1. Introduction
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), recently renamed by an international consensus panel as metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), affects up to 1 billion patients worldwide [
1]. This change in nomenclature is in keeping with more recent understanding of this disease and its inherent link to metabolic syndrome. The National Cholesterol Education Program and the Adult Treatment Panel III defines metabolic syndrome as a constellation of risk factors that promote the development of atherosclerotic CVD [
2]. The presence of three or more of the following components fulfills the criteria for clinical identification of metabolic syndrome: hypertension (≥ 130/85 mmHg), abdominal obesity (> 102 cm in men, > 88 cm in women), dyslipidemia (triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL or low HDL cholesterol < 40 mg/dL in men, < 50 mg/dL in women), and impaired fasting glucose (≥ 100 mg/dL) [
3]. This is summarized in
Figure 1 below.
Table 1.
The most commonly agreed-upon diagnostic criteria of metabolic syndrome according to the NCEP ATP3 2005 guidelines.
Table 1.
The most commonly agreed-upon diagnostic criteria of metabolic syndrome according to the NCEP ATP3 2005 guidelines.
| Parameters |
NCEP ATP3 2005 |
| Number of abnormalities |
≥3 of: |
| Glucose |
Fasting glucose ≥5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) or drug treatment for elevated blood glucose |
| HDL cholesterol |
<1.0 mmol/L (40 mg/dL) (men); <1.3 mmol/L (50 mg/dL) (women) or drug treatment for low HDL cholesterol§ |
| Triglycerides |
≥1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL) or drug treatment for elevated triglycerides § |
| Obesity |
Waist ≥102 cm (men) or ≥88 cm (women)* |
| Hypertension |
≥130/85 mmHg or drug treatment for hypertension |
* In Asian patients, waist ≥90 cm (men) or ≥80 cm (women).
§ Treatment with 1 or more of fibrates or niacin. |
The manifestation of metabolic syndrome in the liver is fat deposition, hence the previous name of NAFLD. This fat deposition leads to inflammation, also known as Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and eventually fibrosis and cirrhosis. There are several theorized mechanisms of this pathogenesis as well as a constellation of contributing factors, both studied and theorized. These will be discussed in detail later.
2. Epidemiology
NAFLD has become the most common chronic liver disease with a prevalence of 25% worldwide. The highest rates are reported from South America (31%) and the Middle East (32%), followed by Asia (27%), United States (24%) and Europe (23%). NAFLD is less common in Africa (14%). Among these patients in the US, the prevalence of NASH was 21% [
2].
Research into NAFLD has rapidly expanded the understanding of its pathophysiology and defined useful diagnostic criteria. Diagnosis has shifted to focus on the metabolic criteria commonly associated with hepatic steatosis, such as T2DM and metabolic syndrome. These key comorbidities have led to the proposal to rename this condition to MAFLD [
4]. The goal with re-defining fatty liver disease is to improve outcomes by identifying high-risk patients and intervening earlier on the metabolic dysfunction contributing to their disease [
5]. Experts state that a focus on metabolic dysfunction better represents the pathophysiologic mechanism of the disease. Studies have shown that obesity, metabolic syndrome, and T2DM are associated with a greater risk of progression of NAFLD to NASH, HCC, or fibrosis [
6]. NASH is predicted to become the most common indication for liver transplantation. [
7] Therefore, the focus on metabolic criteria may better stratify patients who are at increased risk of disease progression. Compared to a diagnosis of exclusion in NAFLD, MAFLD’s positive inclusion of metabolic abnormalities is designed to risk-stratify patients at highest risk for progression to NASH, HCC, or fibrosis. Importantly, the presence of other hepatic disease does not exclude MAFLD diagnosis like the in the NAFLD definition. However, studies show that around 90% of patients meet the criteria of both NAFLD and MAFLD [
8,
9].
The new definition will alter the incidence and prevalence going forward. Given its novelty, prevalence data has been estimated from existing data. A recent meta-analysis by Chan et al of more than 10 million patients globally found the prevalence of MAFLD to be 38% [
5]. One study found the prevalence of MAFLD in North America to be 34.8%, another measured 39.1% [
10,
11]. As obesity and T2DM continue to increase around the world, the prevalence of MAFLD is likely to increase.
The definition of MAFLD includes patients who have 2 or more factors associated with metabolic dysfunction. Thus, the MAFLD definition encompasses lean and nonobese individuals with steatosis. The prevalence of MAFLD among these patients is estimated to be 5% and 12%, respectively [
12].
The incidence of both NAFLD/MAFLD is difficult to determine due to a lack of cohesive screening guidelines and inaccurate tools. Ultrasound is commonly used in initial work-up, but it lacks the sensitivity to detect subtleties in early disease. The generally accepted value is that the incidence of NAFLD is around 2-6% [
13].
3. Prevalence
MAFLD is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in Western countries and is predicted to become the most frequent indication for liver transplantation by 2030 [
14]. This is largely due to the increase in the rates of the components of metabolic syndrome described above.
While it was previously thought that this was a disease of the affluent, new data is emerging showing a rising rate of the individual factors of metabolic syndrome in those living in poverty. Poor nutrition and obesity have been identified as direct effects of living in poverty [
15].
The National Health Service in England released a report on childhood obesity that identified potential reasons for the link between poverty and specifically childhood obesity, some of these included chronic stress exposure during childhood, obesogenic food environments, less access to areas for physical activity as well as absence of high-quality supermarkets reducing access to fresh fruits and vegetables [
16,
17]. These effects spill into adult hood and are contributory to the rapid rise in MAFLD we have seen over the past decade.
Further to this rapid rise in the incidence of MAFLD over the past decade and resultant NASH and NASH cirrhosis, there was a notable increase in the incidence rate of MAFLD during the COVID-19 pandemic of 2019-2022 [
18,
19]. These trends have also been seen in the incidence rates of the individual components of metabolic syndrome such as childhood obesity, high blood pressure, high blood triglycerides, low levels of HDL cholesterol, and insulin resistance [
16,
17].
With this rapid rise in the global incidence rates of MAFLD pre-COVID-19 pandemic and subsequently accelerated rates we are seeing post-COVID-19 pandemic, developing an understanding of MAFLD, and instituting appropriate screening and intervention measures is of paramount importance.
4. Pathogenesis of MAFLD & Progression to Fibrosis
To this date, the pathophysiologic mechanisms resulting in MAFLD have not been clearly delineated. Our understanding of the complex interplay of several metabolic, genetic, and environmental factors leading to MAFLD has evolved significantly over the past 20 years.
Around the turn of the century, the leading theory behind the development of NASH was surmised by the ‘’2-hit hypothesis’’. The first hit in this 2-hit hypothesis was the accumulation of hepatic triglycerides leading to hepatic steatosis, what we know as MAFLD today [
20].
Factors then thought to contribute to this first hit include insulin resistance, high amounts of adipose tissue and excessive dietary lipids. This first hit was suspected to increase the livers susceptibility to additional insult that caused inflammation. These additional insults were the 2nd hit in the 2-hit hypothesis, the resultant inflammation of which would then progress to fibrosis [
20].
More recently however, this hypothesis has been expanded upon to a ‘’multi-hit theory’’ once it was recognized that there are several influencing factors affecting the progression from hepatic fat deposition through to cirrhosis. The first expansion of the original 2-hit theory came around 2010 when it was recognized that hepatic steatosis as a result of triglyceride deposition may be protective against the inflammatory effects of free fatty acid. This, plus the fact that hepatic steatosis in itself was sufficient to lead to fibrosis without an overt ‘’2nd hit’’ led to the proposal that impaired hepatocyte proliferation and other liver regenerative pathways as a result of oxidative stress was a ‘’third hit’’ contributing the progression of fibrosis from MAFLD.
