Figure 1.
The patient was a male in his 80s with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis who was under follow-up observation after surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The right lung and pleural metastases were confirmed by dynamic computed tomography (CT) in the equilibrium phase one year after the initial treatment (Figure 1a, arrow), and oral administration of sorafenib (Bayer Healthcare pharmaceuticals, Tokyo, Japan) was started, but was suspended due to hemoptysis. Since the cause of hemoptysis was suspected due to the pleural metastasis by dynamic CT. Angiography was performed with selective cannulation of the intercostal artery, but tumor staining was unclear (Figure 1b). Intra-arterial (transcatheter) contrast-enhanced ultrasnography (CEUS) (IAUS) [
1] for the artery confirmed contrast enhancement in the metastatic lesion (Figure 1c, arrow head) (Right image: monitor mode), and thus, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) was performed for the lesion using Epirubicin® (Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) 40mg containing Lipiodol® (Laboratoire Guerbet, Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France) 6 ml emulsion (ELE) and Gelpart® (Astellas Pharma, Tokyo, Japan) with a particle size of 1 mm. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® only in the metastatic lesions of the lung and pleura (Figure 1d, arrow). After confirming disappearance of hemoptysis after TACE, lenvatinib (Eisai Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) was started with concomitant radiotherapy. The metastatic lesions have been well controlled for four years after TACE. IAUS was performed after approval by the Ethics Committee of Toho University Ohashi Medical Center (H21079_H17064).
Figure 1.
The patient was a male in his 80s with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis who was under follow-up observation after surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The right lung and pleural metastases were confirmed by dynamic computed tomography (CT) in the equilibrium phase one year after the initial treatment (Figure 1a, arrow), and oral administration of sorafenib (Bayer Healthcare pharmaceuticals, Tokyo, Japan) was started, but was suspended due to hemoptysis. Since the cause of hemoptysis was suspected due to the pleural metastasis by dynamic CT. Angiography was performed with selective cannulation of the intercostal artery, but tumor staining was unclear (Figure 1b). Intra-arterial (transcatheter) contrast-enhanced ultrasnography (CEUS) (IAUS) [
1] for the artery confirmed contrast enhancement in the metastatic lesion (Figure 1c, arrow head) (Right image: monitor mode), and thus, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) was performed for the lesion using Epirubicin® (Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) 40mg containing Lipiodol® (Laboratoire Guerbet, Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France) 6 ml emulsion (ELE) and Gelpart® (Astellas Pharma, Tokyo, Japan) with a particle size of 1 mm. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® only in the metastatic lesions of the lung and pleura (Figure 1d, arrow). After confirming disappearance of hemoptysis after TACE, lenvatinib (Eisai Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) was started with concomitant radiotherapy. The metastatic lesions have been well controlled for four years after TACE. IAUS was performed after approval by the Ethics Committee of Toho University Ohashi Medical Center (H21079_H17064).

Figure 2.
The patient was a male in his 80s with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis who developed a disseminated lesion with a diameter of 55 mm close to the ascending colon by plain CT (Figure 2a, circle) 1.5 years after RFA for primary HCC. Lenvatinib (40mg q.d.: quaque die) was administered at a decreased dose due to proteinuria, but was discontinued since there was no reduction of the disseminated lesion. Since the lesion was large and connected to the intestinal tract, abdominal angiography using IAUS was performed. Gastroduodenal arteriography suggested that the disseminated lesion was supplied by two epiploic branches. A selective contrast study confirmed tumor staining in both of these branches. IAUS for each branch showed contrast enhancement in the disseminated lesion, but no enhancement of the adjacent intestinal tract wall (Figure. 2b, circle) (Right image: monitor mode). Thereafter, TACE using ELE and Gelpart® was performed for the individual branches. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® only in the disseminated lesion (Figure. 2c, circle). Readministration of lenvatinib after TACE was suspended due to redevelopment of proteinuria and decreased activities of daily living. Concomitant therapy of atezolizumab (Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) and bevacizumab (Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) was started, but discontinued due to severe diarrhea after one session. However, the lesion has been well controlled for 3 years after TACE.
Figure 2.
