Submitted:
14 August 2023
Posted:
15 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- the gravitational force inside the region is repulsive.
- test particles cannot reach the center.
- test particles can cross the horizon outward, but only along the axis.
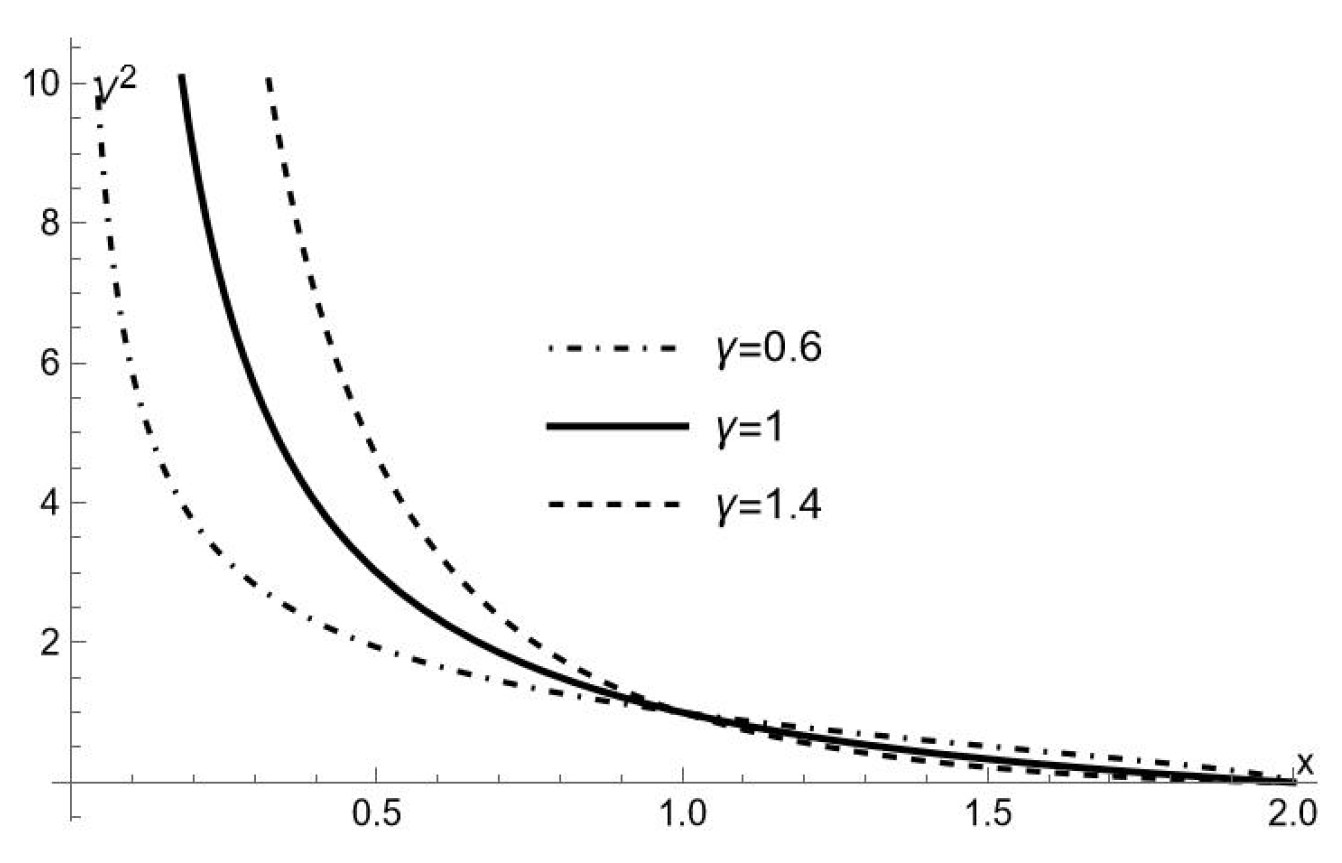
2. The -Metric and its Hyperbolic Version
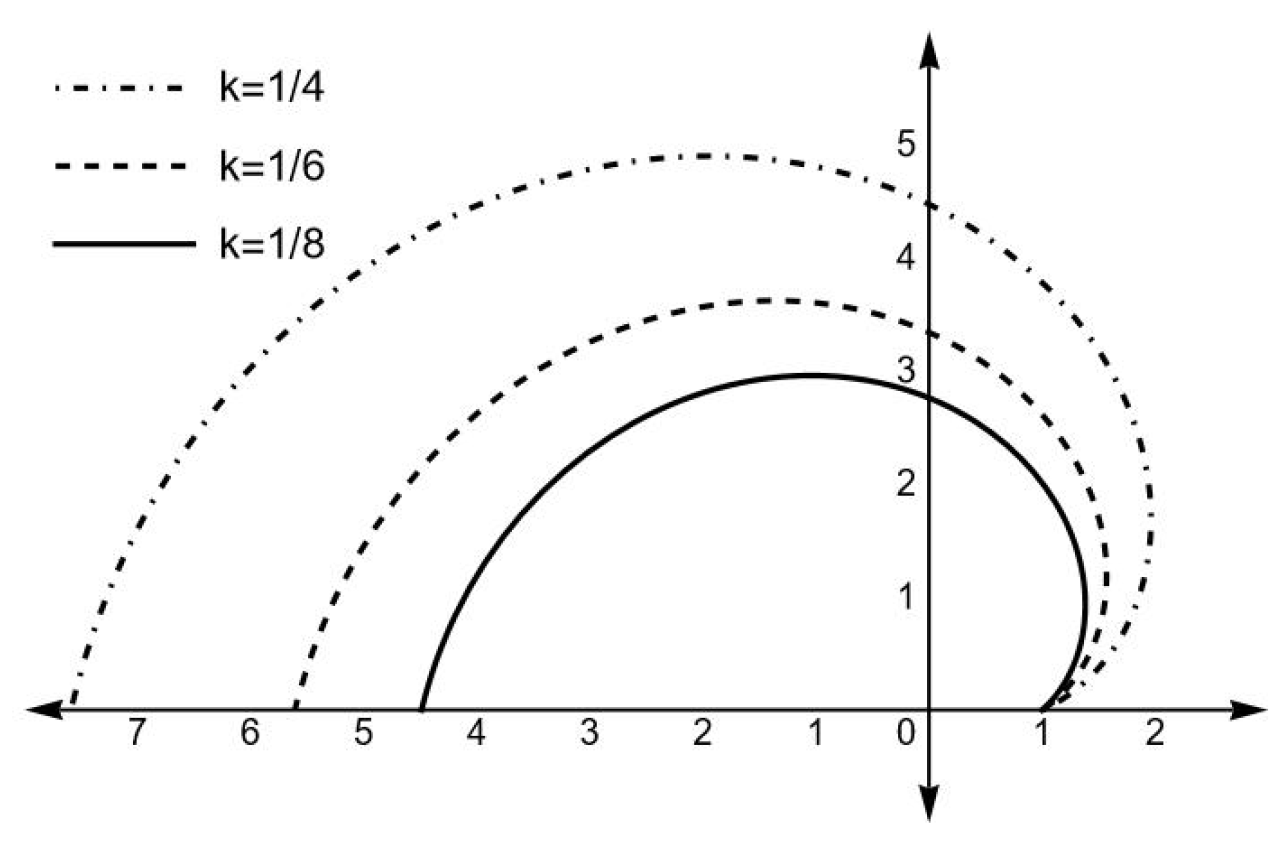
3. Geodesics
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Like in the hyperbolically symmetric case, the test particles never reach the center, however in our case the test particles radially directed to the center bounce back farther from the center as increases. This result becomes intelligible from a simple inspection of (40).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera, L; Witten, L. An alternative approach to the static spherically symmetric vacuum global solutions to the Einstein’s equations. Adv. High Ener. Phys. 2018, 2018, 3839103. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, N. The nature of the Schwarzschild singularity. In Relativity; Carmeli, M., Fickler, S. I., Witten, L., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, USA, 1970; pp. 229–258. [Google Scholar]
- Caroll, S. Spacetime and Geometry. An Introduction to General Relativity, Addison Wesley: San Francisco, USA, 2004; pp. 246.
- Rindler, W. Relativity. Special, General and Cosmological, Oxford University Press: New York, USA, 2001; pp. 260–261.
- Harrison, B. K. Exact Three–Variable Solutions of the Field Equations of General Relativity. Phys. Rev. 1959, 116, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G. Dynamics of Pressure–Free Matter in General Relativity. J. Math. Phys. 1967, 8, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephani, H.; Kramer, D.; MacCallum, M.; Honselaers, C.; Herlt, E. Exact