Submitted:
18 August 2023
Posted:
22 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. What are Sodium Glucose Co-Transporters?
3. Use of selective SGLT2 Inhibition as an anti-diabetic therapy
3.1. Pre-clinical Studies
3.1.1. Blood Pressure Reduction
3.1.2. Improved Digestive Health
3.1.3. Diabetic Retinopathy
3.1.4. Kidney Health
3.1.5. Cardiovascular Benefits
3.1.6. Improved Cognitive Function in T2D
3.2. Human Clinical Trials
3.2.1. Empagliflozin
3.2.2. Dapagliflozin
3.2.3. Canagliflozin
3.2.4. Ertugliflozin
4. Use of selective SGLT2 Inhibition as a non-diabetic therapy
4.1. Preclinical Studies
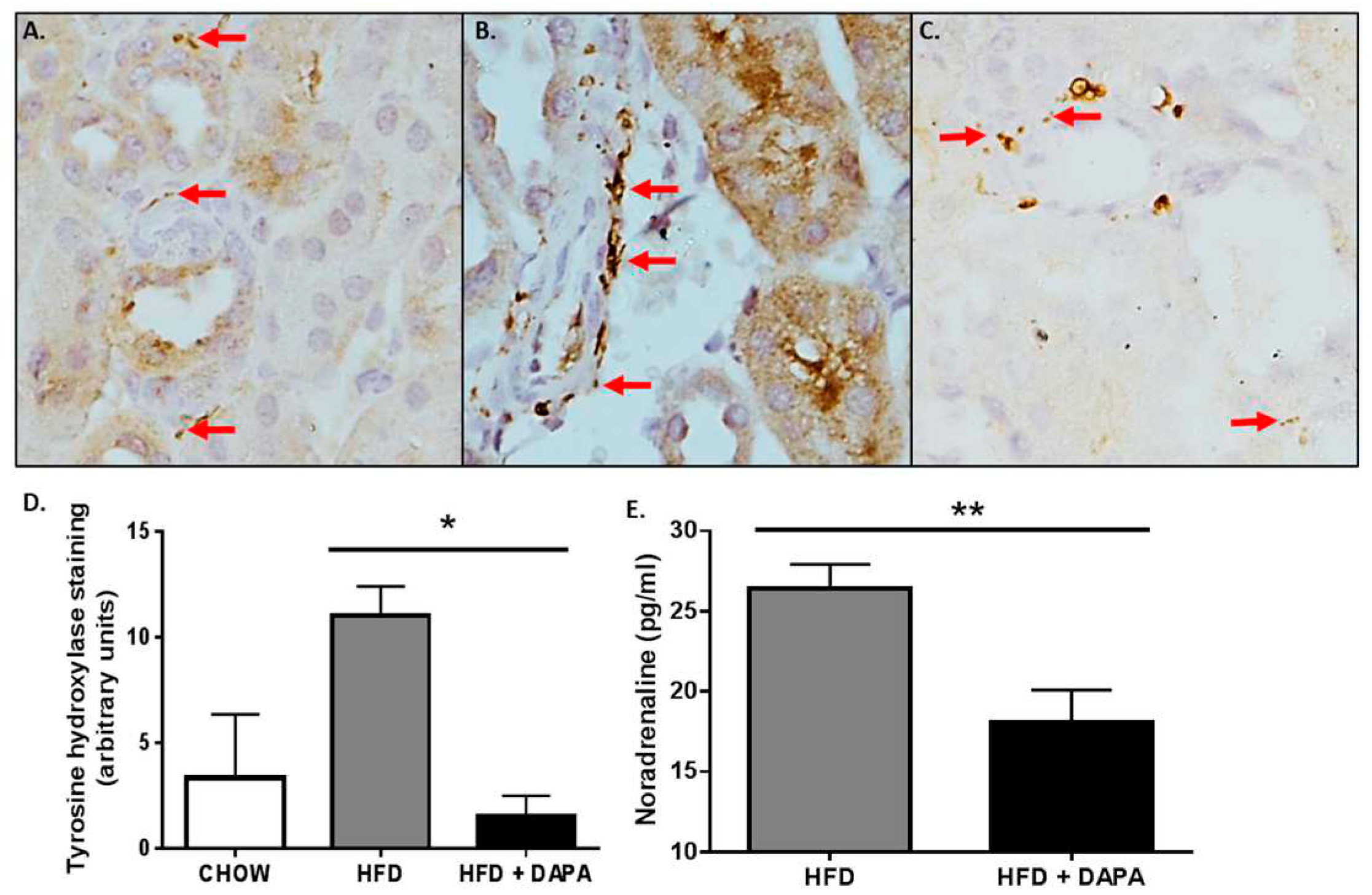
4.1.1. Decreases Sympathetic Nervous System Activity
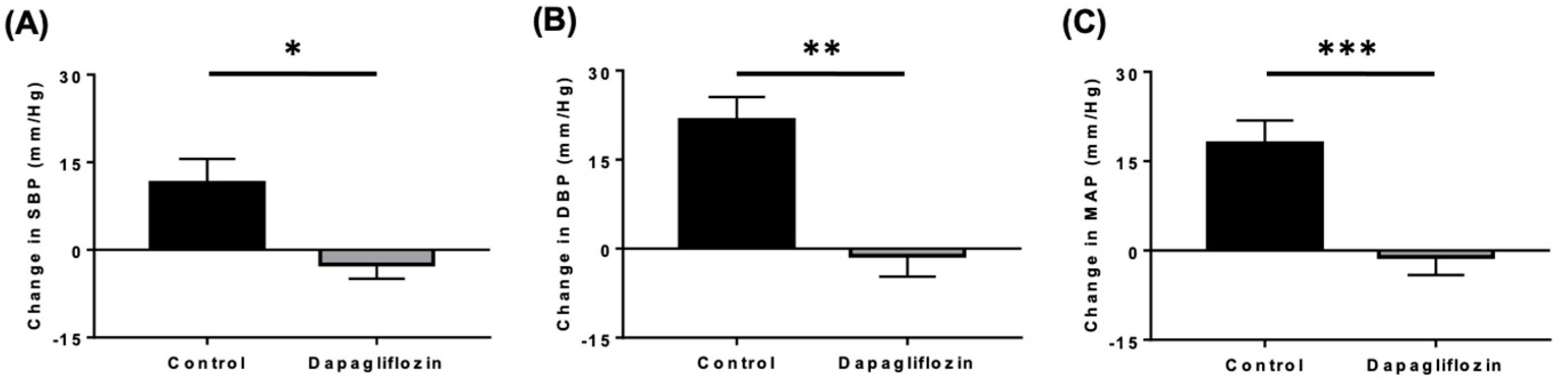
4.1.2. Reductions in Blood Pressure
4.1.3. Inflammation Control
4.1.4. Increases Ketone Levels
4.1.5. Improved Cardiovascular Health
4.1.6. Steatosis and Insulin Resistance
4.2. Human Clinical Trials
4.2.1. Empagliflozin
4.2.2. Dapagliflozin
4.2.3. Ipragliflozin
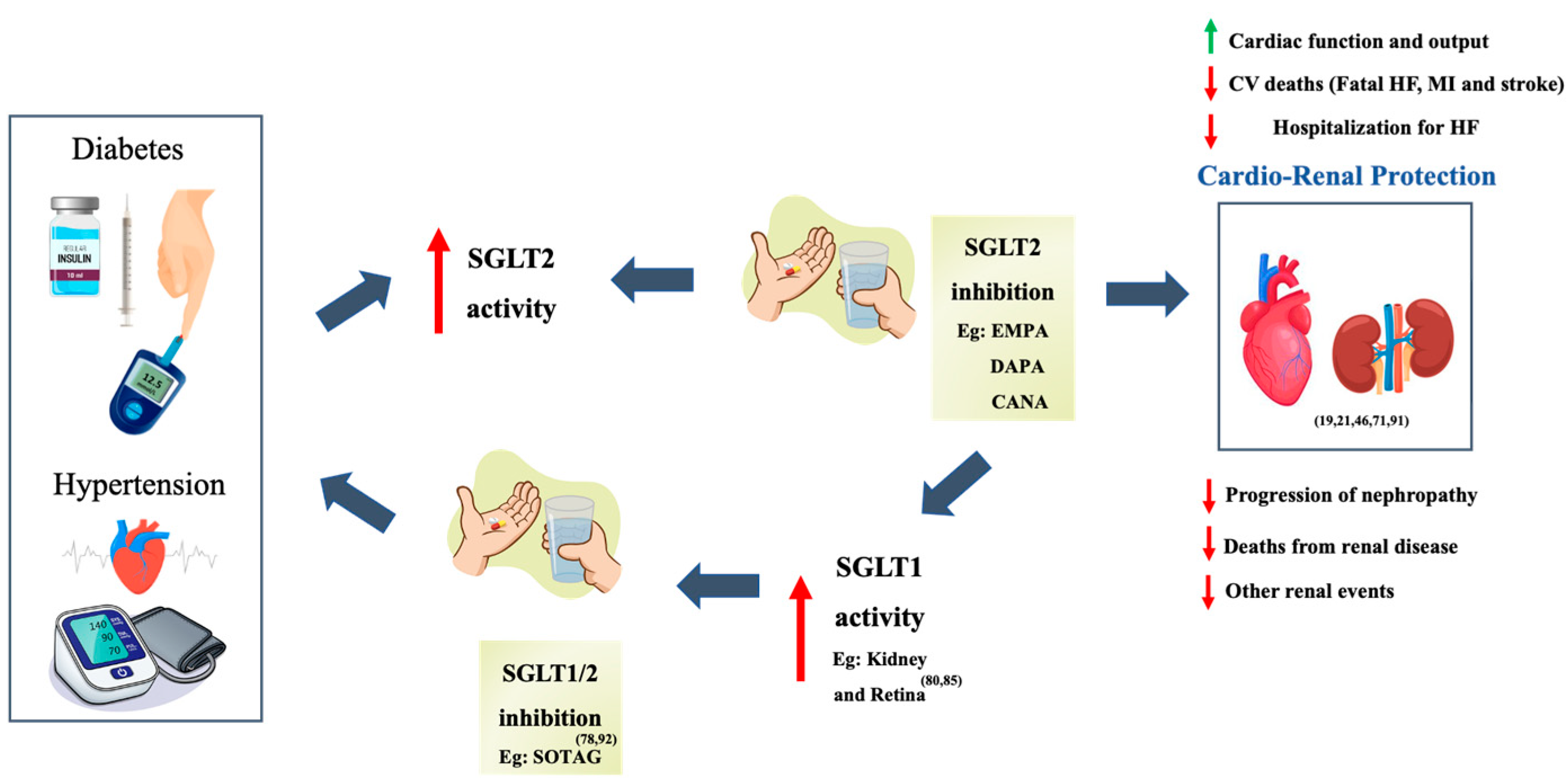
5. Discussion
5.1. Are Dual SGLT1/2 Inhibitors More Effective than Sole SGLT2 Inhibitors?
5.2. Interesting Avenues for SGLT2i Therapy for the Treatment of T1D
5.2.1. Animal Studies Utilizing SGLT2i as a Treatment for T1D
5.2.2. Human Pilot Studies/Clinical Trials utilising SGLT2i as an addon to Insulin for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
5.3. Use of dual SGLT 1 / 2 Inhibitors in T1D
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovesdy, C. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl 2011. 2022, 12(1), 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, D.; Nichols, G.; Guillion, C.; Brown, J.; Smith, D. Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch Intern Med. 2004, 164(6), 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, J.; Nakajima, H.; Mori, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Hatori, M.; Tanimoto, S.; Amiya, E.; Hara, K. Clinical and pathologic characteristics of dilated cardiomyopathy in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2005, 67(1), 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.; Foley, R.; Gilbertson, D.; Chen, S. United States Renal Data System public health surveillance of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2015, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutens, A. Epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 97, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Chand Jamali, M.; Habib, A.; Hussain, M.; Akhtar, M.; Najmi, A. Diabetic kidney disease: An overview of prevalence, risk factors, and biomarkers. Clin. Epidemiol. Global Health. 