Submitted:
09 August 2023
Posted:
10 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
INTRODUCTION
OBJECTIVE
METHODOLOGY
Ethical approval
Preparation of platelet concentrates
Study design
Study setting
Sample size
Materials
- Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs), namely mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) obtained from minimal surgery procedures.
- Bio Safety Cabinet class II
- Centrifuge
- Inverted Microscope
- CO2 Incubator
- Pipette aid and micropipette
- Water bath
- Hot plate magnetic stirrer
- Dissecting set
- Vacuum pump
- 500 mL Beaker glass
- -MEM medium
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) with fetal bovine serum (FBS)
- Triple express
- Collagenase
- NaHCO3
- Trypan Blue
- 70% Alcohol
- 15 mL and 50 mL conical tube
- 5 cm dan 10 cm petri dish
- 24 wells and 12 wells of microplate
- Unit filter 0,22 μm (Millipore)
- CD34, CD45, CD105 staining
- GATA-4 antibody
- cTnT antibody
- Cardiomyocyte differentiated medium MSDS (SCM102; Sigma Aldrich; material safety data sheet)
- Platelet Rich Fibrin
Experimental procedures
- Isolation and culture of ADSCs from adipose tissue obtained from minimal surgery procedures. Retrieval of ADSCs are accomplished from direct lipectomy using minimal invasive surgical procedures. Freshly obtained raw fat is washed with lactated Ringer’s solution to remove contaminating blood and remaining tumescent solution. The non-buoyant nucleated cells are proteolytically released from the adipose matrix by adding a solution 0.075 % Collagenase I dissolved in α -MEM medium is used to obtain 0.075 % Collagenase I (1 % penicillin/streptomycin) solution. Two other solutions are prepared, a red cell lysis and a growth media solution. To prepare the former, solid NH4Cl is dissolved in distilled water at 160 mM and vacuum sterilized with a 0.22 μm filter prior to aliquoting. The growth media is prepared by adding 10 % FBS and 1 % penicillin/streptomycin solution to α-MEM medium and sterile filtering. Both of these solutions are stored at 4 °C. The supernatant is discarded and, if the red blood cell lysis is desired, the cell pellet is resuspended in 2 mL of 160 mM NH4Cl to lyse any remaining red blood cells. The tubes are then incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Additional NH4Cl were added to lyse any remaining red blood cells. The admixture is centrifuged at 3,300 rpm for 10 min to re-pellet the ADSC-rich fraction; the supernatant is aspirated and the pellet resuspended in 5 mL of growth media. Next, the cell suspension is passed through a 70–100 μm cell strainer to eliminate major acellular debris and then rinsed with 5 mL additional growth media.
- Identification of ADSCs from adipose tissue by Flow Cytometry by observing the expression of CD 105 and the non-expression of CD 34 and CD 45.
- Culture of ADSCs on α −MEM medium and differentiation of cardiomyocytes. For culture, the suspension is plated into T-75 (75 cm2) tissue culture flasks at a density of 100,000 cells/cm2 (approximately 1 flask for every ~6 mL of fat used). The flasks are labeled to indicate that this is the primary isolation passage (P = 0) and incubated overnight at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5 % CO2. After 24 h, the media from the flasks is aspirated and rinsed twice with warm PBS before fresh growth media is added. After 7–10 days the cells will reach 70–80 % confluency and should be passaged or frozen. They should not be allowed to reach 100 % confluency, as this can stimulate differentiation of the cells.
