Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
18 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Tumor hypoxia and radioresistance
3. CIRT for hypoxic tumors: evidence of effectiveness
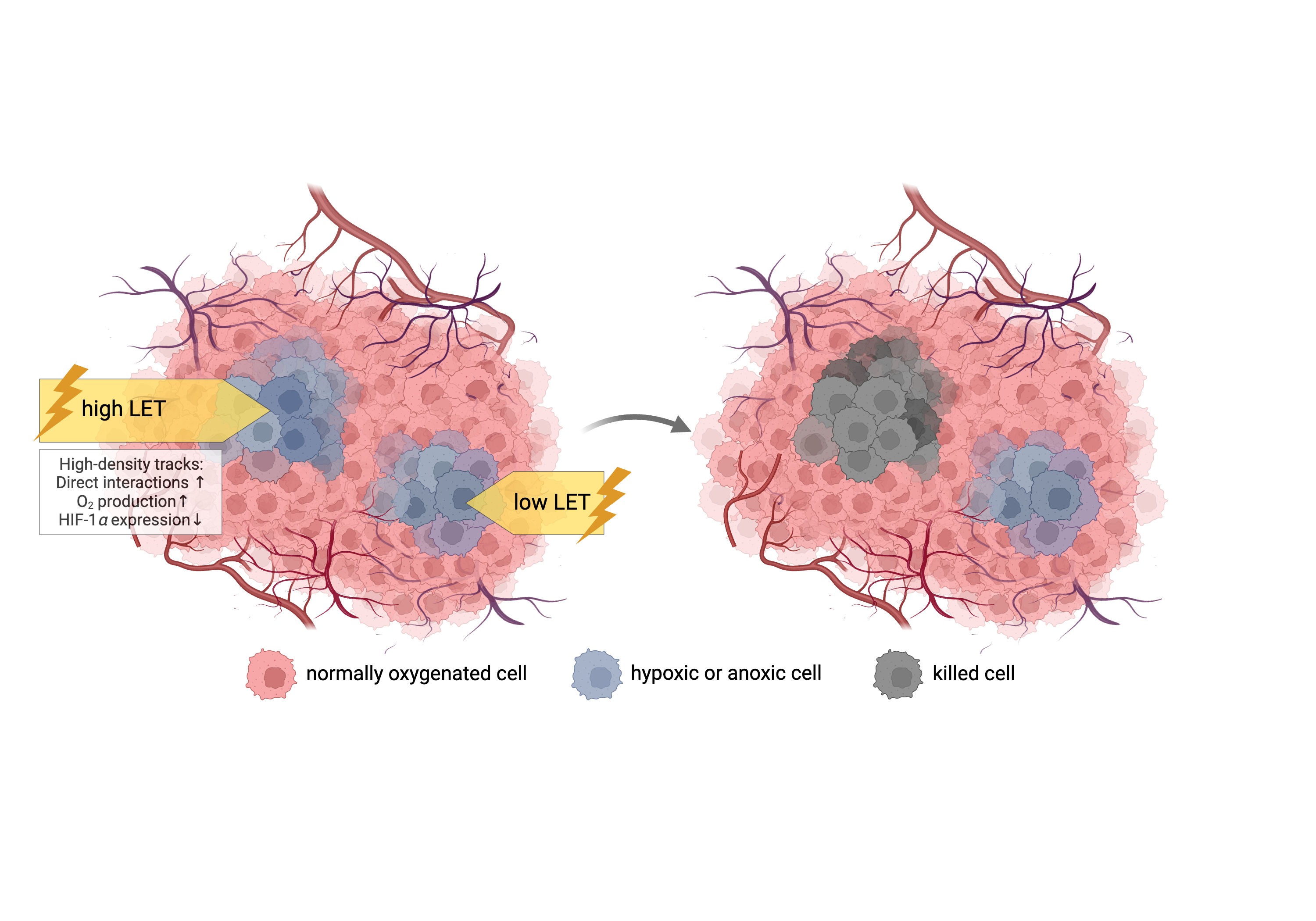
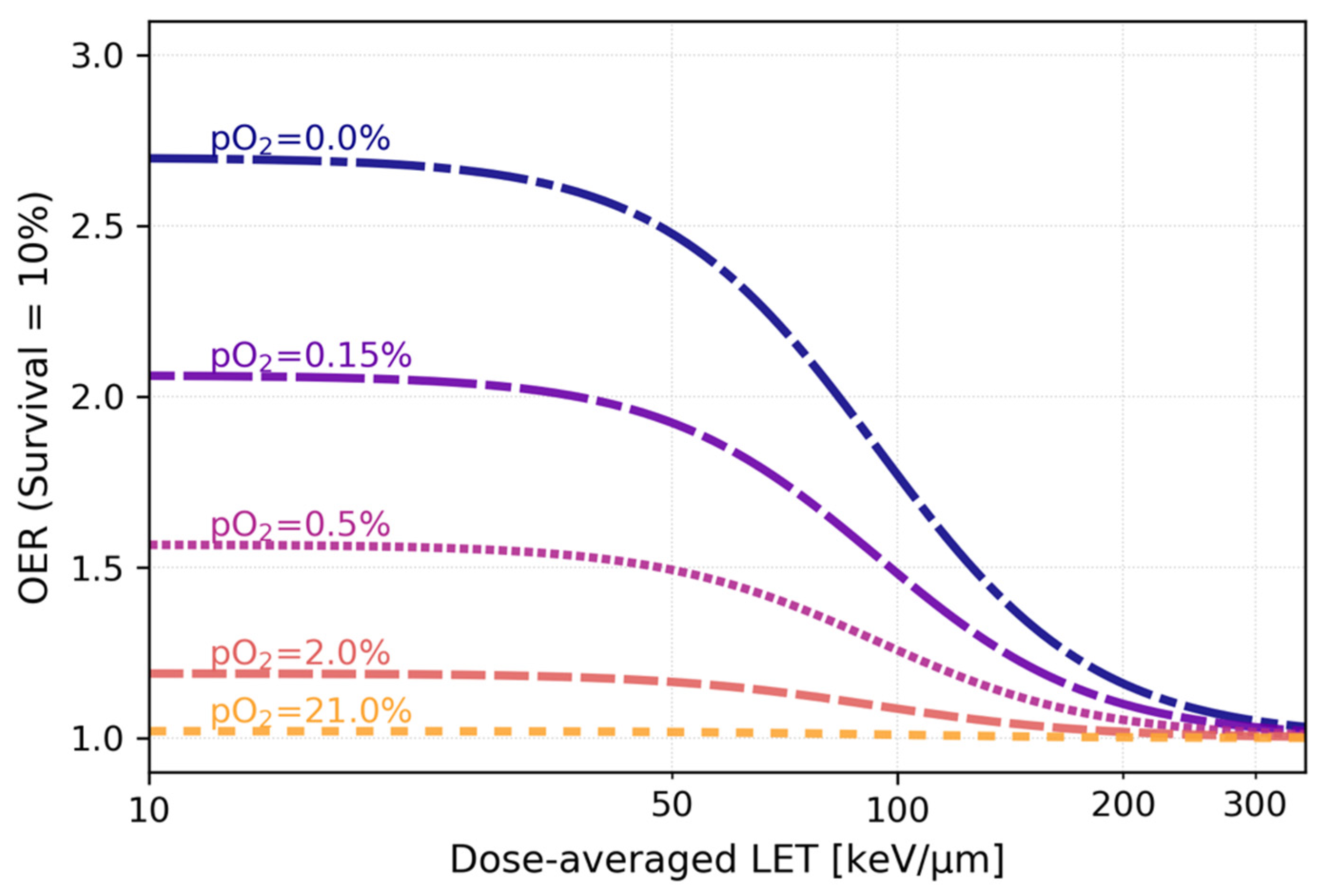
3.1. Decrease of OER with increasing particle LET: mechanisms and in vitro data
3.3. Benefits of CIRT for hypoxic tumors: clinical evidence
3.3.1. Pancreatic cancer
3.3.2. Cervical cancer
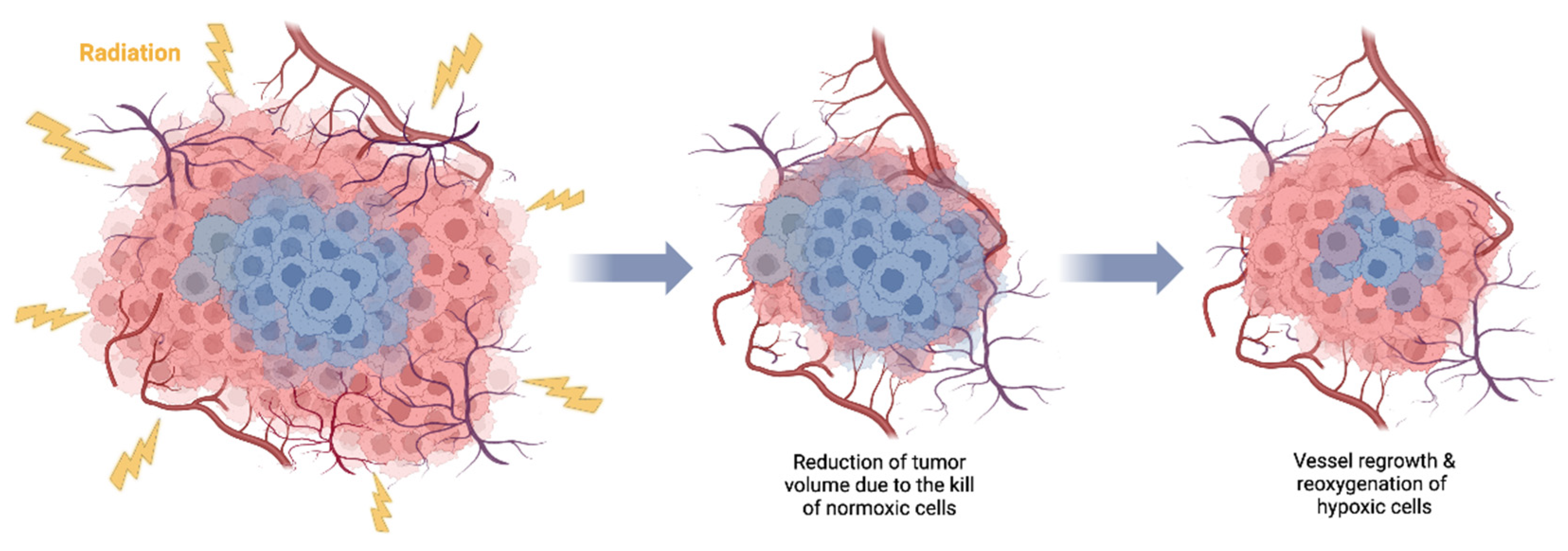
4. Tumor reoxygenation and local oxygenation changes
5. Is carbon LET high enough?
6. Strategies to maximize the carbon ion LET and their limitations
6.1. Simultaneous integrated boost
6.2. Arc therapy
6.3. LET painting
6.4. Multi-ions
6.5. Carbon PATHY
6.6. Challenges of LET optimization
7. Comparison to pharmaceutical approaches
8. Conclusions and future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Particle Therapy Co-Operative Group Particle Therapy Facilities in Clinical Operation. Accessed August 10, 2023. Https://Www.Ptcog.Site/Index.Php/Facilities-in-Operation-Public.
