Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
17 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Discussion of Model and the Wave Structures
2. Glimpse of the Method
3. Finding the Solutions of the Wave Structures
-
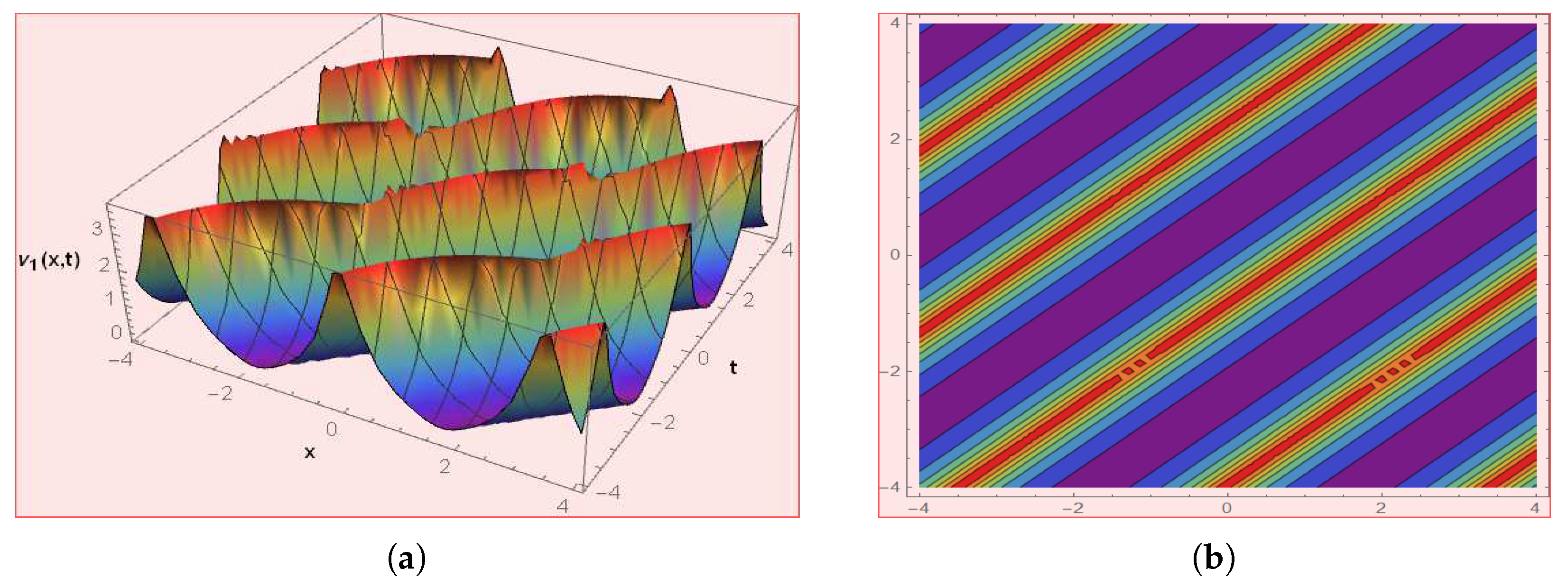
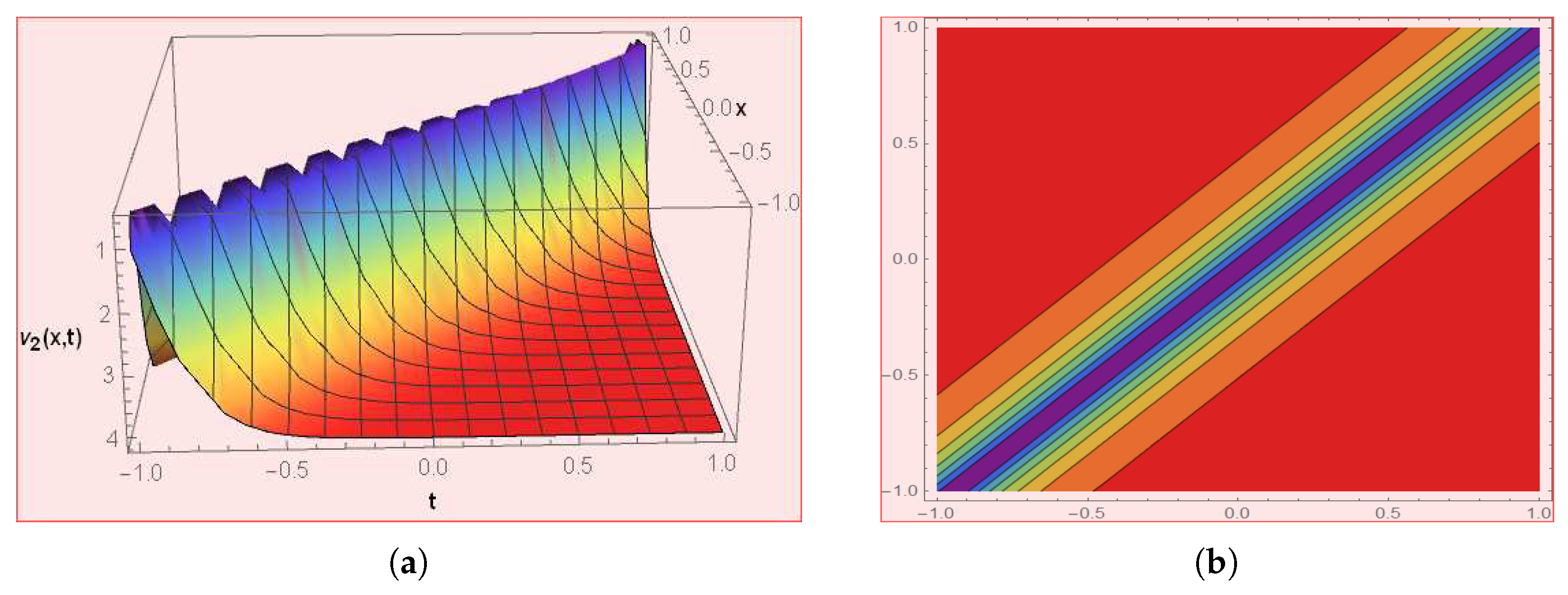
Multiwave solutions: With the help of the following transformation [1], we are able to use the three wave hypothesis to generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (8) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with trigonometric and hyperbolic functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:The multiwave solution of eq. (1) is extracted asThe multiwave solution of eq. (1) is extracted as
-
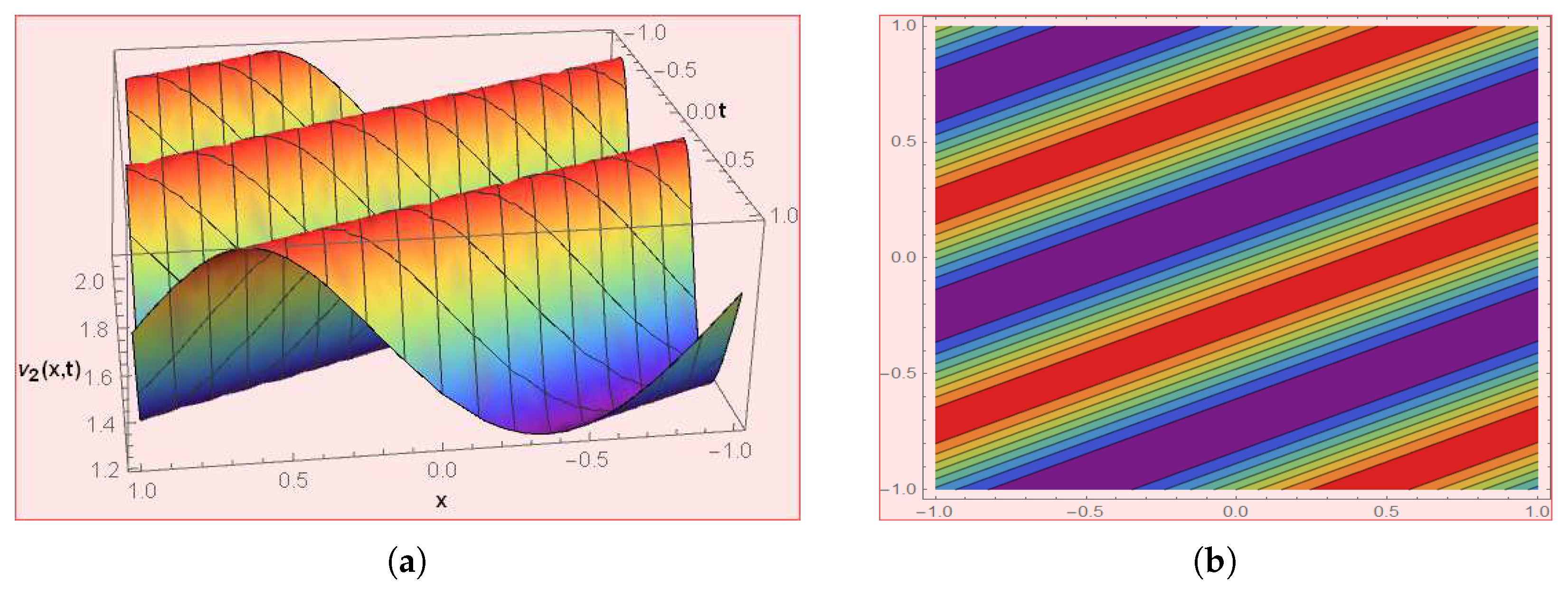
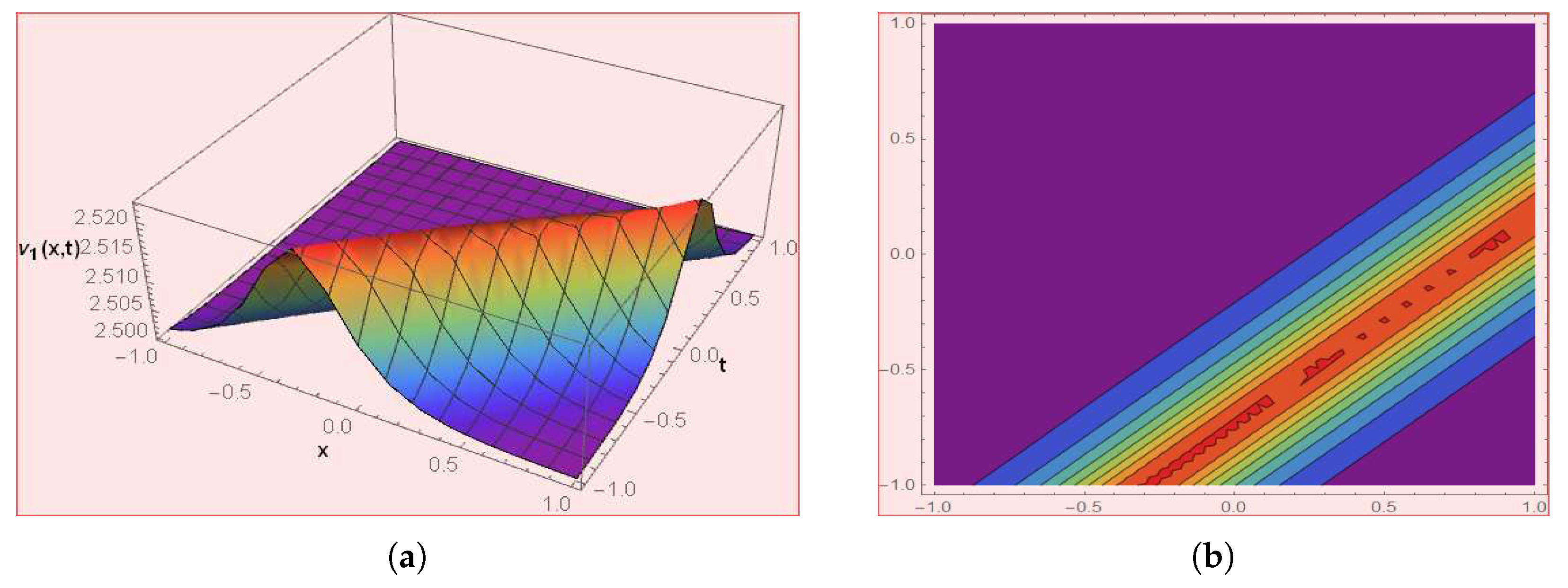
Interaction via double exponential form: With the help of the following transformation [1], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (13) in eq. (5), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
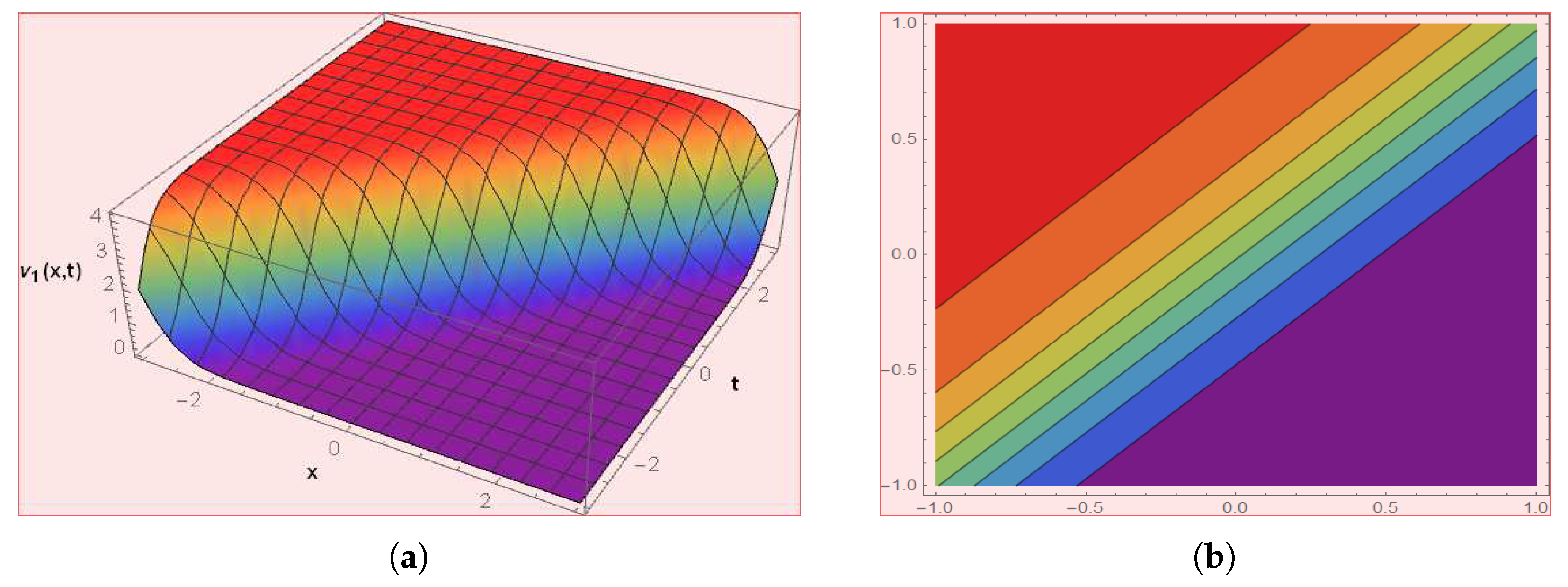
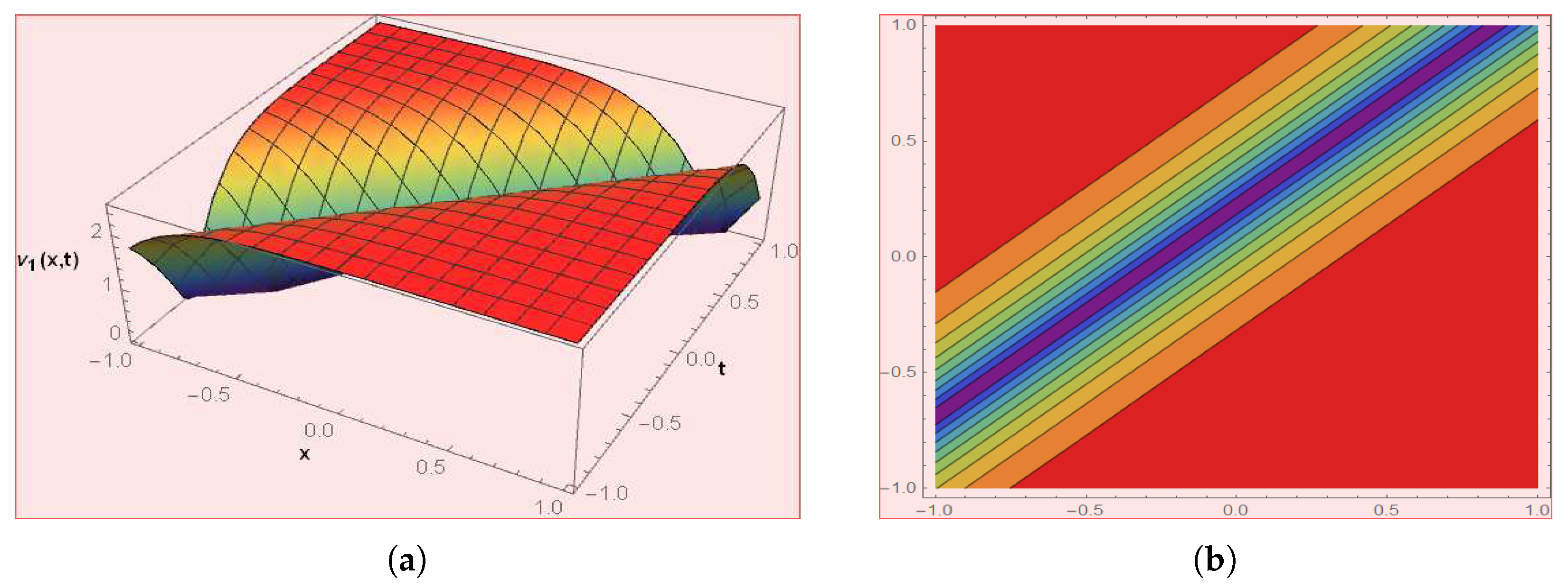
