Submitted:
17 August 2023
Posted:
18 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
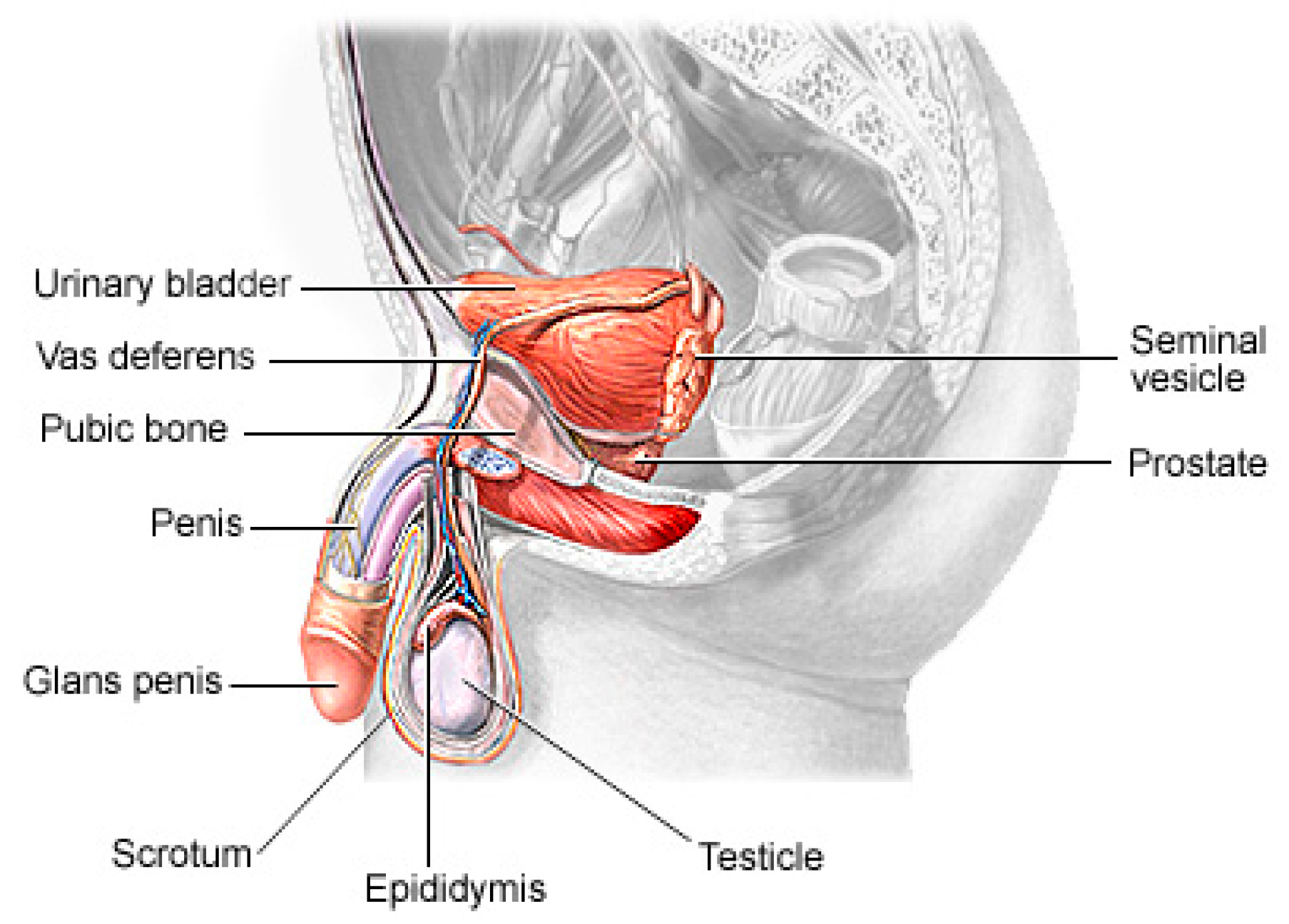
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Scope of Review
| RQ1: | What are the trends and evolutions of this study? |
| RQ2: | What ML and DL models are used for this study? |
| RQ3: | What datasets are publicly available? |
| RQ4: | What are the necessary considerations for application of these artificial intelligence (AI) techniques in PCa diagnosis? |
| RQ5: | What are the limitations so far identified by authors? |
| RQ6: | What are the future directions for this research? |
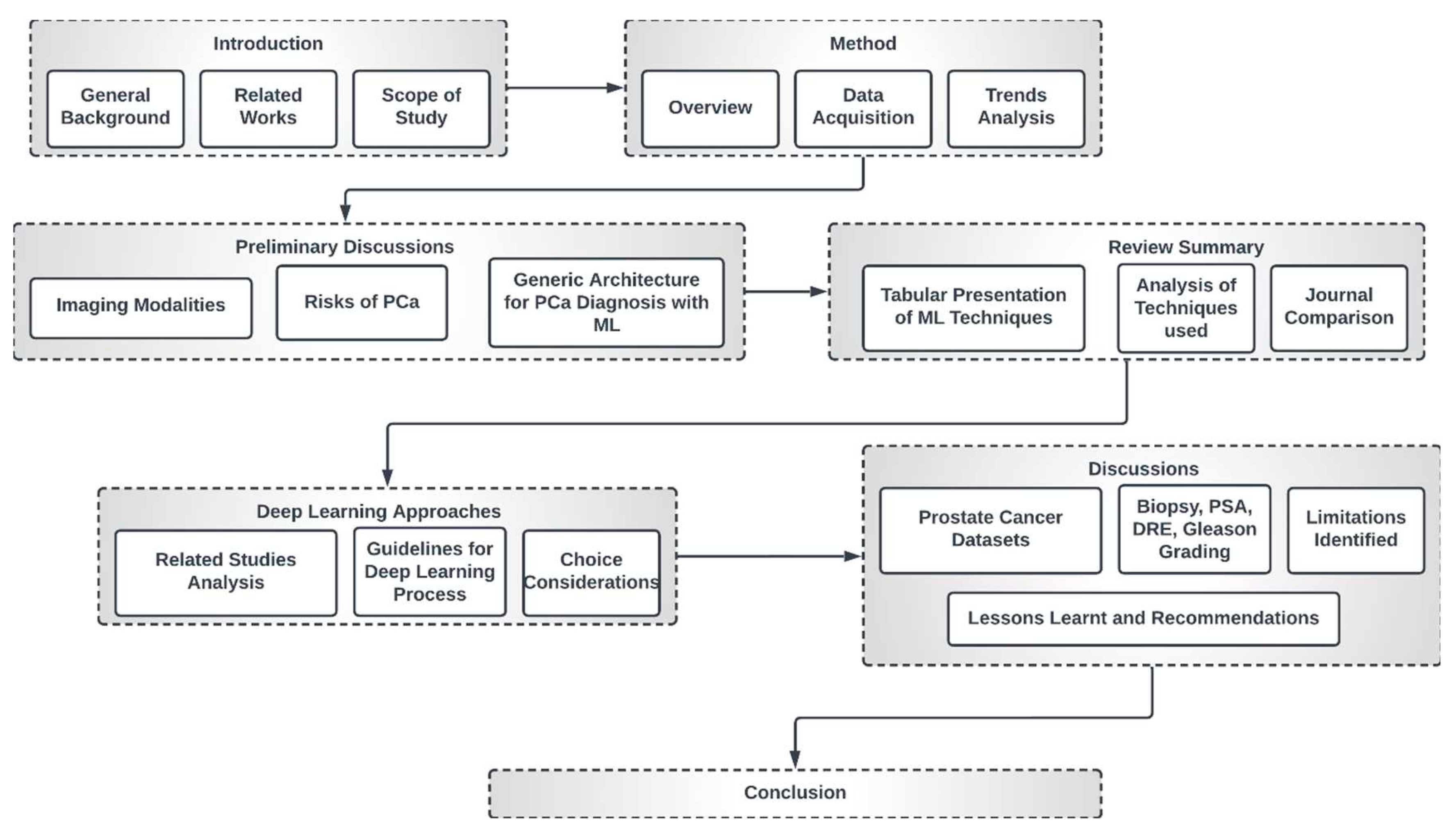
1.3. High-Level Structure of this Study
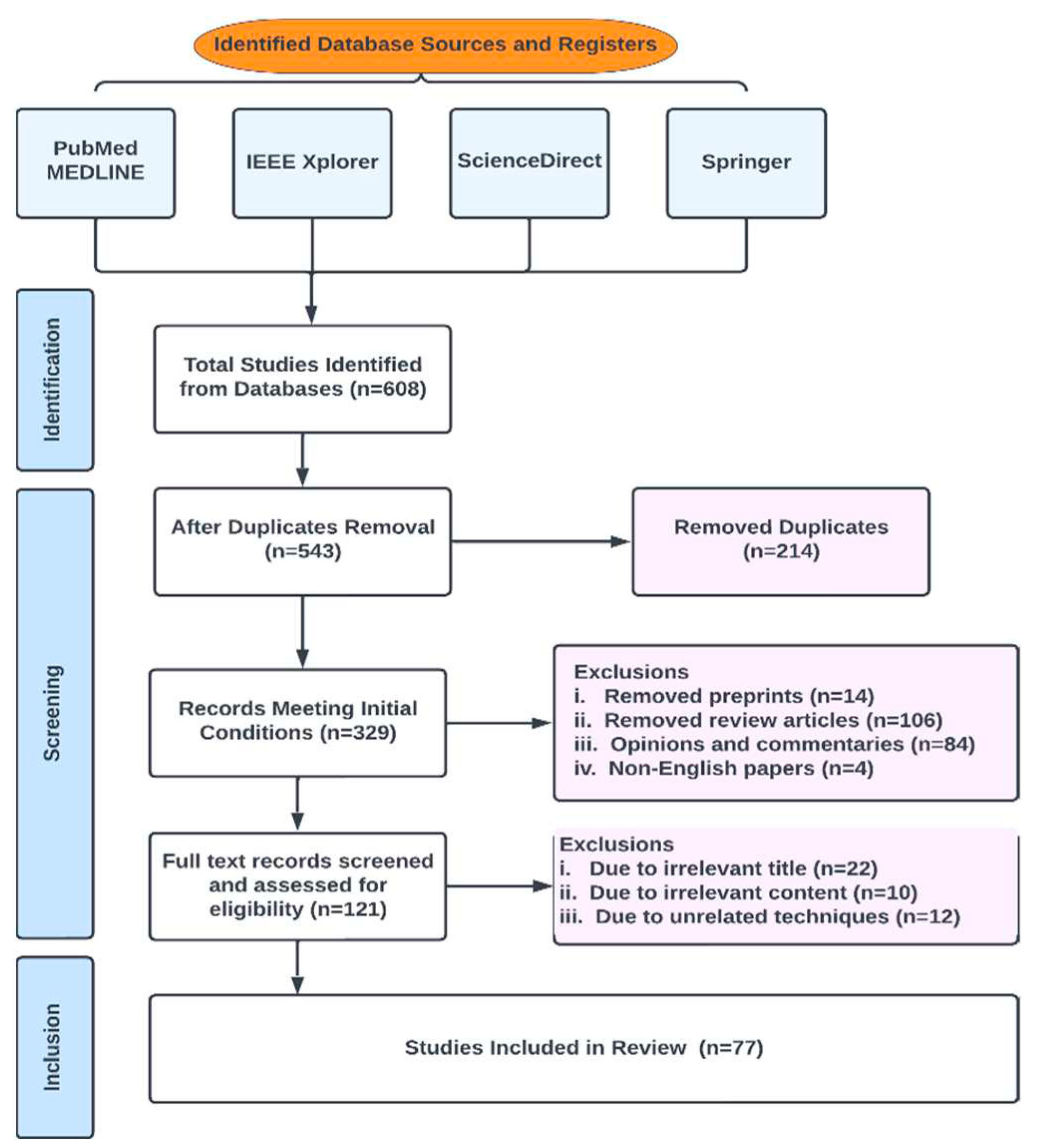
2. Methods
2.1. Database Search and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Review Strategy
- Results for (a): Deep Learning Machine Learning Significant Prostate Cancer Artificial Intelligence Prediction Diagnosis
- Results of (b): Prediction/Diagnosis/Classification Machine/Deep Prostate Cancer/PCa/csPCa
- Results for (c): review, systematic review, preprint, risk factor, treatment, biopsy, gleason grading, DRE
- Result (d): a, b, c combined using AND OR.
