1. Introduction
Exosomes are a subtype of the extracellular vesicles (EVs), which also include apoptotic bodies and microvesicles. EVs are enclosed by a lipid-bilayer membrane and are secreted by the cells into the extracellular space [
1,
2,
3]. The EVs were grouped into these three subtypes based on their origin, size distribution, and surface markers. Apoptotic bodies arise from the outward blabbing of an apoptotic cell membrane and range in size from 500 to 5000 nm. Microvesicles, which are 100-1000 nm in size, originate as particles shed from the plasma membrane. Exosomes are secreted in the extracellular media under all physiological conditions and can be found in amniotic fluid, bile, blood, breast milk, bronchial fluid, cell culture media, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), gastric acid, lymph, plasma, saliva, semen, serum, synovial fluid, tears, and urine [
3,
4,
5,
6]. Being a class of cell-derived EVs of endosomal origin, exosomes are released into the extracellular media upon the fusion of the multivesicular bodies to the cell membrane. The size of exosomes ranges from 30 to 150 nm, and their specific markers are CD9, CD63, CD81, ALIX (apoptosis-linked gene 2-interacting protein X), Ras-related protein GTPase Rab, annexin, flotillin, ceramide, and TSG101. Exosomes contain DNA fragments, miRNAs, siRNA, mRNA, proteins, lipids, and other metabolites [
7,
8]. These compositions are affected by the cells and environment. Exosome secretion has been shown to increase in response to inflammation [
9], hypoxia [
10], and acidic microenvironment [
11].
Exosomes play an important role in intercellular communication and are critical mediators of organ crosstalk. Exosomes can alter the behavior of target cells through autocrine and paracrine signaling. They show therapeutic potential for detection of pathological conditions and can be used for drug delivery. In fact, targeted drug delivery using exosomes has been developed especially in drug delivery to tumor cells and heart tissues. Tumor cells can change their microenvironment by using exosome communication between cells and the immune system [
12,
13,
14,
15]. Acquired exosomes from liquid biopsies are not invasive and therefore have potential for the development of genomic and proteomic research for disease diagnosis and prognosis monitoring. Exosomes are used for treatment of heart after myocardial infarction, which is caused mostly by atherosclerosis. Statins like lovastatin attenuate atherosclerosis and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease previous studies show optimization parameters for lovastatin production [
16,
17,
18,
19].
Exosomes have emerged as a promising source of biomarkers, which can be isolated from small volumes of samples and illustrate tissue-specific molecules representing disease-specific and disease-status biomarkers for various chronic and acute diseases such as CPNE3 in colorectal cancer EVs [
20], miR-451a in non-small cell lung cancer EVs [
21], and miR-451a in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma EVs [
22].
With the increased use of exosomes in clinical practice, the best methods for maximizing the quality and yield of these EVs are needed. The efficient separation of exosomes from protein and other extracellular vesicles in the media or body fluids is critically important for biomarker discovery and validation. Although ultracentrifugation represents a common method for exosome isolation [
23], several commercial exosome methods such as ultrafiltration, microfluidics, precipitation, size exclusion chromatography, and affinity purification based on magnetic beads were elaborated as well [
24,
25].
The ultrafiltration method used one or more filters, mostly an Amicon filter with 100 kDa MW, to separate particles larger than 30 nm. There are several different base precipitation methods for exosome isolation, including neutral charge and polymer-bases precipitation methods. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is primarily used to reduce the solubility of exosomes. These were subsequently isolated using low-speed centrifugation. The classical method is ultracentrifugation, which uses centrifugal force to separate exosomes at a very high speed to move them across the length of the tube in approximately 70 min. To increase the purity and reduce the amount of non-extracellular vesicles, the pellet was dissolved in PBS and centrifuged again for 70 min. ultracentrifugation further exosomes isolation used to separation and collect other nanoparticles such as zinc oxide, copper, iron and noisome [
26,
27,
28]. The goal of this study was to compare three common methods exosome isolation from the cell culture medium, such as ultrafiltration, precipitation, and ultracentrifugation. We hope that this work will serve as a guide for choosing the best exosome isolation methods for downstream therapeutic applications for industrialization according to time, scalability and costs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture
H9c2 cells were purchased from the Institut Pasteur of Iran. Cells were grown in 105/T 75 flask DMEM supplemented with 15% FBS (Biosera, Iran) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Biosera, Iran), and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 [
29,
30].
2.2. Ischemic Preconditioning
To simulate ischemic conditions in vitro and investigate the effect of exosomes on cell viability, we used ischemic preconditioning. After 80% confluency, cells were washed three times with PBS, and the medium was changed to media containing 15% free-exosome FBS. To induce ischemic preconditioning, cells were subjected to repeated cycles of anoxia O2 less than 0.1 mmHg in a hypoxic chamber for 30 min with further reoxygenation (10 min) in a convenient incubator for three cycles. After inducing ischemic preconditioning, cells were returned to incubator for further two days to produce exosomes [
31].
2.3. Exosome isolation methods
After 80% confluency, the medium of cells was changed to free-exosome FBS media. Two days after incubation with free-exosome media, the culture supernatant was collected for exosome isolation.
2.4. Ultrafiltration
In this method, the supernatant of the media was collected in a 15 ml falcon tube, followed by centrifugation at 300 g for 10 min at 4 °C to remove dead cells. The supernatants were centrifuged at 3,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C to eliminate cellular debris and large microvesicles, then the conditioned supernatant media was filtered through a 0.22 μm sterilization filter to remove any cell particulates or apoptotic bodies, the media concentrated and buffer exchanged to PBS using a 100 kDa MWCO ultrafiltration column (Millipore) and stored at −80 °C till use. [
32].