Solutions to Einsteins Field Equations, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin, M.; Gorini, V.; Kamenshchik, A.; Moschella, U.; Pasquier, V. Gravity of a static massless scalar field and a limiting Schwarzschild-like geometry. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, L.; Cacciatori, S.L.; Gorini, V.; Kamenshchik, A.; Piattella, O.F. Dark matter effects in vacuum spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 027301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenshchik, A.Y.; Pozdeeva, E.O.; Starobinsky, A.A.; Tronconi, A.; Vardanyan, T.; Venturi, G.; Yu, S. Verno. Duality between static spherically or hyperbolically symmetric solutions and cosmological solutions in scalar-tensor gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madler, T. On the affine-null metric formulation of General Relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, A.; Delliou, M.L.; Mimoso, J.P. New perspectives on the TOV equilibrium from a dual null approach. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L; Di Prisco, A; Ospino, J; Witten, L. Geodesics of the hyperbolically symmetric black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 064071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M. Z.; Yousaf, Z.; Tariq, Z. Hyperbolically symmetric sources in Palatini f(R) gravity Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 1070. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, L; Di Prisco, A; Ospino, J. Dynamics of hyperbolically symmetric fluids. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L; Di Prisco, A; Ospino. J. Hyperbolically symmetric static fluids: A general study. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 024037.
