Submitted:
10 August 2023
Posted:
15 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Thyroid Morphophysiology: an overview
Parabens
Parabens and TSH
Parabens and TSH in human
Parabens and TSH in rodents
Parabens and Thyroid Hormones
Parabens and Thyroid Hormones in human
Parabens and Thyroid Hormones in rodents
Parabens and Thyroid Hormones in vertebrates
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Mattiuzzi, C., & Lippi, G. (2019). Current cancer epidemiology. Journal of epidemiology and global health, 9(4), 217. [CrossRef]
- Lauretta, R.; Sansone, A.; Sansone, M.; Romanelli, F.; Appetecchia, M. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Effects on Endocrine Glands. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 178. [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-V.; Kitahara, C.M.; de Vathaire, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Journy, N. Thyroid dysfunction and cancer incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2020, 27, 245–259. [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-V.; Kitahara, C.M.; Leenhardt, L.; de Vathaire, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Journy, N. The effect of thyroid dysfunction on breast cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2023, 30. [CrossRef]
- Kogai, T.; Endo, T.; Saito, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Kawaguchi, A.; Onaya, T. Regulation by Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone of Sodium/Iodide Symporter Gene Expression and Protein Levels in FRTL-5 Cells. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2227–2232. [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.W.; Landgrafe, G.; Fotiadou, E.H. TSH and Thyrotropic Agonists: Key Actors in Thyroid Homeostasis. J. Thyroid. Res. 2012, 2012, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Haisenleder, D.J.; A Ortolano, G.; Dalkin, A.C.; Yasin, M.; Marshall, J.C. Differential actions of thyrotropin (TSH)-releasing hormone pulses in the expression of prolactin and TSH subunit messenger ribonucleic acid in rat pituitary cells in vitro.. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 2917–2923. [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Tan, S.W.; Tyl, R.W. General Background on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 11–53. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.O.; Bourguignon, N.S.; Arocena, P.; Rosa, M.; Libertun, C.; Lux-Lantos, V. Neonatal exposure to bisphenol A alters the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in female rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 81–86. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Pereira, P.; Andrade, M.N.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Teixeira, M.P.; Soares, P.; Graceli, J.B.; de Carvalho, D.P.; Dias, G.R.M.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; Miranda-Alves, L. Subacute and low-dose tributyltin exposure disturbs the mammalian hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in a sex-dependent manner. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 254, 109279. [CrossRef]
- Graceli, J.B.; Dettogni, R.S.; Merlo, E.; Niño, O.; da Costa, C.S.; Zanol, J.F.; Rios-Morris, E.A.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Denicol, A.C. The impact of endocrine-disrupting chemical exposure in the mammalian hypothalamic-pituitary axis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110997. [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, A.P.; Andrade, M.N.; Pereira-Rodrigues, P.; Paiva-Melo, F.D.; Soares, P.; Graceli, J.B.; Dias, G.R.M.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; de Carvalho, D.P.; Miranda-Alves, L. Frontiers in endocrine disruption: Impacts of organotin on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 460, 246–257. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Zha, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Z. Butachlor causes disruption of HPG and HPT axes in adult female rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Chem. Interactions 2014, 221, 119–126. [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.-P.; Ma, Y.-B.; Lu, C.-J.; Mirza, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jia, Y.-F.; Li, W.-G.; Pei, D.-S. The Effects of Disturbance on Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis in Zebrafish Larvae after Exposure to DEHP. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0155762–e0155762. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Lou, L.; Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Feng, X. Exposure to deltamethrin in adolescent mice induced thyroid dysfunction and behavioral disorders. Chemosphere 2019, 241, 125118. [CrossRef]
- McLanahan, E. D., Campbell Jr, J. L., Ferguson, D. C., Harmon, B., Hedge, J. M., Crofton, K. M., ... & Fisher, J. W. (2007). Low-dose effects of ammonium perchlorate on the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis of adult male rats pretreated with PCB126. Toxicological sciences, 97(2), 308-317. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P. N., Albrecht, D., Scholz, A., Gutierrez-Buey, G., Lazarus, J. H., Dayan, C. M., & Okosieme, O. E. (2018). Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 14(5), 301-316. [CrossRef]
- Marotta, V.; Russo, G.; Gambardella, C.; Grasso, M.; La Sala, D.; Chiofalo, M.G.; D'Anna, R.; Puzziello, A.; Docimo, G.; Masone, S.; et al. Human exposure to bisphenol AF and diethylhexylphthalate increases susceptibility to develop differentiated thyroid cancer in patients with thyroid nodules. Chemosphere 2018, 218, 885–894. [CrossRef]
- Sur, U., Erkekoglu, P., Bulus, A. D., Andiran, N., & Kocer-Gumusel, B. (2019). Oxidative stress markers, trace elements, and endocrine disrupting chemicals in children with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Toxicology mechanisms and methods, 29(9), 633-643.
