Submitted:
10 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
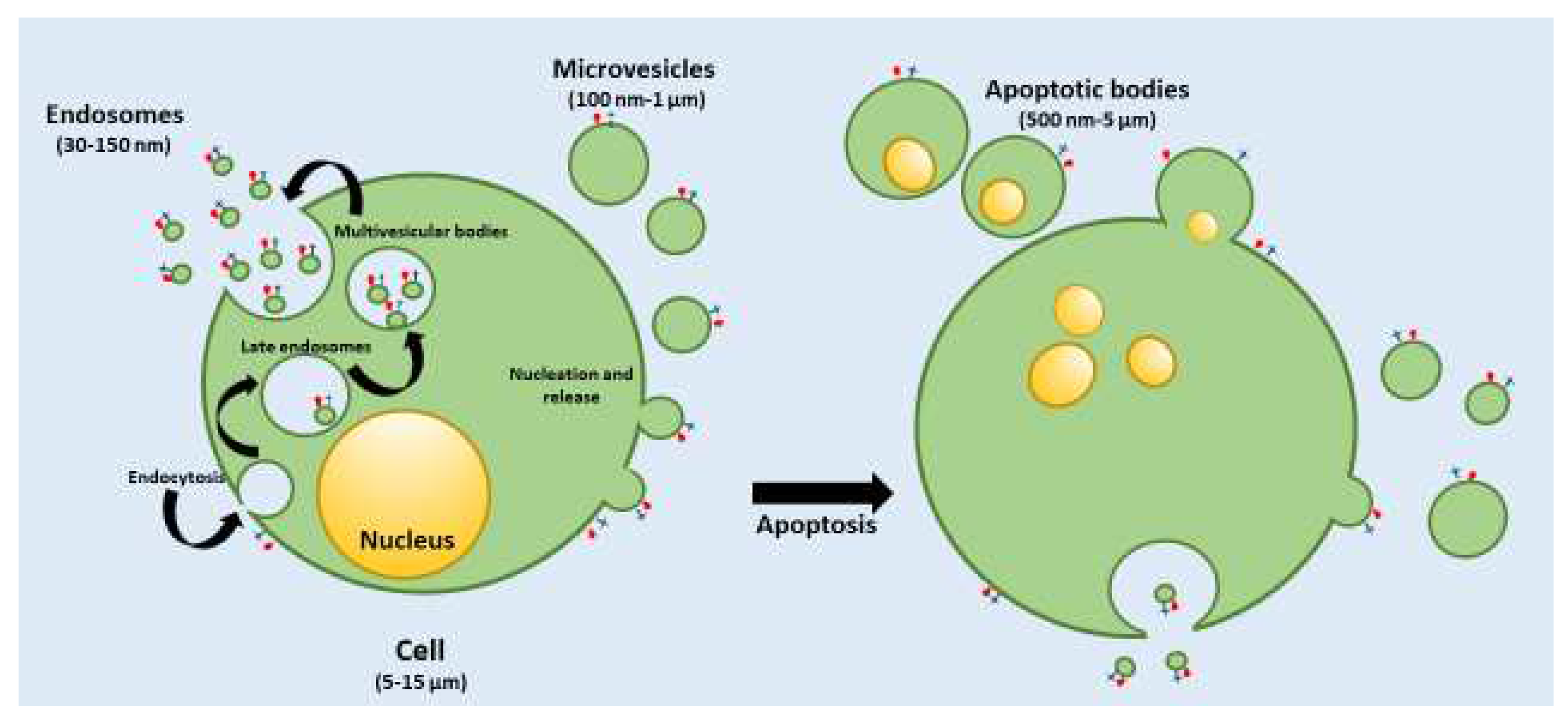
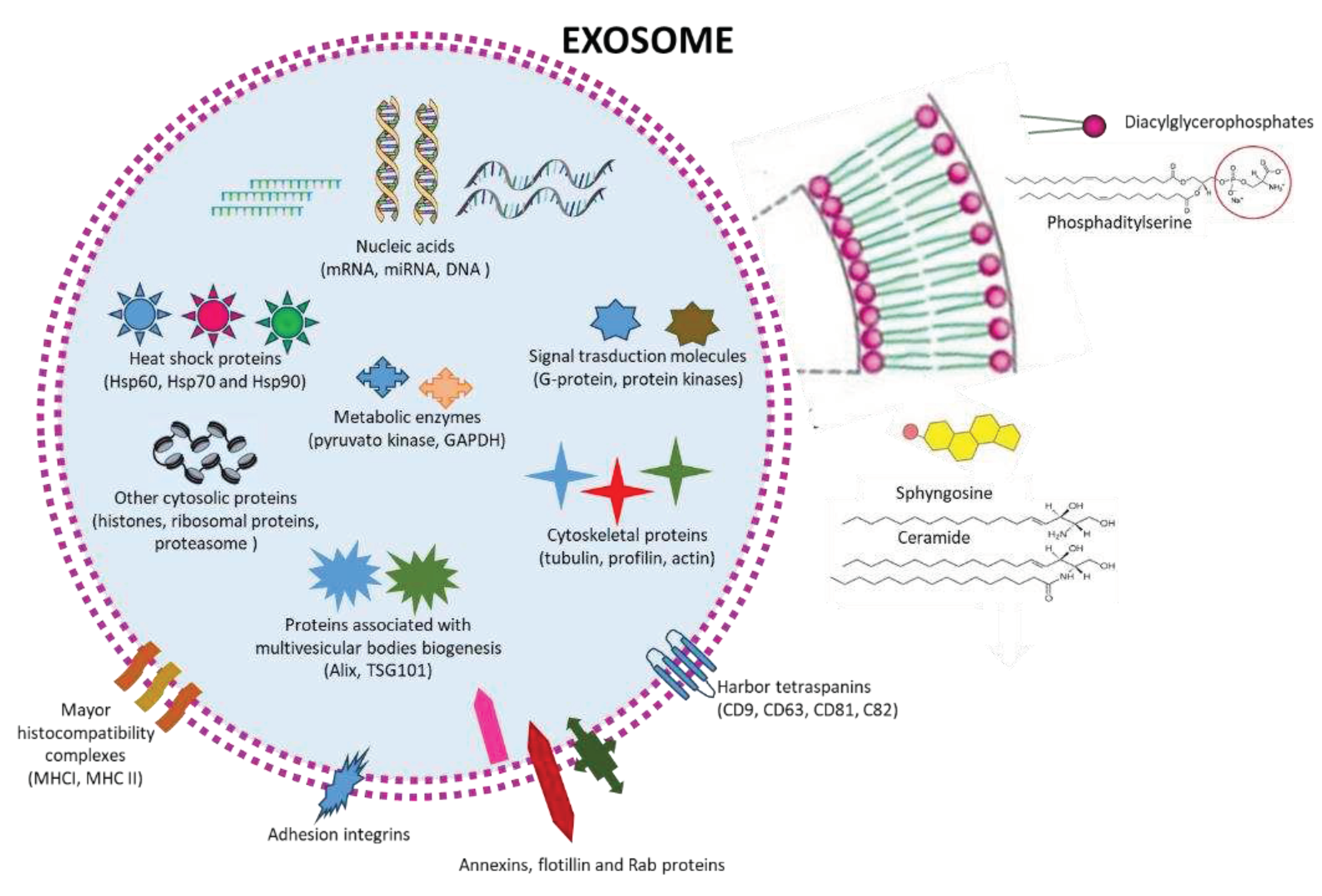
1.1. Classification and characteristics of the different EVs
2. Possible roles of exosomes in therapy
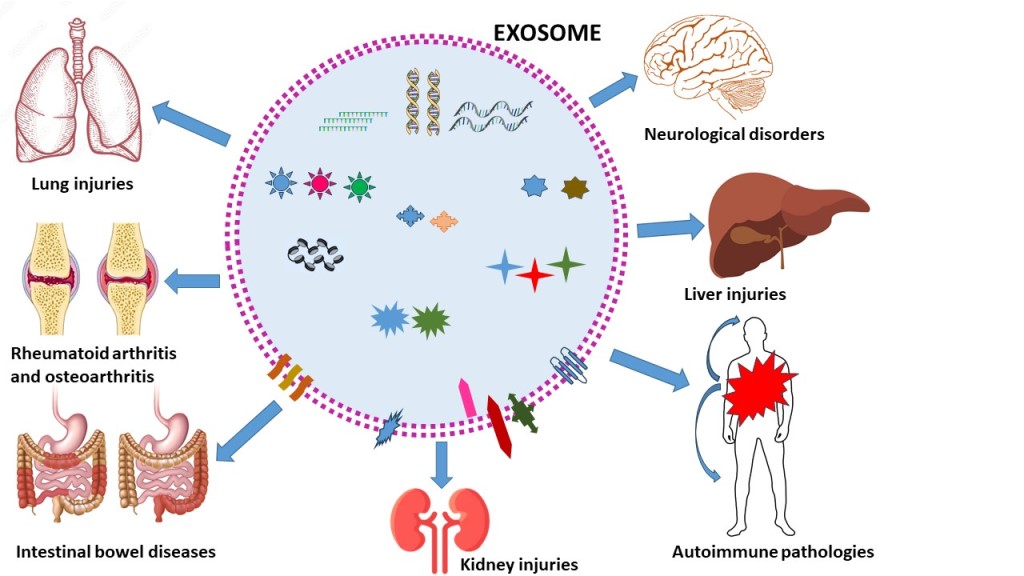
3. Role of EXs in Inflammatory diseases
3.1. Neurological disorders
3.1.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.1.2. Parkinson’s Disease
3.1.3. Ischemic stroke
3.1.4. Multiple sclerosis and autoimmune encephalomyelitis
3.1.5. Spinal cord injury
3.1.6. Traumatic brain injury
3.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
3.4. Lung injuries
3.5. Liver injury
1.4. Kidney injuries
3.6. Intestinal Bowel Disease (IBD)
4. Future perspectives and concluding remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halwani, A.A. Development of Pharmaceutical Nanomedicines: From the Bench to the Market. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14(1), 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Piazzini, V.; Risaliti, L.; Vanti, G.; Casamonti, M.; Wang, M.; Bergonzi, M.C. Nanocarriers: A Successful Tool to Increase Solubility, Stability and Optimise Bioefficacy of Natural Constituents. Curr Med Chem 2019, 26, 4631–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Guccione, C.; Manconi, M.