1. Introduction
Approximately 6.7 million Americans aged 65 and older have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which is expected to rise as high as 16 million by 2050 [
1]. AD is characterized by the accumulation of Amyloid-β (Aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau (pTau) proteins in the brain. Several clinical trials have focused on reducing Aβ in the brain using γ-secretase [
2,
3,
4,
5] or BACE1 inhibitors [
6] to inhibit its production or anti-Aβ immunotherapy to clear it from the brain [
7,
8], however, to date, the effects have been marginal. This has prompted a renewed focus on pTau, whose propagation in the brain correlates more strongly with AD progression compared to Aβ [
9,
10]. It has been hypothesized that the pTau propagation in the brain occurs, in part, via the extracellular vesicles (EVs) [
11,
12]. Despite our understanding of the mechanisms of pTau propagation, therapeutic methods to halt the spread of tau have been underexplored.
EVs are secreted by eukaryotic cells and carry proteins, RNAs and lipids. EVs can be synthesized through two pathways: the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-dependent and ESCRT-independent pathways [
13,
14]. Ceramides play a crucial role in the ESCRT-independent pathway and are generated by the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin by the enzyme neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2). Studies from our lab and others have illustrated that genetic and pharmacological inhibition of nSMase2 inhibits EV biogenesis and pTau propagation [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Despite its promising translational potential, there are no suitable nSMase2 inhibitors for clinical development. Through a high-throughput screening campaign of over 350,000 compounds, our lab identified DPTIP, a highly selective and nM-potent nSMase2 inhibitor [
23]. DPTIP, however, exhibits poor oral pharmacokinetics (PK), modest brain penetration, and rapid clearance, limiting its clinical translation.
To enhance its PK properties, we conjugated DPTIP to a hydroxyl-terminated poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimer brain delivery system, creating dendrimer-DPTIP (D-DPTIP). Dendrimers are a promising new class of nanoparticles that have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases [
24,
25,
26,
27]. Our team has been studying hydroxyl-terminated PAMAM dendrimers and their conjugates for many years in both large and small animal models of neurological and ophthalmic disorders [
26,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41], and in recent Phase 2a trials for severe COVID-19 (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04458298)[
42]. Our hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimers can cross the blood-brain barrier and specifically target activated immune cells [
32,
34,
35,
40,
43,
44]. This allows them to deliver drugs directly to the site of inflammation, where they can have a maximal therapeutic effect.
Previous studies have used the well-characterized murine adeno-associated virus (AAV)-hTau seed injection model to mimic pTau propagation observed in AD patients [
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50]. In these models, tau propagation was shown to be primarily mediated by microglial EVs [
17,
51,
52,
53,
54]. Using a similar model, we recently demonstrated that D-DPTIP could significantly inhibit microglial nSMase2 activity and robustly block tau spread [
15]. To further investigate the therapeutic potential of D-DPTIP, we employed the murine PS19 transgenic model of AD. Unexpectedly, we found that D-DPTIP failed to reverse cognitive deficits, mitigate hippocampal volume loss, or alter Tau levels in the PS19 mice. Through immunofluorescence analyses, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) studies, and nSMase2 target engagement assays, we consistently observed that microglia were the primary cell type containing D-DPTIP. Furthermore, we discovered that D-DPTIP selectively suppressed the release of microglia-derived EVs into plasma in the PS19 mice, with no effect on EVs from other cell types. We conclude that D-DPTIP selectively targets and inhibits the activity of nSMase2 in microglia. Consequently, in the AAV-hTau seeded model, where tau propagation heavily relies on microglial EVs, D-DPTIP effectively inhibited the spread of tau. However, in the PS19 mouse model, where tau propagation is predominantly mediated by mechanisms independent of microglial nSMase2 activity, D-DPTIP had no effect.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Studies and D-DPTIP dosing
All experiments and animal care carried out in accordance with the Johns Hopkins University Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines. Animals were housed in a 14hr light/10hr dark cycle, until 4 weeks prior to behavioral testing. D-DPTIP was synthesized and conjugated as described previously [
15]. D-DPTIP treatment started at 4 months of age just before showing hyperactivity [
55]. D-DPTIP was administered intraperitoneally at a 10mg/kg DPTIP equivalent dose dissolved in 1X Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS). Vehicle control consisted of administering 1X PBS at 1 mL/kg. Doses were given three times per week. Body weights were measured and recorded weekly throughout the entire treatment period. Equal number of male and female mice were enrolled in each study.
2.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Imaging studies were performed on a 9.4T Bruker spectrometer (Bruker BioSpin Corp., Billerica, MA, USA) using a 30 mm diameter volume coil placed around the head of the mouse. Mice (WT N=4; PS19+Vehicle N=4; PS19+D-DPTIP N=4) were anesthetized using 2% isoflurane mixed with air and oxygen. T2 weighted images were acquired using a RARE sequence. The following parameters were used: FOV 20 mm x 20 mm, matrix size 200 x 200, 35 slices with a thickness of 0.5 mm, rare factor 8, number of acquisitions 6, TE 30 ms, TR 3425 ms. Voxel of the hippocampus, ventricle and total brain were measured using “Medical image labeller” in MATLAB (R2022b Update 4) software.
2.3. Behavioral Testing
4 weeks before behavior tests were recorded, mice were transferred to a reverse light cycle room (12hr dark/ 12hr light) to acclimate to this cycle. Behavioral studies were performed on mice of WT (N = 18) and PS19 (N = 23). Following an 18-week treatment period, all subjects underwent the Y-Maze Spatial Recognition test, the Novel Object Recognition Test (NORT), and the Rotarod test sequentially, with a 3-day interval between each test. Mice were placed in the behavioral testing room at least 30 minutes before the start of the test for habituation. All tests were conducted by the same experimenters. Between testing of mice, arenas and objects were cleansed with VIMOBA to prevent odor cues. If behavioral testing occurred on the same day as dosing, mice received their dose after finishing behavioral tests.
2.3.1. Y-Maze Spatial Recognition
Y-Maze Spatial Recognition was utilized to assess novel area preference and spatial memory function. The test used a Y-shaped maze with three arms of equal length (15 inches each) that diverged at equal angles, in tandem. A protocol reported by Sarver et al. [
56] was utilized with slight modifications, utilizing AnyMaze tracking software (Stoelting, Wood Dale, IL, USA) to record training (T1) and testing (T2). During both trials, mice were placed in arm C with their snout oriented towards the central zone. In T1, the novel arm—arm B—was blocked off and mice were allowed to explore the two familiar arms (A & C) for 10 minutes. T2 started after 3 hours of a resting period. During T2, the novel arm was opened and mice were allowed to explore the entire maze freely for 5 minutes. The length of time, in seconds (s), mice explored the novel arm was compared to the length of time (s) mice explored the familiar arms.
2.3.2. Novel Object Recognition Test (NORT)
NORT was conducted to evaluate memory function and object recognition as previously reported in identical square arenas (20x20 cm) [
57]. Tests were run on Training days (T1) and testing days (T2). During training (T1) two identical, by color and shape, objects (familiar objects) were fixed in place in upper half of the box, equal distances (5cm) from the walls. Mice were allowed to explore the arena and objects for 10 minutes. On the second day, during testing (T2) the righthand familiar object was replaced with a novel object. Mice were allowed to explore for 5 minutes. Testing was visually recorded and scored by a blinded scorer. Length of time, in seconds, spent interacting with each object was recorded for analysis. Total Time (TT) was calculated as the sum of time (s) spent interacting with novel and familiar objects during T2. Absolute Discrimination Measure (AD) was calculated as the difference in time spent interacting with the novel object from the time with the familiar object. Relative Discrimination Measure (RD) was calculated as AD divided by TT and Recognition Preference Index (RPI) was calculated as the time spent interacting with the novel object divided by TT.
2.3.3. Rotarod
Motor impairment was assessed via rotarod testing. Three trials were conducted on a 3cm diameter rod on the Rotamex 5 Rotarod (Columbus Instrument, Columbus, OH, USA) with setting of Accel: 0.006, ACC-IN: 005, S-Sp: 4.0, E-Sp: 40.0. Mice were placed on the rod for 1 minute before starting for habituation. Mice were allowed to run a maximum of 5 minutes or until they fell off, whichever occurred first. Mice were allowed to rest for 1 minute before starting the next trial. The maximum time of each three successful trials was recorded and averaged for later analysis of latency to fall.
2.4. Sample collection
At the 20 weeks of treatment, mice were euthanized by isoflurane (Primal Critical Care, Bethlehem, PA, USA) overdose and brain tissues were harvested following blood collection for immunofluorescent staining and immunoblotting analysis. For the purposes of immunostaining, mouse brains were collected after perfusion with ~15mL of ice-cold 1X PBS followed by ~15mL of ice-cold 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) (#15714-S, Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA) solution. Brains were postfixed in 4% PFA for 24 hours at 4°C. Brains were transferred to 30% sucrose for 5 days at 4°C. After dehydration, brains were embedded in Tissue-Tek Optimal Cutting Temperature compound (OCT), flash frozen, and stored at -80°C until used for cryosectioning. Hippocampal tissues of WT (male N=6; female N=6) and PS19 (vehicle-treated male N=6, female N=6; D-DPTIP-treated male N=6, female N=6) mice that were harvested fresh and stored at -80°C until use. Blood was collected via cardiac puncture and placed into lithium heparin microtubes (#41.1393.105, Sarstedt, Nümbrecht, Germany). Plasma samples were collected from the blood by centrifugation at 500 x g for 10 minutes and stored at -80°C until bioanalysis.