- Castro, J.R. Results of Heavy Ion Radiotherapy. Radiat Environ Biophys 1995, 34, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompos, A.; Foote, R.L.; Koong, A.C.; Le, Q.T.; Mohan, R.; Paganetti, H.; Choy, H. National Effort to Re-Establish Heavy Ion Cancer Therapy in the United States. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Paganetti, H. Nuclear Physics in Particle Therapy : A Review. Reports on Progress in Physics 2016, 79, 96702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schardt, D.; Elsässer, T.; Schulz-ertner, D. Heavy-Ion Tumor Therapy : Physical and Radiobiological Benefits. Review of Modern Physics 2010, 82, 383–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinganelli, W.; Durante, M. Carbon Ion Radiobiology. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, C.; Volz, L.; Durante, M. Emerging Technologies for Cancer Therapy Using Accelerated Particles. Prog Part Nucl Phys 2023, 131, 104046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaue, D.; McBride, W.H. Opportunities and Challenges of Radiotherapy for Treating Cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2015, 12, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, O.; Makishima, H.; Kamada, T. Evolution of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy at the National Institute of Radiological Sciences in Japan. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Flanz, J. Charged Particle Beams to Cure Cancer: Strengths and Challenges. Semin Oncol 2019, 46, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Debus, J.; Loeffler, J.S. Physics and Biomedical Challenges of Cancer Therapy with Accelerated Heavy Ions. Nature Reviews Physics 2021, 3, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, C.A. Failla Memorial Lecture. The Future of Heavy-Ion Science in Biology and Medicine. Radiat Res 1985, 103, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckeown, S.R. Defining Normoxia, Physoxia and Hypoxia in Tumours — Implications for Treatment Response. British Journal of Radiology 2014, 87, 20130676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds That Do Not Heal. New England Journal of Medicine 1986, 315, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Benjamin, L.E. Tumorigenesis and the Angiogenic Switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2003, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsman, M.R.; Vaupel, P. Pathophysiological Basis for the Formation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Oncol 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckel, M.; Vaupel, P. Tumor Hypoxia: Definitions and Current Clinical, Biologic, and Molecular Aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001, 93, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells: Biology and Clinical Significance. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, R.Y.; Haake, S.M. Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Cancer Lett 2020, 487, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. A Conduit to Metastasis: Circulating Tumor Cell Biology. Genes Dev 2017, 31, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Qian, C.; Liu, Z.; Luo, D. Factors Involved in Cancer Metastasis: A Better Understanding to “Seed and Soil” Hypothesis. Mol Cancer 2017, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P. Activation of the HIF Pathway in Cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2001, 11, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhry, H.; Harris, A.L. Advances in Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Biology. Cell Metab 2018, 27, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Defining the Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Oncogene 2010, 29, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Pharmacologic Targeting of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2019, 59, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomlinson, R.H.; Gray, L.H. The Histological Structure of Some Human Lung Cancers and the Possible Implications for Radiotherapy. Br J Cancer 1955, 9, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Braun, R.D.; Ong, E.T.; Hsu, R.; Secomb, T.W.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Hong, K.; Dewhirst, M.W. Fluctuations in Red Cell Flux in Tumor Microvessels Can Lead to Transient Hypoxia and Reoxygenation in Tumor Parenchyma. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 5522–5528. [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst, M.W.; Cao, Y.; Moeller, B. Cycling Hypoxia and Free Radicals Regulate Angiogenesis and Radiotherapy Response. Nat Rev Cancer 2008, 8, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, C.; Tellier, C.; Feron, O. Cycling Hypoxia: A Key Feature of the Tumor Microenvironment. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 2016, 1866, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena; Jolly Acute vs. Chronic vs. Cyclic Hypoxia: Their Differential Dynamics, Molecular Mechanisms, and Effects on Tumor Progression. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, M.; de Jong, M.C.; Verhagen, C.V.M.; de Roest, R.H.; Sanduleanu, S.; Hoebers, F.; Leemans, C.R.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Vens, C.; Verheij, M.; et al. Acute Hypoxia Profile Is a Stronger Prognostic Factor than Chronic Hypoxia in Advanced Stage Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.H.; Conger, A.D.; Ebert, M.; Hornsey, S.; Scott, O.C.A. The Concentration of Oxygen Dissolved in Tissues at the Time of Irradiation as a Factor in Radiotherapy. Br J Radiol 1953, 26, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.J.; Giaccia, A.J. Radiobiology for the Radiologist; 7th ed.; Lippincottt Williams & Wilkins, 2012;
- Robert Grimes, D.; Partridge, M. A Mechanistic Investigation of the Oxygen Fixation Hypothesis and Oxygen Enhancement Ratio. Biomed Phys Eng Express 2015, 1, 045209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsman, M.; Wouters, B.; Joiner, M.; Overgaard, J. The Oxygen Effect and Fractionated Radiotherapy. In Basic Clinical Radiobiology Fourth Edition; CRC Press, 2009; pp. 207–216.