2021, 9, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavkov, M.; Bennett, P.; Knowler, W.; Krakoff, J.; Sievers, M.; Nelson, R. Effect of youth-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on incidence of end-stage renal disease and mortality in young and middle-aged Pima Indians. JAMA. 2006, 296, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I. Cost of treating diabetic kidney disease. Indian J. Nephrol. 2014, 24, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, M.; Susztak, K. Developing Treatments for Chronic Kidney Disease in the 21st Century. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Firoz, A.; Garlapati, S.; Sathi, T.; Haris, M.; Dhungana, B.; Ray, B.; Shah, G.; Kc, B.; Paudel, P. Emerging treatments of Cardiorenal Syndrome: An update on Pathophysiology and Management. Cureus. 2021, 13(8), e17240.
- Sasso, F.; Pafundi, P.; Simeon, V.; De Nicola, L.; Chiodini, P.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Nevola, R.; Salvatore, T.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; Adinolfi, L.; Minutolo, R. Efficacy and durability of multifactorial intervention on mortality and MACEs: A randomized clinical trial in type-2 diabetic kidney disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, M.; Susztak, K. The next generation of therapeutics for chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 568–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, R.; Shinozaki, Y.; Ohta, T. Sodium-glucose cotransporters: Functional properties and pharmaceutical potential. J Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11(4), 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E. The Intestinal Na+/- Glucose Cotransporter. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993, 55, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.; Hibbs, M.; Herat, L.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. The Sympathetic Nervous System Regulates Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 1 Expression in the Kidney. Biomedicines. 2023, 11(3), 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herat, L.; Magno, A.; Rudnicka, C.; Hricova, J.; Carnagarin, R.; Ward, N.; Arcambal, A.; Kiuchi, M.; Head, G.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. SGLT2 Inhibitor-Induced Sympathoinhibition: A Novel Mechanism for Cardiorenal Protection. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5(2), 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Day, C.; Bellary, S. Renal Protection with SGLT2 inhibitors: Effects in Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr Diab Rep. 2022, 22(1), 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.; Henry, R. SGLT2 Inhibition – a novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010, 9(7), 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johanssen, E.; Woerle, H.; Broedl, U.; Inzucchi, S. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, SD.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.; Zelniker, T.; Kuder, J.; Murphy, S.; Bhatt, D.; Leiter, L.; McGuire, D.; Wilding, J.; Ruff, C.; Gause-Nilsson, I.; Fredriksson, M.; Johansson, P.; Langkilde, A.; Sabatine, M. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.; Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X. Cardiovascular benefits of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021, 20(1), 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutka, M.; Bobinski, R.; Ulman-Wlodarz, I.; Hajduga, M.; Bujok, J.; Pajak, C.; Cwiertnia, M. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: mechanisms of action in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2021, 26(3), 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffner, J.; Chen, B.; Malhotra, D.; Dworkin, L.; Gong, R. Therapeutic targeting of SGLT2: A New Era in the Treatment of Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 749010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, T.; Kikuchi, O.; Kobayashi, M.; Matsui, S.; Yokota-Hashimoto, H.; Wada, E.; Kohno, D.; Sasaki, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Kakizaki, S.; Yamada, M.; Kitamura, T. SGLT1 in pancreatic a cells regulate glucagon secretion in mice, possibly explaining the distinct effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on plasma glucagon levels. Mol Metab. 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrhovac, I.; Eror, D.; Klessen, D.; Burger, C.; Breljak, D.; Kraus, O.; Radovic, N.; Jadrijevic, S.; Aleksic, I.; Walles, T.; Sauvant, C.; Sabolic, I.; Koepsell, H. Localizations of Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 in human kidney and of SGLT1 in human small intestine, liver, lung and heart. Pflugers Arch. 2015, 467(9), 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herat, LY; Matthews, V; Rakoczy, E; Carnagarin R; Schlaich, M. Focusing on Sodium Glucose Co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) and its potential impact in diabetic retinopathy. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2018, 2018:9254126. [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A; Takasu, T; Yokono, M; Imamura, M; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacologic effects. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016, 130(3): 159-169. [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A; Takasu, T; Yokono, M; Imamura, M; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Part2. Antidiabetic effects in type 2 diabetic mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016, 131(3): 198-208. [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A; Takasu, T; Yokono, M; Imamura, M; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Part3. Effects on diabetic complications in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017, 809: 163-171. [CrossRef]
- Majewski, C.; Bakris, G. Blood Pressure Reduction: An Added Benefit of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38(3), 429-430.