2.5. Immunofluorescence staining
OCT-embedded brains were cryosectioned at a 30 μm thickness. Staining was performed as the previously reported method with a slight modification [
58,
59]. Sections were permeabilized and blocked with 5% normal goat serum in 1X Tris Buffered Saline (TBS) + 0.1% Triton-X (#9002-93-1, Millopore Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 1 hour at room temperature. Sections were then incubated with a primary antibody against pTau Thr181 (1:500, #12885, Cell Signaling Technologies, Danvers, MA, USA) overnight at 4°C and washed thoroughly with 1X TBS 3 times for 5 minutes. Sections were incubated in anti-rabbit AlexaFluor 488 (1:1000, #A11034, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature before washing with the same procedure. Sections were then stained with AlexaFluor 647 conjugated anti-NeuN (1:500, #D4G40, Cell Signaling Technologies, Danvers, MA, USA) antibody overnight at 4°C before washing and treating with Hoechst (1:10000, #33342, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Sections were washed for 5 minutes 3 times with 1X TBS, coverslipped with Prolong Glass Antifade mountant (#P36930, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), and dried overnight at room temperature before storing at 4°C. Slides were imaged on an LSM 800 confocal microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
2.6. Immunoblotting
The immunoblotting technique was utilized as previously described [
60]. Hippocampus samples were lysed via RIPA buffer containing 1X PPI (#87785, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) with mechanical homogenization followed by sonication. The Bicinchoninic Acid Solution (BCA) method was used to quantify total protein concentration (#23225, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Loading samples were prepared by mixing with loading buffer (#NP0007, Invitrogen) and reducing reagent (#NP0009, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) before denaturing in a metal bath heated to 95°C for 5 minutes. Proteins were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, using NuPage 4-12% bis-tris 1.0mm midi protein gel (#WG1402BOX, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) and transferred to PVDF membranes (#IB24001, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) via iBlot Transfer System (#IB21001, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Total protein staining (#926-11016, Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE, USA) was performed before blocking non-specific binding sites and used for normalization. Membranes were incubated with Blocking solution (#12010020, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) for 5 minutes before incubating with primary antibody Tau 46 (1:500, Mouse, #SC-32274, Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA) and pTau (Thr181) (1:500, Rabbit, #D9F4G, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) overnight at 4°C. Membranes were washed with 1XTBS with tween-20 (TBST) 3 times for 5 minutes and incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG horseradish peroxidase (HRP) secondary (1:1000, #31430, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) and goat anti-rabbit 488 fluorescent secondary (1:1000, #A11008, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for 1 hour at room temperature. Utilizing the Bio-Rad ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (#12003154, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA), membranes were imaged at appropriate wavelengths depending on the secondary antibody. With horseradish peroxidase (HRP) antibody, membranes were processed with enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) substrates (#1705061, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) before imaging.
2.7. Microglial Isolation
Microglia were separated for target engagement via the Microglial Isolation beads method. Neural Tissue Dissociation Kit (P) (#130-092-628, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, mice were euthanized via isoflurane overdose and brains were harvested following perfusion with 15mL of chilled 1X PBS. One hemibrain was dissected from each brain harvested and placed in a 35mm petri dish, individually, filled with 2mL of cold Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS) without Ca²+ and Mg²+ (#14170112, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Tissue was cut into small pieces and transferred into 2mL low bind tubes before centrifugation at 300xg for 2 minutes at room temperature. The supernatant was aspirated and enzymatically digested in 1.95mL of Enzyme Mix 1 and 30μL of Mix 2 (#130-092-628, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), separated and followed by an incubation period at 37°C under slow continuous rotation, 15 and 10 minutes respectively. Tissue was dissociated twice, separated by a 10-minute incubation period in the same conditions, before cell suspension application via a 70μm cell strainer over a 50mL conical tube. 10mL of HBSS with Ca²+ and Mg²+ (#24020117, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) were applied to each cell strainer before centrifugation at 300 x g at room temperature for 10 minutes. The supernatant was aspirated. 1.9mL of BSA Stock Solution (#130-091-376, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), was added to each tube alongside 100μL of Myelin Removal Beads II (#130-096-733, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) to each tube. Tubes were mixed and incubated at 4°C for 15 minutes. Cells were washed by adding 8mL of BSA Stock Solution per tube and centrifuged at 300xg at room temperature for 10 minutes. Supernatant was aspirated and 2mL of BSA Stock Solution was added to each tube. LS Column (#130-042-401, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) was prepared in a magnetic field suitable for MACS Separator by adding 3mL of buffer through each column. Cell suspension was passed through, alongside 4mL of BSA Stock Solution, and collected in 50mL conical tubes. Tubes were centrifuged at 300xg at room temperature for 10 minutes and supernatant was aspirated. Pellets were resuspended in 960µL of a Rinsing Solution (#130-091-222, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). 40µL of CD11b Microbeads were added to each tube, mixed well, and centrifuged at 300xg at room temperature for 10 minutes. Supernatant was aspirated and pellets were resuspended in 1mL of Rinsing Solution. LS Columns were prepared as previously described and cell suspensions applied, alongside 3mL of Rinsing Solution, 1mL added at a time, and collected into a 50mL tube as microglia. LS Columns were removed from magnetic field and 5mL of Rinsing Solution was added to each. Immediately, magnetically labelled cells were flushed from column and collected in a separate 50mL conical tubes as non-microglia. All tubes were centrifuged at 300xg for 10 minutes at room temperature and supernatant was aspirated completely. Pellets were resuspended in 1mL of Rinsing Solution and transferred into 2.0mL low bind tubes. Tubes were centrifuged at 300xg at 4°C for ten minutes and pellets were stored in a -80°C freezer until use.
2.7. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
FACS was used for sorting astrocytes, microglia, and neurons and we prepared cell samples as previously published [
61,
62]. Briefly, mice hemispheres were minced in Hibernate A low fluorescence reagent and dissociated using mechanical methods. The resulting homogenates were pushed through a 70μm cell strainer and centrifuged at 300xg for 10 min before removing supernatants. Cell pellets were resuspended and subjected to Miltenyi debris removal reagent (#130-109-398, Miltenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) according to manufacturer instructions. Cell pellets were again resuspended in FACS buffer (0.5% bovine serum albumin in PBS) for cell surface marker staining. The blocking of nonspecific binding was induced in the cell suspensions via incubation for 10 min at 4 °C with anti–CD16/CD32 antibody (5ng/μl, clone 93, #101320, BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA). This was followed by staining for 30 min at 4 °C with the appropriate antibodies: BV421 rat anti-mouse CD45 (2ng/μl, clone 30-F11, #103133, BioLegend, San Diego, CA), BV605 rat anti-mouse/human CD11b (2ng/μl, #101237, Biolegend, San Diego, CA), PE rat anti-mouse ACSA-2 (1:25 dilution, clone IH3-18A3, #130-123-284, Militenyi Biotec, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), AF 488 rat anti-mouse TMEM119 (5ng/μl , clone V3RT1GOsz, #53-6119-82, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), and Alexa 488 rat anti-mouse NeuN (5ng/μl, clone A60, #MAB377X, Millipore sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). After incubation, cells were washed, and then resuspended in 300μl of FACS buffer. Gates were validated by 7-AAD Viability Staining Solution (#00-6993-50, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) to identify live and dead cells. CD45+/CD11b+/TMEM119+ microglia, ACSA2+ astrocytes, and NeuN+ neurons were acquired by a FACS Aria Flow Cytometer for further experimental use.
2.8. nSMase2 Activity Assay
nSMase2 activities in microglia and non-microglia cells were determined using a modification of previously published methods [
63,
64]. Briefly, cell pellets were re-suspended in ice-cold Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.5) containing 250 mM sucrose, 10 mM EGTA (Research Products International, Prospect, IL), 100 µM sodium molybdate and protease inhibitors and then sonicated using Kontes’ Micro Ultrasonic Cell Disrupter (three pulses of 15s duration on ice with 15s between pulses). The resulting lysates were collected for nSMase2 activity measurements and total protein analysis. nSMase2 activity measurements were initiated upon the addition of sphingomyelin (SM) and coupling enzymes in the Amplex Red system (25µl), and SM hydrolysis was carried out in total reaction volumes of 50 µl in 384-well microplates for 3h at 37°C. At the end of the reaction period, the relative fluorescence units were measured at Ex 530nm, Em 590nm. Finally, total protein measurements were carried out per the manufacturer’s instructions using BioRad’s Detergent Compatible Protein Assay kit and data presented as RFU/mg/h.
2.9. EVs Isolation
EVs were isolated from pooled plasma samples of the same experimental group by size-exclusion chromatography using commercial columns (qEVsingle Gen 2, 70 nm, Izon, Christchurch, New Zealand), following the manufacturer’s instruction. Briefly, 100 μl of sample were loaded in the column using freshly filtered PBS as eluent. As already performed in our recent work [
65], fractions containing EVs (from 6 to 11) were collected and stored at -20 °C with protease inhibitors. The total protein content of EV samples was measured by BCA assay.
2.10. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
Isolated EVs were characterized for their size distribution and concentration by NTA, using NanoSight NS300 Instrument (Malvern Panalytical Ltd, Malvern, UK) equipped with flow-cell top-plate and a syringe pump to enable analysis in constant flow. The NTA analysis was performed on EV samples diluted in filtered PBS; recordings of the movements of particles were collected for 60 s, three times for each sample. Data were analyzed using the NTA software v.3.4.