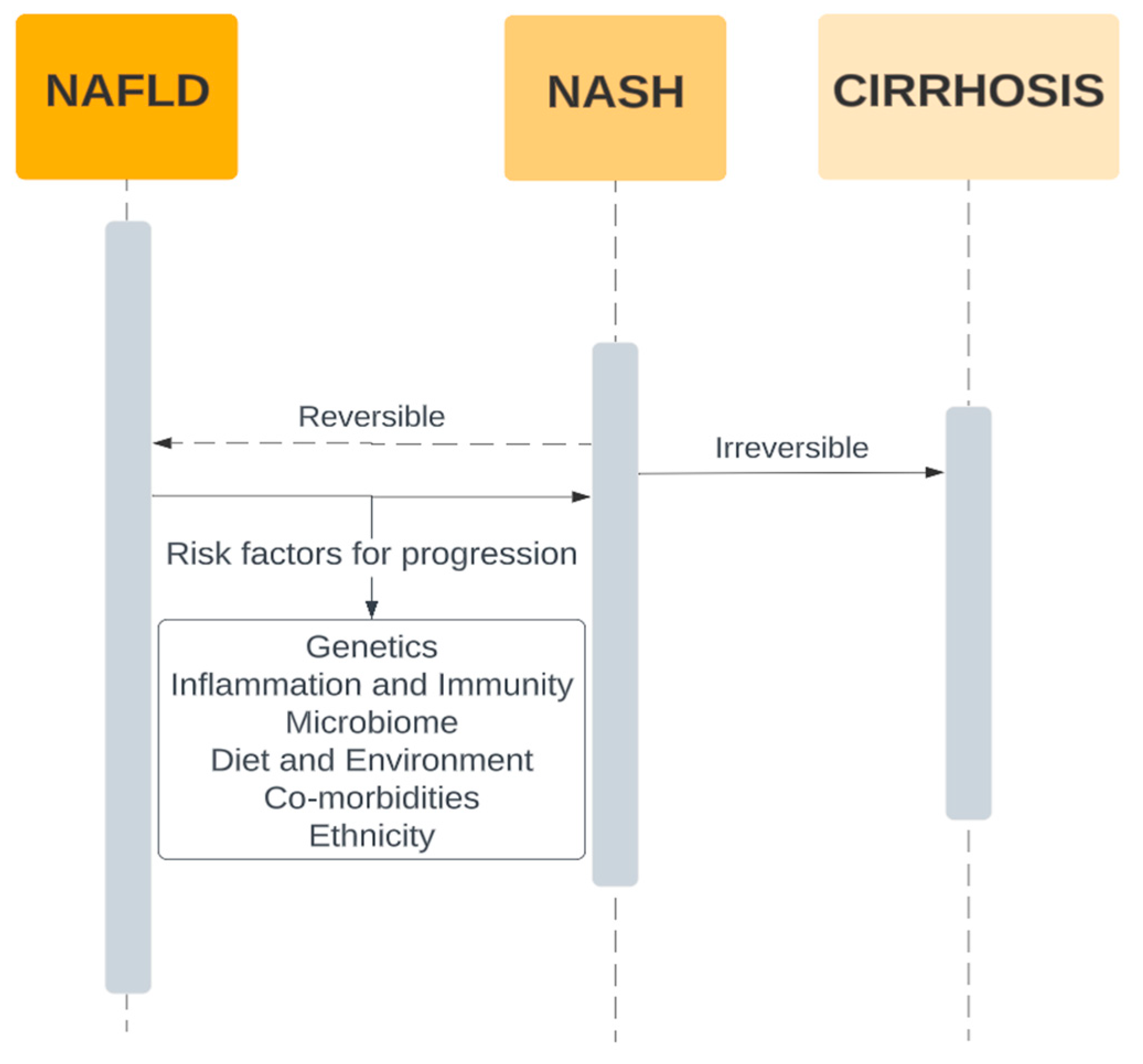
Our most current understanding of the pathogenesis of the pathophysiology of MAFLD and its progression to fibrosis is encapsulated by the multi-hit model. Even in this model however, it has been widely agreed that hepatic fat deposition remains the first hit. Understanding this sentinel process and potential therapies to reduce the effects of and/or reverse this process are of paramount importance. A summary of some of the current known risk factors for the progression of NASH based on studies by Harrison et al and da Silva et al are outlined in
Figure 2 below. [
21,
22] These individual factors are discussed in further detail in subsequent sections.
4.1. Adiposity - Liver Axis and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is mechanistically very closely intertwined with MAFLD. IR refers to the blunted metabolic response by the body to the effect of insulin release. Obesity is closely linked to IR and the obesity epidemic has seen a drastic concurrent rise in Type 2 diabetes as a result of systemic IR [
23]. The effects of this include a reduced ability to lower serum glucose and crucially, an inability to suppress lipolysis. In addition to systemic IR, hepatic steatosis results in hepatic IR which manifests as a reduction in hepatic gluconeogenesis despite a preservation of hepatic lipogenesis. This excess availability of lipids beyond the body’s capacity for lipid accumulation and storage results in a progression of both systemic and hepatic IR [
23,
24]. AS a result of excess adipose lipolysis as well as de-novo hepatic lipogenesis and excess dietary intake, an excessive amount of stored lipids undergo lipolysis with a resultant release of nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) into the blood. NEFA are delivered to the liver to be processed and predominantly become esterified into triglycerides for storage, a relatively inert molecule. Some NEFA however undergo beta-oxidation in the liver and become bio-active lipids that confer increased hepatic oxidative stress. Some of these molecules include free cholesterol, diacylglycerols, and ceramides [
25,
26].
Further, in addition to the quantity of NEFA released, the types of NEFA that accumulate are altered in NAFLD, with more saturated fatty acids being seen than monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. These saturated fatty acids are associated with hepatic IR progression that perpetuates the cycle of excess lipids being released and hepatic steatosis, in triglycerides or other bio-active lipid products of beta-oxidation [
27,
28].
Adiposity and the resultant insulin resistance are a cardinal feature of MAFLD and NASH as it is a progenitor to lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammatory pathway activation that all contribute to the progression of MAFLD to NASH and cirrhosis. As such however, this understanding allows for the targeting of several mechanistic steps in attempt to curb this progression, these are discussed later.
4.2. Inflammatory pathways
While not fully understood, inappropriate activation of the inflammatory cascade in response to hepatic steatosis is fundamental to the progression of NAFLD to NASH. This is a key step in the progression of disease that is not seen in all patients. In fact, while the prevalence of NAFLD is estimated to be approximately 30%, only 5-10% of these patients will progress to have NASH [
26].
What is currently understood about the activation of this inflammatory pathway is that it appears to be triggered by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress [
29]. Mitochondrial dysfunction, Endoplasmic reticulum stress and excessive activation of the enzyme NADPH Oxidase are the primary sources of dysregulated metabolism resulting in the production of ROD such as O2•-, H2O2, malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal [
28,
30].
What is not currently known however is the mechanism by which the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum become dysregulated. Current theories are that the cell architecture is overwhelmed by the excessive FFA resulting in dysregulated metabolism of NEFA [
31]. Further hypothesized is that excessive flow of NEFA as well as other pathogenic molecules, some of which are produced by dysregulated gut microbiota discussed later, are phagocytosed by hepatic Kupffer cells which then differentiate into their M1 phenotype, releasing cytokines such as TNF-α & IL-1. This is made plausible by the fact that TNF-α is one of the key cytokines responsible for the progression of NAFLD to NASH and through to cirrhosis [
28,
30,
32].
4.3. Gut/Liver axis and Gut-microbiome
Humans share a core gut microbiome despite unique individual differences, and distinct alterations in this core gut microbiota and a resultant contribution to the pathogenesis of several diseases has been suspected for nearly 100 years [
30]. Moreover, altered gut microbiota has been specifically found in patients with chronic liver disease over 80 years ago. This was mostly identified by culture growth which was time consuming and not practical in clinical decision making [
33]. Recently however, advances in next generation sequencing (NGS) technology and metagenomics have led to profound advancement in our understanding of the contribution of the gut microbiome to liver disease [
34].
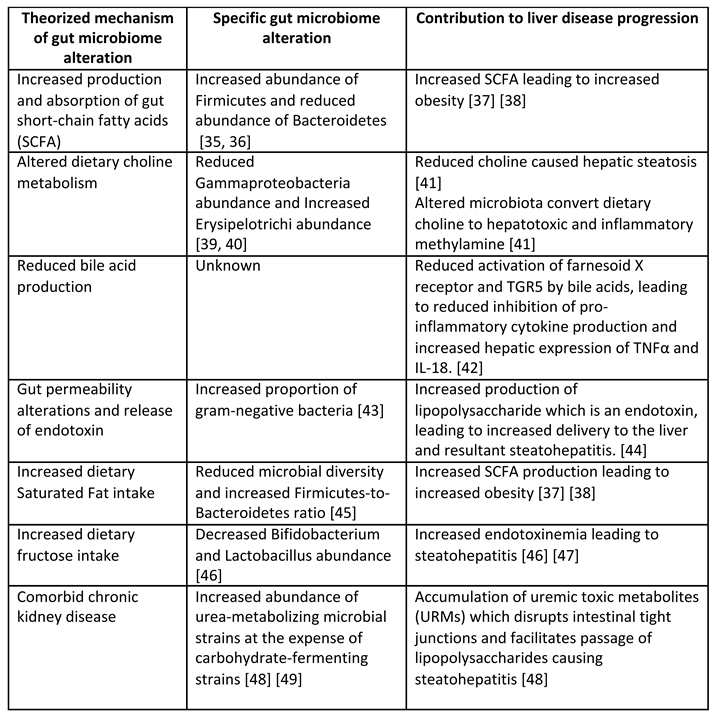
Several different mechanisms within alteration in the gut microbiome have been implicated in their contribution to progression of liver disease. A brief summary of some proposed mechanisms is shown in
Table 2 below.
