Submitted:
21 August 2023
Posted:
21 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
2.1.1. The ""Rational Man"" Hypothesis and Cropland Abandonment
2.1.2. The Sustainable Livelihoods Analytical Framework and the Cropland Desertification Phenomenon
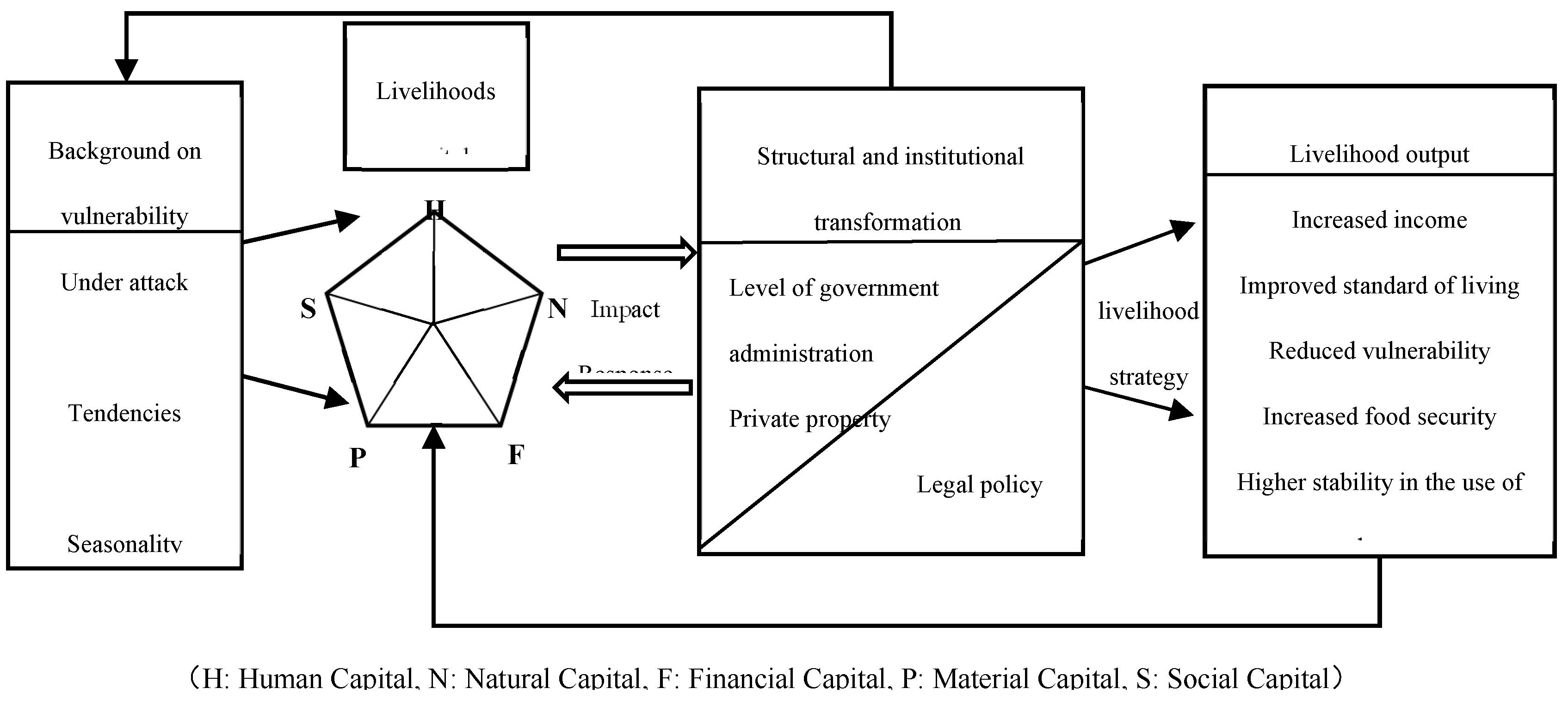
2.1.3. Theoretical Analysis Framework
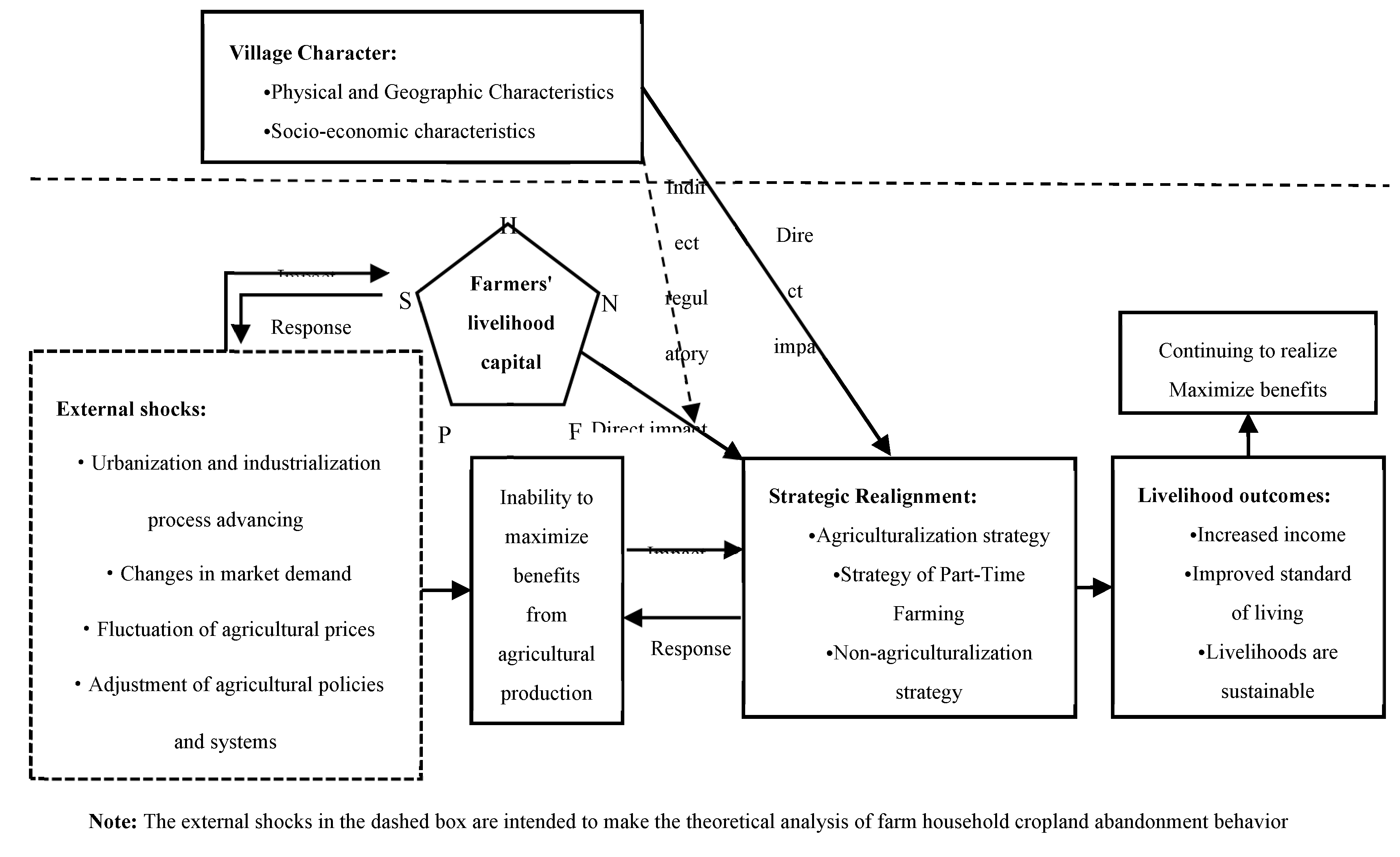
2.2. Research Hypotheses
3. Data Sources and Research Methodology
3.1. Data Sources and Processing
3.1.1. Data Source
3.1.2. Data Processing
3.2. Variable Identification and Indicator System
3.2.1. Explained Variables
3.2.2. Explanatory Variables
3.2.3. Indicator System
| Level | Variable Type | Variable Group | Variable Name and Symbol | Variable Definition and Assignment | Intended Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | Abandonment rate (QGZB) | Proportion of land abandoned by farmers to total cultivated area(%) | |||
| Farm household level | Explanatory variable | Human capital | Do household heads have a high school diploma or higher (EDU) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | + |
| Whether the head of household is in relatively good health (HEAL) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | |||
| Household size (JTRKGM) | Sum of persons living with the family and persons away from the family (person) | - | |||
| Natural capital | Cropland area per capita (RJGDMJ) | Ratio of area of cropland owned by households to total population size (acre/person) | - | ||
| Ratio of transferred cropland (ZRGDB) | Proportion of area of cropland transferred by households to total area of cropland (%) | - | |||
| Presence of contaminated cropland (TRWR) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | |||
| Physical capital | Ownership of large agricultural production machinery or livestock for agricultural production (SCGJ) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | ||
| Whether the number of types of durable goods in the household is five or more (NYZL) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | + | |||
| Financial capital | Total log annual household income per capita (LNRJSR) | Logarithm of the ratio of the sum of all types of household income in a year to the size of the household (yuan) | + | ||
| Agricultural income ratio (NYSRB) | Share of annual household income from agriculture in total annual household income (%) | - | |||
| Non-farm income ratio (FNSRB) | Household annual non-farm income as a share of total annual household income (%) | + | |||
| Social capital | Availability of village cadres (CGB) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | ||