- Wouters, B.G.; Brown, J.M. Cells at Intermediate Oxygen Levels Can Be More Important Than the “Hypoxic Fraction” in Determining Tumor Response to Fractionated Radiotherapy. Radiat Res 1997, 147, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, R.; Ito, A.; Tomita, M.; Tsukada, T.; Yatagai, F.; Noguchi, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kase, Y.; Ando, K.; Okayasu, R.; et al. Contributions of Direct and Indirect Actions in Cell Killing by High-LET Radiations. Radiat Res 2009, 171, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, T.; Bryant, P.E. Reduction in Oxygen Enhancement Ratio with Increase in LET: Tests of Two Hypotheses. Int J Radiat Biol 1974, 26, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVerne, J.A. Track Effects of Heavy Ions in Liquid Water. Radiat Res 2000, 153, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesungnoen, J.; Jay-Gerin, J.-P. High-LET Ion Radiolysis of Water: Oxygen Production in Tracks. Radiat Res 2009, 171, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qutub, A.A.; Popel, A.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α Differentially in Cancer and Ischemia. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 5106–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movafagh, S.; Crook, S.; Vo, K. Regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1a by Reactive Oxygen Species : New Developments in an Old Debate. J Cell Biochem 2015, 116, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozny, A.-S.; Lauret, A.; Battiston-Montagne, P.; Guy, J.-B.; Beuve, M.; Cunha, M.; Saintigny, Y.; Blond, E.; Magne, N.; Lalle, P.; et al. Differential Pattern of HIF-1α Expression in HNSCC Cancer Stem Cells after Carbon Ion or Photon Irradiation: One Molecular Explanation of the Oxygen Effect. Br J Cancer 2017, 116, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valable, S.; Gérault, A.N.; Lambert, G.; Leblond, M.M.; Anfray, C.; Toutain, J.; Bordji, K.; Petit, E.; Bernaudin, M.; Pérès, E.A. Impact of Hypoxia on Carbon Ion Therapy in Glioblastoma Cells: Modulation by LET and Hypoxia-Dependent Genes. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.-Y.; Tinganelli, W.; Maier, A.; Durante, M.; Kraft-Weyrather, W. Influence of Chronic Hypoxia and Radiation Quality on Cell Survival. J Radiat Res 2013, 54, i13–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinganelli, W.; Ma, N.-Y.; Von Neubeck, C.; Maier, A.; Schicker, C.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Durante, M. Influence of Acute Hypoxia and Radiation Quality on Cell Survival. J Radiat Res 2013, 54, i23–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, E.A.; Ngo, F.Q.H.; Curtis, S.B.; Tobias, C.A. Heavy-Ion Radiobiology: Cellular Studies. Adv Radiat Biol 1984, 11, 295–389. [Google Scholar]
- Furusawa, Y.; Fukutsu, K.; Aoki, M.; Itsukaichi, H.; Eguchi-Kasai, K.; Ohara, H.; Yatagai, F.; Kanai, T.; Ando, K. Inactivation of Aerobic and Hypoxic Cells from Three Different Cell Lines by Accelerated (3)He-, (12)C- and (20)Ne-Ion Beams. Radiat Res 2000, 154, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzl, T.; Wilkens, J.J. Modelling of the Oxygen Enhancement Ratio for Ion Beam Radiation Therapy. Phys Med Biol 2011, 56, 3251–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinganelli, W.; Durante, M.; Hirayama, R.; Krämer, M.; Maier, A.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Furusawa, Y.; Friedrich, T.; Scifoni, E. Kill-Painting of Hypoxic Tumours in Charged Particle Therapy. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scifoni, E.; Tinganelli, W.; Weyrather, W.K.; Durante, M.; Maier, A.; Krämer, M. Including Oxygen Enhancement Ratio in Ion Beam Treatment Planning: Model Implementation and Experimental Verification. Phys Med Biol 2013, 58, 3871–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonovic, L.; Lindblom, E.; Dasu, A.; Bassler, N.; Furusawa, Y.; Toma-Dasu, I. Clinical Oxygen Enhancement Ratio of Tumors in Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: The Influence of Local Oxygenation Changes. J Radiat Res 2014, 55, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strigari, L.; Torriani, F.; Manganaro, L.; Inaniwa, T.; Dalmasso, F.; Cirio, R.; Attili, A. Tumour Control in Ion Beam Radiotherapy with Different Ions in the Presence of Hypoxia: An Oxygen Enhancement Ratio Model Based on the Microdosimetric Kinetic Model. Phys Med Biol 2018, 63, 065012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mein, S.; Tessonnier, T.; Kopp, B.; Harrabi, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Debus, J.; Haberer, T.; Mairani, A. Spot-Scanning Hadron Arc (SHArc) Therapy: A Study With Light and Heavy Ions. Adv Radiat Oncol 2021, 6, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaniwa, T.; Kanematsu, N. Event-by-Event Approach to the Oxygen-Effect-Incorporated Stochastic Microdosimetric Kinetic Model for Hypofractionated Multi-Ion Therapy. J Radiat Res 2023, 64, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenforde, T.S.; Curtis, S.B.; Crabtree, K.E.; Tenforde, S.D.; Schilling, W.A.; Howard, J.; Lyman, J.T. In Vivo Cell Survival and Volume Response Characteristics of Rat Rhabdomyosarcoma Tumors Irradiated in the Extended Peak Region of Carbon- and Neon-Ion Beams. Radiat Res 1980, 83, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, T.S.; Afzal, S.M.J.; Parr, S.S.; Howard, J.; Lyman, J.T.; Curtis, S.B. Cell Survival in Rat Rhabdomyosarcoma Tumors Irradiated in Vivo with Extended-Peak Silicon Ions. Radiat Res 1982, 92, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subtil, F.S.B.; Wilhelm, J.; Bill, V.; Westholt, N.; Rudolph, S.; Fischer, J.; Scheel, S.; Seay, U.; Fournier, C.; Taucher-Scholz, G.; et al. Carbon Ion Radiotherapy of Human Lung Cancer Attenuates HIF-1 Signaling and Acts with Considerably Enhanced Therapeutic Efficiency. The FASEB Journal 2014, 28, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, R.; Uzawa, A.; Takase, N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Koda, K.; Ozaki, M.; Yamashita, K.; Li, H.; Kase, Y.; et al. Evaluation of SCCVII Tumor Cell Survival in Clamped and Non-Clamped Solid Tumors Exposed to Carbon-Ion Beams in Comparison to X-Rays. