Submitted:
07 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
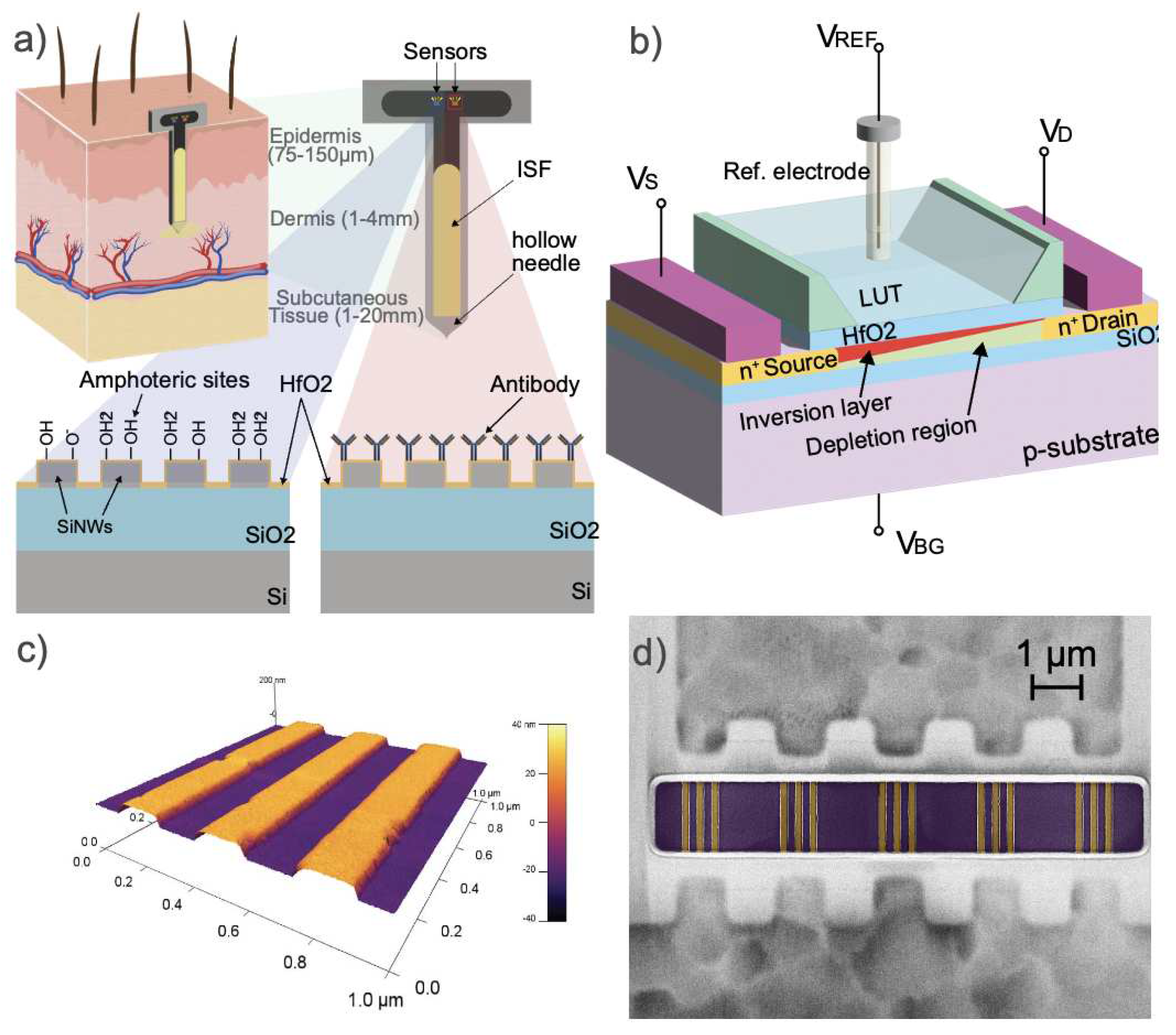
2.1. Silicon-On-Insulator Nanowire FETs
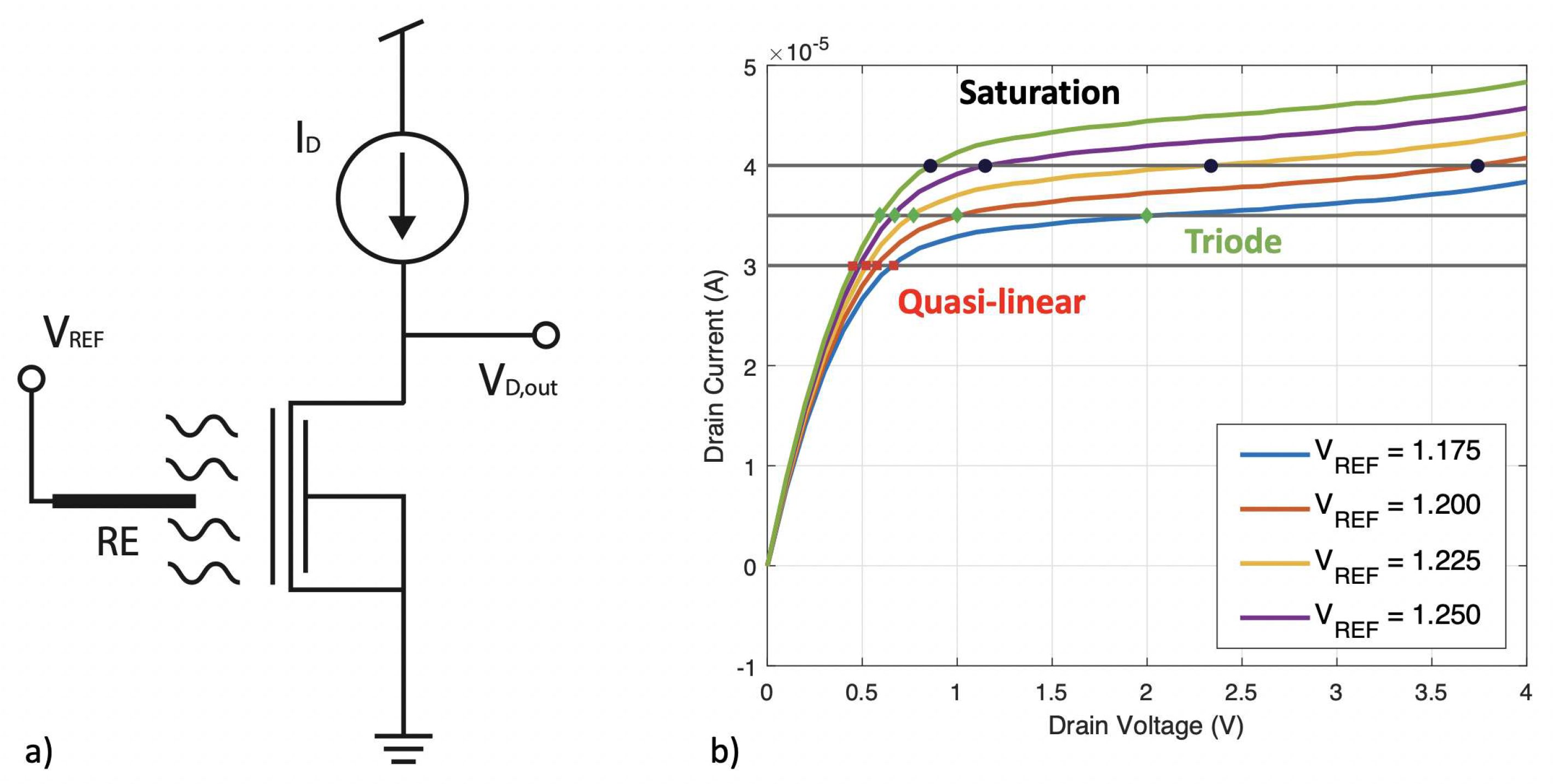
2.2. Constant Current Operation
2.3. Sample preparation and ISF collection
3. Results
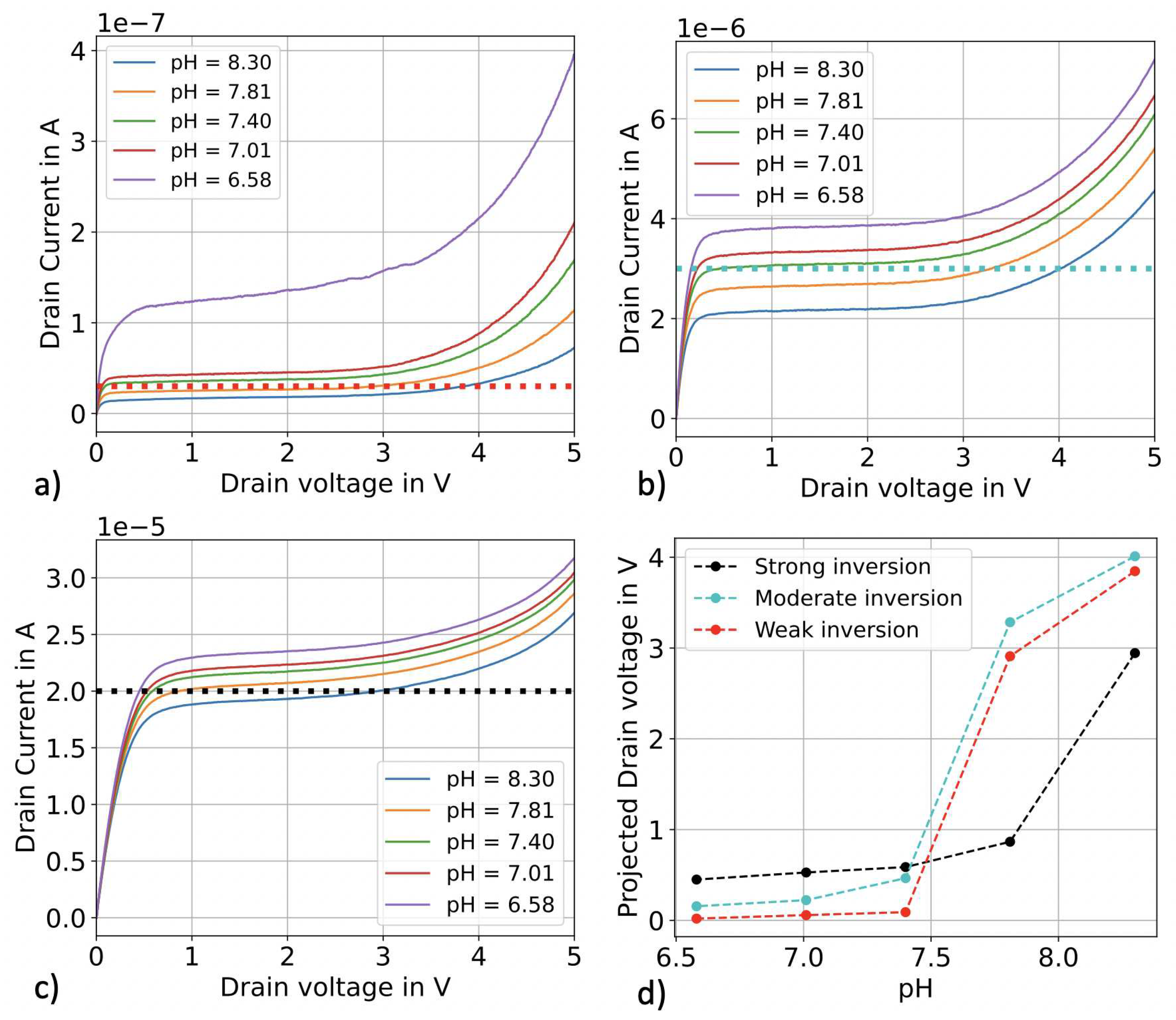
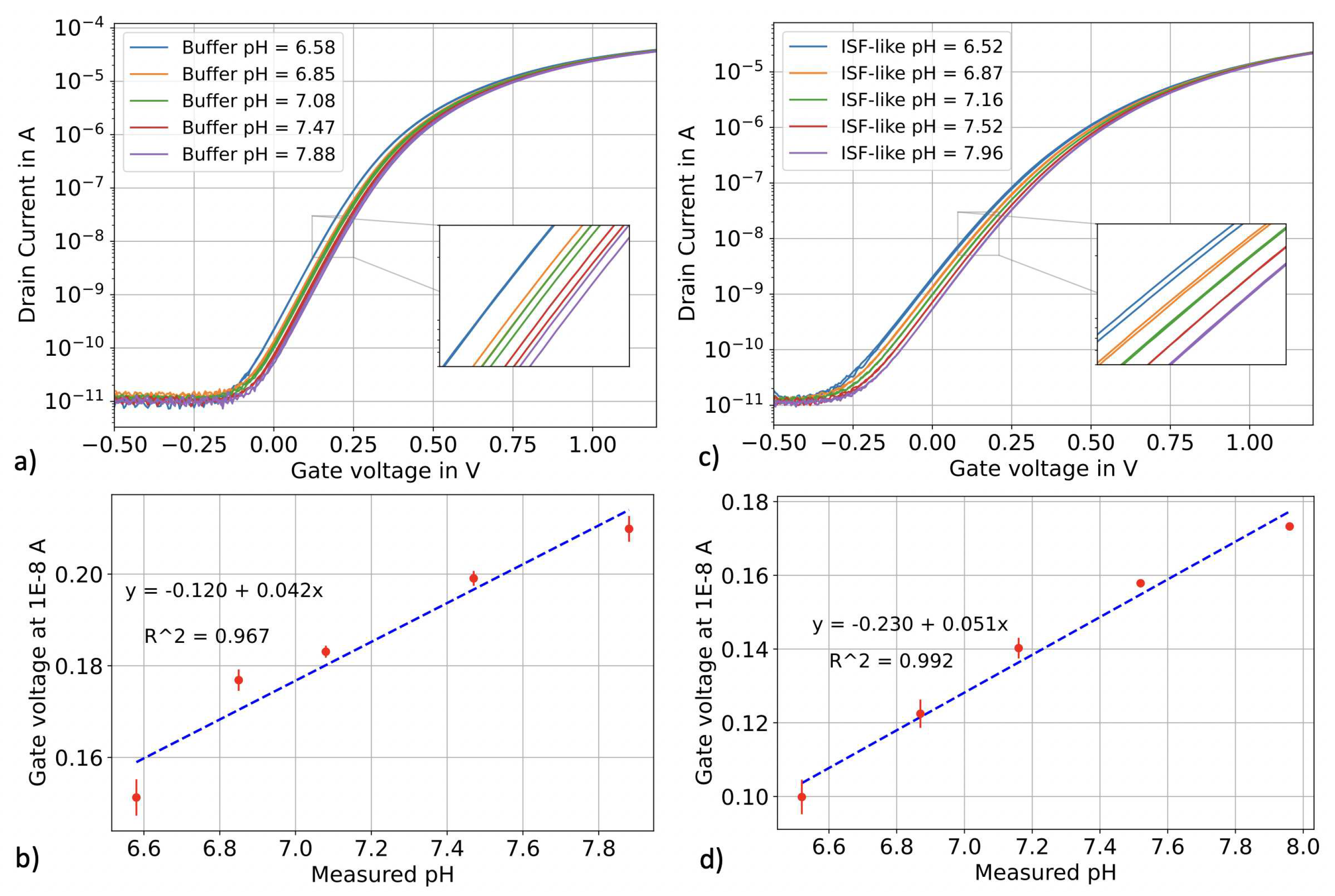
3.1. pH sensing in top-gate configuration
3.2. pH sensing in constant current operation
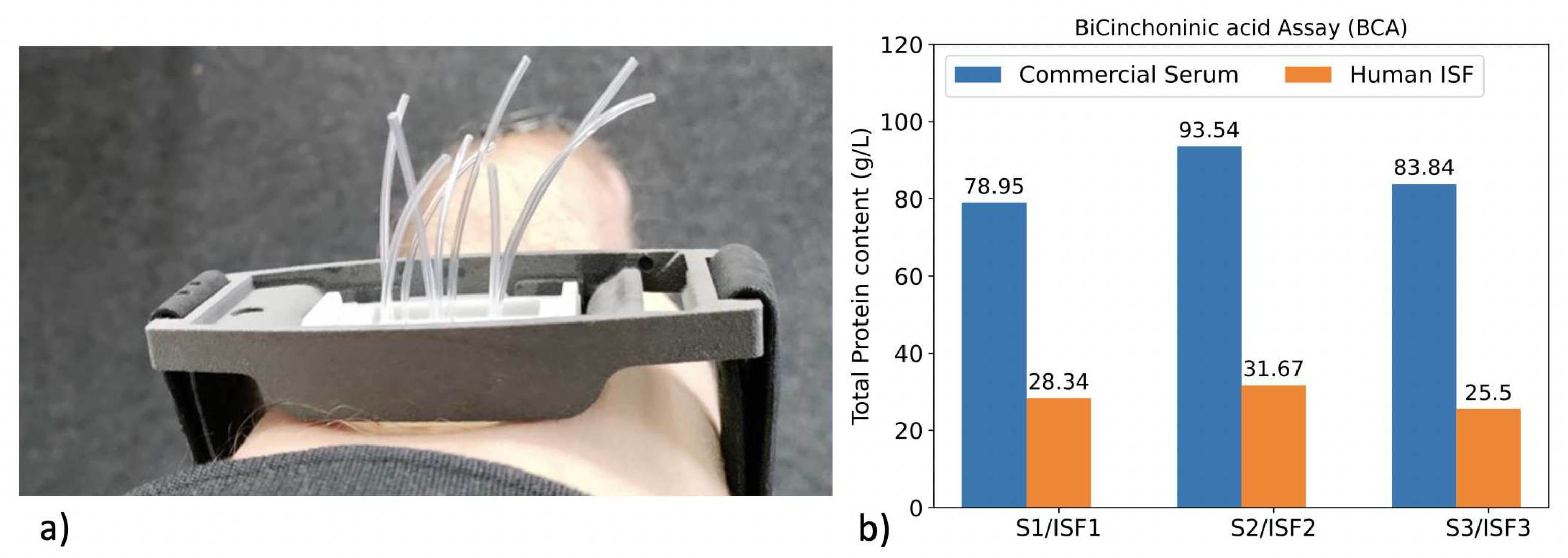
3.3. pH sensing in real human ISF
3.3.1. Protocol
3.3.2. Measurement
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCA | BiCinchoninic acid Assay |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| ISF | Interstitial Fluid |
| ISFETs | Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| pH | Potentiel of hydrogen |
| SiNWs | Silicon Nanowires |
References
- Samanta, S.; Singh, R.K.; Baronia, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Poddar, B.; Azim, A.; Gurjar, M. Early pH change predicts intensive care unit mortality. Indian journal of critical care medicine: peer-reviewed, official publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine 2018, 22, 697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Treatment of acute metabolic acidosis: a pathophysiologic approach. