1. Introduction
More than a half-century has passed since Clark and Lyons introduced the enzyme glucose biosensor in 1962 [
1], and this important area has been a huge focus of research activity. Compared with traditional analytical methods such as gas and liquid chromatography [
2,
3], enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors have significant advantages. For example, high selectivity, high sensitivity, relatively fast and simple analytical procedures, and small size of the measurement unit as well as high throughput and portability [
4,
5]. Based on these findings, enzyme electrochemical biosensors play an important role in the fields of food processing monitoring and quality management, environmental pollution monitoring and analysis, fermentation process control, biomedical and drug sensing [
6,
7]. In recent years, many enzyme electrochemical biosensors were conceived, developed, and commercialized as user-friendly and time-saving analytical methods. By selecting different enzymes as the immobilized and sensitive bioelements that recognize the analytes to construct the corresponding biosensors, they can provide reliable output signals quantitatively correlated with the concentration of a specific analyte for the determination of a variety of substances, such as glucose [
8], lactose [
9], and ethanol [
10], among others. And it has proven to be an innovative technique for qualitative and quantitative analysis of various target substrates in a wide range of applications [
11].
However, enzyme electrochemical biosensors still face several challenges, such as their insufficient reusability and vulnerability to environmental impacts, which must be addressed to increase their commercial value and efficiency of use. Previous studies have focused on electrochemical biosensors designed for single enzyme systems. These studies have proved valuable in improving the sensitivity, reproducibility, and stability of sensor devices. However, further efforts are needed to overcome the limitations associated with enzyme electrochemical biosensors. Yet, most enzymes do not expend or produce Electrochemically Active Substances (EAS) as part of the catalysis process, and therefore electrochemical sensors are not able to directly record enzymatic catalytic reactions. As a result, the number of enzymes available for the development of biosensors, as well as the range of compounds that can be targeted, remains limited [
12]. To address this problem, scientists have attempted to add several enzymes to the biorecognition element of a biosensor to form a cascade reaction for detecting the product of an enzymatic reaction [
11]. The application of multi-enzyme systems in biosensors based on this formation not only aims to realize the detection of single (multiple) analytes, but also improves the performance of biosensors. With the development of technology, it has been found that some of the nanomaterials (1-100nm) have enzyme-like properties and are known as the next generation of artificial enzymes (nano enzymes). Highly stable and inexpensive compared to natural enzymes, these artificial enzymes are favored by many scientists for their ability to mimic the architecture, function, and activity of naturally occurring enzymes, covering their kinetics and mechanisms [
13,
14]. However, due to the excellent specificity and sensitivity of immobilized enzyme biosensors to specific analytes [
15], as well as the problems of nano-enzymes in terms of selectivity, poor biocompatibility, toxicity, and low enzyme activity criteria [
16], natural enzyme biosensors are still the dominant research direction at present.
An important factor to consider in enzyme chemistry biosensor fabrication is how to immobilize the enzyme on the working electrode surface. One challenge to enzyme immobilization is the difficulty of electron exchange with the electrode interface due to the depth of the activity centers; in addition, the shape of the enzyme may change after immobilization on the surface of the working electrode [
17]; another challenge is to prevent denaturation and inactivation of the enzyme, which eventually shortens the biosensor's lifetime. Thus, enzyme immobilization on a compatible substrate is essential to conserve catalytic properties and stability of enzyme biological activity. During the past years, electrochemical biosensor research has been primarily focused on nanomaterial-modified electrodes because these materials show special physio-chemical characteristics at the nanoscale (e.g., metal nanoparticles, graphene-associated materials, metal-organic frameworks, carbon nanotubes, conductive polymers, etc.) [
18], which can be utilized to increase the fundamental analytical properties of biosensors, such as sensitivity, the limit of detection, linear detection range, stability, etc. [
19]. In addition, nanomaterials are characterized by high surface-to-volume ratios, high electrical conductivity, magnetism, and catalytic activity, which ensure a significant increase in sensor-sensitive surfaces, allow for easy immobilization of receptors through covalent and noncovalent bonds, provide more efficient sites for enzyme immobilization, and permit the construction of biosensor devices with improved analytical properties, which are essential for biosensors and other biotechnological assays in which interactions with biomaterials are interactions are critical.
In this article, we focus on summarizing the construction principles of enzyme electrochemical biosensors and the recent research advances in single-enzyme systems, multi-enzyme systems, and nano-enzymatic systems for food bioprocess monitoring. Subsequently, the expanded applications of various types of nanomaterials for enzyme immobilization in electrochemical enzyme biosensors in recent years are presented, and the structures and properties of the corresponding sensing platforms are discussed. Finally, we discuss some of the challenges and emerging trends in the design of enzyme-based biosensors.
2. Enzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Bioprocess Monitoring
In enzyme electrochemical biosensors, enzymes are used as recognition elements and immobilized on/inside the supporting substrate on the face of the transducer to maintain enzyme activity and enzyme stability due to the rapid reaction catalysis, the high-level substrate specificity and the comparatively long-term enzyme stability [
20]. Binding enzymes as receptors can be easily adapted to monitor food quality and bioprocesses, and have a wide range of applications, especially in bioprocess analyses that require precise control and monitoring of substrate and product concentrations.
So far, there are three main systems of enzymes used for receptors, i.e., single-enzyme system, multi-enzyme system, and nano-enzyme system; where nanoenzymes refer to a class of nano materials that harbor enzymatic properties. In this section, the main focus will be on the construction principles of enzyme electrochemical biosensors and the research progress of these three systems in the food field in recent years.
2.1 Principle of Enzyme Electrochemical Biosensor Construction
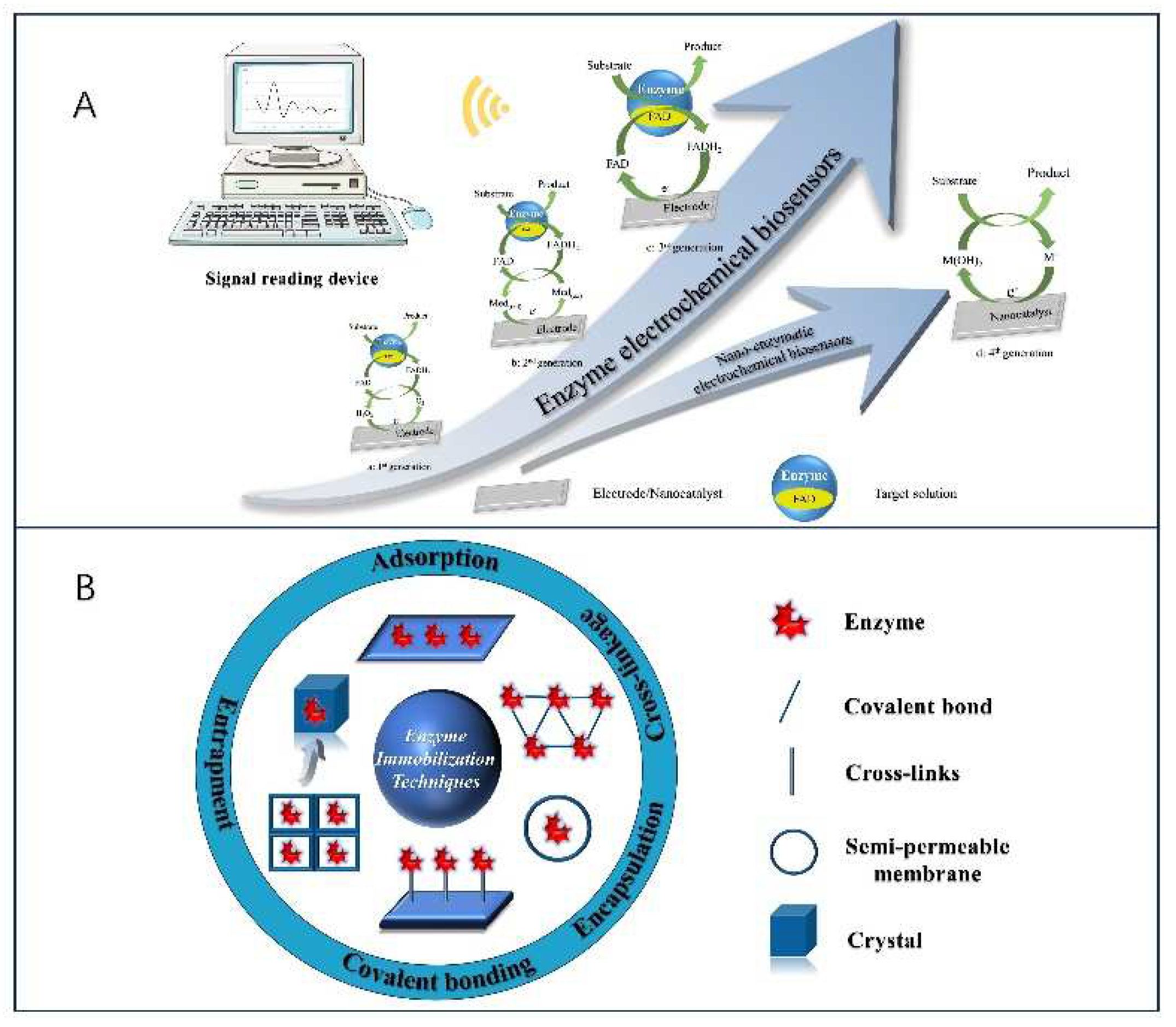
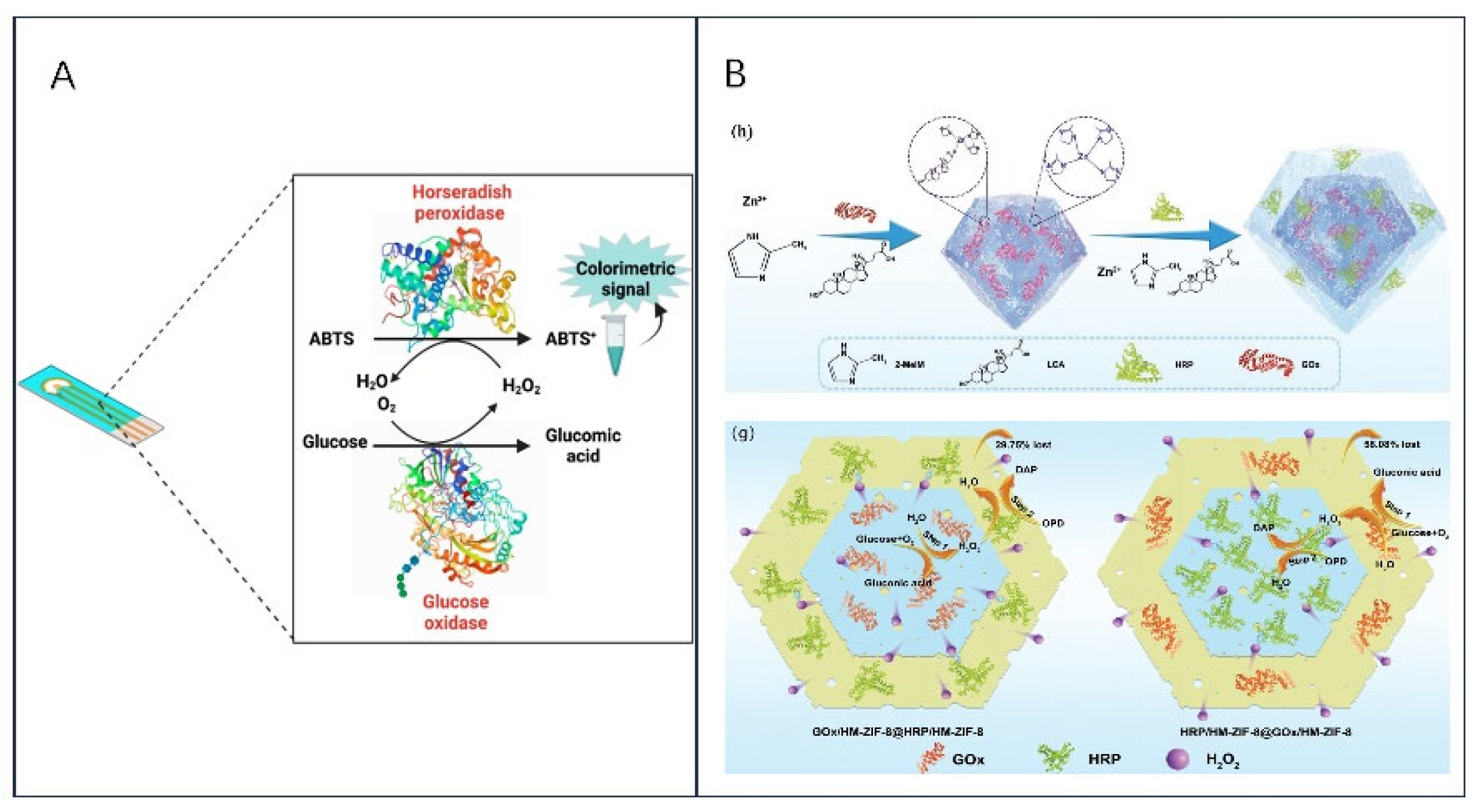
The development of enzyme electrochemical biosensors can be categorized into four generations (
Figure 1A). The first generation of enzyme electrochemical biosensors was based on the measurement of analyte sample concentration based on the generation of H
2O
2 or by reducing the concentration of oxygen (O
2) as a natural cofactor [
21]. In this, enzymes use O
2 as an electron acceptor and participate in the production of products (e.g., gluconic acid) [
22]. In the initial stage, the FAD of the enzyme redox center acts as a catalyst to play the role of the initial electron acceptor, which is reduced to FADH
2 in the analyte, and the reoxidation of FADH
2 with free oxygen produces the oxidized form of the enzyme FAD. Typically, the analyte concentration corresponds to the electrochemical oxidation product, H
2O
2, or the electrochemical reduction product, O
2, at the working electrode [
23], and the transferred electrons are detected and collected by the working electrodes so that an analyte molecule's number of atoms is proportional to the flow of electrons. However, this sensor is overly dependent on dissolved oxygen for electron shuttling, which may lead to fluctuations in oxygen tension due to the limited solubility of oxygen in the liquid to be measured, and thus properties such as hypoxia narrowing the linear range of the sensor can occur [
24]. In addition, co-existing electroactive substances, such as acetaminophen (AP), ascorbic acid (AA), or uric acid (UA), may interfere with sensor use due to the high potentials required for the detection of H
2O
2 products [
25]. To eliminate the dependence on oxygen, second-generation biosensors use natural or synthetic redox mediators to help electron movement between the enzyme and the underlying electrode, such as ferrocene and its derivatives [
26], toluidine blue [
27], and Prussian blue [
28], which first react with the enzyme active site and then react with the electrode surface, thereby transferring electrons to generate a current signal proportional to the detected analyte concentration. In this process, the electroactive medium acts as a mediator to enable the biosensor to undergo mediated electron transfer (MET), also known as MET-type biosensors. In addition, the inclusion of an electroactive dielectric enables the second-generation biosensor to operate at low voltages and also avoids interference from coexisting electroactive substances. Although the second-generation biosensor is oxygen-independent, it is still subject to leaching and interference from the medium due to redox medium selectivity [
29].
In contrast, the response of third generation electrochemical biosensors occurs without the need for a medium. It solely depends on the interaction between the analyte and the bioreceptor, achieved by attaching the FAD-active redox center of the enzyme to the working electrode through nanomaterials either covalently or electrochemically. This arrangement enables direct electron transfer (DET), effectively eliminating any influence from the redox medium. In addition, free electron transfer was exhibited between the oxidoreductase and signaling sensor components, where the oxidoreductase acts as an electrocatalyst to facilitate the electron transfer between the electrode and the substrate molecules with excellent selectivity and sensitivity [
30,
31,
32]. Nevertheless, there are some limitations to this sensor. Specifically, direct electron transfer between the enzyme's deeply embedded FAD-active redox center and the working electrode is enhanced due to the leaching effect of the enzyme and the excellent conductivity of the nanomaterials. Therefore, a research priority to advance sensor technology lies in identifying suitable nanomaterials for electrode modification. Finally, the fourth generation of enzymatic electrochemical biosensors, also known as (nano-enzymatic) non-enzymatic biosensors. In this mechanism, atoms in the nanomaterial act as electrocatalysts to achieve direct electron transfer during chemical reactions [
33]. Thus, by electro oxidising the substrate, the nanomaterial substrate reacts to produce products, a process that shows great electrocatalytic efficacy [
34]. However, as far as the nano-enzyme mimics found so far are concerned, they have limited substrate selectivity.
On the other hand, enzymes have properties as immobilized sensitive biological components that recognize the analyte and are usually immobilized on the surface of an electrode to detect the analyte. However, their inherently fragile nature can lead to early denaturation and short life, but this can be avoided by different methods of enzyme immobilization [
35,
36]. The five most common methods of enzyme immobilization are adsorption, covalent bonding, cross-linkage, entrapment, and electrochemical polymerization, as shown in
Figure 1B.