Unfortunately, however, since our understanding in this field is still early and much of our understanding comes from mouse models under highly controlled settings, it does not offer practical avenues for therapeutic intervention beyond experimental therapy at present time. As a result, much focus will not be placed on emerging treatments to alter gut microbiome in the later sections of this paper.
4.4. Dietary and Environmental factors
Clear links exist between excessive dietary fat intake and an increase in circulating lipid burden ultimately to be cleared by the liver. Dietary fat intake accounts for approximately 15% of the NEFA seen by the liver for processing, so it stands to reason that that the progressive increase in fat consumed in western countries results in an increased hepatic lipid processing burden contributing to both hepatic and systemic IR. Recently however, there have been developments in our understanding of the significant contribution to NAFLD of carbohydrates, specifically, fructose [
50].
With the obesity epidemic, there has been a stark increase in the consumption of fructose consumption, mainly in the form of high fructose corn syrup (HFCS). Studies regarding the effects of fructose metabolism on the development of metabolic syndrome and NAFLD have been astonishing. Diets high in Fructose and Sucrose have been directly linked to increases in incidence of both NAFLD and NASH [
51,
52].
Mechanistically, fructose has been theorized to modulate lipogenic enzymes, increasing hepatic steatosis. Fructose has been shown to cause significant gut microbiome dysregulation and overgrowth of bacteria in animal models. Chronic fructose consumption in the setting of excessive calorie intake will cause weight gain by de novo lipogenesis. While this is to be expected, recent studies have demonstrated that chronic fructose consumption induces resistance to Leptin, a hormone that induces satiety and reduces calorie consumption. More worrisome is that this Leptin resistance has been seen prior to the increase in body weight which significantly accelerates high-fat diet induced obesity. This leptin resistance has been seen to reverse with dietary modification to sugar-free diet despite high fat content [
53].
All these proposed effects of increased fructose consumption led to an increase in both systemic and hepatic IR, contributing a significant ‘’hit’’ in the development of NAFLD and NASH in the context of the ‘’Multi-hit theory’’ [
30,
53,
54]
4.5. Genetics
Family based studies and twin studies have sought to establish heritability estimates of NAFLD with varying success. These differences can largely be attributed to the populations studied and to the modalities used to assess steatosis and categorize severity. Tarnoki et al. found no evidence of NAFLD heritability among a subset of 208 adult Hungarian twins with the use of B-mode ultrasonography [
55]. Schwimmer et al.’s familial aggregation study found a heritability of ~38% when adjusted for demographic variables [
56]. The latter study utilized MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), a more sensitive and accurate modality than ultrasonography for assessing liver fat, though is limited in its generalizability with only overweight predominantly Hispanic patients and their families as participants. In an important study, Loomba et al. saw a ~50% heritability between 60 pairs of adult community dwelling twins and a robust correlation in monozygotic but not in dizygotic twins in hepatic steatosis and fibrosis [
57]. Larger population studies assessing NAFLD via abdominal CT scan had heritability rates of 22-34% with a genetic predisposition seen in African- and Hispanic Americans [
58,
59,
60]. Ethnic groups were consistently shown to have increased susceptibility to NAFLD, with Hispanics more prone to advanced disease than other groups [
61]. Although the exact percentage may vary, a genetic component of NAFLD is evident.
NAFLD is a lifestyle-based complex and multifactorial disease with a spectrum varying from steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The progression through this spectrum is dictated by multiple risk factors including genetic and environmental factors. Recent research has placed focus on the understanding of genetic contribution to NAFLD pathogenesis through genome-wide association studies. The Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein 3 (PNPLA3) hydrolyzes triglycerides and retinyl ester [
62] and a variant (I148M) in this gene leads to reduced hydrolase activity and impairs retinyl ester release, resulting in accumulation of triglycerides and retinyl esters within hepatocytes [
63]. This variant of PNPLA3 is most common in Hispanics and has been shown to be strongly associated with increased hepatic fat levels and inflammation [
64]. A variant (E167K) of the Transmembrane 6 Superfamily 2 (TM6SF2) gene is associated with increased levels of hepatic triglyceride content. Carriers of this variant have been shown to be more likely to accumulate fat in the liver and develop non-alcoholic steatohepatitis than those without the variant [
65]. The MBOAT7-TMC4 variant was associated with increased hepatic fat content, more severe liver damage and increased risk of fibrosis in individuals of European descent, compared to study subjects without the variant [
66]. In a study, patients homozygous for a variant glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR) have higher serum triglycerides levels as well as increased severity in liver fibrosis [
67,
68].
Understanding the contribution of the genetic component of NAFLD to the prevalence, progression, and severity of the disease has important implications for patient care. Benefits may range from early diagnosis and monitoring to targeted gene therapies. Coupled with the potential to assess a patient’s individual level of risk, these strides would lead to better overall patient outcomes. Current implementation of genetic testing in diagnostic strategies remains inconclusive. In one study, incorporation of genetic information into predictive test scores for NAFLD improved the accuracy of the prediction by less than 1%, while another found its inclusion to be an effective predictor of NASH (28268262). Large multinational cohorts are underway to better elucidate the role and relationships of the identified gene loci [
61].
5. Diagnosis
There is debate over whether screening for NAFLD is worthwhile and cost-effective [
69]. Currently, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) does not recommend screening for NAFLD, even in high-risk populations due to the uncertain long-term benefits and cost-effectiveness of screening [
70]. It is well-established that patients with type 2 diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension are at increased risk of cirrhosis, advanced fibrosis, and liver disease mortality [
69,
70]. Therefore, clinicians should have a higher degree of suspicion in patients with these comorbidities. The diagnosis of NAFLD is typically characterized by (1) the presence of chronically elevated liver enzymes and (2) imaging evidence of hepatic steatosis. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are commonly used to monitor liver function. An AST/ALT ratio of greater than 1 has been associated with a higher degree of fibrosis on liver biopsy [
71]. However, elevated ALT alone is not correlated with a higher degree of fibrosis in NAFLD patients [
72]. Although these serum biomarkers have high availability and applicability, they are not liver specific and can therefore be elevated in other comorbid conditions [
73].
With regards to imaging, abdominal ultrasound is currently the first line screening tool for NAFLD given its widespread availability and low cost [
74]. Findings of steatosis on abdominal ultrasound include bright hepatic echoes, increased hepatorenal echogenicity, vascular blurring of the portal or hepatic vein, and subcutaneous tissue thickness [
75]. Limitations of using ultrasound include inter and intra-reader variability and anatomic constraints (bowel gas or a large body habitus) [
76]. Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing NAFLD; however, it is costly, invasive, and susceptible to sampling bias [
77]. Findings on liver biopsy of NAFLD include hepatic steatosis with or without hepatocyte ballooning, hepatic necrosis, Mallory bodies and fibrosis [
78]. Of note, the severity of fibrosis has the greatest association with liver related morbidity and mortality when compared to other histological findings [
79]. MRI- Proton density fat fraction (PDFF) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) are useful for quantifying the triglyceride content in the liver [
77]. However, MRI-PDFF and MRS are more costly and less available than abdominal ultrasound and are more often used in research settings rather than clinical practice [
69]. Before diagnosing NAFLD, secondary causes of fatty liver disease such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver disease, drug induced liver disease, medical conditions (Wilson disease, hereditary hemochromatosis, celiac disease), metabolic diseases (glycogen storage diseases), and poor nutritional status must be excluded [
80].
Once the diagnosis of NAFLD has been established, fibrosis scores are often calculated to assess the degree of NAFLD and guide management. The NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS), Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index, and AST-to-platelet ratio can be calculated from routine laboratory results [
69]. The NFS is based on a patient’s age, BMI, presence of diabetes, AST, ALT, platelet count, and albumin level, while the FIB-4 is based on the patient’s age, AST, ALT, and platelet count. Patients who have a FIB-4 ≤ 1.3 (age <65 years) or FIB-4 ≤ 2.0 (age > 65 years) are at minimal risk for advanced fibrosis and are typically managed in the primary case setting (Figure below). Patients who have a FIB-4 of > 1.3 (age < 65 years) or FIB-4 > 2 (age >65 years) undergo elastography and are referred for specialist care (Figure below). NFS and FIB-4 scores have a negative predictive value > 90%, demonstrating its utility as an initial diagnostic test in assessing for NAFLD [
73].