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Ricci, G.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M.; Imbriani, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroid Disrupting Effects of Old and New Generation PFAS. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Xiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.Q. Short-term exposure of arsenite disrupted thyroid endocrine system and altered gene transcription in the HPT axis in zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 145–152. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.S.; Kizys, M.M.L.; da Conceição, R.R.; Glebocki, G.; Romano, R.M.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Giannocco, G.; da Silva, I.D.C.G.; da Silva, M.R.D.; Romano, M.A.; et al. Perinatal exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide alters the thyrotrophic axis and causes thyroid hormone homeostasis imbalance in male rats. Toxicology 2017, 377, 25–37. [CrossRef]
- EPA, USA (1997). Special report on Environmental endocrine disruption: An effects assessment and analysis office of research and development. REPA/630/R-96/012. In: Washington DC.
- Damstra,T., Barlow,S.,Bergman,A.,Kavlock,R.,VanDerKraak,G.,2002.Global. Assessment of the State-of-the-science of Endocrine Disruptors. WHO publicationhttp://dx.doi.org/10.1089/15305620252933437.No.WHO/PCS/EDC/02.2.180 - Accessed May 23, 2023.
- La Merrill, M.A.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Smith, M.T.; Goodson, W.; Browne, P.; Patisaul, H.B.; Guyton, K.Z.; Kortenkamp, A.; Cogliano, V.J.; Woodruff, T.J.; et al. Consensus on the key characteristics of endocrine-disrupting chemicals as a basis for hazard identification. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 16, 45–57. [CrossRef]
- Gore, A. C., Crews, D., Doan, L. L., La Merrill, M., Patisaul, H., & Zota, A. (2014). Introduction to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). A guide for public interest organizations and policy-makers, 21-22.
- Kabir, E.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, I. A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 241–258. [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Kalita, J.C. Effects of butylparaben exposure on thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase (D1) in female Wistar rats. Toxicology 2020, 443, 152562. [CrossRef]
- Macedo, S.; Teixeira, E.; Gaspar, T.B.; Boaventura, P.; Soares, M.A.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Soares, P. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and endocrine neoplasia: A forty-year systematic review. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 114869. [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, J.; Vogel, M.; Geserick, M.; Eckelt, F.; Körner, A.; Raue, F.; Kiess, W.; Kratzsch, J. Age-Related Association of Calcitonin with Parameters of Anthropometry, Bone and Calcium Metabolism during Childhood. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 361–370. [CrossRef]
- Anast, C.; Arnaud, C.D.; Rasmussen, H.; Tenenhouse, A. Thyrocalcitonin and the Response to Parathyroid Hormone*. J. Clin. Investig. 1967, 46, 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Raue, F., & Scherübl, H. (1995). Extracellular calcium sensitivity and voltage-dependent calcium channels in C cells. Endocrine reviews, 16(6), 752-764. [CrossRef]
- Hall, J. E. (2021). Guyton & Hall. Tratado de fisiología médica. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Gerard, A.; Denef, J.; Colin, I.; Hove, M.v.D. Evidence for processing of compact insoluble thyroglobulin globules in relation with follicular cell functional activity in the human and the mouse thyroid. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 73–80. [CrossRef]
- Citterio, C.E.; Targovnik, H.M.; Arvan, P. The role of thyroglobulin in thyroid hormonogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 323–338. [CrossRef]
- Rousset, B., Dupuy, C., Miot, F., & Dumont, J. (2015). Thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion. Endotext [Internet].