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2012, 8, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, P.M.; Szerlip, H.M. Metabolic acidosis in the intensive care unit. Critical care clinics 2002, 18, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, S.; Yassine, H.M.; Benslimane, F.M.; Smatti, M.K.; Schuchardt, S.; Albagha, O.; Al-Thani, A.A.; Ait Hssain, A.; Diboun, I.; Elrayess, M.A. Predictive biomarkers of intensive care unit and mechanical ventilation duration in critically-ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Frontiers in Medicine 2021, 8, 733657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kutovyi, Y.; Zadorozhnyi, I.; Boichuk, N.; Vitusevich, S. Monitoring of dynamic processes during detection of cardiac biomarkers using silicon nanowire field-effect transistors. Advanced Materials Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Morrow, T.J.; Keating, C.D. Nanowire sensors for multiplexed detection of biomolecules. Current opinion in chemical biology 2008, 12, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.P.; Pham, T.T.T.; Wolfrum, B.; Offenhäusser, A.; Thierry, B. CMOS-compatible silicon nanowire field-effect transistor biosensor: Technology development toward commercialization. Materials 2018, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A. Silicon nanowire field-effect transistors for sensing applications. PhD thesis, University_of_Basel, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.K.; Cho, W.J. Ultra-high sensitivity pH-sensors using silicon nanowire channel dual-gate field-effect transistors fabricated by electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers pattern template transfer. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2021, 326, 128835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, P.; Wang, Z. Highly sensitive pH sensors based on double-gate silicon nanowire field-effect transistors with dual-mode amplification. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2020, 320, 128403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Esser, L.; Easton, C.D.; Cadarso, V.