The patient was a male in his 80s with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis who developed a disseminated lesion with a diameter of 55 mm close to the ascending colon by plain CT (Figure 2a, circle) 1.5 years after RFA for primary HCC. Lenvatinib (40mg q.d.: quaque die) was administered at a decreased dose due to proteinuria, but was discontinued since there was no reduction of the disseminated lesion. Since the lesion was large and connected to the intestinal tract, abdominal angiography using IAUS was performed. Gastroduodenal arteriography suggested that the disseminated lesion was supplied by two epiploic branches. A selective contrast study confirmed tumor staining in both of these branches. IAUS for each branch showed contrast enhancement in the disseminated lesion, but no enhancement of the adjacent intestinal tract wall (Figure. 2b, circle) (Right image: monitor mode). Thereafter, TACE using ELE and Gelpart® was performed for the individual branches. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® only in the disseminated lesion (Figure. 2c, circle). Readministration of lenvatinib after TACE was suspended due to redevelopment of proteinuria and decreased activities of daily living. Concomitant therapy of atezolizumab (Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) and bevacizumab (Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) was started, but discontinued due to severe diarrhea after one session. However, the lesion has been well controlled for 3 years after TACE.
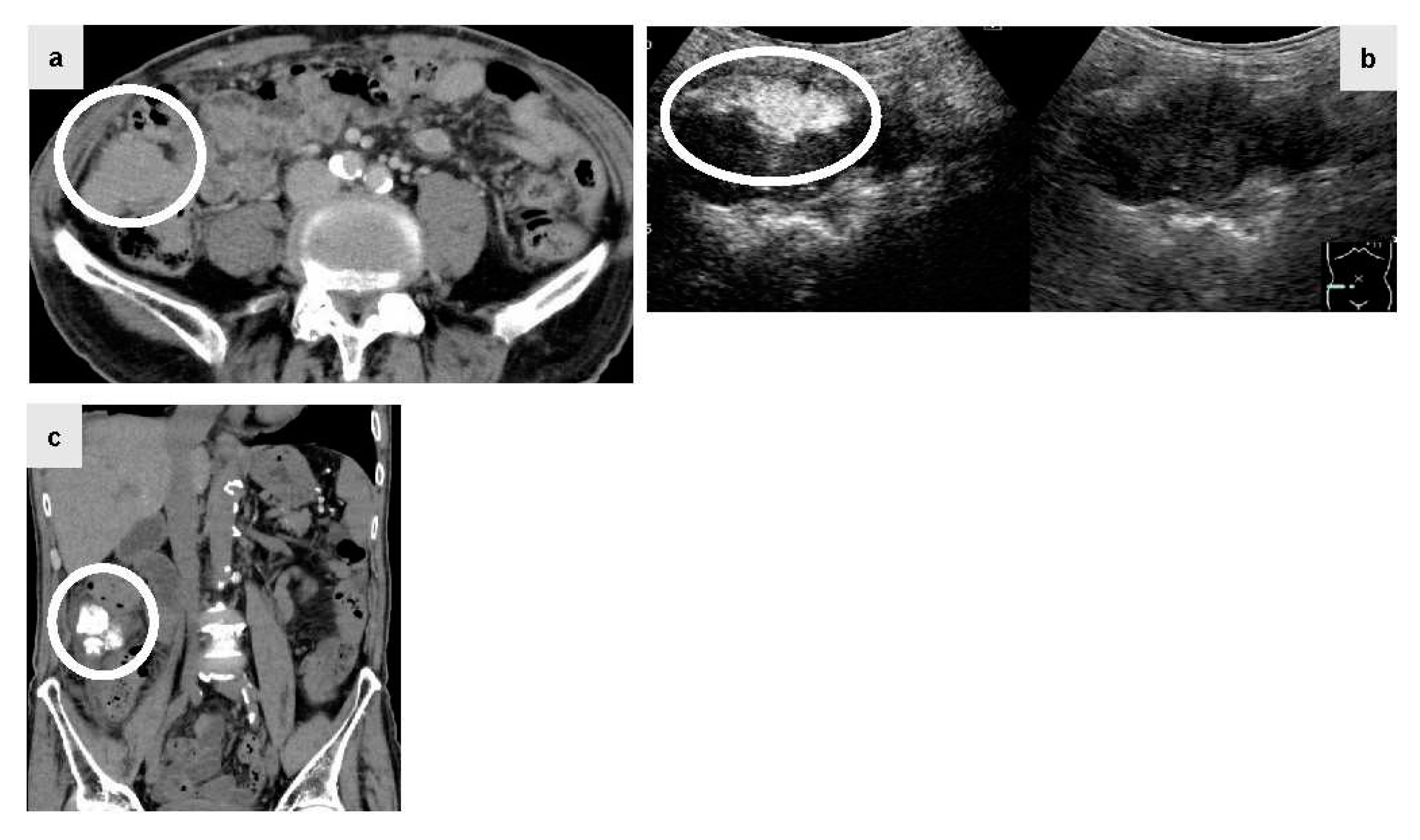
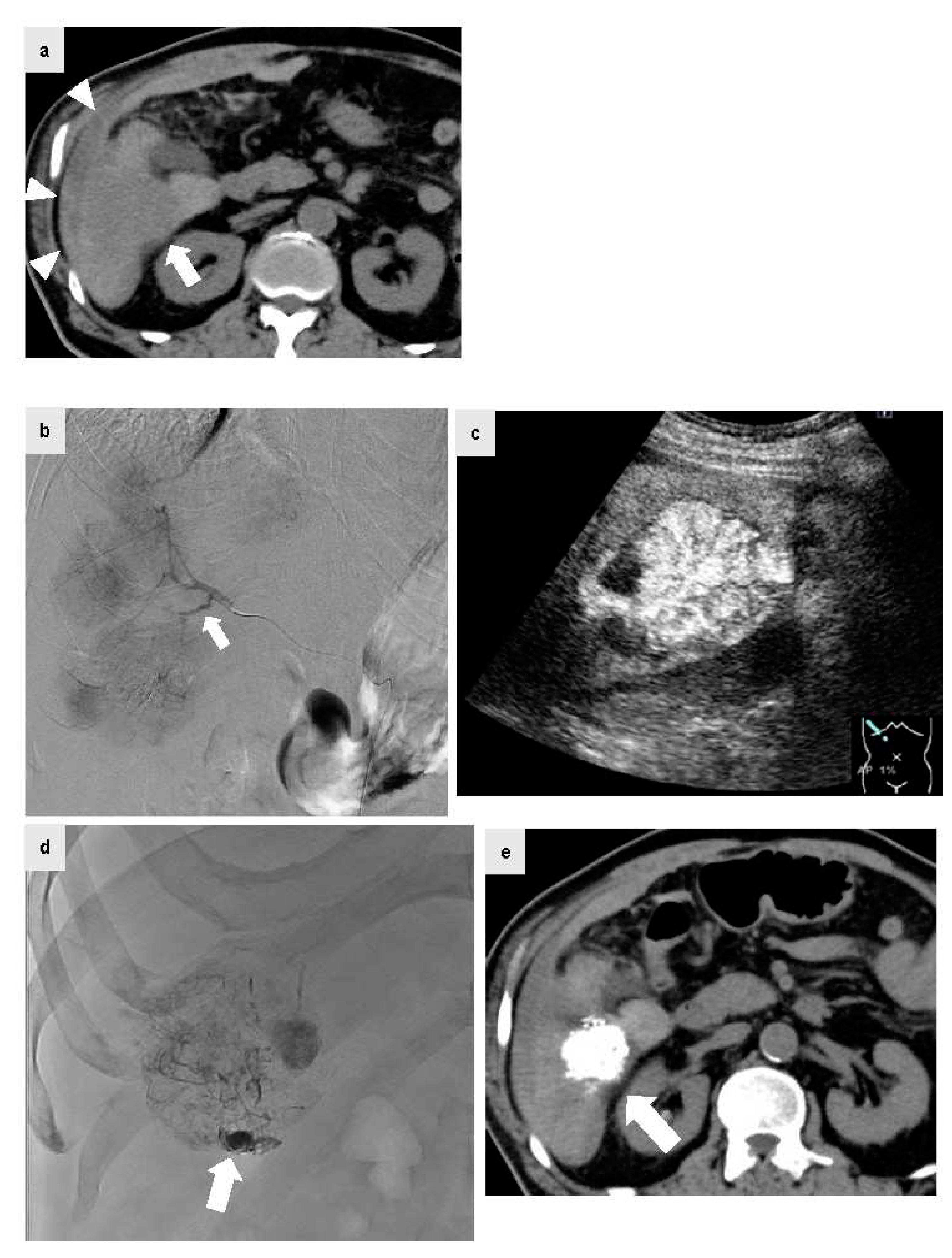
Figure 3.