- Deme, D.; Pommier, J.; Nunez, J. Kinetics of Thyroglobulin Iodination and of Hormone Synthesis Catalyzed by Thyroid Peroxidase. Role of Iodide in the Coupling Reaction. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1976, 70, 435–440. [CrossRef]
- Maurizis, J.-C.; Marriq, C.; Rolland, M.; Lissitzky, S. Thyroid hormone synthesis and reactivity of hormone-forming tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin. FEBS Lett. 1981, 132, 29–32. [CrossRef]
- Gavaret, J.M.; Cahnmann, H.J.; Nunez, J. Thyroid hormone synthesis in thyroglobulin. The mechanism of the coupling reaction.. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 9167–9173. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.T.; Dunn, A.D. The importance of thyroglobulin structure for thyroid hormone biosynthesis. Biochimie 1999, 81, 505–509. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.P.; Dupuy, C. Thyroid hormone biosynthesis and release. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 458, 6–15. [CrossRef]
- Coscia, F., Taler-Verčič, A., Chang, V. T., Sinn, L., O’Reilly, F. J., Izoré, T., ... & Löwe, J. (2020). The structure of human thyroglobulin. Nature, 578(7796), 627-630. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.P.; Dupuy, C. Role of the NADPH Oxidases DUOX and NOX4 in Thyroid Oxidative Stress. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2013, 2, 160–167. [CrossRef]
- Deme, D., Virion, A., Hammou, N.A., & Pommier, J.(1985). NADPH-dependent generation of H2O2 in a thyroid particulate fraction requires Ca2+. FEBS letters, 186(1), 107-110. [CrossRef]
- Ameziane-El-Hassani, R.; Morand, S.; Boucher, J.-L.; Frapart, Y.-M.; Apostolou, D.; Agnandji, D.; Gnidehou, S.; Ohayon, R.; Noël-Hudson, M.-S.; Francon, J.; et al. Dual Oxidase-2 Has an Intrinsic Ca2+-dependent H2O2-generating Activity. PEDIATRICS 2005, 280, 30046–30054. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ruf, J.; Lothaire, P.; Dequanter, D.; Andry, G.; Willemse, E.; Dumont, J.E.; Van Sande, J.; De Deken, X. Association of Duoxes with Thyroid Peroxidase and Its Regulation in Thyrocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 375–382. [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, S., Loo, D. D., Dai, G., Levy, O., Wright, E. M., & Carrasco, N. (1997). Thyroid Na+/I− symporter: mechanism, stoichiometry, and specificity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(43), 27230-27238. [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Function in Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [CrossRef]
- Driessens, N.; Versteyhe, S.; Ghaddhab, C.; Burniat, A.; De Deken, X.; Van Sande, J.; Dumont, J.-E.; Miot, F.; Corvilain, B. Hydrogen peroxide induces DNA single- and double-strand breaks in thyroid cells and is therefore a potential mutagen for this organ. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2009, 16, 845–856. [CrossRef]
- Donkó, .; Morand, S.; Korzeniowska, A.; Boudreau, H.E.; Zana, M.; Hunyady, L.; Geiszt, M.; Leto, T.L. Hypothyroidism-associated missense mutation impairs NADPH oxidase activity and intracellular trafficking of Duox2. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 190–200. [CrossRef]
- Faria, C.C.; Peixoto, M.S.; Carvalho, D.P.; Fortunato, R.S. The Emerging Role of Estrogens in Thyroid Redox Homeostasis and Carcinogenesis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, I.; Alva-Sánchez, C.; Pacheco-Rosado, J. The Role of Thyroid Hormones as Inductors of Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Weyemi, U.; Caillou, B.; Talbot, M.; Ameziane-El-Hassani, R.; Lacroix, L.; Lagent-Chevallier, O.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Roos, D.; Bidart, J.-M.; Virion, A.; et al. Intracellular expression of reactive oxygen species-generating NADPH oxidase NOX4 in normal and cancer thyroid tissues. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2010, 17, 27–37. [CrossRef]
- Brieger, K., Schiavone, S., Miller Jr, F. J., & Krause, K. H. (2012). Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease. Swiss medical weekly, 142(3334), w13659-w13659. [CrossRef]
- Sola, E.; Moyano, P.; Flores, A.; García, J.M.; García, J.; Anadon, M.J.; Frejo, M.T.; Pelayo, A.; Fernandez, M.d.l.C.; del Pino, J. Cadmium-promoted thyroid hormones disruption mediates ROS, inflammation, Aβ and Tau proteins production, gliosis, spongiosis and neurodegeneration in rat basal forebrain. Chem. Interactions 2023, 375, 110428. [CrossRef]
