Submitted:
11 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Models
2.2. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.3. Metabolic Cage Studies
2.4. RNAscope Analysis
2.5. Diuretic Treatments
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
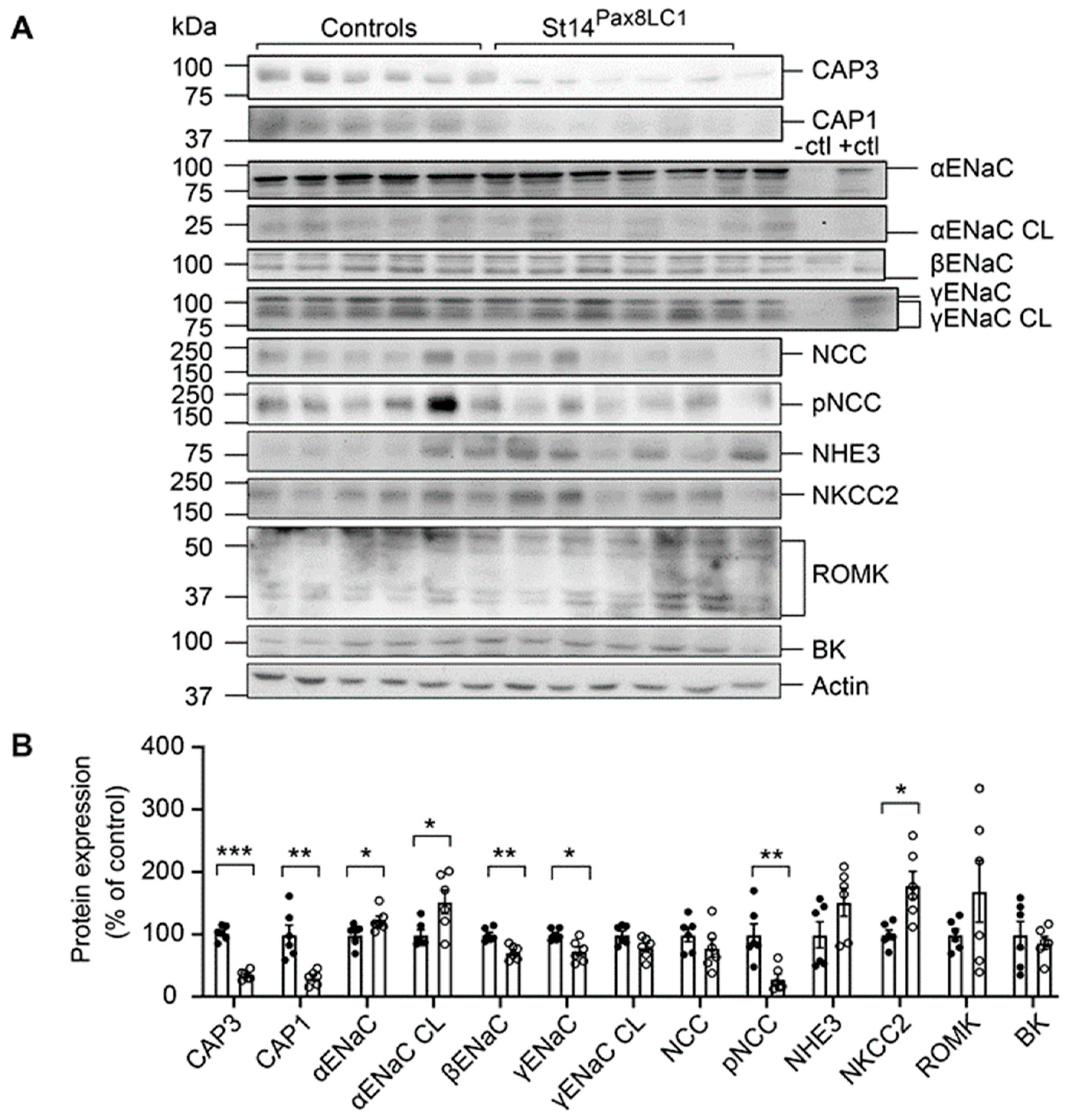
3.1. CAP3 Tubule Specific Deficiency did not Impair Na+ Homeostasis, but Changed Protein Abundances of ENaC Subunits and CAP1
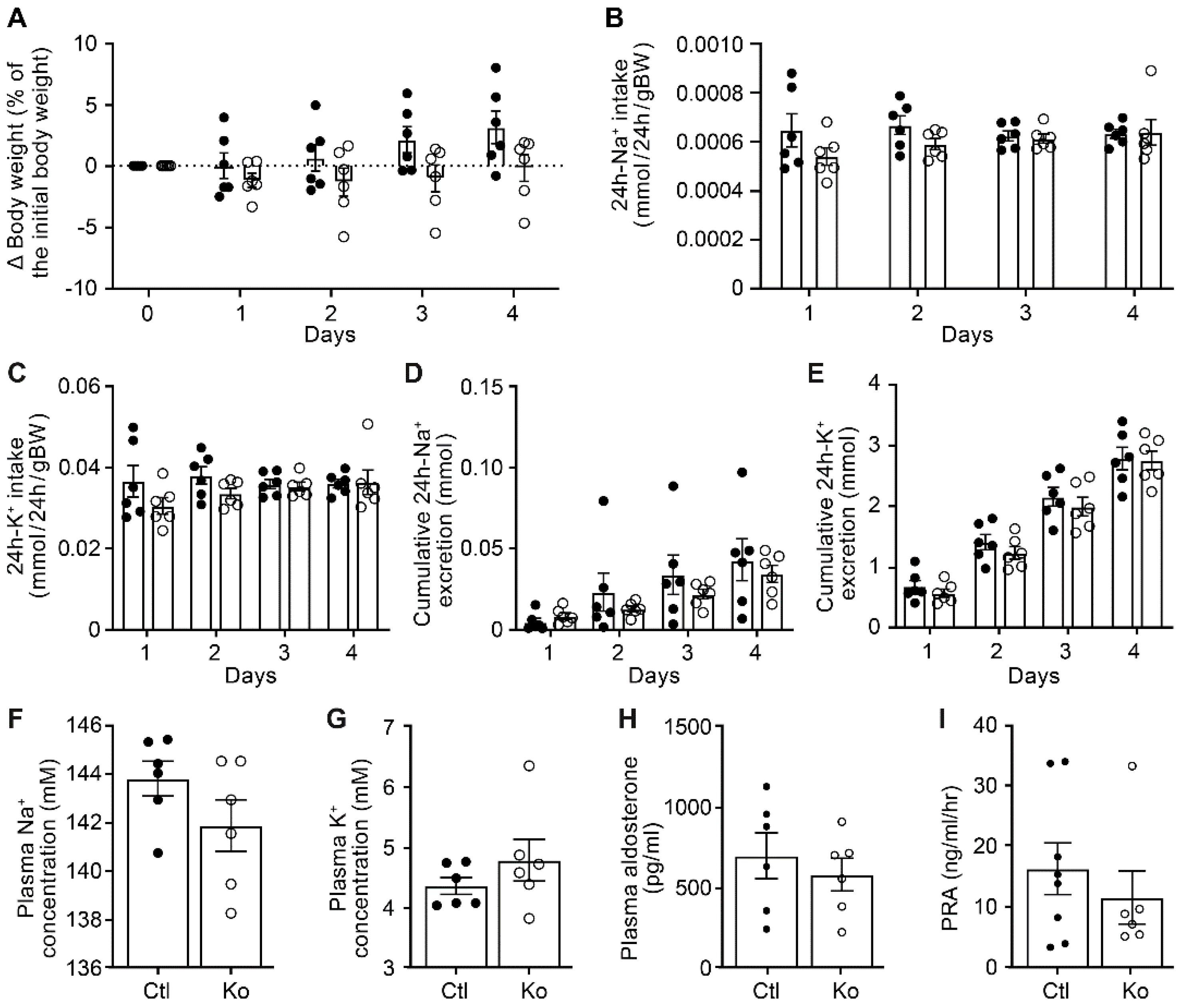
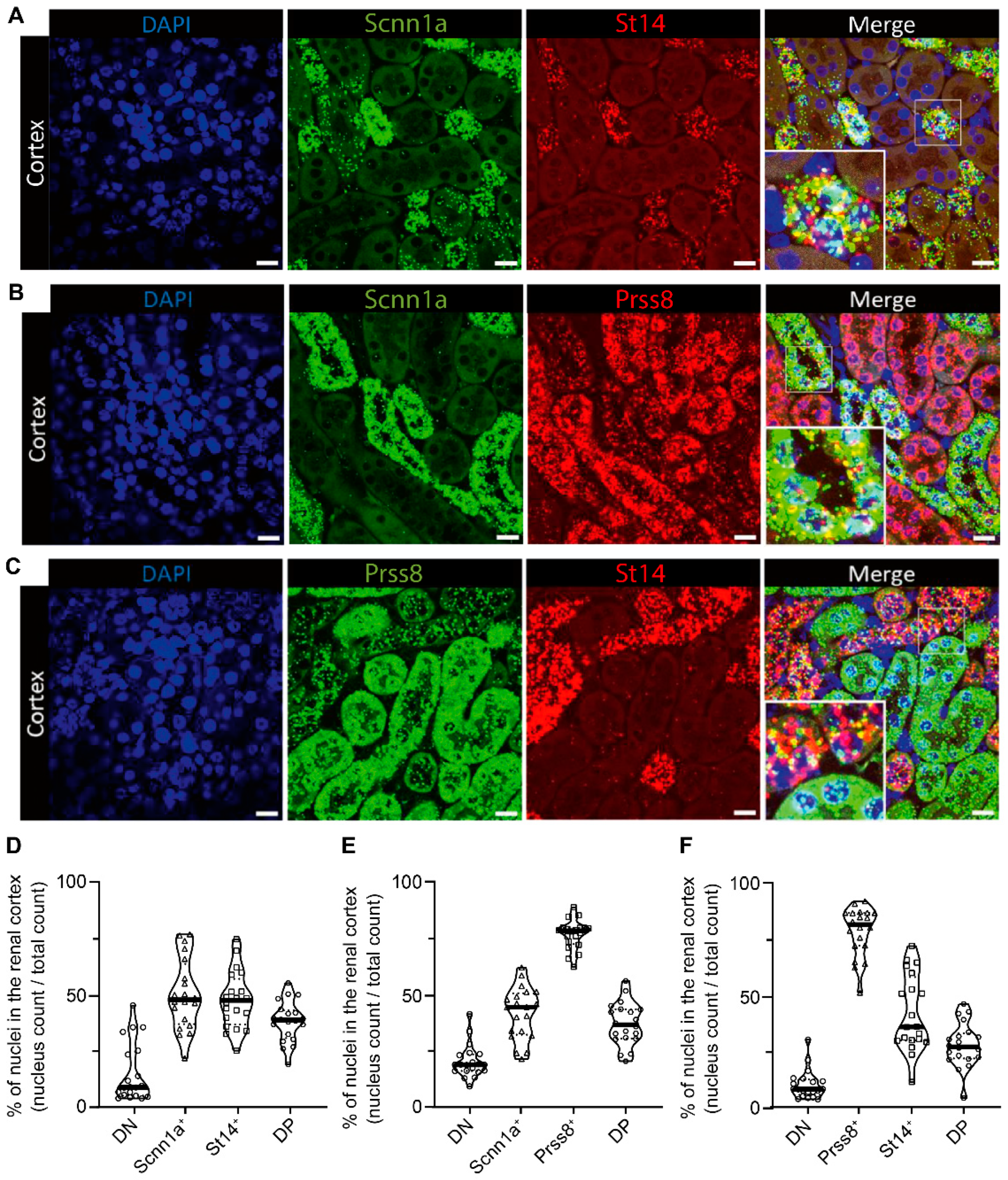
3.2. ENaC is Highly Co-Expressed with CAP3 and Less with CAP1 in Distal Tubules
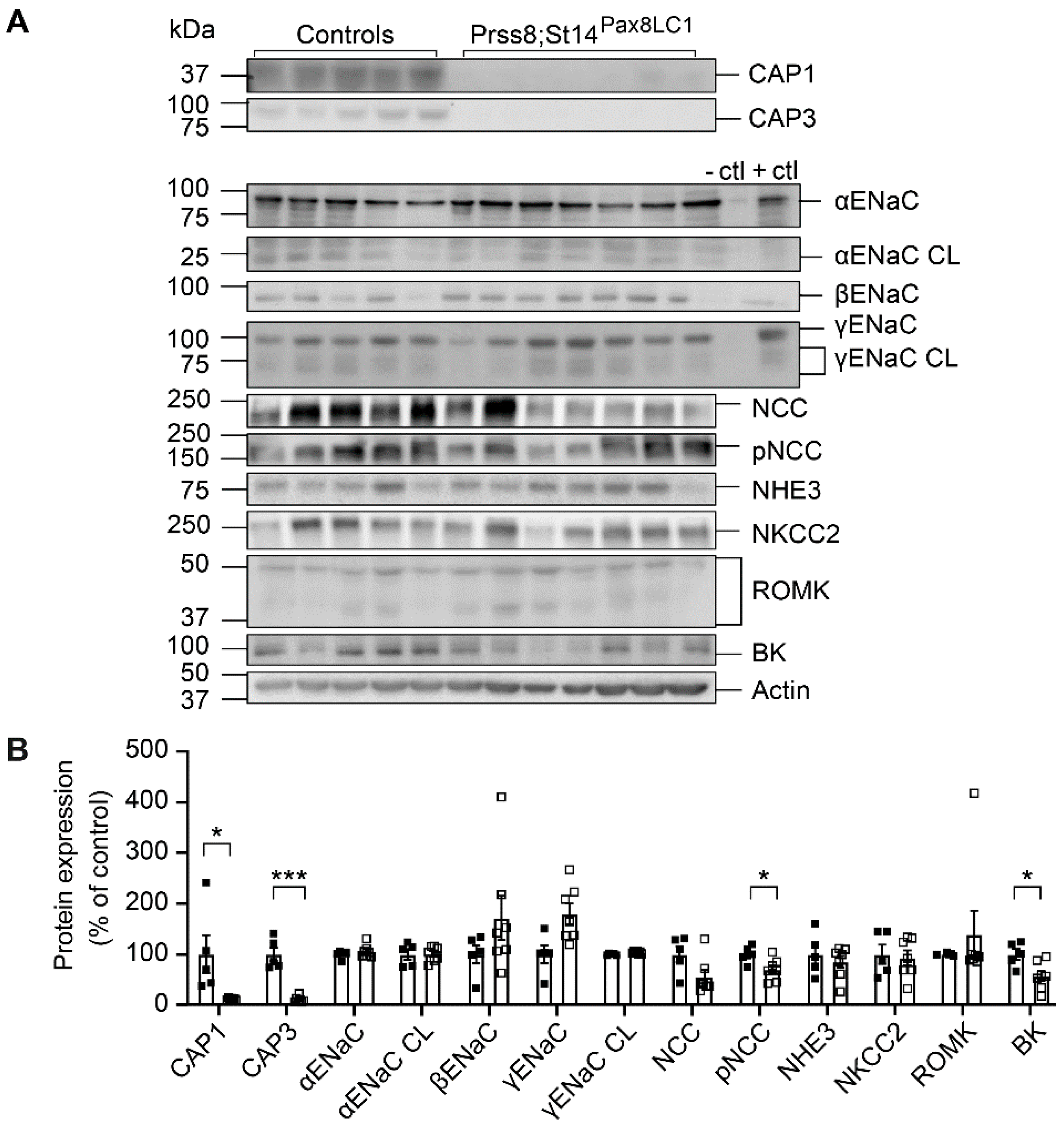
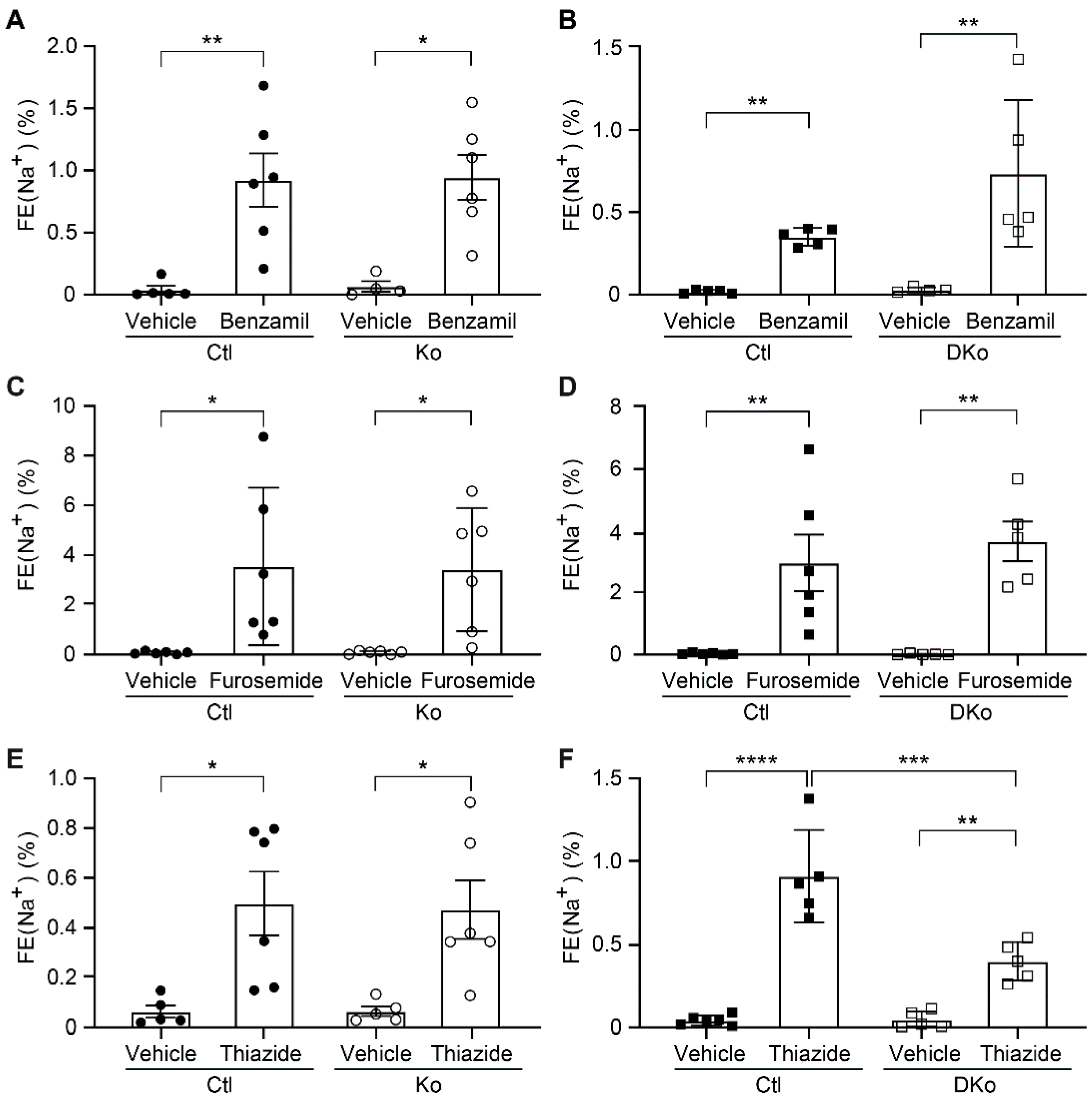
3.3. CAP1/CAP3 DKo Mice Restored ENaC Subunit Protein Abundances and Aldosterone Regulation of ENaC but not of NCC

4. Discussion
4.1. CAP3 Was not Required for Proteolytic ENaC Activation, Albeit Affecting its Protein Abundance
4.2. Aldosterone-Dependent ENaC Activation, but not NCC Activity was Restored in Na+-Deprived CAP1/CAP3 Dko Mice
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- G. Santulli, M. Ciccarelli, B. Trimarco, et G. Iaccarino, « Physical activity ameliorates cardiovascular health in elderly subjects: the functional role of the β adrenergic system », Front. Physiol., vol. 4, 2013, doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00209. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Weinberger, « Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in Humans », Hypertension, vol. 27, no 3, p. 481-490, mars 1996, doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.27.3.481. [CrossRef]
- J. H. Pratt, « Central Role for ENaC in Development of Hypertension », JASN, vol. 16, no 11, p. 3154-3159, nov. 2005, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005050460. [CrossRef]