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Wearable microneedle array-based sensor for transdermal monitoring of pH levels in interstitial fluid. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 222, 114955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midahuen, R.; Previtali, B.; Fontelaye, C.; Nonglaton, G.; Barraud, S.; Stambouli, V. Wafer-scale fabrication of biologically sensitive Si nanowire FET: from pH sensing to electrical detection of DNA hybridization. In Proceedings of the ESSCIRC 2021 - IEEE 47th European Solid State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC); 2021; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capua, L.; Sprunger, Y.; Elettro, H.; Risch, F.; Grammoustianou, A.; Midahuen, R.; Ernst, T.; Barraud, S.; Gill, R.; Ionescu, A. Label-free C-reactive protein Si nanowire FET sensor arrays with super-Nernstian back-gate operation. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 2022, 69, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haljamäe, H.; Fredén, H. Comparative analysis of the protein content of local subcutaneous tissue fluid and plasma. Microvascular research 1970, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellmerer, M.; Schaupp, L.; Brunner, G.A.; Sendlhofer, G.; Wutte, A.; Wach, P.; Pieber, T.R. Measurement of interstitial albumin in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue by open-flow microperfusion. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2000, 278, E352–E356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutili, G.; Arfors, K.E. Protein concentration in interstitial and lymphatic fluids from the subcutaneous tissue. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 1977, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marunaka, Y. Roles of interstitial fluid pH in diabetes mellitus: Glycolysis and mitochondrial function. World journal of diabetes 2015, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marunaka, Y. Roles of interstitial fluid pH and weak organic acids in development and amelioration of insulin resistance. Biochemical Society Transactions 2021, 49, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, P.