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2013, 756, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, R.; Uzawa, A.; Obara, M.; Takase, N.; Koda, K.; Ozaki, M.; Noguchi, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Li, H.; Yamashita, K.; et al. Determination of the Relative Biological Effectiveness and Oxygen Enhancement Ratio for Micronuclei Formation Using High-LET Radiation in Solid Tumor Cells: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2015, 793, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowa, C.; Karger, C.P.; Brons, S.; Zhao, D.; Mason, R.P.; Huber, P.E.; Debus, J.; Peschke, P. Carbon Ion Radiotherapy Decreases the Impact of Tumor Heterogeneity on Radiation Response in Experimental Prostate Tumors. Cancer Lett 2016, 378, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowa, C.; Peschke, P.; Brons, S.; Neels, O.C.; Kopka, K.; Debus, J.; Karger, C.P. Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: Impact of Tumor Differentiation on Local Control in Experimental Prostate Carcinomas. Radiation Oncology 2017, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowa, C.; Peschke, P.; Brons, S.; Debus, J.; Karger, C.P. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Tumor Characteristics Are of Minor Relevance for the Efficacy of Split-Dose Carbon Ion Irradiation in Three Experimental Prostate Tumors. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2019, 133, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Sun, P.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. The Impacts of Different Types of Radiation on the CRT and PDL1 Expression in Tumor Cells Under Normoxia and Hypoxia. Front Oncol 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Zheng, L. The Tumour Microenvironment in Pancreatic Cancer — Clinical Challenges and Opportunities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2020, 17, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koong, A.C.; Mehta, V.K.; Le, Q.T.; Fisher, G.A.; Terris, D.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bastidas, A.J.; Vierra, M. Pancreatic Tumors Show High Levels of Hypoxia. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2000, 48, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkan, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Kleeff, J. The Role of Hypoxia in Pancreatic Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Target? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 10, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wu, X.-L.; Zhou, C.-H.; Yan, J.-Y.; Hu, B.-Y.; et al. The Molecular Biology of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Translational Challenges and Clinical Perspectives. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, D.; Tingstedt, B.; Andersson, B.; Holmquist, F.; Sturesson, C.; Williamsson, C.; Sasor, A.; Borg, D.; Bauden, M.; Andersson, R. Pancreatic Cancer: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. Future Oncology 2016, 12, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liermann, J.; Shinoto, M.; Syed, M.; Debus, J.; Herfarth, K.; Naumann, P. Carbon Ion Radiotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Clinical Data. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2020, 147, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoto, M.; Yamada, S.; Yasuda, S.; Imada, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Honda, H.; Kamada, T.; Tsujii, H.; Saisho, H. Phase 1 Trial of Preoperative, Short-Course Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy for Patients with Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer 2013, 119, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoto, M.; Yamada, S.; Terashima, K.; Yasuda, S.; Shioyama, Y.; Honda, H.; Kamada, T.; Tsujii, H.; Saisho, H.; Asano, T.; et al. Carbon Ion Radiation Therapy With Concurrent Gemcitabine for Patients With Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2016, 95, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Shiba, S.; Okazaki, S.; Miyasaka, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Kiyohara, H.; Ohno, T. Feasibility and Safety of Repeated Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Yamada, S.; Isozaki, Y.; Takiyama, H.; Shinoto, M.; Kawashiro, S.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Nemoto, K.; Tsuji, H. Efficacy and Feasibility of Re-Irradiation Using Carbon Ions for Pancreatic Cancer That Recurs after Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2021, 26, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Tommasino, F.; Yamada, S. Modeling Combined Chemotherapy and Particle Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Front Oncol 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, V.; Cobianchi, L.; Brugnatelli, S.; Barcellini, A.; Peloso, A.; Facoetti, A.; Vanoli, A.; Delfanti, S.; Preda, L.; Molinelli, S.; et al. Preoperative Chemotherapy and Carbon Ions Therapy for Treatment of Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Prospective, Phase II, Multicentre, Single-Arm Study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann, J.; Naumann, P.; Hommertgen, A.; Pohl, M.; Kieser, M.; Debus, J.; Herfarth, K. Carbon Ion Radiotherapy as Definitive Treatment in Non-Metastasized Pancreatic Cancer: Study Protocol of the Prospective Phase II PACK-Study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckel, M.; Schlenger, K.; Höckel, S.; Aral, B.; Schäffer, U.; Vaupel, P. Tumor Hypoxia in Pelvic Recurrences of Cervical Cancer. Int J Cancer 1998, 79, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nakano, T.; Ohno, T.; Kato, S.; Niibe, Y.; Morita, S.; Tsujii, H. Oxygenated and Reoxygenated Tumors Show Better Local Control in Radiation Therapy for Cervical Cancer. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer 2006, 16, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ohno, T.; Kato, S.; Suzuki, M.; Morita, S.; Sato, S.; Oka, K.; Tsujii, H. Carbon Beam Therapy Overcomes the Radiation Resistance of Uterine Cervical Cancer Originating from Hypoxia. Clinical Cancer Research 2006, 12, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, N.; Wakatsuki, M.; Kato, S.; Shiba, S.; Kobayashi, D.; Kiyohara, H.; Karasawa, K.; Ohno, T.; Nakano, T.; Kamada, T.