of metabolites, and three other patients were excluded because they had final histological diagnoses of non-tumor etiology, with pathology reports consistent with reactive brain changes without molecular features of neoplasm (
Figure 2). As such, a total of 24 patients were included (mean age = 48.7 ± 15 years, 11 males and 13 females) in the final data analysis. All cases had histopathological confirmation for infiltrative gliomas (22 newly diagnosed and 2 neoplastic progression), ranging from histological grade 2 to grade 4. The immunohistochemistry analyses revealed 15
IDH-mutant gliomas and 9
IDH-wild type glioblastomas. Patient demographics, along with histopathological grading and immuno-histochemical findings, are presented in
Table 1.
Twelve patients underwent SVS, and 12 underwent
1H-MRSI. Using a CRLB < 40% for the detection of 2HG, 9/12 (75%) cases were correctly identified as
IDH mutant or
IDH wild-type gliomas by SVS and 10/12 (83%) by
1H-MRSI (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, respectively), with an overall concordance rate of 79% (19/24). Of 5 patients incorrectly classified by
1H-MRS for
IDH mutational status, 2 were false positives (1 each on SVS and
1H-MRSI), and 3 were false negatives (2 on SVS, 1 on
1H-MRSI). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) in identifying
IDH-mutant and
IDH-wild-type gliomas were 80%, 77%, 86%, and 70%, respectively (
Table 2). The mean concentration and standard errors of 2HG and metabolite ratio of 2HG/Cr in
IDH mutant cases were 5.24 ± 1.59 mM and 0.55 ± 0.08, respectively. The metabolite 2HG was found to be significant in predicting
IDH-mutant gliomas by Chi-squared test (p<0.01).
The IDH-mutant gliomas also showed a significantly higher mean concentration of NAA/Cr ratio (1.20 ± 0.09 versus 0.75 ± 0.12 p= 0.016) compared with IDH-wild-type patients and significantly lower Glx/Cr ratio (0.86±0.078 versus 1.88±0.66; p=0.029) than IDH wild-type gliomas. There were no significant differences (p>0.05) in the mean concentration ratio for the remaining metabolites between IDH-mutant and IDH-wild-type gliomas. The ROC analyses revealed that areas under the ROC curves for NAA/Cr and Glx/Cr were 0.808 and 0.786, respectively, in distinguishing IDH mutant from IDH wild-type gliomas.
4. Discussion
In this study, we prospectively analyzed the clinical utility of SVS and 1H-MRSI using an optimized TE (97ms) in assessing IDH-mutational status by detecting the characteristic resonances of 2HG in patients presenting with newly diagnosed infiltrative gliomas and suspected neoplastic progression. Our results demonstrated that 1H-MRS can identify IDH-mutant gliomas with high accuracy. Our results also provided evidence that IDH mutation affects other crucial metabolite pools, including Glx and NAA. These observations provide an improved understanding of the pathophysiology of IDH mutations in gliomas. Moreover, the accurate determination of IDH mutational status at the time of initial presentation has important therapeutic implications when a critical decision about the selection of the optimal treatment strategy is to be made.