2.3. Characteristics of Studies
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.6. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.7. Data Extraction
3. Preliminary Discussions
3.1. Imaging Modalities
3.2. Risks of PCa
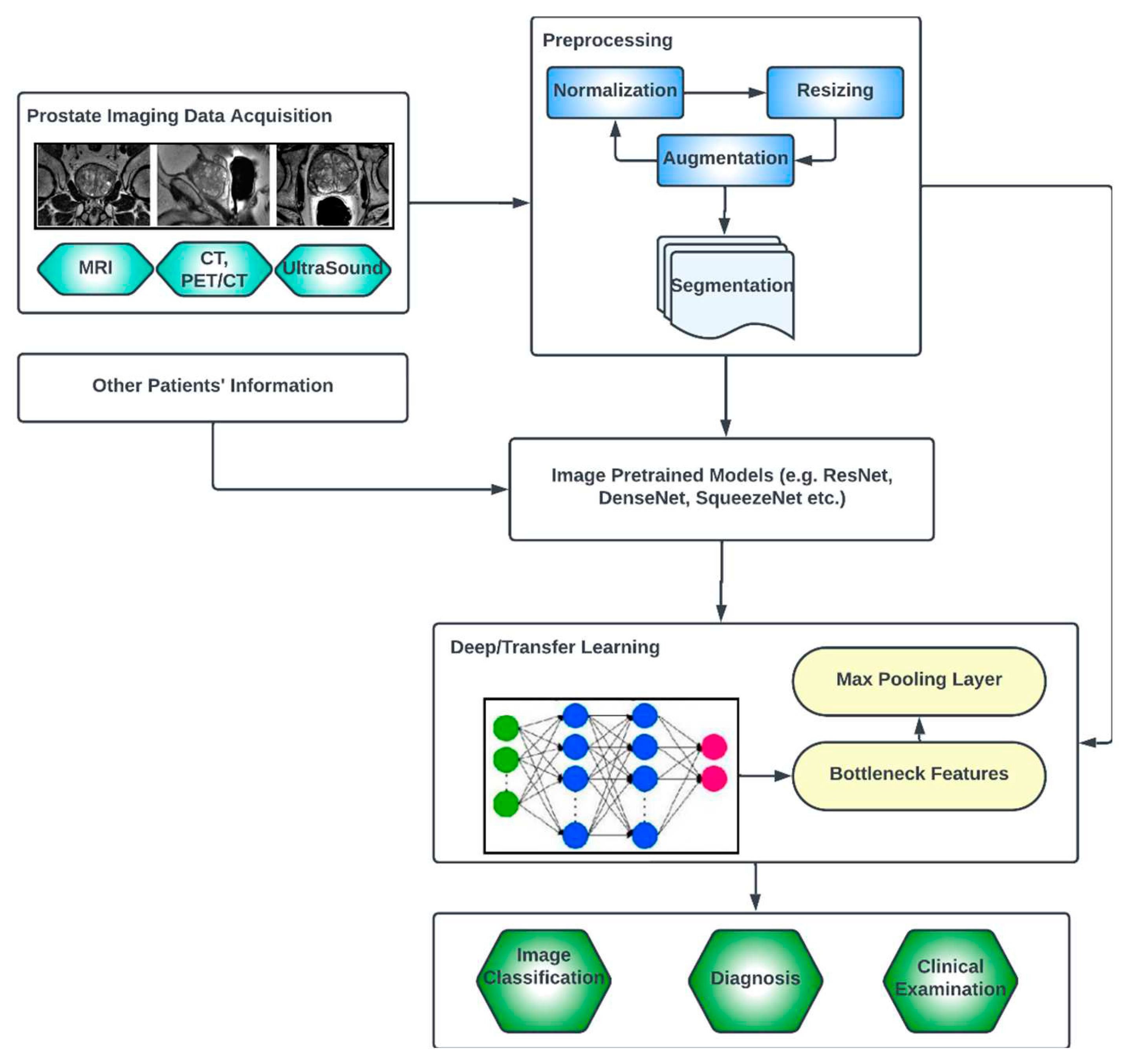
3.3. Generic Overview of Deep Learning Architecture for PCa Diagnosis
4. Results
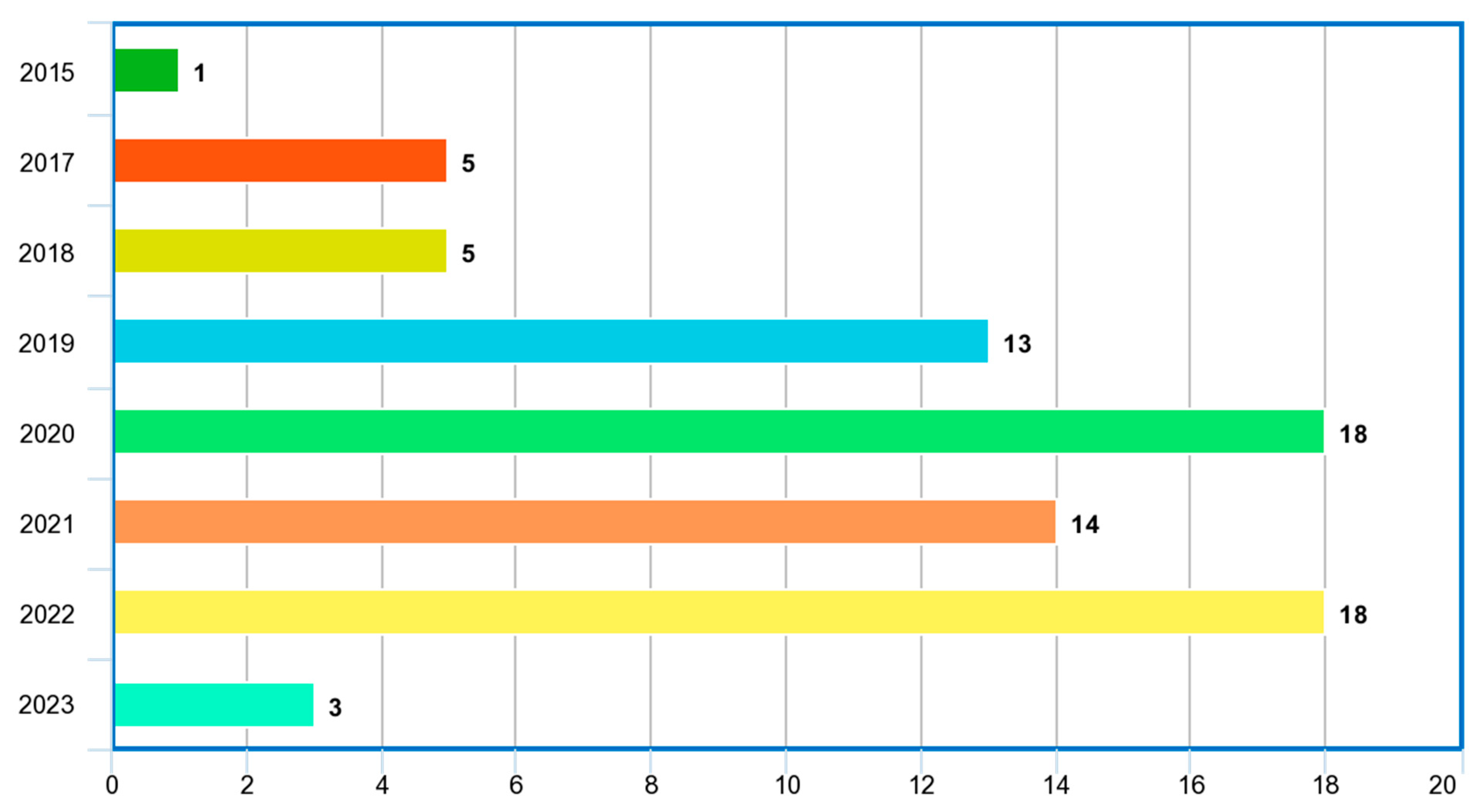
4.1. Review Summary of Relevant Papers
5. Discussion
5.1. Considerations for Choice of Deep Learning for PCa Image Data Analysis
5.2. Considerations for Choice of Loss Functions for PCa Image Data Analysis
5.3. Prostate Cancer Datasets
5.4. Some Important Limitations Discussed in Literature
5.5. Lessons Learned and Recommendations
6. Conclusion
References
- Litwin, M.S. and H.-J. Tan, The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer: a review. Jama, 2017. 317(24): p. 2532-2542.
- Rawla, P., Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World journal of oncology, 2019. 10(2): p. 63.
- Akinnuwesi, B.A.; Olayanju, K.A.; Aribisala, B.S.; Fashoto, S.G.; Mbunge, E.; Okpeku, M.; Owate, P. Application of support vector machine algorithm for early differential diagnosis of prostate cancer. J. Inf. Technol. Data Manag. 2023, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenigbara, I.O. Risk-Reducing Measures for Cancer Prevention. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2023, 44, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musekiwa, A.; Moyo, M.; Mohammed, M.; Matsena-Zingoni, Z.; Twabi, H.S.; Batidzirai, J.M.; Singini, G.C.; Kgarosi, K.; Mchunu, N.; Nevhungoni, P.; et al. Mapping Evidence on the Burden of Breast, Cervical, and Prostate Cancers in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Scoping Review. Front. Public Heal. 2022, 10, 908302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.C. and J.F. Worthington, Dr. Patrick Walsh's guide to surviving prostate cancer. 2010: Grand Central Life & Style.
- Hayes, R.B.; Pottern, L.M.; Strickler, H.; Rabkin, C.; Pope, V.; Swanson, G.M.; Greenberg, R.S.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Liff, J.; Schwartz, A.G.; et al. Sexual behaviour, STDs and risks for prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plym, A.; Zhang, Y.; Stopsack, K.H.; Delcoigne, B.; Wiklund, F.; Haiman, C.; Kenfield, S.A.; Kibel, A.S.; Giovannucci, E.; Penney, K.L.; et al. A Healthy Lifestyle in Men at Increased Genetic Risk for Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2023, 83, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, C.L.; Thomson, C.A.; Sullivan, K.R.; Howe, C.L.; Kushi, L.H.; Caan, B.J.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Bandera, E.V.; Wang, Y.; Robien, K.; et al. American Cancer Society nutrition and physical activity guideline for cancer survivors. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 230–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, R.; Fontham, E.T.H.; Ermilo Barrera, E.B., Jr; Colditz, G.; Church, T.R.; Ettinger, D.S.; Etzioni, R.; Flowers, C.R.; Gazelle, G.S.; Kelsey, D.K.; et al. American Cancer Society lung cancer screening guidelines. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.D.; Wender, R.C.; Etzioni, R.B.; Thompson, I.M.; D'Amico, A.V.; Volk, R.J.; Brooks, D.D.; Dash, C.; Guessous, I.; Andrews, K.; et al. American Cancer Society Guideline for the Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: Update 2010. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 70–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadi, R.; Taher, F.; El-Baz, A.; Werghi, N. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for the Detection and Localization of Prostate Cancer in T2 Magnetic Resonance Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2018, 32, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Uehara, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Kijima, T.; Yoshida, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Saito, K.; Kihara, K.; Numao, N.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer on magnetic resonance imaging using a convolutional neural network algorithm. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, I.; Shalaby, A.; El-Ghar, M.A.; Khalifa, F.; Elmogy, M.; Aboulfotouh, A.; Hosseini-Asl, E.; El-Baz, A.; Keynton, R. A new NMF-autoencoder based CAD system for early diagnosis of prostate cancer. 2016, 1237–1240. [CrossRef]
- Wildeboer, R.R.; van Sloun, R.J.; Wijkstra, H.; Mischi, M. Artificial intelligence in multiparametric prostate cancer imaging with focus on deep-learning methods. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 189, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aribisala, B. and O. Olabanjo, Medical image processor and repository–mipar. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2018. 12: p. 75-80.
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.-I. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; An, X. A classification model for the prostate cancer based on deep learning. 2017, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Weinreb, J.; Han, J.; Li, Q.; Kong, X.; Yan, Y.; Ke, Z.; Luo, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Searching for prostate cancer by fully automated magnetic resonance imaging classification: deep learning versus non-deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Ibarrola, R.; Hein, S.; Reis, G.; Gratzke, C.; Miernik, A. Current and future applications of machine and deep learning in urology: a review of the literature on urolithiasis, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder and prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2019, 38, 2329–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, G.; Tavares, J.M.R. Deep Learning in Radiation Oncology Treatment Planning for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Med Syst. 2020, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Yahya, N.; Alsaih, K.; Al-Hiyali, M.I.; Meriaudeau, F. Recent Automatic Segmentation Algorithms of MRI Prostate Regions: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 97878–97905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roest, C.; Fransen, S.J.; Kwee, T.C.; Yakar, D. Comparative Performance of Deep Learning and Radiologists for the Diagnosis and Localization of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer at MRI: A Systematic Review. Life 2022, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo T, J.M., et al., Automated classification of significant prostate cancer on MRI: a systematic review on the performance of machine learning applications. Cancers, 2020. 12(6): p. 1606.
- Michaely, H.J.; Aringhieri, G.; Cioni, D.; Neri, E. Current Value of Biparametric Prostate MRI with Machine-Learning or Deep-Learning in the Detection, Grading, and Characterization of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.; Tokas, T.; Shetty, D.K.; Hameed, B.Z.; Shastri, S.; Shah, M.J.; Ibrahim, S.; Rai, B.P.; Chłosta, P.; Somani, B.K. Role of Deep Learning in Prostate Cancer Management: Past, Present and Future Based on a Comprehensive Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis-Onofre, R.; Catalá-López, F.; Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C. How to properly use the PRISMA Statement. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hricak, H.; Choyke, P.L.; Eberhardt, S.C.; Leibel, S.A.; Scardino, P.T. Imaging Prostate Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Perspective. Radiology 2007, 243, 28–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, K.Y. and H. Hricak, Imaging prostate cancer. Radiologic Clinics of North America, 2000. 38(1): p. 59-85.
