Submitted:
15 August 2023
Posted:
17 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
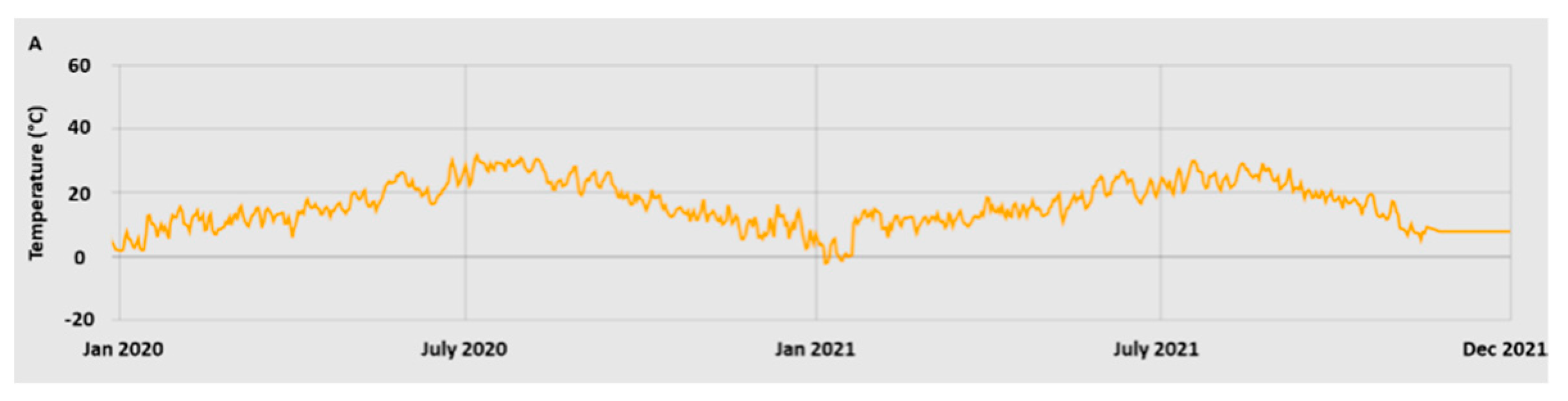
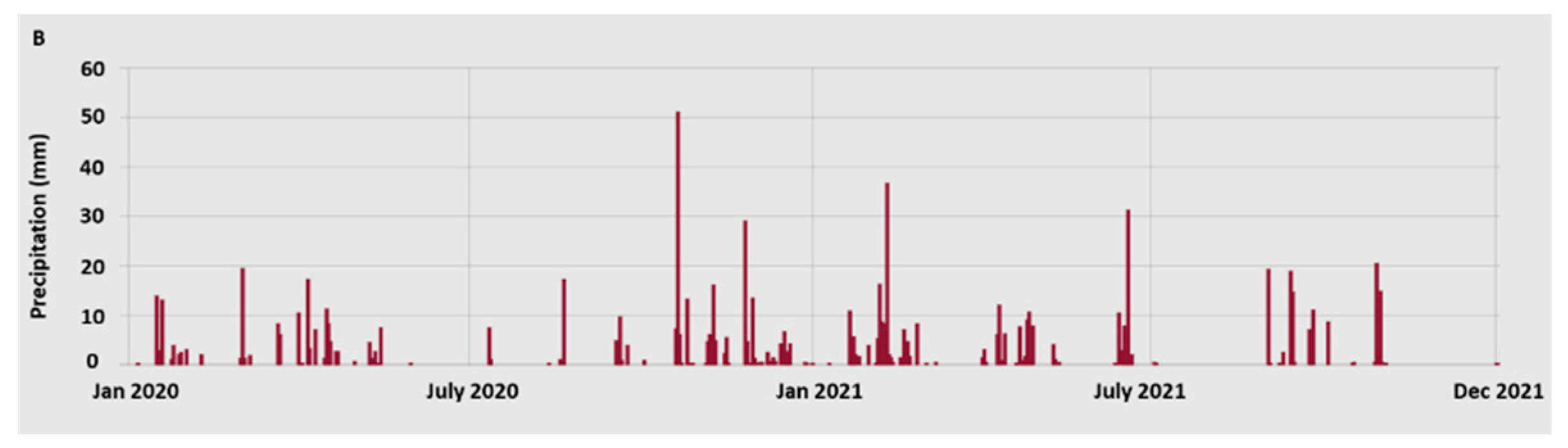
2.1. Plant material and sampling
2.2. Quality assessment of fruits
2.3. Determination of bioactive compounds
2.3.1. Total phenolics
2.3.2. Flavonoids
2.3.3. Ortho-diphenols
2.3.4. Total anthocyanins
2.4. Antioxidant activity assays
2.4.1. ABTS•+ radical-scavenging activity
2.4.2. DPPH radical-scavenging activity
2.4.3. FRAP assay
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
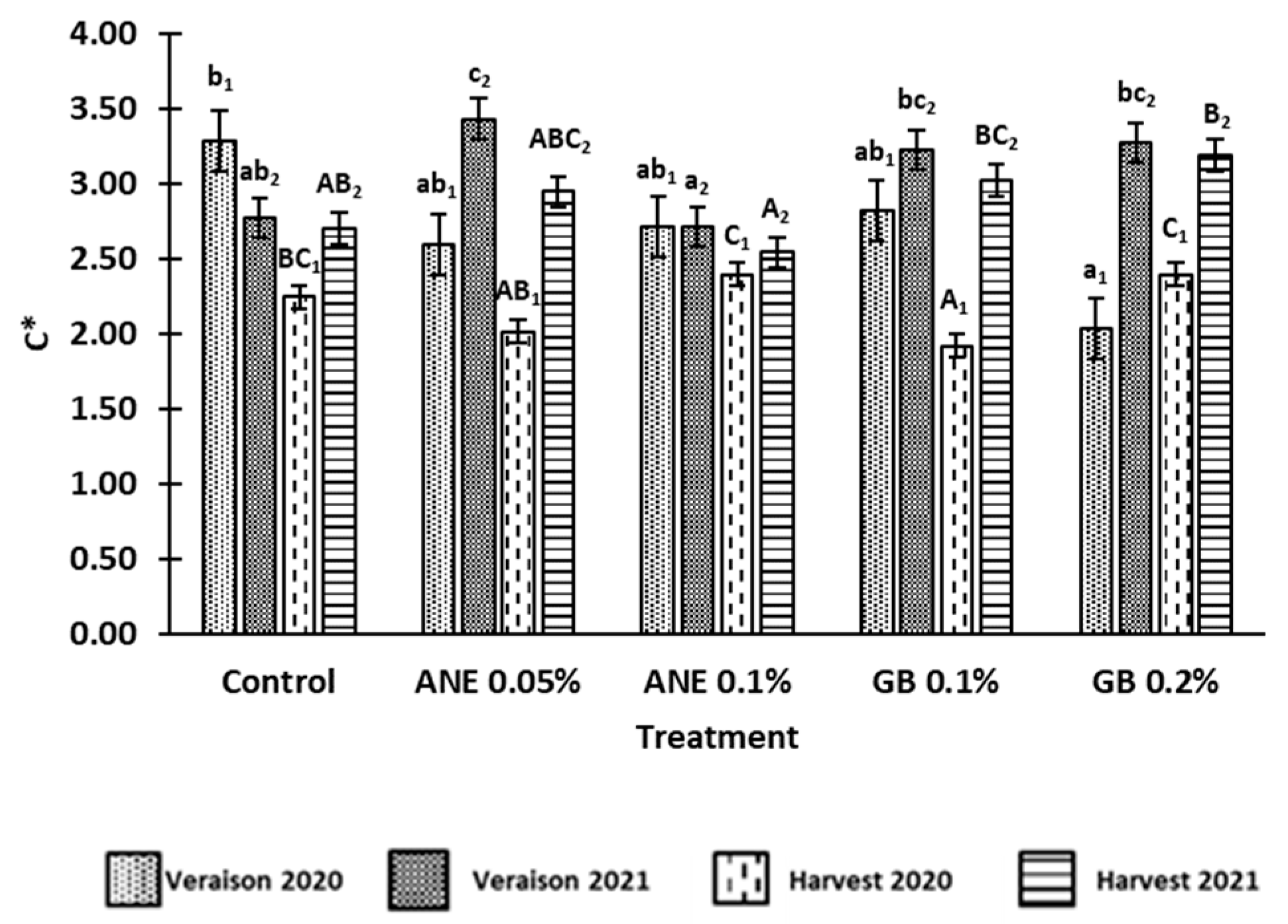
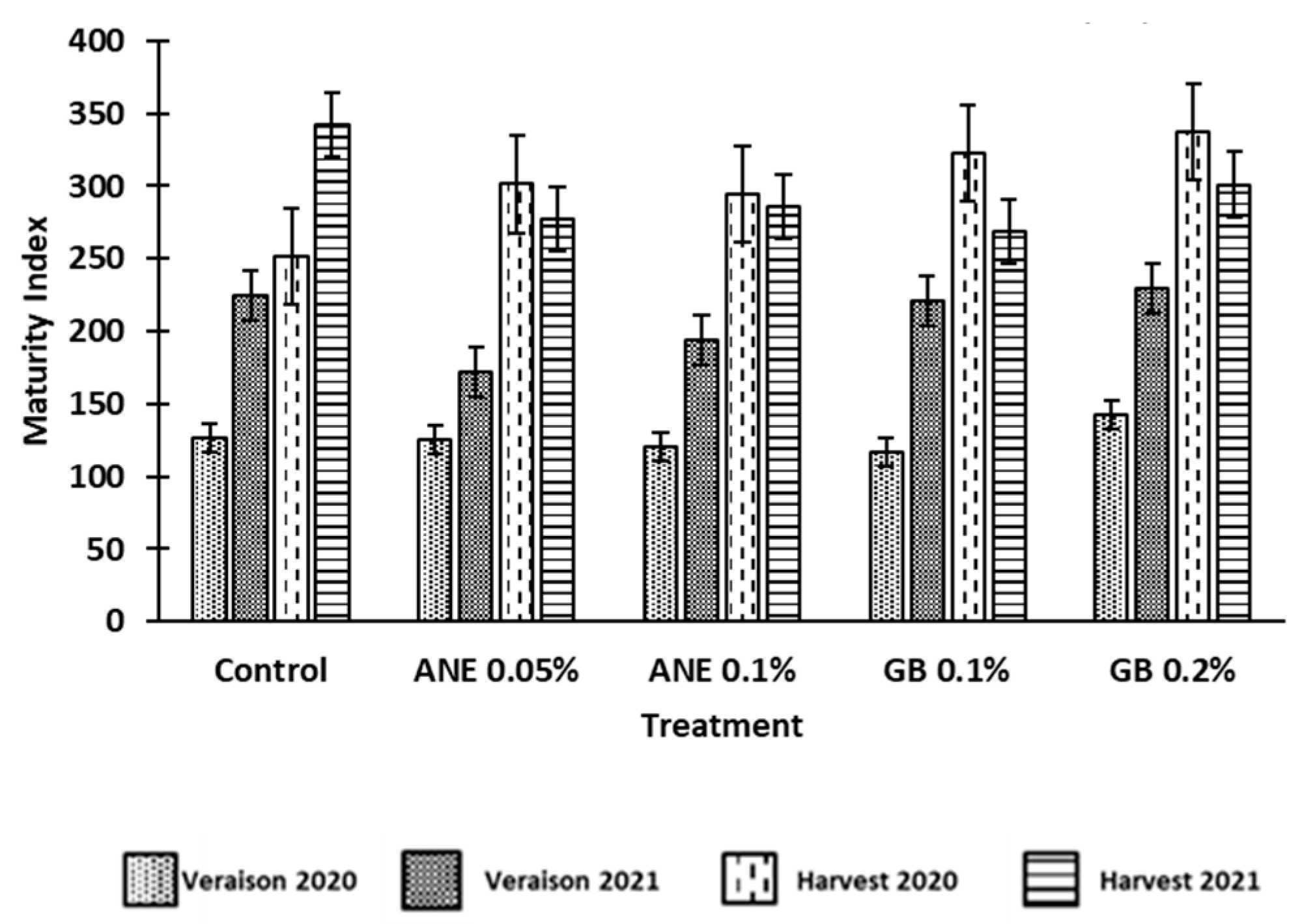
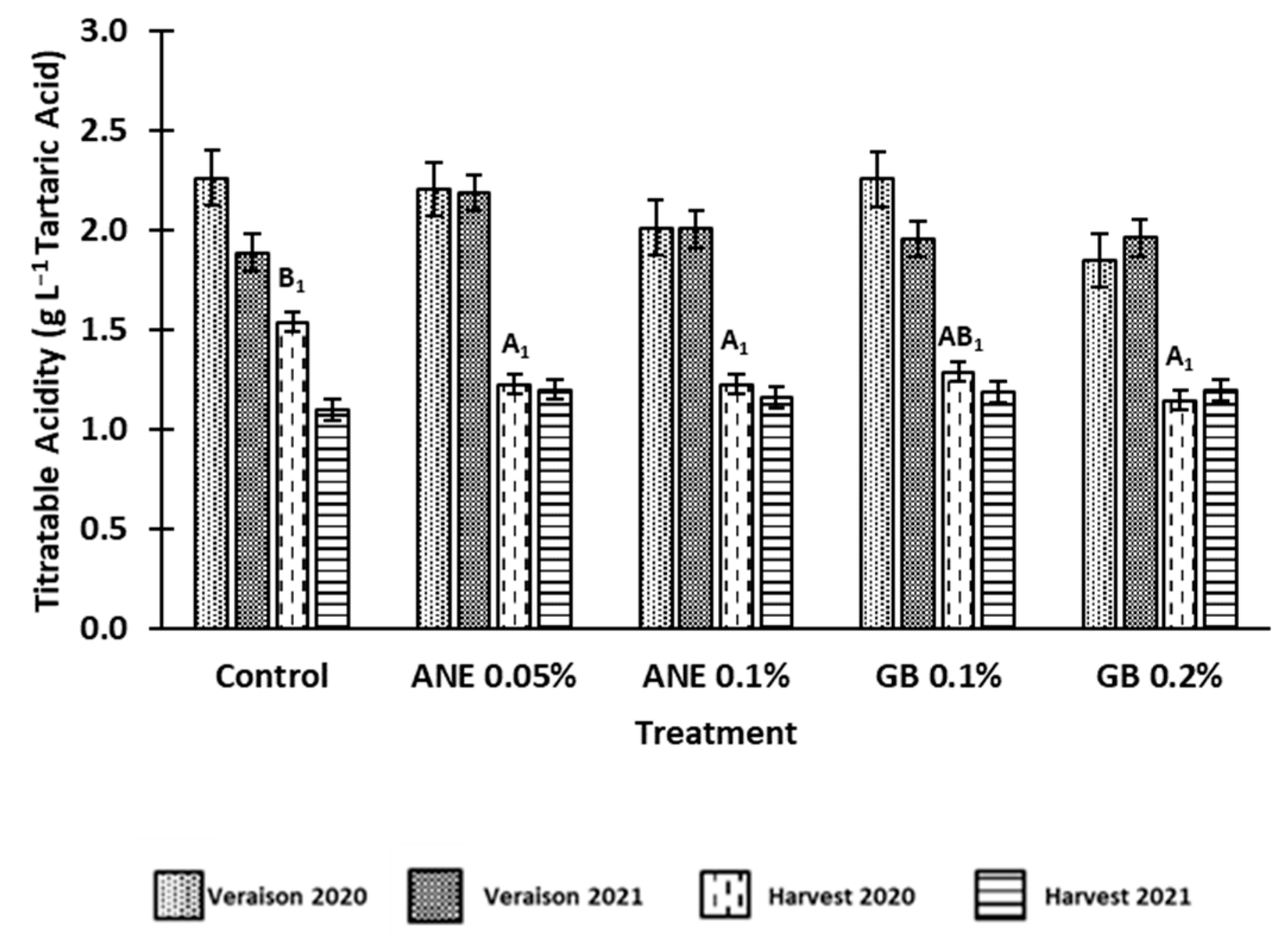
3.1 Effect of biostimulants on berries quality
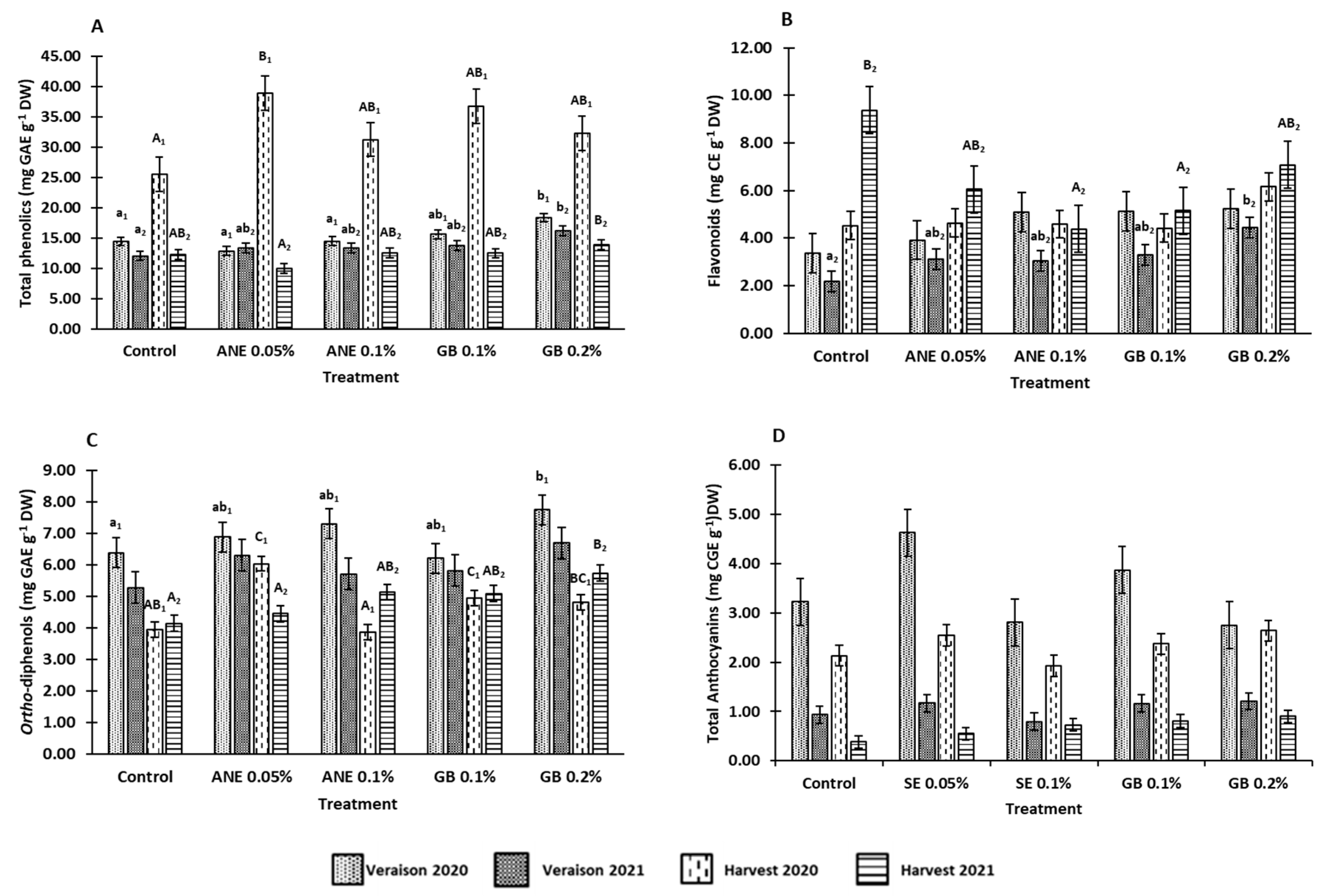
3.2. Effects of biostimulants on berries bioactive compounds
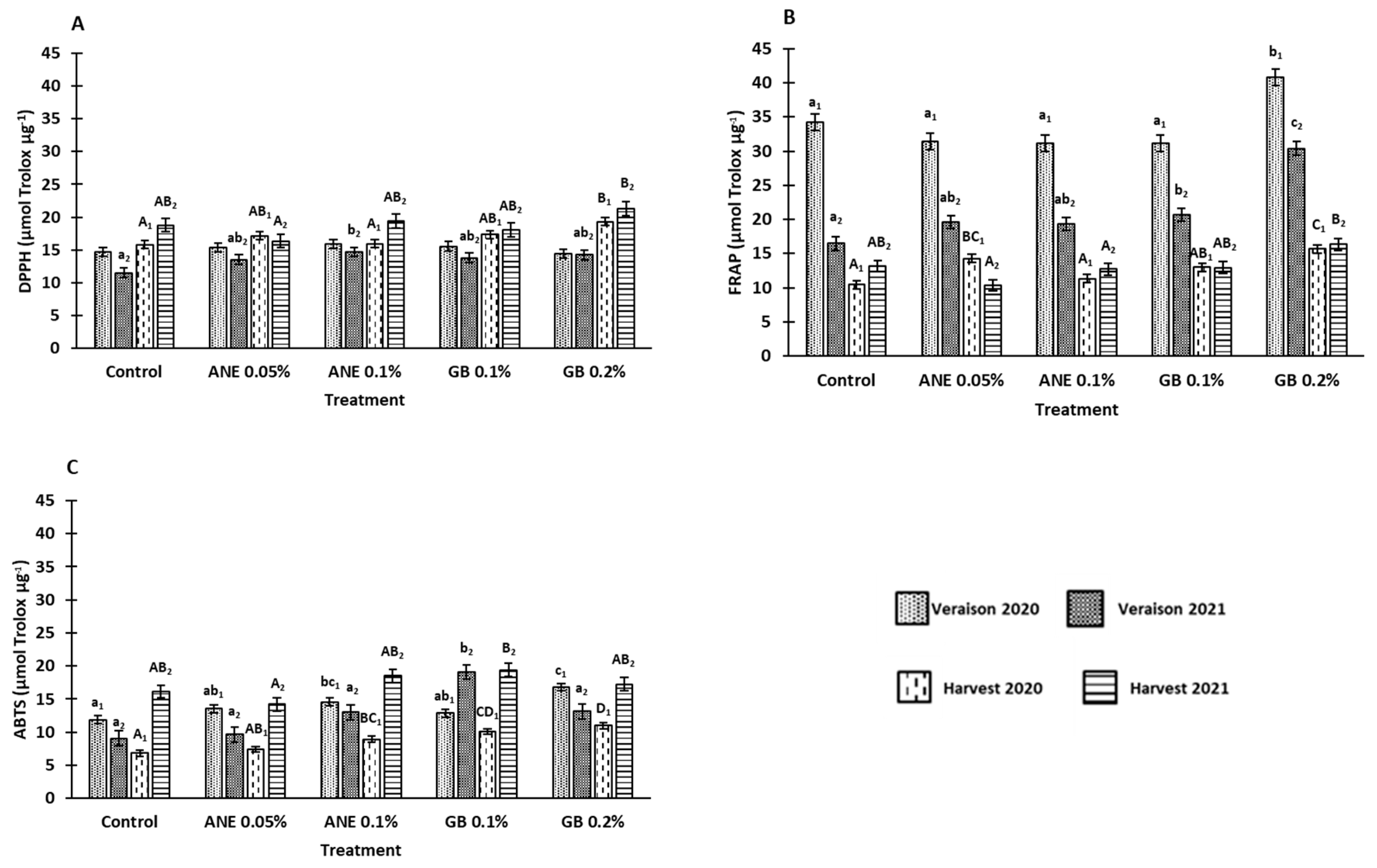
3.3. Influence of biostimulants on antioxidant potential
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of biostimulants positively affected berry quality
4.2. Application of biostimulants positively affected berry bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OIV State of the world vine and wine sector 2021. Int Organ Vine Wine Intergov Organ 2022, 1–19.