2.11. Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRi)Analysis
The SPRi array was prepared coating the gold surface of a SPRi biochip (Horiba, Scientific SAS, Palaiseau, France) with a self-assembled monolayer of a mixture of thiolated PEG with carboxylic or alcoholic groups that were then activated with EDC/NHS chemistry, following our previously described protocol[
66]. The spotting procedure for the ligand immobilization was performed using the iFOUR Dispensing System (M24You). This instrument allows to dispense pico/nanoliter drops of ligands onto the surface thanks to a Piezo Driven Micro-Dispenser (PDMD) equipped with a 130 mm long borosilicate glass capillary and a cylindrical piezo ceramic actuator bonded to it. The ligands used for the SPRi analysis were: anti-CD9 (#14-0098, eBioscience), anti-Glast (EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody, #NB100-1869SS, Novus Biologicals LLC, Centennial, CO, USA), anti-PLP1 (#HBM-PLP-50, HansaBioMed, Tallinn, Estonia), IB4 lectin (from Bandeiraea simplicifolia; L3019, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), anti-CD171/L1CAM (#14-1719-82, eBioscience), anti-CD11b (#553311, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) and anti-CD106 (#MA5-16429, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for EVs detection, and anti-IgG (#407402, BioLegend, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) as a negative control. Four spots per ligand were obtained on the surface of the SPRi biochip. After a night in a humid chamber, the chip was blocked in a solution of ethanolamine (1M, pH 9) for 30 min, washed with water and stored at +4°C until use. The biochip was then loaded in the XelPleX instrument (Horiba Scientific SAS) for the SPRi measurements and calibration was performed by injecting 200 µL of sucrose (3 mg/mL) at a flow rate of 50 µL/min. Experiments were performed using PBS as running buffer. 370 µl of EVs (pool of EVs samples from the same experimental group) diluted in PBS were injected into the SPRi flow chamber with a flow rate of 25 µL/min. SPRi values at the end of the association phase were collected for each ligand family. These values are related to the relative amount of specific EV families present in the analyzed sample. SPRi data were analyzed using EzSuite (Horiba) and Origin (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA) software. For each experiment, the SPRi signal obtained on anti-IgG spots was used as negative control and subtracted to the signals obtained on each ligand spotted on the same chip. Then, signals related to the EV injection were normalized to the mean intensity of Anti-CD9 spots, as a marker of generic EVs, not specific for a particular cell of origin. This allowed us to compare data from different experiments and multiple samples.
3. Results
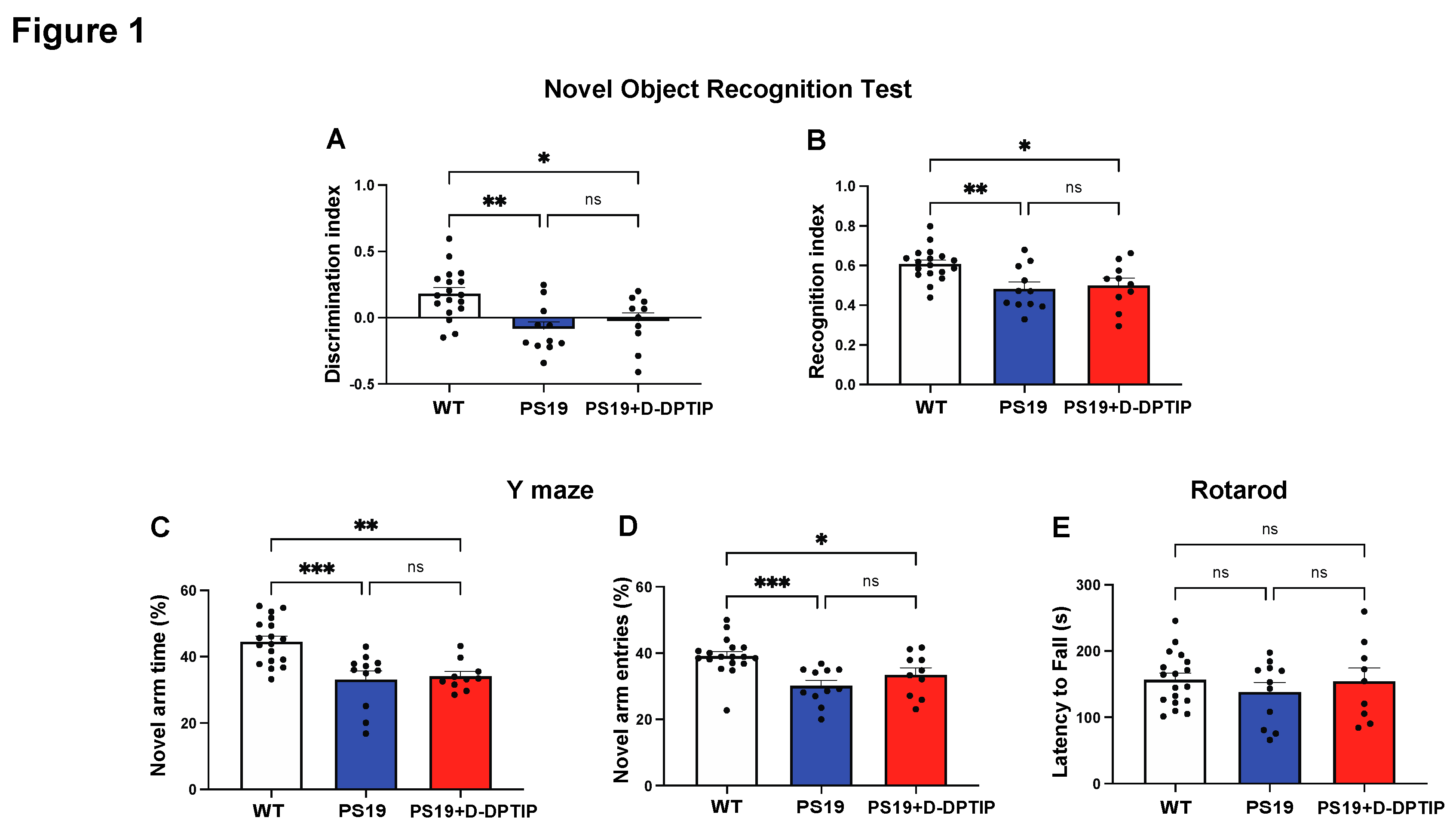
3.1. D-DPTIP had no effect on recognition or spatial memory deficits in PS19 mice
Ten-month-old wild-type (WT) mice, PS19 mice treated with vehicle for 5 months, and PS19 mice treated with D-DPTIP for 5 months were used for behavioral tests. NORT, utilized to study recognition memory, showed a significant decrease in the discrimination and recognition indices in PS19 mice compared to age-matched WT mice (
Figure 1A,B). Treatment of the PS19 mice with D-DPTIP had no effect on NORT. The Y-maze, utilized to study spatial memory deficits, showed a deficit in PS19 mice which was unaffected by D-DPTIP treatment (
Figure 1C,D). Rotarod was used as a control to ensure that the differences in NORT and Y-maze were not influenced by motor differences between the groups. No significant differences were observed between the groups (
Figure 1E), indicating that motor function did not affect the behavior tests.