Ultrasound based elastography, vibration-controlled transient elastography, point-shear wave elastography, two-dimensional shear wave elastography, or magnetic resonance elastography can be used to assess liver fibrosis in patients with intermediate to high risk of NAFLD based on their FIB-4 and NFS [
69]. Transient elastography is most used given its availability.
6. Treatments
Weight loss is the first-line management of NAFLD and is recommended for patients with a BMI >25. In addition to improving the quality of life in patients with NAFLD, weight loss has been shown to improve liver histology, hepatic steatosis, and inflammation [
81,
82,
83,
84]. Weight loss of 3-5% has been shown to be associated with decreased steatosis fibrosis regression, 5-7% with reduced inflammation, 7-10% with NASH resolution, and ≥10% with fibrosis regression [
85].
Lifestyle interventions such as diet modification and exercise are attempted first. In patients with NASH or advanced fibrosis who do not sufficiently meet weight loss goals on lifestyle interventions, other strategies like bariatric surgery may be pursued. Surgical intervention with bariatric surgery can be considered in patients with a BMI >40 or a BMI >35 with one obesity-related comorbidity [
86]. Bariatric surgery has been shown to improve steatosis, reduce inflammation, and improve fibrosis score [
87,
88,
89]. Surgical intervention has also shown benefits in patients with NASH. Lassailly et al studied the effect of bariatric surgery in patients with NASH and found that NASH had disappeared in 85% of patients one year postoperatively [
90]. However, worsening fibrosis has also been reported following bariatric surgery [
88].
Although no drug treatment has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the direct treatment of NAFLD, drug therapies targeting weight loss can be considered. Weight loss pharmacological therapy may be initiated in patients with a BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with metabolic comorbidities such as diabetes or hypertension [
91]. Current drug therapy options include glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, lipase inhibitors, sympathomimetics, or combination drugs. Among these, GLP-1 agonists are the best-studied and evidence consistently demonstrates a positive effect of the drug on NAFLD. Semaglutide and liraglutide are the two GLP-1 receptor agonists that have been approved for the treatment of obesity in the United States and are considered the first-line drug therapy. GLP-1 receptor agonists increase glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon secretion, and slow gastric emptying [
92]. They also act in multiple regions of the brain, where appetite and caloric intake are regulated [
92]. Of the two, semaglutide is preferred given its superior dosing schedule of once weekly compared to once daily with liraglutide, as well as its greater efficacy in weight loss [
93]. Multiple studies have shown that GLP-1 agonists can decrease liver fat content, improve ALT, and even a reduction in the progression of fibrosis [
94,
95,
96,
97]. The leading GLP-1 agonist, Semaglutide, has shown much promise in the treatment of NASH and its effects on decreasing markers of NASH and liver enzymes beyond its weight loss effects are discussed below. Liraglutide, another GLP-1 agonist that has also been known to cause weight loss has also been associated with increased rates of NASH resolution and decreased enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) score when compared to placebo [
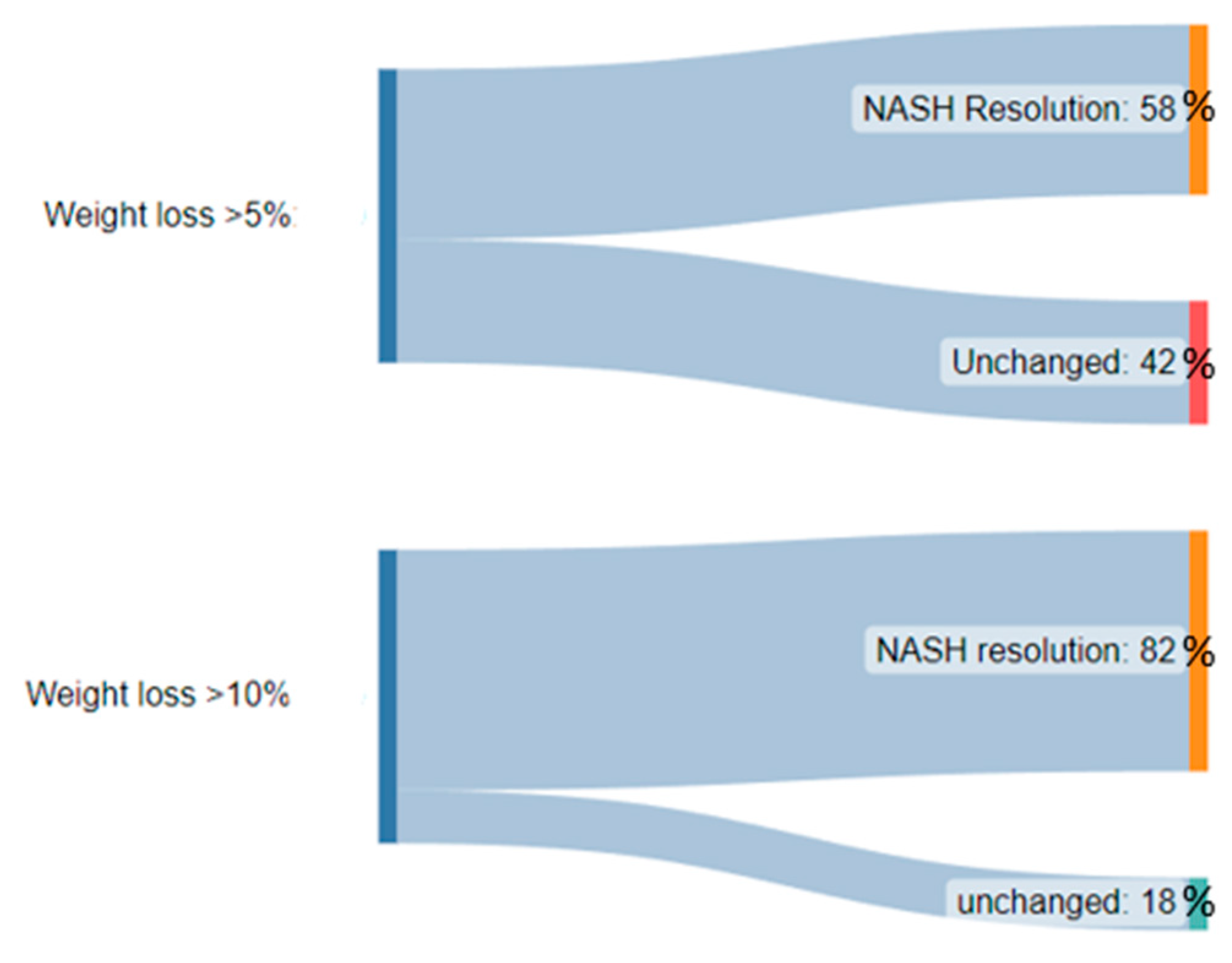
98]. While weight loss is absolutely desired given its theorized and observed benefits in NASH, quantification of this fat-loss is improtant when thinking about weight loss as a treatment specifically for NASH. Several trials such as that by Vilar-Gomez et al have demonstrated that a weight loss of at least 10% of initial body weight is associated with the highest rates of NAFLD activity score reduction, NASH resolution, and even fibrosis regression. The importance of the magnitude of weightloss from this trial are summarised in Figure 3 below. [
81]
Unlike the GLP-1 agonists, other medications traditionally used in weight loss like orlistat, sympathomimetics, and combination drugs have not been studied as extensively in the setting of NAFLD. Orlistat is a gastric and pancreatic lipase inhibitor used primarily for weight loss, but its adverse effects on the gastrointestinal system such as oily stools, diarrhea, and abdominal pain have limited its use [
99]. Randomized controlled trials conducted by Harrison et al and Zelber-Sagi et al showed that using orlistat in the treatment of NAFLD was associated with an improvement in liver histopathology [
100,
101]. Studies have also shown that orlistat may be beneficial in improving liver fat content and reducing inflammatory enzymes [
100,
102,
103,
104]. Unfortunately, few studies exist that investigate the effect of sympathomimetic drugs such as phentermine, diethylpropion, benzphetamine, and phendimetrazine, as well as combination drugs such as phentermine-topiramate and buproprion-naltrexone on NAFLD.