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Mechanisms of sampling interstitial fluid from skin using a microneedle patch. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Taylor, R.M.; Tran, B.Q.; Boyd, G.; Glaros, T.; Chavez, V.H.; Krishnakumar, R.; Sinha, A.; Poorey, K.; Williams, K.P.; et al. Extraction and biomolecular analysis of dermal interstitial fluid collected with hollow microneedles. Communications biology 2018, 1, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, D.; Bangsbo, J.; Juel, C. Interstitial pH in human skeletal muscle during and after dynamic graded exercise. The Journal of physiology 2001, 537, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Guzmán, J.J.; Pérez-Ráfols, C.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. Toward in vivo transdermal pH sensing with a validated microneedle membrane electrode. ACS sensors 2021, 6, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, K. An integrated ISFET sensor array. Sensors 2009, 9, 8831–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

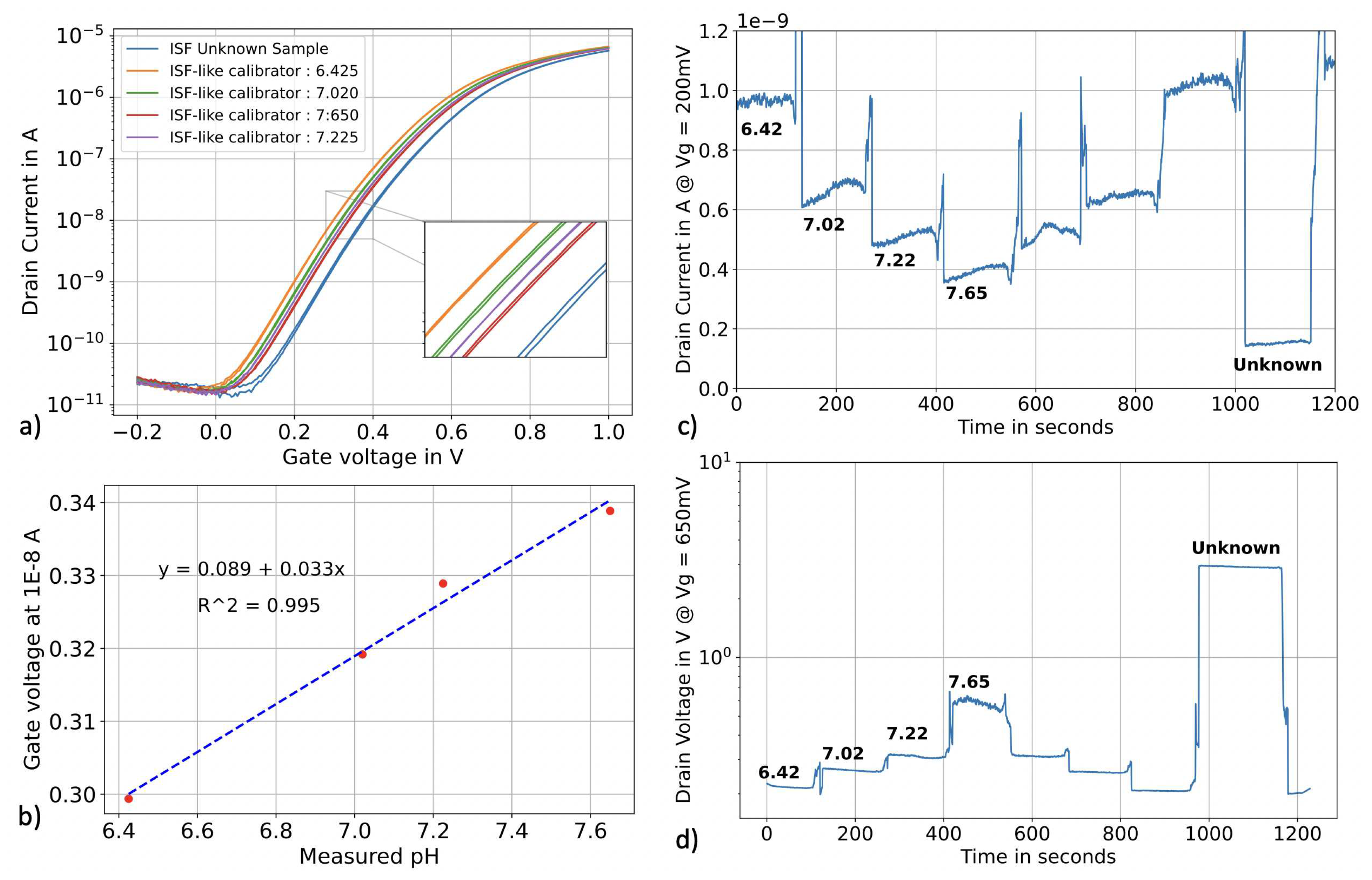