- Fraga, H.; Malheiro, A.C.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Santos, J.A. An overview of climate change impacts on European viticulture. Food Energy Secur 2012, 1, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G. Uma Avaliação do clima para a Região Demarcada do Douro : Uma análise das condições climáticas do passado, presente e futuro para a produção de vinho. ADVID, Portugal 2013 pp 5-80.
- Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Zheng, W.; Martínez de Toda, F. Current viticultural techniques to mitigate the effects of global warming on grape and wine quality: A comprehensive review. Food Res Int 2021, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, E.; Gonçalves, B.; Cortez, I.; Castro, I. The role of biostimulants as alleviators of biotic and abiotic stresses in grapevine: A review. Plants 2022, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, O.T.J.; Sabır, A. Changes in leaf and shoot water statutes of grapevines in response to contrasting water availability and glycine betaine pulverization. Int J Agric Environ Food Sci 2017, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesiński, A.; Mikiciuk, G.; Mikiciuk, M.; Stręk, M.; Płatkowski, M.; Statkiewicz, M. Effect of preharvest use of anti-cracking preparations on changes in selected parameters of sweet cherry fruits during frozen storage. Folia Pomeranae Univ Technol Stetin Agric Aliment Piscaria Zootech 2017, 330, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 8. Frioni T, Sabbatini P, Tombesi S, Norrie J, Poni S, Gatti M, et al. Effects of a biostimulant derived from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum on ripening dynamics and fruit quality of grapevines. Sci Hortic. [CrossRef]