- Cornud, F.; Brolis, L.; Delongchamps, N.B.; Portalez, D.; Malavaud, B.; Renard-Penna, R.; Mozer, P. TRUS–MRI image registration: a paradigm shift in the diagnosis of significant prostate cancer. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynier, C.; Troccaz, J.; Fourneret, P.; Dusserre, A.; Gay-Jeune, C.; Descotes, J.; Bolla, M.; Giraud, J. MRI/TRUS data fusion for prostate brachytherapy. Preliminary results. Med Phys. 2004, 31, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasch, C.; Barillot, I.; Remeijer, P.; Touw, A.; van Herk, M.; Lebesque, J.V. Definition of the prostate in CT and MRI: a multi-observer study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 43, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezaro, C.; Woo, H.H.; Davis, I.D. Prostate cancer: measuring PSA. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Inoue, T.; Lee, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Shizukuishi, K. The Roles of PET and PET/CT in the Diagnosis and Management of Prostate Cancer. Oncology 2007, 72, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturge, J., M.P. Caley, and J. Waxman, Bone metastasis in prostate cancer: emerging therapeutic strategies. Nature reviews Clinical oncology, 2011. 8(6): p. 357.
- Raja, J.; Ramachandran, N.; Munneke, G.; Patel, U. Current status of transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2006, 61, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Xia, W.; Ji, X.; He, D.; Zhao, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Peritumoral Radiomics for Preoperative Prediction of the Presence of Extracapsular Extension With Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, B.H., et al. Adding multiparametric MRI to the MSKCC and Partin nomograms for primary prostate cancer: Improving local tumor staging? in Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations. 2019. Elsevier.
- Maurer, T.; Eiber, M.; Schwaiger, M.; Gschwend, J.E. Current use of PSMA–PET in prostate cancer management. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrinides, V.; Papageorgiou, G.; Danks, D.; Giganti, F.; Pashayan, N.; Trock, B.; Freeman, A.; Hu, Y.; Whitaker, H.; Allen, C.; et al. Mapping PSA density to outcome of MRI-based active surveillance for prostate cancer through joint longitudinal-survival models. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchsjäger, M., et al., Prostate cancer imaging. Acta Radiologica, 2008. 49(1): p. 107-120.
- Ghafoor, S.; Burger, I.A.; Vargas, A.H. Multimodality Imaging of Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, S.; Roberts, W.W.; Walsh, P.C.; Platz, E.A. Family history of prostate cancer and obesity in relation to high-grade disease and extraprostatic extension in young men with prostate cancer. Prostate 2003, 55, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, M.P.; Stanford, J.L. Obesity and the risk of prostate cancer. Prostate 2004, 62, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gann, P.H., Risk factors for prostate cancer. Reviews in urology, 2002. 4(Suppl 5): p. S3.
- Tian, W. and M. Osawa, Prevalent latent adenocarcinoma of the prostate in forensic autopsies. Journal of Clinical Pathology and Forensic Medicine, 2015. 6(3): p. 11-13.
- Marley, A.R. and H. Nan, Epidemiology of colorectal cancer. International journal of molecular epidemiology and genetics, 2016. 7(3): p. 105.
- Kumagai, H.; Zempo-Miyaki, A.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tsujimoto, T.; Tanaka, K.; Maeda, S. Lifestyle modification increases serum testosterone level and decrease central blood pressure in overweight and obese men. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Moyad, M. Is obesity a risk factor for prostate cancer, and does it even matter? A hypothesis and different perspective. Urology 2002, 59, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikesit, D., et al., The impact of obesity towards prostate diseases. Prostate international, 2016. 4(1): p. 1-6.
- Tse, L.A.; Lee, P.M.Y.; Ho, W.M.; Lam, A.T.; Lee, M.K.; Ng, S.S.M.; He, Y.; Leung, K.-S.; Hartle, J.C.; Hu, H.; et al. Bisphenol A and other environmental risk factors for prostate cancer in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, V.; Naidu, V.; Kao, C.H.-J.; Karunasinghe, N.; Bishop, K.S.; Wang, A.; Pallati, R.; Shepherd, P.; Masters, J.; Zhu, S.; et al. Environmental factors and risk of aggressive prostate cancer among a population of New Zealand men – a genotypic approach. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S., et al., Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2021. 44(7): p. 3523-3542.
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, D.; Jing, H.; Li, S.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; et al. Evaluating the Accuracy of Breast Cancer and Molecular Subtype Diagnosis by Ultrasound Image Deep Learning Model. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S. Transfer learning using VGG-16 with Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Classifying Images. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. (IJSRP) 2019, 9, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christlein, V., et al. Deep generalized max pooling. in 2019 International conference on document analysis and recognition (ICDAR). 2019. IEEE.
- Sharma, S., S. Sharma, and A. Athaiya, Activation functions in neural networks. Towards Data Sci, 2017. 6(12): p. 310-316.
- Sibi, P., S.A. Jones, and P. Siddarth, Analysis of different activation functions using back propagation neural networks. Journal of theoretical and applied information technology, 2013. 47(3): p. 1264-1268.
- Fu, J.; Zheng, H.; Mei, T. Look Closer to See Better: Recurrent Attention Convolutional Neural Network for Fine-Grained Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4476–4484. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Schütze, H.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, B. ABCNN: Attention-Based Convolutional Neural Network for Modeling Sentence Pairs. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguistics 2016, 4, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora, S.; Marini, N.; Müller, H.; Atzori, M. Semi-weakly Supervised Learning for Prostate Cancer Image Classification with Teacher-Student Deep Convolutional Networks. 2020, 193–203. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Bao, J.; Qiao, X.; Jin, P.; Ji, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Ji, L.; Shen, J.; et al. Predicting clinically significant prostate cancer with a deep learning approach: a multicentre retrospective study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 50, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, L.; Spielvogel, C.P.; Grubmüller, B.; Grahovac, M.; Krajnc, D.; Ecsedi, B.; Sareshgi, R.A.; Mohamad, D.; Hamboeck, M.; Rausch, I.; et al. Supervised machine learning enables non-invasive lesion characterization in primary prostate cancer with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 48, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildeboer, R.R.; Mannaerts, C.K.; van Sloun, R.J.G.; Budäus, L.; Tilki, D.; Wijkstra, H.; Salomon, G.; Mischi, M. Automated multiparametric localization of prostate cancer based on B-mode, shear-wave elastography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Gujrathi, I.; Haider, M.A.; Khalvati, F. Prostate Cancer Detection using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Bao, M.-L.; Wu, C.-J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Shi, H.-B. A radiomics machine learning-based redefining score robustly identifies clinically significant prostate cancer in equivocal PI-RADS score 3 lesions. Abdom. Imaging 2020, 45, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.; Mirchandani, R.; Papa, N.; Breemer, G.; Effeindzourou, A.; Smith, L.; Swindle, P.; Smith, E. PSA-based machine learning model improves prostate cancer risk stratification in a screening population. World J. Urol. 2020, 39, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderska-Chadaj, Z.; de Bel, T.; Blanchet, L.; Baidoshvili, A.; Vossen, D.; van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G. Impact of rescanning and normalization on convolutional neural network performance in multi-center, whole-slide classification of prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.A.H.; Stürenberg, C.; Gencoglu, O.; Sandeman, K.; Heikkinen, T.; Rannikko, A.; Mirtti, T. Improving Prostate Cancer Detection with Breast Histopathology Images. 2019, 91–99. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Imani, F.; Zhuang, B.; Tahmasebi, A.; Kwak, J.T.; Xu, S.; Uniyal, N.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Pinto, P.; et al. Ultrasound-Based Detection of Prostate Cancer Using Automatic Feature Selection with Deep Belief Networks. 2015, 70–77. 2015; 77. [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, A.; Mehrtash, A.; Jamzad, A.; Amalou, A.; Wells, W.M.; Kapur, T.; Kwak, J.T.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Pinto, P.; et al. Improving detection of prostate cancer foci via information fusion of MRI and temporal enhanced ultrasound. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, N.; Sibille, L.; Chantadisai, M.; Gafita, A.; Langbein, T.; Platsch, G.; Solari, E.L.; Shah, V.; Spottiswoode, B.; Eiber, M.; et al. Whole-body uptake classification and prostate cancer staging in 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT using dual-tracer learning. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 49, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniffel, D.; Abraham, N.; Namdar, K.; Dong, X.; Salinas, E.; Milot, L.; Khalvati, F.; Haider, M.A. Using decision curve analysis to benchmark performance of a magnetic resonance imaging–based deep learning model for prostate cancer risk assessment. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6867–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleker, J.; Kwee, T.C.; Rouw, D.; Roest, C.; Borstlap, J.; de Jong, I.J.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Huisman, H.; Yakar, D. A deep learning masked segmentation alternative to manual segmentation in biparametric MRI prostate cancer radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6526–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X., et al. Deep attentive panoptic model for prostate cancer detection using biparametric MRI scans. in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part IV 23. 2020. Springer. 4 October.
- Korevaar, S.; Tennakoon, R.; Page, M.; Brotchie, P.; Thangarajah, J.; Florescu, C.; Sutherland, T.; Kam, N.M.; Bab-Hadiashar, A. Incidental detection of prostate cancer with computed tomography scans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, K., et al., Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer. NPJ digital medicine, 2019. 2(1): p. 48.
- Tolkach, Y.; Dohmgörgen, T.; Toma, M.; Kristiansen, G. High-accuracy prostate cancer pathology using deep learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, N.; Soni, S.; Bonthu, S.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Samanta, P.; Joshi, U.; Jojera, A.; Chharchhodawala, T.; Agarwal, A.; Desai, M.; et al. A deep learning system for prostate cancer diagnosis and grading in whole slide images of core needle biopsies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, M.; Lianas, L.; Aspegren, O.; Busonera, G.; Versaci, F.; Zelic, R.; Vincent, P.H.; Leo, S.; Pettersson, A.; Akre, O.; et al. AI Support for Accelerating Histopathological Slide Examinations of Prostate Cancer in Clinical Studies. 2022, 545–556. [CrossRef]
- Gour, M.; Jain, S.; Shankar, U. Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Prostate Cancer Grading Using Histopathological Images. 2022, 83–94. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Lim, D.S.; Aung, H.L.; Liu, X.; Seetharaman, A.; Kunder, C.A.; Shao, W.; Soerensen, S.J.C.; Fan, R.E.; Ghanouni, P.; et al. Bridging the gap between prostate radiology and pathology through machine learning. Med Phys. 2022, 49, 5160–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Islam, F.; Uddin, Z.; Ghoshal, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Huda, S.; Fortino, G. Prostate cancer classification from ultrasound and MRI images using deep learning based Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 127, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cheng, J.; Guo, D.; He, X.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, C. Prediction of prostate cancer aggressiveness with a combination of radiomics and machine learning-based analysis of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 896–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, M.; Bosco, M.; Molinaro, L.; Gambella, A.; Papotti, M.; Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F. A hybrid deep learning approach for gland segmentation in prostate histopathological images. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 115, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.E.; Çakar, G. .; Azimjonov, J.; Kösem, M.; Cedi̇moğlu,.H. Automated prostate cancer grading and diagnosis system using deep learning-based Yolo object detection algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Cuocolo, R.; Cocozza, S.; Romeo, V.; Persico, F.; Fusco, F.; Longo, N.; Brunetti, A.; Imbriaco, M. Detection of Extraprostatic Extension of Cancer on Biparametric MRI Combining Texture Analysis and Machine Learning: Preliminary Results. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Lu, X. Deep learning framework based on integration of S-Mask R-CNN and Inception-v3 for ultrasound image-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 114, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Huan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhe, X. A new approach to diagnosing prostate cancer through magnetic resonance imaging. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 60, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinovic, M.; Milicevic, B.; Jankovic, S. Improved predictive performance of prostate biopsy collaborative group risk calculator when based on automated machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 138, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElKarami, B.; Deebajah, M.; Polk, S.; Peabody, J.; Shahrrava, B.; Menon, M.; Alkhateeb, A.; Alanee, S. Machine learning-based prediction of upgrading on magnetic resonance imaging targeted biopsy in patients eligible for active surveillance. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2022, 40, 191–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Kong, G.; Li, M.; Liang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, C.; et al. Ultrasonographic pathological grading of prostate cancer using automatic region-based Gleason grading network. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2022, 102, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambarde, P.; Talbar, S.; Mahajan, A.; Chavan, S.; Thakur, M.; Sable, N. Prostate lesion segmentation in MR images using radiomics based deeply supervised U-Net. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksson, L.J.; Repetto, M.; Summers, P.E.; Pepa, M.; Zaffaroni, M.; Vincini, M.G.; Corrao, G.; Mazzola, G.C.; Rotondi, M.; Bellerba, F.; et al. High-performance prediction models for prostate cancer radiomics. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Weng, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; et al. Support Vector Machines (SVM) classification of prostate cancer Gleason score in central gland using multiparametric magnetic resonance images: A cross-validated study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 98, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Banh, L.; Kunder, C.A.; Fan, R.E.; Soerensen, S.J.; Wang, J.B.; Teslovich, N.C.; Madhuripan, N.; Jawahar, A.; Ghanouni, P.; et al. ProsRegNet: A deep learning framework for registration of MRI and histopathology images of the prostate. Med Image Anal. 2020, 68, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., et al., Stacking-based ensemble learning of decision trees for interpretable prostate cancer detection. Applied Soft Computing, 2019. 77: p. 188-204.