Vitamin E is considered in patients with NASH and fibrosis stage ≥2 without diabetes mellitus. In a large, randomized trial conducted by Sanyal et al studying the efficacy of vitamin E (800 international units daily) and pioglitazone versus placebo, patients treated with vitamin E were more likely to have improvement in their global histology score compared with patients who received placebo [
105]. However, the use of vitamin E has been associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke and prostate carcinoma [
106,
107]. Studies have also found high-dose vitamin E supplementation (≥400 international units per day) to be inconsistently associated with an increase in all-cause mortality [
108].
Pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, can be used in patients with NASH and diabetes mellitus. Pioglitazone has been shown to improve fibrosis, inflammation, and steatosis [
109]. Because the use of pioglitazone is associated with an increased risk of weight gain, heart failure, and fractures, careful consideration of its risk to benefit ratio must be made prior to administration [
110,
111].
6. Emerging Therapeutic Options
Recent randomized control trials and laboratory studies on animal models have identified several potential therapies for NAFLD. These emerging therapies are mainly pharmacologic in nature, with antioxidant, lipid-lowering, nuclear-transcription regulating, cytokine-targeting, hormone-mimetic, GLP-1 agonism or other metabolic profile altering properties [
112]. Of these many agents, several therapeutic options that have reached phase 2 (lanifibranor) or phase 3 clinical trials (obeticholic acid, elafibranor, cenicriviroc, arachidyl amido cholanoic acid, and resmetirom to name a few).
6.1. Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor antagonist that has shown some of the highest promise as a potential therapeutic agent for NASH in recent years. A pivotal study performed by Newsome et al investigating the safety and efficacy of Semaglutide administration in patients with NASH showed a statistically significant increase in patients with NASH resolution compared to placebo. [
113] A recent network meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials studying the efficacy of off-label therapy for NAFLD showed that Semaglutide use led to a significantly higher decrease in AST and ALT levels versus placebo, and that Semaglutide was superior to liraglutide in decreasing AST and ALT in patients with NAFLD [
98]. As discussed prior, weight gain is central to the development of NASH and thus weight loss is paramount in the ability to reverse NASH. The weight loss effects of Semaglutide are well known and sought after in patients with both diabetes and obesity. Interestingly however, in the trial by Newsome et al., while a majority of NASH resolution was attributable to weight loss, the authors describe a small proportion of patients (approximately 25%) in whom there was NASH resolution beyond that which would be expected from weight loss alone. This is congruent with some preclinical studies such as those by Rakipovski et al demonstrating that Semaglutide reduces inflammation in the liver by mechanisms independent of weight loss. [
114] This apparent pleiotropic effect of Semaglutide on NASH in addition to its established safety and availability for weight loss make this agent one of the most promising options for the treatment of NASH at present. Other agents have also shown some promise however they have been marred by undesirable side effects, lack of availability or lack of real-world efficacy beyond clinical trial. Some of these are discussed below.
6.2. Obeticholic acid
Obeticholic acid (OCA) is a synthetic bile acid derivative of chenodeoxycholic acid that acts as a farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist [
115]. FXR is a nuclear receptor found intracellularly in the liver, intestines, kidneys, and adrenal glands, where it plays a role in glucose and lipid metabolism [
112]. Upon stimulation by increasing bile acid levels, FXR suppresses the transcription of CYP7A1 gene, thereby inhibiting 7α-hydroxylase, downregulating bile acid synthesis, and upregulating cholesterol synthesis [
116].
Early studies and clinical trials that demonstrated increased insulin sensitivity; decreased hepatic inflammatory and fibrotic markers; increases in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) that could be mitigated with concomitant statin therapy; and minimal adverse events have prompted further phase 2 and 3 clinical trials [
117,
118].
The FLINT trial was a phase 2b clinical trial that involved 283 patients with noncirrhotic NASH [
119]. The study compared OCA to a placebo, finding a significant improvement in liver histology in the OCA group compared to the placebo. Pruritus was identified as an adverse effect of OCA therapy [
119]. OCA also significantly increased LDL and cholesterol levels and decreased HDL levels, requiring concomitant statin treatment, compared to the placebo [
119].
An ongoing phase 3 clinical trial is the REGENERATE trial, which aims to compare the effects of 10-mg OCA and 25-mg OCA to a placebo on histological improvement and liver-related outcomes in patients with fibrotic, noncirrhotic NASH [
120,
121]. The study involves 2480 participants. A December 2019 interim analysis of the ongoing trial reported a significant fibrosis improvement without exacerbation of NASH in the 25-mg OCA group compared to the placebo, but no significant NASH resolution in either OCA group compared to the placebo [
121]. Mild to moderate pruritus was noted as an adverse event in OCA therapy, corroborating findings of previous randomized control trials [
121].
6.3. Lanifibranor
Lanifibranor is an antifibrotic indole sulfonamide α/γ/δ PPAR agonist that is novel for its ability to activate all three PPAR isoforms [
122]. Early animal studies modeling the effects of lanifibranor on NASH found that lanifibranor normalized insulin sensitivity, decreased histologic characteristics of NASH including hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and ballooning, and inhibited the activity of hepatic stellate cells responsible for fibrinogenesis [
123]. The pan-PPAR activity of lanifibranor is thought to mediate therapeutic improvements in pathways involving glucose metabolism and insulin sensitization, fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism, and energy homeostasis [
124].
A recent phase 2b randomized control trial compared the efficacy of 1200-mg or 800-mg lanifibranor to a placebo in 247 patients with biopsy-proven, highly active, noncirrhotic NASH over 24 weeks [
125]. Of the 247 participants, 42% had type-2 diabetes and 26% had moderate to severe fibrosis [
125]. The study demonstrated a significantly higher percentage of at least a 2-point decrease in Steatosis, Activity, Fibrosis (SAF-A) score in the 1200-mg (but not the 800-mg) lanifibranor experimental group compared to the placebo. Also, compared to the placebo, both the 1200-mg and 800-mg had higher rates of NASH resolution with and without improvement in fibrosis stage [
125]. The lanifibranor groups also demonstrated decreased liver enzyme levels, improvements in measures of glycemic control (such as reductions in glycated hemoglobin), increased HDL cholesterol levels, increased dose-dependent adiponectin levels, and decreases in serum triglycerides [
125]. Adverse effects of lanifibranor therapy included gastrointestinal events such as nausea and diarrhea, peripheral edema, anemia, and weight gain [
125]. Further research on the efficacy and adverse-effect profile of lanifibranor awaits phase 3 clinical trials.
6.4. Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid
Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid (Aramchol) is an inhibitor of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD-1). SCD-1 is the rate-determining enzyme in the conversion of saturated fatty acids to monounsaturated fatty acids [
126]. Animal studies have shown that the inhibition or deficiency of SCD-1 reduced carbohydrate-induced adiposity, hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and insulin resistance [
127,
128,
129].
A phase 2 clinical trial of 60 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH in Israel compared 100-mg or 300-mg Aramchol to a placebo to assess for changes in hepatic steatosis [
130]. The 300-mg Aramchol group experienced a significant reduction in hepatic steatosis, and the study found Aramchol to be well-tolerated without significant adverse effects [
130].
The ARREST trial, a phase 2b clinical trial, administered 400-mg, 600-mg Aramchol, or a placebo to 247 participants with prediabetes or type-2 diabetes and NASH to assess for significant decreases in hepatic triglycerides as its primary endpoint and for improved hepatic histology and aminotransferase as it secondary endpoint [
131]. The group receiving 400-mg Aramchol demonstrated a significant decrease in hepatic steatosis compared to the placebo group. The 600-mg Aramchol group decreased hepatic steatosis but insignificantly compared to the placebo [
131]. Aramchol therapy also decreased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels [
131]. The study also concluded that Aramchol was well tolerated and safe, though a higher incidence of urinary tract infections was noted in both Aramchol groups compared to the group receiving the placebo [
131].
The ARMOR trial is an ongoing, phase 3/4 trial consisting of an open-label part and two double-blind parts that has enrolled 2000 participants [
132]. The primary endpoints of the open-label part include improvement in fibrosis and resolution of NASH, and the endpoints of the double-blind parts include improvement in fibrosis, resolution of NASH, and assessment of long-term clinical outcomes [
132].
6.5. Resmetirom
Resmetirom is a thyroid hormone receptor-β [THR-β] agonist. Thyroid hormones are thought to mediate hepatic triglyceride metabolism by promoting hepatic autophagy to aid the transport of fatty acids to the mitochondria for oxidative metabolism [
133,
134]. Disruptions in lipid metabolism pathways, such as those mediated by thyroid hormones, are thought to contribute to NAFLD [
135]. There are several thyroid hormone receptor (THR) isoforms, but THR-β is the most commonly found THR in the liver [
135]. Thus, targeting this receptor decreases the risk of adverse effects due to the stimulation of other THR isoforms found in heart and bone tissue [
136]. TH analogues have been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis and lipid peroxidation [
135]. In animal studies, resmetirom was found to be well tolerated and caused statistically significant reductions in LDL-c and triglyceride levels [
137]. An early randomized control supported findings from animal models, showing significant reductions compared to the placebo in LDL-c, non-HDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and triglycerides without causing significant adverse events [
138].