- Adak, N. Effects of glycine betaine concentrations on the agronomic characteristics of strawberry grown under deficit irrigation conditions. Appl Ecol Environ Res 2019, 17, 3753–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 10. Correia S, Queirós F, Ribeiro C, Vilela A, Aires A, Barros AI, et al. Effects of calcium and growth regulators on sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) quality and sensory attributes at harvest. Sci Hortic. [CrossRef]
- 11. Salvi L, Brunetti C, Cataldo E, Niccolai A, Centritto M, Ferrini F, et al. Effects of Ascophyllum nodosum extract on Vitis vinifera: Consequences on plant physiology, grape quality and secondary metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem. [CrossRef]
- Taskos, D.; Stamatiadis, S.; Yvin, J.C.; Jamois, F. Effects of an Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. extract on grapevine yield and berry composition of a Merlot vineyard. Sci Hortic, 2: 250. [CrossRef]
- Cabo S, Aires A, Carvalho R, Vilela A, Pascual-Seva N, Silva AP, et al. Kaolin, Ascophyllum nodosum and salicylic acid mitigate effects of summer stress improving hazelnut quality. J Sci Food Agric 2020, 101, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadouri, H.K.; Kandhan, K.; Salem, M.A. Effects of glycine betaine on plant growth and performance of Medicago sativa and Vigna unguiculata under water deficit conditions. J Phytol. [CrossRef]
- Tisarum, R.; Theerawitaya, C.; Samphumphuang, T.; Singh, H.P.; Cha-um, S. Foliar application of glycine betaine regulates soluble sugars and modulates physiological adaptations in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) under water deficit. Protoplasma, 2020; 257, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frioni T, Tombesi S, Quaglia M, Calderini O, Moretti C, Poni S, et al. Metabolic and transcriptional changes associated with the use of Ascophyllum nodosum extracts as tools to improve the quality of wine grapes (Vitis vinifera cv. Sangiovese) and their tolerance to biotic stress. J Sci Food Agric 2019, 99, 6350–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, M.; Correia, S.; Guinan, K.J.; Sujeeth, N.; Bragança, R.; Gonçalves, B. Recent advances in the molecular effects of biostimulants in plants: An overview. Biomolecules. [CrossRef]
- 18. Dutta T, Neelapu NRR, Wani SH, Challa S. Compatible solute engineering of crop plants for improved tolerance toward abiotic stresses. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Hussain Wani, S.; Brajendra Singh, N.; Haribhushan, A.; Iqbal Mir, J. Compatible solute engineering in plants for abiotic stress tolerance - role of glycine betaine. Curr Genomics 2013, 14, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 20. IVV. Vinhos e Aguardentes de Portugal, 2: Lisboa, 2021.