2.5. Precipitation
To isolate exosomes using the precipitation method, cell culture supernatants were processed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, the cell culture supernatants were centrifuged at 300 g for 10 min at 4 °C to remove dead cells. The supernatants were centrifuged at 3,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C to eliminate cellular debris and large microvesicles, and the conditioned supernatant media were filtered through a 0.22 μm sterilization filter to remove any cell particulates or apoptotic bodies, then transferred to a sterile vessel, and an appropriate volume of exosome precipitation solution was added, followed by refrigeration overnight (16 h). After refrigeration, the exosome precipitation/supernatant mixture was centrifuged at 1500 g for 30 min, the supernatant was aspirated and the tube was spun down again to remove residual exosome precipitation solution by centrifugation at 1500 g for 5 min [
33].
2.6. Ultracentrifugation
The exosomes were also isolated by ultracentrifugation. For ultracentrifugation, cell culture supernatants were collected after two days of culture, followed by centrifugation at 300 g for 10 min at 4 °C to remove dead cells. The supernatants were first centrifuged at 3,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C to eliminate cellular debris and large macrovesicles and then additionally centrifuged at 100,000 g for 70 min at 4 °C. The sediment was resuspended in PBS, and the mixture was centrifuged at 100,000 g for 70 min to obtain relatively pure exosomes and stored at −80 °C till use [
34].
2.7. Exosome characterization
2.7.1. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM)
To investigate the morphology of exosomes isolated using three methods mentioned above, we used field emission electron microscopy with a gold coating to increase contrast (JEM-2000EX TEM, Japan).
2.7.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
10 μl of 10 µg/ml isolated exosomes for each method dilutes 100 fold with PBS. The size and polydispersity index (PI) of each sample were measured using dynamic light scattering. The polydispersity index served as a measure of the homogeneity of the exosome isolation methods. Less than 0.3 indicates homogenous and more than 0.3 indicates heterogeneity.
2.7.3. Viability analysis (alamarBlue assay)