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Vesicles and micelles: Two versatile vectors for the delivery of natural products. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2016, 32, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshawwa, S.Z.; Kassem, A.A.; Farid, R.M.; Mostafa, S.K.; Labib, G.S. Nanocarrier Drug Delivery Systems: Characterization, Limitations, Future Perspectives and Implementation of Artificial Intelligence. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatto, S.; Morad, G.; Guo, P.; Moses, M.A. The role of extracellular vesicles in the physiological and pathological regulation of the blood-brain barrier. FASEB BioAdvances 2021, 3(9), 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Feghhi, M.; Etemadi, T. A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun Signal CCS 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Guo, S.; Ren, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, X. Current Strategies for Exosome Cargo Loading and Targeting Delivery. Cells 2023, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsergent, E.; Grisard, E.; Buchrieser, J.; Schwartz, O.; Théry, C.; Lavieu, G. Quantitative characterization of extracellular vesicle uptake and content delivery within mammalian cells. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E. Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication. Biology 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci Rep 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.W.; Schmidtmann, M:; D’Souza-Schorey, C. The ins and outs of microvesicles. FASEB BioAdvances 2021, 3, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.Y.; Kee, L.T.; Al-Masawa, M.E.; Lee, Q.H.; Subramaniam, T.; Kok, D.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. Scalable Production of Extracellular Vesicles and Its Therapeutic Values: A Review. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryabin, G.O.; Komelkov, A.V.; Savelyeva, E.E.; Tchevkina, E.M. Lipid Rafts in Exosome Biogenesis. Biochem Biokhimiia 2020, 85, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal CCS 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, A.; Kabagwira, J.; Senthil, G.N.; Wall, N.R. Internalization of Exosomes through Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis. Mol Cancer Res MCR 2019, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. ClinicalTrials.gov. Accessed July 29, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=exosomes&aggFilters=status:com.