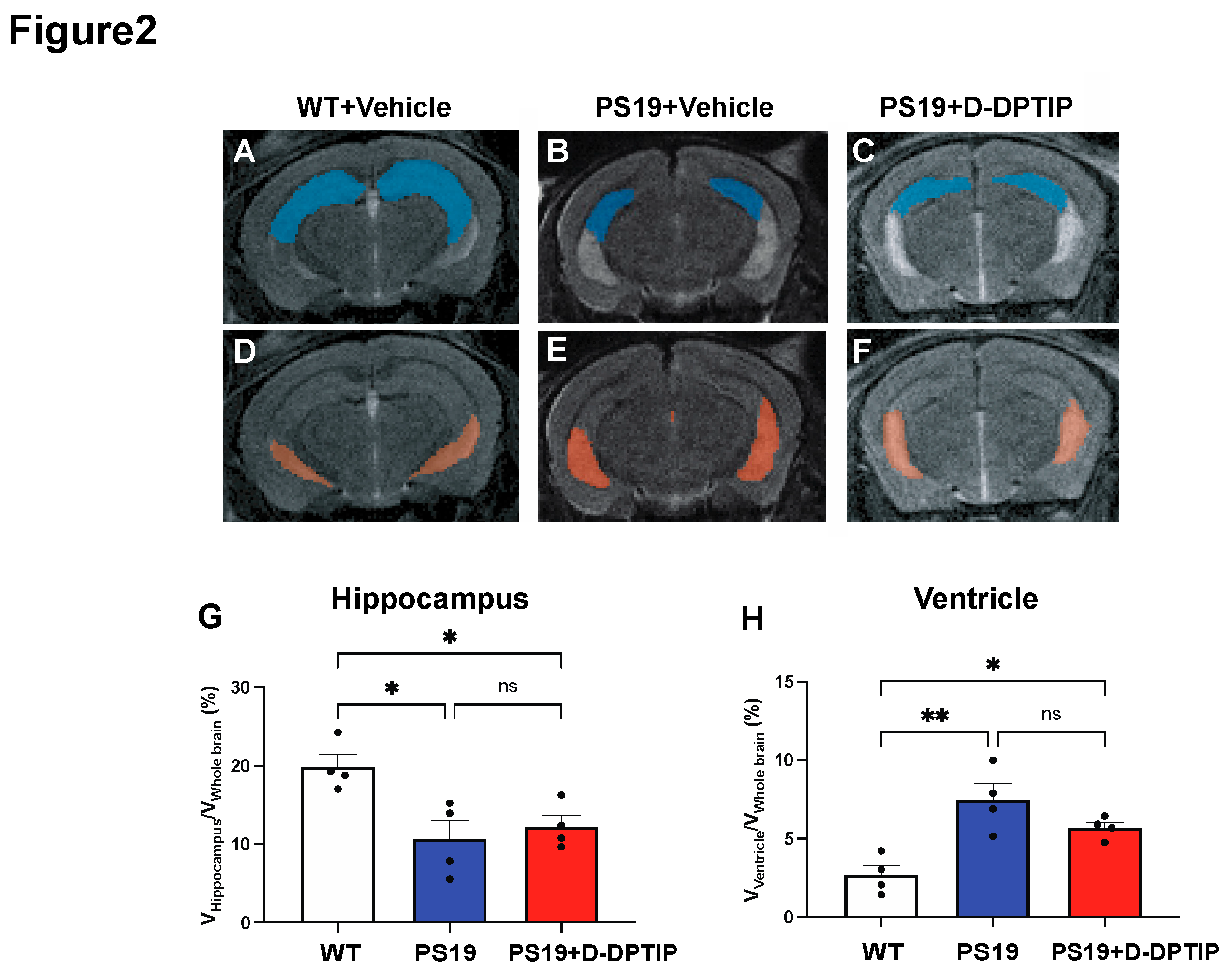
3.2. D-DPTIP had no effect on hippocampal atrophy or ventricular enlargement in PS19 mice
We employed T2-weighted (T2w) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to quantify hippocampal volume and ventricular size in 10-month-old PS19 mice and age-matched WT controls. MATLAB was utilized to calculate the number of voxels corresponding to the hippocampus, ventricle, and entire brain. To account for individual variations in brain size, the sizes of the hippocampus and ventricles were normalized by the whole brain volume, expressed as percentages as has been previously reported [
67]. A significant reduction in hippocampal volume (
Figure 2A,B,G) and an increase in ventricular size (
Figure 2D,E,H) was observed in the PS19 mice compared to the age-matched WT mice. Treatment with D-DPTIP had no effect on either hippocampal volume (
Figure 2B,C,G) or ventricular size (
Figure 2E,F,H).
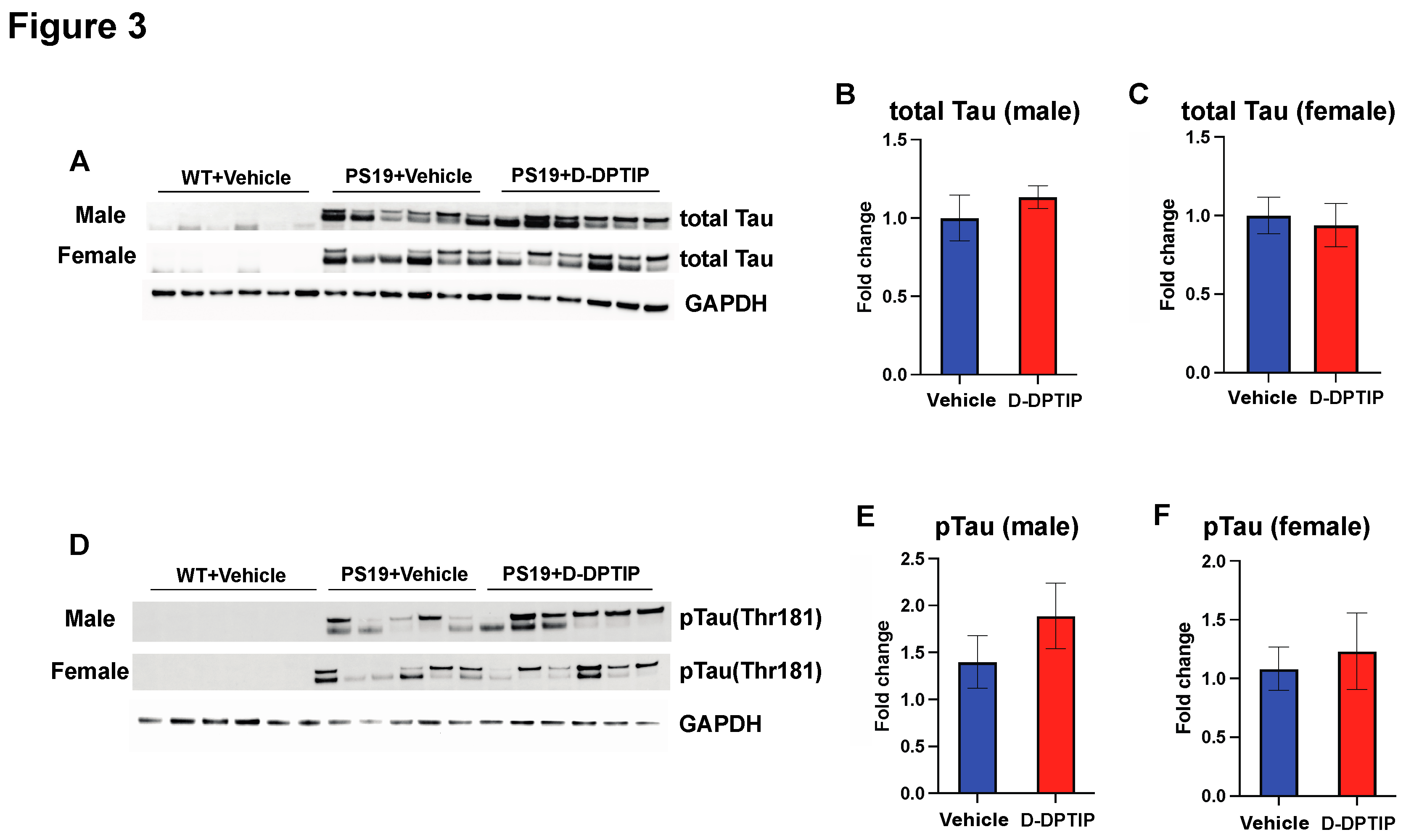
3.3. D-DPTIP had no effect on hippocampal Tau or pTau levels in PS19 mice
Using immunoblotting to quantify total Tau and pTau (Thr181) within the hippocampus, we found that both male and female PS19 mice had large observable bands of total Tau and pTau compared to WT mice who had no discernible bands. D-DPTIP treatment did not affect total Tau (
Figure 3 A, B, C) or pTau levels (
Figure 3 D, E, F) in the PS19 mice.
3.4. D-DPTIP colocalizes with microglia and selectively inhibits microglial nSMase2 activity in PS19 mice
To elucidate the cellular localization of D-DPTIP within the brain, we employed immunofluorescent staining with Cy5-labelled dendrimer using techniques we have previously reported [
15]. In brief, 24 hours after administration of Cy5-labeled D-DPTIP to PS19 mice, mice were sacrificed, their brains were removed, fixed, sectioned and stained with antibodies against Iba1 (microglia), GFAP (astrocytes), and NeuN (neurons). We found that Cy5 fluorescent signal predominantly co-localized with Iba1-positive microglia, with minimal co-localization with GFAP-positive astrocytes or NeuN-positive neurons (
Figure 4 A,B). To confirm the immunofluorescent findings, we also employed fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) using techniques we have previously described [
61,
62]. 24 hours following the administration of Cy5-labeled D-DPTIP or PBS (control) to PS19 mice, we quantified the presence of labelled cells in brain tissue. We found that 0.30% of all brain cells from mice receiving Cy5-labeled D-DPTIP exhibited detectable Cy5 signals (
Figure 4C). In contrast, PS19 and WT mice that received a PBS injection displayed negligible Cy5 signal detection, indicating the success of our gating strategy (
Figure 4D,E). We next compared the distribution of Cy5-positive cells among specific brain cell types, specifically microglia (TMEM119+), astrocytes (ACSA2+), and neurons (NeuN+). Among these cell populations, microglia showed an approximately 17.5-fold higher proportion in Cy5+ cells compared to astrocytes, and a 10.6-fold higher proportion compared to neurons (
Figure 4F,G). These findings support microglia as the primary cell type responsible for the uptake of D-DPTIP. Lastly, we conducted
ex vivo nSMase2 enzymatic activity assays on microglia-enriched CD11b+ cells (microglial-enriched) and CD11b- (non-microglial) cells isolated from the brains of PS19 mice treated with either D-DPTIP or vehicle using methods previously described [
63,
64]. We found that D-DPTIP only inhibited nSMase2 enzymatic activity in the microglial-enriched CD11b+ cells (
Figure 4H, I), further highlighting the cellular specificity of D-DPTIP localization in the brain.