- Tikkanen, I.; Narko, K.; Zeller, C.; Green, A.; Salsali, A.; Broedl, U.; Woerle, H. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38(3), 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, C.; Johansson, P.; Ptaszynska, A.; List, J.; Johnsson, E. Dapagliflozin lowers blood pressure in hypertensive and non-hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2015, 12(5), 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, V.; Elliot, R.; Rudnicka, C.; Hricova, J.; Herat, L.; Schlaich, M. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulation of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2. J Hypertens. 2017, 35(10), 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J; Chen, Y; Yang, H; Gu, L; Ni, Z; Mou, S; Shen, J; Che, X. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition via dapagliflozin improves diabetic kidney disease (DKD) over time associated with increasing effect on the gut microbiota in db/db mice. Front Endocrinol. 2023, 14:1026040. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D; Battson, M; Jarrell, D; Hou, S; Ecton, K; Weir, T; Gentile, C. SGLT2 inhibition via dapagliflozin improves generalized vascular dysfunction and alters the gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018, 17(1):62. [CrossRef]
- Herat, L.; Ward, N.; Magno, A.; Rakoczy, E.; Kiuchi, M.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition reduces succinate levels in diabetic mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2020, 26(23), 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L; Yang, Y; Xu, G. Empagliflozin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-related diabetic nephrophathy via altering the gut microbiota. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022, 1867(12): 159234. [CrossRef]
- Hata, S; Okamura, T; Kobayashi, A; Bamba, R; Miyoshi, T; Nakajima, H; Kitagawa, N; Hashimoto, Y; Majima, S; Senmaru, T; Okada, H; Ushigome, E; Nakanishi, N; Takakuwa, H; Sasano, R; Hamaguchi, M; Fukui, M. Gut Microbiota Changes by an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Luseogliflozin, Alters Metabolites Compared with Those in a Low Carbohydrate Diet in db/db Mice. Nutrients. 2022, 14(17): 3531. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q; Zhang, R; Wei, F; Fang, J; Zhang, J; Sun, J; Sun, Q; Wang, H. SGLT2 inhibitor-empagliflozin treatment ameliorates diabetic retinopathy manifestations and exerts protective effects associated with augmenting branched chain amino acids catabolism and transportation in db/db mice. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy. 2022, 152:113222. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q; Leley, S; Bello, E; Dhami, H; Mathew, D; Bhatwadekar, A. Dapagliflozin protects neural and vascular dysfunciton of the retinas in diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022, 10(3):e002801. [CrossRef]
- Tang, L; Wu, Y; Tian, M; Sjostrom, C; Johansson, U; Peng, X; Smith, D; Huang, Y. Dapagliflozin slows the progression of the renal and liver fibrosis associated with type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017, 313(5): E563-E576. [CrossRef]
- Shin, S; Chung, S; Kim, S; Lee, E; Yoo, Y; Kim, J; Ahn, Y; Kim, E; Moon, S; Kim, M; Ko, S. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, on Renal Renin-Angiotensin System in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS One. 2016, 11(11): e0165703.