Mechanistically, wild-type IDH normally catalyzes the reversible NADP+dependent oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-KG in the citric acid cycle. While IDH mutations confer a neomorphic enzyme activity converting α-KG to 2-HG. The high levels of 2HG change the cellular metabolism by leading to DNA hypermethylation and epigenetic modifications of histone, resulting in tumorigenesis.5,24 The oncometabolite 2HG has been proposed as a putative biomarker for IDH-specific genetic profiles for gliomas. However, not all IDH-mutant gliomas, especially the non-canonical IDH mutant gliomas (about 20-25% of grade-2 and 5-12% of grade-3 gliomas) show the neomorphic activity of 2-HG production,25 suggesting that 2HG detection alone may not always be sufficient for identifying IDH mutation in gliomas. By exploring the reasons for obtaining false positive cases, we noted that small tumor volume was found to be a potential limiting factor for the reliable detection of 2HG resonances in our study. Similar findings were observed in a previous study in which investigators reported higher detection sensitivity of 2HG from larger voxel size.26
The optimized TE allowed us to investigate specific biochemical alterations influenced by the pathologic production of 2HG in IDH-mutant gliomas, showing a clear advantage compared to routine short TE (30-35ms).18 We could detect the 2HG peak at 2.25 ppm with high sensitivity and specificity (80% and 77%, respectively). Additionally, in line with our hypotheses and prior studies,27–29 the Glx (Glutamine + Glutamate)/Cr was found to be significantly decreased in IDH-mutant gliomas in the present study. This result contemplates the pathophysiology of these tumors as glutamate becomes depleted in an attempt to replenish α-KG lost in the conversion to 2HG by the IDH enzyme.30 Metabolomic analyses using glioma cell lines and surgical specimens have also shown that glutaminolysis serves as a key compensatory pathway to maintain metabolic homeostasis in IDH mutant gliomas. As a result, glutamate levels are significantly reduced in IDH mutant gliomas compared to IDH wild-type counterparts.31 Additionally, we observed significantly increased levels of NAA in the IDH-mutant group compared to the IDH-wild-type group. However, the biological mechanism of NAA and whether it contributes to tumor pathogenesis remains unclear, and this metabolite might be a confounder of tumor grade between low- and high-grade gliomas.32,33,34
There is no established optimal CRLB cutoff value or concentration level for the detection of 2HG.18 Using individual patient data and CRLB values, the optimal cutoff for 2HG was found to be lower than 40% in our cohort.20 Further validation of this optimal threshold for 2HG is crucial for the application of glioma management in clinical practice. A benefit of 2HG MRS compared to other MRI techniques is that it can be employed as direct evidence of increased measurements of 2HG with enhanced detection accuracy.35 On the other hand, conventional MRI techniques have shown a wide variability of sensitivities (71–100%) and specificities (51–100%) in the identification of IDH mutant gliomas.36–38 Similarly, studies using diffusion-weighted imaging and perfusion-weighted imaging have also reported a wide range of sensitivities (56–100%) and specificities (63–100%) for distinguishing IDH mutant from IDH-wild-type gliomas.18,39–41
SVS is a broadly available method with substantive findings in clinical practice, generally providing a better signal-to-noise ratio, especially for focal circumscribed lesions.42 We additionally employed 1H-MRSI for the detection of 2HG, which is a valuable technique for ill-defined, irregular heterogeneous lesions, provides a metabolite map to guide therapy or surgery, includes the entire tumor volume avoiding incomplete sampling, and allows the metabolite quantification comparison with the contralateral normal brain.35 Some previous studies have employed sophisticated spectroscopic sequences such as multiple quantum filtered and spectral editing techniques and post-processing tools for unambiguously detecting spectral resonances of 2HG from IDH mutant gliomas.23,27,43,44 Earlier, we have also shown the potential of using two-dimensional localized correlation spectroscopy (2D-L-COSY) at 7 Tesla to detect 2HG in IDH-positive gliomas.23 However, these sophisticated spectroscopic sequences and tools are not readily and widely available in routine clinical settings.
1H-MRS evaluation of the oncometabolite 2HG is of clinical interest in creating a noninvasive detection technique for IDH mutant gliomas for diagnostic purposes, differentiation with other etiologies (i.e., solitary metastasis, demyelinating lesion),45 surgical decision-making, as aggressive resection of both enhancing and nonenhancing disease might improve survival in IDH-mutant, but not in wild-type gliomas,46 treatment monitoring (concentration of 2HG increases sharply with tumor progression, whereas it decreases in response to radio- and chemotherapies),47 and even to differentiate tumor recurrence from treatment-related changes. In addition, a recent phase I clinical trial used 2HG MRS to document treatment response to a mutant-IDH1 inhibitor drug and revealed a significant decrease rate (70%) of 2HG levels after one week of treatment.48 Notably, treatment monitoring of novel target therapies using 2HG detection by MRS may be exploited for personalized and precision medicine and early treatment response in clinical trials.
Despite promising results, our study had some shortcomings, including a small patient sample size and the non-availability of IDH2 mutational status. Although we used a relatively high CRLB value of 40% for detecting 2HG, the optimal threshold value for enhanced diagnostic accuracy for this metabolite is yet to be established. Importantly, we showed that 2HG and Glx might be integrated into algorithm models in clinical practice to encourage the noninvasive workup of patients with IDH mutant gliomas. These findings warrant further validation in large-scale and multicenter prospective studies for developing a fast, reliable, and reproducible method for identifying IDH mutational status in gliomas.