Homoclinic breather approach: With the help of the following transformation [1], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (20) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential, trigonometric and exponential-trigonometric functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So, the homoclinic breather solution of eq. (1) extracted asSet 2: and putting them in eq. (20) and then in eq. (5), we obtainwhere . So, the Homoclinic breather solution of eq. (1) extracted aswhere .So, the Homoclinic breather solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
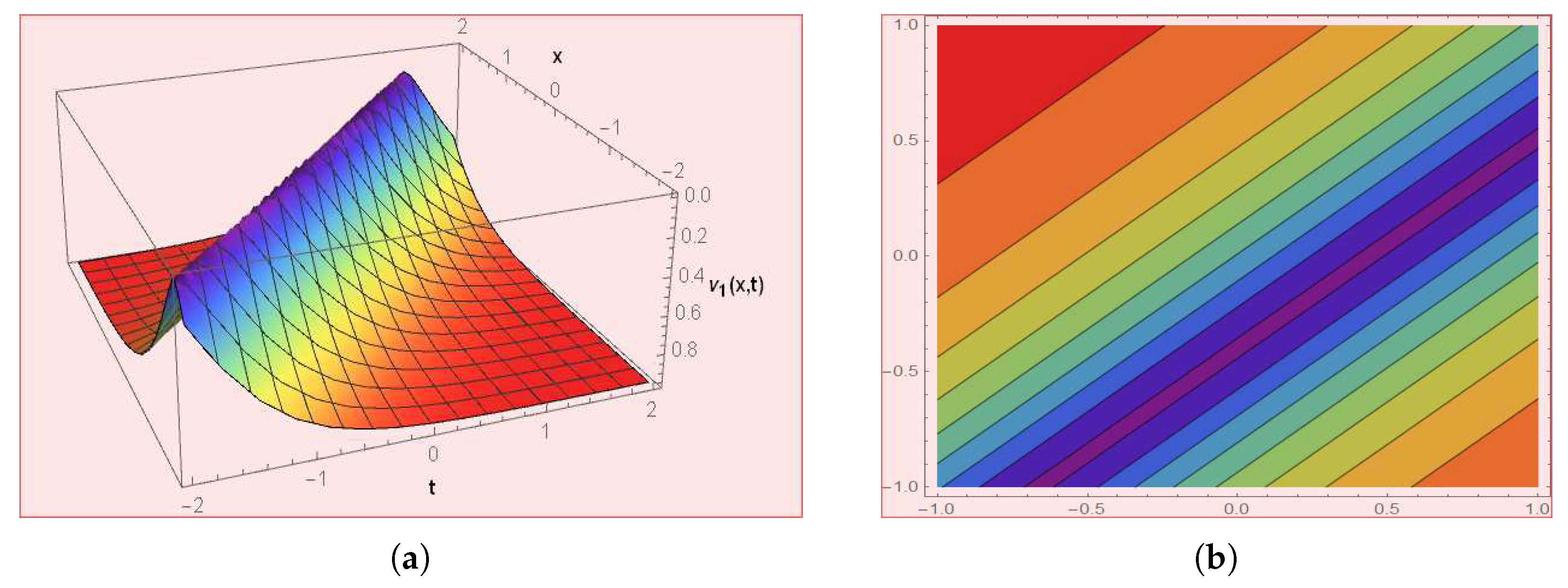
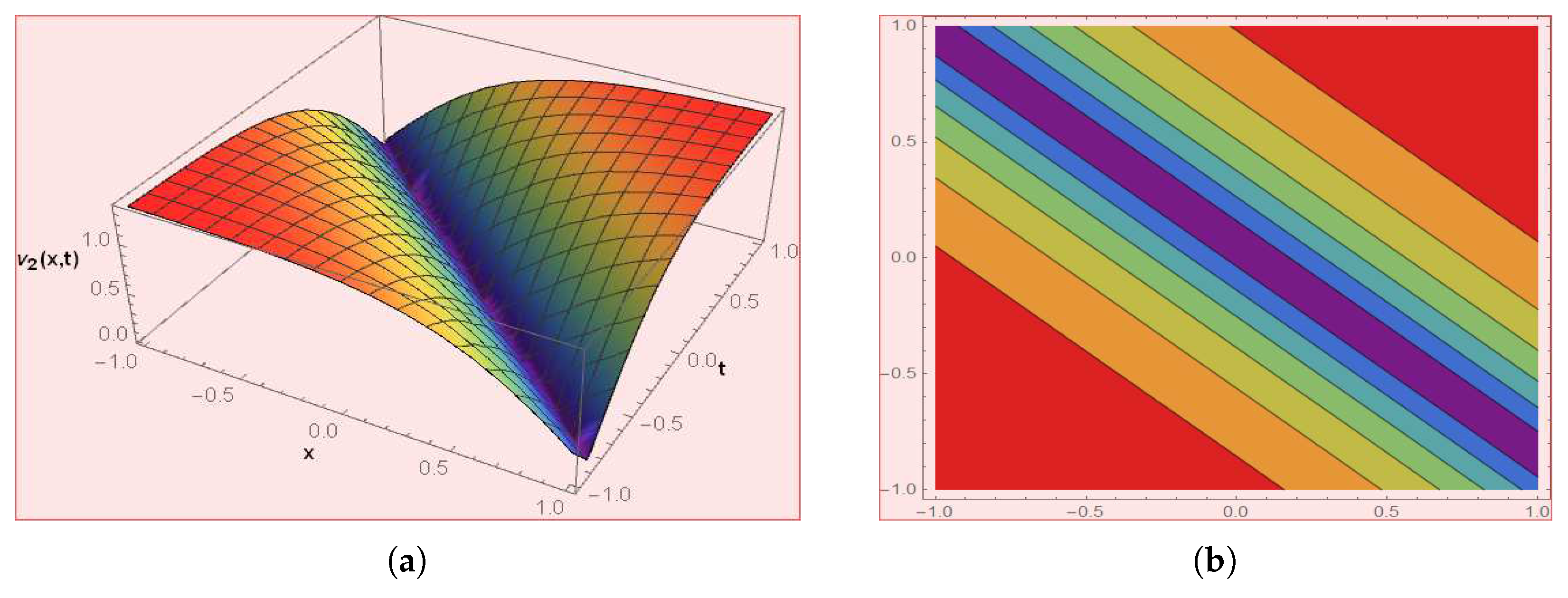
Mixed type solutions: With the help of the following transformation [1], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting in eq. (27) and then in eq. (7), we obtain, simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential, trigonometric and exponential-trigonometric functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:The mixed type solution of eq. (1) extracted aswhere .The mixed type solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