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix. Anticancer Res 2018, 38, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, D.; Okonogi, N.; Wakatsuki, M.; Kato, S.; Ohno, T.; Karasawa, K.; Kiyohara, H.; Kobayashi, D.; Tsuji, H.; Nakano, T.; et al. Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy for Inoperable Endometrial Carcinoma. J Radiat Res 2018, 59, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, H.R. The Four R’s of Radiotherapy. In Advances in Radiation Biology; Academic Press: New York, 1975; pp. 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Stieb, S.; Eleftheriou, A.; Warnock, G.; Guckenberger, M.; Riesterer, O. Longitudinal PET Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia during the Course of Radiotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2018, 45, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zips, D.; Zöphel, K.; Abolmaali, N.; Perrin, R.; Abramyuk, A.; Haase, R.; Appold, S.; Steinbach, J.; Kotzerke, J.; Baumann, M. Exploratory Prospective Trial of Hypoxia-Specific PET Imaging during Radiochemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Head-and-Neck Cancer. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2012, 105, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedenmann, N.E.; Bucher, S.; Hentschel, M.; Mix, M.; Vach, W.; Bittner, M.-I.; Nestle, U.; Pfeiffer, J.; Weber, W.A.; Grosu, A.L. Serial [18F]-Fluoromisonidazole PET during Radiochemotherapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer and Its Correlation with Outcome. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2015, 117, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löck, S.; Perrin, R.; Seidlitz, A.; Bandurska-Luque, A.; Zschaeck, S.; Zöphel, K.; Krause, M.; Steinbach, J.; Kotzerke, J.; Zips, D.; et al. Residual Tumour Hypoxia in Head-and-Neck Cancer Patients Undergoing Primary Radiochemotherapy, Final Results of a Prospective Trial on Repeat FMISO-PET Imaging. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2017, 124, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanduleanu, S.; Hamming-Vrieze, O.; Wesseling, F.W.R.; Even, A.J.G.; Hoebers, F.J.; Hoeben, A.; Vogel, W. V.; Tesselaar, M.E.T.; Parvin, D.; Bartelink, H.; et al. [18F]-HX4 PET/CT Hypoxia in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Treated with Chemoradiotherapy: Prognostic Results from Two Prospective Trials. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2020, 23, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, N.; Sasai, K.; Shibata, T.; Takagi, T.; Shibuya, K.; Koike, S.; Nojima, K.; Furusawa, Y.; Ando, K.; Hiraoka, M. Time Course of Reoxygenation in Experimental Murine Tumors after Carbon-Beam and X-Ray Irradiation. J Radiat Res 2001, 42, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukawa, T.; Takematsu, K.; Oka, K.; Koike, S.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Tanishita, K. Differences in PO2 Peaks of a Murine Fibrosarcoma between Carbon-Ion and X-Ray Irradiation. J Radiat Res 2004, 45, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K. Accelerated Reoxygenation of a Murine Fibrosarcoma after Carbon-Ion Radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 1999, 75, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendinger, A.L.; Seyler, L.; Saager, M.; Debus, C.; Peschke, P.; Komljenovic, D.; Debus, J.; Peter, J.; Floca, R.O.; Karger, C.P.; et al. Impact of Single Dose Photons and Carbon Ions on Perfusion and Vascular Permeability: A Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Pilot Study in the Anaplastic Rat Prostate Tumor R3327-AT1. Radiat Res 2019, 193, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, N.; Jäkel, O.; Søndergaard, C.S.; Petersen, J.B. Dose- and LET-Painting with Particle Therapy. Acta Oncol 2010, 49, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
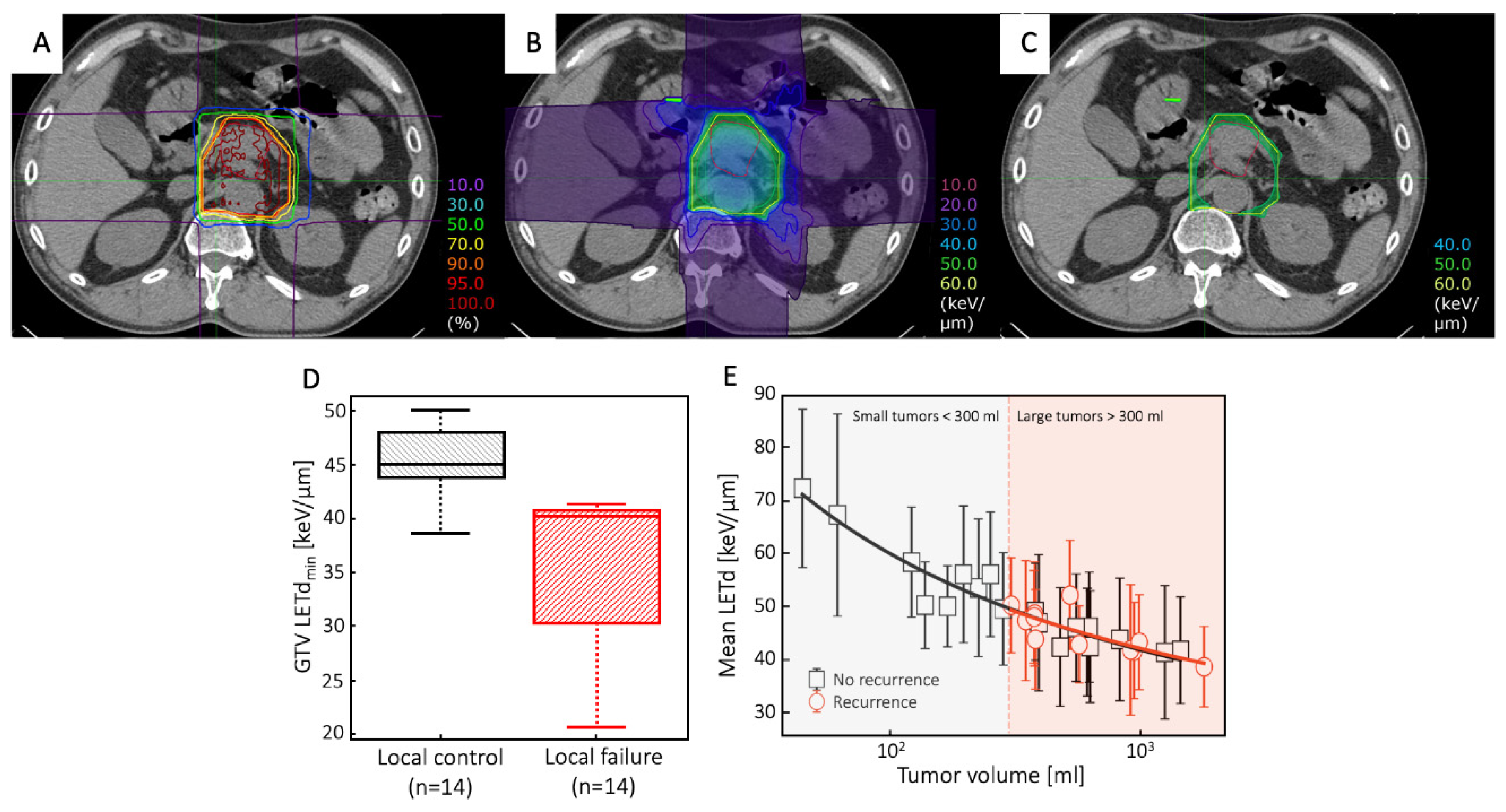
- Hagiwara, Y.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Matsufuji, N.; Isozaki, Y.; Takiyama, H.; Nemoto, K.; Tsuji, H.; Yamada, S. Influence of Dose-Averaged Linear Energy Transfer on Tumour Control after Carbon-Ion Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2020, 21, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Lee, S.H.; Imai, R.; Inaniwa, T.; Matsufuji, N.; Fukahori, M.; Kohno, R.; Yonai, S.; Okonogi, N.; Yamada, S.; et al. Unresectable Chondrosarcomas Treated With Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: Relationship Between Dose-Averaged Linear Energy Transfer and Local Recurrence. Anticancer Res 2020, 40, 6429–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, S.; Magro, G.; Mairani, A.; Allajbej, A.; Mirandola, A.; Chalaszczyk, A.; Imparato, S.; Ciocca, M.; Fiore, M.R.; Orlandi, E. How LEM-Based RBE and Dose-Averaged LET Affected Clinical Outcomes of Sacral Chordoma Patients Treated with Carbon Ion Radiotherapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2021, 163, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, L.; Parrella, G.; Molinelli, S.; Magro, G.; Annunziata, S.; Mairani, A.; Chalaszczyk, A.; Fiore, M.R.; Ciocca, M.; Paganelli, C.; et al. A Dosiomics Analysis Based on Linear Energy Transfer and Biological Dose Maps to Predict Local Recurrence in Sacral Chordomas after Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonogi, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Fukahori, M.; Furuichi, W.; Inaniwa, T.; Matsufuji, N.; Imai, R.; Yamada, S.; Kanematsu, N.; Tsuji, H. Dose-Averaged Linear Energy Transfer per Se Does Not Correlate with Late Rectal Complications in Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2020, 153, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
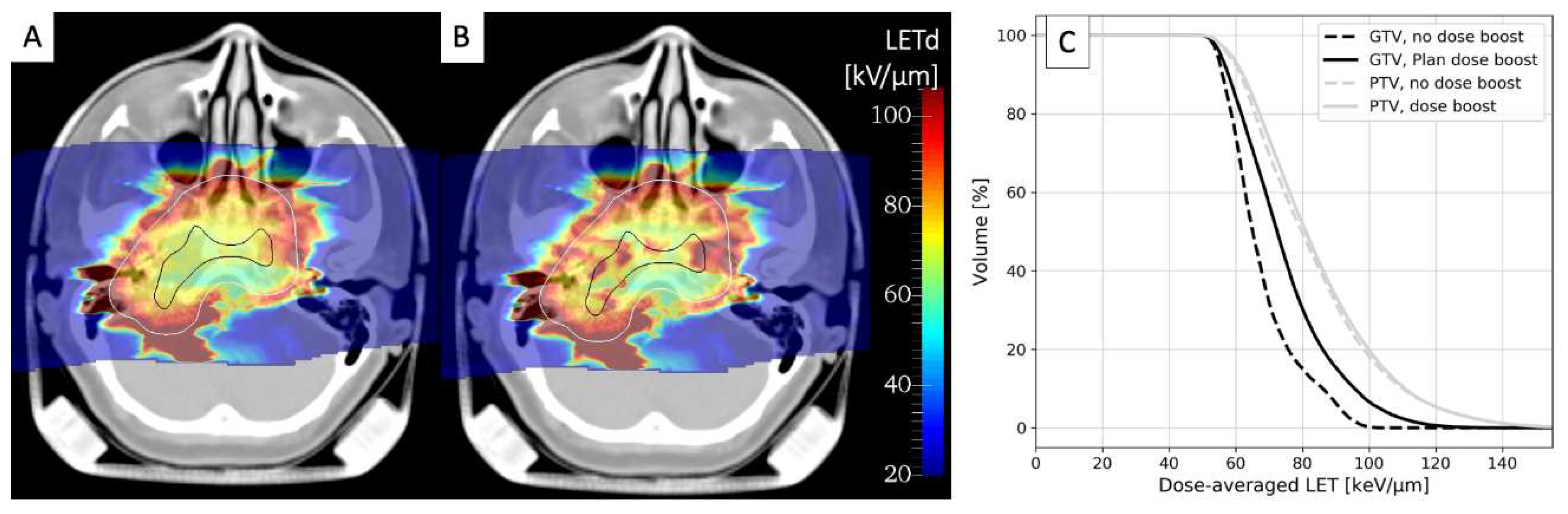
- Mastella, E.; Molinelli, S.; Magro, G.; Russo, S.; Bonora, M.; Ronchi, S.; Ingargiola, R.; Jensen, A.D.; Ciocca, M.; Vischioni, B.; et al. In Silico Feasibility Study of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy With Simultaneous Integrated Boost for Head and Neck Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simultaneous Integrated Boost in Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (SIBACIRT). ClinicalTrials.Gov Identifier: NCT05733910. Updated May 25, 2023. Accessed August 9, 2023. Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Study/NCT05733910.