- Bhattacharya, I.; Seetharaman, A.; Kunder, C.; Shao, W.; Chen, L.C.; Soerensen, S.J.; Wang, J.B.; Teslovich, N.C.; Fan, R.E.; Ghanouni, P.; et al. Selective identification and localization of indolent and aggressive prostate cancers via CorrSigNIA: an MRI-pathology correlation and deep learning framework. Med Image Anal. 2021, 75, 102288–102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Huisman, H. End-to-end prostate cancer detection in bpMRI via 3D CNNs: Effects of attention mechanisms, clinical priori and decoupled false positive reduction. Med Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigui, R.; Mitéran, J.; Walker, P.; Sellami, L.; Ben Hamida, A. Automatic classification and localization of prostate cancer using multi-parametric MRI/MRS. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2017, 31, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y. Medical image segmentation and reconstruction of prostate tumor based on 3D AlexNet. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 200, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Cai, W.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D.D. Atlas registration and ensemble deep convolutional neural network-based prostate segmentation using magnetic resonance imaging. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Oka, R.; Xuan, P.; Yoshimura, Y.; Nakaguchi, T. Robust multi-modal prostate cancer classification via feature autoencoder and dual attention. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2022, 30, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsanis, A.; Sunoqrot, M.R.; Langørgen, S.; Wang, H.; Selnæs, K.M.; Bertilsson, H.; Bathen, T.F.; Elschot, M. A comparison of Generative Adversarial Networks for automated prostate cancer detection on T2-weighted MRI. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2023, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.; Nair, M.S. Automated grading of prostate cancer using convolutional neural network and ordinal class classifier. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2019, 17, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Sofue, K.; Murakami, T.; Yoneyama, M.; Obara, M.; Van Cauteren, M. Application of hierarchical clustering to multi-parametric MR in prostate: Differentiation of tumor and normal tissue with high accuracy. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 74, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Le Min, H.; Wang, L.; Cheng, K.-T. (. Co-trained convolutional neural networks for automated detection of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI. Med Image Anal. 2017, 42, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; La Civita, E.; Della Ventura, B.; Ferro, M.; Cennamo, M.; Bruzzese, D.; Crocetto, F.; Velotta, R.; Terracciano, D. A Combinatorial Neural Network Analysis Reveals a Synergistic Behaviour of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance and Prostate Health Index in the Identification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, e406–e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.A.; Mercaldo, S.; Chung, R.; Ulrich, E.; Jones, R.W.; Harisinghani, M. Improving Prostate Cancer Detection With MRI: A Multi-Reader, Multi-Case Study Using Computer-Aided Detection (CAD). Acad. Radiol. 2022, 30, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otálora, S.; Atzori, M.; Khan, A.; Jimenez-Del-Toro, O.; Andrearczyk, V.; Müller, H. A systematic comparison of deep learning strategies for weakly supervised Gleason grading. 2020, 11320, 113200L. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M., et al. A machine learning classification technique for predicting prostate cancer. in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT). 2020. IEEE.
- Feng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Tang, F.; Ren, F.; Guo, J.; Ji, S. A Deep Learning Approach for Targeted Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Based Prostate Cancer Detection. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vente, C.; Vos, P.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Pluim, J.; Veta, M. Deep Learning Regression for Prostate Cancer Detection and Grading in Bi-Parametric MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Siddiqui, G.F.; Rehman, A.; Hussain, L.; Saba, T.; Tariq, U.; Abbasi, A.A. Prostate Cancer Detection Using Deep Learning and Traditional Techniques. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 27085–27100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Lopez, L.; Dominguez-Morales, J.P.; Conde-Martin, A.F.; Vicente-Diaz, S.; Linares-Barranco, A. PROMETEO: A CNN-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for WSI Prostate Cancer Detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 128613–128628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Kucharczyk, M.J.; Desrosiers, C.; Okuwobi, I.P.; Katib, Y.; Zhang, M.; Rathore, S.; Sargos, P.; Niazi, T. Deep Radiomic Analysis to Predict Gleason Score in Prostate Cancer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 167767–167778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Cheng, D.; Wanga, L.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.-T. Automated Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in mp-MRI Images Based on an End-to-End Deep Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 37, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Sarma, K.V.; Ho, K.C.; Shen, S.; Knudsen, B.S.; Gertych, A.; Arnold, C.W. Path R-CNN for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Gleason Grading of Histological Images. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiratchawa, K., et al. Training Deep CNN's to Detect Prostate Cancer Lesion with Small Training Data. in 2022 37th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC). 2022. IEEE.
- Reda, I., et al. A new CNN-based system for early diagnosis of prostate cancer. in 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018). 2018. IEEE.
- Cao, R.; Bajgiran, A.M.; Mirak, S.A.; Shakeri, S.; Zhong, X.; Enzmann, D.; Raman, S.; Sung, K. Joint Prostate Cancer Detection and Gleason Score Prediction in mp-MRI via FocalNet. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2019, 38, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.A., M.H. Hamoud, and A.A. Alsabri. Detection of Prostate Cancer Using MRI Images Classification with Deep Learning Techniques. in 2022 2nd International Conference on Emerging Smart Technologies and Applications (eSmarTA). 2022. IEEE.
- Castillo, J.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Niessen, W.J.; Schoots, I.; Klein, S.; Veenland, J.F. Classification Of Prostate Cancer: High Grade Versus Low Grade Using A Radiomics Approach. 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019) Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019, 1319–1322. 8–11 April. [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, T.; Hamey, L.G.C.; Ho-Shon, K. Convolutional Neural Networks for Prostate Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36748–36760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.C.; Chan, D.Y.; Chen, H.; Palmeri, M.L.; Polascik, T.J.; Foo, W.-C.; Huang, J.; Mamou, J.; Nightingale, K.R. Multiparametric Ultrasound for the Targeting of Prostate Cancer using ARFI, SWEI, B-mode, and QUS. 2019, 880–883. [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, E.; Mercatelli, L.; Marzi, C.; Pachetti, E.; Baccini, M.; Barucci, A.; Colantonio, S.; Gherardini, L.; Lattavo, L.; Pascali, M.A.; et al. Machine and Deep Learning Prediction Of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness Using Multiparametric MRI. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 802964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Park, J.H.; Yoo, S.; D’imperio, N.; McMahon, B.H.; Rentsch, C.T.; Tate, J.P.; Justice, A.C. Survival analysis of localized prostate cancer with deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.A.; Hussain, L.; Awan, I.A.; Abbasi, I.; Majid, A.; Nadeem, M.S.A.; Chaudhary, Q.-A. Detecting prostate cancer using deep learning convolution neural network with transfer learning approach. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2020, 14, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, A.; Shiradkar, R.; Fu, P.; Mahran, A.; Rastinehad, A.R.; Tewari, A.; Tirumani, S.H.; Purysko, A.; Ponsky, L.; Madabhushi, A. An integrated nomogram combining deep learning, Prostate Imaging–Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scoring, and clinical variables for identification of clinically significant prostate cancer on biparametric MRI: a retrospective multicentre study. Lancet Digit. Heal. 2021, 3, e445–e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehralivand, S.; Yang, D.; Harmon, S.A.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Roth, H.; Masoudi, S.; Kesani, D.; Lay, N.; Merino, M.J.; et al. Deep learning-based artificial intelligence for prostate cancer detection at biparametric MRI. Abdom. Imaging 2022, 47, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Saha, A.; Brand, P.; Slootweg, I.; de Rooij, M.; Huisman, H. Deep learning–assisted prostate cancer detection on bi-parametric MRI: minimum training data size requirements and effect of prior knowledge. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 32, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, P.; Lysandrou, M.; Eljalby, M.; Li, Q.; Kazemi, E.; Zisimopoulos, P.; Sigaras, A.; Brendel, M.; Barnes, J.; Ricketts, C.; et al. A Deep Learning Approach to Diagnostic Classification of Prostate Cancer Using Pathology–Radiology Fusion. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Hattori-Kato, M.; Okuno, Y.; Iwai, S.; Mikami, K. Prediction of prostate cancer by deep learning with multilayer artificial neural network. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2018, 13, E145–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.; Khan, I.R.; Babu, K.S.; Nasrullah, S.; Madduri, A.; Rahin, S.A. Light Weighted Healthcare CNN Model to Detect Prostate Cancer on Multiparametric MRI. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Bayat, S.; Yan, P.; Tahmasebi, A.; Kwak, J.T.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Pinto, P.; Wood, B.; et al. Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for Prostate Cancer Detection: Analysis of Temporal Enhanced Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 37, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laabidi, A.; Aissaoui, M. Performance analysis of Machine learning classifiers for predicting diabetes and prostate cancer. 2020, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Magome, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Sato, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Oguchi, M. Fully automated dose prediction using generative adversarial networks in prostate cancer patients. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0232697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, S., et al., Adversarial networks for the detection of aggressive prostate cancer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.08014, 2017. arXiv:1702.08014, 2017.
- Yu, H.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of Prostate MR Images for Classification Using Capsule Network-Based GAN Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Patel, P.; Mao, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Prostate gleason score prediction via MRI using capsule network. 2023, 12465, 507–512. [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Lin, Z.; Lee, C.H.; Tan, C.H.; Huang, W. A Multi-Scale Channel Attention Network for Prostate Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lian, C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, T.; Chen, R.C.; Wang, A.Z.; Royce, T.J.; Yap, P.-T.; Shen, D.; Lian, J. Asymmetric multi-task attention network for prostate bed segmentation in computed tomography images. Med Image Anal. 2021, 72, 102116–102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Qin, W.; Buyyounouski, M.; Ibragimov, B.; Hancock, S.; Han, B.; Xing, L. Prostate cancer classification with multiparametric MRI transfer learning model. Med Phys. 2018, 46, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janocha, K.; Czarnecki, W.M. On Loss Functions for Deep Neural Networks in Classification. Schedae Informaticae 2017, 1/2016, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H., et al., Loss functions for neural networks for image processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.08861, 2015. arXiv:1511.08861, 2015.
- Ghosh, A.; Kumar, H.; Sastry, P.S. Robust Loss Functions under Label Noise for Deep Neural Networks. Proc Conf AAAI Artif Intell 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C., et al., Multi-loss regularized deep neural network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2015. 26(12): p. 2273-2283.
- Kim, T.; Oh, J.; Kim, N.Y.; Cho, S.; Yun, S.-Y. Comparing Kullback-Leibler Divergence and Mean Squared Error Loss in Knowledge Distillation. 2021, 3, 2628–2635. [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Du, J.; Siniscalchi, S.M.; Ma, X.; Lee, C.-H. On Mean Absolute Error for Deep Neural Network Based Vector-to-Vector Regression. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, U. and V. Yendapalli, Binary cross entropy with deep learning technique for image classification. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng, 2020. 9(10).
- Ho, Y.; Wookey, S. The Real-World-Weight Cross-Entropy Loss Function: Modeling the Costs of Mislabeling. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 4806–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Rodriguez, E., et al., Uses and abuses of the cross-entropy loss: Case studies in modern deep learning. 2020.
- Sudre, C.H., et al. Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. in Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Third International Workshop, DLMIA 2017, and 7th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, September 14, Proceedings 3. 2017. Springer. 14 September.
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Rethinking the Dice Loss for Deep Learning Lesion Segmentation in Medical Images. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Science) 2021, 26, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhoti, J., et al., Calibrating deep neural networks using focal loss. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020. 33: p. 15288-15299.
- Lin, T.-Y., et al. Focal loss for dense object detection. in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2017.