- Herrera, L.; Di Prisco, A.; Ospino, J. Hyperbolically symmetric versions of Lemaitre–Tolman–Bondi spacetimes. Entropy 2021, 23, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.Z.; Yousaf, Z.; Tariq, Z. Influence of electromagnetic field on hyperbolically symmetric source. Eur. Phys. J. P. 2021, 136, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M. Z.; Yousaf, Z.; Hanif, S. Hyperbolically symmetric sources, a comprehensive study in f(T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. P. 2022, 137, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y. Motion of charged particles in spacetimes with magnetic fields of spherical and hyperbolic symmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 064023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, Z.; Bhatti, M.; Khlopov, M.; Asad, H. A Comprehensive Analysis of Hyperbolical Fluids in Modified Gravity. Entropy 2022, 24, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, Z.; Bhatti, M.; Asad, H. Hyperbolically symmetric sources in f(R,T) gravity. Ann. Phys. 2022, 437, 168753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, Z.; Nashed, G.; Bhatti, M. , Asad, H. Significance of Charge on the Dynamics of Hyperbolically Distributed Fluids. Universe 2022, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, Z. Spatially Hyperbolic Gravitating Sources in Λ-Dominated Era Universe 2022, 8, 131. 8.
- Bhatti, M. Z.; Yousaf, Z.; Hanif. S. Electromagnetic influence on hyperbolically symmetric sources in f(T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipoy, D.M. Topology of Some Spheroidal Metrics. J. Math. Phys. 1966, 7, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, B. Static Axially Symmetric Gravitational Fields. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 2, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espósito, F.; Witten, L. On a static axisymmetric solution of the Einstein equations. Phys. Lett. B 1975, 58, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Esposito, F.; Lee, S. Effects of naked singularities: Particle orbits near a two-parameter family of naked singularity solutions. Phys. Rev. D 1978, 17, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.; Paiva, F.; Santos, N.O. Geodesics in the γ spacetime. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2000, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. B. Bonnor, Proceedings of the 3rd Canadian Conference on General Relativity and Relativistic Astrophysics eds. A. Coley, F. I.Cooperstock and B. Tupper (World Scientific Publishing Co., Singapore, 1990) p. 216.
- Herrera, L.; Paiva, F. M.; Santos, N. O. The Levi-Civita spacetime as a limiting case of the γ spacetime. J. Math. Phys. 1999, 40, 4064–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richterek, L.; Novotny, J.; Horsky, J. Einstein-Maxwell Fields Generated from the γ Metric and Their Limits. Czech. J. Phys. 202, 52, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Patil, M; Malafarina, D. ; Joshi, P. Circular geodesics and accretion disks in the Janis-Newman-Winicour and gamma metric spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 104031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikamalov, A.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Ayzenberg, D.; Malafarina, D.; Bambi, C.; Ahmedov. B. Black hole mimicker hiding in the shadow: Optical properties of the γ metric. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 024014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvear Terrero, D.; Hernandez Mederos, V.; Lopez Perez, S.; Manreza Paret, D.; Perez Martinez, A.; Quintero Angulo, G. Modeling anisotropic magnetized white dwarfs with γ metric. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 02301. [Google Scholar]
- Toshmatov, B.; Malafarina, D.; Dadhich, N. Harmonic oscillations of neutral particles in the γ metric. Phys. Rev.D 2019, 100, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshmatov, B.; Malafarina, D. Spinning test particles in the γ spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides Gallego, C.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Malafarina, D.; Ahmedov, B.; Bambi, C. Charged particle motion and electromagnetic field in γ spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 044012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capistrano, A.; Zeidel, P.; Cabral, L. Effective apsidal precession from a monopole solution in a Zipoy spacetime Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 730. [Google Scholar]
- Benavides Gallego, C.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Malafarina, D.; Bambi, C. Quasiharmonic oscillations of charged particles in static axially symmetric space-times immersed in a uniform magnetic field. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 124024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narziloev, B.; Malafarina, D.; Abdujabbaraov, A.; Bambi, C. On the properties of a deformed extension of the NUT space-time. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-Rong Hu; Guo-Qing Huang, Dynamics of charged particles in the magnetized γ space–time. Eur. Phys. J. P. 2021, 136, 1210. [CrossRef]