| Log of annual expenditure on favours (LNRQZC) | Total household expenditure on gifts and gratuities in a year (yuan) | ± | |||
| Use of the Internet or not (HLWQK) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | ± | |||
| Village level | Explanatory variable | Physical geographic characteristics | Commute distance (TQJL) | Distance of villages from township offices (kilometers) | - |
| Whether it is a suburb of a medium-sized city (DLWZ) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | + | |||
| Topography of the village is plain or not (CZDX) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | |||
| Socio-economic characteristics | Number of village agricultural producers (CZNYSCB) | Percentage of people engaged in agriculture in villages compared to the total number of people in villages (%) | - | ||
| Availability of non-farm enterprises (FNQY) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | + | |||
| Whether or not to implement agricultural services (HNFW) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | - | |||
| Experiencing land expropriation or not (TDZY) | No = 0; Yes = 1 | + |
3.2.4. Descriptive Statistics of Variables
| Variable Type | Variable Name | Sample Size | Mean | Standard Deviation | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | QGZB | 13120 | 8.75 | 24.92 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| Farm household level explanatory variables | EDU | 13120 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| HEAL | 13120 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| JTRKGM | 13120 | 5.17 | 2.75 | 1.00 | 15.00 | |
| RJGDMJ | 13120 | 1.68 | 2.58 | 0.02 | 50.00 | |
| ZRGDB | 13120 | 5.58 | 18.65 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |
| TRWR | 13120 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| SCGJ | 13120 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| NYZL | 13120 | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| LNRJSR | 13120 | 8.39 | 1.21 | 0.18 | 12.21 | |
| NYSRB | 13120 | 36.85 | 42.70 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |
| FNSRB | 13120 | 39.77 | 44.09 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |
| CGB | 13120 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| LNRQZC | 13120 | 5.39 | 3.65 | 0.00 | 9.90 | |
| HLWQK | 13120 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| Village level explanatory variables | TQJL | 645 | 5.68 | 5.22 | 0.00 | 30.00 |
| DLWZ | 645 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| CZDX | 645 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| CZNYSCB | 645 | 64.51 | 34.09 | 0.00 | 100.00 | |