- Yu, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 2014, 15, 4142–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leñero, C.; Kaplan, L.D.; Best, T.M.; Kouroupis, D. CD146+ Endometrial-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Subpopulation Possesses Exosomal Secretomes with Strong Immunomodulatory miRNA Attributes. Cells 2022, 11, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroupis, D.; Kaplan, L.D.; Best, T.M. Human infrapatellar fat pad mesenchymal stem cells show immunomodulatory exosomal signatures. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Pulliam, L. Exosomes as mediators of neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cesca, F.; Loers, G.; Schweizer, M.; Buck, F.; Benfenati, F.; Schachner, M.; Kleene, R. Synapsin I is an oligomannose-carrying glycoprotein, acts as an oligomannose-binding lectin, and promotes neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival when released via glia-derived exosomes. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 7275–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.R.; Robinson, M.B.; Gifondorwa, D.J.; Tytell, M.; Milligan, C.E. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 release in astrocytes: role of signaling kinases. Dev Neurobiol 2007, 67, 1815–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytell, M. Release of heat shock proteins (Hsps) and the effects of extracellular Hsps on neural cells and tissues. Int J Hyperth 2005, 21, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Verrilli, M.A.; Picou, F.; Court, F.A. Schwann cell-derived exosomes enhance axonal regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Glia 2013, 61, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, H.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, F.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Liu, F.X.; Zhang, Y.K. Potential regulatory effects of stem cell exosomes on inflammatory response in ischemic stroke treatment. World J Stem Cells 2023, 15, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perets, N.; Hertz, S.; London, M.; Offen, D. Intranasal administration of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates autistic-like behaviors of BTBR mice. Mol Autism 2018, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.M.; Dennahy, I.S.; Bhatti, U.F.; Halaweish, I.; Xiong, Y.; Chang, P.; Nikolian, V.C.; Chtraklin, K.; Brown, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M.; Buller, B.; Alam, H.B. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Provide Neuroprotection and Improve Long-Term Neurologic Outcomes in a Swine Model of Traumatic Brain Injury and Hemorrhagic Shock. J Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, L.; Bari, E.; Jommi, C.; Tartara, F.; Armocida, D.; Garbossa, D.; Cofano, F.; Torre, M.L.; Segale, L. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and extracellular vesicles for neurodegenerative diseases: Risk-benefit profile and next steps for the market access. Bioact Mater 2023, 29, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabpour, M.; Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 97, 107823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andjus, P.; Kosanović, M.; Milićević, K.; Gautam, M.; Vainio, S.J.; Jagečić, D.; Kozlova, E.N.; Pivoriūnas, A.; Chachques, J.C.; Sakaj, M.; Brunello, G.; Mitrecic, D.; Zavan, B. Extracellular Vesicles as Innovative Tool for Diagnosis, Regeneration and Protection against Neurological Damage. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Buller, B.; Chopp, M. Exosomes - beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat Rev Neurol 2019, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Hao, Y.; Han, F.; Hong, J.; Zheng, W.; Ma, S.; Yang, L.; Cheng, G. High-efficiency brain-targeted intranasal delivery of BDNF mediated by engineered exosomes to promote remyelination. Biomater Sci 2022, 10, 5707–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, R.; Madhu, L.N.; Attaluri, S.; Gitaí, D.L.G.; Pinson, M.R.; Kodali, M.; Shetty, G.; Zanirati, G.; Kumar, S.; Shuai, B.; Weintraub, S.T.; Shetty, A.K. Extracellular vesicles from human iPSC-derived neural stem cells: miRNA and protein signatures, and anti-inflammatory and neurogenic properties. J Extracell Vesicles 2020, 9, 1809064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhya, R.; Zingg, W.; Shetty, S.; Shetty, A.K. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: Neuroreparative properties and role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. J Control Release 2020, 323, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Hao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Cui, M. Microglial Exosomes in Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Mol Neurosci 2021, 14, 630808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer-Albers, E.M.; Bretz, N.; Tenzer, S.; Winterstein, C.; Möbius, W.; Berger, H.; Nave, K.A.; Schild, H.; Trotter, J. Oligodendrocytes secrete exosomes containing major myelin and stress-protective proteins: Trophic support for axons? Proteomics Clin Appl 2007, 1, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimardanova, A.A.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Chulpanova, D.S.; James, V.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Rizvanov, A.A. Extracellular vesicles in the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases. Neural Regen Res 2020, 15, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elia, C.A.; Losurdo, M.; Malosio, M.L.; Coco, S. Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Pleiotropic Effects on Amyloid-β, Inflammation, and Regeneration: A Spark of Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease from Tiny Structures? BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol 2019, 41, e1800199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Godoy, M.A.; Saraiva, L.M.; de Carvalho, L.R.P.; Vasconcelos-Dos-Santos, A.; Beiral, H.J.V.; Ramos, A.B.; Silva, L.R.P.; Leal, R.B.; Monteiro, V.H.S.; Braga, C.V.; de Araujo-Silva, C.A.; Sinis, L.C.; Bodart-Santos, V.; Kasai-Brunswick, T.H.; Alcantara, C.L.; Lima, A.P.C.A.; da Cunha-E Silva, N.L.; Galina, A.; Vieyra, A.; De Felice, F.G.; Mendez-Otero, R.; Ferreira, S.T. Mesenchymal stem cells and cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect hippocampal neurons from oxidative stress and synapse damage induced by amyloid-β oligomers. J Biol Chem 2018, 293, 1957–1975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Sakai, S.; Mitsutake, S.; Okada, M.; Tahara, H.; Furukawa, J.; Fujitani, N.; Shinohara, Y.; Igarashi, Y. Decreased amyloid-β pathologies by intracerebral loading of glycosphingolipid-enriched exosomes in Alzheimer model mice. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 24488–24498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.H.; Wu, J.; Mou, F.F.; Xie, W.H.; Wang, F.B.; Wang, Q.L.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.W.; Dong, Y.R.; Liu, J.R.; Guo, H.D. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate cognitive decline by rescuing synaptic dysfunction and regulating inflammatory responses in APP/PS1 mice. FASEB J 2018, 32, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhai, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, G. The Regulatory Functionality of Exosomes Derived from hUMSCs in 3D Culture for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Small Weinh Bergstr Ger. 2020, 16, e1906273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, A.S.; Yuan, X.; Sun, L.; Duke, L.C.; Vreones, M.P.; Carrier, A.N.; Kenyon, S.M.; Carver, S.R.; Benthem, S.D.; Stimmell, A.C.; Moseley, S.C.; Hike, D.; Grant, S.C.; Wilber, A.A.; Olcese, J.M.; Meckes, D.G. Jr. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8129–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, L.C.; Katsuda, T.; Gailhouste, L.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Int Immunol 2017, 29, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, F.; Ekstrom, K.; Nazarenko, I.; Maugeri, M.; Valadi, H.; Hill, A.F.; Camussi, G.; Nawaz, M. Non-coding RNAs in Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Deciphering Regulatory Roles in Stem Cell Potency, Inflammatory Resolve, and Tissue Regeneration. Front Genet. 2017, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Jia, J.; Wang, Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppresses iNOS Expression and Ameliorates Neural Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. J Alzheimers Dis 2018, 61, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Zhao, Y.; Gupta, R.; Plotnikova, E.G.; He, Z.; Patel, T.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release 2015, 207, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, R.; Bojar, D.; Rizzi, G.; Hamri, G.C.; El-Baba, M.D.; Saxena, P.; Ausländer, S.; Tan, K.R.; Fussenegger, M. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhao, R.; Lu, Z.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. Intranasal Administration of Self-Oriented Nanocarriers Based on Therapeutic Exosomes for Synergistic Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Tu, Z.; Yang, D.; Hu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, B.; Hou, S. Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Neurosci Lett 2022, 769, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhu, H.; Yu, F.; Zhao, W. Resveratrol-loaded macrophage exosomes alleviate multiple sclerosis through targeting microglia. J Control Release 2023, 353, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazifar, M.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Pone, E.J.; Yeri, A.; Lässer, C.; Segaliny, A.I.; McIntyre, L.L.; Shelke, G.V.; Hutchins, E.; Hamamoto, A.; Calle, E.N.; Crescitelli, R.; Liao, W.; Pham, V.; Yin, Y.; Jayaraman, J.; Lakey, J.R.T.; Walsh, C.M.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.; Lotvall, J.; Zhao, W. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Nanotherapeutics for Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Disorders. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6670–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F.; Liang, H.; Sun, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Chen, X. Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances neuroprotective effects of neural stem cell exosomes after spinal cord injury via an miR-219a-2-3p/YY1 mechanism. Aging 2019, 11, 12278–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Rong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ge, X.; Ji, C.; Jiang, D.; Gong, F.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Kong, F.; Gu, C.; Fan, J.; Cai, W. Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Silva, M.; Feng, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhong, J.; Zheng, W. Exosomes derived from human placental mesenchymal stem cells enhanced the recovery of spinal cord injury by activating endogenous neurogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hong, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y. Astrocyte-derived exosomes protect hippocampal neurons after traumatic brain injury by suppressing mitochondrial oxidative stress and apoptosis. Aging 2021, 13, 21642–21658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Wang, Y.D.; Shen, D.F.; Zheng, P.D.; Tu, M.D.; You, W.D.; Zhu, Y.R.; Wang, H.; Feng, J.F.; Yang, X.F. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 2022, 17, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Xue, C.; Han, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhao, R.C. MSC-derived exosomes promote recovery from traumatic brain injury via microglia/macrophages in rat. Aging 2020, 12, 18274–18296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lei, B.; Zhang, E.; Gong, P.; Gu, J.; He, L.; Han, L.; Yuan, Z. Targeted Therapy for Inflammatory Diseases with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Derived Exosomes: From Basic to Clinics. Int J Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1757–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol 2018, 201, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.G.; Lim, G.T.; Kwon, S.; Um, W.; Oh, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.; Jo, D.G.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, J.H. Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Adv 2021, 7, eabe0083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Jia, M.; Mei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, C. M2-type exosomes nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage re-polarization. J Control Release 2022, 341, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Zhang, Q.; Mo, X.B.; Lin, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Lu, X.; He, P.; Wu, J.; Guo, Y.F.; Wang, M.J.; Ren, W.Y.; Deng, H.W.; Lei, S.F.; Deng, F.Y. Identification of novel rheumatoid arthritis-associated MiRNA-204-5p from plasma exosomes. Exp Mol Med 2022, 54, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Stöckl, S.; Lukas, C. Herrmann M, Brochhausen C, König MA, Johnstone B, Grässel S. Curcumin-primed human BMSC-derived extracellular vesicles reverse IL-1β-induced catabolic responses of OA chondrocytes by upregulating miR-126-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian Bo, S.; Chen, W.; Chang, L.; Hao Ran, Y.; Hui Hui, G.; Ya Kun, Z.; Wu Kun, X.; Hai Tao, F.; Wen Dan, C. The Research Progress of Exosomes in Osteoarthritis, With Particular Emphasis on the Therapeutic Effect. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 685623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, L.; Fang, X.; Zang, M. Exosome-Encapsulated microRNA-127-3p Released from Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Osteoarthritis Through Regulating CDH11-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J Pain Res 2021, 14, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Lin, R.; Liao, W.; Kang, Y. Exosomal miR-95-5p regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage degradation via histone deacetylase 2/8. J Cell Mol Med 2018, 22, 5354–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liu, G.; Wu, X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med 2021, 11, e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q. MiR-129-5p shuttled by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves IL-1β induced osteoarthritis via targeting HMGB1. Life Sci 2021, 269, 118987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, D.-P.; Xiao, D.-W.; Tian, D.-C.; Su, Y.-W.; Jin, S.-F. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via p38, ERK, and Akt pathways. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2019, 55, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, K.; Ge, G.; Zhang, D.; Bai, J.; Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Xu, T.; Xu, M.; Long, X.; et al. Exosomes derived from miR-155-5p-overexpressing synovial mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteoarthritis via enhancing proliferation and migration, attenuating apoptosis, and modulating extracellular matrix secretion in chondrocytes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 37, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, S.; Ruiz, M.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Xing, J.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Tian, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Xu, X.; Yi, P.; Hao, Y. Curcumin reinforces MSC-derived exosomes in attenuating osteoarthritis via modulating the miR-124/NF-kB and miR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 10855–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Qian, D.; Gao, P.; Qin, T.; Jiang, T.; Yi, J.; Xu, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Yin, G. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma administration in site mediate cartilage protection in subtalar osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, W.C.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Hui, J.H.P.; Toh, W.S. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthr Cartil 2016, 24, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.-C.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Yin, W.-J.; Guo, S.-C.; Zhang, C.-Q. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics 2017, 7, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 83 Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int J Biol Sci 2016, 12, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ji, J.; Fu, T.; Yang, J.; Gu, Z. The effect of exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2018, 77, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Mortaz, E.; Alipoor, S.D.; Varahram, M.; et al. Exosomes in Severe Asthma: Update in Their Roles and Potential in Therapy. BioMed Res Int 2018, 2862187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Li, X.; Bi, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, K. Exosome membrane-modified M2 macrophages targeted nanomedicine: Treatment for allergic asthma. J Control Release 2021, 338, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiao, K.; Xie, L. Advances in the use of exosomes for the treatment of ALI/ARDS. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 971189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yi, X.; Lv, H.; Sui, X.; Lu, P.; Li, L.; An, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, H.; Chen, G. Microrna-377-3p released by mesenchymal stem cell exosomes ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting RPTOR to induce autophagy. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 657. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Cui, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J. Exosomal microrna-16-5p from adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes Tlr4-mediated M2 macrophage polarization in septic lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 98, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Goodwin, A.J.; Cook, J.A.; Halushka, P.V.; Chang, E.; Zingarelli, B.; Fan, H. Exosomes from endothelial progenitor cells improve outcomes of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care 2019, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, L.; Gu, W.; Zhu, L. Exosomes derived from endothelial progenitor cells ameliorate acute lung injury by transferring mir-126. Exp Cell Res 2018, 370, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gong, L.; Peng, X; Richard, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Fornage, M.; Alcorn, J.L.; Wang, D.A.; Zhang, J.; Fornage, M.; Alcorn, J.L.; Wang, D. Exosome mir-371b-5p promotes proliferation of lung alveolar progenitor type ii cells by using pten to orchestrate the Pi3k/Akt signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther 2017, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ni, J.; Shen, G.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xia, S.; Pan, S.; Qu, H.; Li, X. Upregulation of endothelial cell-derived exosomal microrna-125b-5p protects from sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting topoisomerase ii alpha. Inflammation Res 2021, 70, 205–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, D:, Wen; Tang, X.; Qi, D.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhu, T. Adipose-derived exosomes protect the pulmonary endothelial barrier in ventilator-induced lung injury by inhibiting the Trpv4/Ca(2+) signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2020, 318, L723–l41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Lee, Y.; Ha, J.; Han, S.; Lee, M. Engineering exosomes for pulmonary delivery of peptides and drugs to inflammatory lung cells by inhalation. J Control Release 2021, 330, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Long, J.; Meng, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. Immune cells-derived exosomes: A promising strategy for COVID-19 treatment. Clin Transl Discov 2022, 2, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrani, M.I.; Bellio, M.A.; Sagel, A.; Saylor, M.; Kapp, W.; VanOsdol, K.; Haskell, G.; Stewart, D.; Abdullah, Z.; Santos, I.; Milberg, J.; Arango, A.; Mitrani, A.; Shapiro, G.C. Case report: Administration of amniotic fluid-derived nanoparticles in three severely ill covid-19 patients. Front Med 2021, 8, 583842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, V.; Sengupta, S.; Lazo, A.; Woods, P.; Nolan, A.; Bremer, N. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19. Stem Cells Dev 2020, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; Sengupta, V.; Qian, S.; Ransom, J.T.; Suzuki, S.; Park, D.J.; Melson, T.I.; Williams, B.P.; Walsh, J.J.; Awili, M. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Infusion for the Treatment of Respiratory Failure From COVID-19: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Dosing Clinical Trial. CHEST article in press. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Investig 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shang, J.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Liang, Y.; Lai, C.; Feng, T.; Zhong, D.; Zou, H.; Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Yan, S.; Chen, J.; Yao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, X. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and remodeling choline metabolism. J Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21(1), 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknam, B.; Baghaei, K.; Mahmoud Hashemi, S.; Hatami, B.; Reza Zali, M.; Amani, D. Human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes enriched by miR-124 promote an anti-fibrotic response in an experimental model of liver fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 119, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Piao, C; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Ma, H.; Wang, H. ADSCs-exo attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury after hepatectomy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. J Cell Physiol 2023, 238, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Yim, J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, W. Exosomes: Nomenclature, Isolation, and Biological Roles in Liver Diseases. Biomol Ther 2023, 31, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, K.; Hazrati, A.; Soudi, S.; Roshangar, L.