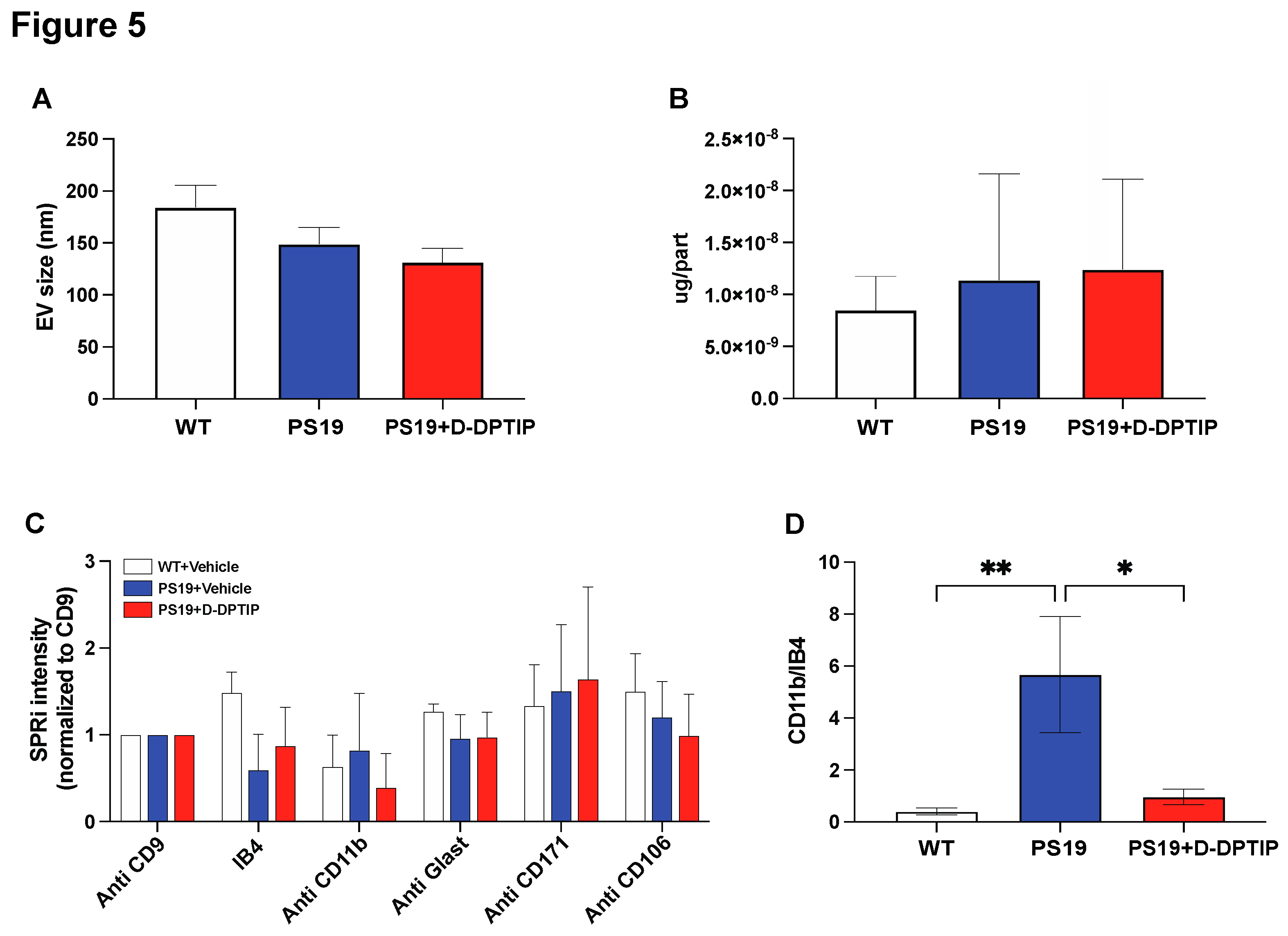
3.5. D-DPTIP selectively reduced the number of microglia-derived EVs in the plasma of PS19 mice, with no effect on EVs from other brain cell types.
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) was utilized to assess the impact of D-DPTIP on the size distribution of brain-derived EVs isolated from the plasma of PS19 mice using methods we have previously reported [
68]. D-DPTIP had no effect on EV size or EV protein concentration when compared to WT mice and vehicle-treated PS19 mice (
Figure 5A, B). To investigate the effects of D-DPTIP on specific brain-derived EVs in plasma, we leveraged Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRi) technology as we have previously reported [
16] which allows for the capturing and profiling EV populations based on the expression of cell-specific antigens. We prepared an SPRi array by immobilizing antibodies against IB4, CD11b, Glast, PLP1, CD171, and CD106, which specifically capture EVs derived from microglia, activated microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, neurons, and endothelial cells, respectively. PLP1 data is not shown because the signal detected was not above background. The SPRi signal intensity analysis revealed no significant changes in EV populations between PS19 and WT mice or between D-DPTIP-treated PS19 mice and vehicle-treated PS19 mice (
Figure 5C). However, when the intensity of activated microglia (CD11b+) was normalized to the total microglia signal (IB4+), we found that PS19 mice displayed an increase in the CD11b+/IB4+ ratio, indicating elevated levels of activated microglia. Notably, D-DPTIP treatment completely normalized this ratio (
Figure 5D), again supporting D-DPTIP’s ability to preferentially target activated microglia [
15].
4. Discussion
In this study, we aimed to investigate the therapeutic potential of D-DPTIP, a potent nSMase2 inhibitor conjugated to a hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimer nanoparticle delivery system, in the PS19 transgenic model of AD. Our previous research utilizing a murine AAV-hTau brain injection and propagation model demonstrated a significant inhibitory effect of D-DPTIP on hTau propagation [
15]. Herein we aimed to extend these findings to evaluate the therapeutic utility of D-DPTIP in the transgenic PS19 mouse model of AD. We evaluated the effect of chronic D-DPTIP administration using multiple cognition and MRI-based endpoints including discrimination and recognition deficits, spatial memory deficits, hippocampal atrophy, and enlarged brain ventricles. However, despite acceptable tolerance and proven brain penetration and target engagement of D-DPTIP, we found that it failed to alter any of these pathological features. Additionally, there were no significant changes in total Tau or pTau (Thr181) levels following D-DPTIP treatment. Using three independent techniques including immunofluorescent staining, FACS and nSMase2 activity assay, we showed that D-DPTIP specifically targeted activated microglial cells, with little localization in oligodendrocytes, astrocytes or neurons. Moreover, D-DPTIP selectively inhibited microglial nSMase2 activity and reversed the increased number of activated microglia-derived EVs in PS19 mice plasma with no effect on EVs derived from any other brain cell type.
The differential response of D-DPTIP between the AAV-hTau model and the PS19 mice can be attributed to the distinct mechanisms of tau spread in these two models. Recent findings from our lab and others reveal a crucial contribution of microglia to the spread of tau in various AAV-hTau injection and propagation models [
17,
69,
70,
71]. Notably, when microglia are depleted using the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) inhibitor PLX5622 in an AAV propagation model, Tau propagation is significantly halted. More recently, amyloid plaque-associated microglia were shown to exhibit enhanced phagocytosis of tau-containing neurites while hyper-secreting EVs containing pTau, suggests a link between amyloid plaque deposition, microglia activation, and exacerbation of tau propagation [
17,
69]. These data in AAV hTau seeding models suggest essential interactions between microglia and tau propagation.
Given the prominent role of microglial EVs in the propagation of Tau in AAV models, in our prior studies, we utilized the hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimer delivery system to target our nSMase2 inhibitors to microglia specifically. We demonstrated that D-DPTIP robustly blocked EV-mediated tau propagation, effectively inhibiting the spread of pTau to the contralateral hippocampus in an AAV hTau seeding model [
15].
Our research team has extensively investigated the application of hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimers in over a dozen nervous system disorders involving six species, including primates [
26,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]. We have shown that these hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimers selectively deliver drugs to activated immune cells in the brain [
35,
43]. Notably, one of our initial dendrimer conjugates has advanced to clinical development, demonstrating significant therapeutic benefits in preclinical models[
29,
30,
36], as well as in a recent Phase 2 clinical trial [
42].
Utilizing this microglial nSMase2 inhibitor targeting system in the PS19 transgenic mice, however, showed limited effects. Within the PS19 mouse model there is strong evidence that pathological tau transmits along synaptically connected circuits between neurons. Pathological tau species, such as pTau, undergo misfolding within neurons, forming intracellular tau aggregates which are secreted at the synaptic terminus, in part, through EVs [
12,
72,
73,
74,
75,
76]. Once released, pathological tau aggregates are internalized by neighboring neurons, initiating a cascade of events that contribute to the propagation of tau pathology. Unlike the AAV models described above, when preformed tau fibrils are injected into the locus coeruleus (LC) of the PS19 mouse, tau pathology propagated to brain regions that are anatomically interconnected with LC neurons through either efferent or afferent projections [
77], suggesting that the PS19 mouse model exhibits tau propagation primarily through neuronal pathways. Interestingly, the broad inhibition of nSMase2 led to the elimination of tau propagation in PS19 mice [
78]. Therefore, addressing this in neurons, rather than just microglia, may be a key mechanism to produce therapeutic improvements in this model.
Importantly, microglia actively contribute to tau propagation both in AD patients and PS19 mice model [
79,
80,
81,
82]. However, the role of microglial nSMase2 is uninvestigated. A recent in vivo study using PET imaging demonstrated the relationship between microglia and tau in 130 individuals spanning the aging and AD spectrum, revealing parallel spatial propagation of microglial activation and tau accumulation along predicted brain circuits [
79]. Additionally, investigation of the PS19 mouse model highlighted the significant role of microglial NF-κB signaling in tau spreading and toxicity. Activating NF-κB by tau enhanced microglial-mediated tau pathology, while inhibiting NF-κB activation reduced tau seeding, improved microglial autophagy, and mitigated cognitive deficits associated with tauopathy [
81]. Our current findings suggest that while microglia are critical in Tau pathology, the specific role of microglial nSMase2-mediated EV biogenesis in PS19 mice may not play a central role.