AalamarBlue assay-based analysis was performed as a cell viability indicator. The blue color of alamarBlue changes to red if the cells are viable. In this analysis, after inducing hypoxic conditions we utilized exosomes isolated by different methods to increase viability, after which 10% (v/v) alamarBlue was added to each well and incubated for 6 h in an incubator then use 570-600 nm for detection [
35].
2.7.4. Flow cytometry
To confirm the results of alamarBlue after inducing hypoxic conditions, we used flow cytometry (annexin-PI) to show the effects of different exosome isolation methods on cell viability. In this analysis, the percentage of live cells, apoptosis, and necrosis are shown in plot [
36].
2.7.5. Total protein content of exosome isolation
To investigate the protein content of each exosome isolation method, we used 100 µL of exosomes isolated from 1 million cells after 2 days of incubation with free-exosome medium. Bradford assay analysis was used to show total content of protein. Each protein content group was calculated at 595 nm and compared with the standard curve for 1-1000 µg/ml BSA to report the results of the analysis.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data are represented as the mean SEM. The significance of differences between two groups was tested by Student’s t-test and multiple groups by ANOVA. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. All experiments were repeated at least three times.
3. Results and Discussion
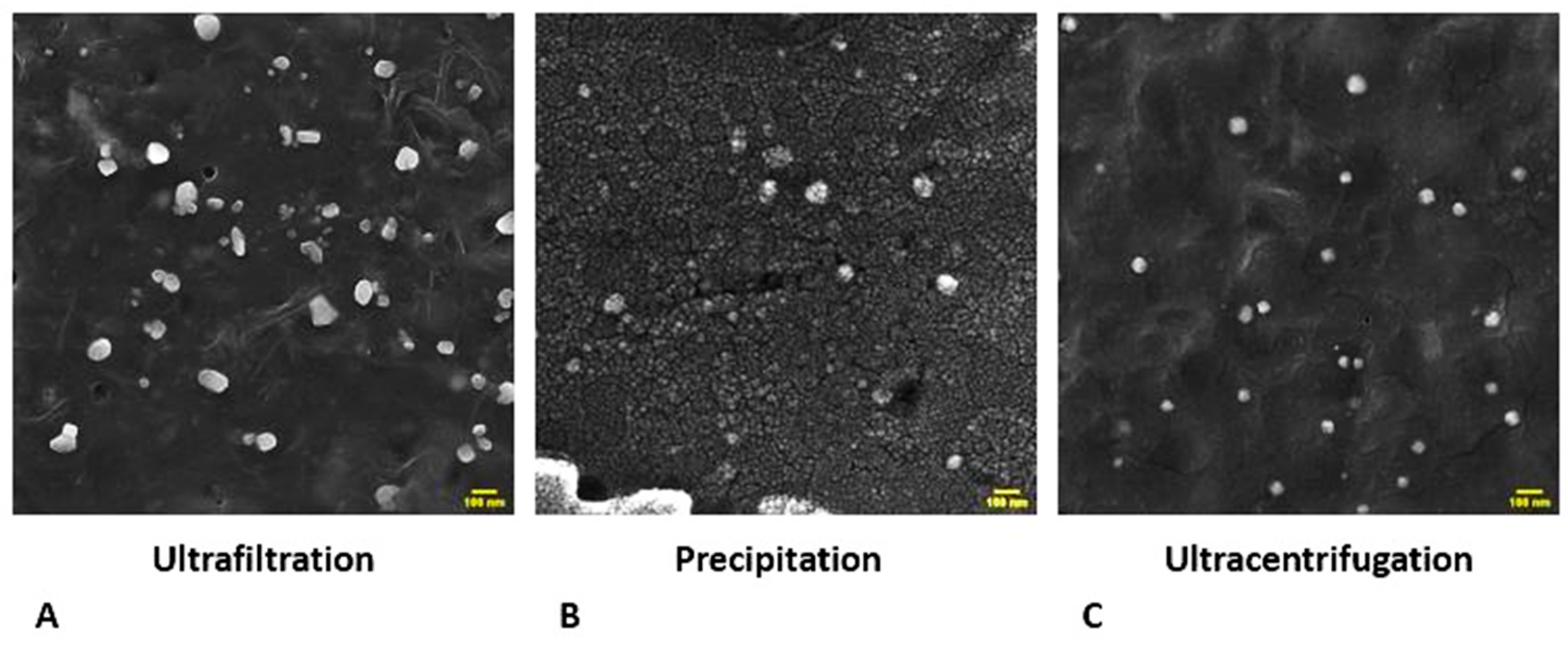
As previous reports show that exosomes have variety of sizes and forms, ranging from round to ellipsoid shape [
37,
38,
39]. Our FESEM image results (
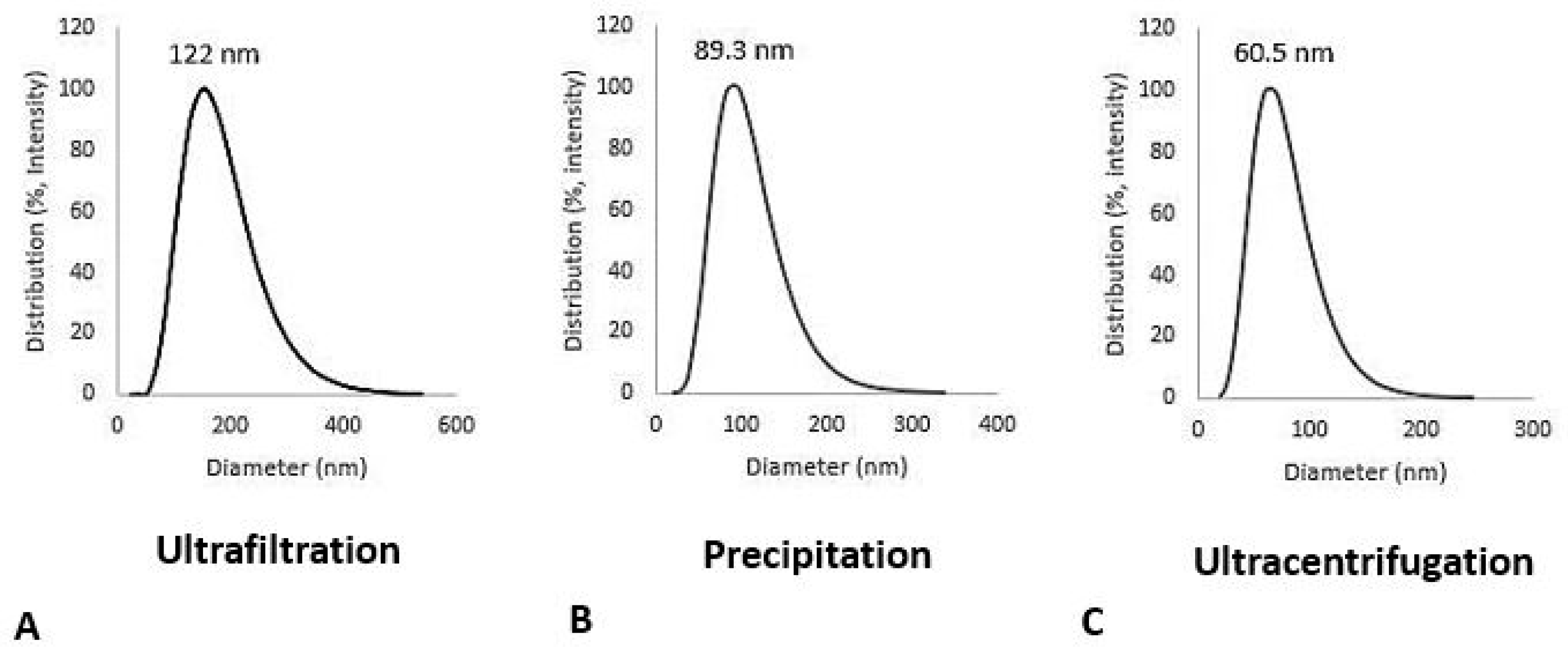
Figure 1) show that exosomes isolated using the ultrafiltration method have more variety in shape, from rounded to ellipsoid, but exosomes isolated by precipitation and ultracentrifugation methods have less variety in shape and mostly have rounded and uniform shapes (scale bare, 100 nm). Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis confirmed that the exosome isolation methods have an impact on the size distribution of the isolated exosomes.
The results showed a distribution range for the ultrafiltration method of 40-320 nm with a mean diameter of 122 nm. For precipitation methods with polyethylene glycol (PEG), the distribution ranges from 30 to 220 nm with a mean diameter of 83 nm. For the ultracentrifugation methods, the distribution ranges from 30 to 180 nm with a mean diameter of 60 nm (
Figure 2). Polydispersity (PI) index for all experiments was less than 0.3, which indicates the homogeneity of samples prepared by all methods of the exosome isolation.