- Lorenz, D.H.; Eichhorn, K.W.; Bleiholder, H.; Klose, R.; Meier, U.; Weber, E. Growth stages of the grapevine: phenological growth stages of the grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. ssp. vinifera)—Codes and descriptions according to the extended BBCH scale. Aust J Grape Wine Res 1995, 1, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombe, B.G.; Dundon, R.J.; Short, A.W.S. Indices of sugar—acidity as ripeness criteria for winegrapes. J Sci Food Agric 1980, 31, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.; Rossi, J. Colorometry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol, 1: (16).
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem, 3010. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, C.; Costa, C.M.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A.; Gouvinhas, I. Assessing the relationship between the phenolic content and elemental composition of grape (Vitis vinifera L. ) Stems. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvinhas, I.; De Almeida, J.M.M.M.; Carvalho, T.; Machado, N.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Discrimination and characterisation of extra virgin olive oils from three cultivars in different maturation stages using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in tandem with chemometrics. Food Chem. [CrossRef]
- Lee J, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE, Eisele T, Giusti MM, Haché J, et al. Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.F.; Fang, Y.L.; Qin, M.Y.; Zhuang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.W. Varietal differences among the phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties of four cultivars of spine grape (Vitis davidii Foex) in Chongyi County (China). Food Chem 2012, 134, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Shehat, W.; Sohail Akh, M.; Alam, T. Extraction and estimation of anthocyanin content and antioxidant activity of some common fruits. Trends Appl Sci Res 2020, 15, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratil, P.; Klejdus, B.; Kubáň, V. Determination of total content of phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in vegetables evaluation of spectrophotometric methods. J Agric Food Chem 2006, 54, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebnsm Wiss Technol.
- Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Larrauri, J.A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A procedure to measure the antiradical efficiency of polyphenols. J Sci Food Agric 1998, 76, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhraju, P.; Becker, K. Antioxidant