One of the simplest methods is a reversible weak non-specific force adsorption process through non-covalent bonds such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals forces, or other ionic bonds [
37,
38]. As such binding are weak, the basic structure and activity of the enzyme is not altered and the enzyme is immobilized in a random orientation on the surface of the nanomaterial-modified electrode. Covalent bonding immobilization of receptors is one of the most commonly used methods of irreversible enzyme immobilization. Covalent binding immobilization of enzymes involves the formation of covalent bonds between one or more functional groups of the enzyme to share electron pairs [
39], and the direction of enzyme binding can be controlled by chemical binding; in contrast to adsorption, the enzyme is firmly linked to the nanomaterial-modified electrode, ensuring long stability of the immobilized bioreceptor. Cross-linking is another irreversible method of enzyme immobilization that does not require support to prevent enzyme loss into the substrate solution and is carried out by the formation of intermolecular cross-links between enzyme molecules by bifunctional or multifunctional reagents such as aldol condensation of glutaraldehyde, ensuring a strong chemical bond [
38]. Embedding is defined as an irreversible method of enzyme immobilization and is divided into two main types: entrapment and encapsulation [
40], which can be encapsulated inside a carrier or fiber by polymeric membranes, gels, or nano-lattice materials such as metal-organic frameworks [
41], allowing substrates and products to pass through but leaving the enzyme behind, ensuring the integrity of its properties. Another interesting method of immobilizing enzymes is the generation of polymers on the electrode surface by methods of electrochemical polymerization, in which the enzyme is immobilized in a 3D matrix (electropolymerized membrane, amphiphilic network, polysaccharide, etc.); this approach makes it possible to immobilize the enzyme, the medium, and the additives all together on the same detection layer, without the need to modify the biomolecule and ensuring that the immobilized enzyme is well protected during the immobilization operation.
2.2. Electrochemical Biosensors for Single-Enzyme Systems
Electrochemical biosensors for single enzyme systems have an important role in the monitoring of food bioprocess monitoring. During fermentation, it is possible to determine the speed of the fermentation process and the appropriate fermentation endpoints based on the magnitude of the concentration of the analyte, to obtain industrial products with good flavor and nutritional value. Due to their very stable catalysis of the oxidation-reduction reaction, oxidoreductases and peroxidases are the most widely reported enzymes in electrochemical biosensors. This chapter will concentrate on the research progress on electrochemical biosensors for enzymes such as glucose oxidase and lactate dehydrogenase in the monitoring of food bioprocesses.
2.2.1. Glucose Oxidase
Glucose oxidase (GOx) is a glycoprotein with autophosphorylated proteins with reliable stability and substrate specificity. Glucose is an important hydrolysis product of food, and its concentration magnitude can be used as a key indicator for quality and process control. Electrochemical biosensors constructed based on GOx as a bioreceptor play an important role in food quality monitoring, especially in the control of biofermentation processes. The working principle is that the enzymatic oxidation of glucose produces H
2O
2, and then H
2O
2 and FAD, and FADH
2 undergo an electrochemical reaction to be oxidized to produce O
2, and when an operating current is supplied, the current generated in the sensing element is proportional to the amount of glucose present [
42], which enables the detection of glucose concentration. Considering Clark's study, many glucose-sensing electrodes were initially developed under the consideration of being based on enzyme membranes, which exhibit advantages such as high selectivity and high linearity [
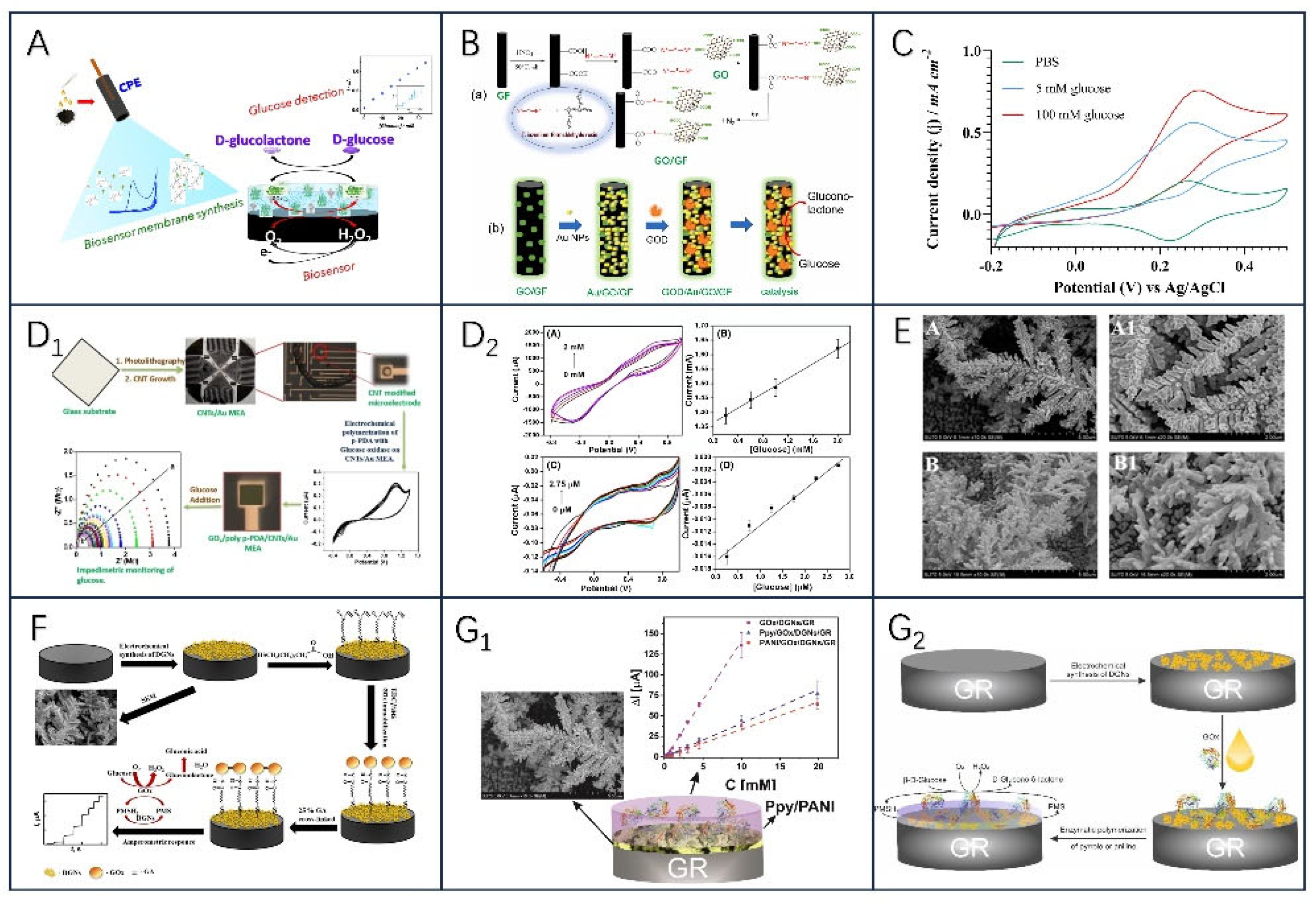
43]. For example, Valdés-Ramírez & Galicia synthesized biosensing membranes of ferulic acid (FA) and glucose oxidase on carbon paste electrodes via an electropolymerization reaction in aqueous media at neutral pH [
44]. The results show that the novel poly ferulic acid membrane synthesized by electropolymerization is a promising method for immobilization of glucose oxidase and the developed glucose biosensor exhibits a wider linear glucose response compared with other polymer-based glucose biosensors (
Figure 2A). The feasibility of synthesizing polyFA membranes in aqueous media with acidic, alkaline, and neutral pH was also demonstrated, increasing the potential of polymer membranes for the development of biosensing membranes. Furthermore, for the design of glucose biosensors, substances such as p-coumaric acid (p-CA) and vanadium dioxide (VO
2) can be used [
45,
46].
In the last few years, to avoid the influence of complex environments on the final detection results, the sensors have mainly immobilized GOx on nanomaterial-modified electrodes, which are modified using nanomaterials or polymers to facilitate the electron transfer process and to reduce electrochemical interferences and the intervention of exogenous substances [
47,
48]. Another new idea is immobilization strategies using physical barriers (Nafion layer, etc.) to improve the instability of the enzyme layer [
49]. As a recent example, Han et al. demonstrated a novel approach to fabricating excellent electrochemical glucose biosensors using covalent bonding and self-assembly on graphite fiber (GF) surface (
Figure 2B)[
50]. Graphite fiber electrode (GFE) was modified using graphene oxide (GO)/gold nanoparticles (AuNP); GO and AuNP were interconnected along the GFE to form an efficient charge transfer channel, which, in addition to increasing the surface area, had the catalytic activity to prevent inactivation of the enzyme on the GFE surface. Moreover, the sensor's detections were linear with glucose concentration, with a detection limit of 1.2 μM and excellent selectivity for dopamine (DA), uric acid (UA), ascorbic acid (AA) and other interferents molecules (fructose, lactose, and galactose). Notably, the covalent bonding of GO with GF enhanced the contact between the electrode and the enzyme redox center and reduced the spacing between the electrode and the enzyme redox center.
Additionally, the stability and specificity of the enzyme were improved by using carbon nanotubes in glucose biosensors. Using covalently bonded nanoconjugates of GOx and MWCNTs (CNT-GOx) to improve the dispersion of the nanocarriers (
Figure 2C), an electrochemical glucose biosensor based on osmium redox polymers cross-linked with GOx and GOx grafted on multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) has been reported to aid in the fabrication of enzyme electrodes and enhance enzyme activity [
47]. After 50 hours of continuous use, the stability was only 12 percent, but the Nafion protective layer increased the stable to between 72 and 75 percent, suggesting that engineering the relationship between the enzyme and the nano-support enhances the enzyme activity, thereby increasing the electrical density and enabling significantly lower amounts of active ingredient to be used. In this work, Singh et al. by immobilizing GOx/poly(p-PDA)/CNTs/Au MEA) in a poly(p-phenylenediamine) matrix (
Figure 2D)[
51], and by modifying CNTs/Au MEA, the selectivity of the resulting MEA for the detection of glucose was realized, whereby glucose could be separately measured for 64 samples with good reproducibility and immunity to interference, and the usability of the sensor was successfully verified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
In another study, Ramanaviciene et al. demonstrated the optimal scheme for the one-step electrochemical synthesis of dendritic gold nanostructures (DGNs) on graphite rod (GR) electrodes using three electrochemical methods, including constant potential amperometry (CPA), pulsed amperometry (PA), and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and the formed gold nanostructures (including DGNs) were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy (
Figure 2E)[
52]. The optimal HAuCl
4 concentration (6.0 mmol L
-1), DGNs synthesis time (400s), electrodeposition potential (-0.4 V), and optimal electrochemical method (CPA) were determined; the sensors obtained by adsorption of GOx on the surface of DGNs and covalent crosslinking with glutaraldehyde (GA) vapor had linear ranges of up to 9.97 mmol L
-1 (with dynamic ranges up to 49 mmol L
-1), that has been successfully used for highly accurate glucose determination in real samples.
To further investigate the effect of DGNs as carrier nanomaterials on glucose biosensors, the team further analyzed the performance of GOx-immobilised sensors on DGNs as well as the development of enzyme biosensors with conductive polymer-modified DGNs in real-life samples [
53,
54]. The first results showed that covalently immobilized multilayer GOx on gold nanostructures is a very promising direction to improve the analytical parameters of biosensors; after covalently immobilizing GOx on 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid self-assembled monolayer (SAM), the application of GA crosslinked GOx significantly improved that the sensitivity and stability of biosensor as well as the reproducibility of current response after multiple glucose detection(
Figure 2F). It is worth noting that DGNs are very fragile and may be damaged or detached from the surface along with the enzyme under inappropriate experimental conditions. The second study, on the other hand, demonstrated the significant advantages of the glucose biosensor designed with Ppy/GOx/DGNs/GR electrodes over PANI/GOx/DGNs/GR and successfully applied the constructed biosensor for the glucose concentration determination in authentic samples (
Figure 2G). In conclusion, the immobilization of GOx on DGNs is of great importance for the further evaluation of glucose biosensors.
2.2.2. Lactate Oxidase and Lactate Dehydrogenase
Lactic acid is the end product of sugar metabolism, L-lactic acid, and D-lactic acid are the two isomers of lactic acid. Where L-lactic acid is a by-product of cellular metabolism indicating the transition from aerobic to anaerobic state, i.e. anaerobic metabolism produces L-lactic acid through the action of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as the end product of glycolysis [
55], and its food products related to the fermentation and dairy industry sector is widely used [
56,
57]. In food quality testing and fermentation processes, electrochemical lactate sensors have been intensively investigated due to their low cost, simplicity, on-site detection, rapid response, portability, and minimal or no sample pretreatment [
58]. Through these sensors, lactate oxidase(LOx) and lactate dehydrogenase(LDH) have been widely exploited, with a focus on electrochemical biosensors constructed with nanomaterial-modified electrodes, and a variety of nanoparticles including metals, metal oxides, mixed metal oxides, polymers, and composites have been investigated for L-lactic acid biosensing, with great advantages in terms of stability, selectivity, and improved sensitivity [
59].
More recently, Narayanan & Slaughter prepared AuNP-cysteamine-LDH biosensing electrodes with good selectivity for lactic acid, and the electrodes obtained after coating with a Nafion layer remained stable for up to 18 days [
60]. Istrate et al. constructed a GA-LDH/AuNPs-ERGO-PAH/SPE disposable biosensor modified by a ternary composite of gold nanoparticles, electrochemically reduced graphene oxide, and poly(allylamine) hydrochloride on the surface of a carbon screen-printed electrode, and crosslink the immobilized enzyme with GA [
61]. The enzyme activity stability of LDH based on this construct was used for up to seven weeks. However, the use of LDH as a biologically active receptor means that the detection scheme is more complex compared to LOx-based biosensors, as the amperometric biosensing approach using LDH results in a complex biosensor structure due to the need for NAD
+ as a mediator for shuttling electrons between the enzyme and the sensor [
62]. Furthermore, the presence of additional compounds that are prone to oxidation (such as AA and UA) hinders the achievement of the necessary level of detection for NADH oxidation. This interference results in a heightened level of reversibility in the reaction involving lactic acid and pyruvic acid, ultimately impacting the sensitivity of the sensor and potentially causing blockages. Consequently, due to the aforementioned constraints experienced by LDH, there has been a greater focus on LOx, primarily due to the straightforward nature of its reaction. LOx plays a key role in the oxidation of lactic acid and its main function is to catalyze the conversion of lactic acid to pyruvic acid. In addition, the inactive state of LOx (red) is reduced in the presence of dissolved oxygen and this reduced form is subsequently oxidized to its active state, LOx (ox). The detection of LOx(ox) is achieved by electrochemically monitoring the generated hydrogen peroxide at highly positive potentials [
63]. For example, Tvorynska et al. developed a novel biosensing system for electrochemical flow injection analysis (FIA) that incorporates an easily replaceable LOx-based bioreactor biometric section (
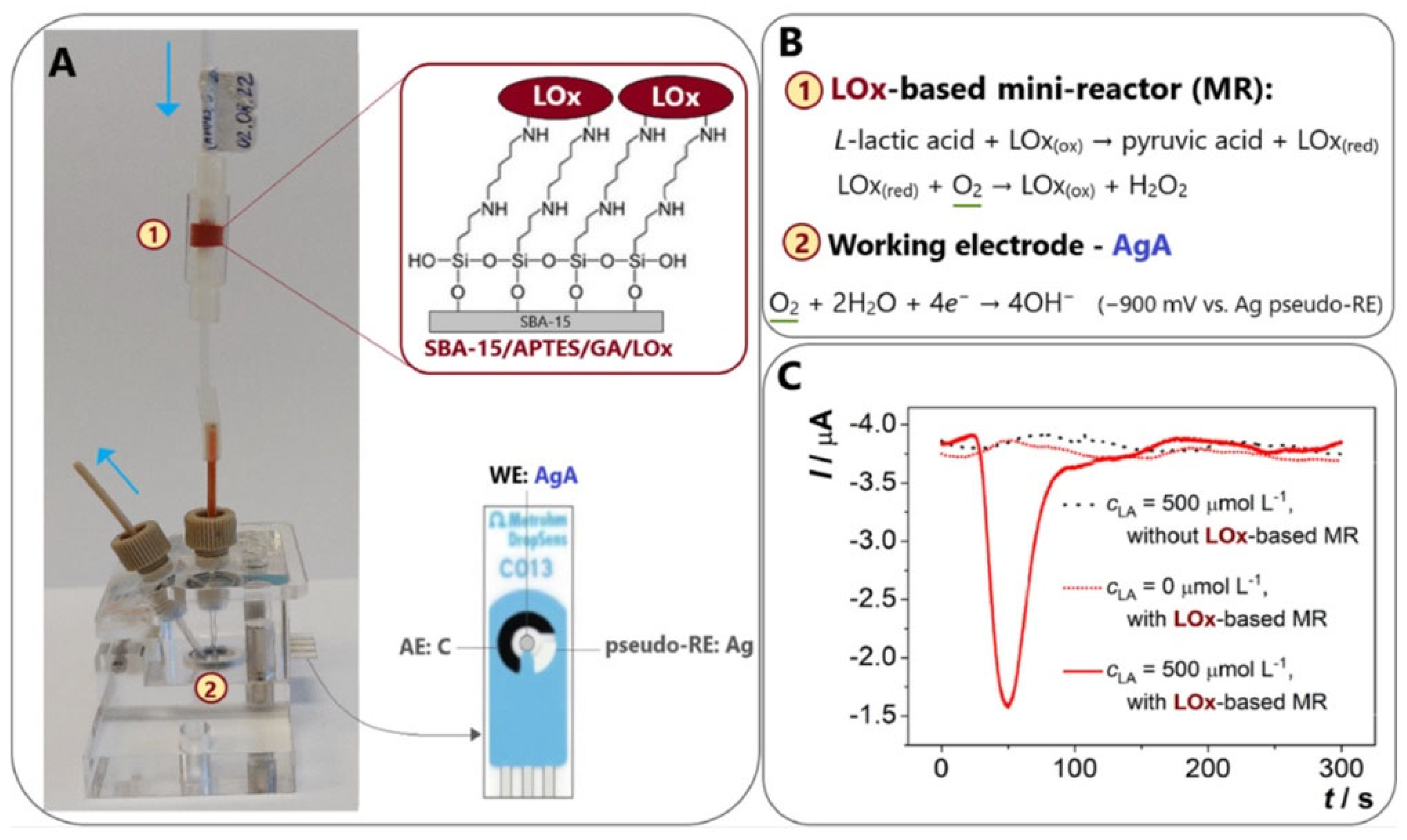
Figure 3)[
64]. The microreactor consists of a mesoporous silica powder, SBA-15, coated with covalently immobilized LOx. immobilization is achieved through the use of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) and glutaraldehyde (GA). This immobilized LOx is referred to as SBA-15/APTES/GA/LOx. It is worth noting that the system is attached in front of an amalgam screen-printed electrode (AgA-SPE) that acts as a sensor. Oxygen consumption was monitored amperometric ally by four-electron reduction with the Ag pseudo-reference electrode at a voltage of -900 mV, thus avoiding interference from common interfering compounds. The spatial separation strategy of the biorecognition and detection sections allows the immobilization of large amounts of enzyme (one microreactor contains ~270 μg LOx), thereby ensuring excellent operational and storage stability. The sensor greatly improves, simplifies, and saves the monitoring of lactic acid in biological samples for laboratory analysis and foods and wines for fermentation control, and is now successfully used for the quantitative detection of lactic acid in saliva, wine, and dairy products. In another study, Ozoglu et al. presented the design of an enzyme-based amperometric lactate biosensor with a linear range of 50-350 μM, a detection limit of 31 μM, and a sensitivity of 0.04 μA μM
-1 cm
-2 for the detection of lactate produced by six different, morphologically defined putative LAB [
65]. This study demonstrates that improving the interface of biosensors using a modification of composites or immobilization of mediators and enzymes on a catalyst layer is useful for designing interference-free measurement systems, especially for the detection of bacterial metabolites.