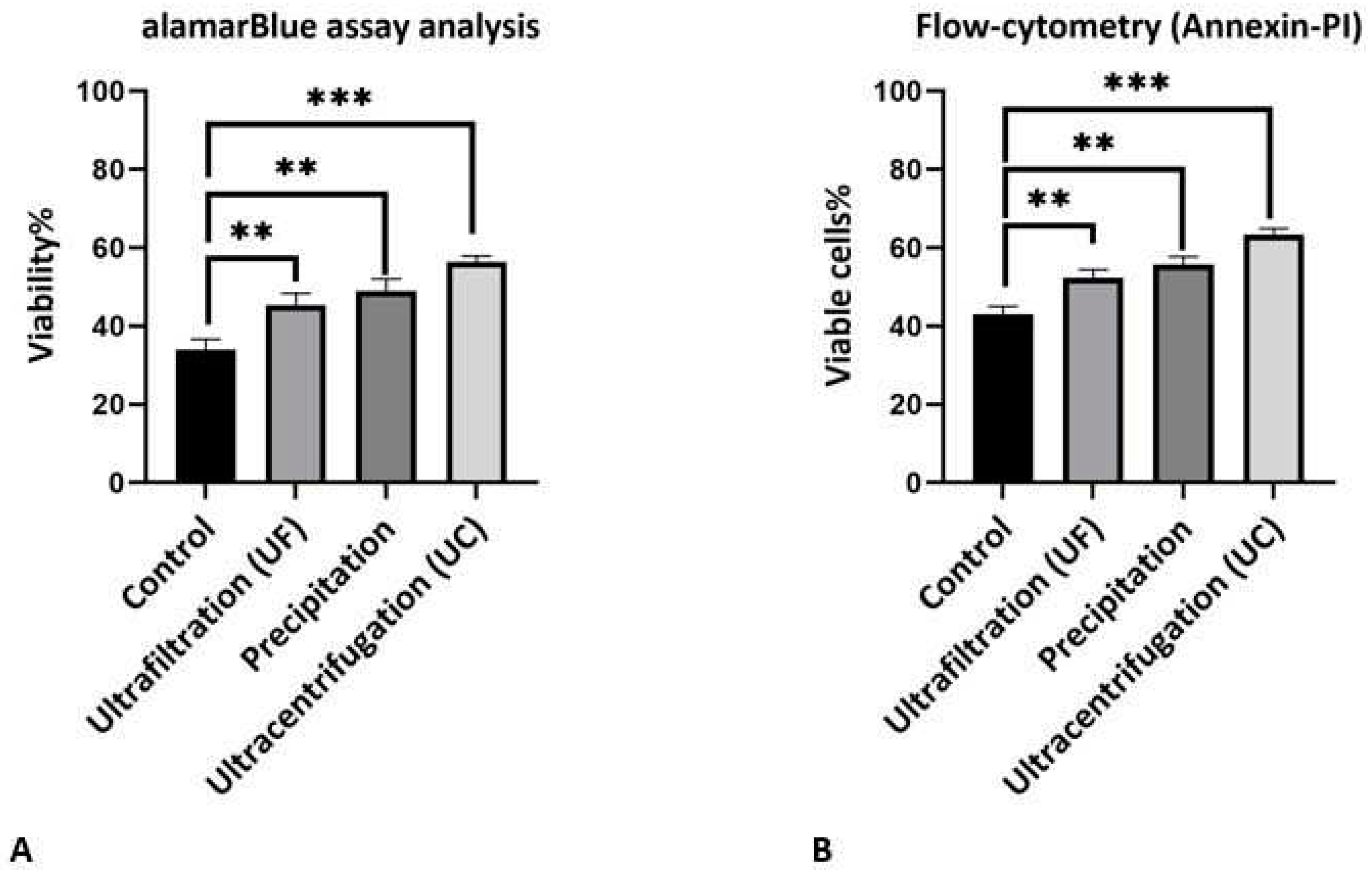
As noted above, exosomes contain many metabolites and various types of genetic content such as short fragments of DNA, microRNA, siRNA, and mRNA, which increase the viability and change the performance of the cells or organs with respect to their source. To investigate the effect of isolation methods on the purity and quality of exosomes, we used the alamarBlue assay to determine cell viability. In these methods, if cells are viable, blue color from alamarBlue changes to red color. We applied ischemic preconditioning protocol in order to simulate ischemia in H9c2 cells and investigated the effect of exosomes obtained by different isolation methods on the cell viability. As shown in (
Figure 3A), the viability levels for hypoxic H9c2 cells treated by exosomes obtained by different isolation methods were 45.3±3.1%, 49±3% and 56.3±1.5% for the ultrafiltration, precipitation, and ultracentrifugation methods respectively. The percentage viability in control group was 34.0±2.6%. All groups treated with exosomes showed significantly increased viability compared to that of the control group. Ultracentrifugation had the greatest effect on the viability of the hypoxic H9c2 cells. Although the mean viability of the precipitation method was higher than that of the ultrafiltration method, the difference in terms of viability was not significant. To confirm the viability assay, we used flow cytometry (annexin-PI) to show the effect of exosomes obtained by different isolation methods on the viable cells under the hypoxic conditions (
Figure 3B). This analysis showed the significant increase in viable cells to 52.33±2.08%, 55.66±2.08% and 63.33±1.52% for ultrafiltration, precipitation, and ultracentrifugation, respectively, as compared to 43±2% viable cells observed in the control group. The ultracentrifugation method resulted in a significant increase in the viable cells compared to the other methods. In this analysis, there was no significant difference between the ultrafiltration and precipitation methods. A previous study showed that exosomes increased the viability of cells under the same stress conditions, such as increasing H
2O
2 [
40].