In conclusion, although D-DPTIP exhibits preferential targeting of microglia nSMase2, its limited impact on Tau-associated pathologies in PS19 mice highlights the importance of developing strategies that directly address the cell-specific mechanisms underlying tau spread. A comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms is essential for developing effective targeted interventions. Further research in this area is warranted to advance translational considerations and improve therapeutic approaches for attenuating tau-mediated neurodegeneration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H., C.T., X.Z., R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; methodology, M.H., C.T., X.Z., R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; validation, M.H., C.T., X.Z., K.D.J.H., S.P., F.R., A.G., A.G.T.; formal analysis, M.H., X.Z., K.D.J.H., S.P., F.R., A.G., and A.G.T.; investigation, M.H., C.T., X.Z., K.D.J.H., S.P., A.G.T., and L.T.; resources, X.Z., R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; data curation, M.H., C.T., X.Z., K.D.J.H., S.P., F.R., A.G., A.G.T., L.T. and W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H., K.D.J.H., A.G.T., and S.P.; writing—review and editing, M.H., C.T., X.Z., K.D.J.H., S.P., F.R., A.G., A.G.T., L.T., W.L., R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; visualization, M.H. and X.Z.; supervision, R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; project administration, M.H., R.M.K., M.B., R.R. and B.S.S.; funding acquisition, R.M.K., R.R. and B.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Institute of Health grants R01 AG063831, R01 AG059799, P30MH075673, K01AT010984, a grant from the Tau Consortium and Alzheimer’s Association (T-PEP-18-579974C), and a Maryland Innovation Initiative award (135726) from Maryland Technology Development Corporation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Johns Hopkins University Animal Care and Use Committee of Johns Hopkins University (protocol code MO20M71; approved on 18 March 2020).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the manuscript and supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
C.T., B.S.S., A.G.T., R.R., and K.M.R. are listed as inventors in patent applications filed by Johns Hopkins Technology Ventures covering novel compositions and utilities of nSMase2 inhibitors, including DPTIP and D-DPTIP. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. Other authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
References
- Alzheimer’s association. Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. 2023.
- Bateman, R.J., et al., A gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system. Ann Neurol, 2009. 66(1): p. 48-54. [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, A.S., et al., Phase 2 Safety Trial Targeting Amyloid β Production With a γ-Secretase Inhibitor in Alzheimer Disease. Archives of Neurology, 2008. 65(8): p. 1031-1038. [CrossRef]
- Henley, D.B., et al., Development of semagacestat (LY450139), a functional γ-secretase inhibitor, for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 2009. 10(10): p. 1657-1664. [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.S., γ-Secretase as a target for Alzheimer's disease. Adv Pharmacol, 2012. 64: p. 127-53.
- Bazzari, F.H. and A.H. Bazzari, BACE1 Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease: The Past, Present and Any Future? Molecules, 2022. 27(24). [CrossRef]
- Panza, F., et al., Amyloid-based immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease in the time of prevention trials: the way forward. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology, 2014. 10(3): p. 405-419. [CrossRef]
- Schenk, D., M. Hagen, and P. Seubert, Current progress in beta-amyloid immunotherapy. Current Opinion in Immunology, 2004. 16(5): p. 599-606. [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, N., M. Sjögren, and K. Blennow, CSF markers for Alzheimer's disease: Total tau, phospho-tau and Aβ42. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 2003. 4(4): p. 147-155. [CrossRef]
- Karikari, T.K., et al., Blood phospho-tau in Alzheimer disease: analysis, interpretation, and clinical utility. Nature Reviews Neurology, 2022. 18(7): p. 400-418. [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.S., V.M.Y. Lee, and J.Q. Trojanowski, Mechanisms of Cell-to-Cell Transmission of Pathological Tau: A Review. JAMA Neurol, 2019. 76(1): p. 101-108. [CrossRef]
- Simón, D., et al., Tau overexpression results in its secretion via membrane vesicles. Neurodegener Dis, 2012. 10(1-4): p. 73-5. [CrossRef]
- Juan, T. and M. Fürthauer, Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2018. 74: p. 66-77. [CrossRef]
- Urbanelli, L., et al., The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infection and Transmission. Vaccines, 2019. 7(3): p. 102. [CrossRef]
- Tallon, C., et al., Dendrimer-Conjugated nSMase2 Inhibitor Reduces Tau Propagation in Mice. Pharmaceutics, 2022. 14(10). 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102066.
- Tallon, C., et al., Inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase 2 reduces extracellular vesicle release from neurons, oligodendrocytes, and activated microglial cells following acute brain injury. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2021. 194: p. 114796. 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114796.
- Asai, H., et al., Depletion of microglia and inhibition of exosome synthesis halt tau propagation. Nat Neurosci, 2015. 18(11): p. 1584-93. 10.1038/nn.4132.
- Ruan, Z., et al., Alzheimer's disease brain-derived extracellular vesicles spread tau pathology in interneurons. Brain, 2021. 144(1): p. 288-309. 10.1093/brain/awaa376.
- DeLeo, A.M. and T. Ikezu, Extracellular Vesicle Biology in Alzheimer's Disease and Related Tauopathy. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2018. 13(3): p. 292-308. 10.1007/s11481-017-9768-z.
- Ruan, Z., et al., Elucidating the pathogenic mechanisms of AD brain-derived tau-containing extracellular vesicles: Highly transmissible and preferential propagation to GABAergic neurons. bioRxiv, 2020: p. 2020.03.15.992719. 10.1002/alz.037316.
- Pampuscenko, K., et al., Extracellular tau induces microglial phagocytosis of living neurons in cell cultures. J Neurochem, 2020. 154(3): p. 316-329. [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.J., et al., Sowing the Seeds of Discovery: Tau-Propagation Models of Alzheimer's Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2020. 11(21): p. 3499-3509. 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00531.
- Rojas, C., et al., DPTIP, a newly identified potent brain penetrant neutral sphingomyelinase 2 inhibitor, regulates astrocyte-peripheral immune communication following brain inflammation. Scientific Reports, 2018. 8(1): p. 17715. 10.1038/s41598-018-36144-2.
- Shaunak, S., et al., Polyvalent dendrimer glucosamine conjugates prevent scar tissue formation. Nat Biotechnol, 2004. 22(8): p. 977-84. 10.3410/f.1000147.300817.
- Hayder, M., et al., A phosphorus-based dendrimer targets inflammation and osteoclastogenesis in experimental arthritis. Sci Transl Med, 2011. 3(81): p. 81ra35. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002212.
- Menjoge, A.R., R.M. Kannan, and D.A. Tomalia, Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov Today, 2010. 15(5-6): p. 171-85. 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.009.