2.2.3. Other enzymes for the Development of Electrochemical Biosensors
Lactose, the major disaccharide in milk and dairy products, is formed by the β-1,4-glycosidic bond between galactose and glucose, and as a carbohydrate substitute, the sensitive detection of lactose content in food is an important factor in human health management [
66,
67]. It was found that carbon nanotubes interact well with lactase (LAC), and the biosensor obtained by immobilizing LAC with CNT had a sensitivity of up to 5.67 μA cm
-2 mmol
-1 L, with a limit of detection of about 100 × 10
-6 mol L
-1; and the stability of the system was improved with the introduction of CNT as, after about 12 h of use, the current signal did not change after about 12 h of use [
68]. Building on this, the team further used only CNT as a substrate to immobilize LAC by adsorption without any polymer stabilization layer or external membrane for the rapid and sensitive detection of lactose in skimmed milk samples [
69]. In this regard, Villalonga et al. argued that the variations in the anodic and cathodic peaks in the article could be due to metal residues in the CNT, as well as to the influence of other enzymes or material components present in the enzyme preparation [
70]. Therefore, the finding could not be attributed to the adsorption of the non-oxidoreductase enzymes on the surface of the electrode in the article. Moreover, the electrode is not just a single enzyme-modified electrode, since the signals analyzed are induced simply by lactose hydrolysis mediated by beta-galactosidase. In another work, Bollella & Gorton found that cellobiose dehydrogenase (CDH) is selective for lactose and therefore can be used as an alternative for constructing lactose-catalyzed biosensors [
71]. Recently, Nasiri et al. developed magnetic chitosan-supported graphitic nitride (MNPs/CS/g-C
3N
4) metal-free nanocomposite electrochemical lactose sensors by applying MNPs/CS/g-C
3N
4/CDH as a modifier to GCE electrodes, which exhibited excellent electrochemical performance within a large linear range up to 0.9-100 mm and a response time as fast as 5 s (
Figure 4A)[
67]. The sensor has great promise for real sample analysis and has been successfully validated for the quantitative detection of lactose in dairy products.
Biogenic amines (BA) are organic nitrogenous compounds naturally formed by bacterial decarboxylation of the corresponding amino acids in food, as a result of bacterial contamination under poor handling and storage conditions, and are considered to be a quality indicator of food freshness or deterioration [
75,
76]. And include histamine (His), tyramine (Tyr), dopamine, cadaverine (Cad), and putrescine (Put), among others, and excessive intake can affect human health [
77]. Histamine is one of the main factors affecting the freshness of aquatic products. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) and diamine oxidase (DAO) as biorecognition molecules are modified on the electrode, which can effectively convert information such as analyte concentration into electrochemical signals with excellent selectivity and specificity [
78]. Recently, X. Tian et al. designed a temperature-regulated biosensor to better monitor histamine levels in high-temperature foods [
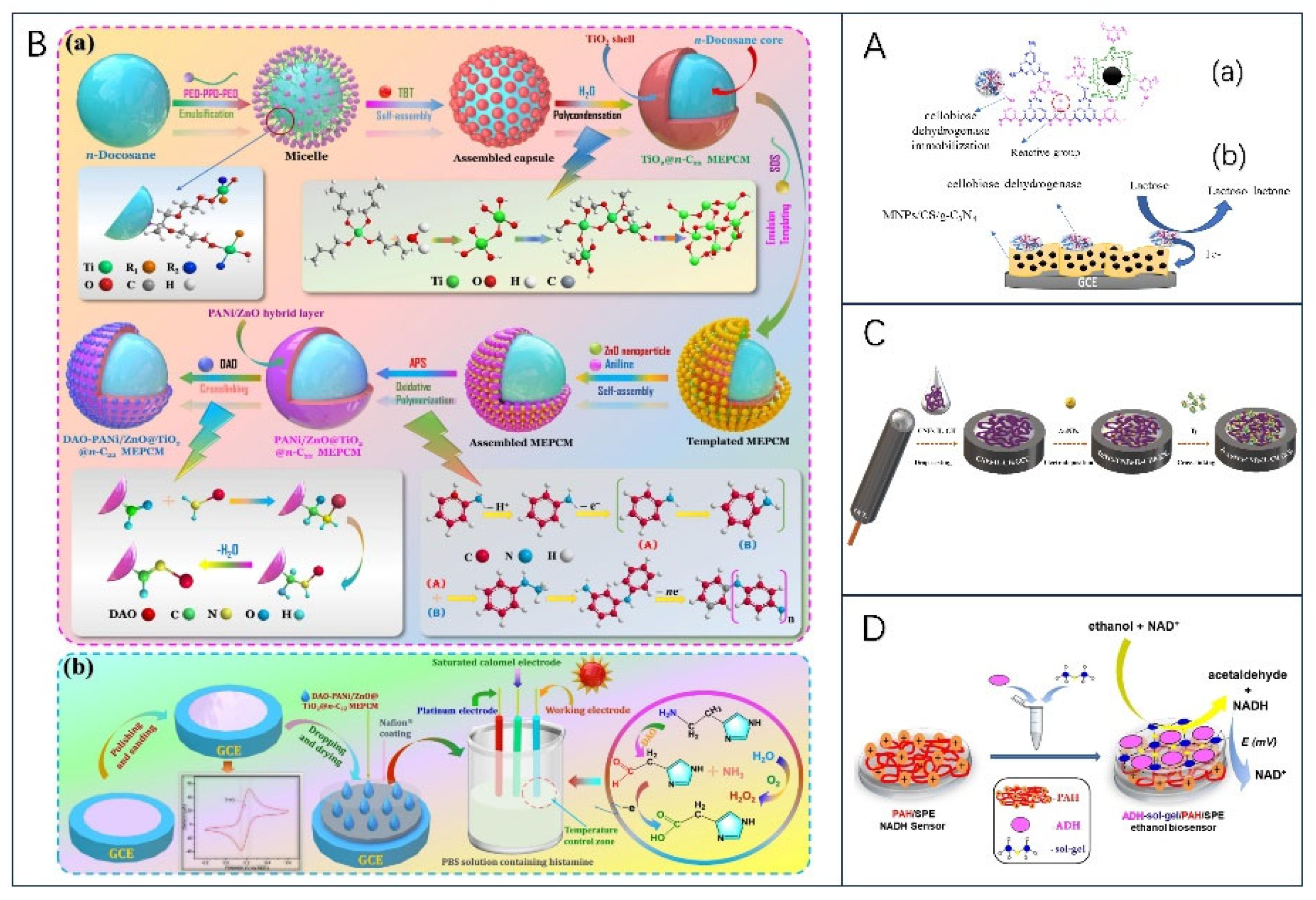
72]. The sensor is based on DAO-immobilised phase-change microcapsules, which are constructed by encapsulating n-docosane (n-C22) in a TiO
2 shell, with a PANi/ZnO conductive layer deposited on the surface, and DAO is immobilized on the surface of the microcapsules (DAO-PANi/ZnO@TiO
2@n-C22 MEPCM). The n-C22 core acquires thermoregulation through a reversible phase transition at high temperatures and can change the ambient temperature around the working electrode to improve the biocatalytic activity of immobilized DAO (
Figure 4B). Compared with the conventional histamine biosensor, the biosensor had a detection limit of 0.473 mu mol/L at high temperature and a high sensitivity of 28.57 mu A.mM(-1).cm(-2). In another study, Erden et al. investigated a novel amperometric tyramine biosensor (Ty/AuNPs/CNFs-IL-CH/GCE) modified with a composite membrane of carbon nanofibres (CNFs), chitosan (CH), ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (IL) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)[
73]. The results showed that the Ty/AuNPs/CNFs-IL-CH/GCE biosensor was highly selective for tyramine in the presence of other biogenic amines (
Figure 4C). To further delve into the development and trends of biogenic amines in food safety applications, researchers conducted a comprehensive review of meat products [
79], fermented foods [
80,
81]. It is believed that amino acid decarboxylase is a key factor in the production of BAs, that convenient, rapid, accurate and environmentally friendly methods for the detection of biogenic amines are emerging, and that the combination of physical and biological methods is a promising approach for the control of BAs. Future research could also focus on the development of a platform combining multi-sensor arrays and pattern recognition techniques for the high-throughput detection of biogenic amines.
The expanding global alcohol market has led to research on biosensors for the determination of ethanol content in alcoholic beverages. Here, Prasanna Kumar et al. designed to immobilize alcohol oxidase on carboxylated graphene/poly(diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride)-modified graphite electrodes and constructed a responsive biosensor system [
82]. In a recent study by O.-M. Istrate et al., a screen-printed electrode was modified to detect ethanol in commercial beverages [
74]. The researchers used a sol-gel matrix to immobilize ethanol dehydrogenase on the sensor surface and applied a layer of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) to enhance the accumulation of NADH (
Figure 4D). This modification led to an increase in the oxidation current of NADH, allowing for the accurate detection of ethanol. The sensor exhibited a sensitivity of 13.45 ± 0.67 μA/mM·cm² and a detection limit of 20 μM, making it highly suitable for determining ethanol content in alcoholic beverages and foods.
In addition, the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food can be achieved using enzyme-based biosensors [
83,
84]. Xanthine oxidase-based biosensors can be used to detect levels of hypoxanthine and xanthine, which are markers of spoilage in meat [
85], hypoxanthine-sensitive electrochemical biosensors can detect fish freshness [
86]. Nitrate reductase (NaR) or microorganisms containing NaR can be used to detect nitrate, Engineered L-glutamate oxidase for monitoring glutamate during microbial fermentations [
87], Laccase can be used to improve food quality, determine phenols in tea and wine [
88,
89], etc.
2.3. Electrochemical Biosensors for Multi-Enzyme Systems
To conveniently detect the products of one or more enzymatic reactions, avoid the inability of single enzymes to be catalyzed in electrochemical reactions, and effectively prevent the inhibitory effect of enzymes, researchers usually add multiple enzymes to the biorecognition elements of biosensors to form a multi-enzymatic system, which improves the performance of biosensors [
90]. Kucherenko et al. in their article reviewed the advantages and limitations of the development of multi-enzyme biosensors, gave suggestions on the rationality of novel multi-enzyme biosensors, and based on different enzyme-associated reaction principles can be categorized into biosensors based on enzyme cascade, cyclic enzyme-promoted, enzyme-competitive substrate, and enzyme-independent reactions [
91]. Among them, the biosensor based on enzyme cascade reaction is the most common type of multi-enzyme biosensor, which consists of several consecutive biocatalytic steps, i.e., the first enzyme converts substance A to the substance unstable intermediate B, the second enzyme converts substance B to C, and so on, to form the final stable electrochemically active product for detection (
Figure 5A). Which has the advantages of eliminating the need for intermittent product separation, saving cost and reagents, high reversibility and low inhibition, etc., and is widely used in food processing [
92], disease treatment and industrial production [
93].
Currently, the longest enzyme cascade reaction in the biosensor consists of five enzymes including glycerol kinase/creatine kinase/creatinase/sarcosine oxidase/peroxidase [
94], and has been successfully used to analyze glycerol in various white and red wine samples. However, although multi-stage material conversions using multiple enzymes are possible, in most instances the amount of enzymes is limited to two because each additional enzyme has a different sensitivity to the substrate, a different method of enzyme immobilization, a different storage time of the enzyme activity, and can cause an increase in sensor response time and higher manufacturing costs.
Multi-enzyme partitioning contributes to the optimization of the channels for substrate transport and promotes the controlled and tunable progression of the reactions in complex cascade biocatalysis. G. Wu et al. proposed to partition GOx and HRP in a core-shell zeolite imidazolium framework (ZIF)-8@ZIF-8 nanostructure to construct a partitioned GOx/HRP dual enzyme system based on core-shell ZIF@ZIF nanostructures (
Figure 5B)[
96]. Nucleation was induced using bionic mineralization and slow seeding to obtain a homogeneous shell wrapped around the core surface by epitaxial growth, whereas the dual enzyme system segregates in the shell and core. Meanwhile, the pore structure of ZIF was improved from a single microporous to a hierarchical microporous/mesoporous network to further improve the mass transfer efficiency, and the system can also covalently bind lithocholic acid (LCA) with divalent metal ions as a competitive ligand. Interestingly, the core-shell ZIF@ ZIF nanostructures proved to be versatile when adjusting the positions of the different ZIF types included or separated multi-enzymes, which provides a facile synthetic strategy for the development of efficient multi-enzyme biocatalysts.
Although multi-enzyme cascade reactions can directly reduce biomanufacturing costs and increase productivity by eliminating the tedious isolation and purification steps required to remove reaction intermediates. However, the precursor condition used for multi-enzyme systems is that the enzymes to be found are all relatively similar in terms of sufficient activity and stability, and due to the inherent instability of the enzymes under non-physiological conditions, the low stability of the enzymes in practice, and the poor reusability, are all major challenges to be overcome [
97]. Therefore how to achieve the immobilization of a multi-enzyme system on an electrode platform in a way that ensures its activity and is stable is a question that needs to be investigated. Indeed, the number of publications related to enzyme immobilization has steadily increased over time, and co-immobilization of enzymes has also emerged as a fruitful approach for controlled multi-enzyme immobilization, where two or more enzymes can be confined in the same space and the immobilization sequences can be regulated to enable highly sensitive multi-enzyme systems for analyte detection [
98]. In turn, immobilization of enzymes on carrier materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, metal-organic frameworks, and conductive polymers is one of the most effective methods to increase enzyme activity through substrate channeling and to improve enzyme stability and reusability [
99]. For example, He et al. immobilized GOx and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) ligated MOFs and graphene oxide (GO) dual carrier platforms SSDNA bridged the dual carriers and reduced enzyme leakage, and the dual carriers increased enzyme loading and accelerated enzyme efficiency, this enzyme immobilization strategy has a promising application in biocatalysis and diagnostics [
97]. This enzyme immobilization strategy has a broad application and practical value in the field of biocatalysis and diagnostics.
Table 1. below shows a few examples of constructing electrochemical biosensors based on the immobilization of multiple enzymes.
2.4. Electrochemical Biosensors for Nano-Enzymatic Systems
Even though enzymatic reactions are efficient and selective, they are still characterized by high cost, poor stability, difficulty in storage, and susceptibility of catalytic activity to the external environment, and there is an urgent need to find an effective way to solve these problems. In recent years, a new class of nanomaterials called nanoenzymes (NZs) has emerged, which have catalytic activities that mimic those of enzymes and are expected to replace natural enzymes [
111]. NZs are nanomaterials with unique physicochemical properties and mimic the properties of natural biological enzymes that perform the same kinetic behavior as natural enzymes and catalyze the conversion of substrates to oxidative coloration products [
112,
113]. Whose enzymatic activity is mainly responsible by atoms on the surface of the nanoparticles and inside the core, and the nanomaterials, by coupling with biological molecules acting as oxidoreductases and used in the structure of NZs to provide high surface-to-volume ratios to enhance adsorption and advance electron transport, accelerating the analytical technique and showing the advantages of being fast, sensitive, efficient, inexpensive, and having superior signals [
114], and thus an effective alternative to address the weaknesses of natural enzymes [
115,
116]. Notably, the incorporation of various nanoparticles may alter the basic characteristics of NZs and may also make them multifunctional [
117].