- Macvanin, M.T.; Gluvic, Z.; Zafirovic, S.; Gao, X.; Essack, M.; Isenovic, E.R. The protective role of nutritional antioxidants against oxidative stress in thyroid disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1092837. [CrossRef]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Gao, B.; Bose, S.K.; McCord, J.M. Oxidative stress in health and disease: The therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. Mol. Asp. Med. 2011, 32, 234–246. [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.G.; Carabin, I.G.; Burdock, G.A. Safety assessment of esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (parabens). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 985–1015. [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F. A. (2008). Final amended report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, isopropylparaben, butylparaben, isobutylparaben, and benzylparaben as used in cosmetic products. Int J Toxicol, 27(Suppl 4), 1-82. [CrossRef]
- Haman, C.; Dauchy, X.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.-F. Occurrence, fate and behavior of parabens in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2015, 68, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Moon, H.-B.; Nakata, H.; Kannan, K. Occurrence and Human Exposure of p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Esters (Parabens), Bisphenol A Diglycidyl Ether (BADGE), and Their Hydrolysis Products in Indoor Dust from the United States and Three East Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11584–11593. [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Chen, L.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of parabens in foodstuffs from China and its implications for human dietary exposure. Environ. Int. 2013, 57-58, 68–74. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Kannan, K. A Survey of Phthalates and Parabens in Personal Care Products from the United States and Its Implications for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14442–14449. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Bishop, A.M.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. Parabens as Urinary Biomarkers of Exposure in Humans. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2006, 114, 1843–1846. [CrossRef]
- Janjua, N.R.; Frederiksen, H.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Wulf, H.C.; Andersson, A.-M. Urinary excretion of phthalates and paraben after repeated whole-body topical application in humans. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 31, 118–130. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Karam, N.; Piet, M.-H.; Netter, P.; Magdalou, J. Metabolism of Parabens (4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Esters) by Hepatic Esterases and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases in Man. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 25, 568–577. [CrossRef]
- Moos, R. K., Angerer, J., Dierkes, G., Brüning, T., & Koch, H. M. (2016). Metabolism and elimination of methyl, iso-and n-butyl paraben in human urine after single oral dosage. Archives of toxicology, 90, 2699-2709. [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, H., Nielsen, J. K. S., Mørck, T. A., Hansen, P. W., Jensen, J. F., Nielsen, O., ... & Knudsen, L. E. (2013). Urinary excretion of phthalate metabolites, phenols and parabens in rural and urban Danish mother–child pairs. International journal of hygiene and environmental health, 216(6), 772-783. [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshinaga, J.; Shiraishi, H.; Mizumoto, Y. Urinary excretion of parabens in pregnant Japanese women. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 35, 96–101. [CrossRef]
- Fransway, A. F., Fransway, P. J., Belsito, D. V., & Yiannias, J. A. (2019). Paraben toxicology. Dermatitis, 30(1), 32-45. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Lv, S.; Lu, D.; Qi, X.; Feng, C.; Liang, W.; et al. Effects of prenatal exposure to five parabens on neonatal thyroid function and birth weight: Evidence from SMBCS study. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109710. [CrossRef]
- Boberg, J.; Taxvig, C.; Christiansen, S.; Hass, U. Possible endocrine disrupting effects of parabens and their metabolites. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 301–312. [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Ratajczak–Wrona, W.; Górska, M.; Jabłońska, E. Parabens and their effects on the endocrine system. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 474, 238–251. [CrossRef]
- ANVISA, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Resolução da diretoria colegiada - RDC N° 528, de 4 de agosto de 2021. Disponível em: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/assuntos/noticias-anvisa/2021/novas-normas-tratam-de-produtos-de-higiene-pessoal-cosmeticos-e-perfumes - Accessed May 15, 2023.
- SCCS. EU Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety, 2010. Opinion on parabens. 14 December, 2010. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/opinions/index_en.htm.