- Lee, C.C., et al., Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat Biotechnol, 2005. 23(12): p. 1517-26. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., et al., Dendrimers Target the Ischemic Lesion in Rodent and Primate Models of Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. PLoS One, 2016. 11(4): p. e0154437. [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S., et al., Dendrimer-based postnatal therapy for neuroinflammation and cerebral palsy in a rabbit model. Sci Transl Med, 2012. 4(130): p. 130ra46. [CrossRef]
- Niño, D.F., et al., Cognitive impairments induced by necrotizing enterocolitis can be prevented by inhibiting microglial activation in mouse brain. Sci Transl Med, 2018. 10(471). [CrossRef]
- Kambhampati, S.P., et al., Systemic dendrimer nanotherapies for targeted suppression of choroidal inflammation and neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. J Control Release, 2021. 335: p. 527-540. [CrossRef]
- Kambhampati, S.P., et al., Systemic and Intravitreal Delivery of Dendrimers to Activated Microglia/Macrophage in Ischemia/Reperfusion Mouse Retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2015. 56(8): p. 4413-24. [CrossRef]
- Kambhampati, S.P. and R.M. Kannan, Dendrimer nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther, 2013. 29(2): p. 151-65. [CrossRef]
- Nance, E., et al., Dendrimer-mediated delivery of N-acetyl cysteine to microglia in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. J Neuroinflammation, 2017. 14(1): p. 252. [CrossRef]
- Nance, E., et al., Nanoscale effects in dendrimer-mediated targeting of neuroinflammation. Biomaterials, 2016. 101: p. 96-107. [CrossRef]
- Turk, B.R., et al., Dendrimer-N-acetyl-L-cysteine modulates monophagocytic response in adrenoleukodystrophy. Ann Neurol, 2018. 84(3): p. 452-462. [CrossRef]
- Inapagolla, R., et al., In vivo efficacy of dendrimer-methylprednisolone conjugate formulation for the treatment of lung inflammation. Int J Pharm, 2010. 399(1-2): p. 140-7. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F., et al., Microglial migration and interactions with dendrimer nanoparticles are altered in the presence of neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation, 2016. 13(1): p. 65. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K., et al., Dendrimer brain uptake and targeted therapy for brain injury in a large animal model of hypothermic circulatory arrest. ACS Nano, 2014. 8(3): p. 2134-47. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A., et al., Effect of mannose targeting of hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimers on cellular and organ biodistribution in a neonatal brain injury model. J Control Release, 2018. 283: p. 175-189. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R., et al., Activated Microglia Targeting Dendrimer-Minocycline Conjugate as Therapeutics for Neuroinflammation. Bioconjug Chem, 2017. 28(11): p. 2874-2886. [CrossRef]
- Gusdon, A.M., et al., Dendrimer nanotherapy for severe COVID-19 attenuates inflammation and neurological injury markers and improves outcomes in a phase2a clinical trial. Sci Transl Med, 2022. 14(654): p. eabo2652. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F., et al., Surface functionality affects the biodistribution and microglia-targeting of intra-amniotically delivered dendrimers. J Control Release, 2016. 237: p. 61-70. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R., et al., Activated Microglia Targeting Dendrimer–Minocycline Conjugate as Therapeutics for Neuroinflammation. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2017. 28(11): p. 2874-2886. [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, T., et al., AAV-tau mediates pyramidal neurodegeneration by cell-cycle re-entry without neurofibrillary tangle formation in wild-type mice. PLoS One, 2009. 4(10): p. e7280. [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, S., et al., Experimental evidence for the age dependence of tau protein spread in the brain. Sci Adv, 2019. 5(6): p. eaaw6404. [CrossRef]
- You, Y., et al., Cre-inducible Adeno Associated Virus-mediated Expression of P301L Mutant Tau Causes Motor Deficits and Neuronal Degeneration in the Substantia Nigra. Neuroscience, 2019. 422: p. 65-74. [CrossRef]
- Siman, R., et al., A rapid gene delivery-based mouse model for early-stage Alzheimer disease-type tauopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2013. 72(11): p. 1062-71. [CrossRef]
- Luengo, E., et al., Pharmacological doses of melatonin impede cognitive decline in tau-related Alzheimer models, once tauopathy is initiated, by restoring the autophagic flux. J Pineal Res, 2019. 67(1): p. e12578. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., et al., Expression of P301L-hTau in mouse MEC induces hippocampus-dependent memory deficit. Sci Rep, 2017. 7(1): p. 3914. [CrossRef]
- Clayton, K.A., et al., Amyloid plaque deposition accelerates tau propagation via activation of microglia in a humanized APP mouse model. bioRxiv, 2020: p. 2020.09.22.308015. [CrossRef]
- Clayton, K., et al., Plaque associated microglia hyper-secrete extracellular vesicles and accelerate tau propagation in a humanized APP mouse model. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 2021. 16(1): p. 18. [CrossRef]
- Španić, E., et al., Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease Tau Propagation. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2019. 11. [CrossRef]
- Duwat, C., et al., Development of an AAV-based model of tauopathy targeting retinal ganglion cells and the mouse visual pathway to study the role of microglia in Tau pathology. Neurobiology of Disease, 2023. 181: p. 106116. [CrossRef]
- Dumont, M., et al., Bezafibrate administration improves behavioral deficits and tau pathology in P301S mice. Hum Mol Genet, 2012. 21(23): p. 5091-105. [CrossRef]
- Sarver, D.C., et al., CTRP4 ablation impairs associative learning and memory. Faseb j, 2021. 35(11): p. e21910. [CrossRef]
- Lueptow, L.M., Novel Object Recognition Test for the Investigation of Learning and Memory in Mice. J Vis Exp, 2017(126). [CrossRef]
- Su, Y., et al., Deletion of Neuronal CuZnSOD Accelerates Age-Associated Muscle Mitochondria and Calcium Handling Dysfunction That Is Independent of Denervation and Precedes Sarcopenia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021. 22(19): p. 10735. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S., et al., Molecular Signatures of Neuroinflammation Induced by alphaSynuclein Aggregates in Microglial Cells. Front Immunol, 2020. 11: p. 33. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M., et al., Network analysis of the progranulin-deficient mouse brain proteome reveals pathogenic mechanisms shared in human frontotemporal dementia caused by GRN mutations. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2020. 8(1): p. 163. [CrossRef]
- Nedelcovych, M.T., et al., Glutamine Antagonist JHU083 Normalizes Aberrant Glutamate Production and Cognitive Deficits in the EcoHIV Murine Model of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2019. 14(3): p. 391-400. [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.J., et al., Glutamine antagonist JHU083 improves psychosocial behavior and sleep deficits in EcoHIV-infected mice. Brain Behav Immun Health, 2022. 23: p. 100478. [CrossRef]
- Peyron, L., M. Henry, and R. Sohier, [Biological diagnosis of influenza B. Observations made during a recent influenza epidemic]. Ann Biol Clin (Paris), 1966. 24(10): p. 1135-45.
- Rojas, C., et al., DPTIP, a newly identified potent brain penetrant neutral sphingomyelinase 2 inhibitor, regulates astrocyte-peripheral immune communication following brain inflammation. Sci Rep, 2018. 8(1): p. 17715. [CrossRef]
- Tallon, C., et al., Inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase 2 reduces extracellular vesicle release from neurons, oligodendrocytes, and activated microglial cells following acute brain injury. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021. 194: p. 114796. [CrossRef]
- Picciolini, S., et al., Detection and Characterization of Different Brain-Derived Subpopulations of Plasma Exosomes by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging. Anal Chem, 2018. 90(15): p. 8873-8880. [CrossRef]
- Yoshiyama, Y., et al., Synapse Loss and Microglial Activation Precede Tangles in a P301S Tauopathy Mouse Model. Neuron, 2007. 53(3): p. 337-351. [CrossRef]
- Picciolini, S., et al., An SPRi-based biosensor pilot study: Analysis of multiple circulating extracellular vesicles and hippocampal volume in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2021. 192: p. 113649. [CrossRef]
- Clayton, K., et al., Plaque associated microglia hyper-secrete extracellular vesicles and accelerate tau propagation in a humanized APP mouse model. Mol Neurodegener, 2021. 16(1): p. 18. [CrossRef]
- Duwat, C., et al., Development of an AAV-based model of tauopathy targeting retinal ganglion cells and the mouse visual pathway to study the role of microglia in Tau pathology. Neurobiol Dis, 2023. 181: p. 106116. [CrossRef]
- Spanic, E., et al., Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer's Disease Tau Propagation. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019. 11: p. 271. [CrossRef]
- Pooler, A.M., et al., Physiological release of endogenous tau is stimulated by neuronal activity. EMBO Rep, 2013. 14(4): p. 389-94. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.J., et al., Regional profiles of the candidate tau PET ligand 18F-AV-1451 recapitulate key features of Braak histopathological stages. Brain, 2016. 139(Pt 5): p. 1539-50. [CrossRef]
- Calafate, S., et al., Synaptic Contacts Enhance Cell-to-Cell Tau Pathology Propagation. Cell Rep, 2015. 11(8): p. 1176-83. [CrossRef]
- Demaegd, K., J. Schymkowitz, and F. Rousseau, Transcellular Spreading of Tau in Tauopathies. Chembiochem, 2018. 19(23): p. 2424-2432. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., et al., The release and trans-synaptic transmission of Tau via exosomes. Mol Neurodegener, 2017. 12(1): p. 5. [CrossRef]
- Iba, M., et al., Tau pathology spread in PS19 tau transgenic mice following locus coeruleus (LC) injections of synthetic tau fibrils is determined by the LC's afferent and efferent connections. Acta Neuropathol, 2015. 130(3): p. 349-62. [CrossRef]
- Tallon, C., et al., Inhibiting tau-induced elevated nSMase2 activity and ceramides is therapeutic in murine Alzheimer's disease. Res Sq, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, T.A., et al., Microglial activation and tau propagate jointly across Braak stages. Nat Med, 2021. 27(9): p. 1592-1599. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. and C. Xie, Microglia activation linking amyloid-beta drive tau spatial propagation in Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci, 2022. 16: p. 951128. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., Microglial NF-kappaB drives tau spreading and toxicity in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nat Commun, 2022. 13(1): p. 1969. [CrossRef]
- Stancu, I.C., et al., The NLRP3 inflammasome modulates tau pathology and neurodegeneration in a tauopathy model. Glia, 2022. 70(6): p. 1117-1132. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
PS19 mice exhibit deficits in recognition and memory that are not improved by D-DPTIP. WT mice with vehicle treatment (N=18), PS19 with vehicle treatment (N=11), and PS19 with D-DPTIP treatment (N=10) mice were used for behavioral tests. The treatment began at 4 months of age and lasted until they were 10 months old. A) Discrimination index of NORT. Discrimination index=(Time spent with novel object-Time spent with familiar object)/total time. B) Recognition index of NORT. Recognition index=Time spent with novel object/total time. C) Percentage of time spent in the Y maze novel arm. D) Percentage of Y maze novel arm entries. E) Time to fall in Rotarod assessment, measured in seconds. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in A-F with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
Figure 1.
PS19 mice exhibit deficits in recognition and memory that are not improved by D-DPTIP. WT mice with vehicle treatment (N=18), PS19 with vehicle treatment (N=11), and PS19 with D-DPTIP treatment (N=10) mice were used for behavioral tests. The treatment began at 4 months of age and lasted until they were 10 months old. A) Discrimination index of NORT. Discrimination index=(Time spent with novel object-Time spent with familiar object)/total time. B) Recognition index of NORT. Recognition index=Time spent with novel object/total time. C) Percentage of time spent in the Y maze novel arm. D) Percentage of Y maze novel arm entries. E) Time to fall in Rotarod assessment, measured in seconds. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in A-F with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
Figure 2.