| FNQY | 645 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| HNFW | 645 | 0.84 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| TDZY | 645 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
3.3. Hierarchical Linear Model
4. Analysis of Empirical Results
4.1. Normality Test of the Explanatory Variables
| Variable Name | Sample Size | Mean | Standard Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skewness value | standard error | Kurtosis value | standard error | ||||
| QGZB | 13120 | 8.751 | 24.924 | 2.953 | 0.021 | 7.420 | 0.043 |
4.2. Null Model
| Fixed Effects and Significance test | Random effects and significance test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Regression coefficient | T-test | P-value | Parameters | Standard Deviation | Variance component | Chi-square test | P-value |
| γ00 | 9.0206 | 19.8610 | 0.000 | μ0 | 10.0978 | 101.9664 | 3164.5207 | 0.000 |
| r | 22.8258 | 521.0150 | ||||||
4.3. Random Effects Regression Model
4.3.1. One-factor Random Effects Regression Model
| Variable Name | Regression coefficient | standard error | T-test | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDU | -0.5046 | 0.6864 | -0.735 | 0.462 |
| HEAL | -1.6655 | 0.4355 | -3.824 | 0.000*** |
| JTRKGM | -0.0124 | 0.1004 | -0.124 | 0.902 |
| RJGDMJ | -0.5925 | 0.0523 | -11.341 | 0.000*** |
| ZRGDB | -0.0617 | 0.0086 | -7.213 | 0.000*** |
| TRWR | -0.4463 | 0.5051 | -0.884 | 0.378 |
| SCGJ | -4.3581 | 0.5950 | -7.325 | 0.000*** |
| NYZL | -0.6327 | 0.4236 | -1.494 | 0.136 |
| LNRJSR | -0.3407 | 0.2185 | -1.559 | 0.119 |
| NYSRB | -0.0872 | 0.0061 | -14.313 | 0.000*** |
| FNSRB | 0.0431 | 0.0061 | 7.078 | 0.000*** |
| CGB | -2.7299 | 1.2966 | -2.105 | 0.035** |
| LNRQZC | -0.0250 | 0.0641 | -0.390 | 0.697 |
| HLWQK | -0.2000 | 0.4305 | -0.465 | 0.642 |
4.3.2. Multi-factor Random Effects Regression Model
| Variable Name | Fixed effects regression results | Random effects regression results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression coefficient | standard error | T-test | Variance component | Chi-square test | |
| γ00 | 13.2053 | 0.8196 | 16.112*** | 222.4776 | 141.8825*** |
| HEAL | -1.9220 | 0.4144 | -4.638*** | 3.3173 | 45.7651 |
| RJGDMJ | -0.1843 | 0.0460 | -4.006*** | 0.0344 | 47.4904 |
| ZRGDB | -0.0374 | 0.0087 | -4.300*** | 0.0022 | 55.0921* |
| SCGJ | -2.3390 | 0.5426 | -4.310*** | 21.1288 | 59.3682** |
| NYSRB | -0.0792 | 0.0075 | -10.522*** | 0.0124 | 84.2431*** |
| FNSRB | 0.0003 | 0.0078 | 0.036 | 0.0108 | 57.9672* |
| CGB | -3.8157 | 1.2928 | -2.951*** | 22.7815 | 38.7926 |
4.4. Intercept Model
| Variable Name | Regression coefficient | Standard error | T-test |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ00 | 15.3173 | 1.7085 | 8.965*** |