- Preparation and administration of PRF in in vitro cultured ADSCs in treatment group
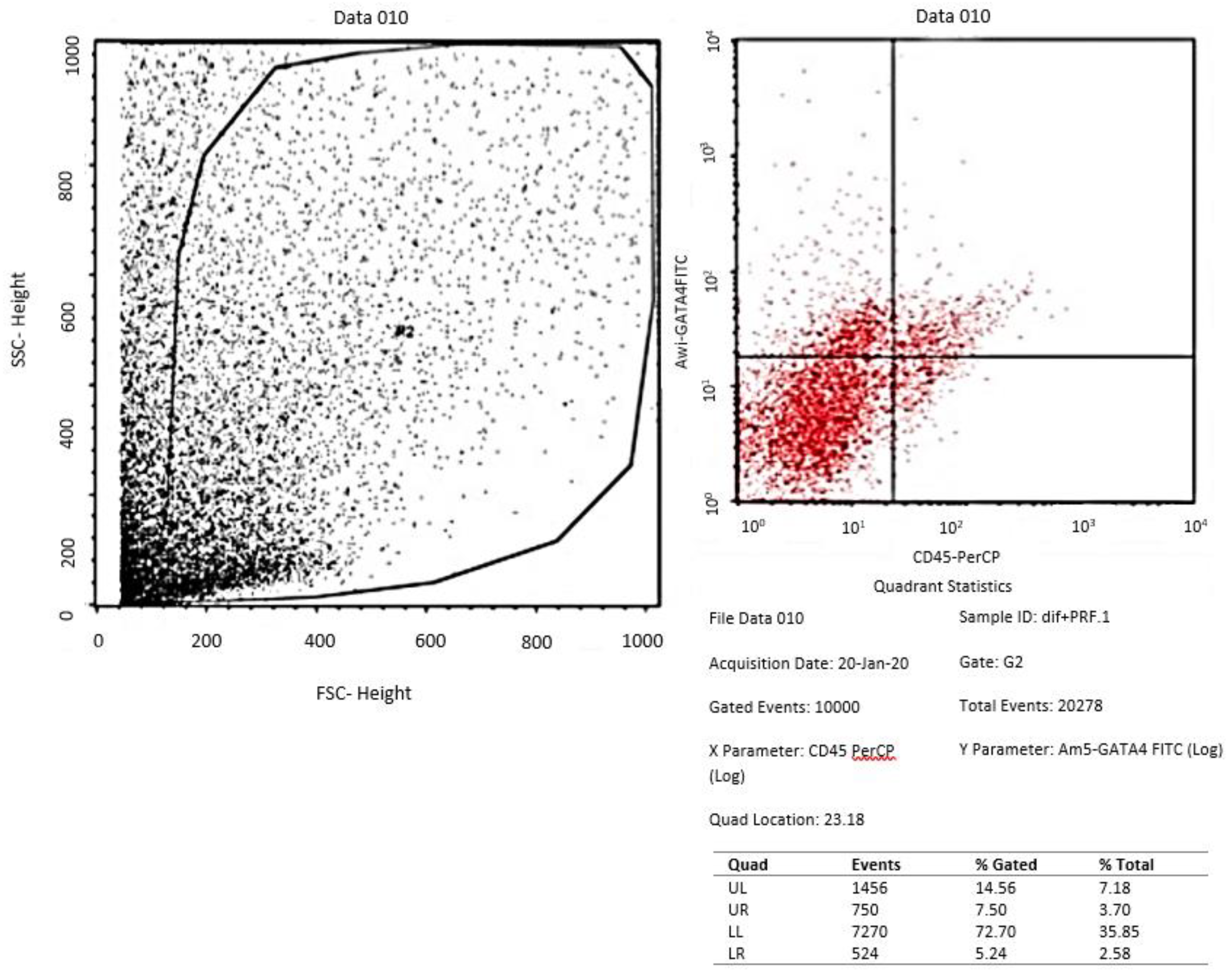