- Turimov, B.; Ahmedov, B. Zipoy-Voorhees Gravitational Object as a Source of High-Energy Relativistic Particles. Galaxies 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafarina, D.; Sagynbayeva, S. What a difference a quadrupole makes? Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2021, 53, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmen, J.; Perlick, V. Geometrically thick tori around compact objects with a quadrupole moment. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2021, 38, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzilloev, B.; Malafarina, D.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Ahmedov, B.; Bambi, C. Particle motion around a static axially symmetric wormhole. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 064016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, H.; Borah, D.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Malafarina, D.; Ahmedov, B. Effects of gravitational lensing on neutrino oscillation in γ spacetime. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibarat, A.; Mirza, B.; Azizallahi, A. γ Metrics in higher dimensions. Nucl. Phys. B 2022, 978, 115739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, R.; Paul, S.; Banerjejee, P.; Sarkar, T. Shadows and thin accretion disk images of the γ -metric. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtug, O.; Halilsoy, M.; Mangut, M. The charged Zipoy-Voorhees metric with astrophysical applications. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mirzaev, T.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Malafarina, D.; Ahmedov, B. ; Wen-Biao Han, Constraining the deformation of a rotating black hole mimicker from its shadow. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 08041. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K. et al. (Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration). First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L1. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K. et al. (Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration). First Sagittarius A Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 930, L12. [Google Scholar]
- Psaltis, D. Testing general relativity with the Event Horizon Telescope. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2019, 51, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S. E. Can the EHT M87 results be used to test general relativity? Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 024023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glampedakis, K.; Pappas, G. Can supermassive black hole shadows test the Kerr metric? Phys. Rev. D 021, 104, L081503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi–Nodehi, M.; Azreg–Ainou, M.; Jusufi, K.; Jamil, M. Shadow, quasinormal modes, and quasiperiodic oscillations of rotating Kaluza-Klein black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusufi, K.; Azreg–Ainou, M.; Jamil, M.; Wei, S.W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, A. Quasinormal modes, quasiperiodic oscillations, and the shadow of rotating regular black holes in nonminimally coupled Einstein-Yang-Mills theory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Wu, Q.; Jusufi, K.; Jamil, M.; Azreg–Ainou, M.; Wang, A. Shadow and quasinormal modes of a rotating loop quantum black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 084001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusufi, K.; Jamil, M.; Chakrabarty, H.; Wu, Q.; Bambi, C.; Wang, A. Rotating regular black holes in conformal massive gravity. Phys. Rev. D 101 2020, 044035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, M.; Kumar, R.; Ghosh, S.G. Parameter estimation of hairy Kerr black holes from its shadow and constraints from M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, M.S. Self-accelerating cosmologies and hairy black holes in ghost-free bigravity and massive gravity. Classical Quantum Gravity 2013, 30, 184009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkel, R.; Sotiriou, T. P.; Witek, H. Black hole hair formation in shift-symmetric generalised scalar-tensor gravity. Classical Quantum Gravity 2017, 34, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.; Gualtieri, L. Testing the black hole “no-hair” hypothesis. Classical Quantum Gravity 2016, 33, 174001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmanov, E.; Boshkayev, K.; Giambo, R.; Konysbayev, T.; Luongo, O.; Malafarina, D.; Quevedo, H. Accretion Disk Luminosity for Black Holes Surrounded by Dark Matter with Anisotropic Pressure. Astrophys. J. 2022, 925, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshkayev, K.; Konysbayev, T.; Kurmanov, E.; Luongo, O.; Malafarina, D.; Mutalipova, K.; Zhumakhanova, G. Effects of non-vanishing dark matter pressure in the Milky Way Galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshkayev, K.; Idrissov, A.; Luongo, O.; Malafarina, D. Accretion disc luminosity for black holes surrounded by dark matter. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, W. Event Horizons in Static Vacuum Space-Times Phys. Rev. 1967, 164, 1776. [Google Scholar]
- Bladford, R. D.; Rees, M. J. A “Twin-Exhaust” Model for Double Radio Sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 169, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margon, B. A. Observations of SS 433. Annu. Rev. Astr. Astrophys 1984, 22, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sams, B. J.; Eckart, A.; Sunyaev, R. Near-infrared jets in the Galactic microquasar GRS1915+105. Nature 1996, 382, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