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Ahmadi, M. Combinational administration of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and metformin reduces inflammatory responses in an in vitro model of insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Heliyon 2023, 9(5), e15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrojerdi, A.; Soudi, S.; Hosseini, A.Z.; Khaligh, S.G.; Hashemi, S.M. The combination of mesenchymal stem cell- and hepatocyte-derived exosomes, along with imipenem, ameliorates inflammatory responses and liver damage in a sepsis mouse model. Life Sci 2023, 326, 121813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Tang, D.; Hao, X.; Liu, E.; Li, W.; Shi, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome alleviates sepsis- associated acute liver injury by suppressing MALAT1 through microRNA-26a-5p: an innovative immunopharmacological intervention and therapeutic approach for sepsis. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1157793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellakany, A.R.; El Baz, H.; Shoheib, Z.S.; Elzallat, M.; Ashour, D.S.; Yassen, N.A. Stem cell-derived exosomes as a potential therapy for schistosomal hepatic fibrosis in experimental animals. Pathog Glob Health 2023, 30, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.M.; Pollock, C.A. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Med 2022, 9, 816656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Ferris, A.H. Chronic Kidney Disease. Prim Care 2020, 47, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, R.R.; Juncosa, E.M.; Masereeuw, R.; Lindoso, R.S. Extracellular Vesicles as a Therapeutic Tool for Kidney Disease: Current Advances and Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaishi, K.; Mizue, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Otani, M.; Nakano, M.; Konari, N.; Fujimiya, M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 34842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, N.; Ahmed, I.A.; Hussien, N.I.; Dessouky, A.A.; Farid, A.S.; Elshazly, A.M.; Mostafa, O.; Gazzar, W.B.E.; Sorour, S.M.; Seleem, Y.; Hussein, A.M.; Sabry, D. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorated diabetic nephropathy by autophagy induction through the mTOR signaling pathway. Cells 2018, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Shi, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Huang, H. Exosome secreted from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting autophagy flux and inhibiting apoptosis in podocyte. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shen, L.; Long, C.; Butnaru, D.; Timashev, P.; He, D.; Lin, T.; Xu, T.; Zhang, D.; Wei, G. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against renal interstitial fibrosis through ROS-mediated P38MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 2020, 12, 4998–5014. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiy, C.; Ormanji, M.S.; Maquigussa, E.; Ribeiro, R.S.; da Silva Novaes, A.; Boim, MA. Comparison of the effects of mesenchymal stem cells with their extracellular vesicles on the treatment of kidney damage induced by chronic renal artery stenosis. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 8814574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Shi, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Sun, D. PSC-MSC-derived exosomes protect against kidney fibrosis in vivo and in vitro through the SIRT6/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Stem Cells 2021, 14, 310–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, J.; Liu, W.; Cai, K.; Huang, X.; Peng, L. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carry microRNA-125a to protect against diabetic nephropathy by targeting histone deacetylase 1 and downregulating endothelin-1. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2021, 14, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Niu, X.; Yin, J.Y.; Hu, B.; Guo, S.C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.S. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.R.; Chen, B.P.; Chen, F.; Yang, S.X.; Zhu, C.Y.; Ma, Y.L. Exosomal microRNA-16-5p from human urine-derived stem cells ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through protection of podocyte. J Cell Mol Med 2021, 25, 10798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zuo, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, D. Protective function of exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury through SIRT1 pathway. Life Sci 2020, 255, 117719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zuo, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Sun, D. Exosomes derived from GDNF-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate peritubular capillary loss in tubulointerstitial fibrosis by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9425–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, E.; Muise, A. Inflammatory bowel disease: what very early onset disease teaches us. Gastroenterol Clin 2018, 47, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.M.; Subedi, S.; LeLeiko, N.S. Inflammatory bowel disease. Pediatr Rev 2016, 37, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocansey, D.K.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Mao, F. Exosome-mediated effects and applications in inflammatory bowel disease. Biological Reviews 2020, 95, 1287–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D.; An, Q.; Yue, G.; Jin, Z.; Ding, J.; Hu, Y.; Du, Q.; Xu, J.; Xie, R. Exosome-mediated effects and applications in inflammatory diseases of the digestive system. Eur J Med Res 2022, 27, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yuan, J.T.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qian, H.; Xu, W.R.; Qiu, W.; Mao, F. hucMSC-derived exosomes colitis by regulating macrophage pyroptosis via the miR-378a-5p/ NLRP3 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