- V. Vallet, A. Chraibi, H.-P. Gaeggeler, J.-D. Horisberger, et B. C. Rossier, « An epithelial serine protease activates the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel », Nature, vol. 389, no 6651, p. 607-610, oct. 1997, doi: 10.1038/39329. [CrossRef]
- D. Andreasen, G. Vuagniaux, N. Fowler-Jaeger, E. Hummler, et B. C. Rossier, « Activation of Epithelial Sodium Channels by Mouse Channel Activating Proteases (mCAP) Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes Requires Catalytic Activity of mCAP3 and mCAP2 but not mCAP1 », JASN, vol. 17, no 4, p. 968-976, avr. 2006, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005060637. [CrossRef]
- G. Vuagniaux, V. Vallet, N. F. Jaeger, E. Hummler, et B. C. Rossier, « Synergistic Activation of ENaC by Three Membrane-bound Channel-activating Serine Proteases (mCAP1, mCAP2, and mCAP3) and Serum- and Glucocorticoid-regulated Kinase (Sgk1) in Xenopus Oocytes », Journal of General Physiology, vol. 120, no 2, p. 191-201, août 2002, doi: 10.1085/jgp.20028598. [CrossRef]
- R. Zachar et al., « Mannan-binding lectin serine protease-2 (MASP-2) in human kidney and its relevance for proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel », Sci Rep, vol. 12, no 1, p. 15955, sept. 2022, doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20213-8. [CrossRef]
- D. Anand, E. Hummler, et O. J. Rickman, « ENaC activation by proteases », Acta Physiologica, vol. 235, no 1, mai 2022, doi: 10.1111/apha.13811. [CrossRef]
- T. R. Kleyman et D. C. Eaton, « Regulating ENaC’s gate », American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, vol. 318, no 1, p. C150-C162, janv. 2020, doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00418.2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Planès et al., « ENaC-mediated alveolar fluid clearance and lung fluid balance depend on the channel-activating protease 1 », EMBO Mol Med, vol. 2, no 1, p. 26-37, janv. 2010, doi: 10.1002/emmm.200900050. [CrossRef]