Since the discovery of the first nano enzymes (Fe
3O
4 NPs) in 2007 [
118], materials such as metals, metal oxides, carbon nanomaterials, metal-organic frameworks, polymer-coated nanoparticles and nanocomposites have been used for the synthesis of NZs [
119,
120], and some of these materials have been shown to have multiple enzymatic activities at once. For example, molybdenum disulfide (MoS
2), simultaneously mimics the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase. Whereas metal nanoparticles (NPs) are considered to have significant potential for analyte determination due to their abundant redox sites [
121]; Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new materials due to their customizable pore sizes, functional groups, and biocompatibility, and are regarded as highly promising platforms in the study of enzyme-host material interactions [
122].
Currently, NZs have been demonstrated to be used in the field of detecting glucose, phenols, hydrogen peroxide, pesticides, bacteria, cancer cells, and so on. However, since nanoenzymes are a novel technology and their official classification has not yet been determined. Huang et al. suggested that NZs should be classified into two groups [
123]: oxidoreductases and hydrolases, and the family members of the oxidoreductase class have redox catalytic roles, which are usually used in biosensing applications, such as catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), oxidative enzymes, peroxidases, and nitrate reductase [
124,
125,
126]. Similar to phosphatases, proteases, nucleases, esterases, and silicate lyases, hydrolases catalyze the hydrolysis process [
120].
More recently, Smutok et al. used a combination of two nanoenzymes with peroxidase activity and LOx in their work to construct an electrochemical lactate biosensor [
127]. Fragments of carbon microfibres (CFs) functionalized with hemin (H) and decorated with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) or platinum microparticles (PtMPs) were used to synthesize the two nano enzymes. Among them, the constructed LOx-CF-H-PtMPs/GE nano-electrode showed good catalytic and operational characteristics in real sample detection. Q.-Y. Yang, Wan, et al. constructed a metal-organic framework nano-enzyme BiO-BDC-NH2 using three-dimensional globular bismuth formate oxide (BiOCOOH) as a precursor and template, which possesses intrinsic peroxidase mimetic activity and efficiently catalyzes the oxidation of colorless 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine to produce blue oxidation in the presence of an enzyme [
128]. This product can be used for the detection of unlabelled and trace/super trace Cr6
+.
In addition several review papers have been related to the sensing applications of NZs, such as the research progress on NZs in food quality and safety detection [
116], the NZs in integrated instant diagnostic biosensor development [
120], and a comprehensive review paper on the application of NZs (Single-atom enzyme) in the electrochemical monitoring of food safety and human health [
129].
In summary, it can be seen that in recent years, nano enzymes biosensors have been developed rapidly and in a wide variety, therefore, in this section, the cases of representative nano enzymes in electrochemical biosensors mainly used in the field of food applications, such as nano-materials with peroxidase activity, oxidase activity are listed in
Table 2: Selected studies on nano enzymes based in food analysis, which is hoped to promote and inspire the research of nano enzymes electrochemical biosensors based on nano enzymes.
As can be seen in
Table 2, most of the nano enzymatic biosensing studies have focused on redox enzyme-based nanomaterials (e.g., oxidases and peroxidases), which is mainly because the enzyme catalytic efficiencies of peroxidase and oxidase-based nano enzymes are slightly higher than those of the natural enzymes. Furthermore, despite all the advantages of nano enzymes, their applications still lack substrate specificity and application limitations that need to be solved; therefore, there is a need for continuous research on the natural active sites of enzymes and the construction of new integrated nano enzymes systems to mimic and improve specificity. Binding or synergistic mechanisms of enzymes and nano enzymes have been reported to be a promising option to address this issue, as their interactions can improve the selectivity and sensitivity of these systems [
130,
131,
127,
132,
133]. For better applications in areas such as clinical diagnostics, food analysis, and environmental monitoring, future work should concentrate on learning about the mechanism of action between nanomaterials and enzymes, as well as on the fabrication of novel materials with more enzyme similar activities.
3. Nanomaterials for Enzyme Immobilization
Enzyme electrochemical biosensor performance is largely influenced by three factors: morphology, structure, and enzyme immobilization technique, whereby enzyme immobilization technique has the greatest impact on sensor performance. Immobilization of enzymes is almost mandatory for most of their applications [
146], and in addition to advances in structural bioengineering of enzymes, methods of immobilization can range from random to charge-driven enzyme targeting. For example, stabilization by modification of functional groups on the enzyme or electrode surface, physical adsorption, covalent cross-linking, entrapment, or by incorporation into the cubic phase [
147]. Currently, there are comprehensive reviews of technical methods for the arrangement control and enzyme immobilization of oxidoreductases on planar electrodes that have been published [
148,
149]. In addition, nanomaterials have also been used to address enzyme immobilization and are emerging as a dominant trend in current biosensor research.
With further research, the interaction between enzymes and different types of nanomaterial-modified surfaces such as metals and their oxides, graphene-related materials, metal-organic frameworks, conductive polymers, carbon nanotubes, etc., has been considered as a new strategy for enzyme immobilization [
150,
151]. Nanomaterial-modified electrodes can improve the rate and stability of electron transfer for enzyme immobilization, increase the sensitive surface of the sensor to immobilize more enzyme molecules, and have a fast response time due to their high conductivity that facilitates the rapid transfer of electrons from the redox region of the enzyme to the sensor [
146,
31]. Immobilization of appropriate enzymes close to nanomaterial-modified electrode surfaces is very effective for ensuring stable and efficient enzyme chemical biosensors, and it is a hot research priority to solve the enzyme immobilization problem [
152].
In summary, the use of nanomaterials to modify electrodes to improve the various properties of sensors has become one of the main trends in the field of biosensing technology today, and therefore this section will focus on the progress of research on biosensors based on several nanomodified electrodes in the field of food engineering.
3.1. Metal-Based Nanomaterials Modified Electrodes
Metal-based nanomaterials (metals and their metal oxide nanoparticles) can be modified on the electrode surface to provide more binding sites for enzyme immobilization; in addition, combining with other nanomaterials can be involved in the immobilization of enzymes and further improves the conductivity and stability of the material, which is widely used in the field of electrochemical biosensors [
153,
154]. Metal-based nanomaterials commonly used for modifying sensor electrodes include gold (Au), silver (Ag), platinum (Pt), and iron (Fe), etc., among them, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been widely studied and used due to their excellent properties such as high electrical conductivity, high biocompatibility, catalytic activity, chemical stability, and nanocomposite modifications.
Research is currently being carried out on the application of AuNPs to various materials to improve the electrode performance of the sensors by immobilizing the AuNPs to significantly increase the activity of the enzyme through the formation of strong thiol bonds between the cysteine residues of the enzyme and the AuNPs. For example, Cerrato-Alvarez et al. immobilized tyrosinase crosslinked with glutaraldehyde on the surface of screen-printed electrodes modified with gold nanoparticles (Tyr-AuNPS-SPCEs), and the fabricated sensors obtained good analytical and kinetic performance [
155]. In a further study, Narayanan & Slaughter, constructed an improved electrochemical lactate biosensor by immobilizing LDH on a flexible tungsten microfilament electrode using a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of cysteamine-modified AuNPs [
156]. The sensor electrode (AuNP-cysteamine-LDH) remains stable for up to 18 days and the Nafion layer used effectively shields the sensor from electrochemically active substances, resulting in excellent sensor performance at a potential of +0.4V, a temperature of 35℃ and pH 6.
In addition, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) are common. To detect the presence of sugars (β-galactosidase, glucose oxidase, and galactose oxidase) in milk in combination with silver nanomaterials combined with biosensors to improve the performance of the multisensor system, Salvo-Comino et al. developed a voltammetric bioelectronic tongue (bioET) specifically designed for the analysis of milk [
157]. The results show that silver nanowires (AgNWs) provide a more efficient platform than silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for the immobilization of biomolecules, with unique performance characteristics in terms of sensitivity and detection limits. In another study, Sadak synthesized rGO/AuNPs nanocomposites and drop-cast them on SPCE for the preparation of enzyme glucose biosensors using GA as a cross-linking reagent and 2,5-dihydroxy benzaldehyde (DHB) as a medium using a one-pot method [
158]. The protein cross-linking method was used to immobilize GOx on the pretreated SPCE to improve its electrochemical performance. Studies have found that a combination of several nanomaterials offers a greater advantage in improving the stability and sensitivity of biosensors.
Notably, metal oxides are also frequently used as modified materials for modifying electrodes, such as zinc oxide (ZnO), which is considered an excellent material for the preparation of high-performance electrochemical biosensors due to its intrinsic wide bandgap (3.2 eV), good biocompatibility good and better adsorption and catalytic properties [
159]. Another aspect, by comparing pristine ZnO with Co, Fe, and Co-Fe doped ZnO mixtures for glucose sensing, Baruah et al. found that the Co-Fe doped ZnO sensor modified with GOx showed a 2-fold increase in sensitivity over the pristine sensor (32.2 μA mM-1cm-2), a linear range of 0-4 mM and a response time of 6.21 s, demonstrating the advantages of composite nanomaterials in the field of biosensing [
160]. In addition, commonly used metal oxide nanomaterials include iron oxide (Fe
3O
4), titanium oxide (TiO), and molybdenum oxide (MoO). For example, to achieve high-sensitivity monitoring of ochratoxin A (OTA) in real samples (fruit juice, red wine, and serum), Y. Wang et al. proposed an aptasensor based on gold nanoparticle-modified molybdenum oxide (AuNPs-MoO), hybridization chain reaction (HCR), and restriction nucleic acid endonuclease (Nb.BbvCI)-assisted helper DNA machine aptasensor [
161]. In this electrochemical platform, HCR and Nb.BbvCI-assisted DNA walkers were used to achieve signal amplification, which demonstrated excellent analytical performance in the range of 0.01-10000 pg mL
-1, with detection limits as low as 3.3 fg mL
-1. In another study, Hui et al. designed a sandwich-type electrochemical sensor based on AgNPs@Ti
3C
2 nanocomposites to detect Staphylococcus aureus in milk, where the self-assembled aptamer acts as a signal probe immobilized on CuO/GR nanocomposites by π-π stacking [
162]. The bacterial recoveries monitored by this sensor ranged between 92.64% and 109.58%, providing a new approach to the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food bioprocess monitoring.
3.2. Graphene Nanomaterials Modified Electrodes
Graphene (GR) is a class of monolayers of carbon atoms based on a honeycomb lattice arrangement. As a new type of carbon nanomaterial, GR has a two-dimensional (2D) conjugated structure, excellent electrical conductivity, high specific surface area, and satisfactory biocompatibility [
163]. Graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) are functionalized derivatives of GR, which are widely used due to their abundant oxygen-containing functional groups, good biocompatibility, and excellent electrochemical properties [
164]. Whereas RGO is mainly synthesized by reducing GO through various chemical methods [
165]. It was found that while the defects and functional groups of GO favored enzyme immobilization and gained high sensitivity detection properties at the expense of electron transfer ability, reduced GO balanced both [
166]. Investigated the effect of GO reduction on glucose detection, and they found that the surface functional groups of partially reduced GO favored GOD uptake, while highly reduced GO facilitated rapid electron transfer, suggesting that an increase in the number of oxygen functional groups leads to an increase in GOD uptake, which in turn improves the affinity and sensitivity of the biosensor. With further research, scientists have found that RGO has become the most effective transducer material for biosensor design due to its high surface area, abundant functional groups, ultra-high electron mobility, remarkable electrocatalytic properties, and good electrical conductivity [
167,
168,
169].
In addition, to obtain high GOD loading and highly sensitive biosensor detection properties, Fang et al. prepared edge-modified multilayered graphene with high structural integrity, which demonstrated its great potential in preparing multifunctional nanofillers for high-performance composites [
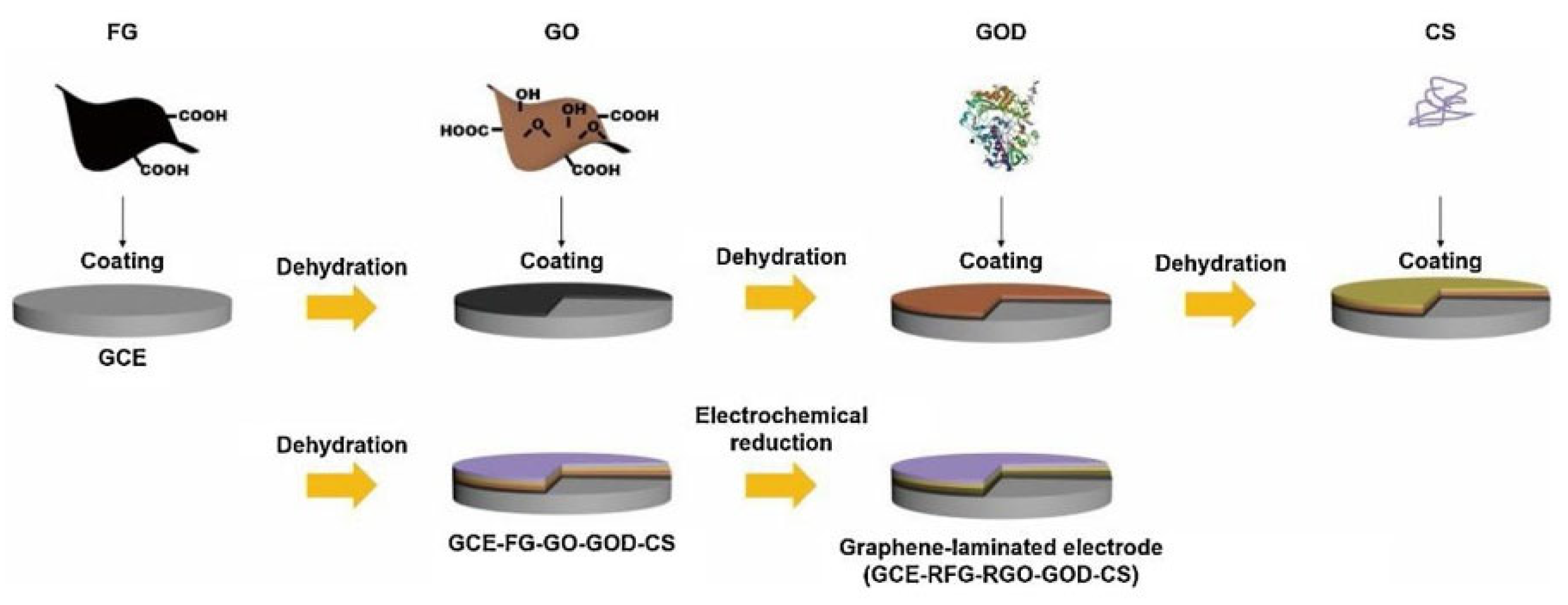
171]; on this basis, Hao et al. combined GO and edge-functionalized graphene (FG) layers combined onto a glassy carbon electrode to prepare graphene laminate electrodes (
Figure 6)[
170]. Due to the rich functional groups of GO, the high conductivity of FG, and the strong interactions between the components in the graphene-laminated electrode, the graphene-laminated electrode exhibited a faster electron transfer rate, a higher GOD loading of 3.80-10
-9 mol cm
-2, and a detection sensitivity as high as 46.71uA mM
-1 cm
-2.
Due to its good electrochemical properties and biocompatibility, graphene is also frequently used for biosensing by making nanocomposites with other materials such as metal nanomaterials, metal-organic frameworks, Mxene, carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, and conductive polymers [
172]. It has been found that GOx covalently immobilized on GR electrodes modified with dendritic gold nanostructures (DGNs) is a very promising direction to improve the analytical parameters of biosensors [
173,
174]. In contrast, Popov et al. attempted to use a GR electrode pre-modified with the conductive polymer polyaniline (PANI) and rGO, Nafion, and GOx dispersions as a working electrode for biosensors, and the developed glucose biosensor had wide linear range (0.5-50 mM), a low detection limit (0.089 mM), and good reproducibility [
175].
On the other hand, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)/ graphene nanomaterials can be easily transformed into structurally complex materials (carbonaceous materials, metal carbides, etc.) due to their compositional and structure modifiability; moreover, the stable chemical interface between MOFs and GO/rGO is an effective way to improve the various properties of the sensor. However, other factors such as enzyme catalytic activity and reusability should also be concerned when designing biosensing platforms [
176,
177]. Indeed, biosensing platforms with high performance have been constructed by combining MOF/GO [
178]. In conclusion, graphene-based nanocomposites are currently a promising option for the development of electrochemical biosensors.
3.3. Metal-Organic Framework Modified Electrodes
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous crystalline materials consisting of metal ions or clusters bonded to organic linkers through coordination bonds [
179]. Its high porosity, large surface area, tunable pore size, highly ordered pore structure, and good stability enable MOF to provide suitable sites for enzyme attachment and can be used as an effective platform for the construction of various chemical sensors and biosensors [
180,
181]. Currently, biosensors prepared with MOFs materials have been applied to various fields such as food safety and food quality control [
182,
183,
184,
185]. However, due to the poor conductivity and poor surface affinity of MOF, the performance of most MOF-based biosensing platforms so far has not reached the desired level. Currently, researchers are working on introducing nanomaterials with good conductivity into the MOF to modify the bioelectrode, which in turn improves the efficiency of electron transfer between the enzyme and the electrode. For instance, Xiao et al. enhanced the substrate biocatalytic effect of the substrate by in-situ growth of ZIF-8 nanoparticles ZIF-8/GO composite on the GO surface, which enhanced the substrate biocatalytic effect with the enzyme by co-sedimentation under mild conditions, catalysis and obtained a sensor with high sensitivity, reproducibility, and good stability [
186]. C. Chen et al. combined hydrophilic multi-walled carbon nanotubes (HKUST-1-MWCNTs) with good electrical conductivity with copper-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), and used a one-pot method to prepare a biosensing platform based on PDA-enzyme-HKUST-1-MWCNTs, which was carried out by the high porosity of HKUST-1, the good adhesive property of PDA immobilization [
187]. The sensitivity of this sensor for glucose was 178 mu A mM(-1) cm(-2) over a wide linear range of 0.005-7.05 mM, and the detection limit was 0.12 mu M, with a corresponding RSD of 3.8%.