- Kojima, N; Williams, J; Takahashi, T; Miyata, N; Roman, R. Effects of a new SGLT2 inhibitor, Luseogliflozin, on diabetic nephropathy in T2D rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013, 345(3): 464-72. [CrossRef]
- Lin, B; Koibuchi, N; Hasegawa, Y; Sueta, D; Toyama, K; Uekawa, K; Ma, M; Nakagawa, T; Husaka, H; Kim-Mitsuyama, S. Glycemic control with empagliflozin, a novel selective SGLT2 inhibitor, ameliorates cardiovascular injury and cognitive dysfunction in obese and type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014, 13:148. [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.; Lachin, J.; Fitchett, D.; Von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, E.; Woerle, H.; Broedl, U.; Zinman, B. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.; Stefansson, B.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.; Mann, J.; McMurray, J.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, D.; Toto, R.; Langkilde, A.; Wheeler, D. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Eng J Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.; Charytan, D.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; Cannon, C.; Capuano, G.; Chu, P.; Zeeuw, D.; Greene, T.; Levin, A.; Pollock, C.; Wheeler, D.; Yavin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zinman, B.; Meininger, G.; Brenner, B.; Mahaffey, K. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.; Pratley, R.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Mancuso, J.; Huyck, S.; Masiukiewicz, U.; Charbonnel, B.; Frederich, R.; Gallo, S.; Cosentino, F.; Shih, W.; Gantz, I.; Terra, S.; Cherney, D.; McGuire, D. Cardiovascular Outcomes with Ertugliflozin in Type 2 Diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2020, 383, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herat, L.; Matthews, J.; Azzam, O.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Targeting features of the metabolic syndrome through sympatholytic effects of SGLT inhibition. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022, 24(3), 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, B.; Kang, L. Empagliflozin Alleviates Atherosclerosis Progression by Inhibiting Inflammation and Sympathetic Activity in a Normoglycemic Mouse Model. J Inflamm Res. 2021, 14, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.; Herat, L.; Magno, A.; Gorman, S.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. SGLT-2 Inhibitor-Induced Sympathoexcitation in White Adipose Tissue: A Novel Mechanism of Beiging. Biomedicines. 2020, 8(11), 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G.; Santos da Silva, D.; Farias, G.; de Oliveira Santos, I.; Baptista, L.; Magalhaes, K. Browning of the white adipose tissue regulation: new insights into nutritional and metabolic relevance in health and diseases. Nutr Metab. 2022, 19(1), 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Ouyang, X.; Lei, X.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Deng, W.; Liang, Z. The SGLT-2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Has a Therapeutic Effect on Atherosclerosis in Diabetic ApoE-/- Mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Papazafiropoulou, A.; Georgopoulos, M.; Katsilambros, N. Ketone bodies and the heart. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2021, 6, e209–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, C.; Lu, C.; Cao, R.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J. Ketogenic diet alleviates renal fibrosis in mice by enhancing fatty acid oxidation through the free fatty acid receptor 3 pathway. Front Nutr. 2023, 10, 1127845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschner, R.; Kolwelter, J.; Bosch, A.; Striepe, K.; Jung, S.; Kannenkeril, D.; Ott, C.; Schiffer, M.; Achenbach, S.; Schmieder, R. Effect of empagliflozin on ketone bodies in patients with chronic heart failure. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2021, 20(1), 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Farooq, M.; Gaertner, S.; Bruckert, C.; Qureshi, A.; Lee, H.; Benrahla, D.; Pollet, B.; Stephan, D.; Ohlmann, P.; Lessinger, J.; Mayoux, E.; Auger, C.; Morel, O.; Schini-Kerth, V. Empaglifozin improved systolic blood pressure, endothelial dysfunction and heart remodeling in the metabolic syndrome ZSF1 rat. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020, 19(1), 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, I.; Kume, S.; Sugahara, S.; Osawa, N.; Yamahara, K.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Takeda, N.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Kaneko, T.; Mayoux, E.; Mark, M.; Yanagita, M.; Ogita, H.; Araki, S.; Maegawa, H. SGLT2 inhibition mediates protection from diabetic kidney disease by promoting ketone body-induced mTORC1 inhibition. Cell Metab. 2020, 32(3), 404-419.e6. [CrossRef]
- Khunti, K.; Ruan, Y.; Davies, J.; Field, B.; Harris, S.; Kosiborod, M.; Nagi, D.; Narendran, P.; Patel, D.; Ryder, R.; Varnai, K.; Wild, S.; Wilmot, E.; Rea, R. Association between SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment and Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Mortality in People with Type 2 Diabetes Admitted to Hospital with COVID-19. Diabetes Care. 2022, 45(12), 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, I; Inoue, D; Maeda, T; Hara, T; Ichimura, A; Miyauchi, S; Kobayashi, M; Hirasawa, A; Tsujimoto, G. Short-chain fatty acids and ketones directly regulate sympathetic nervous system via G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011, 108(19): 8030-8035. [CrossRef]