- S. Malsure et al., « Colon-Specific Deletion of Epithelial Sodium Channel Causes Sodium Loss and Aldosterone Resistance », JASN, vol. 25, no 7, p. 1453-1464, juill. 2014, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013090936. [CrossRef]
- S. Frateschi et al., « Mutations of the Serine Protease CAP1/Prss8 Lead to Reduced Embryonic Viability, Skin Defects, and Decreased ENaC Activity », The American Journal of Pathology, vol. 181, no 2, p. 605-615, août 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.05.007. [CrossRef]
- N. Picard et al., « Defective ENaC Processing and Function in Tissue Kallikrein-deficient Mice », Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 283, no 8, p. 4602-4611, févr. 2008, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705664200. [CrossRef]
- Z. Chen et al., « Regulation of epithelial sodium channels in urokinase plasminogen activator deficiency », American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, vol. 307, no 8, p. L609-L617, oct. 2014, doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00126.2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Keppner et al., « Deletion of the serine protease CAP2/Tmprss4 leads to dysregulated renal water handling upon dietary potassium depletion », Sci Rep, vol. 9, no 1, p. 19540, déc. 2019, doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55995-x. [CrossRef]
- C.-H. Lai et al., « Matriptase Complexes and Prostasin Complexes with HAI-1 and HAI-2 in Human Milk: Significant Proteolysis in Lactation », PLoS ONE, vol. 11, no 4, p. e0152904, avr. 2016, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152904. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang, J. Chao, et L. Chao, « Adenovirus-mediated human prostasin gene delivery is linked to increased aldosterone production and hypertension in rats », American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, vol. 284, no 4, p. R1031-R1036, avr. 2003, doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00660.2002. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhu et al., « Prostasin: A Possible Candidate Gene for Human Hypertension », American Journal of Hypertension, vol. 21, no 9, p. 1028-1033, sept. 2008, doi: 10.1038/ajh.2008.224. [CrossRef]
- O. Olivieri et al., « Urinary Prostasin: A Candidate Marker of Epithelial Sodium Channel Activation in Humans », Hypertension, vol. 46, no 4, p. 683-688, oct. 2005, doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000184108.12155.6b. [CrossRef]
- D. Essigke et al., « Sodium retention in nephrotic syndrome is independent of the activation of the membrane-anchored serine protease prostasin (CAP1/PRSS8) and its enzymatic activity », Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol, vol. 474, no 6, p. 613-624, juin 2022, doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02682-y. [CrossRef]
- E. Ehret et al., « Kidney-Specific CAP1/Prss8-Deficient Mice Maintain ENaC-Mediated Sodium Balance through an Aldosterone Independent Pathway », IJMS, vol. 23, no 12, p. 6745, juin 2022, doi: 10.3390/ijms23126745. [CrossRef]
- S. Friis et al., « A Matriptase-Prostasin Reciprocal Zymogen Activation Complex with Unique Features », Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 288, no 26, p. 19028-19039, juin 2013, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.469932. [CrossRef]