A phase 2 clinical trial involved 125 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH and a hepatic fat fraction greater than or equal to 10% were administered 80-mg resmetirom or a placebo for 36 weeks [
139]. The primary endpoint was a change in hepatic steatosis measured by MRI-proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) in the resmetirom group at 12 weeks [
139]. At weeks 12 and 36, the resmetirom grup demonstrated a significant reduction in hepatic steatosis compared to the placebo group. Resmetirom was mosly well-tolerated, but transient mild diarrhea and nausea were significant adverse effects [
139].
7. Discussion
In terms of pharmacologic treatment, no drug has yet been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the specific treatment of NAFLD. Over 100 drugs have been studied in clinical trials for the treatment of NAFLD and NASH given its rapidly rising prevalence in the United States and the downstream effects being seen of cirrhosis. Unfortunately, several drugs thought to have shown promise have faltered along the process. Given the vast array of medications targeting various contributors to the progression of NASH including lipogenesis, bile-acid metabolism, fibrogenesis, glucose metabolism and metabolic regulation, it is abundantly clear that NAFLD has no silver bullet.
As a result, the most optimal way to manage NAFLD and NASH at present remains combination therapeutics based on known risk factors for the progression of NASH and NAFLD. Lifestyle modification as a result remains a fundamental pillar in the prevention of NASH progression, with dietary counselling being key. Referral to subspecialists for the management of factors defining metabolism should be made immediately at their discovery for initiation of therapeutics such as blood pressure, glucose, triglyceride and lipid lowering agents.
In those with comorbidities of obesity and or diabetes, drugs that target weight loss, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, can be used. Semaglutide and liraglutide are the two GLP-1 agonists currently approved for the treatment of obesity in the United States and have been shown to be effective in reducing liver fat content and improving liver function in patients with NAFLD. The study of GLP-1 agonist, especially Semaglutide, and its effects on NASH that are weight-loss mediated and possibly pleiotropically mediated is absolutely necessary given the promise these medications have shown. In the interim, given their increasing availability, these medications should be considered first line pharmacotherapy in patients with qualifying comorbidities warranting treatment with a GLP-1 agonist. Other medications traditionally used for weight loss, such as orlistat, sympathomimetics, and combination drugs, have not been studied as extensively in the context of NAFLD. Orlistat, for example, has been shown to improve liver histopathology and reduce inflammatory enzymes in some studies, but its adverse effects on the gastrointestinal system may limit its use. Similarly, the effectiveness of sympathomimetic drugs like phentermine and diethylpropion in the treatment of NAFLD has not been well-established, and combination drugs like naltrexone-bupropion have only been studied in small trials with mixed results.
Finally, bariatric surgery or bariatric endoscopy referral should be sought aggressively in potentially eligible patients given its demonstrated efficacy at weight loss and resultant improvement in steatohepatitis. The advent of novel bariatric endoscopic procedures may increase the patient population eligible for procedural intervention when previously deemed too high risk for surgical intervention.
Overall, these emerging therapies for NAFLD show promise but also highlight a large gap between both: NASH and our understanding of contributory factors as well as our current understanding of contributory factors and available medications to target these. Future efforts should be focused on continuation of the advent of novel therapeutics, increasing availability of current efficacious therapies to those who are eligible and finally validation of non-invasive testing for NASH as end-points for clinical trials to allow for easier testing if we are to have any hope of combating the rapid increase in incident NASH. The MAESTRO-NASH and MAESTRO-NAFLD trials are ongoing phase 3 clinical trials [
139,
140]. MAESTRO-NASH aims to compare 80-mg or 100-mg resmetirom treatment to a placebo [
140]. The primary endpoint of the trial is resolution of NASH in patients with stage-2 or 3 fibrotic, noncirrhotic NASH and an evaluation of long-term clinical outcomes [
140]. The secondary endpoint is change in LDL-c levels from baseline and histologic hepatic fibrosis improvement [
140]. MAESTRO-NAFLD aims to describe adverse effects and safety of 80-mg and 100-mg resmetirom compared to a placebo [
139]. The trial will secondarily measure changes in LDL-C, apolipoprotein B, hepatic fat fraction measured by MRI-PDFF, triglycerides, and collagen type-III propeptide [
139].
Author Contributions
J.B. (Jacob Beiriger), K.C., A.K., T.S., N.S., P.Z., S.C., A.N., B.Y., J.B. (John Bruckbauer), D.D.: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Janssen, A.; E Grobbee, D.; Dendale, P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a new and growing risk indicator for cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M., et al., Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology, 2016. 64(1): p. 73-84.
- Parikh, R.M.; Mohan, V. Changing definitions of metabolic syndrome. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Yuen, M.-F.; Seto, W.-K. Letter regarding “A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement”. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1573–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.E.; Koh, T.J.L.; Tang, A.S.P.; Quek, J.; Yong, J.N.; Tay, P.; Tan, D.J.H.; Lim, W.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Huang, D.; et al. Global Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Metabolic-associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of 10 739 607 Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.-X.; Weng, J.-P.; Xu, F. MAFLD vs. NAFLD: shared features and potential changes in epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacotherapy. Chin. Med J. 2020, 134, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M. Liver transplantation for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New challenges and new opportunities. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5320–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Kumar, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Woo, J.; Abrigo, J.M.; Chan, C.K.-M.; Shu, S.S.-T.; Leung, J.K.-Y.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Kong, A.P.-S.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; et al. Impact of the New Definition of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease on the Epidemiology of the Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J. and R. Cheung, Trends in the Prevalence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in the United States, 2011-2018. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022. 20(3): p. e610-e613.
- Ciardullo, S.; Perseghin, G. Prevalence of NAFLD, MAFLD and associated advanced fibrosis in the contemporary United States population. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, J.; Huang, D.Q.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Kam, L.Y.; Tan, X.X.E.; et al. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Wong, V.W.-S. Epidemiology and Clinical Outcomes of Metabolic (Dysfunction)-associated Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, F.; Salam, R.A.; Lassi, Z.S.; Das, J.K. The Intertwined Relationship Between Malnutrition and Poverty. Front. Public Heal. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, B.P.; Kelly, M.K.; Powell, M.; Bouchelle, Z.; Mayne, S.L.; Fiks, A.G. COVID-19 and Changes in Child Obesity. PEDIATRICS 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, R.J. Poverty, Weight Status, and Dietary Intake among UK Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2018, 15, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, C., et al., Liver, NAFLD and COVID-19. Horm Metab Res, 2022. 54(8): p. 522-531.
- Fujii, H.; Nakamura, N.; Fukumoto, S.; Kimura, T.; Nakano, A.; Nadatani, Y.; Tauchi, Y.; Nishii, Y.; Takashima, S.; Kamada, Y.; et al. Lifestyle changes during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic impact metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, H.E.; Arendt, B.M.; Noureldin, S.A.; Therapondos, G.; Guindi, M.; Allard, J.P. A Cross-Sectional Study Assessing Dietary Intake and Physical Activity in Canadian Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease vs Healthy Controls. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.D.; Stengel, J.; Asike, M.I.; Torres, D.M.; Shaw, J.; Contreras, M.; Landt, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Among a Largely Middle-Aged Population Utilizing Ultrasound and Liver Biopsy: A Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bengmark, S.; Qu, S. The role of hepatic fat accumulation in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Lipids Heal. Dis. 2010, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, G.I., Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N Engl J Med, 2014. 371(23): p. 2237-8.
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Roles of Diacylglycerols and Ceramides in Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Molecular Mechanisms of Lipotoxicity in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojsavljević, S.; Gomerčić Palčić, M.; Virović Jukić, L.; Smirčić Duvnjak, L.; Duvnjak, M. Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18070–18091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.L., et al., Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescence: From "two hit theory" to "multiple hit model". World J Gastroenterol, 2018. 24(27): p. 2974-2983.
- Lebeaupin, C.; Vallée, D.; Hazari, Y.; Hetz, C.; Chevet, E.; Bailly-Maitre, B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Balakrishnan, V. Role of Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 26, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendijk, P.S., et al., Quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization of Bifidobacterium spp. with genus-specific 16S rRNA-targeted probes and its application in fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1995. 61(8): p. 3069-75.