- Kolanowski, J; Young, J; Landsberg, L. Stimulatory influence of D(-)3-hydroxybutyrate feeding on sympathetic nervous system activity in the rat. Metabolism. 1994, 43(2): 180-5. [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Yang, N.; Luo, W.; Qian, J.; Zhu, W.; Ye, S.; Yuan, C.; Xu, D.; Liang, G.; Huang, W.; Shan, P. Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022, 43(10), 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Nagata, N.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Chen, G.; Mayoux, E.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice. EbioMedicine. 2017, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radlinger, B; Ress, C; Folie, S; Salzmann, K; Lechuga, A; Weiss, B; Salvenmoser, W; Graber, M; Hirsch, J; Holfeld, J; Kremser, C; Moser, P; Staudacher, G; Jelenik, T; Roden, M; Tilg, H; Kaser, S. Empagliflozin protects mice against diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Diabetologia. 2023, 66(4): 754-767. [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Yan, W.; Liu, Y.; Ren, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, L. Effects of canagliflozin on weight loss in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One. 2017, 12(6), e0179960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Subodh, V.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; Jamal, W.; Kimura, K.; Schnee, J.; Zeller, C.; Cotton, D.; Bocchi, E.; Bohm, M.; Choi, D.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure, E.; Giannetti, N.; Janssens, S.; Zhang, J.; Gonzalez Juanatey, J.; Kaul, S.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.; Merkely, B.; Nicholls, S.; Perrone, S.; Pina, I.; Ponikowski, P.; Sattar, N.; Senni, M.; Seronde, M.; Spinar, J.; Squire, I.; Taddei, S.; Wanner, C.; Zannad, F. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N Eng J Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Butler, J.; Zannad, F.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.; Pocock, S.; Carson, P.; Anand, I.; Doehner, W.; Haass, M.; Komajda, M.; Miller, A.; Pehrson, S.; Teerlink, J.; Schnaidt, S.; Zeller, C.; Schnee, J.; Anker, S. Effect of Empagliflozin on Worsening Heart Failure Events in Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: EMPEROR-Preserved Trial. Circulation. 2021, 144(16), 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinski, D; Kolesnik, E; Tripolt, N; Pferschy, P; Benedikt, M; Wallner, M; Alber, H; Berger, R; Lichtnauer, M; Saely, C; Moertl, D; Auersperg, P; Reiter, C; Rieder, T; Siller-Matula, J; Gager, G; Hasun, M; Weidinger, F; Pieber, T; Zechner, P; Herrmann, M; Zirlik, A; Holman, R; Oulhaj, A; Sourij, H. Empagliflozin in acute myocardial infarction: the EMMY trial. Eur Heart J. 2022, 43(41): 4421-4432. [CrossRef]
- Herrington, W.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.; Hauske, S.; Emberson, J.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.; Ng, S.; Sammon, E.; Zhu, D.; Hill, M.; Stevens, W.; Wallendszus, K.; Brenner, S.; Cheung, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Hooi, L.; Liu, W.; Kadowaki, T.; Nangaku, M.; Levin, A.; Cherney, D.; Maggioni, A.; Pontremoli, R.; Deo, R.; Goto, S.; Rossello, X.; Tuttle, K.; Steubl, D.; Petrini, M.; Massey, D.; Eilbracht, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Landray, M.; Baigent, C.; Haynes, R. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med. 2023, 388(2), 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.; Solomon, S.; Inzucchi, S.; Kober, L.; Kosiborod, M.; Martinez, F.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.; Anand, I.; Belohlavek, J.; Bohm, M.; Chiang, C.; Chopra, V.; deBoer, R.; Desai, A.; Diez, M.; Drozdz, J.; Dukat, A.; Ge, J.; Howlett, J.; Katova, T.; Kitakaze, M.; Ljungman, C.; Merkely, B.; Nicolau, J.; O’Meara, E.; Petrie, M.; Vinh, P.; Schou, M.; Tereshchenko, S.; Verma, S.; Held, C.; DeMets, D.; Docherty, K.; Jhund, P.; Bengtsson, O.; Sjostrand, M.; Langkilde, A. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Eng J Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; McMurray, J.; Claggett, B.; Boer, R.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.; Inzucchi, S.; Kosiborod, M.; Lam, C.; Martinez, F.; Shah, S.; Desai, A.; Jhund, P.; Belohlavek, J.; Chiang, C.; Borleffs, C.; Comin-Colet, J.; Dobreanu, D.; Drozdz, J.; Fang, J.; Alcocer-Gamba, M.; Habeeb, W.; Han, Y.; Honorio, J.; Janssens, S.; Katova, T.; Kitakaze, M.; Merkely, B.; O’Meara, E.; Saraiva, J.; Tereshchenko, S.; Thierer, J.; Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Verma, S.; Pham, V.; Wilderang, U.; Zaozerska, N.; Bachus, E.; Lindholm, D.; Petersson, M.; Langkilde, A. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med. 2022, 387(12), 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.; Dekkers, C.; Barbour, S.; Cattran, D.; Abdul Gafor, AH.; Greasley, P.; Laverman, G.; Kun Lim, S.; Di Tanna, G.; Reich, H.; Vervloet, M.; Wong, M.; Gansevoort, R.; Heerspink, H. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8(7), 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.; Cherney, D. Clinical Implications of an Acute Dip in eGFR after SGLT2 Inhibitor Initiation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021, 16(8), 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuchi, S.; Hisatake, S.; Kabuki, T.; Fujii, T.; Oka, T.; Dobashi, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Ikeda, T. Long-term use of ipragliflozin improved cardiac sympathetic nerve activity in a patient with heart failure: A case report. Drug Discov Ther. 2018, 12(1), 51-54.