| Sample | pH meter reading | pH SiNWs in top-gate | error % | pH SiNWs in constant current operation | error % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISF-like S1 | 7.61 | 7.68 | 0.92 | 7.68 | 0.92 |
| ISF-like S2 | 7.59 | 7.68 | 1.19 | 7.62 | 0.40 |
| ISF-like S3 | 7.62 | 7.75 | 1.71 | 7.66 | 0.52 |
| Method | pH meter reading | pH measured | error % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-gate sweeping | 8.60 | 8.79 | 2.2 |
| Top-gate real-time | 8.60 | 8.78 | 2.2 |
| Constant-current | 8.60 | 8.61 | 0.2 |
| Sensor | Method | Substrate | Sensitivity (mV/pH) | Accuracy (pH units) | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Potentiometry | Polyaniline-coated PMNA | 62.9 | ± 0.036 | Artificial ISF buffer |
| [9] | Dual-Gate ISFETs | Silicon nanowires | 938.4 | N.A | pH calibrators |
| [22] | Potentiometry | Hydrogen selective membrane (HSM) |
± 0.3 | Euthanized rat ISF | |
| [23] | Constant current | Silicon nitride | 41 | N.A | pH calibrators |
| This work | Top-gate ISFETs | Silicon nanowires | 42 ± 10 | ± 0.18 | Human ISF |
| This work | Constant current | Silicon nanowires | ≈400 | ±0.01 | Human ISF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