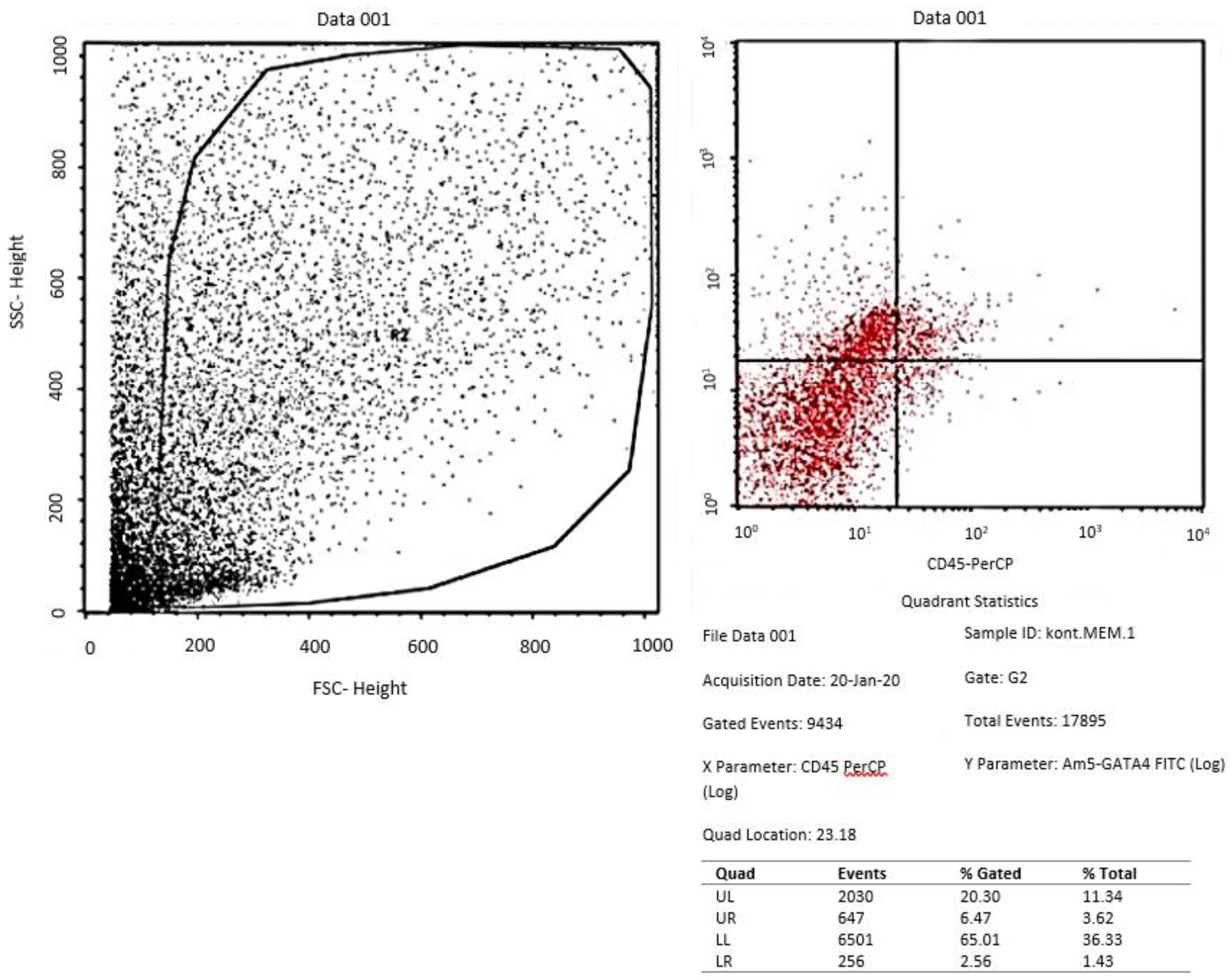
- Evaluation of tissue culture of ADSCs in the three groups with flowcytometry for GATA-4 and