PS19 mice exhibit hippocampal atrophy and enlarged ventricles which are not improved by D-DPTIP. A-F) Representative MRI images from WT+vehicle (A,D), PS19+Vehicle (B,E), PS19+D-DPTIP (C,F), hippocampus area was marked as blue (A-C) and ventricle area was marked as orange (D-F). N=4 mice/group. G) Quantification of hippocampal voxels. H) Quantification of ventricle voxels. Hippocampal and ventricle voxels are normalized by whole-brain voxels. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in G and H with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.
Figure 2.
PS19 mice exhibit hippocampal atrophy and enlarged ventricles which are not improved by D-DPTIP. A-F) Representative MRI images from WT+vehicle (A,D), PS19+Vehicle (B,E), PS19+D-DPTIP (C,F), hippocampus area was marked as blue (A-C) and ventricle area was marked as orange (D-F). N=4 mice/group. G) Quantification of hippocampal voxels. H) Quantification of ventricle voxels. Hippocampal and ventricle voxels are normalized by whole-brain voxels. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in G and H with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.
Figure 3.
D-DPTIP does not affect tau and pTau expression levels in PS19 mice. A) Representative immunoblotting images from hippocampal tissue of male mice showing total Tau (upper blot) and pTau (lower blot). GAPDH used as a loading control. WT+ vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+Vehicle treatment (N=5), PS19+D-DPTIP treatment (N=6) were utilized. B) Quantification of A for total Tau normalized by total protein. C) Quantification of A for pTau normalized by total protein. D) Representative immunoblotting images from hippocampal tissue of female mice showing total human Tau (upper blot) and pTau (lower blot), GAPDH used as a loading control. WT+ vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+Vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+D-DPTIP treatment (N=6) were utilized. E) Quantification of D for total Tau normalized by total protein. F) Quantification of D for pTau normalized by total protein. Statistics were performed using unpaired student t-tests in B, C, E and F. Bars represent mean ± SEM.
Figure 3.
D-DPTIP does not affect tau and pTau expression levels in PS19 mice. A) Representative immunoblotting images from hippocampal tissue of male mice showing total Tau (upper blot) and pTau (lower blot). GAPDH used as a loading control. WT+ vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+Vehicle treatment (N=5), PS19+D-DPTIP treatment (N=6) were utilized. B) Quantification of A for total Tau normalized by total protein. C) Quantification of A for pTau normalized by total protein. D) Representative immunoblotting images from hippocampal tissue of female mice showing total human Tau (upper blot) and pTau (lower blot), GAPDH used as a loading control. WT+ vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+Vehicle treatment (N=6), PS19+D-DPTIP treatment (N=6) were utilized. E) Quantification of D for total Tau normalized by total protein. F) Quantification of D for pTau normalized by total protein. Statistics were performed using unpaired student t-tests in B, C, E and F. Bars represent mean ± SEM.
Figure 4.
D-DPTIP is preferentially taken up by microglia and selectively inhibits microglial nSMase2 activity. A) Representative hippocampal images showing Cy5-D-DPTIP signal (red) was co-localized with Iba1 (microglia) signal (green), but not with GFAP (astrocyte) or NeuN (neuron) signal. B) Single cells were selected by gating singlets (upper panel) and live cells were selected by gating PI negative signals (lower panel). C-E) Cy5 positive cells were gated from brain samples of PS19 mice treated with Cy5-D-DPTIP (C), PS19 mice treated with vehicle (D), and WT mice treated with vehicle (E). F) Cy5 positive cells gated from C were used for gating by ACSA2 (astrocyte) and TMEM119 (microglia) and (NeuN) positive signals. Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) are used for negative controls. G) Quantification of F. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA. H-I) Quantification of nSMase2 activity assay performed on isolated CD11b- cells (H) and CD11b+ cells (I). Statistics were performed using unpaired student t-tests in H and I, and one-way ANOVA in G with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Scale bar is 30µm.
Figure 4.
D-DPTIP is preferentially taken up by microglia and selectively inhibits microglial nSMase2 activity. A) Representative hippocampal images showing Cy5-D-DPTIP signal (red) was co-localized with Iba1 (microglia) signal (green), but not with GFAP (astrocyte) or NeuN (neuron) signal. B) Single cells were selected by gating singlets (upper panel) and live cells were selected by gating PI negative signals (lower panel). C-E) Cy5 positive cells were gated from brain samples of PS19 mice treated with Cy5-D-DPTIP (C), PS19 mice treated with vehicle (D), and WT mice treated with vehicle (E). F) Cy5 positive cells gated from C were used for gating by ACSA2 (astrocyte) and TMEM119 (microglia) and (NeuN) positive signals. Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) are used for negative controls. G) Quantification of F. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA. H-I) Quantification of nSMase2 activity assay performed on isolated CD11b- cells (H) and CD11b+ cells (I). Statistics were performed using unpaired student t-tests in H and I, and one-way ANOVA in G with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Scale bar is 30µm.
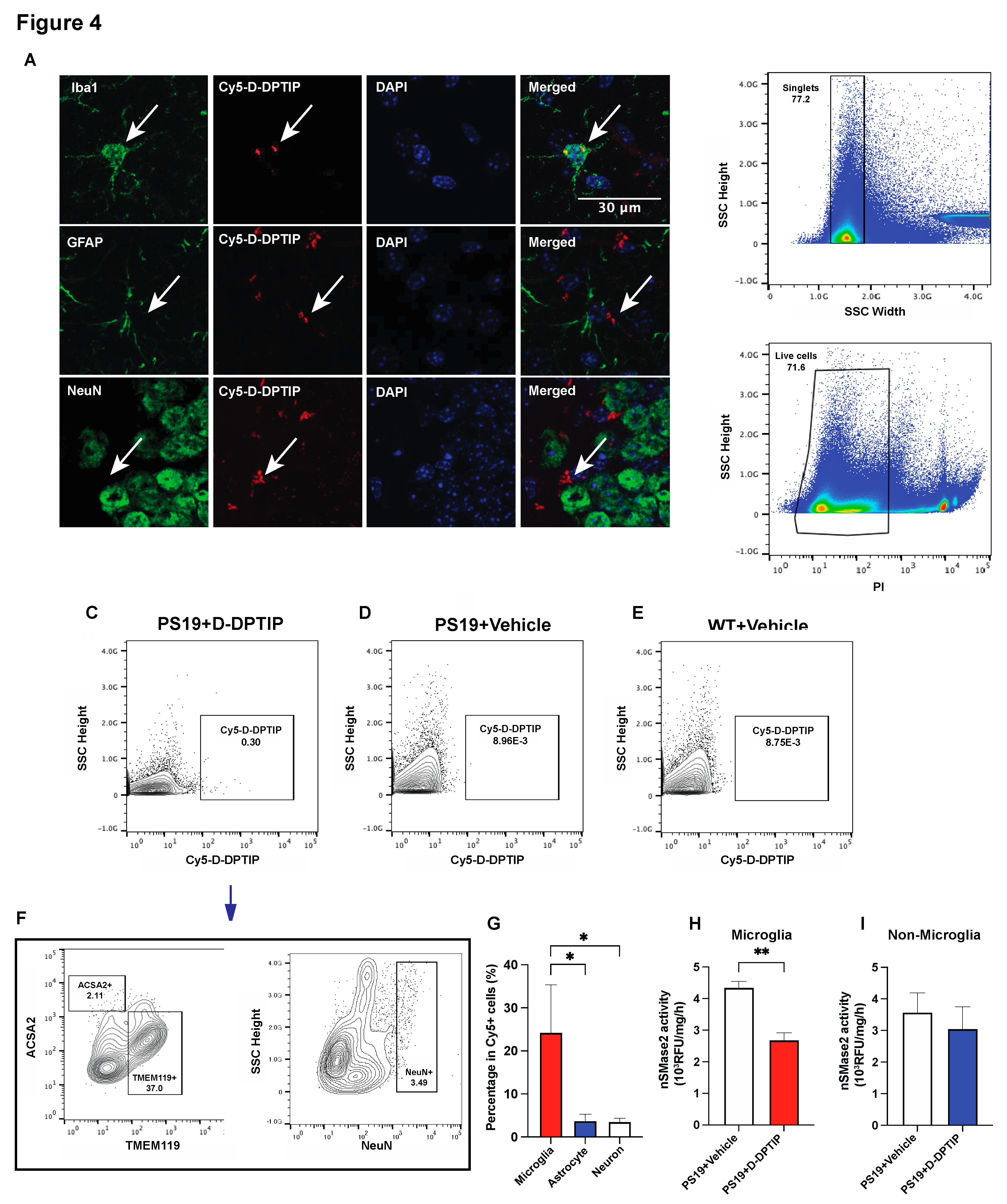
Figure 5.
D-DPTIP selectively reduced activated microglia-derived EVs found in PS19 mice plasma. A) EV sizes measured by NTA. B) Protein concentrations per EV particle measured by BCA. C) SPRi analysis intensity of specific brain cell type derived EVs in plasma normalized to CD9 (general EV). D) CD11b+ (activated microglia) signals normalized by IB4 (total microglia) signals. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in A, B, and D with Tukey’s multiple comparisons, and two-way ANOVA in C. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.
Figure 5.
D-DPTIP selectively reduced activated microglia-derived EVs found in PS19 mice plasma. A) EV sizes measured by NTA. B) Protein concentrations per EV particle measured by BCA. C) SPRi analysis intensity of specific brain cell type derived EVs in plasma normalized to CD9 (general EV). D) CD11b+ (activated microglia) signals normalized by IB4 (total microglia) signals. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA in A, B, and D with Tukey’s multiple comparisons, and two-way ANOVA in C. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).