properties of various solvents extracts of total phenolic constituents from three different agroclimatic origins of drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam) leaves. J Agric Food Chem.
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Ashraf, M. Influence of water stress and exogenous glycine betaine on sunflower achene weight and oil percentage. Int J Environ Sci Technol 2005, 2, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwaly, E.S.E.; Al-Yasi, H.M.; Ali, E.F.; Farouk, H.A.; Farouk, S. Deteriorating harmful effects of drought in cucumber by spraying glycinebetaine. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, S.; Ertan, E. Exogenous applications of kaolin and glycine betaine increased the yield and quality of olive fruit and olive oil. Erwerbs-Obstbau. [CrossRef]
- Campbell J, Sarkhosh A, Habibi F, Gajjar P, Ismail A, Tsolova V, et al. Evaluation of biochemical juice attributes and color-related traits in muscadine grape population. Foods 2021, 10, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rätsep, R.; Karp, K.; Vool, E. Yield maturity parameters of hybrid grapevine (Vitis sp.) cultivar “Zilga.” In: Research for Rural Development. 2014. page 44–50.
- 41. ADVID. Boletim Ano Vitícola 2020, w: Real: 2020. Available from, 2020.
- 42. ADVID. Boletim final do ano vitícola 2021, w: Real: 2021. Available from, 2021.