Immunocytochemistry for cTnT
Cells counting
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Isolation and culture of ADSCs
Phenotype Characterization of ADSCs
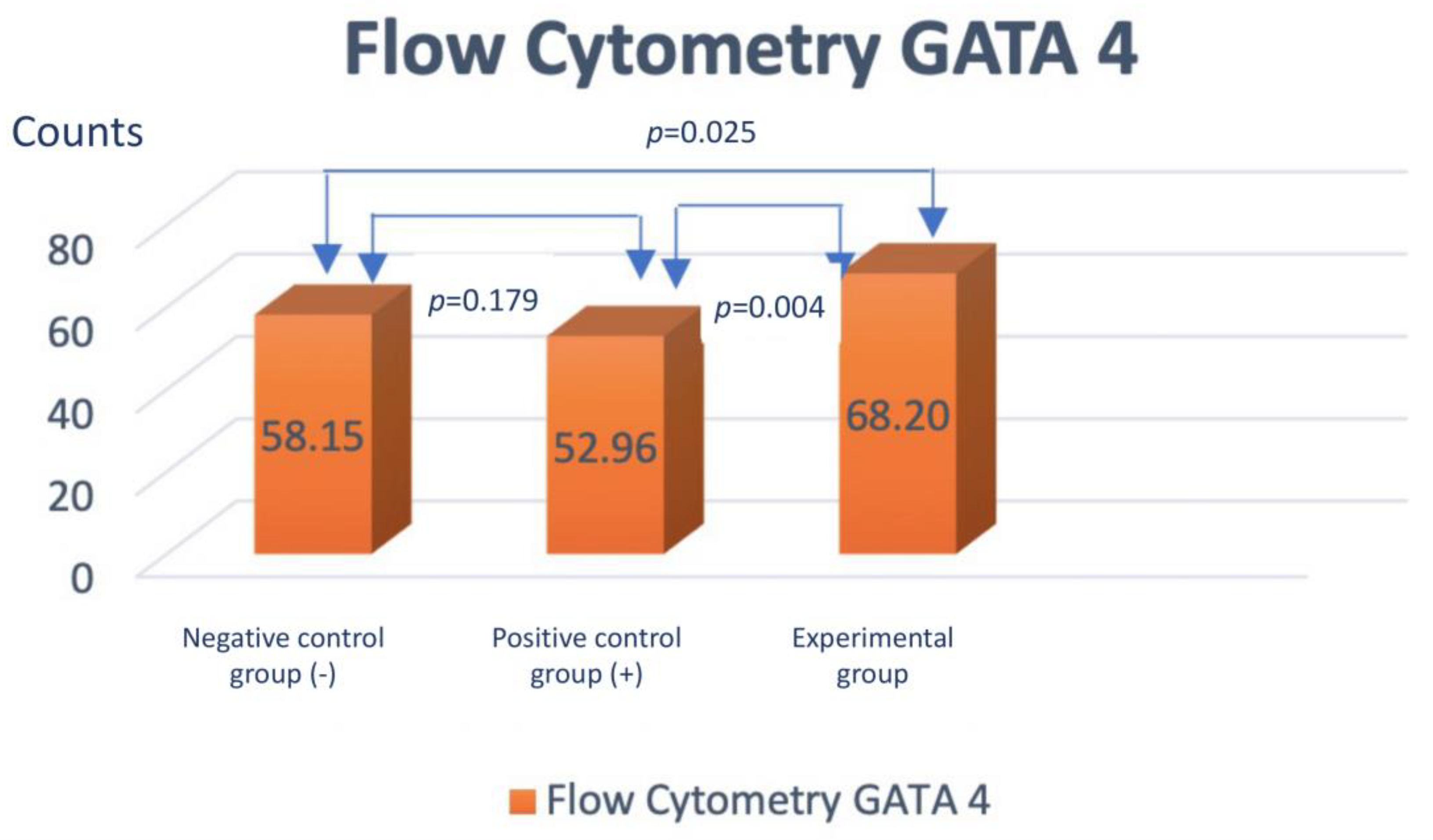
Assessment of GATA-4 differentiation marker cardiomyocyte-like