- L. Holt-Danborg et al., « Insights into the regulation of the matriptase-prostasin proteolytic system », Biochemical Journal, vol. 477, no 22, p. 4349-4365, nov. 2020, doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200630. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Su et al., « Natural Endogenous Human Matriptase and Prostasin Undergo Zymogen Activation via Independent Mechanisms in an Uncoupled Manner », PLoS ONE, vol. 11, no 12, p. e0167894, déc. 2016, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167894. [CrossRef]
- B. N. Bohnert et al., « Aprotinin prevents proteolytic epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activation and volume retention in nephrotic syndrome », Kidney International, vol. 93, no 1, p. 159-172, janv. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.07.023. [CrossRef]
- K. List et al., « Epithelial Integrity Is Maintained by a Matriptase-Dependent Proteolytic Pathway », The American Journal of Pathology, vol. 175, no 4, p. 1453-1463, oct. 2009, doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090240. [CrossRef]
- E. Hummler et al., « The Channel-Activating Protease CAP1/Prss8 Is Required for Placental Labyrinth Maturation », PLoS ONE, vol. 8, no 2, p. e55796, févr. 2013, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055796. [CrossRef]
- R. Perrier et al., « Severe Salt–Losing Syndrome and Hyperkalemia Induced by Adult Nephron–Specific Knockout of the Epithelial Sodium Channel α -Subunit », JASN, vol. 27, no 8, p. 2309-2318, août 2016, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015020154. [CrossRef]
- E. Boscardin et al., « Severe hyperkalemia is rescued by low-potassium diet in renal βENaC-deficient mice », Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol, vol. 469, no 10, p. 1387-1399, oct. 2017, doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-1990-2. [CrossRef]