- Asperti, A.; Trentin, M. Balancing Reconstruction Error and Kullback-Leibler Divergence in Variational Autoencoders. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 199440–199448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Mikkelsen, K.; Chén, O.Y.; Koch, P.; Mertins, A.; Kidmose, P.; De Vos, M. Personalized automatic sleep staging with single-night data: a pilot study with Kullback–Leibler divergence regularization. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. Review The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 2015, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jensen, M.A.; Zenklusen, J.C. A.; Zenklusen, J.C. A Practical Guide to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). In Statistical Genomics; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1418, pp. 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, C.; Zenklusen, J.C. The Cancer Genome Atlas: Creating Lasting Value beyond Its Data. Cell 2018, 173, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaske, C.J.; Benz, S.C.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Earl, D.; Szeto, C.; Zhu, J.; Haussler, D.; Stuart, J.M. Inference of patient-specific pathway activities from multi-dimensional cancer genomics data using PARADIGM. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, i237–i245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganini, C.; Amelio, I.; Bertolo, R.; Bove, P.; Buonomo, O.C.; Candi, E.; Cipriani, C.; Di Daniele, N.; Juhl, H.; Mauriello, A.; et al. Global mapping of cancers: The Cancer Genome Atlas and beyond. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2823–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Oto, A.; Turkbey, B.; Westphalen, A.C. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS), Version 2: A Critical Look. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphalen, A.C.; Rosenkrantz, A.B. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS): Reflections on Early Experience With a Standardized Interpretation Scheme for Multiparametric Prostate MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Li, H.; Guan, Y. Treatment Stratification of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer by Machine Learning. iScience 2020, 23, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, K.; Hugh-Jones, C.; Norman, T.; Friend, S.; Stolovitzky, G. The Prostate Cancer DREAM Challenge: A Community-Wide Effort to Use Open Clinical Trial Data for the Quantitative Prediction of Outcomes in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Oncol. 2015, 20, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, F.; Smith, K.; Sharma, A.; Kirby, J.; Tarbox, L.; Clark, K.; Bennett, W.; Nolan, T.; Freymann, J. The public cancer radiology imaging collections of The Cancer Imaging Archive. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Mirak, S.A.; Hosseiny, M.; Azadikhah, A.; Zhong, X.; Reiter, R.E.; Lee, Y.; Raman, S.S.; Sung, K. Automatic Prostate Zonal Segmentation Using Fully Convolutional Network With Feature Pyramid Attention. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 163626–163632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrtash, A.; Sedghi, A.; Ghafoorian, M.; Taghipour, M.; Tempany, C.M.; Wells, W.M.; Kapur, T.; Mousavi, P.; Abolmaesumi, P.; Fedorov, A. Classification of clinical significance of MRI prostate findings using 3D convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, FL, USA, 3 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
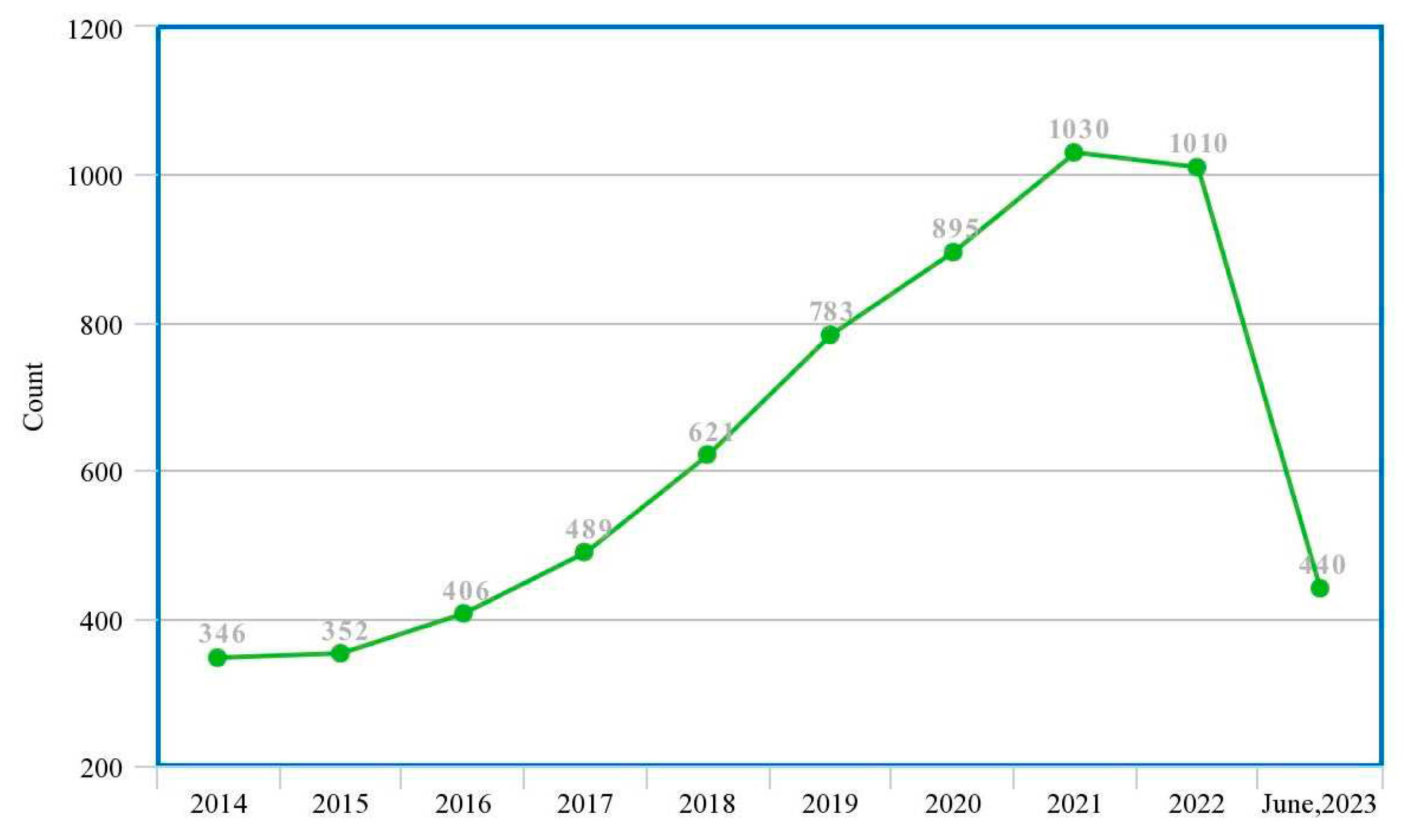
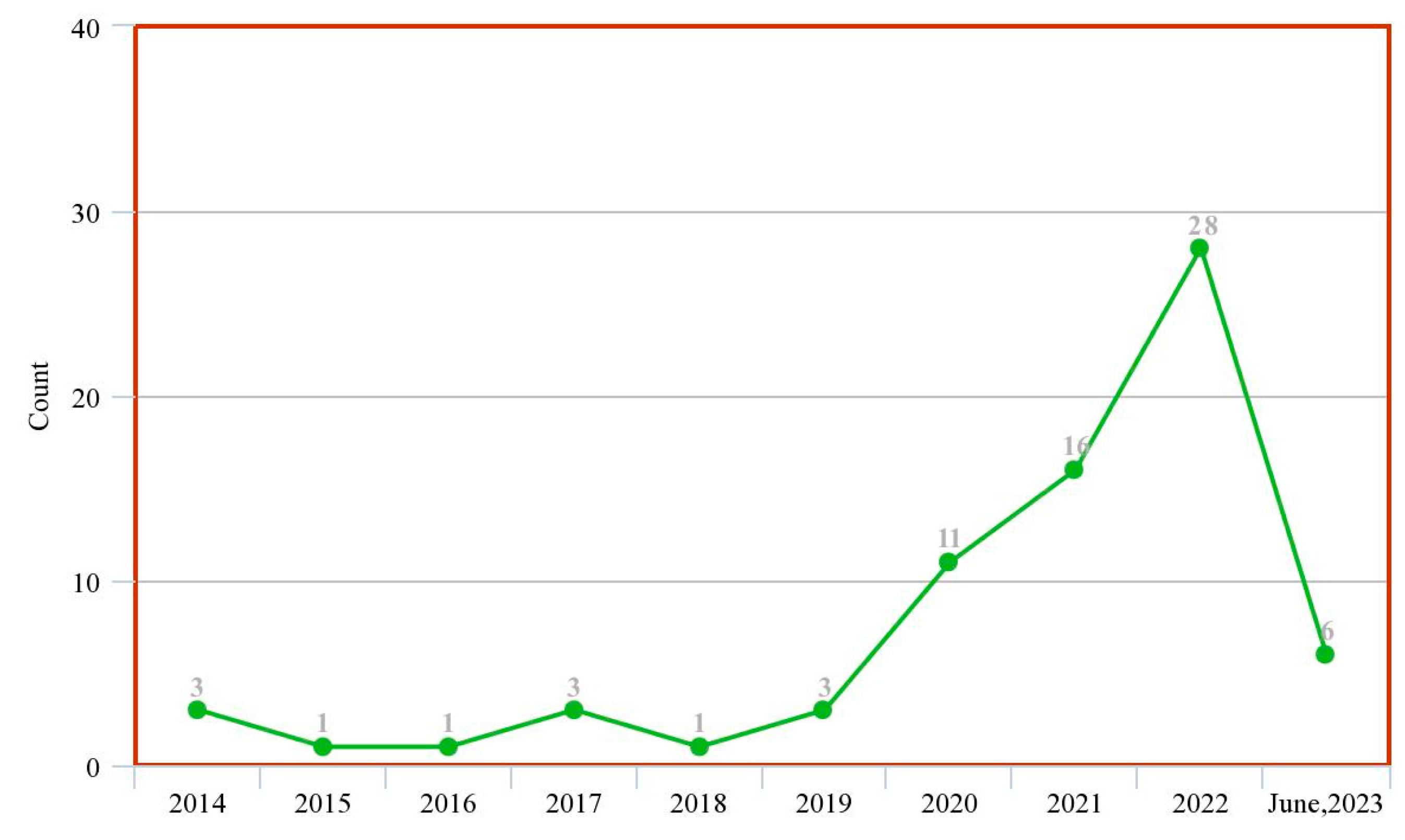

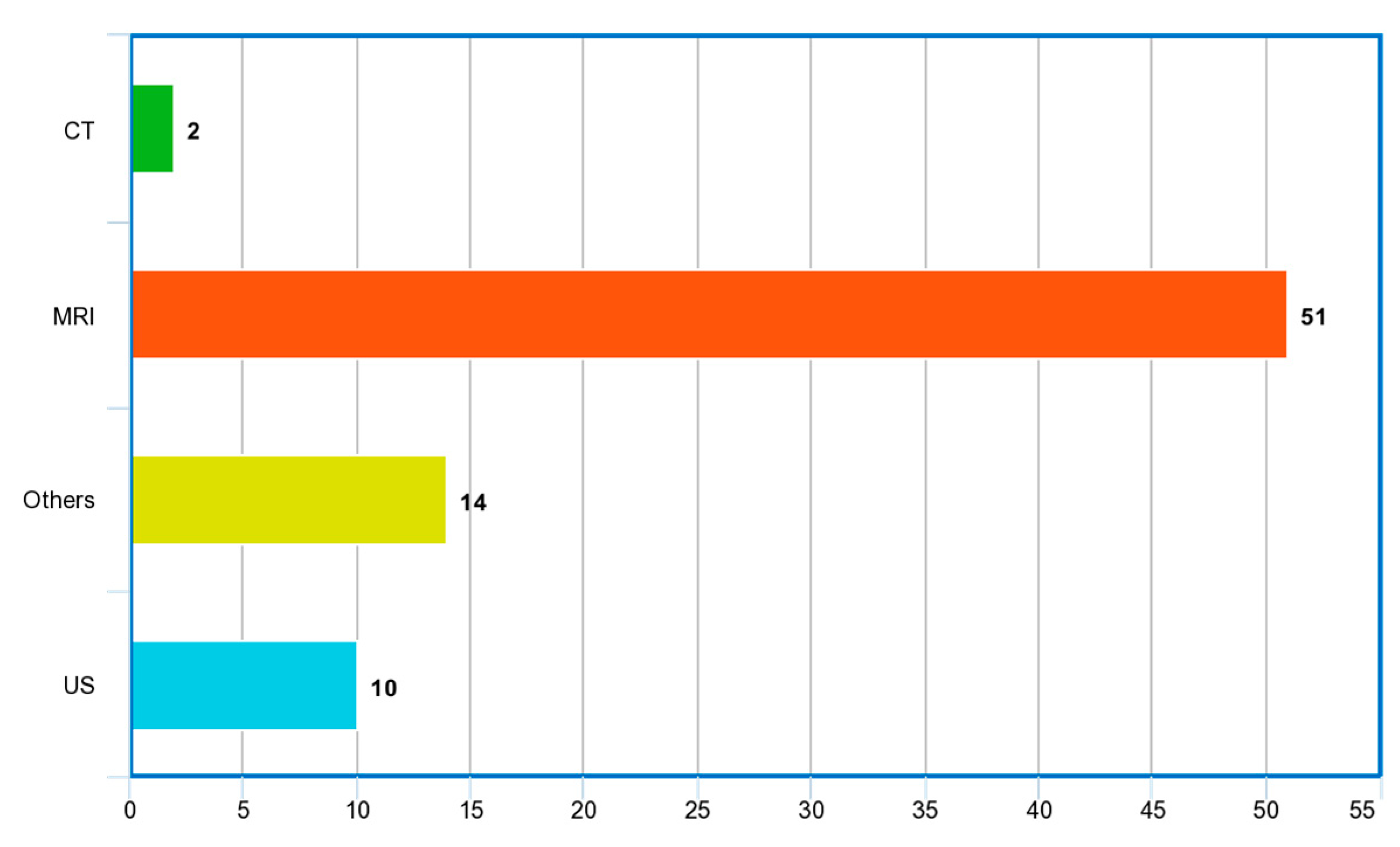
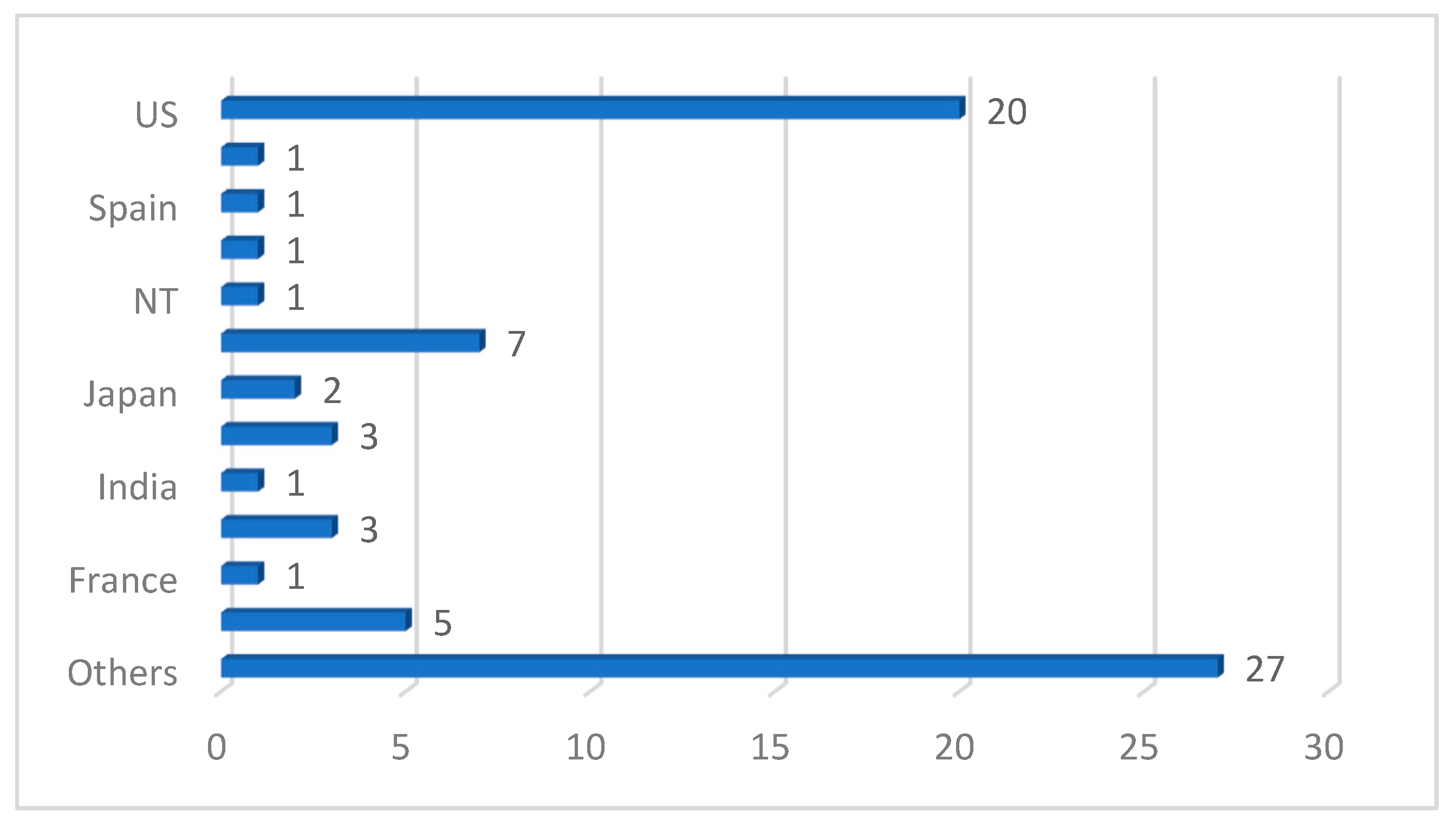
| Ref. | Year | Articles Included | Work Done |
|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | 2019 | 43 | Authors investigated current and future applications of ML and DL urolithiasis, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder and prostate cancer. Only PubMed database was used. It was concluded in study that machine learning techniques outperform classical statistical methods. |
| [21] | 2020 | 28 | Study investigated deep learning methods for CT and MRI images for PCa diagnosis and analysis. It was concluded that most deep learning models are limited by the size of the dataset used in model training. |
| [22] | 2021 | 100 | Study investigated 22 machine learning and 88 deep learning-based segmentation of only MRI images. Authors also presented popular loss functions for the training of these models and discussed public PCa-related datasets. |
| [23] | 2022 | 8 | Authors reviewed eight papers on the use of bi-parametric MRI (bpMRI) for deep learning diagnosis of clinically significant PCa. It was discovered that although deep learning proves highly performing in terms of accuracy, there is lower sensitivity when compared to human radiologists. Dataset size has also been identified as a major limitation in these deep learning experiments |
| [24] | 2020 | 27 | Embase and Ovid MEDLINE databases were searched for application of ML and DL for differential diagnosis of PCa using multi-parametric MRI. |
| [25] | 2022 | 29 | Authors investigated the current value of bpMRI using ML and DL in the grading, detection and characterization of PCa. |
| [26] | 2022 | 24 | Authors reviewed the role of deep learning in PCa management. Study also recommended that focus should be on model improvement in order to make these models verifiable as well as clinically acceptable. |
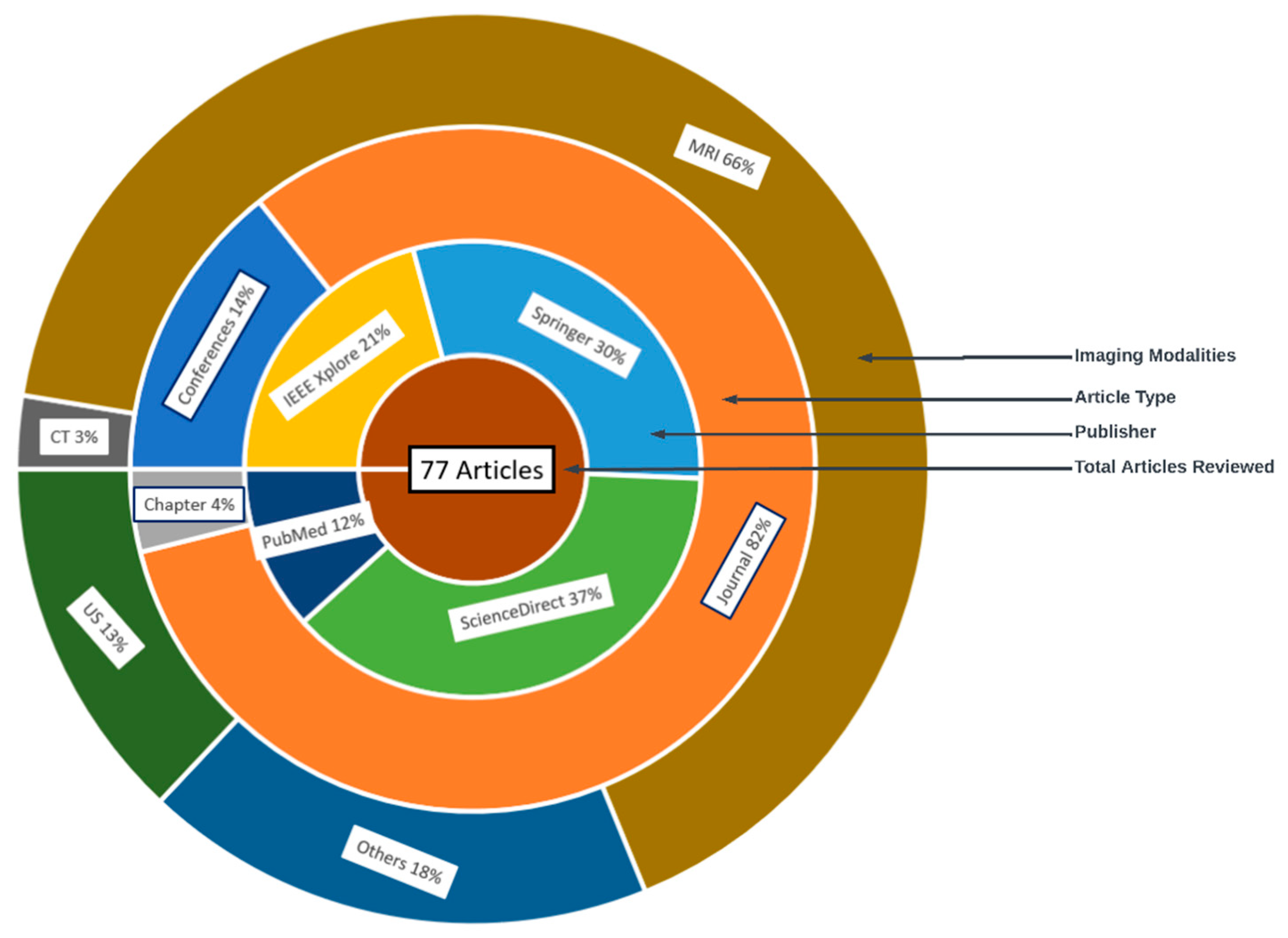
| SN | Databases | URL | Count | % Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IEEE Xplorer | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | 16 | 20.78 |
| 2 | Springer | https://link.springer.com | 23 | 29.87 |
| 3 | ScienceDirect | https://sciencedirect.com | 29 | 37.66 |
| 4 | PubMed | https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ | 9 | 11.69 |
| Ref. | Year | Imaging Modality | ML/DL Model | Problem Addressed | Metrics Reported | Hyperparameter Reported | Country | Citations | MV | Dataset | ML Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | 2017 | MRI | DCNN, SIFT-BoW, Linear-SVM | Comparison between deep learning and non-deep classifier for performance evaluation of classification of PCa. | AUC=0.84, Sensitivity = 69.6%, Specificity = 83.9%, PPV=78.6%, NPV=76.5% | Gamma= 0.1, momentum= 0.9, weight decay = 0.1, Max Training iteration = 1000, 10-fold CV | China | 175 | Y | 172 Samples | SL/PD |
| [62] | 2020 | WSI | CNN, DenseNet121 | Classifying PCa tissue with weakly semi-supervised technique | - | Batch-size =128,32, learning rate = , decay -rate = , Adam optimizer | - | 11 | N | 1368 Whole Slides Images | Semi-SL/SD |
| [63] | 2023 | bpMRI | PI-RADS, CNN (ResNet3D, DenseNet3D, ShfeNet3D, and MobileNet3D) | Predicting clinically significant prostate cancer with a deep learning approach in a multi-centre study. | Sensitivity = 98.6%, p-value>0.99, Specificity = 35.0% | cross-entropy loss, Adam optimizer, learning rate = 0.01, epochs =30, batch size=32 | China | 1 | Y | 1861 patients | SL |
| [64] | 2021 | MRI | Ga-PSMA-11 SUV (Ensemble ML), RH | Classification of patient overall risk with ML on high or low lesion in PCa | AUC =0.86 | 1000-fold CV, | - | 58 | Y | 52 Patients | - |
| [65] | 2020 | US | RF | Localization of PCa lesion using multiparametric ML on transrectal US. | ROC-AUC for PCa and Gleason>3+4 = 0.75, 0.90 | Depth = 50 nodes, | NT | 62 | Y | 50 Patients | SL/PD |
| [66] | 2019 | MRI | CNN, ResNet | Clinically significant PCa detection using CNN | AUC= 0.87 | ReLU, learning rate = 0.001, batch size = 8, dropout rate = 0.90, weight decay = 0.000001 and momentum = 0.90 | - | 134 | Y | 427 Patients | SL/SD |
| [67] | 2020 | mpMRI | Radiomics ML (RML), SVM | ML model capable of predicting PI-RADS score 3 lesions differentiating between non-csPCa from csPCa. | AUC =0.89 | misclassification penalty = (0.1- 10, 0.1), Regressionloss epsilon = (0.1- 10, 0.1) and numerical tolerance | - | 22 | Y | 263 Patients | - |
| [68] | 2021 | MRI | Dense NN, | PCa risk classification using ML techniques | AUC=0.72, Sensitivity = 80%, Specificity = 45.3% | Epochs =2500, stochastic gradient descent, learning rate = 0.001, drop-out layers = 50% | - | 15 | Y | 4548 Patients | SL |
| [12] | 2019 | MRI | Deep convolutional encoder-decoder, CNN | Prostate detection, segmentation and localization in MRI. | AUC=0.995, Accuracy=0.894, recall =0.928 | Epochs= 100, learning rate = 0.001, batch-size = 2 | - | 78 | N | 19 Patients | SL/SD |