- EFSA. European Food Safety Agency, 2004. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food on a Request from the Commission related to para-hydroxybenzoates. The EFSA Journal 83, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR), Andersen, F. A. (2008). Final amended report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, isopropylparaben, butylparaben, isobutylparaben, and benzylparaben as used in cosmetic products. Int J Toxicol, 27(Suppl 4), 1-82. [CrossRef]
- Hoberman, A.M.; Schreur, D.K.; Leazer, T.; Daston, G.P.; Carthew, P.; Re, T.; Loretz, L.; Mann, P. Lack of effect of butylparaben and methylparaben on the reproductive system in male rats. Birth Defects Res. Part B: Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 83, 123–133. [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Núñez, Z.; Ashrap, P.; Barrett, E.S.; Llanos, A.A.; Watkins, D.J.; Cathey, A.L.; Vélez-Vega, C.M.; Rosario, Z.; Cordero, J.F.; Alshawabkeh, A.; et al. Personal care products: Demographic characteristics and maternal hormones in pregnant women from Puerto Rico. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112376–112376. [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.H.; Wu, H.; Laue, H.E.; Boivin, A.; Gillet, V.; Langlois, M.-F.; Bellenger, J.-P.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Takser, L. Methylparaben in meconium and risk of maternal thyroid dysfunction, adverse birth outcomes, and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105716–105716. [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, K.; Lee, E.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kho, Y. Parabens in breast milk and possible sources of exposure among lactating women in Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113142. [CrossRef]
- Valle-Sistac, J.; Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz, M.; Ibanez, L.; Barceló, D.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S. Determination of parabens and benzophenone-type UV filters in human placenta. First description of the existence of benzyl paraben and benzophenone-4. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 243–249. [CrossRef]
- Philippat, C.; Wolff, M.S.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Bausell, R.; Meadows, M.; Stone, J.; Slama, R.; Engel, S.M. Prenatal Exposure to Environmental Phenols: Concentrations in Amniotic Fluid and Variability in Urinary Concentrations during Pregnancy. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2013, 121, 1225–1231. [CrossRef]
- Geer, L.A.; Pycke, B.F.; Waxenbaum, J.; Sherer, D.M.; Abulafia, O.; Halden, R.U. Association of birth outcomes with fetal exposure to parabens, triclosan and triclocarban in an immigrant population in Brooklyn, New York. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 323, 177–183. [CrossRef]
- Taxvig, C.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Hass, U.; Axelstad, M.; Boberg, J.; Hansen, P.R.; Frederiksen, H.; Nellemann, C. Do Parabens Have the Ability to Interfere with Steroidogenesis?. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 206–213. [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, G.; Pohl, J.; Athanassiadis, I.; Norrgren, L.; Weiss, J. Thyroid disruption properties of three indoor dust chemicals tested in Silurana tropicalis tadpoles.. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 1248–1256. [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.; Gunier, R.B.; Chevrier, J.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Eskenazi, B.; Harley, K.G. Associations of maternal exposure to triclosan, parabens, and other phenols with prenatal maternal and neonatal thyroid hormone levels. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 379–386. [CrossRef]
- i Ara, L.B.; Katugampola, H.; Dattani, M.T. Congenital Hypopituitarism During the Neonatal Period: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Therapeutic Options, and Outcome. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Egalini, F.; Marinelli, L.; Rossi, M.; Motta, G.; Prencipe, N.; Giaccherino, R.R.; Pagano, L.; Grottoli, S.; Giordano, R. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: effects on pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands. Endocrine 2022, 78, 395–405. [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Mei, H.; Cai, X.; Hu, X.; Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Yang, P.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, A. Maternal paraben exposure and intra-pair thyroid-stimulating hormone difference in twin neonates. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 250, 114502. [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, O.; Nakiwala, D.; Rolland, M.; Malatesta, A.; Lyon-Caen, S.; Chovelon, B.; Faure, P.; Gauchez, A.S.; Guergour, D.; Sakhi, A.K.; et al. Exposure to a mixture of non-persistent environmental chemicals and neonatal thyroid function in a cohort with improved exposure assessment. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107840. [CrossRef]