| TQJL | -0.2571 | 0.0682 | -3.771*** |
| DLWZ | -2.5563 | 1.3533 | -1.889* |
| CZDX | -4.7083 | 0.8881 | -5.302*** |
| CZNYSCB | -0.0586 | 0.0147 | -3.993*** |
| FNQY | 0.0227 | 1.0449 | 0.022 |
| HNFW | 0.2797 | 1.3159 | 0.213 |
| TDZY | 1.9319 | 0.9553 | 2.022** |
4.5. Full Model
| Variable Name | Regression coefficient | Standard error | T-test | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | Intercept term γ00 | 12.0579 | 0.7842 | 15.377 | 0.000 |
| TQJL γ01 | -0.2528 | 0.0677 | -3.735 | 0.000 | |
| DLWZ γ02 | -2.4540 | 1.3157 | -1.865 | 0.062 | |
| CZDX γ03 | -4.7223 | 0.8827 | -5.350 | 0.000 | |
| CZNYSCB γ04 | -0.0548 | 0.0148 | -3.690 | 0.000 | |
| TDZY γ05 | 1.8234 | 0.9293 | 1.962 | 0.050 | |
| β1 | HEAL γ10 | -1.9073 | 0.4164 | -4.581 | 0.000 |
| β2 | RJGDMJ γ20 | -0.1975 | 0.0503 | -3.927 | 0.000 |
| β3 | ZRGDB γ30 | -0.0541 | 0.0125 | -4.338 | 0.000 |
| ZRGDB*TQJL γ31 | 0.0028 | 0.0015 | 1.820 | 0.069 | |
| ZRGDB*DLWZ γ32 | -0.0387 | 0.0290 | -1.337 | 0.182 | |
| ZRGDB*CZDX γ33 | 0.0058 | 0.0164 | 0.354 | 0.723 | |
| ZRGDB*CZNYSCB γ34 | 0.0007 | 0.0003 | 2.440 | 0.015 | |
| ZRGDB*TDZY γ35 | 0.0111 | 0.0188 | 0.592 | 0.554 | |
| β4 | SCGJ γ40 | -3.5314 | 0.8546 | -4.132 | 0.000 |
| SCGJ*TQJL γ41 | 0.0038 | 0.0879 | 0.044 | 0.966 | |
| SCGJ*DLWZ γ42 | -2.3175 | 1.3835 | -1.675 | 0.094 | |
| SCGJ*CZDX γ43 | 3.0912 | 1.2162 | 2.542 | 0.012 | |
| SCGJ*CZNYSCB γ44 | 0.0071 | 0.0201 | 0.352 | 0.725 | |
| SCGJ*TDZY γ45 | -1.1113 | 1.2374 | -0.898 | 0.370 | |
| β5 | NYSRB γ50 | -0.0685 | 0.0097 | -7.093 | 0.000 |
| NYSRB*TQJL γ51 | 0.0020 | 0.0011 | 1.849 | 0.064 | |
| NYSRB*DLWZ γ52 | 0.0026 | 0.0224 | 0.116 | 0.908 | |
| NYSRB*CZDX γ53 | 0.0251 | 0.0120 | 2.092 | 0.037 | |
| NYSRB*CZNYSCB γ54 | -0.0000 | 0.0002 | -0.018 | 0.985 | |
| NYSRB*TDZY γ55 | -0.0364 | 0.0127 | -2.862 | 0.005 | |
| β6 | CGB γ60 | -3.6382 | 1.2818 | -2.838 | 0.005 |
| Variable Name | Random effects regression results | |
|---|---|---|
| Variance component | Chi-square test | |
| γ00 | 130.3265 | 116.5629*** |
| HEAL | 2.7051 | 49.5024 |
| RJGDMJ | 0.0773 | 43.2623 |
| ZRGDB | 0.0027 | 52.8242* |
| SCGJ | 35.0686 | 59.8170** |
| LNRJSR | 8.7962 | 98.1779 |
| NYSRB | 0.0080 | 86.9579*** |
| CGB | 19.6672 | 34.9425 |
5. Conclusion and Discussion
5.1. Conclusion
5.2. Discussion
Short Biography of Authors
References
- Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A.; Olejniczak, N.J. People on the land: Changes in global population and croplands during the 20th century[J]. AMBIO A Journal of the Human Environment, 2002, 31(3): 251-257.