- Yu, J.; Marsh, S.; Hu, J.; Feng, W.; Wu, C. The Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Interplay between Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Genetic Background. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 2862173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E., et al., Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature, 2006. 444(7122): p. 1022-3.
- Turnbaugh, P.J., et al., An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature, 2006. 444(7122): p. 1027-31.
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schäfer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in Lean and Overweight Healthy Subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, M.-E.; Barton, R.H.; Toye, A.; Cloarec, O.; Blancher, C.; Rothwell, A.; Fearnside, J.; Tatoud, R.; Blanc, V.; Lindon, J.C.; et al. Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution of gut microbiota to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12511–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, E., et al., Assessment of biopsy-proven liver fibrosis by two-dimensional shear wave elastography: An individual patient data-based meta-analysis. Hepatology, 2018. 67(1): p. 260-272.
- Spencer, M.D.; Hamp, T.J.; Reid, R.W.; Fischer, L.M.; Zeisel, S.H.; Fodor, A.A. Association Between Composition of the Human Gastrointestinal Microbiome and Development of Fatty Liver With Choline Deficiency. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, R.H.; Wang, X.X.; Cheng, L.L.; Krisko, T.; Smith, M.; El Kasmi, K.; Pruzanski, M.; Adorini, L.; Golden-Mason, L.; Levi, M.; et al. Bile Acid Receptor Activation Modulates Hepatic Monocyte Activity and Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PEDIATRICS 2013, 288, 11761–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artis, D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Lin, H.Z.; Lane, M.D.; Clemens, M.; Diehl, A.M. Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: Implications for the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, N., et al., Saturated fat stimulates obesity and hepatic steatosis and affects gut microbiota composition by an enhanced overflow of dietary fat to the distal intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2012. 303(5): p. G589-99.
- Jegatheesan, P.; Beutheu, S.; Ventura, G.; Sarfati, G.; Nubret, E.; Kapel, N.; Waligora-Dupriet, A.-J.; Bergheim, I.; Cynober, L.; De-Bandt, J.-P. Effect of specific amino acids on hepatic lipid metabolism in fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Willment, A.; Patel, S.S.; Sun, X.; Song, M.; Mannery, Y.O.; Kosters, A.; McClain, C.J.; Vos, M.B. Fructose Induced Endotoxemia in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; Cohney, S.; Pinach, S.; Saba, F.; Gambino, R. Emerging Liver–Kidney Interactions in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Piceno, Y.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Pahl, M.; Andersen, G.L.; Vaziri, N.D. Expansion of Urease- and Uricase-Containing, Indole- and p-Cresol-Forming and Contraction of Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Intestinal Microbiota in ESRD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Duseja, A.; Sharma, B.K.; Singla, B.; Chakraborti, A.; Das, A.; Ray, P.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor signaling in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Cicerchi, C.; Garcia, G.; Li, N.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Rivard, C.J.; Hunter, B.; Andrés-Hernando, A.; Ishimoto, T.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; et al. Counteracting Roles of AMP Deaminase and AMP Kinase in the Development of Fatty Liver. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e48801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A., et al., Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J Biol Chem, 2012. 287(48): p. 40732-44.
- Shapiro, A.; Tümer, N.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Scarpace, P.J. Prevention and reversal of diet-induced leptin resistance with a sugar-free diet despite high fat content. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Mu, W.; Roncal, C.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Johnson, R.J.; Scarpace, P.J.; Patel, C.; Sugimoto, K.; Douard, V.; Shah, A.; et al. Fructose-induced leptin resistance exacerbates weight gain in response to subsequent high-fat feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1370–R1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Bata, P.; Littvay, L.; Osztovits, J.; Jermendy, G.; Karlinger, K.; Lannert, A.; Preda, I.; Kiss, R.G.; et al. Heritability of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and association with abnormal vascular parameters: A twin study. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Celedon, M.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Salem, R.; Campbell, N.; Schork, N.J.; Shiehmorteza, M.; Yokoo, T.; Chavez, A.; Middleton, M.S.; et al. Heritability of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Schork, N.; Chen, C.-H.; Bettencourt, R.; Bhatt, A.; Ang, B.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Richards, L.; Salotti, J.; et al. Heritability of Hepatic Fibrosis and Steatosis Based on a Prospective Twin Study. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speliotes, E.K., et al., Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet, 2011. 7(3): p. e1001324.
- Wagenknecht, L.E.; Scherzinger, A.L.; Stamm, E.R.; Hanley, A.J.; Norris, J.M.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Bryer-Ash, M.; Haffner, S.M.; Rotter, J.I. Correlates and Heritability of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Minority Cohort. Obesity 2009, 17, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.D.; Musani, S.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Feitosa, M.F.; Bielak, L.F.; Hernaez, R.; Kahali, B.; Carr, J.J.; Harris, T.B.; Jhun, M.A.; et al. Characterization of european ancestry nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated variants in individuals of african and hispanic descent. Hepatology 2013, 58, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Seth, D.; Day, C.P. Genetic Factors That Affect Risk of Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wuyunerdeni, N.; Yao, S. Expression, purification of herpes simplex virus type 1 US11 Protein, and production of US11 polyclonal antibody. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 490–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingitore, P.; Pirazzi, C.; Mancina, R.M.; Motta, B.M.; Indiveri, C.; Pujia, A.; Montalcini, T.; Hedfalk, K.; Romeo, S. Recombinant PNPLA3 protein shows triglyceride hydrolase activity and its I148M mutation results in loss of function. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S., et al., Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet, 2008. 40(12): p. 1461-5.
- Sookoian, S.; Castaño, G.O.; Scian, R.; Mallardi, P.; Gianotti, T.F.; Burgueño, A.L.; Martino, J.S.; Pirola, C.J. Genetic variation in transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and histological disease severity. Hepatology 2015, 61, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancina, R.M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Pingitore, P.; Meroni, M.; Rametta, R.; Borén, J.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Wiklund, O.; et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Kim, N.; Shin, H.Y. Modeling Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Using “Good-Fit” Genome-Editing Tools. Cells 2020, 9, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Miele, L.; Bugianesi, E.; Cammà, C.; Rosso, C.; Boccia, S.; Cabibi, D.; Di Marco, V.; Grimaudo, S.; Grieco, A.; et al. Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Gene Polymorphism Affects Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e87523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.E., V.W. Wong, and M. Rinella, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet, 2021. 397(10290): p. 2212-2224.
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Keach, J.C.; Batts, K.P.; Lindor, K.D. Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Tsang, S.W.-C.; Hui, A.Y.; Chan, A. ..-H.; Choi, P.C.-L.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Chu, S.; Chan, F.K.-L.; Sung, J.J.-Y.; et al. Metabolic and histological features of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with different serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Disease in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1264–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridi, M.; Cholongitas, E. Diagnosis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Concepts. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 4574–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khov, N., A. Sharma, and T.R. Riley, Bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol, 2014. 20(22): p. 6821-5.
- Kinner, S.; Reeder, S.B.; Yokoo, T. Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers of NAFLD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R. Role of imaging-based biomarkers in NAFLD: Recent advances in clinical application and future research directions. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dhyani, M.; Grajo, J.R.; Sirlin, C.; Samir, A.E. Current status of imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.; Bayliss, S.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Ishigami, M.; Toyoda, H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Peleg, N.; et al. Association Between Fibrosis Stage and Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, E.; Lee, T.-P. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, Including Noninvasive Biomarkers and Transient Elastography. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Lehrke, M.; Hendler, R.E.; Shulman, G.I. Reversal of Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis, Hepatic Insulin Resistance, and Hyperglycemia by Moderate Weight Reduction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; K, P.; DE, K.; Hm, N.; E, J.; M, K.; Jr, W.; Jl, F.; Rr, W. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, W.N.; Harrison, S.A. Effect of Weight Loss, Diet, Exercise, and Bariatric Surgery on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ensen, M.D., et al., 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation, 2014. 129(25 Suppl 2): p. S102-38.
- Bower, G.; Toma, T.; Harling, L.; Jiao, L.R.; Efthimiou, E.; Darzi, A.; Athanasiou, T.; Ashrafian, H. Bariatric Surgery and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: a Systematic Review of Liver Biochemistry and Histology. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; I Tellez-Avila, F.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Lizardi-Cervera, J.; Uribe, M. Bariatric surgery for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD007340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathurin, P.; Hollebecque, A.; Arnalsteen, L.; Buob, D.; Leteurtre, E.; Caiazzo, R.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Prospective Study of the Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Liver Injury in Patients Without Advanced Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Buob, D.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Raverdy, V.; Leteurtre, E.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T., et al., AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS AND AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY COMPREHENSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MEDICAL CARE OF PATIENTS WITH OBESITYEXECUTIVE SUMMARYComplete Guidelines available at https://www.aace.com/publications/guidelines. Endocr Pract, 2016. 22(7): p. 842-84.