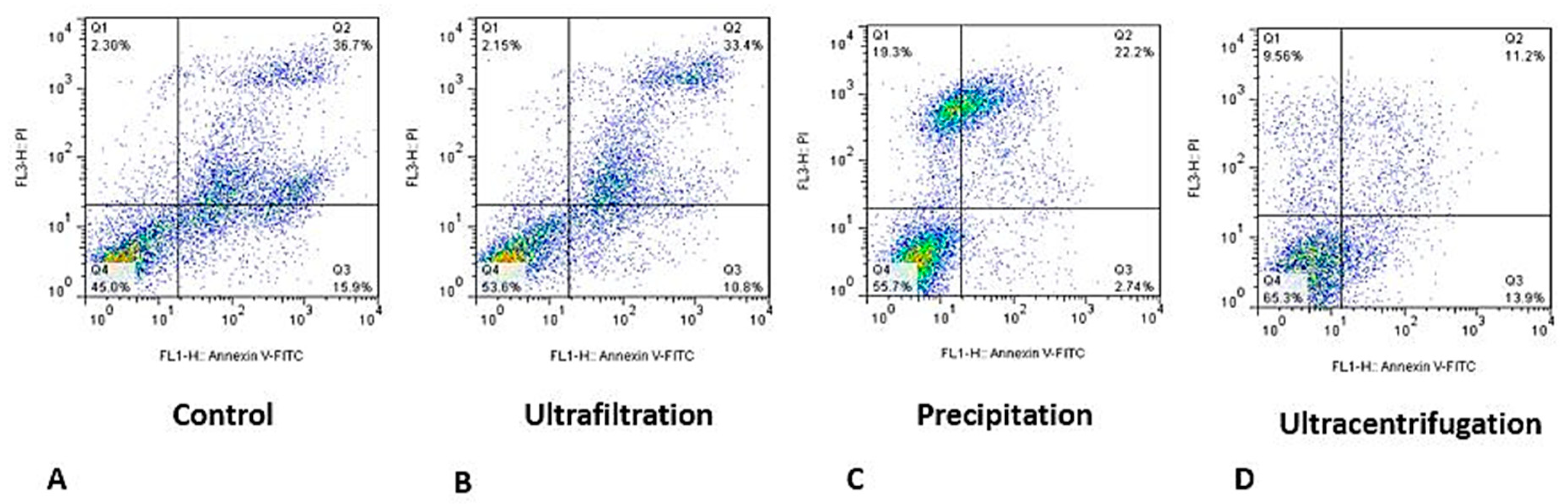
A set of representative flow cytometry plots for evaluating the effect of exosomes obtained by different methods is shown in (
Figure 4), which shows that the percentage of viable cells increased in all exosome-treated groups compared to the control group. In addition, the percentage of apoptotic cells were reduced in all methods, especially when we used exosomes obtained by precipitation and ultracentrifugation methods. All results of the viability analysis showed that ultracentrifugation isolation method significantly increased the viability compared to other methods, showing that exosomes obtained by this method have better quality than those obtained by the other two methods.
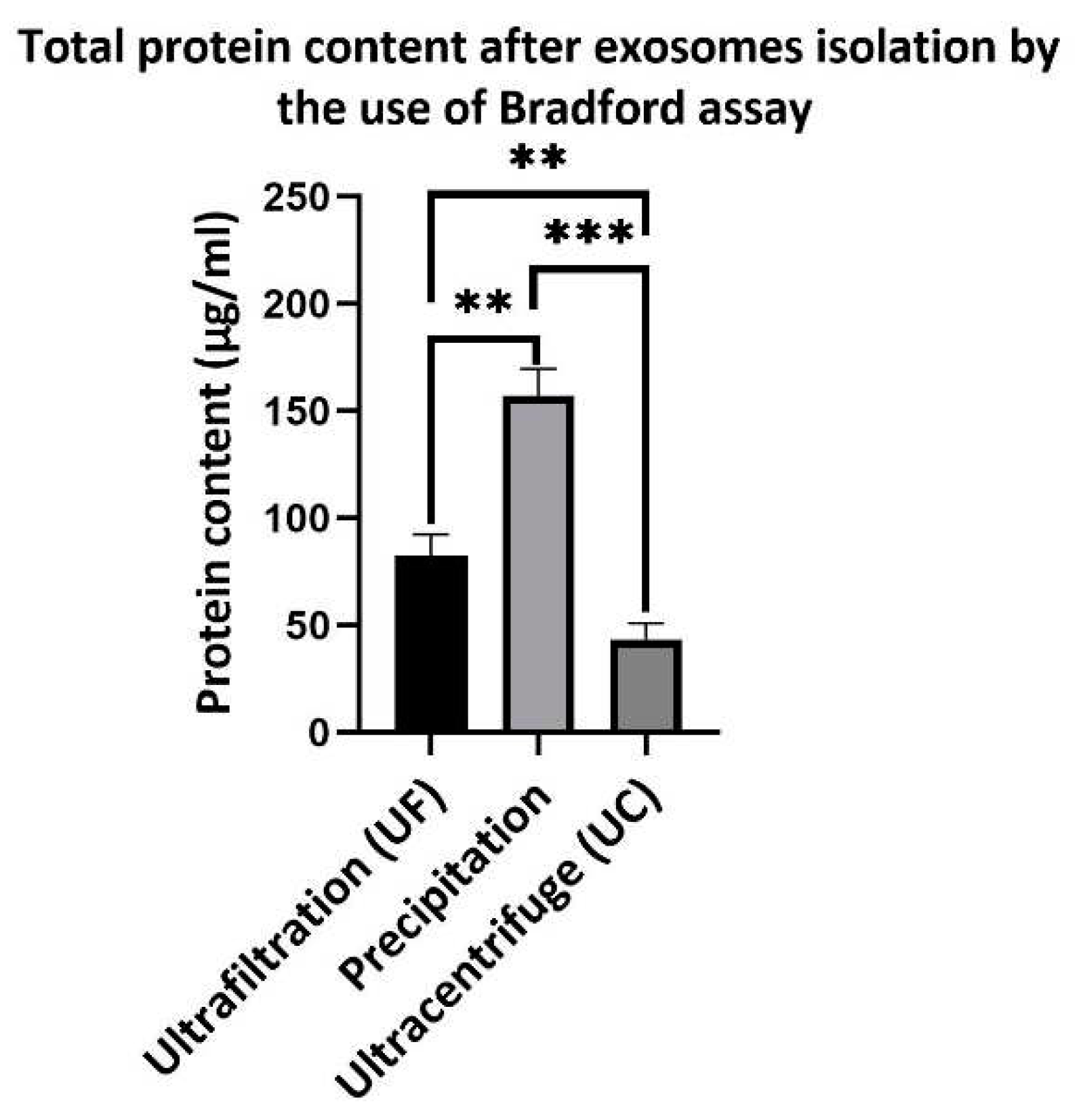
Exosomes contain various types of proteins both inside and on their surface. Therefore, the protein content can be used to determine the amount of exosomes isolated from the media. In this study, we used total protein content by the Bradford method to show the protein content of exosomes obtained by different methods. As shown in (
Figure 5) total protein content of exososme isolated by the ultrafiltration method was 82.33±10.01 µg/ml, whereas for exososmes isolated by ultracentrifugation method this amount was 43.33±7.5 µg/ml. In the exosomes isolated by the precipitation method, the total protein content was 157±12 µg/ml, which was significantly higher than that in other two methods. The difference in the protein content of samples isolated by ultrafiltration and ultracentrifugation is likely due to the presence of residual microvesicles and apoptotic bodies, which cannot be separated from exosomes by ultrafiltration because their size is larger than the pore size of the filter.