- E. Boscardin et al., « Plasma PotassiumDetermines NCC Abundance in Adult Kidney-Specific γ ENaC Knockout », JASN, vol. 29, no 3, p. 977-990, mars 2018, doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017030345. [CrossRef]
- G. Vuagniaux et al., « Activation of the Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel by the Serine Protease mCAP1 Expressed in a Mouse Cortical Collecting Duct Cell Line », JASN, vol. 11, no 5, p. 828-834, mai 2000, doi: 10.1681/ASN.V115828. [CrossRef]
- P. Kota, A. García-Caballero, H. Dang, M. Gentzsch, M. J. Stutts, et N. V. Dokholyan, « Energetic and Structural Basis for Activation of the Epithelial Sodium Channel by Matriptase », Biochemistry, vol. 51, no 16, p. 3460-3469, avr. 2012, doi: 10.1021/bi2014773. [CrossRef]
- S. N. Verouti, E. Boscardin, E. Hummler, et S. Frateschi, « Regulation of blood pressure and renal function by NCC and ENaC: lessons from genetically engineered mice », Current Opinion in Pharmacology, vol. 21, p. 60-72, avr. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2014.12.012. [CrossRef]
- C. Leyvraz et al., « The epidermal barrier function is dependent on the serine protease CAP1/Prss8 », Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 170, no 3, p. 487-496, août 2005, doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501038. [CrossRef]
- H. Yin et al., « Matriptase Deletion Initiates a Sjögren’s Syndrome-Like Disease in Mice », PLoS ONE, vol. 9, no 2, p. e82852, févr. 2014, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082852. [CrossRef]
- T. Higashi et al., « EpCAM proteolysis and release of complexed claudin-7 repair and maintain the tight junction barrier », Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 222, no 1, p. e202204079, janv. 2023, doi: 10.1083/jcb.202204079. [CrossRef]