The patient was a male in his 70s with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis who visited the emergency department for a chief complaint of acute upper abdominal pain during a period of oral administration of lenvatinib for HCC and multiple bone metastases. At the visit, plain CT was performed because anemia of Hb 9.0 g/dl with blood pressure 80/60 mmHg and renal failure with Cr 2.54 mg/dl were confirmed. Since high density fluid collection (Figure 3a, arrow head) was confirmed on the S6 liver surface contiguous HCC by plain CT (Figure 3a, arrow), HCC rupture was suspected and urgent abdominal angiography was performed. IAUS was then performed frequently to reduce the amount of iodinated contrast agent as much as possible because the patient had renal failure, and a microcatheter was extended to the A6 culprit vessel confirmed by CT. Digital subtraction angiography was performed from the A6 culprit vessel. The tumor staining was confirmed, but no clear extravasation was found. The microcatheter was peripherally inserted (Figure 3b, arrow) and IAUS was performed. IAUS showed the enhanced tumor protruding from the surface of the liver (arrow), and surrounding hematoma (Figure 3c). TACE using ELE and Gelpart® was performed at the same site. During TACE, significant accumulation of Lipiodol® was confirmed in the vascular lake of the tumor on the caudal (Figure 3d, arrow), and this was thought to be a site of HCC rupture. After TACE, IAUS was performed again at the site and showed elimination of contrast enhancement. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® in the HCC (Figure 3e, arrow). After TACE, blood pressure was stable with no rebleeding, and at 3 days after TACE the Cr level had improved to the normal range. Concomitant use of IAUS enabled reduction of the amount of contrast agent to 9 ml in abdominal angiography.
Figure 3.
The patient was a male in his 70s with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis who visited the emergency department for a chief complaint of acute upper abdominal pain during a period of oral administration of lenvatinib for HCC and multiple bone metastases. At the visit, plain CT was performed because anemia of Hb 9.0 g/dl with blood pressure 80/60 mmHg and renal failure with Cr 2.54 mg/dl were confirmed. Since high density fluid collection (Figure 3a, arrow head) was confirmed on the S6 liver surface contiguous HCC by plain CT (Figure 3a, arrow), HCC rupture was suspected and urgent abdominal angiography was performed. IAUS was then performed frequently to reduce the amount of iodinated contrast agent as much as possible because the patient had renal failure, and a microcatheter was extended to the A6 culprit vessel confirmed by CT. Digital subtraction angiography was performed from the A6 culprit vessel. The tumor staining was confirmed, but no clear extravasation was found. The microcatheter was peripherally inserted (Figure 3b, arrow) and IAUS was performed. IAUS showed the enhanced tumor protruding from the surface of the liver (arrow), and surrounding hematoma (Figure 3c). TACE using ELE and Gelpart® was performed at the same site. During TACE, significant accumulation of Lipiodol® was confirmed in the vascular lake of the tumor on the caudal (Figure 3d, arrow), and this was thought to be a site of HCC rupture. After TACE, IAUS was performed again at the site and showed elimination of contrast enhancement. Plain CT after TACE showed accumulation of Lipiodol® in the HCC (Figure 3e, arrow). After TACE, blood pressure was stable with no rebleeding, and at 3 days after TACE the Cr level had improved to the normal range. Concomitant use of IAUS enabled reduction of the amount of contrast agent to 9 ml in abdominal angiography.
Author Contributions
All authors (K.S., T.M., T.M., K.I., M.W.) have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shiozawa, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ikehara, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsui, T.; Saigusa, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Maetani, I. efficacy of intra-arterial contrast-enhanced ultrasonography during transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2018, 10, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).