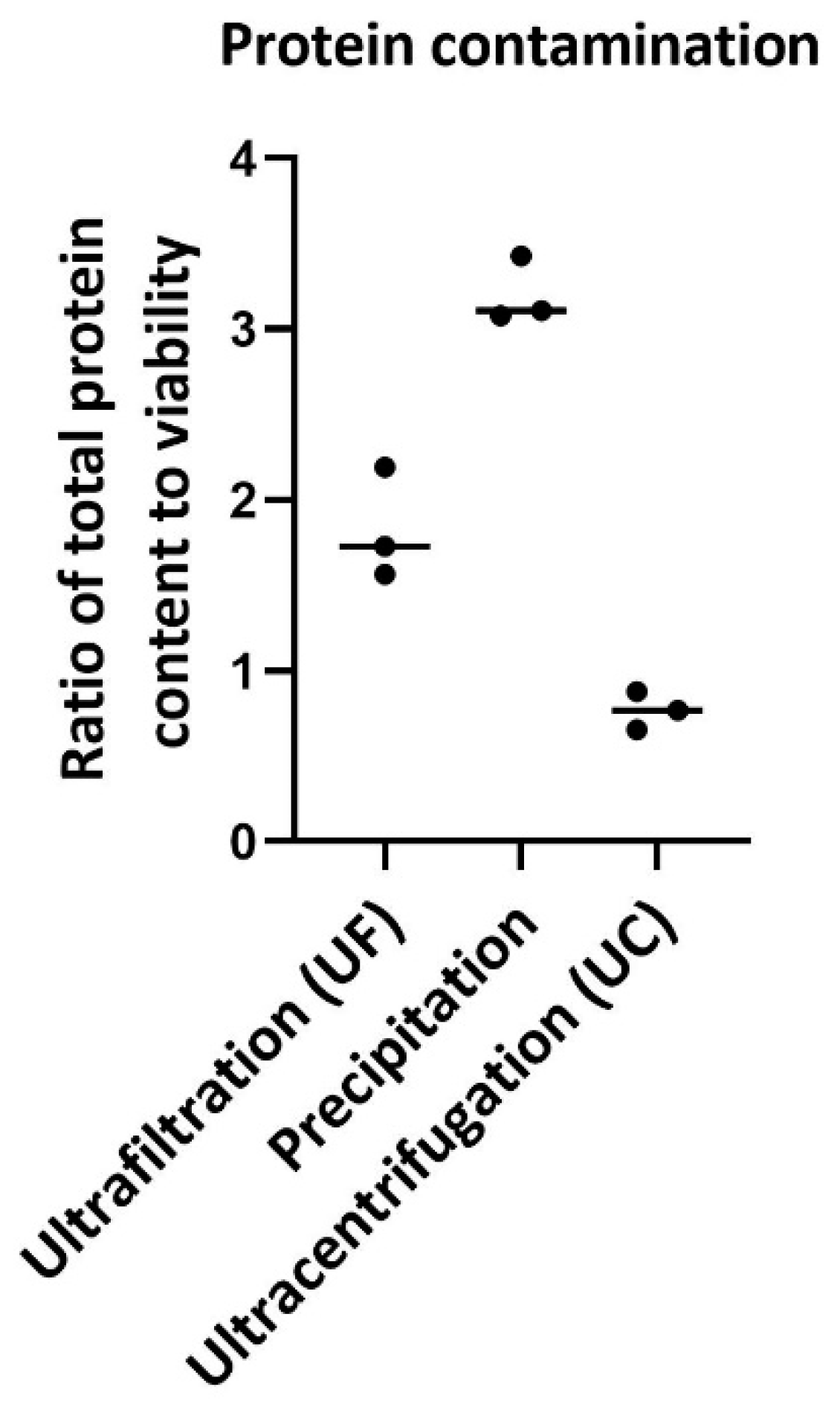
The ratio of total protein content to viability was considered as a measure of protein contamination (
Figure 6). Previous reports have shown that the protein content can be used to investigate impurities in exosome isolation methods. Ratio of total protein content to viability were 1.82±0.32%, 3.2±0.19% and 0.767±0.11 for ultrafiltration, precipitation and ultracentrifugation respectively. The results show that contamination with protein in the precipitation method is higher and that in ultracentrifugation is lower than in other two methods. Previous reports have shown that PEG precipitation methods also result in high protein contamination due to the precipitation of some other proteins.