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, D.M., et al., Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA, 2022. 327(2): p. 138-150.
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; A Aldersley, M.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.-M.; Cercueil, J.-P.; Loffroy, R.; Denimal, D.; Bouillet, B.; Fourmont, C.; Chevallier, O.; Duvillard, L.; Vergès, B. Effect of liraglutide therapy on liver fat content in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. The Lira-NAFLD study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Feng, W.; Li, C.; Tong, G.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Shen, S.; et al. Effects of exenatide, insulin, and pioglitazone on liver fat content and body fat distributions in drug-naive subjects with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J., et al., Comparative effects of liraglutide 3 mg vs structured lifestyle modification on body weight, liver fat and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2017. 19(12): p. 1814-1817.
- Luo, Q.; Wei, R.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.J. Efficacy of Off-Label Therapy for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Improving Non-invasive and Invasive Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 793203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, T.D., et al., Orlistat-associated adverse effects and drug interactions: a critical review. Drug Saf, 2008. 31(1): p. 53-65.
- Zelber–Sagi, S.; Kessler, A.; Brazowsky, E.; Webb, M.; Lurie, Y.; Santo, M.; Leshno, M.; Blendis, L.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Orlistat for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; Sa, H.; W, F.; Em, B.; Ba, N.-T. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology 2009, 49, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, N.; Hussein, O.; Abassi, Z. Weight loss induced by orlistat reverses fatty infiltration and improves hepatic fibrosis in obese patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2007, 56, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Fincke, C.; Helinski, D.; Torgerson, S.; Hayashi, P. A pilot study of orlistat treatment in obese, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, P.M.; Harrat, Z.; Hamrioui, B.; Thellier, M.; Datry, A.; Danis, M. [A simple media for isolation and culture of leishmania]. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1996, 89, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J., et al., Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med, 2010. 362(18): p. 1675-85.
- Klein, E.A.; Thompson, I.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Goodman, P.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Gaziano, J.M.; Karp, D.D.; et al. Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: Updated results of the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). JAMA 2011, 306, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürks, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Rist, P.M.; Tzourio, C.; Kurth, T. Effects of vitamin E on stroke subtypes: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2010, 341, c5702–c5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.R., 3rd, et al., Meta-analysis: high-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann Intern Med, 2005. 142(1): p. 37-46.
- Boettcher, E.; Csako, G.; Pucino, F.; Wesley, R.; Loomba, R. Meta-analysis: pioglitazone improves liver histology and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, H.; Rivera, K.; Lomonaco, R.; Cusi, K. The Future of Thiazolidinedione Therapy in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Cusi, K. Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Call to Action. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S., et al., Current treatment paradigms and emerging therapies for NAFLD/NASH. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2021. 26(2): p. 206-237.
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakipovski, G., et al., The GLP-1 Analogs Liraglutide and Semaglutide Reduce Atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) and LDLr(-/-) Mice by a Mechanism That Includes Inflammatory Pathways. JACC Basic Transl Sci, 2018. 3(6): p. 844-857.
- Ho, P.P.; Steinman, L. Obeticholic acid, a synthetic bile acid agonist of the farnesoid X receptor, attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirguis, E.; Grace, Y.; Bolson, A.; DellaVecchia, M.J.; Ruble, M. Emerging therapies for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2021, 41, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pockros, P.J.; Fuchs, M.; Freilich, B.; Schiff, E.; Kohli, A.; Lawitz, E.J.; Hellstern, P.A.; Owens-Grillo, J.; Van Biene, C.; Shringarpure, R.; et al. CONTROL: A randomized phase 2 study of obeticholic acid and atorvastatin on lipoproteins in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Morrow, L.; Marschall, H.; Kipnes, M.; Adorini, L.; Sciacca, C.I.; Clopton, P.; Castelloe, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist Obeticholic Acid in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A., et al., Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet, 2015. 385(9972): p. 956-65.
- Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.; Anstee, Q.M.; Goodman, Z.; Bedossa, P.; MacConell, L.; Shringarpure, R.; et al. REGENERATE: Design of a pivotal, randomised, phase 3 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of obeticholic acid in patients with fibrosis due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2019, 84, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Ratziu, V.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Goodman, Z.; Bedossa, P.; Geier, A.; Beckebaum, S.; Newsome, P.N.; et al. Obeticholic acid for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Interim analysis from a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubia, B., et al., Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of a Novel Series of Indole Sulfonamide Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor (PPAR) alpha/gamma/delta Triple Activators: Discovery of Lanifibranor, a New Antifibrotic Clinical Candidate. J Med Chem, 2018. 61(6): p. 2246-2265.
- Wettstein, G.; Luccarini, J.; Poekes, L.; Faye, P.; Kupkowski, F.; Adarbes, V.; Defrêne, E.; Estivalet, C.; Gawronski, X.; Jantzen, I.; et al. The new-generation pan-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist IVA337 protects the liver from metabolic disorders and fibrosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Gupta, P.; Saini, A.S.; Kaushal, C.; Sharma, S. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: A family of nuclear receptors role in various diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.M.; Bedossa, P.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Balabanska, R.; Mateva, L.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Pan-PPAR Agonist Lanifibranor in NASH. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, L. and B.A. Fielding, Stearoyl-CoA desaturase: rogue or innocent bystander? Prog Lipid Res, 2013. 52(1): p. 15-42.
- Walle, P.; Takkunen, M.; Männistö, V.; Vaittinen, M.; Lankinen, M.; Kärjä, V.; Käkelä, P.; Ågren, J.; Tiainen, M.; Schwab, U.; et al. Fatty acid metabolism is altered in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis independent of obesity. Metabolism 2016, 65, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issandou, M., et al., Pharmacological inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant rat models. Eur J Pharmacol, 2009. 618(1-3): p. 28-36.
- Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta, M.; Varela-Rey, M.; Fernández-Ramos, D.; Martínez-Arranz, I.; Delgado, T.C.; Simon, J.; Juan, V.G.; Delacruz-Villar, L.; Azkargorta, M.; Lavin, J.L.; et al. Role of aramchol in steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safadi, R.; Konikoff, F.M.; Mahamid, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Halpern, M.; Gilat, T.; Oren, R.; Hershkovitz, A.; Rosenthal-Galili, Z.; Zuckerman, E.; et al. The Fatty Acid–Bile Acid Conjugate Aramchol Reduces Liver Fat Content in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; de Guevara, L.; Safadi, R.; Poordad, F.; Fuster, F.; Flores-Figueroa, J.; Arrese, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Ben Bashat, D.; Lackner, K.; et al. Aramchol in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, V.R.; Bojanic, K.; Smolic, M.; Rubin, J.; Tabll, A.; Smolic, R. An Update on Efficacy and Safety of Emerging Hepatic Antifibrotic Agents. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Reciprocal Crosstalk Between Autophagic and Endocrine Signaling in Metabolic Homeostasis. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; You, S.-H.; Zhou, J.; Siddique, M.M.; Bay, B.-H.; Zhu, X.; Privalsky, M.L.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Stevens, R.D.; Summers, S.A.; et al. Thyroid hormone stimulates hepatic lipid catabolism via activation of autophagy. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Bruinstroop, E.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists. Thyroid® 2019, 29, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, S.I., et al., Augmented hepatic and skeletal thyromimetic effects of tiratricol in comparison with levothyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1997. 82(7): p. 2153-8.
- Kelly, M.J., et al., Discovery of 2-[3,5-dichloro-4-(5-isopropyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yloxy)phenyl]-3,5-dio xo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro[1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonitrile (MGL-3196), a Highly Selective Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta agonist in clinical trials for the treatment of dyslipidemia. J Med Chem, 2014. 57(10): p. 3912-23.
- Taub, R.; Chiang, E.; Chabot-Blanchet, M.; Kelly, M.J.; Reeves, R.A.; Guertin, M.-C.; Tardif, J.-C. Lipid lowering in healthy volunteers treated with multiple doses of MGL-3196, a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A., et al., Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet, 2019. 394(10213): p. 2012-2024.
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.; Moussa, S.E.; McCarty, K.; Frias, J.P.; Taub, R.; Alkhouri, N. Effects of Resmetirom on Noninvasive Endpoints in a 36-Week Phase 2 Active Treatment Extension Study in Patients With NASH. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).