- Aker, A.M.; Ferguson, K.K.; Rosario, Z.Y.; Mukherjee, B.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Calafat, A.M.; Cordero, J.F.; Meeker, J.D. A repeated measures study of phenol, paraben and Triclocarban urinary biomarkers and circulating maternal hormones during gestation in the Puerto Rico PROTECT cohort. Environ. Heal. 2019, 18, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- de Cock, M.; Maas, Y.G.; van de Bor, M. Does perinatal exposure to endocrine disruptors induce autism spectrum and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders? Review. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 811–818. [CrossRef]
- Cowell, W.J.; Wright, R.J. Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Exposure to Chemical and Non-chemical Stressors on Neuroendocrine Development: a Review of Recent Findings and Putative Mechanisms. Curr. Environ. Heal. Rep. 2017, 4, 415–425. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kwack, S.J.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Roh, T.H.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.M. Toxicological evaluation of isopropylparaben and isobutylparaben mixture in Sprague–Dawley rats following 28 days of dermal exposure. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 544–551. [CrossRef]
- Darbre, P.D.; Harvey, P.W. Paraben esters: review of recent studies of endocrine toxicity, absorption, esterase and human exposure, and discussion of potential human health risks. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 561–578. [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.T.; Yoo, Y.-M.; Choi, K.-C.; Jeung, E.-B. Potential estrogenic effect(s) of parabens at the prepubertal stage of a postnatal female rat model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 306–316. [CrossRef]
- Pitto, L.; Gorini, F.; Bianchi, F.; Guzzolino, E. New Insights into Mechanisms of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Thyroid Diseases: The Epigenetic Way. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 7787. [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, V.; Dendele, B.; Huet, T.; Grimaldi, M.; Boulahtouf, A.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Beucher, B.; Roecklin, D.; Muller, C.; Rahmani, R.; et al. Synergistic activation of human pregnane X receptor by binary cocktails of pharmaceutical and environmental compounds. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8089. [CrossRef]
- Aker, A.M.; Watkins, D.J.; Johns, L.E.; Ferguson, K.K.; Soldin, O.P.; Del Toro, L.V.A.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Cordero, J.F.; Meeker, J.D. Phenols and parabens in relation to reproductive and thyroid hormones in pregnant women. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 30–37. [CrossRef]
- Aker, A.M.; Johns, L.; McElrath, T.F.; Cantonwine, D.E.; Mukherjee, B.; Meeker, J.D. Associations between maternal phenol and paraben urinary biomarkers and maternal hormones during pregnancy: A repeated measures study. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 341–349. [CrossRef]
- Koeppe, E.S.; Ferguson, K.K.; Colacino, J.A.; Meeker, J.D. Relationship between urinary triclosan and paraben concentrations and serum thyroid measures in NHANES 2007–2008. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445-446, 299–305. [CrossRef]
- Genuis, S.J.; Birkholz, D.; Curtis, L.; Sandau, C. Paraben Levels in an Urban Community of Western Canada. ISRN Toxicol. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J. Thyroid hormone receptors in brain development and function. Nat. Clin. Pr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 3, 249–259. [CrossRef]
- Meeker, J.D.; Yang, T.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Hauser, R. Urinary Concentrations of Parabens and Serum Hormone Levels, Semen Quality Parameters, and Sperm DNA Damage. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2011, 119, 252–257. [CrossRef]
- Moeller, L. C., & Führer, D. (2013). Thyroid hormone, thyroid hormone receptors, and cancer: a clinical perspective. Endocr Relat Cancer, 20(2), R19-R29. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. Y., Chin, Y. T., Yang, Y. C. S., Lai, H. Y., Whang-Peng, J., Liu, L. F., ... & Davis, P. J. (2011). Thyroid hormone, cancer, and apoptosis. Comprehensive Physiology, 6(3), 1221-1237. [CrossRef]
- Taha, M., Marie, A. M., & Ahmed-Farid, O. A. (2020). Combined approaches for evaluation of xenoestrogen neural toxicity and thyroid dysfunction: Screening of oxido-nitrosative markers, DNA fragmentation, and biogenic amine degradation. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 34(9), e22521. [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.S.; Sun, Z.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Assessment of Thyroid Endocrine Disruption Effects of Parabens Using In Vivo, In Vitro, and In Silico Approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 460–469. [CrossRef]
| Class | Nº CAS | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Chemical formula | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzylparaben | 94-18-8 | 228.2433 | C14H12O3 | 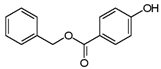 |
| Butylparaben | 94-26-8 | 194.2271 | C11H14O3 |  |