In the ultrafiltration methods, all particles larger than 30 nm, such as protein aggregates and other EVs, are separated from exosomes; therefore, the quality and purity of these methods are reduced. This method requires an Amicon filter, which makes this method expensive. The sample volume and scalability of this method are very restricted. The required time for this method is very short 0.5-1 h, which favors the isolation of exosomes [
41]. The main problem with these methods is related to the scalability and cost of the Amicon filters. In precipitation methods, similar proteins and particles, which range in the size of exosomes, isolated from media; quality and purity in this method are low compared to other methods, but the sample volume and scalability are high. This method does not require special equipment and its cost is very low [
42]. If problems of quality and purity were solved due to other advantages, this method can be used most widely in laboratories as the best method for the isolation of exosomes; the time required for this method is 12-16 h. Ultracentrifugation is the classical method for exosome isolation. This process reduces particle yield but increase the purity and quality of exosomes. This method requires ultracentrifugation, the sample volume is restricted, scalability is low and cost is relatively high, and the time required for this method is 3-4 h [
43]. A summary of the different exosome isolation methods is presented in (
Table 1) for a better comparison of different base exosome isolation methods related to time, cost, scalability, and commercialization potential.
4. Conclusions
Exosomes have become increasingly important in medicine for drug delivery in heart, kidney, and tumor therapies, as well as for diagnosis and prognosis of diseases. Their isolation methods have a significant impact on quality, purity, sample volume, scalability, and cost. There are several different methods for exosome isolation, each with its advantages and disadvantages, such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, ultrafiltration, size exclusion chromatography, affinity isolation, and microfluidic techniques.
The ultrafiltration method typically uses a 100 kDa MW Amicon filter to isolate exosomes. However, this method also separates all particles larger than 30 nm, including protein aggregates and other extracellular vesicles, which reduces the quality and purity of the exosomes. Although this method is relatively expensive, it requires only an Amicon filter. The sample volume and scalability of this method are limited, but it could be improved if cost and scalability issues were addressed.
In the precipitation method, proteins and particles similar in size to exosomes are isolated from the media, resulting in lower quality and purity, but higher sample volume and scalability. This method is inexpensive and does not require special equipment. If the quality and purity issues can be resolved, it could become the most widely used method for exosome isolation in laboratories.
The classical method for exosome isolation is ultracentrifugation, which reduces particle yield but increases the purity and quality of exosomes. However, this method requires an ultracentrifuge, and the sample volume and scalability are limited. The cost is also relatively high for research and analysis that involve multiple stages and manipulation of exosomes. Therefore, we suggest combining two methods, such as isolating exosomes by ultracentrifugation and using ultrafiltration in subsequent processes, to save time and obtain purified exosomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H. and H.G.; validation, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., and H.G.; formal analysis, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., and H.G.; investigation, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., and H.G.; data curation, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., V.N.U., and H.G.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., V.N.U., and H.G.; writing—review and editing, F.J.A., H.A.T., A.Amanzadeh, S.R., M.A.S., R.H., J.B., V.N.U., and H.G.; supervision, R.H., V.N.U., and H.G.; funding acquisition, H.G.
Funding
This research was funded by Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) grant no. 97-02-87-38483.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
Hereby we thank National Cell Bank of Pasteur Institute of Iran.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J. , et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.K.; Rajgor, D.; Lv, Y.; Chung, K.Y.; Tang, Y.C.; Cheng, H. Noncoding RNome as enabling biomarkers for precision health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, B.; Sabo, A.A.; Birolo, G.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNAs in extracellular fluids as cancer biomarkers: the new frontier of liquid biopsies. Cancers 2019, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Bala, S.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Exosomes derived from alcohol-treated hepatocytes horizontally transfer liver specific miRNA-122 and sensitize monocytes to LPS. Scientific reports 2015, 5, 9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Yim, J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, E.; Lee, Y.-S.; Seo, W. Exosomes: Nomenclature, Isolation, and Biological Roles in Liver Diseases. Biomolecules & Therapeutics 2023, 31, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.M.; Bøtker, H.; Carr, R.; Davidson, S.; Downey, J.; Dutka, D.; Heusch, G.; Ibanez, B.; Macallister, R.; Stoppe, C. 9th Hatter Biannual Meeting: position document on ischaemia/reperfusion injury, conditioning and the ten commandments of cardioprotection. Basic Research in Cardiology 2016, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, F.; Capece, M.; Rotondo, A.; Cangelosi, D.; Ferracin, M.; Franceschini, A.; Raffaghello, L.; Pistoia, V.; Varesio, L.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 receptor is a key modulator of the PI3K/GSK3β/VEGF signaling network: evidence in experimental neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5240–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausenloy, D.J.; Yellon, D.M. Ischaemic conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nature Reviews Cardiology 2016, 13, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenazy, F.; Harbi, M.; Kavanagh, D.; Price, J.; Brady, P.; Hargreaves, O.; Harrison, P.; Slater, A.; Connolly, D.; Kirchhof, P. GPVI inhibition by glenzocimab synergistically inhibits atherosclerotic plaque-induced platelet activation when combined with conventional dual antiplatelet therapy. European Heart Journal 2021, 42, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.; Li, I.T. Targeting capabilities of native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinikhah, S.M.; Gheybi, F.; Moosavian, S.A.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Sillanpää, M.; Kesharwani, P.; Alavizadeh, S.H.; Sahebkar, A. Role of exosomes in tumour growth, chemoresistance and immunity: State-of-the-art. Journal of Drug Targeting 2023, 31, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, A. Adipose extracellular vesicles in intercellular and inter-organ crosstalk in metabolic health and diseases. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 608680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, F.J.; Jalili, H.; Bizukojc, M.; Amrane, A. Optimization of date syrup as a novel medium for lovastatin production by Aspergillus terreus ATCC 20542 and analyzing assimilation kinetic of carbohydrates. Annals of microbiology 2018, 68, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaberi Ansari, F.; Jafari Mansoorian, H.; Jalili, H.; Azizi, M. A review of the effective factors for lovastatin production by Aspergillus terreus ATCC 20542 in liquid submerged fermentation. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 2016, 18, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jaberi Ansari, F.; Jalili, H. Effect of Spore Age and Inducers on Lovastatin Production in Aspergillus terreus. Modares Journal of Biotechnology 2018, 9, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Jaberi Ansari, F.; Jalili, H.; Azizi, M. A Study of the Factors Effective in Morphogenesis of Aspergillus terreus in order to Increase the Production of Lovastatin. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 2017, 19, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, K.; Martin, K.; FitzGerald, S.; O’sullivan, J.; Wu, Y.; Blanco, A.; Richardson, C.; Mc Gee, M. A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, R.; Iinuma, H.; Dejima, H.; Sakai, T.; Uehara, H.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M. Usefulness of plasma exosomal microRNA-451a as a noninvasive biomarker for early prediction of recurrence and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology 2018, 94, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahasi, K.; Iinuma, H.; Wada, K.; Minezaki, S.; Kawamura, S.; Kainuma, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Shibuya, M.; Miura, F.; Sano, K. Usefulness of exosome-encapsulated microRNA-451a as a minimally invasive biomarker for prediction of recurrence and prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sciences 2018, 25, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares Martins, T.; Catita, J.; Martins Rosa, I.; AB da Cruz e Silva, O.; Henriques, A.G. Exosome isolation from distinct biofluids using precipitation and column-based approaches. PloS one 2018, 13, e0198820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-M.; Li, A.; Chen, J.-J.; Sun, E.-J. Research development on exosome separation technology. The Journal of Membrane Biology 2023, 256, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Larcher, L.M.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation-efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhassani Targhi, A.; Mousavi-Niri, N.; Jaberi Ansari, F.; Jafari Mansoorian, H. The Antibacterial Effects of Curcumin-Silver Nanoparticle and Curcumin-Copper Nanoparticle Loaded Niosomes. Health and Development Journal 2022, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, M.; Bargahi Nasab, H.; Abdipour, H.; Jafari Mansoorian, H.; jaberi Ansari, F. Comparison of the effect of metal oxide nanoparticles (copper, zinc, and iron) on the removal of cobalt by electrocoagulation processes from refinery wastewater. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtbari, Y.; Afshin, S.; Hamzezadeh, A.; Gholizadeh, A.; Ansari, F.J.; Poureshgh, Y.; Fazlzadeh, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon prepared from walnut peel extract for the removal of Eosin Y and Erythrosine B dyes from aqueous solution: Experimental approaches, kinetics models, and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-T.; Xiao, F.-J.; Wang, H.; Ge, R.-L.; Wang, L.-S. Hypoxia protects H9c2 cells against Ferroptosis through SENP1-mediated protein DeSUMOylation. International Journal of Medical Sciences 2021, 18, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Long, K.; Qiu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, A.; Jin, L. Overexpression of exosomal cardioprotective miRNAs mitigates hypoxia-induced H9c2 cells apoptosis. International journal of molecular sciences 2017, 18, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, W.; Wani, M.; Yu, X.; Ashraf, M. Ischemic preconditioning potentiates the protective effect of stem cells through secretion of exosomes by targeting Mecp2 via miR-22. PloS one 2014, 9, e88685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escate, R.; Padro, T.; Suades, R.; Camino, S.; Muñiz, O.; Diaz-Diaz, J.L.; Sionis, A.; Mata, P.; Badimon, L. High miR-133a levels in the circulation anticipates presentation of clinical events in familial hypercholesterolaemia patients. Cardiovascular research 2021, 117, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, E.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, B.; Yi, G.; Mao, X. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglio, E.; Puddighinu, G.; Fasanaro, P.; D'Arcangelo, D.; Perrone, G.A.; Mocini, D.; Campanella, C.; Coppola, L.; Logozzi, M.; Azzarito, T. Exosomal clusterin, identified in the pericardial fluid, improves myocardial performance following MI through epicardial activation, enhanced arteriogenesis and reduced apoptosis. International journal of cardiology 2015, 197, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, P.; Sharma, S.; Korutla, L.; Datla, S.R.; Shoja-Taheri, F.; Mishra, R.; Bigham, G.E.; Sarkar, M.; Morales, D.; Bittle, G. Circulating exosomes derived from transplanted progenitor cells aid the functional recovery of ischemic myocardium. Science translational medicine 2019, 11, eaau1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; Galasso, G.; Ambrosio, P.; Stiuso, P.; Lama, S.; Di Zazzo, E.; Schiavon, S.; Vecchio, D.; D’ambrosio, L.; Quagliuolo, L. H9c2 Cardiomyocytes under Hypoxic Stress: Biological Effects Mediated by Sentinel Downstream Targets. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.E.; Stanley, P.F.; Randeva, H.; Banerjee, S. Microvesicle-mediated release of soluble LH/hCG receptor (LHCGR) from transfected cells and placenta explants. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2011, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Pham, S.; Adomat, H.; Li, N.; Guns, E.S.T. Exosomes as biomarker enriched microvesicles: characterization of exosomal proteins derived from a panel of prostate cell lines with distinct AR phenotypes. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2012, 11, 863–885. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wu, X.-H.; Wang, D.; Luo, C.-L.; Chen, L.-X. Bladder cancer cell-derived exosomes inhibit tumor cell apoptosis and induce cell proliferation in vitro. Molecular medicine reports 2013, 8, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, D.; Cores, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Mei, X.; Cheng, X.; Su, T. Platelet membrane and stem cell exosome hybrids enhance cellular uptake and targeting to heart injury. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, Z.; Effah, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Qu, L. A holistic review of the state-of-the-art microfluidics for exosome separation: an overview of the current status, existing obstacles, and future outlook. Small 2021, 17, 2007174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumans, F.A.; Brisson, A.R.; Buzas, E.I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.F. Methodological guidelines to study extracellular vesicles. Circulation research 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Miao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Song, J.; Cui, D. Progress in microfluidics-based exosome separation and detection technologies for diagnostic applications. Small 2020, 16, 1903916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).