- Borghezan, M. Formation and ripening of grape and effects on the wines: Review. Ciência e Técnica Vitivinícola 2017, 32, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.V.; White, M.A.; Cooper, O.R.; Storchmann, K. Climate change and global wine quality. Clim Change 2005, 73, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen C, Darriet P. The impact of climate change on viticulture and wine quality. J Wine Econ 2016, 11, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Al-Qurashi, A.D.; Mohamed, S.A. Postharvest trans -resveratrol and glycine betaine treatments affect quality, antioxidant capacity, antioxidant compounds and enzymes activities of ‘El-Bayadi’ table grapes after storage and shelf life. Sci Hortic, 3: 2015, 197, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, S.; Akram, N.A.; Ashraf, M.; García-Caparrós, P.; Ali, O.M.; Latef, A.A.H.A. Influence of glycine betaine (natural and synthetic) on growth, metabolism and yield production of drought-stressed maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Plants 2021, 10, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safwat, G.; Abdel Salam, H.S. The effect of exogenous proline and glycine betaine on phyto-biochemical responses of salt-stressed basil plants. Egypt J Bot 2022, 0, 0–0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabo S, Morais MC, Aires A, Carvalho R, Pascual-Seva N, Silva AP, et al. Kaolin and seaweed-based extracts can be used as middle and long-term strategy to mitigate negative effects of climate change in physiological performance of hazelnut tree. J Agron Crop Sci 2020, 206, 28–42. [CrossRef]
| Biometric parameters | Growth stage/Year | C | ANE 0.05% | ANE 0.1% | GB 0.1% | GB 0.2% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | Veraison 2020 | 1.92±0.05b1 | 1.90±0.05b1 | 1.86±0.05ab1 | 1.71±0.04a1 | 2.02±0.04b1 |
| Veraison 2021 | 2.11±0.04 | 1.99±0.05 | 2.10±0.04 | 2.13±0.04 | 2.14±0.04 | |
| Harvest 2020 | 2.09±0.04A1 | 2.09±0.04A1 | 2.04±0.05A1 | 2.09±0.05A1 | 2.28±0.05B1 | |
| Harvest 2021 | 2.14±0.04BC2 | 1.83±0.06A2 | 2.08±0.05B2 | 2.27±0.04C2 | 2.23±0.04BC2 | |
| Height (mm) | Veraison 2020 | 14.15±0.14a1 | 14.21±0.13a1 | 14.63±0.17ab1 | 14.18±0.12a1 | 15.07±0.11b1 |
| Veraison 2021 | 15.41±0.10c2 | 14.78±0.13a2 | 15.36±0.15bc2 | 14.94±0.08ab2 | 15.70±0.14c2 | |
| Harvest 2020 | 14.83±0.13A1 | 14.71±0.13A1 | 15.00±0.16AB1 | 15.03±0.15AB1 | 15.39±0.12B1 | |
| Harvest 2021 | 16.51±0.13B2 | 15.47±0.20A2 | 16.44±0.17B2 | 16.62±0.14B2 | 16.91±0.12B2 | |
| Width (mm) | Veraison 2020 | 13.91±0.12a1 | 14.06±0.12ab1 | 14.11±0.13ab1 | 13.72±0.12a1 | 14.43±0.10b1 |
| Veraison 2021 | 14.73±0.10 | 14.58±0.12 | 14.88±0.11 | 14.90±0.10 | 14.83±0.11 | |
| Harvest 2020 | 14.20±0.11AB1 | 14.12±0.11AB1 | 13.81±0.14A1 | 13.86±0.12A1 | 14.33±0.12B1 | |
| Harvest 2021 | 14.13±0.12B2 | 13.29±0.18A2 | 13.87±0.13B2 | 14.73±0.12C2 | 14.36±0.11BC2 | |
| Thickness (mm) | Veraison 2020 | 13.45±0.12a1 | 13.58±0.12ab1 | 13.61±0.13ab1 | 13.25±0.12a1 | 13.99±0.10b1 |
| Veraison 2021 | 14.20±0.09 | 14.22±0.12 | 14.47±0.11 | 14.43±0.10 | 14.32±0.12 | |
| Harvest 2020 | 13.71±0.10AB1 | 13.59±0.10AB1 | 13.28±0.14A1 | 13.45±0.13AB1 | 13.84±0.13B1 | |
| Harvest 2021 | 13.49±0.14BC2 | 12.82±0.17A2 | 13.26±0.14AB2 | 13.92±0.11C2 | 13.60±0.12BC2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