5. Conclusion
1H-MRS with an optimized TE may be useful for noninvasively detecting the abnormally high levels of 2HG with high accuracy and understanding its interaction with other important metabolites in infiltrative gliomas. Our findings indicate that 2HG and Glx are potential noninvasive surrogate biomarkers for detecting IDH mutations, which has significant clinical implications for prognostication and implementation of appropriate clinical management procedures in patients with glioma.
Competing interest
The authors report no competing interests.
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Zhang, W.; You, G.; et al. Correlation of IDH1 mutation with clinicopathologic factors and prognosis in primary glioblastoma: A report of 118 patients from China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-B.; Bao, Z.-S.; Wang, H.-J.; et al. Correlation of IDH1/2 mutation with clinicopathologic factors and prognosis in anaplastic gliomas: A report of 203 patients from China. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 2014, 140, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertholdo, D.; Watcharakorn, A.; Castillo, M. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Introduction and overview. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2013, 23, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posse, S.; Otazo, R.; Dager, S.R.; et al. MR spectroscopic imaging: Principles and recent advances. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013, 37, 1301–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzillo, T.C.; Hu, J.; Nguyen, L.; et al. Interrogating Metabolism in Brain Cancer. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2016, 24, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Noguerol, T.; Sánchez-González, J.; Martínez Barbero, J.P.; et al. Clinical Imaging of Tumor Metabolism with 1H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2016, 24, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Krejza, J.; Vossough, A.; et al. Differentiation between oligodendroglioma genotypes using dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted imaging and proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013, 34, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Oleaga, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in differentiating oligodendrogliomas from astrocytomas. J Neuroimaging 2010, 20, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Nanga, R.P.R.; Verma, G.; et al. Emerging MR Imaging and Spectroscopic Methods to Study Brain Tumor Metabolism. Front Neurol 2022, 13, 789355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Ganji, S.; Hulsey, K.; et al. A comparative study of short- and long-TE 1H MRS at 3 T for in vivo detection of 2-hydroxyglutarate in brain tumors. NMR Biomed 2013, 26, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Williams Parsons, D.; Jones, S.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Williams Parsons, D.; Jin, G.; et al. IDH1andIDH2Mutations in Gliomas. New England Journal of Medicine 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preusser, M.; Wöhrer, A.; Stary, S.; et al. Value and Limitations of Immunohistochemistry and Gene Sequencing for Detection of theIDH1-R132HMutation in Diffuse Glioma Biopsy Specimens. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 2011, 70, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.; Raisanen, J.M.; Ganji, S.K.; et al. Prospective Longitudinal Analysis of 2-Hydroxyglutarate Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Identifies Broad Clinical Utility for the Management of Patients With IDH-Mutant Glioma. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 4030–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate MR spectroscopy for prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant glioma: A systemic review and meta-analysis using individual patient data. Neuro Oncol 2018, 20, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localizedin vivo proton NMR spectra. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 1993, 30, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsios, G.; Viswanath, P.; Subramani, E.; et al. PI3K/mTOR inhibition of IDH1 mutant glioma leads to reduced 2HG production that is associated with increased survival. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.H.; et al. In-VivoProton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of 2-Hydroxyglutarate in Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-Mutated Gliomas: A Technical Review for Neuroradiologists. Korean Journal of Radiology 2016, 17, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, A.; Choi, C.; Mickey, B.; et al. Noninvasive assessment of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation status in cerebral gliomas by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a clinical setting. Journal of Neurosurgery 2018, 128, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, G.; Mohan, S.; Nasrallah, M.P.; et al. Non-invasive detection of 2-hydroxyglutarate in IDH-mutated gliomas using two-dimensional localized correlation spectroscopy (2D L-COSY) at 7 Tesla. J Transl Med 2016, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.G.; Alves, C.A.P.F.; Vossough, A. Updates in Pediatric Malignant Gliomas. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2020, 29, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, E.; De Biase, D.; Di Nunno, V.; et al. IDH1 Non-Canonical Mutations and Survival in Patients with Glioma. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Viswanath, P.; Eriksson, P.