- WANG, X.Y.; WANG, Y.J. Bibliometric analysis of cropland abandonment: pulse and outlook[J]. Arid Zone Geography: 1-15.
- LI, S.F; LI, X.B. Progress and outlook of research on cropland abandonment[J]. Journal of Geography, 2016, 71(03): 370-389.
- Gan, Li.; Yin, Z.C. China Household Finance Survey Report 2014.Chengdu: Southwest University of Finance and Economics Press, 2015.
- Xiang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Q.; et al. Progress and review of domestic and international land abandonment research based on CiteSpace software[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 42(04): 670-681.
- DUAN, Y.M.; ZHOU, H.; LIU, X.H.; et al. Research progress and prospect of cropland abandonment in China[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2018, 46(13): 13-17.
- Doorn, A.M.V.; Bakker, M.M. The destination of arable land in a marginal agricultural landscape in South Portugal an exploration of land use change determinants. Landscape Ecology, 2007, 22(7): 1073-1087.
- Rudel, T.; Fu, C. A requiem for the southern regionalists: Reforestation in the South and the uses of regional social science. Social Science Quarterly, 1996, 77(4): 804-820.
- Ding, G.P.; Liu, C.W.; Huang, L.M. Theoretical Analysis and Empirical Evidence of Farmland Marginalization in Hilly Mountainous Areas under Rural Benefit Policies--Taking Tongcheng County of Hubei Province as an Example[J]. Geography Research, 2009, 28(01): 109-117.
- Cao, Z.H.; Hao, J.M.; Liang, L.T. Economic analysis and strategy research on farmland abandonment behavior[J]. Agricultural Technology and Economics, 2008(03): 43-46.
- Alcantara, C.; Kuemmerle, T.; Baumann, M.; et al. Mapping the extent of abandoned farmland in Central and Eastern Europe using MODIS time series satellite data. Environmental Research Letters, 2013, 8(3): 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Elbakidze, M.; et al. Patterns and drivers of post-socialist farmland abandonment in western Ukraine. Land Use Policy, 2011, 28(3): 552-562. [CrossRef]
- Rudel, T. Did a green revolution restore the forests of the American South//Angelsen A, Kaimowitz D. Agricultural Technologies and Tropical Deforestation. London, UK: CABI Publishing, 2001: 53-68.
- Mather, A.S.; Needle, C.L. The forest transition a theoretical basis. Area, 1998, 30(2): 117-124. [CrossRef]
- He, B.B. Study on the Security of Regional Cultivated Land Resources [D]. Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009.
- Zhang, H.F. Characteristics of vegetation communities and soil erosion and non-point source pollution in abandoned cropland in the water source area of the South-to-North Water Diversion [D]. Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2005.
- Keenleyside, C.; Tucker, G.M. Farmland abandonment in the EU: An assessment of trends and prospects. Report prepared for WWF. London:Institute for European Environmental Policy, 2010.
- Benayas, J.M.R.; Martins, A.; Nicolau, J.M. Abandonment of agricultural land: An overview of drivers and consequences. CAB reviews:Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources, 2007, 57(2): 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Strijker, D. Marginal lands in Europe: Causes of decline. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2005, 6(2): 99-106. [CrossRef]
- ZHU, X.W.; MA, N.W.; HU, P.F.; et al. Study on the abandonment of cropland and its driving force in the Longdong Loess Plateau in the last 20 years--Taking Kongdong District, Pingliang City, Gansu Province as an example[J]. Chinese Agronomy Bulletin, 2019, 35(09): 95-101.
- GUO, B.B.; FANG, Y.L.; ZHOU, Y.K. Farm household-scale influences and spatial differentiation of cropland abandonment[J]. Resource Science, 2020, 42(04): 696-709.
- Xie, H.L.; Huang, Y.Q. Impacts of non-farm employment and land transfer on farm households' cropland abandonment behaviors--A case study in the mountainous areas of Fujian, Jiangxi and Hunan[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(02): 408-423.
- Basanta, P.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Farmland abandonment and its determinants in the different ecological villages of the Koshi River Basin, Central Himalayas: Synergy of high-resolution remote sensing and social surveys[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 188(prepublish).
- Muller, D.; Leitão, P.J.; Sikor, T. Comparing the determinants of cropland abandonment in Albania and Romania using boosted regression trees[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2013, 117. [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Huang, Y.Q. Study on farmland abandonment behavior of farm households under different generational perspectives--Based on a questionnaire survey of 293 farm households in Xingguo County, Jiangxi Province[J]. China Land Science, 2021, 35(02): 20-30.
- Lieskovský, J.; Bezák, P.; Špulerová, J.; et al. The abandonment of traditional agricultural landscape in Slovakia-Analysis of extent and driving forces[J]. Journal of Rural Studies, 2015, 37. [CrossRef]
- Subedi, Y.R.; Kristiansen, P.; Cacho, O.; et al. Agricultural Land Abandonment in the Hill Agro-ecological Region of Nepal: Analysis of Extent, Drivers and Impact of Change[J]. Environmental Management, 2021, 67(6). [CrossRef]
- NIE, X.; XIAO, T.; MU, W.H.; et al. Influencing factors of farmland abandonment behavior of farm households based on the "rational man" hypothesis--an empirical analysis from 2010 CGSS data[J]. Land Resources Science and Technology Management, 2015, 32(03): 134-142.