- G. Crisante et al., « The CAP1/Prss8 catalytic triad is not involved in PAR2 activation and protease nexin-1 (PN-1) inhibition », FASEB j., vol. 28, no 11, p. 4792-4805, nov. 2014, doi: 10.1096/fj.14-253781. [CrossRef]
- S. Frateschi et al., « PAR2 absence completely rescues inflammation and ichthyosis caused by altered CAP1/Prss8 expression in mouse skin », Nat Commun, vol. 2, no 1, p. 161, sept. 2011, doi: 10.1038/ncomms1162. [CrossRef]
- K. List et al., « Deregulated matriptase causes ras -independent multistage carcinogenesis and promotes ras -mediated malignant transformation », Genes Dev., vol. 19, no 16, p. 1934-1950, août 2005, doi: 10.1101/gad.1300705. [CrossRef]
- R. Szabo et al., « Reduced Prostasin (CAP1/PRSS8) Activity Eliminates HAI-1 and HAI-2 Deficiency–Associated Developmental Defects by Preventing Matriptase Activation », PLoS Genet, vol. 8, no 8, p. e1002937, août 2012, doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002937. [CrossRef]
- M. Kawaguchi et al., « Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-2 stabilizes Epcam and maintains epithelial organization in the mouse intestine », Commun Biol, vol. 2, no 1, p. 11, janv. 2019, doi: 10.1038/s42003-018-0255-8. [CrossRef]
- R. Szabo, L. K. Callies, et T. H. Bugge, « Matriptase drives early-onset intestinal failure in a mouse model of congenital tufting enteropathy », Development, p. dev.183392, janv. 2019, doi: 10.1242/dev.183392. [CrossRef]
- T. Breiderhoff et al., « Deletion of claudin-10 rescues claudin-16–deficient mice from hypomagnesemia and hypercalciuria », Kidney International, vol. 93, no 3, p. 580-588, mars 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.08.029. [CrossRef]