Periodic Cross-kink: With the help of the following transformation [1], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (32) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential, trigonometric and exponential-trigonometric functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the periodic Cross-kink solution of eq. (1) extracted aswhere .The periodic Cross-kink solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the periodic Cross-kink solution of eq. (5) extracted as
-
Cross-Kink Rational Wave Solution: With the help of the following transformation [18], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (39) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the Cross-Kink rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo, the Cross-Kink rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the Cross-Kink rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
M-Shaped Rational Wave Solution: With the help of the following transformation [18], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (46) in eq. (7), simplifying and like terms and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the M-Shaped rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted aswhere .So the M-Shaped rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the M-Shaped rational wave solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
M-Shaped Rational Wave Solution with One Kink Wave: With the help of the following transformation [18], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (53) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the solution of eq. (1) extracted as
-
M-Shaped Rational Wave Solution with Two Kink Waves: With the help of the following transformation [18], we generate different types of solutions:Substituting eq. (60) in eq. (7), simplifying and collecting like terms with exponential functions and equating the coefficients of each obtained expressions to zero. So, we obtained the system of equation and simplified with the help of Mathematica to gain the different sets of unknown constants such as:So the solution of eq. (1) extracted asSo the solution of eq. (1) extracted aswhere .So the solution of eq. (1) extracted as