| [69] | 2020 | WSI | DenseNetFCN, U-Net, EfcientNet | Impact of Scanning systems and cycle-GAN-based normalization on performance of DL algorithms in detecting PCa | AUC =0.98, Sensitivity = 1, Specificity = 0.5-0.75 | CV = 3, batch size = 3, learning rate = 0.0005, Stochastic gradient descent, categorical cross entropy lossfunction | - | 37 | N | 582 slides | SL/SD |
| [70] | 2019 | Histopathological images | Transfer learning, deep CNN | Transfer learning approach from breast histopathological images for detection of PCa | AUC = 0.936 | Epochs = 50 | US | 14 | Y | ImageNet, BrCa | SL/SD |
| [71] | 2015 | US | DBN, SVM, | Developed a feature extraction framework from US Prostate tissue. | AUC = 0.91, Accuracy = 93%, Sensitivity = 98%,and Specificity =90% | Radial basis function, leave-one-core-out CV | - | 35 | N | 31 Patients with 35 biopsy cores | SL/NG |
| [72] | 2020 | US, bpMRI | FCN, U-Net | Multimodality to improve detection of PCa in cancer foci during biopsy | AUC for PCa foci= 0.76, of all PCa with larger foci = 0.89 | Mini-batch stochastic gradient descent with Adam update rule, learning rate = , Exponentially decayed = 0.75 epochs = 10 | - | 21 | N | 107 patients with 145 biopsy cores | SL |
| [73] | 2022 | CT | CNN | Image-based PCa staging support system | AP = 80.4%, (CI: 71.1–87.8), Acc = 77% (CI: 70.0–83.4) | 4-fold CV = 121 | - | 19 | Y | 173 subjects (F-FDG data) | SL |
| [74] | 2020 | mpMRI | 3D-CNN | Risk assessment of csPCa using mpMRI | Hosmer-Lemeshow calibration test p = 0.41 and good discrimination (C = 0.85) | Cross-entropy loss function, Adam optimizer with learning rate = and weight decay = , epochs =100 | - | 16 | Y | 499 Patients | - |
| [75] | 2022 | bpMRI | deep learning masked (DLM) | Proposed a better segmentation technique of csPCa. | AUC = 0.76 | CV = 10, Optuna objective function, cross-entropy, Adam optimizer | - | 4 | N | 930 patients with 524 PCa lesions | - |
| [76] | 2020 | mpMRI | ResNet50, FPN, UNet, Mask R-CNN | Lesion detection and novel segmentation method for both local and global image features | Sensitivity =89%, 85% False Positive= 0.94 and 0.62 per patient,ROC curve (AUC) = 0.897 | binary cross entropy, Adam optimizer, learning rate = , epochs = 100 | - | 18 | Y | 243 patients | SL/PD |
| [77] | 2021 | CT | CNN | Incident detection of csPCa on CT scan | ROC-AUC = 0.88 (95%CI 0.86–0.90) per patient csPCa detection on CT, Sensitivity = 0.56, Specificity = 0.99 | cross entropy loss function, CV =5, AdamW optimizer (weight decay) | - | 7 | N | 571 scans | SL |
| [78] | 2019 | WSI | DLS, CNN, InceptionV3 | Gleason grading of whole-slide images of prostatectomies | Accuracy = 0.70 | - | United States | 320 | Y | 1226 slides | SL |
| [79] | 2020 | WSI | NASNetLarge, CNN | Detection of PCa tissue in whole-slide images | Accuracy = 97.3% | - | - | 81 | Y | 600 slides | SL |
| [80] | 2022 | WSI | CNN | Segmentation and grading of epithelial tissue for PCa region detection | Accuracy = 89.4%, κquad = 0.92 | - | India | 15 | Y | 3741 biopsies | SL |
| [81] | 2022 | WSI | DeepHealth-based DL | Image analysis AI support for PCa and tissue region detection | AUC = 0.986, F1-score = 0.969, Accuracy = 0.96 | CV = 5, Epochs = 30, | - | 2 | Y | 533 slides | SL |
| [82] | 2022 | Histopathological images | CNN, MobileNet-V2, ResNet50, DenseNet121, DenseNet169, VGG16, VGG19, Xception, InceptionV3, InceptionResNet-V2, and EfficientNet-B7 | Gleason grading for PCa in biopsy tissues. | Accuracy = 90.90% | - | - | 2 | N | PANDA | SL |
| Ref. | Year | Imaging Modality | ML/DL Model | Problem Addressed | Metrics Reported | Hyperparameter Reported | Country | Citations | MV | Dataset | ML Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [83] | 2022 | MRI | SPCNet, U-Net, branched UNet and DeepLabv3+ | Effect of labelling strategies on performance of PCa detection | ROC-AUC = 0.91-0.94 | loss fn, Adam optimizer, batch size = 22, epochs =30, Cross-entropy | USA | 3 | Y | 390 Patients | SL/PD |
| [84] | 2022 | MRI, US | CNN, SVM, Adaboost, K-NN, and RF | Detection of PCa with an explainable early detection classification model. | Acc = 97%. | ReLU fn | USA | 31 | N | 61,1119 images from 1151 patients | SL/SD |
| [85] | 2019 | MRI | LR, SVM on linear kernel, RF, DT and KNN | Radiomics and machine learning techniques to detect PCa aggressiveness biopsy. | AUC=0.93 | fold cross validation (K=5) | USA | 33 | Y | 40 Patients | SL/SD |
| [86] | 2021 | Histopathological images | RINGS, CNN | Segmentation of prostate glands with an ensemble deep and classical learning method | DICE = 90.16% | Batch-size =128, learning rate = , epochs=30 | - | 26 | Y | 18851 glands | SL/SD |
| [87] | 2022 | Digital camera | YOLO, CNN | A grading automated prostate cancer detection model with YOLO | Acc=97% | AF= Sigmoid, Tanh, batch size=24, max_batches=500,200,LR = 0.001, filters =27 | Turkey | 13 | Y | 500 tissue biopsy images | SL |
| [88] | 2019 | MRI | C4.5, DT, RT, RF, SVM, kNN, locally weighted learning,BN and NB | Textual Analysis and Machine Learning models to detect extraprostatic cancer. | Acc = 82%, AUC=88%, TP rate= 82%, TN =80% | fold cross validation (K=10) | Italy | 60 | Y | 39 patients | SL |
| [89] | 2021 | US | S-Mask, R-CNN and Inception-v3. | Diagnosis of PCa with integration of multiple deep leaning approaches. | Map=88%, DICE=87%, IOU=79%, AP=92% | Vector =0.001, weight decay rate=0.0001, number of iterations =3000 | China | 68 | Y | 704 images | SL |
| [90] | 2021 | MRI | GrowCut and Zernik feature extraction, Voting (KNN, SVM and MLP) | Detection of PCa with an Improved feature extraction methods with ensemble machine learning. | Acc=80.97%, Preci =76.69%, recall=77.32%, Error rate =19.02% | - | - | 9 | Y | 271 Samples | SL |
| [91] | 2021 | US | Ensemble Machine learning techniques | Prostate biopsy calculator using an automated machine learning technique. | high-grade PCa AUC=0.990, detection of PCa AUC= 0.703 | - | Serbia | 5 | Y | 832 patients | SL |
| [92] | 2022 | MRI, US | AdaBoost, RF | Upgrading a patient from MRI targeted biopsy to active surveillance with machine learning model. | Acc= 94.3%, 88.1%, Pre=94.6%, 88.0%, Recall = 94.3%, 88.1% for Adaboost and RF. | - | USA | 3 | Y | 592 patients | SL/PD |
| [93] | 2022 | US | Region labeling object detection (RLOD), Gleason grading network (GNet) | A pathological grading of PCa on single US image. | Pre= 0.830, mean Dice=0.815 | - | - | 0 | Y | ||
| [94] | 2020 | MRI | U-Net | A radiomics deeply supervised Segmentation method for prostate gland and lesion | mean Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) = 0.8958 and 0.9176 | - | - | 35 | Y | 50 Patients | SL/SD |
| [95] | 2023 | MRI | GBDTs, Multilayer perceptions, CNN, and Transformers. | Performance comparison of promising machine learning models on a typical PCa radiomics. | MCC=4.47, AUC Rank = 4, Acc =4.0 | - | Italy | 1 | Y | 949 PCa patients | SL/PD |
| [96] | 2018 | MRI | SVM | SVM on Gleason grading of PCa based image features (mpMRI) | AUC=0.99 | 10-fold cross-validation | - | 67 | 48 PCa patients | SL | |
| [97] | 2021 | MRI | ProsRegNet | Deep learning model to simplify PCa image registration in order to map regions of interest. | Dice-Co=0.96-0.98, H dis=1.7-2.0mm, UD =2.4-2.9mm and landmark error =2.7mm | 50 epochs | USA | 34 | Y | 152 Patients | |
| [98] | 2019 | US | RF Classifier | An interpretable PCa ensemble deep learning model to enhance decision making for clinicians. | Acc= 0.8602, Sensitivity= 0.8571, specificity= 0.8923 | Tree no =50, depth of tree =5 | China | 114 | N | 1402 cases | SL/SD |
| [99] | 2022 | MRI | CorrSigNIA, CNN | Ensemble feature extraction methods for PCa aggressiveness and indolent detection. | Acc =80%, ROC-AUC= 0.81±0.31 | Epochs=100, batch size =8, Adam optimizer, learning rate = , weight decay = 0.1 | USA | 14 | Y | 98 Men | SL |
| [100] | 2021 | MRI | CNN | Detection of PCa using 3D-CAD in bpMR images | Sen = 75.31± 3.64%, Spec = 85.83 ±2.22%, kappa =76.69%,81.08% | - | Netherlands | 58 | Y | 1950 scans, 2317 patients | SL/PD |
| [101] | 2017 | MRI | SVM, RF | PCa localization and classification with ML. | Global ER=1%, Sens=99.1% and Speci= 98.4% | - | Germany | 35 | Y | 34 patients | SL/SD |
| [102] | 2021 | MRI | CNN, 3D AlexNet | Segmentation of MR images tested on DL methods. | Acc =0.921, Speci = 0.896, Sens = 0.902, AUC= 0.964, MAD= 0.356 mm, HD= 1.024 mm, Dice= 0.9768. | - | - | 53 | Y | 500 PCa patients | SL/PD |