In addition, because of the MOFs' weak electrical conductivity and low surface affinity, X. Liu et al. proposed a new strategy to address them [
188]: (i) the use of MOFs with their catalytic properties towards the substrate to enhance the synergistic catalytic effect of the combination of MOFs and immobilized enzyme; (ii) introducing hydrophilic carbon nanomaterials to prepare MOF/carbon nanocomposites to improve the electrical properties of the materials and the surface affinity of the enzyme-substrate to the hydrophilic nanocomposites. This strategy indirectly demonstrates that hydrophilic metal-organic skeletons can significantly enhance enzyme immobilization and protection, while promising the design of relevant MOF nanocomposites, which will be beneficial for the development of biosensing technologies. In another study, since zeolite imidazole framework-90 (ZIF-90) can modulate interfacial interactions to maintain the catalytic activity of the encapsulated enzyme, Ge et al. designed a cascade catalytic reaction in which ZIF-90 encapsulated with GOx was combined with Pt NPs (GOx@ZIF-90-Pt NPs) for biosensing (
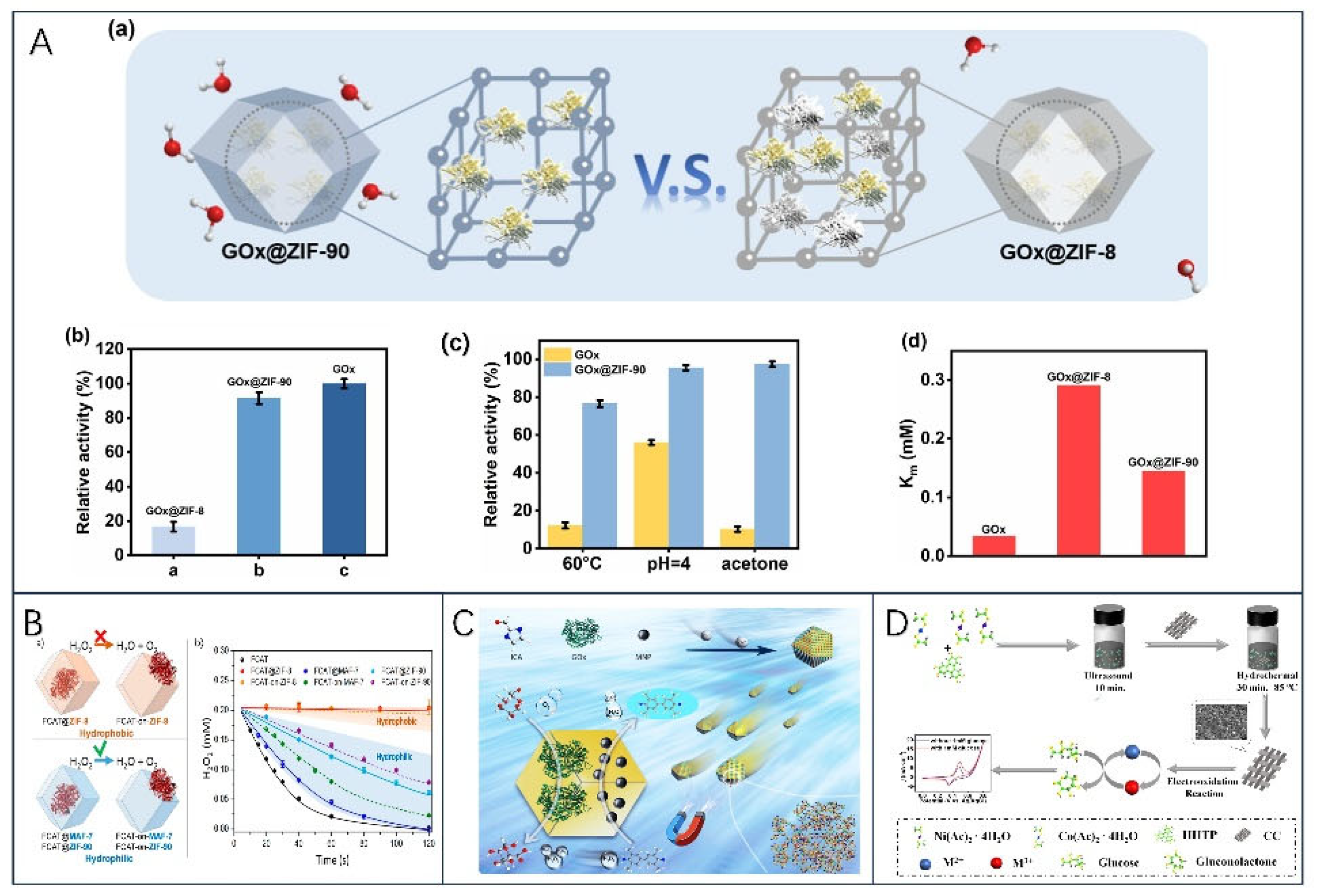
Figure 7A)[
189]. The results showed that the activity of GOx in GOx@ZIF-90 (90%) was 4.5 times higher than that of GOx in GOx@ZIF-8 (20%) when the catalytic activity of free enzyme was set at 100%. Meanwhile, GOx@ZIF-90 showed a 2.0-fold increase in substrate affinity over GOx@ZIF-8, promoting its potential application in biosensing.
Recently, W. Liang et al. investigated the effect of hydrophilic and hydrophobic MOFs on the activity of encapsulated enzymes by finding that hydrophobic ZIF-8, on the other hand, provided inactive catalase and negligible urease protection, whereas the enzymes encapsulated in hydrophilic MAF-7 or ZIF-90 retained their enzymatic activity in the presence of high temperatures, protein hydrolyzing agents, and organic solvents (
Figure 7B)[
190]. It was demonstrated that hydrophilic MOFs provide considerable protection to enzymes loaded therein, whereas hydrophobic materials do not provide the same degree of protection. This study suggests that optimizing the hydrophobic/hydrophilic interaction between the enzyme and the encapsulation material is essential for efficient encapsulation and improved stability of the biomolecule, which is highly protective for the enzyme in acidic environments during fermentation.
In another study, Ji et al. attempted to develop biocatalysts with multifunctional properties by combining nanoenzymes with natural enzymes to form a cascade reaction in response to enzyme instability and mass transfer barriers in sensor systems [
191]. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) and GOx were encapsulated in aZIF-90 (GOx/MNP@aZIF-90) by using amorphous ZIF-90 (aZIF-90) as the host material (Fig. 7C). aZIF-90 generates mesopores and internal voids that effectively enhance the performance of the enzyme cascade reaction and provide confined protection against this reaction. The final results show that aZIF-90 exhibits almost four times the catalytic activity of the crystalline composite and has a residual activity higher than 80% after 9 days of storage. This is the first time that both GOx and MNP have been confined in aZIF-90 with mesopores, suggesting that amorphous metal-organic frameworks are promising in the development of enzymatic cascades.
In addition, MOF can also be utilized for the preparation of electrochemical enzyme-free glucose sensors, such as Z. Xu et al. where conductive Ni/Co bimetallic MOF [Ni/Co(HHTP)MOF/CC] was directly grown on carbon cloth via a simple hydrothermal method [
192]. Due to the synergistic catalytic effect of Ni and Co elements and good electrical conductivity, the bimetallic MOF and CC provided more catalytically active sites and larger specific surface area, and the prepared Ni/Co(HHTP)MOF/CC exhibited excellent electrocatalytic performance (Fig. 7D) and was applied in real samples. The final results demonstrated that the sensing platform had a linear range of 0.3 mu M-2.312 mM with a LOD of 100 nM, a fast reaction time of 2 s, and a high sensitivity of 3,250 mu A mM(-1) cm(-2).
3.4. Carbon Nanotube-Modified Electrodes
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are hexagonal sp2 hybridized carbon/graphite sheets rolled concentrically in a specific manner, dominated by single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) depending on the number of graphene sheets rolled into the tube. Due to its inherent desirable properties such as high biocompatibility and high electrical conductivity, it is widely used in the field of biosensing [
193,
192,
194].
Growing carbon nanotubes directly on the working electrode in situ is a strategy to take advantage of their electrochemical properties. Singh et al. used carbon nanotubes grown in situ at low temperatures and imprinted a lithographically defined gold microelectrode array (CNTs/Au MEA) on a glass substrate for glucose detection [
195]. GOx was immobilized in a poly(p-phenylenediamine) matrix (GOx/poly(p-PDA)/CNTs/Au MEA), and CNTs/Au MEA electrode arrays were prepared to exhibit high conductivity and high enzyme loading due to the high surface area of the CNTs themselves and enzyme selectivity. The sensing platform shows good electrocatalytic properties and can individually detect glucose levels in 64 samples.
In addition, CNTs, as a special material, have been found to have a great capacity to be used in combination with enzymes [
196]. H. Song et al. constructed a hybridized system consisting of poly(vinylglycerol) swing-arm tethered NAD(+) and xylose dehydrogenase (XDH) with platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs@MWCNTs) deposited on carbon nanotubes for real-time sensing of xylose [
197]. The use of PtNPs@MWCNTs composites improved the sensitivity of the electrical response, significantly reduced the oxidation potential of NADH, and maintained 30% of the initial performance after 82 days, demonstrating its great potential for practical applications.
A study conducted by Maity et al. involved immobilizing GOx on MWCNT/polyaniline/rGO/AuNPs/GCE to construct a glucose biosensor [
198]. The biosensing system achieved promising results, including 90.23% reproducibility (based on 7 trials) and high stability of 96% (74.5% after 30 days of storage at -20℃ and 2 weeks of storage at -4℃). In addition, the biosensor has a wide linear range of 1-10 mM, a low detection limit of 64 µM, and a high sensitivity of 246 µAcm(-2) mM(-1). Similarly, chitosan-based glucose biosensors were immobilized on polypyrrole (PPy)-Nafion (Nf)-functionalized MWCNTs to develop high-performance glucose biosensors [
199]. The resulting nanohybrid composites provided a large surface area for GOx immobilization leading to high enzyme loading and hence improved sensitivity.
In summary, it has been shown that bio-nanocomposites prepared from CNTs with MEA, metal nanoparticles, metal-organic skeletons, and conductive polymers provide a biocompatible environment that can help increase the electrocatalytic activity of immobilized enzymes, enhance the electron transfer rate and improve properties such as high immunity to interference, longevity, reusability and storage time [
196].
3.5. Polymer Modified Electrodes
Conductive polymers, such as poly(aniline), poly(pyrrole), and poly(acetylene) are extensively employed in electrochemical biosensors to facilitate electron transfer between the enzyme and the electrode, as well as to enhance enzyme immobilization [
200]. These polymers are particularly useful in oxidoreductase-based biosensors, where charge transfer is essential [
201]. Compared to biosensors without polymers, biosensors incorporating conductive polymers exhibit heightened sensitivity due to the significant improvement in electron transfer between the enzyme active center and the electrode surface [
202].
And one-step in situ electropolymerization of conducting polymers in the presence of monomers and enzymes has developed into an important and easy method for enzyme immobilization. A single-step procedure for the modification of graphite electrodes with polypyrrole (PPy), Prussian blue (PB), and GOx-based composite layers (PPy/PB/GOx) was investigated [
203]. In addition, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT), polydopamine, and silica are often used for one-step in situ enzymatic polymerization [
204]. J. Li et al. designed and constructed a GOx/AuNP/PEDOT(BSA)/Pt electrode platform for glucose sensing [
205]. The platform was determined to have a detection range of 0.416-50 mM by linear voltammetry, and the average value of sensitivity was about 3.124 mu A/mM/cm(2). Additionally, the electrode's stability was demonstrated through uninterrupted glucose measurements spanning seven consecutive days, exhibiting a margin of error of approximately 5%. In the study conducted by Senel et al., a groundbreaking film with exceptional conductivity was generated through the electrochemical polymerization of pyrrole (Py) along with thiophene-grafted chitosan (Th-Ch) [
206]. The remarkable Ch-based conductive film was further enhanced by the incorporation of GOx, leading to a significant boost in sensitivity, surpassing the Py-Ch composite by approximately 40%. This novel composite film is promising in biosensor technology due to its biocompatibility, chemically and physically modifiable structure, and its conductivity.
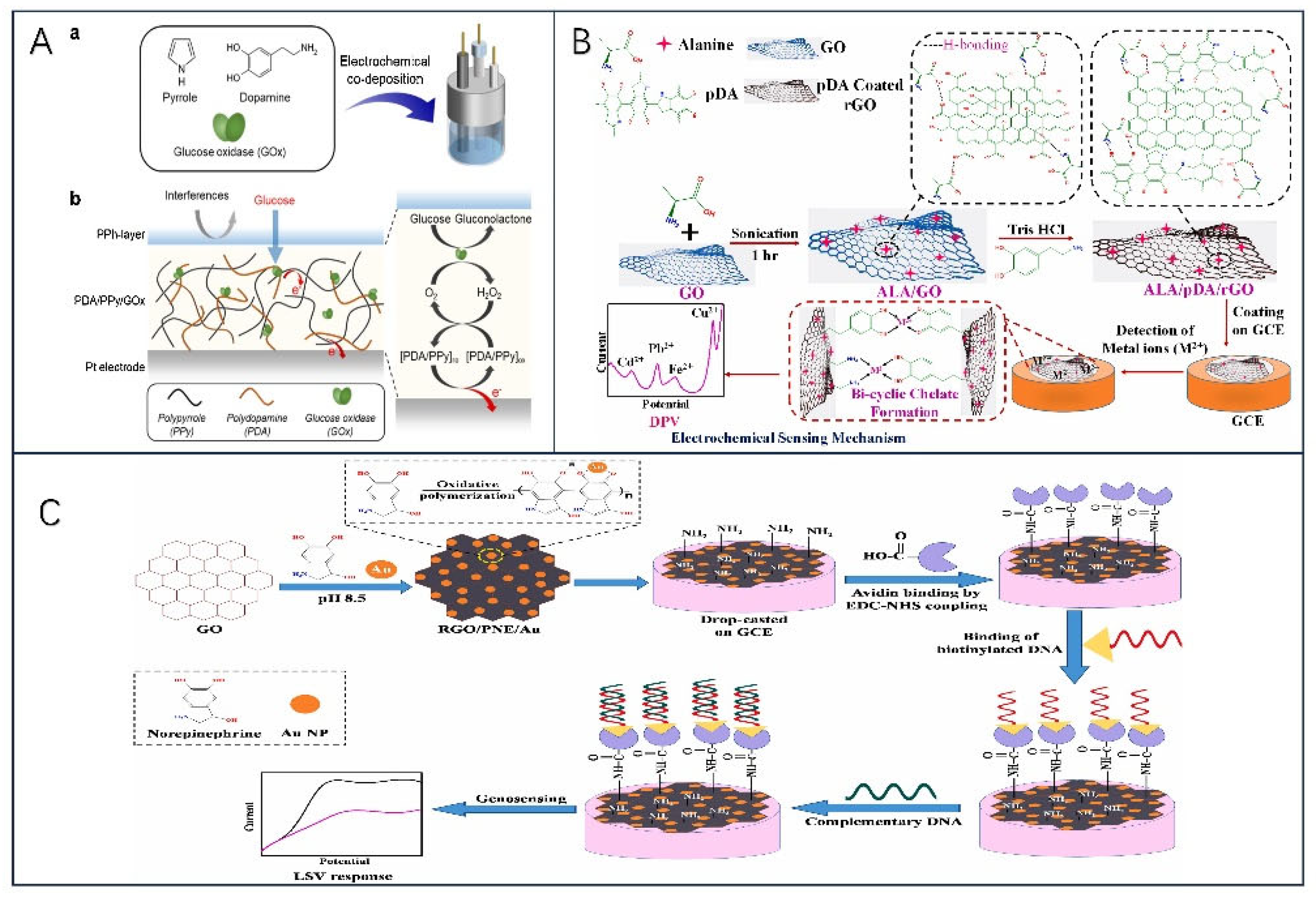
Besides conductive polymers, some biopolymers such as polydopamine (PDA) and polynephrine (PNE) have been widely reported and applied in the field of biosensors. PDA, as a biopolymer, has a wide range of functional groups that can be used for surface functionalization/nanocoating of materials through covalent bonding (acting as a cross-linking agent) or non-covalent bonding effects with the substrate, including metal coordination, π-π stacking and hydrogen bonding, etc. [
207,
208]. A biosensor for glucose and lactate was developed through a one-step electrochemical coating process by M. Lee et al.. The GOx biosensor exhibited an impressive sensitivity of 22.15 A mM cm, a rapid response time of 5-6 seconds, a wide linear range of up to 5.0 mM, and a remarkable glucose detection limit of 138μM (R=0.995) [
209]. Furthermore, the PDA/PPy/LOx biosensor exhibited enhanced lactate sensing capabilities in comparison to the PPy/LOx sensor (
Figure 8A). This straightforward fabrication approach involving PDA/PPy and enzymes holds great promise in developing biosensors that are both highly sensitive and stable.