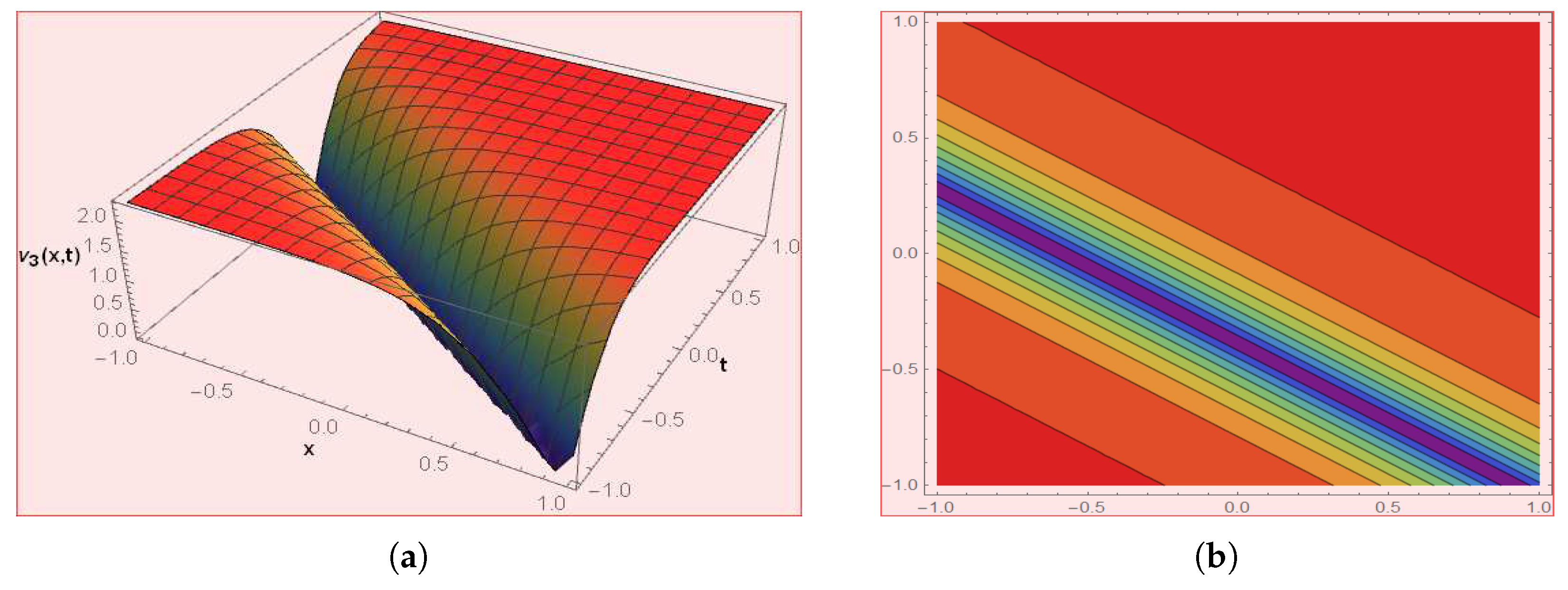
4. Graphical Presentations
5. Conclusion
References
- Younas, U. , Ren, J., Baber, M. Z., Yasin, M. W., & Shahzad, T. (2022). Ion-acoustic wave structures in the fluid ions modeled by higher dimensional generalized Korteweg-de Vries–Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation. Journal of Ocean Engineering and Science 7(4), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A., Singh, J., Kumar, D., & Gupta, S. (2019). An efficient analytical technique for fractional partial differential equations occurring in ion acoustic waves in plasma. Journal of Ocean Engineering and Science, 4(2), 85-99. [CrossRef]
- Dubinov, A. E. (2023). Gas-dynamic approach to the theory of non-linear ion-acoustic waves in plasma with Kaniadakis’ distributed species. Advances in Space Research, 71(1), 1108-1115. [CrossRef]
- Usman, M. , Hussain, A., Zaman, F. D., Khan, I., & Eldin, S. M. (2023). Reciprocal Bäcklund transformations and travelling wave structures of some nonlinear pseudo-parabolic equations. Partial Differential Equations in Applied