- Zhuang, J.; Luo, B.L. How the distance to work affects agricultural land abandonment-an examination of differences taking into account time, gender and generation[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 2022, 22(05): 112-123.
- Renwick, A.; Jansson, T.; Verburg, P.H.; et al. Policy reform and agricultural land abandonment in the EU[J]. Land Use Policy, 2013, 30(1). [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Wang, Y.K.; Dixit, A.M.; et al. A Synopsis of Farmland Abandonment and Its Driving Factors in Nepal[J]. Land, 2020, 9(3). [CrossRef]
- ZHOU, X.H.; HU, X.; LU, C.J. The impact of non-farm employment on cropland abandonment--an empirical analysis based on CHFS data[J]. Research World, 2022(02): 12-20.
- Nhung, P.T.; Martin, K.; Heiko, F. Impacts of Agricultural Land Acquisition for Urbanization on Agricultural Activities of Affected Households: A Case Study in Huong Thuy Town, Thua Thien Hue Province, Vietnam[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(15).
- Sroka, W.; Pölling, B.; Wojewodzic, T.; et al. Determinants of Farmland Abandonment in Selected Metropolitan Areas of Poland: A Spatial Analysis on the Basis of Regression Trees and Interviews with Experts[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(11). [CrossRef]
- LEI, K.; YAN, J.Z.; HE, W.F. Analysis of influencing factors of cropland abandonment in mountainous areas based on farm household scale[J]. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 38(07): 149-157.
- Ge, L.; Gao, M.; Hu, Z.F.; et al. Analysis of reasons for abandonment of cropland in mountainous areas based on the perspective of farmers[J]. China Agricultural Resources and Zoning, 2012, 33(04): 42-46.
- Su, G.D.; Hidenori, O.; Lin, C. Spatial Pattern of Farmland Abandonment in Japan: Identification and Determinants[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(10).
- Wang, Q.; Qiu, J.J.; Yu, J. Does Migration Relocation Exacerbate Cropland Desertion in Mountainous Areas? --Based on panel data of 1578 farm households in three cities of southern Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(07): 1376-1390.
- CHENG, X.T.; ZHOU, H.; LIU, X.H.; et al. Research on the impact of the degree of part-time farming on the abandonment of cropland in mountainous areas--Taking Wuling Mountain Area as an example[J]. Yangtze River Basin Resources and Environment, 2021, 30(01): 246-256.
- LI, Z.H.; YAN, J.Z.; HUA, X.B.; et al. Research on different types of farm abandonment and their influencing factors--Taking 12 typical villages in Chongqing as an example[J]. Geography Research, 2014, 33(04): 721-734.
- Kolecka, N.; Kozak, J.; Kaim, D.; et al. Understanding farmland abandonment in the Polish Carpathians[J]. Applied Geography, 2017, 88. [CrossRef]
- ZHOU, L.J.; RAN, R.P.; LIN W.Y.; et al. Research on the factors influencing the abandonment of farmland by farm households - A survey based on 158 farm households in Nanxi District, Yibin City[J]. Rural Economy, 2014(04): 46-50.
- LI, H.S.; GUO, X.Z.; QU, C.H. The influence of location effect on farmland abandonment behavior and heterogeneity of farm households--an empirical analysis based on a survey of 529 farm households in four provinces[J]. Economy, 2020(10): 86-95.
- Yamaguchi; Ngodup; Nose; et al. Community-scale analysis of the farmland abandonment occurrence process in the mountain region of Ladakh, India[J]. Journal of Land Use Science, 2016, 11(4).
- Vidal-Macua, J.J.; Ninyerola, M.; Zabala, A.; et al. Environmental and socioeconomic factors of abandonment of rainfed and irrigated crops in northeast Spain[J]. Applied Geography, 2018, 90. [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, X.B.; et al. Impacts of plot quality characteristics on terrace abandonment in southwestern mountainous areas--A case study of Baidu Village, Jianhe County, Guizhou[J]. Geography Research, 2022, 41(03): 903-916.
- SHI, T.C.; LI, X.B. Research on the risk of abandonment of cropland in mountainous areas of Chongqing based on plot scale[J]. Journal of Mountain Geography, 2017, 35(04): 543-555.
- Muller, D.; Kuemmerle, T.; Rusu, M.; et al. Lost in transition: determinants of post-socialist cropland abandonment in Romania[J]. Journal of Land Use Science, 2009, 4(1-2). [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Müller, D.; Dubinin, M.; et al. Determinants of agricultural land abandonment in post-Soviet European Russia[J]. Land Use Policy, 2013, 30(1). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J. Scale problems in economic geography research[J]. Economic Geography, 2005(04): 433-436.