In another study, Patel et al. prepared alanine-decorated polydopamine-coated reduced graphene oxide (ALA/pDA/rGO) nanocomposites, and the developed ALA/pDA/rGO was used for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd
2+, Pb
2+, Cu
2+, and Fe
2+ in solution (
Figure 8B)[
210]. Efficient detection of targets can also be realized in combination with a variety of nanomaterials [
211,
209,
187]. Notably, inspired by the exponential growth of PDA research, scientists investigated the structure of PDA's sister compound, polynorepinephrine (PNE), and found that PNE has greater coating uniformity and biocompatibility than PDA, which facilitates electron transfer between the enzyme's active centers to the electrode [
212].
Notably, the PNE chemical structure has one more -OH than PDA and contains abundant amino and hydroxyl groups with strong metal chelating and redox capabilities [
213], allowing the material to serve as a multifunctional platform for surface functionalization, which has a great potential for application in the field of biosensors [
214]. For example, Y. Liu, Nan, et al. prepared Au electrodes modified by PNE, GOD, and AuNP (PNE/GOD/AuNPs@ PNE/Au), a sensor with excellent selectivity and stability [
212]. On the other hand, Bisht et al. developed RGO/PNE/Au nanocomposite-based sensors for TB diagnostics and found that PNE modified bioelectrodes have better DNA loading, sensitivity, and excellent electrochemical response, their findings further emphasize the importance of PNE-based biomimetic nanocoatings for the evolution towards the design of electrochemical biosensors for the significance of electrochemically active nanomaterials such as GR, RGO, MXene, etc. where functional groups are missing (
Figure 8C)[
169].
4. Challenges and Future Trends of Enzyme Electrochemical Biosensors
4.1. Challenges
According to the article's explanation about the sensors, it is evident that exploiting the distinct electrochemical characteristics of nanomaterials as modifications on electrode surfaces is an ingenious approach to enhancing the efficacy of electrochemical biosensors. This method facilitates the provision of additional electrocatalytic sites and immobilized sites for biomolecule binding. Nevertheless, despite numerous research endeavors focusing on biosensor development, the utilization and optimization of enzymatic-based electrochemical biosensors encounter various obstacles. These hurdles encompass:
- (1)
The major hindrances to the widespread usage of enzyme electrochemical biosensors are still the reusability and stability of these biosensors. Moreover, the complexity of food matrices, harsh environments, and their interference with biorecognition elements can significantly impact the reproducibility and selectivity of biosensors. Henceforth, scientists must prioritize the enhancement of sensor efficacy in forthcoming research endeavors. Specifically, rigorous investigation is necessary to address and resolve the issue of interferences encountered in authentic specimens, ensure the endurance of enzyme-chemical biosensors in adverse surroundings, and assess the impact of varying storage conditions on the biosensors' lifespan [
86].
- (2)
The addition of multiple enzymes to a biosensor in multi-enzyme systems can create complications during biosensor fabrication. Furthermore, it can impose substantial limitations on the characterization and application possibilities of the biosensor. This arises due to variations in the sensitivity to substrates, effectiveness in storage, and conditions required for enzyme immobilization among different enzymes. Hence, a critical consideration in designing a multi-enzyme biosensor is the meticulous selection of enzyme systems. This selection aims to prevent their sensitization to substances other than the target substance and ensure the requisite stability of the biosensor.
- (3)
Compared with natural enzymes, the catalytic activity of nano enzymes is still relatively low, and most nano enzymes are difficult to catalyze a specific substrate like biological enzymes. Therefore, despite all the advantages of nano enzymes, nano enzymes with high catalytic activity, excellent selectivity, and specificity for constructing nano enzymes-based biosensors still need to be further developed. In the future, integrating biological enzymes or nano enzymes into mesoporous nanomaterials to prepare integrated nano enzymes (INAzymes), or constructing a binding or synergistic mechanism between an enzyme and a nano-enzyme may be a promising strategy to obtain this type of problem.
- (4)
Achieving high homogeneity, reproducibility and chemical stability in electrode materials is a challenging task that cannot be accomplished by simple synthesis alone. Obtaining these desirable properties requires continuous efforts to advance advanced synthetic methods and their application to the analysis of real samples. Therefore, future prospective studies could prioritize the assessment of the stability of biosensor electrode materials in complex environments. In addition, it would be beneficial to explore more reliable modification strategies to enhance compatibility between biorecognition molecules and electrodes, as well as other potential avenues of exploration.
While these factors present challenges to the commercialization of electrochemical biosensors, they have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in ensuring the analysis of food industry analytes as well as precise monitoring for bioprocess monitoring. Taken together in the full article, it is clear that the application of nanomaterials is expected to enhance the selectivity, sensitivity, storage stability, and other analytical properties of electrochemical biosensors. This enhancement is expected to make biosensors more resilient and expand their potential for practical applications.
4.2. Future Development Trends
Nowadays, with the development of science and technology, the requirements for biosensors that can achieve multi-functional rapid real-time monitoring are getting higher and higher, and integration and automation will also become one of the future development trends of biosensors. The integration and automation of smart devices in the food industry have the potential to greatly enhance the monitoring of food-related analytes. By integrating detection and analysis technologies, this approach can streamline and simplify the process of preparing biosensors. In addition, it has the potential to reduce the cost of sensors, making them more accessible for widespread use. Most importantly, these advancements are crucial for the development of real-time, online detection of target analytes during the monitoring of food bioprocesses [
194]. For example, with the help of smart microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanotechnology, biosensors can be miniaturized to the micron and nanometer scale and integrated into lab-on-a-chip devices for integrated and intelligent high-precision monitoring. Forouzanfar et al. developed a carbon-microelectromechanical system (C-MEMS)-based highly sensitive electrochemical capacitive lactase sensor [
215]. The sensor showed good selectivity and high stability for lactate detection over a wide dynamic range of 0.1-5000 mu M with a detection limit of 1.45 mu M (signal-to-noise ratio = 3). In addition, it is often applied for rapid and efficient detection of product quality and safety [
216].
In addition, self-powered biosensors have gained scientific interest; self-powered electrochemical biosensors utilize biofuel cells as a simultaneous power source and biosensor, which simplifies the biosensor system. The possibility of realizing self-powered biosensors for glucose detection was first demonstrated by Katz et al. in 2001 [
217], and a comprehensive overview of enzyme-modified electrodes for biosensors and biofuel cells was provided by [
218]. Recently, there have been advancements in developing cost-effective and user-friendly paper-based biosensors that are disposable [
219,
220,
221]. For instance, an innovative study by Pagkali et al. introduced electrochemical paper-based analytical devices (ePADs) with a fluidic setup [
222]. These ePADs were designed for creating enzyme-based biosensors by immobilizing GOx and utilizing potassium ferricyanide as a mediator within the designated test region. The fabrication of these biosensors incurred a manufacturing cost of less than 0.05 € each, making them highly affordable. By utilizing ePADs, the determination of glucose in food samples was successfully performed, exhibiting remarkable recoveries ranging from 94% to 106%.
5. Conclusions
In this review, an effort is made to compile the most recent developments in electrochemical biosensors for food analysis and bioprocess monitoring utilizing enzymes. Nevertheless, given the vast number of samples, it becomes impractical to offer a comprehensive survey of all sensors. Therefore, this review exclusively presents a chosen range of well-known enzymes employed in biosensors. Among enzyme-based biosensors, those constructed as single-enzyme systems, multi-enzyme systems, and nano-enzyme systems have already covered most of the fields of practical applications, but, although these systems have been used in all kinds of fields, they still need to be improved continuously. Single-enzyme systems are the most studied class of biosensors, but are unable to detect multiple analytes simultaneously due to enzyme specificity limitations. Detection of one or more analytes can be effectively accomplished through the utilization of multi-enzyme biosensors. The selection of enzymes plays a critical role in the advancement of biosensors designed for multi-enzymatic systems. This is due to the requirement of enzymes to have comparable operating conditions, such as temperature, pH, and concentration. In addition, the use of economical nano enzymes is a favorable technology to promote the development of biosensors. However, despite all the advantages of utilizing nano enzymes, there are still many hurdles to overcome to advance their application. These challenges include the lack of substrate specificity, possible contamination of the apoenzymes surfaces due the uptake of dominant mixtures, and the limited range of enzyme types they can mimic. Hence, it is imperative to persistently explore the inherent active sites of enzymes to imitate and augment specificity. Furthermore, the combination or synergy between natural enzymes and nano enzymes holds potential as viable alternatives to tackle this issue effectively, as their interplay can amplify the selectivity and sensitivity of these systems.
At present, the primary challenge in enzyme electrochemical biosensors revolves around the process of immobilizing enzymes. This process directly impacts the sensor's stability, reproducibility, and other functionalities. Despite the promising development of electrochemical biosensors in recent years, their storage and stability are still challenges that need to be addressed. In response to these issues, this paper discusses how several nanomaterials such as metals and their oxides, graphene-related materials, metal-organic frameworks, carbon nanotubes, and conductive polymers can be used as support materials to improve biosensors for the detection of various analytes. Enzyme electrochemical biosensors centered around nanomaterials represent a pivotal focus in the realm of biosensor investigation. Despite the diverse assortment of nanomaterials, which exhibit distinct chemical structures, properties, and morphologies, the favorable influence of nanomaterials in biosensors can be ascribed to three primary factors: substantial surface-area-to-volume ratios, elevated electrical conductivity, and exceptional biocompatibility. It was found that enzyme-based nanomaterials for electrochemical biosensor applications have three major effects. Firstly, they enhance the charge transfer between the enzyme and the electrode, allowing direct electron transfer, which improves the efficiency and high conductivity of the biosensor. Second, nanomaterials improve the immobilization and stabilization conditions of the enzyme, which ensures that the enzyme maintains its biocatalytic activity for a longer period. Finally, nanomaterials enhance the catalysis of electrochemical reactions, leading to faster and more efficient detection of target analytes. On the other hand, scientists are increasingly favoring the use of nanomaterials for biosensors because they are easy to synthesize and can be easily electrochemically treated directly on the electrode surface. In addition, biosensors based on nanocomposites and newly discovered nanostructures have shown promising applications. These new advances have the potential to revolutionize the field of electrochemical biosensors, enabling more accurate and sensitive detection of a wide range of analytes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.F., G.S., H.L., D.Z., X.W. and L.H.; investigation, H.F., G.S., H.L., D.Z., X.W. and L.H.; resources, H.F.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S.; writing—review and editing, H.F., X.W. and H.L.; project administration, H.F. and H.L.; supervision, H.F. and H.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia (NO.2022BDE02004), Graduate science and technology innovation project (No. 2022020801010420), Industry-University-Research collaboration of Zhuhai (No. 2220004002701), Helanshan Scholars Program of Ningxia University and The Youth Talent Support Program in Ningxia(2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank ACS publications, MDPI publications, Wiley Online Libraryand publications, SPRINGER LINKEl publications and sevier publications for the permission for reuse of the original figures published by publishers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. ELECTRODE SYSTEMS FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY. Ann Ny Acad Sci 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Barfidokht, A.; Tehrani, F.; Mishra, R. Food Safety Analysis Using Electrochemical Biosensors. Foods 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdinasab, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Tang, X.; Marty, J.L. Detection of Antibiotics in Food: New Achievements in the Development of Biosensors. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 127, 115883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Qin, W. Recent Advances in Potentiometric Biosensors. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 124, 115803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankole, O.E.; Verma, D.K.; Chávez González, M.L.; Ceferino, J.G.; Sandoval-Cortés, J.; Aguilar, C.N. Recent Trends and Technical Advancements in Biosensors and Their Emerging Applications in Food and Bioscience. Food Biosci 2022, 47, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.; Vernekar, P.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Chandra, P. Biosensor Nanoengineering: Design, Operation, and Implementation for Biomolecular Analysis. Sensors International 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Yao, J.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, W. Rapid Advances of Versatile MXenes for Electrochemical Enzyme-Based Biosensors, Immunosensors, and Nucleic Acid-Based Biosensors. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Transdermal Amperometric Biosensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes. Talanta 2023, 253, 124033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, C.; Salvo-Comino, C.; Martín-Pedrosa, F.; García-Cabezón, C.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. Bioelectronic Tongue Dedicated to the Analysis of Milk Using Enzymes Linked to Carboxylated-PVC Membranes Modified with Gold Nanoparticles. Food Control 2023, 145, 109425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, V.; Kumar, V.; Gahlaut, A.; Hooda, V. Alcohol Quantification: Recent Insights into Amperometric Enzyme Biosensors. Artif Cell Nanomed B 2018, 46, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, U.J.; Fermin, C.D.; Kim, M. Immobilized Enzymes in Biosensor Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Multienzyme Systems: Main Groups, Advantages and Limitations – A Review. Anal Chim Acta 2020, 1111, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with Enzyme-like Characteristics (Nanozymes): Next-Generation Artificial Enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev 2019, 48, 1004–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbanoglu, S.; Erkmen, C.; Uslu, B. Frontiers in Electrochemical Enzyme Based Biosensors for Food and Drug Analysis. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 124, 115809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska Nery, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Jönsson-Niedziółka, M. Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Is There Still Room for Improvement? Anal Chem 2016, 88, 11271–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Biswas, R.; Banerjee, R.; Biswas, P. A Gold Nanoparticle-Intercalated Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanozyme for the Selective Colorimetric Detection of Dopamine. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.B.; Zhang, F.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Nano-Biocatalysts for Food Applications; Immobilized Enzymes within Different Nanostructures. Crit Rev Food Sci 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Raza, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Microbial Toxins, Pathogenic Bacteria in Food Matrices. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 401, 123379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Kucherenko, D.Yu.; Soldatkina, O.V.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Advances in Nanomaterial Application in Enzyme-Based Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Nanoscale Adv 2019, 1, 4560–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Razib, M.S.; Latip, W.; Abdul Rashid, J.I.; Knight, V.F.; Wan Yunus, W.M.Z.; Ong, K.K.; Mohd Kasim, N.A.; Mohd Noor, S.A. An Enzyme-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Organophosphate Compounds Using Mutant Phosphotriesterase Immobilized onto Reduced Graphene Oxide. Journal of Chemistry 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.-H.; Lee, S.-Y. Glucose Biosensors: An Overview of Use in Clinical Practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruen, D.; Delaney, C.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Glucose Sensing for Diabetes Monitoring: Recent Developments. Sensors 2017, 17, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddiraju, S.; Burgess, D.J.; Tomazos, I.; Jain, F.C.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Technologies for Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Current Problems and Future Promises. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2010, 4, 1540–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, F. Oxygen-Rich Oxidase Enzyme Electrodes for Operation in Oxygen-Free Solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management: An Updated Review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çevik, E.; Şenel, M.; Fatih Abasıyanık, M. Construction of Biosensor for Determination of Galactose with Galactose Oxidase Immobilized on Polymeric Mediator Contains Ferrocene. Current Applied Physics 2010, 10, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostiar, I.; Tkac, J.; Sturdik, E.; Gemeiner, P. Amperometric Urea Biosensor Based on Urease and Electropolymerized Toluidine Blue Dye as a PH-Sensitive Redox Probe. Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 56, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, P. A Novel Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Dynamic Polymerase-Extending Hybridization for E. Coli O157:H7 DNA Detection. Talanta 2009, 78, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga Martinez, C.C.; Treo, E.F.; Madrid, R.E.; Felice, C.C. Real-Time Measurement of Glucose Using Chrono-Impedance Technique on a Second Generation Biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2011, 29, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Lata, S.; Narwal, V. Biosensors for Determination of D and L- Amino Acids: A Review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2018, 117, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, T.; Almeida, M.G. Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensors Revisited: Old Solutions for New Problems. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry 2019, 49, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, U.J.; Fermin, C.D.; Kim, M. Immobilized Enzymes in Biosensor Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Prestgard, M.; Tiwari, A. A Review of Recent Advances in Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensors. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2014, 41, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, J. Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, H. Biosensors: Enzyme Immobilization Chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 64–71. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Zhang, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B.; Fang, Y. Recent Advances in Enzyme Inhibition Based-Electrochemical Biosensors for Pharmaceutical and Environmental Analysis. Talanta 2023, 253, 124092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowski, T.; Zdarta, J.; Krajewska, B. Enzyme Immobilization by Adsorption: A Review. Adsorption 2014, 20, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.R.; Marzuki, N.H.C.; Buang, N.A.; Huyop, F.; Wahab, R.A. An Overview of Technologies for Immobilization of Enzymes and Surface Analysis Techniques for Immobilized Enzymes. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2015, 29, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Immobilization Strategies to Develop Enzymatic Biosensors. Biotechnology Advances 2012, 30, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Apetrei, C. Tyrosinase Immobilization Strategies for the Development of Electrochemical Biosensors—A Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wu, X.-L.; Xiong, J.; Zong, M.-H.; Lou, W.-Y. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Novel Matrices for Efficient Enzyme Immobilization: An Update Review. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2020, 406, 213149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Probst, D.; Klonoff, D.; Sode, K. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems - Current Status and Future Perspectives of the Flagship Technologies in Biosensor Research -. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2021, 181, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alp, B.; Mutlu, S.; Mutlu, M. Glow-Discharge-Treated Cellulose Acetate (CA) Membrane for a High Linearity Single-Layer Glucose Electrode in the Food Industry. Food Research International 2000, 33, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Galicia, L. Biosensing Membrane Base on Ferulic Acid and Glucose Oxidase for an Amperometric Glucose Biosensor. Molecules 2021, 26, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, N.S.; De Souza, F.A.; Da Rocha, R.C.F.; Cestarolli, D.T.; Guerra, E.M. Development of Amperometric Biosensors Using VO2/GOx Films for Detection of Glucose. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 2021, 121, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Galicia, L. Glucose Oxidase Captured into Electropolymerized P-Coumaric Acid towards the Development of a Glucose Biosensor. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, K.; Bennett, R.; Leech, D. Electrochemical Glucose Biosensor Based on an Osmium Redox Polymer and Glucose Oxidase Grafted to Carbon Nanotubes: A Design-of-Experiments Optimisation of Current Density and Stability. Electrochimica Acta 2021, 371, 137845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Osorio, D.V.; Escalona-Villalpando, R.A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Arriaga, L.G.; Ledesma-García, J. Poly-L-Lysine-Modified with Ferrocene to Obtain a Redox Polymer for Mediated Glucose Biosensor Application. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Enhanced Amperometric Response of a Glucose Oxidase and Horseradish Peroxidase Based Bienzyme Glucose Biosensor Modified with a Film of Polymerized Toluidine Blue Containing Reduced Graphene Oxide. Microchim Acta 2015, 182, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y. Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticle/Graphite Fiber Microelectrodes for Directing Electron Transfer of Glucose Oxidase and Glucose Detection. Journal of Power Sources 2022, 521, 230956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jaiswal, N.; Tiwari, I.; Ahmad, M.; Silva, S.R.P. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on in Situ Grown Carbon Nanotubes on Gold Microelectrode Array Fabricated on Glass Substrate for Glucose Determination. Microchim Acta 2023, 190, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Glucose Biosensor Based on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures Electrodeposited on Graphite Electrode by Different Electrochemical Methods. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskiene, L.; Popov, A.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. The Impact of Glucose Oxidase Immobilization on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures on the Performance of Glucose Biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Development and Practical Application of Glucose Biosensor Based on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures Modified by Conducting Polymers. Biosensors 2022, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, K.S.; Oh, M.S.; Halperin, M.L. L-Lactic Acidosis: Pathophysiology, Classification, and Causes; Emphasis on Biochemical and Metabolic Basis. Kidney International 2020, 97, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teusink, B.; Molenaar, D. Systems Biology of Lactic Acid Bacteria: For Food and Thought. Current Opinion in Systems Biology 2017, 6, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.F.; Rokana, N.; Panwar, H.; Heller, K.J.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics for Dietary Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Environ Chem Lett 2019, 17, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Topolnikova, Ya.V.; Soldatkin, O.O. Advances in the Biosensors for Lactate and Pyruvate Detection for Medical Applications: A Review. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2019, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yata, V.K. Engineered Nanostructured Materials: Benefits and Risks. Environ Chem Lett 2019, 17, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.S.; Slaughter, G. Lactic Acid Biosensor Based on Lactate Dehydrogenase Immobilized on Au Nanoparticle Modified Microwire Electrode. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, O.-M.; Rotariu, L.; Bala, C. Amperometric L-Lactate Biosensor Based upon a Gold Nanoparticles/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polyallylamine Hydrochloride Modified Screen-Printed Graphite Electrode. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Rahman, Md.A.; Shim, Y.-B. A Lactate Biosensor Based on Lactate Dehydrogenase/Nictotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (Oxidized Form) Immobilized on a Conducting Polymer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Composite Film. Analytical Biochemistry 2009, 384, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaus, N.; Strehlitz, B. Amperometric Lactate Biosensors and Their Application in (Sports) Medicine, for Life Quality and Wellbeing. Microchim Acta 2008, 160, 15–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvorynska, S.; Barek, J.; Josypcuk, B. High-Performance Amperometric Biosensor for Flow Injection Analysis Consisting of a Replaceable Lactate Oxidase-Based Mini-Reactor and a Silver Amalgam Screen-Printed Electrode. Electrochimica Acta 2023, 445, 142033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozoglu, O.; Uzunoglu, A.; Unal, M.A.; Gumustas, M.; Ozkan, S.A.; Korukluoglu, M.; Gunes Altuntas, E. Electrochemical Detection of Lactate Produced by Foodborne Presumptive Lactic Acid Bacteria. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 2023, 135, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccheria, F.; Mariani, M.; Scotti, N.; Psaro, R.; Ravasio, N. Catalytic Upgrading of Lactose: A Rest Raw Material from the Dairy Industry. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, H.; Baghban, H.; Teimuri-Mofrad, R.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Graphitic Carbon Nitride/Magnetic Chitosan Composite for Rapid Electrochemical Detection of Lactose. International Dairy Journal 2023, 136, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, A.R.; dos Santos Reis, N.; Oliveira, P.C.; Rezende, D.V.B.; Monteiro, G.P.; Soares, G.A.; de Jesus, R.S.; Santos, A.S.; Salay, L.C.; de Oliveira, J.R.; et al. Development of Amperometric Biosensor in Modified Carbon Paste with Enzymatic Preparation Based on Lactase Immobilized on Carbon Nanotubes. J Food Sci Technol 2020, 57, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, A.R.; De Jesus, R.S.; Tavares, I.M.D.C.; Silva, F.N.; Santana, N.B.; Barbosa Ferrão, S.P.; Bilal, M.; De Santana Santos, A.; Salay, L.C.; De Oliveira, J.R.; et al. Application of the Electrochemical Biosensor in the Detection of Lactose in Skimmed Milk. Surfaces and Interfaces 2021, 22, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Sánchez, A.; Mayol, B.; Reviejo, J.; Villalonga, R. Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Bioprocess Monitoring. Current Opinion in Food Science 2022, 43, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Gorton, L. Enzyme Based Amperometric Biosensors. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry 2018, 10, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Immobilizing Diamine Oxidase on Electroactive Phase-Change Microcapsules to Construct Thermoregulatory Smart Biosensor for Enhancing Detection of Histamine in Foods. Food Chemistry 2022, 397, 133759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erden, P.E.; Kaçar Selvi, C.; Kılıç, E. A Novel Tyramine Biosensor Based on Carbon Nanofibers, 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate and Gold Nanoparticles. Microchemical Journal 2021, 170, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, O.-M.; Rotariu, L.; Bala, C. Amperometric L-Lactate Biosensor Based upon a Gold Nanoparticles/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polyallylamine Hydrochloride Modified Screen-Printed Graphite Electrode. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Novel Techniques for Evaluating Freshness Quality Attributes of Fish: A Review of Recent Developments. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2019, 83, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, L.; Grasso, S.; De Gara, L.; Pennazza, G.; Zompanti, A.; Rapa, M.; Ruggieri, R.; Vinci, G.; Santonico, M. An Electrochemical Sensor for Monitoring Biogenic Amines in Anchovies as Quality and Safety Index. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2021, 347, 130648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ehsani, A.; Uslu, B. Latest Trends for Biogenic Amines Detection in Foods: Enzymatic Biosensors and Nanozymes Applications. Trends Food Sci Tech 2021, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, C.; Erden, P.E.; Dalkiran, B.; İnal, E.K.; Kiliç, E. Amperometric Biogenic Amine Biosensors Based on Prussian Blue, Indium Tin Oxide Nanoparticles and Diamine Oxidase– or Monoamine Oxidase–Modified Electrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem 2020, 412, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, D.; Fu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Biogenic Amines Detection in Meat and Meat Products: The Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Trends. Journal of Future Foods 2024, 4, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, S. The Importance of Amine-Degrading Enzymes on the Biogenic Amine Degradation in Fermented Foods: A Review. Process Biochemistry 2020, 99, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Ho, C.-T. Research Advances on Biogenic Amines in Traditional Fermented Foods: Emphasis on Formation Mechanism, Detection and Control Methods. Food Chemistry 2023, 405, 134911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna Kumar, S.; Parashuram, L.; Suhas, D.P.; Krishnaiah, P. Carboxylated Graphene-Alcohol Oxidase Thin Films Modified Graphite Electrode as an Electrochemical Sensor for Electro-Catalytic Detection of Ethanol. Materials Science for Energy Technologies 2020, 3, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.-T.D.; Phan, L.M.T.; Park, J.; Cho, S. Review—Electrochemical Aptasensor for Pathogenic Bacteria Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 087501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Kuang, D.; Feng, Q.; Wu, M.; Yang, J. A Dual-Mode Ratiometric Aptasensor for Accurate Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria Based on Recycling of DNAzyme Activation. Food Chemistry 2023, 423, 136287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbanoglu, S.; Erkmen, C.; Uslu, B. Frontiers in Electrochemical Enzyme Based Biosensors for Food and Drug Analysis. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 124, 115809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Tan, Y.; Mubango, E.; Shi, C.; Regenstein, J.M.; Yang, Q.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Rapid Freshness and Survival Monitoring Biosensors of Fish: Progress, Challenge, and Future Perspective. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2022, 129, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bai, R.; Xie, B.; Zhuang, N.; Lv, Z.; Chen, M.; Dong, W.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, M. A Biosensor Based on Oriented Immobilization of an Engineered L-Glutamate Oxidase on a Screen-Printed Microchip for Detection of l-Glutamate in Fermentation Processes. Food Chemistry 2023, 405, 134792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, E.; Kato, C.G.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Peralta Muniz Moreira, R.D.F.; Peralta, R.A.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Zanin, G.M.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Laccases in Food Processing: Current Status, Bottlenecks and Perspectives. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 115, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, X.-Y.; Zheng, Q.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, L.; Xu, Q.-X.; Chen, J.-C.; He, S.-B.; Chen, W. Construction of Platinum Nanozyme by Using Carboxymethylcellulose with Improved Laccase-like Activity for Phenolic Compounds Detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2023, 393, 134165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, U.J.; Fermin, C.D.; Kim, M. Immobilized Enzymes in Biosensor Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Multienzyme Systems: Main Groups, Advantages and Limitations – A Review. Analytica Chimica Acta 2020, 1111, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Cai, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, L.; Gao, X.-D. One-Pot Multienzyme Synthesis of Rare Ketoses from Glycerol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, F.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, Z.; He, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, L.; Madzak, C.; Yan, J. Design of a New Multienzyme Complex Synthesis System Based on Yarrowia Lipolytica Simultaneously Secreted and Surface Displayed Fusion Proteins for Sustainable Production of Fatty Acid-Derived Hydrocarbons. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 17035–17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monošík, R.; Ukropcová, D.; Streďanský, M.; Šturdík, E. Multienzymatic Amperometric Biosensor Based on Gold and Nanocomposite Planar Electrodes for Glycerol Determination in Wine. Analytical Biochemistry 2012, 421, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Ramírez, L.; Rostro-Alanis, M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Enzyme (Single and Multiple) and Nanozyme Biosensors: Recent Developments and Their Novel Applications in the Water-Food-Health Nexus. Biosensors 2021, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Li, M.; Luo, Z.; Qi, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H. Designed Synthesis of Compartmented Bienzyme Biocatalysts Based on Core–Shell Zeolitic Imidazole Framework Nanostructures. Small 2023, 19, 2206606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Shen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chao, H.; Song, J.; Su, P.; Yang, Y. Janus DNA Bridges Metal-Organic Frameworks and Graphene Oxide for Convenient and Efficient Multienzyme Co-Immobilization with Boosted Activity. Applied Surface Science 2021, 570, 151242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana-Peña, S.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterlling, R.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Alcántara, A.R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Enzyme Co-Immobilization: Always the Biocatalyst Designers’ Choice…or Not? Biotechnology Advances 2021, 51, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, Y. Immobilization of Multi-Enzymes on Support Materials for Efficient Biocatalysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J. Preparation and Properties of a Glucose Biosensor Based on an Ionic Liquid-Functionalized Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Composite. New Carbon Materials 2020, 35, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal-Kestwal, D.R.; Chiang, B.-H. Electrochemical Invertase Probes with Nanocomposite of Microfibrillated Cellulose-Tragacanth Gum-Metal Nanoparticles for Direct Sucrose Analysis in Sweetened Beverages. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B720–B727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, O.; Sen Gursoy, S.; Cogal, S.; Celik Cogal, G. Development of a New Two-Enzyme Biosensor Based on Poly(Pyrrole-Co-3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) for Lactose Determination in Milk. Polym Eng Sci 2018, 58, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, G.; McEntee, S.; Dwyer, C.; Lawless, F.; Dempsey, E. Lactose Biosensor Development and Deployment in Dairy Product Analysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 037528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyeshkova, V.M.; Dudchenko, O.Y.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Alekseev, S.A.; Seker, T.; Kurc, B.A.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Development of Three-Enzyme Lactose Amperometric Biosensor Modified by Nanosized Poly (Meta-Phenylenediamine) Film. Appl Nanosci 2022, 12, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Gómez, P.; Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Capdevila, F.; Puig-Pujol, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C. Monitoring of Malolactic Fermentation in Wine Using an Electrochemical Bienzymatic Biosensor for L-Lactate with Long Term Stability. Analytica Chimica Acta 2016, 905, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Jin, K.; Luo, X.; Piao, J.; Wang, F. Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Chitosan- and Thioctic-Acid-Modified Nanoporous Gold Co-Immobilization Enzyme for Glycerol Determination. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, M.A.; Songkakul, T.; Pozdin, V.A.; Bozkurt, A.; Daniele, M.A. Wearable Multiplexed Biosensor System toward Continuous Monitoring of Metabolites. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2020, 153, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalvand, A.R. An Intelligent and Novel Electrochemical Biosensor for Simultaneous Enzymatic Biosensing of Cholesterol and Glucose in the Presence of Uric Acid Based on First-and Second-Order Calibration Methods. Microchemical Journal 2023, 191, 108824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Lang, Q.; Liang, B.; Shi, J. Sensitive Detection of Maltose and Glucose Based on Dual Enzyme-Displayed Bacteria Electrochemical Biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2017, 87, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Kang, X.; Zhang, H.; Tao, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yao, S. Poly(Noradrenalin) Based Bi-Enzyme Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Multi-Analyte Determination. Talanta 2019, 194, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudunnabi, R.G.; Farhana, F.Z.; Kashaninejad, N.; Firoz, S.H.; Shim, Y.-B.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Nanozyme-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Disease Biomarker Detection. Analyst 2020, 145, 4398–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.L.S.; Vuong, K.Q.; Chow, E. Nanozymes for Environmental Pollutant Monitoring and Remediation. Sensors 2021, 21, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, F.; Mohd-Naim, N.F.; Chandrawati, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Ahmed, M.U. Nanozyme-Based Sensors for Detection of Food Biomarkers: A Review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 26160–26175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with Enzyme-like Characteristics (Nanozymes): Next-Generation Artificial Enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres Castillo, N.E.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Ochoa Sierra, J.S.; Ramírez-Torres, N.M.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Enzyme Mimics In-Focus: Redefining the Catalytic Attributes of Artificial Enzymes for Renewable Energy Production. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 179, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Ying, R.; Su, E. The Recent Development of Nanozymes for Food Quality and Safety Detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasyuk, N.; Smutok, O.; Demkiv, O.; Prokopiv, T.; Gayda, G.; Nisnevitch, M.; Gonchar, M. Synthesis, Catalytic Properties and Application in Biosensorics of Nanozymes and Electronanocatalysts: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic Peroxidase-like Activity of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles. Nature Nanotech 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ehsani, A.; Uslu, B. Latest Trends for Biogenic Amines Detection in Foods: Enzymatic Biosensors and Nanozymes Applications. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, C.P.; Ahmed, M.U. Nanozymes towards Personalized Diagnostics: A Recent Progress in Biosensing. Biosensors 2023, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Chai, H.; Huang, Y. High Peroxidase-like Activity of Metallic Cobalt Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Metal–Organic Frameworks Derived Carbon for Biosensing. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2018, 255, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lan, P.C.; Ma, S. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Enzyme Immobilization: Beyond Host Matrix Materials. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, Activity Regulation, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gunasekaran, S. Nanozymes-Based Biosensors for Food Quality and Safety. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 126, 115841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C. Advances in Oxidase-Mimicking Nanozymes: Classification, Activity Regulation and Biomedical Applications. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Du, T.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Nanozymes for Foodborne Microbial Contaminants Detection: Mechanisms, Recent Advances, and Challenges. Food Control 2022, 141, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smutok, O.; Kavetskyy, T.; Prokopiv, T.; Serkiz, R.; Šauša, O.; Novák, I.; Švajdlenková, H.; Maťko, I.; Gonchar, M.; Katz, E. Biosensor Based on Peroxidase-Mimetic Nanozyme and Lactate Oxidase for Accurate L-Lactate Analysis in Beverages. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.-Y.; Wan, C.-Q.; Wang, Y.-X.; Shen, X.-F.; Pang, Y.-H. Bismuth-Based Metal-Organic Framework Peroxidase-Mimic Nanozyme: Preparation and Mechanism for Colorimetric-Converted Ultra-Trace Electrochemical Sensing of Chromium Ion. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 451, 131148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Guan, J. Single-Atom Nanozyme-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Health and Food Safety Monitoring. Food Chemistry 2023, 425, 136518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasyuk, N.; Gayda, G.; Zakalskiy, A.; Zakalska, O.; Serkiz, R.; Gonchar, M. Amperometric Biosensors Based on Oxidases and PtRu Nanoparticles as Artificial Peroxidase. Food Chemistry 2019, 285, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasyuk, N.; Gayda, G.; Demkiv, O.; Darmohray, L.; Gonchar, M.; Nisnevitch, M. Amperometric Biosensors for L-Arginine Determination Based on L-Arginine Oxidase and Peroxidase-Like Nanozymes. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Cheng, N. Single-Atom Ce-N-C Nanozyme Bioactive Paper with a 3D-Printed Platform for Rapid Detection of Organophosphorus and Carbamate Pesticide Residues. Food Chemistry 2022, 387, 132896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Pang, X.; Luo, Y.; Huang, K.; He, X.; Yao, Z.; Li, J.-C.; Cheng, N. Fe-N-C Nanozyme Mediated Bioactive Paper-3D Printing Integration Technology Enables Portable Detection of Lactose in Milk. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 368, 132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Du, J.; Liu, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Qi, W.; Lu, X. Enhanced His@AuNCs Oxidase-like Activity by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Application for Colorimetric and Electrochemical Detection of Nitrite. Anal Bioanal Chem 2019, 411, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Y.; Sun, H.; Dan, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Yue, T.; Wang, J. Oxidase-like Fe–Mn Bimetallic Nanozymes for Colorimetric Detection of Ascorbic Acid in Kiwi Fruit. LWT 2022, 154, 112821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, L.; Gong, H.; Luo, L.; Han, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, C.; Yue, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Dextran-Stabilized Fe-Mn Bimetallic Oxidase-like Nanozyme for Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay of Fruit and Vegetable Food. Food Chemistry 2022, 371, 131115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Tong, Y.; Wu, L.; Huang, X. Nanozyme-Catalysed CRISPR-Cas12a System for the Preamplification-Free Colorimetric Detection of Lead Ion. Analytica Chimica Acta 2023, 1243, 340827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Chi, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Wei, Q. Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Modified Thiol Graphene as Sensing Platform and Gold-Palladium Modified Zirconium Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanozyme as Signal Enhancer for Ultrasensitive Detection of Mercury Ions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2022, 606, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, H.; Lv, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, L.; Niu, X. Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Au2Pt Nanozymes for Antioxidant Nutrition Quality Evaluation in Food. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 236, 115417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, R.; Zhu, L. S-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Peroxidase Mimetic and Its Application in Sensitive Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide and Glucose. Anal Bioanal Chem 2020, 412, 5477–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh Van, T.; Dang Thi Thuy, N.; Dao Vu Phuong, T.; Nguyen Thi, N.; Nguyen Thi, T.; Nguyen Phuong, T.; Vu Van, T.; Vuong-Pham, H.; Phuong Dinh, T. High-Performance Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Biosensor Based on AgNP-Decorated MoS2 Microflowers. Current Applied Physics 2022, 43, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gao, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, T. A Smartphone-Assisted Colorimetric Sensor Based on Fe1-XS Nanozyme for Detection of Glucose and Ascorbic-Acid in Soft Drinks. Microchemical Journal 2023, 193, 109018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, F.; Mu, F.; Dai, B. The Preparation of Fe-Based Peroxidase Mimetic Nanozymes and for the Electrochemical Detection of Histamine. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2022, 908, 116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Hao, M.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, L. Rapid and Ultrasensitive Activity Detection of α-Amylase Based on γ-Cyclodextrin Crosslinked Metal-Organic Framework Nanozyme. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 242, 124881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, S.; Zeng, M.; Xie, H.; Gan, N. Dual-Mode Colorimetric-Electrochemical Biosensor for Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Detection Based on CuO2 Nanodot-Encapsulated Metal-Organic Framework Nanozymes. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2023, 387, 133835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.I.; Olstad, H.E.; García-Torres, R. Stability and Stabilization of Enzyme Biosensors: The Key to Successful Application and Commercialization. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Gorton, L. Enzyme Based Amperometric Biosensors. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry 2018, 10, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitaishi, V.; Clement, R.; Bourassin, N.; Baaden, M.; De Poulpiquet, A.; Sacquin-Mora, S.; Ciaccafava, A.; Lojou, E. Controlling Redox Enzyme Orientation at Planar Electrodes. Catalysts 2018, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemiwal, M.; Zhang, T.C.; Kumar, D. Enzyme Immobilized Nanomaterials as Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of Biomolecules. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 2022, 156, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Nor, N.; Ridhuan, N.S.; Abdul Razak, K. Progress of Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Biosensor Based on Nanomaterial-Modified Electrode. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, N.M.; Singh, S.; Keles, G.; Cinti, S.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Odaci, D. Novel Approaches to Enzyme-Based Electrochemical Nanobiosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinkova, P. Main Streams in the Construction of Biosensors and Their Applications. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 7386–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, Varnakavi. ; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Jiang, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, D. Emerging Electrochemical Biosensing Approaches for Detection of Allergen in Food Samples: A Review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2022, 121, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato-Alvarez, M.; Bernalte, E.; Bernalte-García, M.J.; Pinilla-Gil, E. Fast and Direct Amperometric Analysis of Polyphenols in Beers Using Tyrosinase-Modified Screen-Printed Gold Nanoparticles Biosensors. Talanta 2019, 193, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.S.; Slaughter, G. Lactic Acid Biosensor Based on Lactate Dehydrogenase Immobilized on Au Nanoparticle Modified Microwire Electrode. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo-Comino, C.; Martín-Bartolomé, P.; Pura, J.L.; Perez-Gonzalez, C.; Martin-Pedrosa, F.; García-Cabezón, C.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. Improving the Performance of a Bioelectronic Tongue Using Silver Nanowires: Application to Milk Analysis. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 364, 131877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, O. One-Pot Scalable Synthesis of RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposite and Its Application in Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor. Nanocomposites 2021, 7, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Garkani Nejad, F.; Safaei, M. Recent Advances in ZnO Nanostructure-Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5826–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Maibam, B.; Borah, C.K.; Agarkar, T.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. A Highly Receptive ZnO-Based Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor for Glucose Sensing. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 14601–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Yang, S.; Qiao, X.; Sheng, Q.; Yue, T. DNA Walker-Assisted Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive Determination of Ochratoxin A. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2021, 182, 113171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Jia, R.; Song, Y.; Wang, B. An Ultrasensitive Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor Using Silver Nanoparticle/Titanium Carbide Nanocomposites for the Determination of Staphylococcus Aureus in Milk. Microchim Acta 2022, 189, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Q.; Yang, N. Recent Advances of Porous Graphene: Synthesis, Functionalization, and Electrochemical Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1903780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniselass, S.; Arshad, M.K.M.; Gopinath, S.C.B. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Monitoring Noncommunicable Disease Biomarkers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2019, 130, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Lai, G.; Yu, A. Electroanalysis of Dopamine Using Polydopamine Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide-Gold Nanocomposite. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, Q.; Chu, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Structure Effect on Graphene-Modified Enzyme Electrode Glucose Sensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2014, 52, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Hu, X.; Zeng, R.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Tang, D. CRISPR/Cas12a-Based Photoelectrochemical Sensing of MicroRNA on Reduced Graphene Oxide-Anchored Bi2WO6 Coupling with Catalytic Hairpin Assembly. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 369, 132307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdu, M.; Sandhu, T.; Kaur, N.; Abebe, M.; Olu, F.; Sabherwal, P. Synergetic Effect of Three-in-One Nanocomposite Based on AuNPs and RGO-MWCNTs for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Bio-Diagnostic Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 047513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Patel, M.; Dwivedi, N.; Kumar, P.; Mondal, D.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Dhand, C. Bio-Inspired Polynorepinephrine Based Nanocoatings for Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Composite for High-Performance Biosensing of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Environmental Research 2023, 227, 115684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Fang, M.; Xu, C.; Ying, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, H.-M.; Zeng, Y. A Graphene-Laminated Electrode with High Glucose Oxidase Loading for Highly-Sensitive Glucose Detection. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2021, 66, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Hao, Y.; Ying, Z.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.-M.; Zeng, Y. Controllable Edge Modification of Multi-Layer Graphene for Improved Dispersion Stability and High Electrical Conductivity. Appl Nanosci 2019, 9, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.V.M.; Shin, J.H.; Palakollu, V.N.; Sravani, B.; Choi, C.-H.; Park, K.; Kim, S.-K.; Madhavi, G.; Park, J.P.; Shetti, N.P. Strategies, Advances, and Challenges Associated with the Use of Graphene-Based Nanocomposites for Electrochemical Biosensors. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2022, 304, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Glucose Biosensor Based on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures Electrodeposited on Graphite Electrode by Different Electrochemical Methods. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskiene, L.; Popov, A.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. The Impact of Glucose Oxidase Immobilization on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures on the Performance of Glucose Biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, A.; Aukstakojyte, R.; Gaidukevic, J.; Lisyte, V.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Barkauskas, J.; Ramanaviciene, A. Reduced Graphene Oxide and Polyaniline Nanofibers Nanocomposite for the Development of an Amperometric Glucose Biosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xue, H.; Pang, H. Metal-Organic Frameworks/Graphene-Based Materials: Preparations and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Liao, D.; Aboud, M.F.A.; Shakir, I.; Xu, Y. A Universal Strategy toward Ultrasmall Hollow Nanostructures with Remarkable Electrochemical Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8247–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Chen, W.; Aboud, M.F.A.; Shakir, I.; Gu, J.; Xu, Y. Microwave-Assisted Ultrafast Synthesis of Adjustable Bimetal Phosphide/Graphene Heterostructures from MOFs for Efficient Electrochemical Water Splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 14526–14535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakollu, V.N.; Chen, D.; Tang, J.-N.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. Recent Advancements in Metal-Organic Frameworks Composites Based Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors. Microchim Acta 2022, 189, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, Y. Metal–Covalent Organic Frameworks (MCOFs): A Bridge Between Metal–Organic Frameworks and Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13722–13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Guo, C.; Jia, Q.; Song, Y.; Tian, J.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; He, L.; Du, M. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based Chemosensors/Biosensors for Analysis of Food Contaminants. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 118, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharanyakanth, P.S.; Radhakrishnan, M. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and Its Application in Food Packaging: A Critical Review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2020, 104, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Yang, W. Applications of Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Sensors for Food Safety: Enhancing Mechanisms and Recent Advances. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 112, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Luminescent Metal-Organic Frameworks (LMOFs): An Emerging Sensing Platform for Food Quality and Safety Control. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 111, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Zhu, N.; Wu, Y.; Li, G. Antibacterial Mechanisms and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Derived Nanomaterials. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 109, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Fan, C.; Xu, T.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. An Electrochemical Wearable Sensor for Levodopa Quantification in Sweat Based on a Metal–Organic Framework/Graphene Oxide Composite with Integrated Enzymes. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 359, 131586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, H.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Tang, H.; Xie, Q. Preparation of Novel HKUST-1-Glucose Oxidase Composites and Their Application in Biosensing. Microchim Acta 2023, 190, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Lian, M.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, W. Enzyme Immobilization on ZIF-67/MWCNT Composite Engenders High Sensitivity Electrochemical Sensing. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2019, 833, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Li, M.; Wei, D.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H. Enhanced Activity of Enzyme Encapsulated in Hydrophilic Metal-Organic Framework for Biosensing. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 469, 144067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xu, H.; Carraro, F.; Maddigan, N.K.; Li, Q.; Bell, S.G.; Huang, D.M.; Tarzia, A.; Solomon, M.B.; Amenitsch, H.; et al. Enhanced Activity of Enzymes Encapsulated in Hydrophilic Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X. Confining Natural/Mimetic Enzyme Cascade in an Amorphous Metal-Organic Framework for the Construction of Recyclable Biomaterials with Catalytic Activity. Langmuir 2022, 38, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhangsun, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Carbon Cloth-Supported Nanorod-like Conductive Ni/Co Bimetal MOF: A Stable and High-Performance Enzyme-Free Electrochemical Sensor for Determination of Glucose in Serum and Beverage. Food Chemistry 2021, 349, 129202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, M.; Prasher, P.; Vasić, K.; Leitgeb, M.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, R.; Knez, Ž.; Pandey, J.K.; Kumar, S. Enzyme Modified CNTs for Biosensing Application: Opportunities and Challenges. Colloid and Interface Science Communications 2021, 44, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Jiang, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, D. Emerging Electrochemical Biosensing Approaches for Detection of Allergen in Food Samples: A Review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2022, 121, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jaiswal, N.; Tiwari, I.; Ahmad, M.; Silva, S.R.P. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on in Situ Grown Carbon Nanotubes on Gold Microelectrode Array Fabricated on Glass Substrate for Glucose Determination. Microchim Acta 2023, 190, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Rajeev, R.; Benny, L.; Sudhakar, Y.N.; Varghese, A.; Hegde, G. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanotubes-Based Biocatalysts and Their Applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 297, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Gao, G.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Z. A Hybrid System Integrating Xylose Dehydrogenase and NAD+ Coupled with PtNPs@MWCNTs Composite for the Real-Time Biosensing of Xylose. Analyst 2020, 145, 5563–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, D.; C. R., M.; R.T., R.K. Glucose Oxidase Immobilized Amine Terminated Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polyaniline/Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitive Amperometric Glucose Detection. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2019, 105, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.K.; Ahmad, R.; Mousa, H.M.; Kim, I.-G.; Kim, J.I.; Neupane, M.P.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. High-Performance Glucose Biosensor Based on Chitosan-Glucose Oxidase Immobilized Polypyrrole/Nafion/Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Bio-Nanohybrid Film. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2016, 482, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Alam, M.M.; Aijaz, M.O.; Asiri, A.M.; Dar, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Fabrication of 1,4-Dioxane Sensor Based on Microwave Assisted PAni-SiO2 Nanocomposites. Talanta 2019, 193, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, M. Application of Conducting Polymers to Biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2002, 17, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Kucherenko, D.Yu.; Soldatkina, O.V.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Advances in Nanomaterial Application in Enzyme-Based Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4560–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Rekertaitė, A.I.; Valiūnas, R.; Valiūnienė, A. Single-Step Procedure for the Modification of Graphite Electrode by Composite Layer Based on Polypyrrole, Prussian Blue and Glucose Oxidase. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2017, 240, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Arshi, S.; Magner, E.; Ulstrup, J.; Xiao, X. One-Step Electrochemical Approach of Enzyme Immobilization for Bioelectrochemical Applications. Synthetic Metals 2022, 291, 117205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bi, X.; Tamulevičius, S.; Erts, D.; Chang, C.-F.; Gu, Y. Fabrication of a Biocompatible and Continuous Glucose Biosensor with the Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Modified Electrode. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2019, 104, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, M.; Dervisevic, M.; Esser, L.; Dervisevic, E.; Dyson, J.; Easton, C.D.; Cadarso, V.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Performance by in Situ Electrocopolymerization of Pyrrole and Thiophene-Grafted Chitosan. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 143, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Lei, S.; Amirfazli, A. Unexpected Superhydrophobic Polydopamine on Cotton Fabric. Progress in Organic Coatings 2020, 147, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.; Sen, R.K.; Patel, M.; Shruti; Dwivedi, N. ; Singh, S.; Kumar, P.; Chouhan, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Mondal, D.P.; et al. Development of Copper Impregnated Bio-Inspired Hydrophobic Antibacterial Nanocoatings for Textiles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Jang, M.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. One-Pot Electrochemical Fabrication of High Performance Amperometric Enzymatic Biosensors Using Polypyrrole and Polydopamine. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2021, 97, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Bisht, N.; Prabhakar, P.; Sen, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Dwivedi, N.; Ashiq, M.; Mondal, D.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Dhand, C. Ternary Nanocomposite-Based Smart Sensor: Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polydopamine/Alanine Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Cd2+, Pb2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ Ions. Environmental Research 2023, 221, 115317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.-Y.; Kim, H.-H.; Choi, Y.-B. Development of a Glucose Sensor Based on Glucose Dehydrogenase Using Polydopamine-Functionalized Nanotubes. Membranes 2021, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nan, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ge, D. A Glucose Biosensor Based on the Immobilization of Glucose Oxidase and Au Nanocomposites with Polynorepinephrine. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 16439–16446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoneschi, V.; Palladino, P.; Banchini, M.; Minunni, M.; Scarano, S. Norepinephrine as New Functional Monomer for Molecular Imprinting: An Applicative Study for the Optical Sensing of Cardiac Biomarkers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2020, 157, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Teo, B.M.; Tabor, R.F. Recent Developments in Polynorepinephrine: An Innovative Material for Bioinspired Coatings and Colloids. J. Mat. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7895–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, S.; Alam, F.; Khakpour, I.; Baboukani, A.R.; Pala, N.; Wang, C. Highly Sensitive Lactic Acid Biosensors Based on Photoresist Derived Carbon. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 8965–8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Gorton, L. Enzyme Based Amperometric Biosensors. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry 2018, 10, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Bückmann, A.F.; Willner, I. Self-Powered Enzyme-Based Biosensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 10752–10753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyou, P.; Blay, V.; Muresan, L.M.; Noguer, T. Enzyme-Modified Electrodes for Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1336–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Hahn, Y.K.; Kim, M.S. Recent Advances of Fluid Manipulation Technologies in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (ΜPADs) toward Multi-Step Assays. Micromachines 2020, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M. An Origami Paper-Based Analytical Device for Rapid and Sensitive Analysis of Acrylamide in Foods. Micromachines 2021, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. A Microfluidic PET-Based Electrochemical Glucose Sensor. Micromachines 2022, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagkali, V.; Soulis, D.; Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A. Fully Drawn Electrochemical Paper-Based Glucose Biosensors Fabricated by a High-Throughput Dual-Step Pen-on-Paper Approach with Commercial Writing Stationery. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 358, 131546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).