- Hu, W.; Li, P.; Hong, Z.; Guo, X.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Functional Imaging-Guided Carbon Ion Irradiation with Simultaneous Integrated Boost for Localized Prostate Cancer: Study Protocol for a Phase II Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Trials 2022, 23, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Functional Image-Guided Carbon Ion Irradiation With Simultaneous Integrated Boost for Prostate Cancer. ClinicalTrials.Gov Identifier: NCT05010343. Updated November 15, 2021. Accessed August 9, 2023. Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Study/NCT05010343.
- Ablative Carbon Ion Radiotherapy With Pencil Beam Scanning for Locally Advanced Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. ClinicalTrials.Gov Identifier: NCT05424159. Updated June 24, 2022. Accessed August 9, 2023. Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Study/NCT05424159.
- Gemmel, A.; Hasch, B.; Ellerbrock, M.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Krämer, M. Biological Dose Optimization with Multiple Ion Fields. Phys Med Biol 2008, 53, 6691–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, X.; Zheng, W.; Liu, G.; Janssens, G.; Souris, K.; Barragán-Montero, A.M.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P. Linear Energy Transfer Incorporated Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy Optimization: A Feasibility Study. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mein, S.; Tessonnier, T.; Kopp, B.; Schömers, C.; Harrabi, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Debus, J.; Haberer, T.; Mairani, A. Biological Dose Optimization for Particle Arc Therapy Using Helium and Carbon Ions. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2022, 114, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, L.; Sheng, Y.; Durante, M.; Graeff, C. Considerations for Upright Particle Therapy Patient Positioning and Associated Image Guidance. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, S.; Hardcastle, N.; Korte, J.; Kron, T.; Everitt, S.; Rahim, S.; Hegi-Johnson, F.; Franich, R. Please Place Your Seat in the Full Upright Position: A Technical Framework for Landing Upright Radiation Therapy in the 21st Century. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachankar, A.; Schafasand, M.; Hug, E.; Carlino, A.; Stock, M.; Góra, J.; Fossati, P. Retrospective Evaluation of LET Distribution in Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy for Pelvic Sarcomas and LET Optimization by Blocking Method: The MedAustron Approach. In Proceedings of the Proceedings to the 61th Annual Conference of the Particle Therapy Cooperative Group; 2023.
- Bassler, N.; Toftegaard, J.; Lühr, A.; Sørensen, B.S.; Scifoni, E.; Krämer, M.; Jäkel, O.; Mortensen, L.S.; Overgaard, J.; Petersen, J.B. LET-Painting Increases Tumour Control Probability in Hypoxic Tumours. Acta Oncol (Madr) 2014, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinen, E.; Søvik, Å. Dose or ‘LET’ Painting – What Is Optimal in Particle Therapy of Hypoxic Tumors? Acta Oncol (Madr) 2015, 54, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, R.; Koto, M.; Ikawa, H.; Lee, S.H.; Sato, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Inaniwa, T.; Shirai, T. High-LET Irradiation in Clinical Carbon-Ion Beam with the LET Painting Technique for Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Adv Radiat Oncol 2023, 101317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, O.; Scifoni, E.; Tinganelli, W.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Wiedemann, J.; Maier, A.; Boscolo, D.; Friedrich, T.; Brons, S.; Durante, M.; et al. Oxygen Beams for Therapy: Advanced Biological Treatment Planning and Experimental Verification. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaniwa, T.; Kanematsu, N.; Noda, K.; Kamada, T. Treatment Planning of Intensity Modulated Composite Particle Therapy with Dose and Linear Energy Transfer Optimization. Phys Med Biol 2017, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaniwa, T.; Kanematsu, N.; Shinoto, M.; Koto, M.; Yamada, S. Adaptation of Stochastic Microdosimetric Kinetic Model to Hypoxia for Hypo-Fractionated Multi-Ion Therapy Treatment Planning. Phys Med Biol 2021, 66, 205007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, O.; Krämer, M.; Hild, S.; Durante, M.; Scifoni, E. Kill Painting of Hypoxic Tumors with Multiple Ion Beams. Phys Med Biol 2019, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubin, S.; Popper, H.H.; Brcic, L. Novel Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)-Based Partial Tumor Irradiation Targeting Hypoxic Segment of Bulky Tumors (SBRT-PATHY): Improvement of the Radiotherapy Outcome by Exploiting the Bystander and Abscopal Effects. Radiation Oncology 2019, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubin, S.; Gupta, S.; Grusch, M.; Popper, H.H.; Brcic, L.; Ashdown, M.L.; Khleif, S.N.; Peter-Vörösmarty, B.; Hyden, M.; Negrini, S.; et al. Shifting the Immune-Suppressive to Predominant Immune-Stimulatory Radiation Effects by SBRT-PArtial Tumor Irradiation Targeting HYpoxic Segment (SBRT-PATHY). Cancers (Basel) 2020, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Brenner, D.J.; Formenti, S.C. Does Heavy Ion Therapy Work Through the Immune System? International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2016, 96, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubin, S.; Fossati, P.; Carlino, A.; Martino, G.; Gora, J.; Stock, M.; Hug, E. Novel Carbon Ion and Proton Partial Irradiation of Recurrent Unresectable Bulky Tumors (Particle-PATHY): Early Indication of Effectiveness and Safety. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubin, S.; Vozenin, M.C.; Prezado, Y.; Durante, M.; Prise, K.M.; Lara, P.C.; Greco, C.; Massaccesi, M.; Guha, C.; Wu, X.; et al. Novel Unconventional Radiotherapy Techniques: Current Status and Future Perspectives – Report from the 2nd International Radiation Oncology Online Seminar. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2023, 40, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Rao Allu, S.; Jiang, S.; Jia, M.; Gunn, J.R.; Yao, C.; LaRochelle, E.P.; Shell, J.R.; Bruza, P.; Gladstone, D.J.; et al. Tissue PO2 Distributions in Xenograft Tumors Dynamically Imaged by Cherenkov-Excited Phosphorescence during Fractionated Radiation Therapy. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllylä, T.; Korhonen, V.; Karthikeyan, P.; Honka, U.; Lohela, J.; Inget, K.; Ferdinando, H.; Karhula, S.S.; Nikkinen, J. Cerebral Tissue Oxygenation Response to Brain Irradiation Measured during Clinical Radiotherapy. J Biomed Opt 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsman, M.R.; Mortensen, L.S.; Petersen, J.B.; Busk, M.; Overgaard, J. Imaging Hypoxia to Improve Radiotherapy Outcome. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2012, 9, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, M.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A.; Lesueur, P.; Collet, S.; Chérel, M.; Bourgeois, M.; Stefan, D.; Limkin, E.J.; Perrio, C.; Guillamo, J.-S.; et al. Hypoxia Imaging and Adaptive Radiotherapy: A State-of-the-Art Approach in the Management of Glioma. Front Med (Lausanne) 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busk, M.; Overgaard, J.; Horsman, M.R. Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia for Radiotherapy: Current Status and Future Directions. Semin Nucl Med 2020, 50, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, F.; Toma-Dasu, I.; Lindblom, E.K. Perfusion-Limited Hypoxia Determines the Outcome of Radiation Therapy of Hypoxic Tumours. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XLIII. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Scholkmann, F., LaManna, J., Wolf, U., Eds.; Springer, 2022; Vol. 1395, pp. 249–254.
- Schiavo, F.; Kjellsson Lindblom, E.; Toma-Dasu, I. Towards the Virtual Tumor for Optimizing Radiotherapy Treatments of Hypoxic Tumors: A Novel Model of Heterogeneous Tissue Vasculature and Oxygenation. J Theor Biol 2022, 547, 111175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeroni, M.; Toma-Dasu, I.; Ureba, A.; Schiavo, F.; Wiedenmann, N.; Bunea, H.; Thomann, B.; Baltas, D.; Mix, M.; Stoykow, C.; et al. Quantification of Tumor Oxygenation Based on FMISO PET: Influence of Location and Oxygen Level of the Well-Oxygenated Reference Region. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XLI. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Ryu, P.D., LaManna, J., Harrison, D., Lee, S.S., Eds.; Springer, 2020; Vol. 1232, pp. 177–182.
- Overgaard, J. Hypoxic Radiosensitization: Adored and Ignored. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007, 25, 4066–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Horsman, M.R. Tumor Hypoxia: Impact on Radiation Therapy and Molecular Pathways. Front Oncol 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozny, A.-S.; Gauthier, A.; Alphonse, G.; Malésys, C.; Varoclier, V.; Beuve, M.; Brichart-Vernos, D.; Magné, N.; Vial, N.; Ardail, D.; et al. Involvement of HIF-1α in the Detection, Signaling, and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks after Photon and Carbon-Ion Irradiation. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Xia, C.; Cun, X.; Long, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, M.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Knockdown of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha by Tumor Targeted Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 System Suppressed the Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer. Journal of Controlled Release 2019, 304, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, K.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Targeted Co-Delivery of the Iron Chelator Deferoxamine and a HIF1α Inhibitor Impairs Pancreatic Tumor Growth. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2176–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhao, T.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Shu, H.; Zhu, L.; Fan, M. Heat Shock Protein 90 Is Involved in Regulation of Hypoxia-Driven Proliferation of Embryonic Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, N.; Martinez, C.-A.; Kerr, B.; Zaiter, S.S.; Morgan, M.; McAlpine, S.R.; Cook, K.M. C-Terminal HSP90 Inhibitors Block the HIF-1 Hypoxic Response by Degrading HIF-1α through the Oxygen-Dependent Degradation Pathway. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2019, 53, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Kamada, T. PU-H71, a Novel Hsp90 Inhibitor, as a Potential Cancer-Specific Sensitizer to Carbon-Ion Beam Therapy. J Radiat Res 2016, 57, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Li, H.K.; Masaoka, A.; Sunada, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Fujimori, A.; Nickoloff, J.A.; Okayasu, R. The Purine Scaffold Hsp90 Inhibitor PU-H71 Sensitizes Cancer Cells to Heavy Ion Radiation by Inhibiting DNA Repair by Homologous Recombination and Non-Homologous End Joining. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2016, 121, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting Hypoxia in Cancer Therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Arambula, J.F.; Koo, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, H.; Sessler, J.L.; Kim, J.S. Hypoxia-Targeted Drug Delivery. Chem Soc Rev 2019, 48, 771–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.-F. Targeting Hypoxia: Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs in Cancer Therapy. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, I.N.; Thomas, M.; Calder, E.D.D.; Conway, S.J.; Hammond, E.M. Clinical Advances of Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs in Combination With Radiation Therapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2017, 98, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.S.; O’Cathail, S.M.; Muschel, R.J.; McKenna, W.G. Drug Radiotherapy Combinations: Review of Previous Failures and Reasons for Future Optimism. Cancer Treat Rev 2015, 41, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, F.W.; Wouters, B.G.; Wilson, W.R. Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs: Paths Forward in the Era of Personalised Medicine. Br J Cancer 2016, 114, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelberg, L.; Houben, R.; Niemans, R.; de Ruysscher, D.; Yaromina, A.; Theys, J.; Guise, C.P.; Smaill, J.B.; Patterson, A. V.; Lambin, P.; et al. Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs and (Lack of) Clinical Progress: The Need for Hypoxia-Based Biomarker Patient Selection in Phase III Clinical Trials. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2019, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anduran, E.; Dubois, L.J.; Lambin, P.; Winum, J.-Y. Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug Derivatives of Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Patent Review 2006 – 2021. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2022, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