- Young, S; Ryan, L; Mullins, T; Flint, M; Steane, S; Walton, S; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H; Carter, D; Reichelt, M; Gallo, L. Sotagliflozin, a dual SGLT1/2 Inhibitor, improves cardiac outcomes in a mouse model of early heart failure without diabetes. Front Physiol. 2021, 12: 738594. [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D; Szarek, M; Steg, P; Cannon, C; Leiter, L; McGuire, D; Lewis, J; Riddle, M; Voors, A; Metra, M; Lund, L; Komajda, M; Testani, J; Wilcox, C; Ponikowski, P; Lopes, R; Verma, S; Lapuerta, P; Pitt, B. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384(2):117-128. [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.; Szarek, M.; Pitt, B.; Cannon, C.; Leiter, L.; McGuire, D.; Lewis, J.; Riddle, M.; Inzucchi, S.; Kosiborod, M.; Cherney, D.; Dwyer, J.; Scirica, B.; Bailey, C.; Diaz, R.; Ray, K.; Udell, J.; Lopes, R.; Lapuerta, P.; Steg, P. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384(2), 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M; Rodriguez-Capitan, J; Requena-Ibanez, J; Santos-Gallego, C; Zafar, M; Escolar, G; Mancini, D; Mitter, S; Lam, D; Contreras, J; Fergus, I; Atallah-Lajam, F; Abascal, V; Lala, A; Moreno, P; Moss, N; Lerakis, S; Sanz, J; Fuster, V; Badimon, J. Rationale and Design of the SOTA-P-CARDIA Trial (ATRU-V): Sotagliflozin in HFpEF Patients Without Diabetes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Herat, L.; Matthews, J.; Ong, W.; Rakoczy, E.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Determining the Role of SGLT2 Inhibition with Dapagliflozin in the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front Biosci. 2022, 27(12), 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herat, L.; Matthews, J.; Rakoczy, E.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Comparing and Contrasting the Effects of the SGLT Inhibitors Canagliflozin and Empagliflozin on the Progression of Retinopathy. Front Biosci. 2023, 28(4), 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Herat, L.; Rooney, J.; Rakoczy, E.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Determining the Role of SGLT2 inhibition with Empagliflozin in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Biosci Rep. 2022, 42(3), BSR20212209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J; Schlaich, M; Rakoczy, E; Matthews, V; Herat, L. The Effect of SGLT2 Inhibition on Diabetic Kidney Disease in a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Biomedicines. 2022, 10(3): 522. [CrossRef]
- Kesherwani, V; Shahshahan, H; Mishra, P. Cardiac transcriptome profiling of diabetic Akita mice using microarray and next generation sequencing. PLoS One. 2017, 12(8): e0182828. [CrossRef]
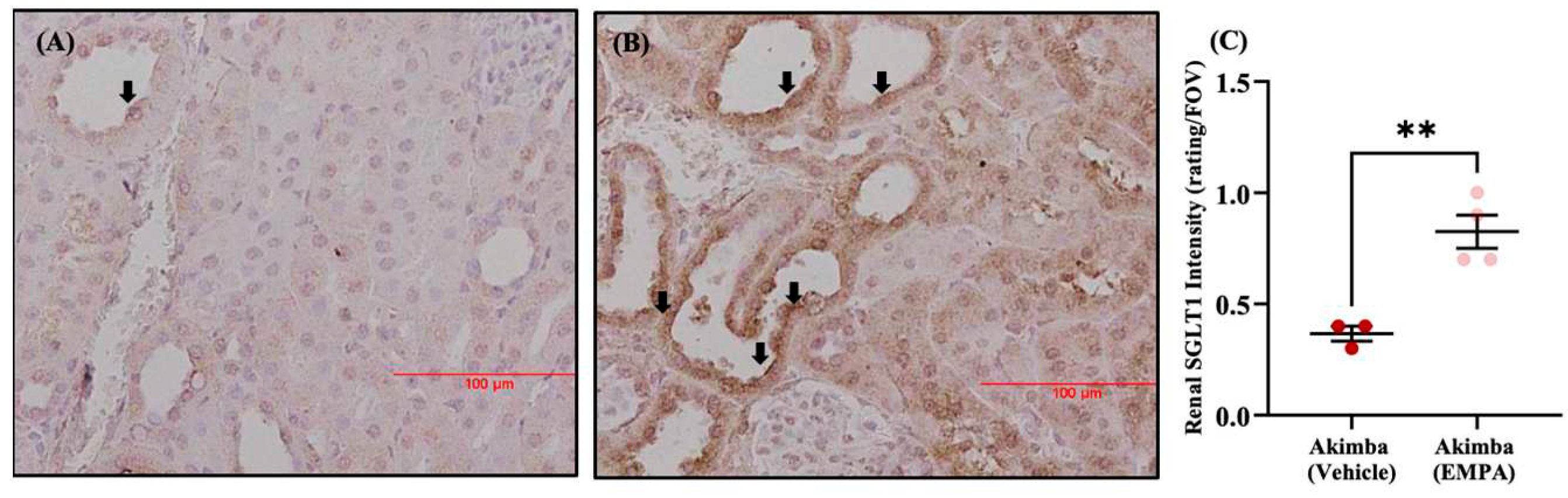
- Herat, L.; Matthews, J.; Hibbs, M.; Rakoczy, E.; Schlaich, M.; Matthews, V. Combined SGLT1 and 2 inhibition is associated with improved glucose control and multi-organ protection in the type 1 diabetic Akimba mouse. iScience. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Henry, R; Thakkar, P; Tong, C; Polidori, D; Alba, M. Efficacy and Safety of Canagliflozin, a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, as Add-on to Insulin in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38(12): 2258-65. [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P; Mathieu, C; Phillip, M; Hansen, L; Griffen, S; Tschope, D; Thoren, F; Xu, J; Langkilde, A. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (DEPICT-1): 24 week results from a multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2017, 5(11): 864-876. [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C; Rudofsky, G; Phillip, M; Araki, E; Lind, M; Arya, N; Thoren, F; Scheerer, M; Iqbal, N; Dandona, P. Long-term efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (the DEPICT-2 study): 52-week results from a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2020, 22(9): 1516-1526. [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J; Marquard, J; Laffel, L; Neubacher, D; Kaspers, S; Cherney, D; Zinman, B; Skyler, J; George, J; Soleymanlou, N; Perkins, B. Empagliflozin as Adjunctive to Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes: The EASE Trials. Diabetes Care. 2018, 41(12): 2560-2569. [CrossRef]
- Paik, J; Blair, H. Dapagliflozin: A Review in Type 1 Diabetes. Drugs. 2019, 79(17): 1877-1884. [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B; Lachin, J; Inzucchi, S. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med (Letter). 2016, 374(11): 1094.