- R. H. Oakley et al., « Cardiomyocyte glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors directly and antagonistically regulate heart disease in mice », Sci. Signal., vol. 12, no 577, p. eaau9685, avr. 2019, doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau9685. [CrossRef]
- K. List et al., « Epithelial Integrity Is Maintained by a Matriptase-Dependent Proteolytic Pathway », The American Journal of Pathology, vol. 175, no 4, p. 1453-1463, oct. 2009, doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090240. [CrossRef]
- M. Traykova-Brauch et al., « An efficient and versatile system for acute and chronic modulation of renal tubular function in transgenic mice », Nat Med, vol. 14, no 9, p. 979-984, sept. 2008, doi: 10.1038/nm.1865. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Sorensen et al., « Rapid dephosphorylation of the renal sodium chloride cotransporter in response to oral potassium intake in mice », Kidney International, vol. 83, no 5, p. 811-824, mai 2013, doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.14. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Kaplan, M. D. Plotkin, W.-S. Lee, Z.-C. Xu, J. Lytton, et S. C. Hebert, « Apical localization of the Na-K-Cl cotransporter, rBSC1, on rat thick ascending limbs », Kidney International, vol. 49, no 1, p. 40-47, janv. 1996, doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.6. [CrossRef]
- P. Wu et al., « Effect of Angiotensin II on ENaC in the Distal Convoluted Tubule and in the Cortical Collecting Duct of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Deficient Mice », JAHA, vol. 9, no 7, p. e014996, avr. 2020, doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014996. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