| Ethylparaben | 120-47-8 | 166.1739 | C9H10O3 | 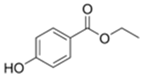 |
| Methylparaben | 99-76-3 | 152.1473 | C8H8O3 | 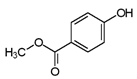 |
| Propylparaben | 94-13-3 | 180.2005 | C10H12O3 | 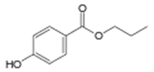 |
| Model | Exposure/Dose/Analyzes | Main results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human (men) | Serum hormone analysis of Inhibin, FSH, LH, testosterone, estradiol, TSH, T3 and T4. | BP was associated with ↑ TSH, T4, fT4 after 96h of exposure | Janjua, 2007. |
| Pregnant women (12-14 weeks) |
Urine collection at 3 different gestational moments (16-20, 20-24, 24-28 gestation weeks) and hormone analyses. |
T3 and TSH levels did not change between visits; ↑ Estradiol and progesterone with ↓fT3 and fT4 at visit 3. |
Aker, 2016 |
| Pregnant women - Boston (>15 weeks) |
Collection of urine and blood at 4 different gestational moments (9, 17, 26 and 35 weeks of gestation) | BP was associated with ↓T3, ↓T3/T4 ratio and ↑ TSH. |
Aker, 2018 |
| Pregnant women - Puerto Rico | Urine collection at 3 different gestational moments (16-20, 20-24, 24-28 weeks of gestation) | Exposure to BP has been associated with ↓SHBG | Aker, 2019 |
| Male Wistar rats | Oral exposure BP (10 mg/kg/day), BP (50mg/kg/day) and BP+TCS (50mg+10mg/kg/day) for 60 days | BP (50mg/kg/d) was associated with a ↑TSH and ↓T3 and T4. | Taha, 2020 |
| Pregnant women | Collection of maternal urine on the day of delivery and collection of umbilical cord blood for hormone measurement | BP associated with ↑boys’ body weight at birth | Li, 2020 |
| Female Wistar rats | Subcutaneous administration of BP at doses of 1, 5 and 10 mg/kg/day for 7 and 21 days. | ↑TSH in BP1 at 7 and 21 days; ↓fT4 and tT4 at all concentrations (7 and 21 days); ↑fT3, tT3 and TPO in SP1 and SP5 at 7 and 21 days. | Gogoi, 2020 |
| Zebrafish larvae | Larvae were exposed to the following concentrations: 0, 2, 5 and 10 μM of BP |
Serum T4 concentrations decreased at most concentrations tested (BP 5 and 10μM) and T3 concentrations decreased at all concentrations tested. That exposure also led to an increase in TSH gene expression at all concentrations of BP. | Liang, 2022 |
| Model | Exposure/ Dose/ Analyze | Main results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female Sprague Dawley Rats | Oral exposure to methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, isopropylparaben, butylparaben and isobutylparaben (62.5; 250 and 1000 mg/kg/day) from the 21st to the 40th postnatal day. | Propylparaben and isopropylparaben were associated with ↓T4 and estradiol and changes in thyroid weight. | Vo, 2010 |
| Male and female Sprague Dawley rats | Injections of Isopropylparaben (IPP), isobutylparaben (IBP), or mixture of IPP and IBP at 50, 100, 300, and 600 mg/kg bw dissolved in 100 ml of ethanol (99%), 5 days per week for 28 days | Mixture of isopropylparaben (IPP) and isobutylparaben (IBP) induce a decrease of TSH in exposed individuals at an exposure of 600 mg/kg/bw | Kim, 2015 |
| Pregnant women (PROTECT) | Blood collection at two different gestational moments for measurement of SHBG, TSH, fT3, fT4 and progesterone/estradiol ratio; Urine collection for detection of phenols and parabens by HPLC | ↑ Estradiol and progesterone at last visit; ↓fT3 and fT4 at last visit with no changes in TSH levels. | Wang, 2015 |
| Pregnant women - Puerto Rico | Urine and blood collection at 4 time points during pregnancy. Parabens were detected in urine by chromatography. In the blood, tT4, fT4, TSH and T3 were measured | Propylparaben was inversely associated with fT4 | Aker, 2018 |
| Pregnant women - California | Urine and blood collection in the second gestational trimester and blood collection from neonates for measurement of tT4 and TSH. | Exposure to propylparaben was confirmed by chromatography performed on urine samples; Propylparaben was inversely associated with TSH levels with no changes in tT4 levels. |
Berger, 2018 |
| Pregnant women - Puerto Rico | Urine collection at 3 different gestational moments (16-20, 20-24, 24-28 weeks of gestation) | Exposure to propylparaben was associated with ↓SHBG and T3/T4 ratio | Aker, 2019 |
| Amphibian tadpoles | Oral exposure to propylparaben (0.05; 0.5 and 5 mg/L) for 14 days. | An increase in propylparaben concentrations in water has been associated with an acute toxic effect. | Carlsoon, 2019 |
| Human (population of Wuhan, China) | Urine collection and detection of methylparaben, ethylparaben and propylparaben. | Propylparaben has been associated with an increased risk of thyroid cancer. | Wu, 2022 |
| Zebrafish larvae | Larvae were exposed to the following concentrations: 0, 5, 10 and 20 μM of Propylaraben. |
Serum T3 and T4 concentrations decreased at all concentrations tested. At 10 and 20 μM groups propylparaben increases TSH gene expression. | Liang, 2022 |
| Newborn Human | Newborn blood spots (from Guthrie cards) were collected as part of the neonatal screening program, TSH and total T4 were assessed using immunofluorescence | Propylparaben decreased T4 hormone levels has been demonstrated in newborns and women with less than 150μg/L of iodine. | Coiffier, 2023 |