- Cefalo, C; Cinti, F; Moffa, S; Impronta, F; Sorice, G; Mezza, T; Pontecorvi, A; Giaccari, A. Sotagliflozin, the first dual SGLT inhibitor: current outlook and perspectives. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019, 18(1):20. [CrossRef]
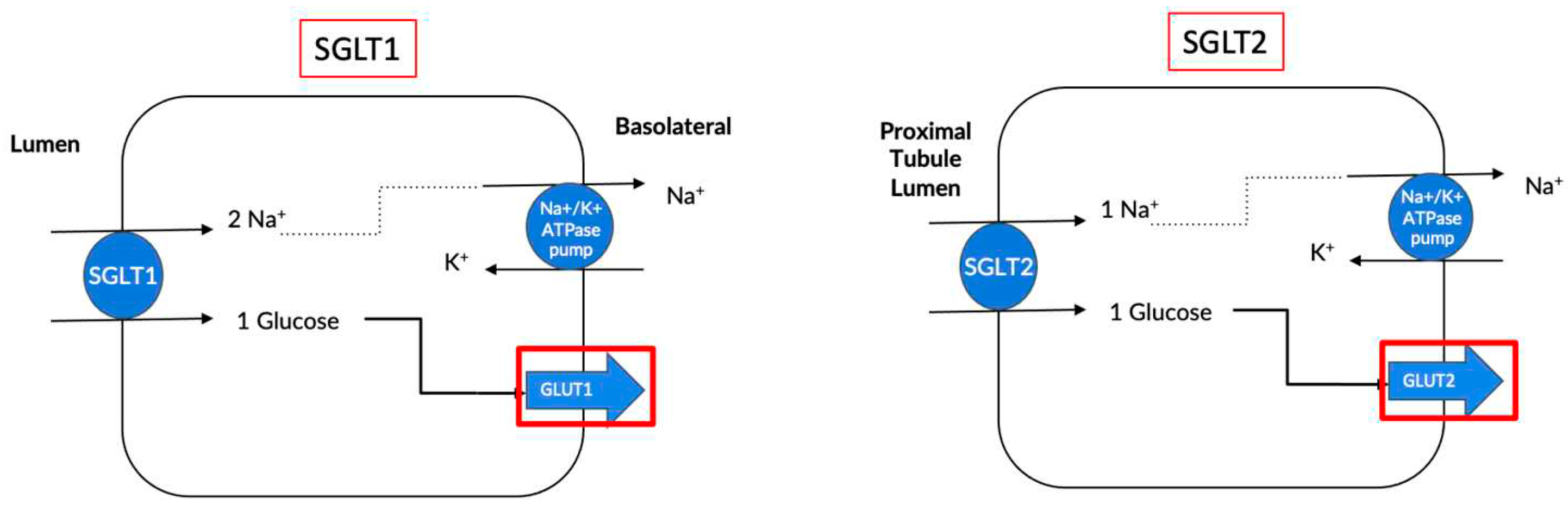
| Location | SGLT1 | SGLT2 |
|---|---|---|
| Small Intestine | Apical membrane, K and L cells (26). | Not expressed. |
| Eye | Retina (27). | Retina, cornea and lens (27). |
| Kidney | Section 3 of the proximal tubule. (15). | Section 1 and 2 of the proximal tubules (16). |
| Pancreas | Pancreatic alpha cells (25). | Not expressed. |
| Liver | Biliary duct cells (26). | Not expressed. |
| Heart | Capillaries (26). | Not expressed. |
| Study Parameters | Key Findings |
|---|---|
|
Pharmacokinetic properties |
Longest plasma half-life: canagliflozin. |
| Longest half-life in the kidney: dapagliflozin. | |
| Highest distribution in the kidney: ipragliflozin. | |
| Drug distribution in the kidney suggested to be dependent on chemical structure. | |
|
Pharmacodynamic properties |
All SGLT2i’s increased urinary glucose excretion in dose-dependent manner. |
| Long-acting SGLT2i exhibited persistent action even after 18h post-dose. | |
| Close correlation between the duration of action, plasma drug concentration, drug distribution and kidney retention. | |
|
Pharmacologic properties |
Significant reductions in blood glucose and plasma insulin with all SGLT2i. |
| Significant improvement in glucose tolerance with all SGLT2i. | |
| Long-acting SGLT2i’s exert stronger anti-hyperglycaemic effects through persistent urine glucose excretion. | |
| Intermediate-acting SGLT2i may provide better glycaemic control when administered twice daily. | |
|
Anti-diabetic effects |
All SGLT2i significantly improved hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinemia. |
| All SGLT2i significantly increased pancreatic insulin content by prevention of pancreatic exhaustion. | |
| Long-acting SGLT2i exert favourable glycaemic control over 24 hours and may have slightly enhanced anti-diabetic effects as compared to intermediate-acting SGLT2i. | |
|
Effects on diabetic complications |
All SGLT2i’s exhibited significant improvements/trends in obesity parameters (e.g. body and visceral fat weights, lipid metabolism markers), pro-inflammatory cytokines and endothelial dysfunction markers. |
| All SGLT2i’s significantly decreased or showed a decreasing trend in steatohepatitis parameters (e.g. liver weight, plasma levels of liver enzymes) and renal parameters (e.g. creatinine clearance, renal tubular injury markers). | |
| Long-acting SGLT2i (0.3 mg/kg) demonstrated slight superiority in comparison to intermediate-acting SGLT2i (3mg/kg) on several parameters (e.g. daily blood glucose control, visceral fat weight). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