- ZHU, T.; WU, Y.F.; LIU, N.; et al. Study on the abandonment of farmland in Wusheng County, Sichuan Province[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2014, 42(26): 9183-9185.
- YANG, T.; GUO, X.D.; YU, X.; et al. Analysis and model simulation of village abandonment driving force based on multi-source data[J]. Arid Zone Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(11): 62-69.
- Li, J.J. Research on the spatial distribution characteristics of land abandonment and the reasons for abandonment in the parallel ridge and valley area of east Sichuan[D]. Chongqing Normal University, 2018.
- Shi, T.C.; Li, X.B.; Xin, L.J.; et al. The spatial distribution of farmland abandonment and its influential factors at the township level: A case study in the mountainous area of China[J]. Land Use Policy, 2018, 70. [CrossRef]
- Renwick, A.; Jansson, T.; Verburg, P.H.; et al. Policy reform and agricultural land abandonment in the EU[J]. Land Use Policy, 2013, 30(1).
- Shi, J.H.; Wang, F. The Effect of High-Speed Rail on Cropland Abandonment in China[J]. Land, 2022, 11(7). [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zeng, M.; Xu, D.D.; et al. Why do landslides impact farmland abandonment? Evidence from hilly and mountainous areas of rural China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2022, 113(1). [CrossRef]
- Seungjoo; Heeyeun, Y.; Yeankyoung, H. Assessment of spatial interactions in farmland abandonment: A case study of Gwangyang City, Jeollanam-do Province, South Korea[J]. Habitat International, 2022, 129.
- XU, X.T.; YUAN, J.W.; LI, X.H.Q.; et al. Analysis of driving factors and countermeasures of cropland abandonment in Xianyang city[J]. Journal of Xianyang Normal College, 2021, 36(02): 69-71.
- Ustaoglu, E.; Collier, M.J. Farmland abandonment in Europe: an overview of drivers, consequences, and assessment of the sustainability implications[J]. Environmental Reviews, 2018 ,26(4). [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Pascual, N.; et al. Space–time process and drivers of land abandonment in Europe[J]. Catena, 2017, 149. [CrossRef]
- LI, F.Q.; XIE, H.L.; ZHOU, Z.H. Analysis of factors influencing the abandonment of cropland in village areas based on qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) (in English)[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2021, 12(02): 241-253.
- Yi, L. Research on the influencing factors of cropland abandonment and its management countermeasures in the main grain producing areas of Guangdong Province[D]. South China Agricultural University, 2019.
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.B.; Song, W. Determinants of cropland abandonment at the parcel, household and village levels in mountain areas of China: A multi-level analysis[J]. Land Use Policy, 2014, 41. [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wei, S. Degree of Abandoned Cropland and Socioeconomic Impact Factors in China: Multi-Level Analysis Model Based on the Farmer and District/County Levels[J]. Land, 2021, 11(1).
- ZHANG, F.Y.; WANG, H.D. Multilevel model and its application in population science research[J]. China Population Science, 1995(06): 1-7.
- SONG, J.N.; JIN, X.B.; ZHOU, Y.K. Analysis of the contribution of intensive utilization of cropland to food productivity based on multilayer linear model--Taking Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region as an example[J]. Resource Science, 2010, 32(06): 1161-1168.
- ZHOU, Y.Q. Application of multilevel linear model in management research[J]. Jiangxi Social Science, 2006(10): 180-182.
- YANG, W.G.; CHEN, H.; YANG, M.N.; et al. Analysis of influencing factors on land use decision-making of farmers based on multilevel model - Taking Gaoxigou Village in Mili County, Shaanxi Province as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2010, 25(04): 646-656.
- Wu, K.M.; Sun, Q.N. Causes and Countermeasures of the Ant Tribe Phenomenon of University Graduates:The Perspective of the Rational Man Hypothesis[J]. Fudan Education Forum, 2012, 10(01): 28-31+44.
- Samuel, L.P. The Rational Peasant[M]. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1979.
- LI, G.Y.; JIANG, G.H.; ZHANG, Y.H.; et al. Research on the mechanism and revitalization countermeasures of cropland abandonment in China[J]. China Land Resources Economy, 2021, 34(02): 36-41.
- Wang, W.W. Research on land transfer behavior and regional differences under the perspective of rural habitat environment and farmers' livelihood capital[D]. China University of Geosciences, 2022.
- ZHOU, L.; LI, H.M.; LI, P. Impact of livelihood capital on the choice of livelihood strategies of relocated farmers in relocation for poverty alleviation - A survey based on relocated farmers in Hunan[J]. Economic Geography, 2020, 40(11): 167-175.
- Xu, F.F. Research on sustainable livelihoods of farmers in relocation areas for poverty alleviation based on SLA framework[D]. Guizhou University, 2018.