| [103] | 2018 | MRI | DNN | Segmenting MR images of PCa using deep learning separation techniques | Dice=0.910 ± 0.036, ABD = 1.583 ± 0, Hausdorff Dis = 441,4.579 ± 1.791 | - | Norway, US, UK, Netherlands | 85 | N | 304 Samples (PROMIS12, PROSTATEx17) | SP/SD |
| [104] | 2022 | MRI | CNN, RMANet | Detection of PCa leveraging on the strength of multi-modality of MR images. | AUC = 0.84, Sens = 0.84, Speci = 0.78 | cross-entropy loss, batch size = 2, trained epochs = 200, Adam optimization method, learning rate= 1e-5 | Japan | 1 | Y | 379 Samples | SL, UL (for features extraction), SD |
| [105] | 2023 | MRI | GANs | GANs were investigated for detection of PCa with MRI. | AUC=0.73, Average AUCs SD = 0.71 ± 0.01 and 0.71 ± 0.04. | GANs parameters were maintained. | Norway, US, UK, Netherlands | 0 | Y | 1160 Samples | SL/SD |
| [106] | 2019 | MR guided biopsy | VGG-16 CNN, J48 | Gleason grading for PCa detection with deep learning techniques. | Quadratic weighted kappa score = 0.4727, Positive predictive = 0.9079 | - | Norway, US, UK, Netherlands | 39 | N | PROSTATEx-2 dataset () | SL/SD |
| [107] | 2020 | MRI | Hierarchical clustering (HC) | HC for early diagnosis of PCa | Acc =96.3% in and TZ=97.8% | - | Netherlands | 10 | N | 50 subjects | US/PD |
| [108] | 2017 | MRI | CNN, SVM | Detection of PCa in an image and lesion simultaneously with deep learning feature and a classifier. | Sens=0.46, 0.92 0.97 at FP = 0.1,1,10 | SoftMax function | - | 126 | Y | 160 Patients | SL/SD |
| [109] | 2022 | mpMRI | ANN | Ensemble method of mpMRI and PHI for diagnosis of early PCa | Sensi = 80%, Speci=68% | - | - | 7 | Y | 177 patients | |
| [110] | 2022 | MRI | RF, CAD | An improved CAD MRI for significantly PCa detection. | AUC = 0.72 | - | - | 1 | Y | 150 samples | SL/PD |
| [111] | 2020 | WSI | DLN, CNN | Compared deep learning models for classification of PCa with GG | kappa score = 0:44 | Layer = 121, LR = 0.0001, Adam optimizer | - | 17 | 341 Sliding Images | SL/SD |
| Ref. | Year | Imaging Modality | ML/DL Model | Problem Addressed | Metrics Reported | Hyperparameter Reported | Country | Citations | MV | Dataset | ML Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | 2017 | MRI | CNN, DL | Classification of MRI images for easy diagnosis of PCa. | Accuracy for training = 0.80, Accuracy for testing = 0.78 | ReLU | China | 33 | N | Patients = 200, diffusion weighted images (DWI) = 13,408 (LSVRC Dataset) | SL/SD |
| [112] | 2020 | MRI | MLR, DT, ANN, KNN, SVM,RF, LR. | Classification of prostate cancer using ML techniques. | Accuracy = 0.97, Specificity = 98%.Sensitivity= 96% | LeastAbsolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO), log loss function | 17 | N | 387 samples with 188 PCa and 190 not PCa images. | SL/ | |
| [113] | 2018 | US | 3D-CNN | Detection of PCa in sequential CEUS images. | Specificity =91%, Average accuracy =0.90 | Layers = 6, kernels = 2-12 | Netherlands | 49 | Y | 21844 samples and non-targeted 25738 samples for (contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) imaging | SL/SD |
| [114] | 2020 | MRI | They adapted U-Net network. | A neural network that detects and grade a prostate cancer tissue. | voxel-wise weighted kappa=0:446± 0:082, Dice similarity=0:37±0 0:046 | Cross-validation =5 | Netherlands | 73 | Y | For training 99 patients and 112 lesions while 63 patients and 70 Lesions for testing. | SL/SD |
| [115] | 2021 | MRI | Long short-term memory (LSTM) and Residual Net (ResNet−101), SVM, Gaussian Kernel, (KNN − Cosine), Kernel-NB, DT, RUSBoost tree | They compared the performance of deep learning models to classical models in detection of PCa. | Accuracy =1.00, AUC = 1 | 10-fold cross-validation | USA | 40 | N | 230 patients | SL/SD |
| [116] | 2020 | WSI | CNN, | CNN based WSI for PCa detection. | Accuracy = 0.99, F1 score = 0.99, AUC = 0.99 | Cross-validation =3 | Spain | 41 | N | 97 WSI | SL/PD |
| [117] | 2020 | mpMRI | DEF, CNN, RF, NASNet-mobile | Deep entropy features (DEFs)from CNNs applied to MRI images of PCa to predict Gleason score (GS) of PCa lesions | AUC = 0.80, 0.86, 0.97, 0.98, and 0.86 | Number of trees = 500, maximum tree depth= 15 and minimum number of samples in a node = 4 | USA | 16 | Y | Patient = 99, with 112 lesions | SL/SD |
| [118] | 2018 | mpMRI | Tissue DeformationNetwork (TDN), CNN | An automated csPCa detection using deep neural network. | Sensitivity= 0.6374, 0.8978 at 0.1 and1 false positive/ patient | Cross-validation = 5, loss function (classification loss, inconsistency loss and overlap loss), | Germany | 124 | N | 360 patients | SL/SD |
| [119] | 2017 | WSI | R-CNN | Epithelial cells detection and Gleason grading in histological images | Accuracy = 0.99,AUC = 0.998, | Cross validation = 5 | USA | 97 | N | 513 images from 20 patients | SL/SD |
| [120] | 2020 | MRI | Deep-CNN, EfficientDet, YOLOv4, YOLOv5 | Detecting PCa lesions in MRI with minimal dataset | Accuracy = 52.63% | 0 | |||||
| [121] | 2018 | Diffusion weighted MRI | CNN | Early diagnosis of PCa using CNN-CAD system | Accuracy = 0.96, Sensitivity = 100%, Specificity = 91.67% | ReLU, layers = 6 | 48 | Y | 23 Patients | SL/PD | |
| [122] | 2019 | mpMRI | FocalNet (Multi-class CNN) | Detection of PCa and Gleason grading for PCa aggressiveness | Sensitivity= 89.7%, 87.9%, e AUC = 0.81, 0.79(PCa for GS≥3+4 and PCa GS≥4+3) | Cross validation = 5 | Germany | 131 | Y | 417 patients | SL/PD |
| [123] | 2022 | MRI | CNN, Inception-v3, Inception-v4, Inception-Resent-v2=, Xception, PolyNet | Detection of PCa with CNN | Accuracy = 0.99 | 0 | N | 1524 samples | SL/SD | ||
| [124] | 2019 | MRI | SVM | Classify PCa lesions into high-grade and low-grade | AUC= 77[0.66-0.87], Sensitivity 0.74[0.57-0.91], Specificity = 0.66[0.50-0.82 | Cross validation = 100 | Netherlands | 13 | Y | 40 Patients with 72 lesions | SL/SD |
| [125] | 2019 | MRI | FCNN | Improved MRI segmentation for PCa | Average mean Dice Coefficient (DSC) of EndorectalCoil (ERC) = 0.8576,Average DSC of non-ERC = 0.8727 | Cross validation = 50, ADAM optimizer, learning rate = 0.001, batch size = 32, epoch = 25, dropout = 0.2 | France | 35 | Y | PROMISE12 dataset (50 Volume of MRI) | SL/SD |
| [126] | 2019 | TRUS | Linear SVM, KNN, RF, Multilayer perceptron, DT, LDA | Improved TRUS for detection of csPCa | Accuracy =0.79, PPV = 95% | Cross validation =11 | USA | 2 | Y | 30 Patients | SL/PD |
| Ref. | Year | Imaging Modality | ML/DL Model | Problem Addressed | Metrics Reported | Hyperparameter Reported | Country | Citations | MV | Dataset | ML Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [127] | 2022 | mpMRI | CNN | The aggressiveness of PCa was predicted using ML/DL frameworks | AUROC – 0.75Specificity –78%Sensitivity –60% | 5-fold CV, 87-13 train-test splitting | Italy | 20 | Y | 112 patients | SL/SD |
| [128] | 2022 | PSA, Biopsy | RNN | Survival analysis of localized prostate cancer was conducted | - | 80/20 splitting | USA | 1 | Y | 112,276 samples | SL/PD |
| [129] | 2020 | MRI | CNN (GoogleNet) | Transfer learning approach with CNN framework for detecting PCa | AUC-1.00Accuracy-100% | ReLU activationMax pooling | USA | 71 | N | 230 Images | SL/SD |
| [130] | 2021 | bpMRI | Logistic Regression | Construction of integrated nomogram combining deep-learning-based imaging predictions, PI-RADS scoring and clinical variables to identify csPCa on bpMRI | AUC – 0.81 | - | USA | 31 | Y | 592 patients | SL/SD |
| [131] | 2022 | bpMRI | CNN-UNet | UNet-based PCa detection system using MRI. | Sensitivity – 72.8%PPV – 35.5% | 70/30 splitting, Dice Coefficient used | USA | 7 | Y | 525 patients | SL/PD |
| [114] | 2020 | bpMRI | CNN-UNet | DL regression analysis for PCa detection and gleason sscoring | Weighted kappa of 0.446 ± 0.082, Dice similarity coefficient of 0.370 ± 0.046, | Dice Coefficient used, 5 fold CV | Netherlands | 75 | Y | - | SL/SD |
| [132] | 2021 | mpMRI | CNN-UNet | Development of a UNet architecture for PCa detection with minimum training data size with effect of prior knowledge | Sensitivity – 87%AUC – 0.88 | -- | Netherlands | 36 | Y | 1952 patients | SL/SD |
| [133] | 2021 | MRI + histological data | CNN-GoogleNet | Bi-modal deep learning model fusion of Pathology-Radiology data for PCa diagnostic classification | AUC – 0.89 | - | USA | 33 | Y | 1484 images | SL/PD |
| [134] | 2019 | mpMRI | Multi-layer ANN | ANN was used to accurately predicted PCa withoutbiopsy marginally better than LR | - | 5 fold CV,Cross-entropyLearning rate 0.0001L2 regularization penalty of 0.0005 | Japan | 37 | Y | 334 patients | SL/PD |