Mathematics, 100490. [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, A. S. (2002). The hybrid multiscale simulation technology: an introduction with application to astrophysical and laboratory plasmas. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Xiang, C. , & Wang, H. (2020). New Exact Solutions for Benjamin-Bona-Mahony-Burgers Equation. Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 10(8), 543-550. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. (2014). Application of classification of traveling wave solutions to the Zakhrov-Kuznetsov- Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation. Applied Mathematics, 5(10), 1432.
- Akcagil, S. , Aydemir, T., & Gozukizil, O. F. (2016). Exact travelling wave solutions of nonlinear pseudoparabolic equations by using the G′G Expansion Method. New Trends in Mathematical Sciences, 4(4), 51-66.
- Ghosh, S. , & Bharuthram, R. (2008). Ion acoustic solitons and double layers in electron–positron–ion plasmas with dust particulates. Astrophysics and Space Science, 314, 121-127. [CrossRef]
- Petviashvili, V. I. , & Pokhotelov, O. A. (1992). Solitary Waves in Plasmas and in the Atmosphere. Taylor & Francis.
- Yuan, W., Xiao, B., Wu, Y., & Qi, J. (2014). The general traveling wave solutions of the Fisher type equations and some related problems. Journal of Inequalities and Applications, 2014(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. , Cao, J., & Chen, Y. (2015). Higher-order rogue wave solutions of the three-wave resonant interaction equation via the generalized Darboux transformation. Physica Scripta, 90(10), 105. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. G. , Du, J. Q., Zeng, Z. F., & Nie, B. (2017). New three-wave solutions for the (3+ 1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation. Nonlinear Dynamics, 88, 655-661. [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, D. (2021). Localized structures in optical and matter-wave media: a selection of recent studies. Rom. Rep. Phys, 73(2), 403.
- Liu, W. , Qin, Z., Chow, K. W., & Lou, S. (2020). Families of Rational and Semirational Solutions of the Partial Reverse Space-Time Nonlocal Mel’ nikov Equation. Complexity, 2020, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Ma, H. , Zhang, C., & Deng, A. (2020). New periodic wave, cross-kink wave, breather, and the interaction phenomenon for the (2+ 1)-dimensional Sharmo–Tasso–Olver equation. Complexity, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. G., Du, J. Q., Zeng, Z. F., & Ai, G. P. (2016). Exact periodic cross-kink wave solutions for the new (2+ 1)-dimensional KdV equation in fluid flows and plasma physics. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 26(10), 103114. [CrossRef]
- Alsallami, S. A. , Rizvi, S. T., & Seadawy, A. R. (2023). Study of Stochastic–Fractional Drinfel’d–Sokolov– Wilson Equation for M-Shaped Rational, Homoclinic Breather, Periodic and Kink-Cross Rational Solutions. Mathematics, 11(6), 1504. [CrossRef]
- Seadawy, A. R. , Rizvi, S. T., Younis, M., & Ashraf, M. A. (2021). Breather, multi-wave, periodic-cross kink, M-shaped and interactions solutions for perturbed NLSE with quadratic cubic nonlinearity. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 53, 1-14. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