- Zhang, K.X. Research on Precision Poverty Alleviation Issues and Countermeasures under the Perspective of Sustainable Livelihood [D]. South China University of Technology, 2020.
- Su, F.; Shang, H.Y. Impact of Farmers' Livelihood Capital on Their Risk Coping Strategies: The Case of Zhangye City in the Black River Basin[J]. China Rural Economy, 2012(08): 79-87+96.
- SU, F.; XU, Z.M.; SHANG, H.Y. A review of sustainable livelihood analysis[J]. Progress in Earth Sciences, 2009, 24(01): 61-69.
- Ma, C.; Liu, L.M.; Yuan, C.C.; et al. Characteristics of livelihood capital differentiation of farm households in rapidly urbanizing areas and its impact on livelihood strategies--Taking Qingpu District of Shanghai as an example[J]. Research on Agricultural Modernization, 2018, 39(02): 316-324.
- Wang, X.L.; Xue, C.; Xu, J.X. Does agricultural land empowerment promote farmers' self-employment? --An empirical study based on CLDS data[J]. Economic Science, 2020(06): 111-123.
- Deng, J.X.; Shan, L.B.; He, D.Q.; et al. Processing methods of missing data and its development trend[J]. Statistics and Decision Making, 2019, 35(23): 28-34.
- ZHAO, X.F.; HUANG, X.J.; ZHONG, T.Y.; et al. Empirical study on stratified linear model of intensive land utilization in development zones in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geography Research, 2012, 31(09): 1611-1620.
- Jiang, J.L. Empirical analysis of influencing factors of livable city construction based on hierarchical linear model[D]. Southwest University of Finance and Economics, 2016.
- Kline, R.; Kline, R.B.; Kline, R. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modelling[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2011, 101(12).
- ZHONG, H.Y.; ZHANG, A.L. Research on the economic driving mechanism of urban transfer of agricultural land in Wuhan city circle based on hierarchical linear model[J]. Economic Geography, 2014, 34(05): 76-82.
- LIU, L.G.; WANG, J.Y. Rational choice of migrant population's willingness to stay in cities for a long period of time-an empirical study based on a nonlinear stratified model[J]. Journal of Population, 2019, 41(03): 100-112.
- Wang, Y. Influential factors of urban residents' living garbage classification behavior[D]. East China Normal University, 2017.
- QU, M.; ZHAO, K. Influence of farmers' livelihood capital on their cropland protection behavior - based on a sample of 473 farmers in Henan's Slide County[J]. Research on Agricultural Modernization, 2018, 39(05): 808-816.
- Xie, W.B.; Cao, C.; Liu, G.Y.; et al. Analysis of Regional Differences and Driving Factors of Cropland Desertion-A Study Based on CFD and CHFS Farm Household Survey Data[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 2022, 31(06): 23-30.
- Hong, W.J. Natural endowment and agricultural land abandonment--Based on the examination of the scale of contracted land of farmers[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 2022, 22(05): 124-135.
- ZHANG, Y.; LI, X.B.; SONG, W.; et al. Different scales of agricultural labor force impacts on cropland abandonment under agricultural land transfer in Wulong County, Chongqing Municipality[J]. Advances in Geoscience, 2014, 33(04): 552-560.
- Kuang, F.Y.; Chen, M.Q.; Lu, Y.F.; et al. Analysis of the impact of livelihood capital on farmers' willingness to protect farmland--taking 587 questionnaires in Jiangxi Province as an example[J]. China Land Science, 2017, 31(02): 58-66.
- WU, Y. A study on the impact of livelihood capital on livelihood strategies of farm households in poor mountainous areas-based on survey data from Pingwu and Nanjiang counties in Sichuan province[J]. Agricultural Economic Issues, 2016, 37(03): 88-94+112.
- Li H.Y.; Cai Yinying. The effect of livelihood capital on farmers' willingness to participate in farmland protection--Taking Yong'an and Jinqiao towns in Chengdu city, and Jiangyuan town in Chongzhou city as examples [J]. Glacial permafrost, 2015, 37( 2) : 545-554.
- ZHANG, B.L.; YANG, Q.Y.; YAN, Y.; et al. Characteristics and Reasons of Different Types of Farming Households Abandoning Farming in Rapid Urbanization--Based on a Survey of 540 Farming Households in Ten Districts and Counties of Chongqing Municipality[J]. Resource Science, 2011, 33(11): 2047-2054.
- FENG, Y.F.; DONG, Y.X.; WANG, F. Analysis of farm abandonment behavior and influencing factors in suburban areas of large cities: A case study of farm household survey in Panyu District, Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2010, 25(05): 722-734.
- QIU, Y.Z.; PENG, R.X.; CAO, G.Z. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Cultivated Land abandonment under the Perspective of Urban-Rural Relations--Taking Xintai City as an Example[J]. Small Town Construction, 2022, 40(09): 46-54.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