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming in mutant IDH1 glioma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdas, S.; Chadzynski, G.L.; Braun, C.; et al. MR spectroscopy for in vivo assessment of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate and its effects on cellular metabolism in human brain gliomas at 9.4T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016, 44, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsumeda, M.; Motohashi, K.; Igarashi, H.; et al. Reliable diagnosis of IDH-mutant glioblastoma by 2-hydroxyglutarate detection: A study by 3-T magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurosurg Rev 2018, 41, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, H.; Tanaka, K.; Sasayama, T.; et al. Diagnostic value of glutamate with 2-hydroxyglutarate in magnetic resonance spectroscopy for IDH1 mutant glioma. Neuro Oncol 2016, 18, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Ohka, F.; Ito, M.; Ranjit, M.; et al. Quantitative metabolome analysis profiles activation of glutaminolysis in glioma with IDH1 mutation. Tumour Biol 2014, 35, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, L.J.M.; Verheul, C.; Wensveen, N.; et al. Effects of the IDH1 R132H Mutation on the Energy Metabolism: A Comparison between Tissue and Corresponding Primary Glioma Cell Cultures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3568–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitman, Z.J.; Jin, G.; Karoly, E.D.; et al. Profiling the effects of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations on the cellular metabolome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branzoli, F.; Marjańska, M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutated gliomas: Current knowledge on the neurochemical profile. Curr Opin Neurol 2020, 33, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. The diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in differentiating high-from low-grade gliomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 2016, 26, 2670–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Ganji, S.K.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; et al. 2-hydroxyglutarate detection by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in IDH-mutated patients with gliomas. Nat Med 2012, 18, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.A.; Lai, A.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; et al. Relationship between tumor enhancement, edema, IDH1 mutational status, MGMT promoter methylation, and survival in glioblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012, 33, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasocki, A.; Tsui, A.; Gaillard, F.; et al. Reliability of noncontrast-enhancing tumor as a biomarker of IDH1 mutation status in glioblastoma. J Clin Neurosci 2017, 39, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Vallières, M.; Bai, H.X.; et al. MRI features predict survival and molecular markers in diffuse lower-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 2017, 19, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, K.; Ott, G.A.; Lai, A.; et al. Perfusion and diffusion MRI signatures in histologic and genetic subtypes of WHO grade II-III diffuse gliomas. J Neurooncol 2017, 134, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Hiwatashi, A.; Togao, O.; et al. MR Imaging-Based Analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme: Estimation of IDH1 Mutation Status. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016, 37, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Yang, X.; She, D.; et al. Noninvasive Assessment of Mutational Status in World Health Organization Grade II and III Astrocytomas Using DWI and DSC-PWI Combined with Conventional MR Imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2017, 38, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Taub, E.; Salibi, N.; et al. Comparison of reproducibility of single voxel spectroscopy and whole-brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging at 3T. NMR Biomed 2018, 31, e3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronesi, O.C.; Kim, G.S.; Gerstner, E.; et al. Detection of 2-hydroxyglutarate in IDH-mutated glioma patients by in vivo spectral-editing and 2D correlation magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Sci Transl Med 2012, 4, 116ra4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir, U.E.; Larkin, S.J.; de Pennington, N.; et al. Noninvasive Quantification of 2-Hydroxyglutarate in Human Gliomas with IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, A.; Choi, C.; Mickey, B.; et al. Noninvasive assessment of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation status in cerebral gliomas by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a clinical setting. J Neurosurg 2018, 128, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiko, J.; Suki, D.; Hess, K.R.; et al. IDH1 mutant malignant astrocytomas are more amenable to surgical resection and have a survival benefit associated with maximal surgical resection. Neuro Oncol 2014, 16, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, M.I.; Young, R.J.; Rubel, J.; et al. Integration of 2-hydroxyglutarate-proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy into clinical practice for disease monitoring in isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant glioma. Neuro Oncol 2016, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronesi, O.C.; Arrillaga-Romany, I.C.; Ly, K.I.; et al. Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).