| Model | Exposure/ Dose/ Analyze | Main results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Urine samples were collected from patients at Wuhan Central Hospital who had thyroid disease and required surgery. Some types of parabens were detected in these samples such as MP, EP and PP | MP, EP and PP were found in urine samples in 99.06%, 95.29% and 92% respectively. There was an increase in the concentration of all parabens in the urine of both the nodule and cancer groups. MP and EP were associated with a benign nodule, especially when in higher concentrations. All three parabens studied were associated with an increased risk of thyroid cancer, with PE having the greatest association | Wu, 2022 |
| Mother-children | Urine samples from mothers of newborns were collected on the day of delivery. The concentrations of 5 parabens were determined by chromatography. Umbilical cord blood was collected immediately after birth, in which TT3, TT4, FT3, FT4, TSH, anti-TPO and anti-TG were measured | MP, EP, PP, BP and Benzyl-paraben were detected in the urine of the evaluated mothers. EP was positively related to increased TT3 in the umbilical cord and with anti-TPO. Likewise, there was a positive correlation between PP and Anti-TPO. EP and BP correlated with increased birth weight in boys, but not in girls | Li, 2020 |
| Human-Korea | Population study with 1254 people from Korea. Urine samples from this population were collected for analysis of the presence of EDC. Blood serum samples were also collected for measurement of TT4 and FT4, TT3 and FT3, TSH, anti-TPO, anti-thyroglobulin, TGB and DIO activity | Parabens were found in most of the studied population (more than 90%). MP showed a positive association with altered levels of TT3. The increase in MP, EP and PP parabens was correlated with an increase in thyroxine-binding globulin (TGB) | Choi, 2020 |
| Pregnant women - Puerto Rico | Urine collection at 3 different gestational moments (16-20, 20-24, 24-28 weeks of gestation) | MP was associated with a decrease in SHGB. MP leads to a significant decrease in TSH and with a decrease in the T3/T4 ratio particularly at weeks 24-28 of gestation | Aker, 2019 |
| Pregnant women - California | Urine and blood collection in the second gestational trimester and blood collection from neonates for measurement of tT4 and TSH | MP was inversely associated with TSH levels with no changes in tT4 levels. | Berger, 2018 |
| Pregnant women - Puerto Rico | Urine and blood collection at 4 time points during pregnancy. Parabens were detected in urine by chromatography. In the blood, tT4, fT4, TSH and T3 were measured | MP was associated with increased T3 and negatively associated with FT4 at gestational age less than 21 weeks | Aker, 2018 |
| Pregnant women (12-14 weeks) |
Urine collection at 3 different gestational moments (16-20, 20-24, 24-28 gestation weeks) and hormone analyses. | MP was associated with a 7.70% increase in SHBG | Aker, 2016 |
| Wistar rats | Oral exposure for 90 days to BPA (50 mg/kg) or BPA+MP (250 mg/kg). | A minimal thyroid receptor antagonistic effect was only observed after treatment with BPA+MP. MP demonstrated antioxidant properties by reducing lipid peroxidation and generation of hydroxyl radicals induced by exposure to BPA. | Popa, 2014 |
| Human | Samples from a community in Canada, among the participants, samples were collected from 28 women, including 9 pregnant women, and 11 men | High urinary concentrations of parabens have been found in some patients, with the highest urinary concentrations reported at around 966.46 μg/L PM and 220.6 μg/L EP | Genuis, 2013 |
| Human | Urine samples from a representative portion of the US population to assess urinary concentrations of triclosan and parabens | Inverse associations have been found between parabens and circulating levels of thyroid hormones in adults, where women appear to be more vulnerable to exposure. | Koeppe, 2013 |
| Mother-children | Maternal blood was collected during the first prenatal care visit for TSH measurement. MP was detected in meconium samples from newborns | MP exposure leads to a decrease in gestational age, a significant change in newborn weight and a decrease in maternal TSH levels. Besides, MP in meconium was associated with about a 16% decrease in TT3 and a decrease in FT4. MP may influence maternal thyroid physiology during pregnancy and this may lead to the development of ADHD | Baker, 2020 |
| Zebrafish larvae | Larvae were exposed to the following concentrations: 0, 20, 50 and 100 μM of EP, and 0, 20, 100 e 200 μM of MP. |
Serum T3 concentrations decreased at most concentrations tested ((EP 50, 100μM and MP 20,100 e 200μM) and T4 concentrations decreased at all concentrations tested. | Liang, 2022 |
| Mother-twin pairs | MP were extracted in urine samples of pregnant women using liquid-liquid extraction. Neonatal TSH level were abstracted from medical records in China | MP exposure in early pregnancy was associated with an increased intra-twin TSH difference | Hu, 2023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