| Ref | Title | Journal | Publisher | Year | Citation | Impact Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [78] | Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer. | NPJ digital medicine | Nature | 2019 | 320 | 80 |
| [89] | Deep learning framework based on integration of S-Mask R-CNN and Inception-v3 for ultrasound image-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer. | Future Generation Computer Systems | Elsevier | 2021 | 68 | 34 |
| [66] | Prostate cancer detection using deep convolutional neural networks. | Scientific reports | Springer | 2019 | 134 | 33.5 |
| [122] | Joint prostate cancer detection and Gleason score prediction in mp-MRI via FocalNet. | IEEE transactions on medical imaging | IEEE | 2019 | 131 | 32.75 |
| [84] | Prostate cancer classification from ultrasound and MRI images using deep learning based Explainable Artificial Intelligence. | Future Generation Computer Systems | Elsevier | 2022 | 31 | 31 |
| [19] | Searching for prostate cancer by fully automated magnetic resonance imaging classification: deep learning versus non-deep learning. | Scientific reports | Springer | 2017 | 175 | 29.16667 |
| [64] | Supervised machine learning enables non-invasive lesion characterization in primary prostate cancer with [68 Ga] Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI. | European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging | Springer | 2021 | 58 | 29 |
| [100] | End-to-end prostate cancer detection in bpMRI via 3D CNNs: effects of attention mechanisms, clinical priori and decoupled false positive reduction. | Medical image analysis | Elsevier | 2021 | 58 | 29 |
| [98] | Stacking-based ensemble learning of decision trees for interpretable prostate cancer detection. | Applied Soft Computing | Elsevier | 2019 | 114 | 28.5 |
| [79] | High-accuracy prostate cancer pathology using deep learning. | Nature Machine Intelligence | Nature | 2020 | 81 | 27 |
| Model | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)[116,121,135] | CNNs are the most used deep learning method for PCa image analysis tasks. They are effective in capturing spatial patterns and features from images. CNN architectures, such as VGG, ResNet, and Inception, have achieved remarkable success in various cancer image analysis applications, including detection, classification, and segmentation. |
| Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)[136,137] | RNNs are suited for sequential data, such as time-series or sequential medical data. In cancer image analysis, RNNs are often used for tasks like analyzing electronic health records or genomic data to predict cancer outcomes or identify potential biomarkers. |
| Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) [138,139] | GANs are used for generating synthetic data or enhancing existing data. In cancer image analysis, it can be employed to generate realistic synthetic images for data augmentation or to address data imbalance issues. GANs can also be used for image-to-image translation tasks, such as converting MRI images to PET images for multi-modal analysis. |
| Capsule Networks[140,141] | Capsule Networks are an alternative to CNNs that aim to capture hierarchical relationships between features. They have shown promise in tasks such as lung cancer detection in CT scans. Capsule Networks offer the advantage of better handling spatial relationships and viewpoint variations within images. |
| Attention Models[142,143] | Attention mechanisms have been integrated into deep learning models for cancer image analysis to focus on relevant regions or features. They help to identify important areas in the image and improve the interpretability and performance of the model. Attention mechanisms can be applied in CNNs, RNNs, or other architectures. |
| Transfer Learning[129,144] | Transfer learning involves utilizing pre-trained models trained on large-scale datasets and adapting them to cancer image analysis tasks. By leveraging the learned features from pre-training, transfer learning enables effective learning even with limited labeled medical data. |
| Loss Functions | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss[149,150] | MSE loss measures the average squared difference between predicted and target values. It is commonly used for regression tasks. It penalizes large errors heavily, which can be useful when the magnitude of errors is important. However, it is sensitive to outliers and can result in slow convergence. |
| Binary Cross-Entropy Loss[151,152] | Binary cross-entropy loss is used for binary classification tasks. It measures the dissimilarity between the predicted probability and the true label for each binary class separately. It encourages the model to assign high probabilities to the correct class and low probabilities to the incorrect class. It is robust to class imbalance and is widely used in tasks like cancer classification. |
| Categorical Cross-Entropy Loss[152,153] | Categorical cross-entropy loss is used for multi-class classification tasks. It extends binary cross-entropy loss to handle multiple classes. It measures the average dissimilarity between the predicted class probabilities and the true one-hot encoded labels. It encourages the model to assign high probabilities to the correct class and low probabilities to other classes. |
| Dice Loss[154,155] | Dice loss is commonly used in segmentation tasks, where the goal is to segment regions of interest (ROI) in images. It measures the overlap between predicted and target segmentation masks. It is especially useful when dealing with class imbalance, as it focuses on the intersection between predicted and target masks. It can handle partial matches and is robust to the background class. |
| Focal Loss[156,157] | Focal loss is designed to address class imbalance in classification tasks, especially when dealing with rare classes. It introduces a balancing factor to downweight easy examples and focus on hard examples. It emphasizes learning from the difficult samples, helps mitigate the impact of class imbalance and improves model performance on rare classes by assigning higher weights to misclassified examples |
| Kullback-Leibler Divergence (KL Divergence) Loss [158,159] | KL divergence loss is used in tasks involving probability distributions. It measures the dissimilarity between the predicted probability distribution and the target distribution. It is commonly used in tasks such as generative modeling or when training variational autoencoders. |
| Databases | Description |
|---|---|
| The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)[160–164] | TCGA provides comprehensive molecular characterization of various cancer types, including prostate cancer. It includes genomic data, gene expression profiles, DNA methylation data, and clinical information of patients. |
| The Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS)[165,166] | PI-RADS is a standardized reporting system for prostate cancer imaging. Datasets based on PI-RADS provide radiological imaging data, such as MRI scans, annotated with regions of interest and corresponding clinical outcomes. |
| The Prostate Imaging Database (PRID) | PRID is a database that contains MRI data of prostate cancer patients, along with associated clinical information. It can be used for developing and evaluating machine learning algorithms for prostate cancer detection and segmentation. |
| The Prostate Cancer DREAM Challenge dataset[167,168] | This dataset was part of a crowdsourced competition aimed at developing predictive models for prostate cancer prognosis. It includes clinical data, gene expression profiles, and survival outcomes of prostate cancer patients. |
| The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA)[169,170] | TCIA (https://www.cancerimagingarchive.net/) provides a collection of publicly available medical imaging data, including some datasets related to prostate cancer. While not exclusively focused on prostate cancer, it contains various imaging modalities, such as MRI and CT scans, from patients with prostate cancer. |
| SPIE-AAPM-NCI PROSTATEx Challenge[171,172] | The SPIE-AAPM-NCI PROSTATEx Challenge dataset for prostate cancer (https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/ProstateChallenge/PROSTATEx+Challenges) was released as part of a challenge aimed at developing computer-aided detection and diagnosis algorithms for prostate cancer. It includes multi-parametric MRI images, pathology data, and ground truth annotations. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