cells differentiation with flowcytometry
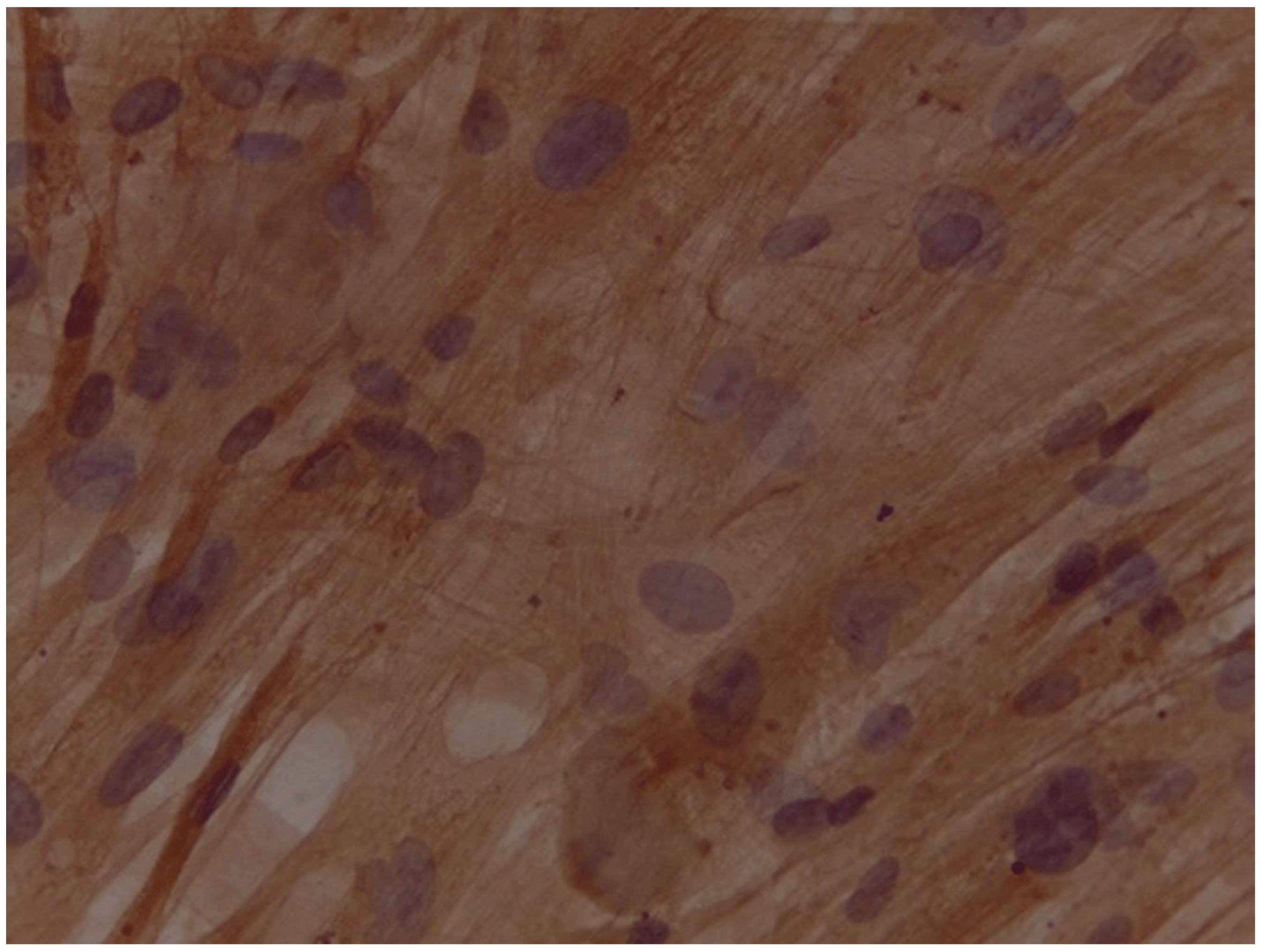
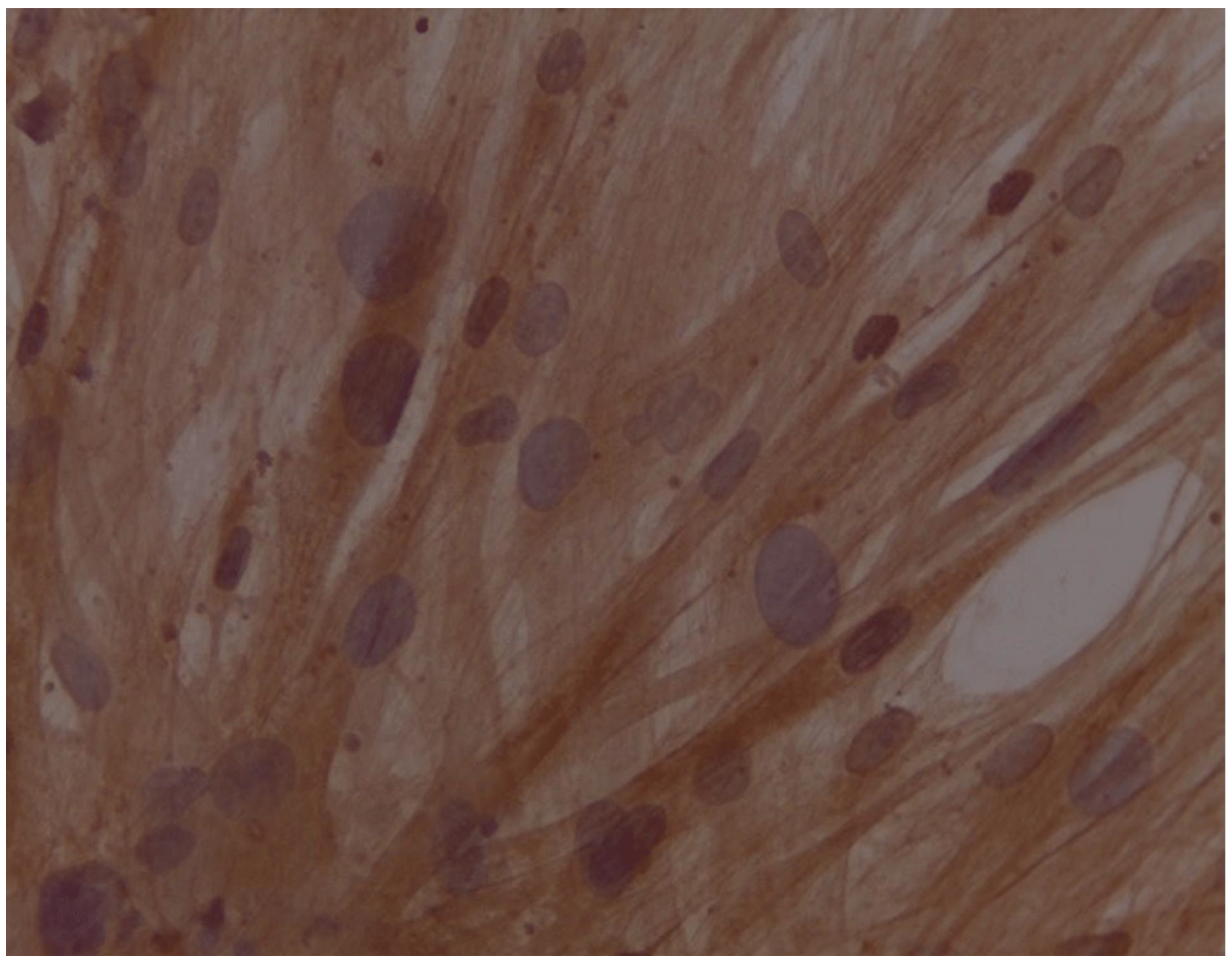
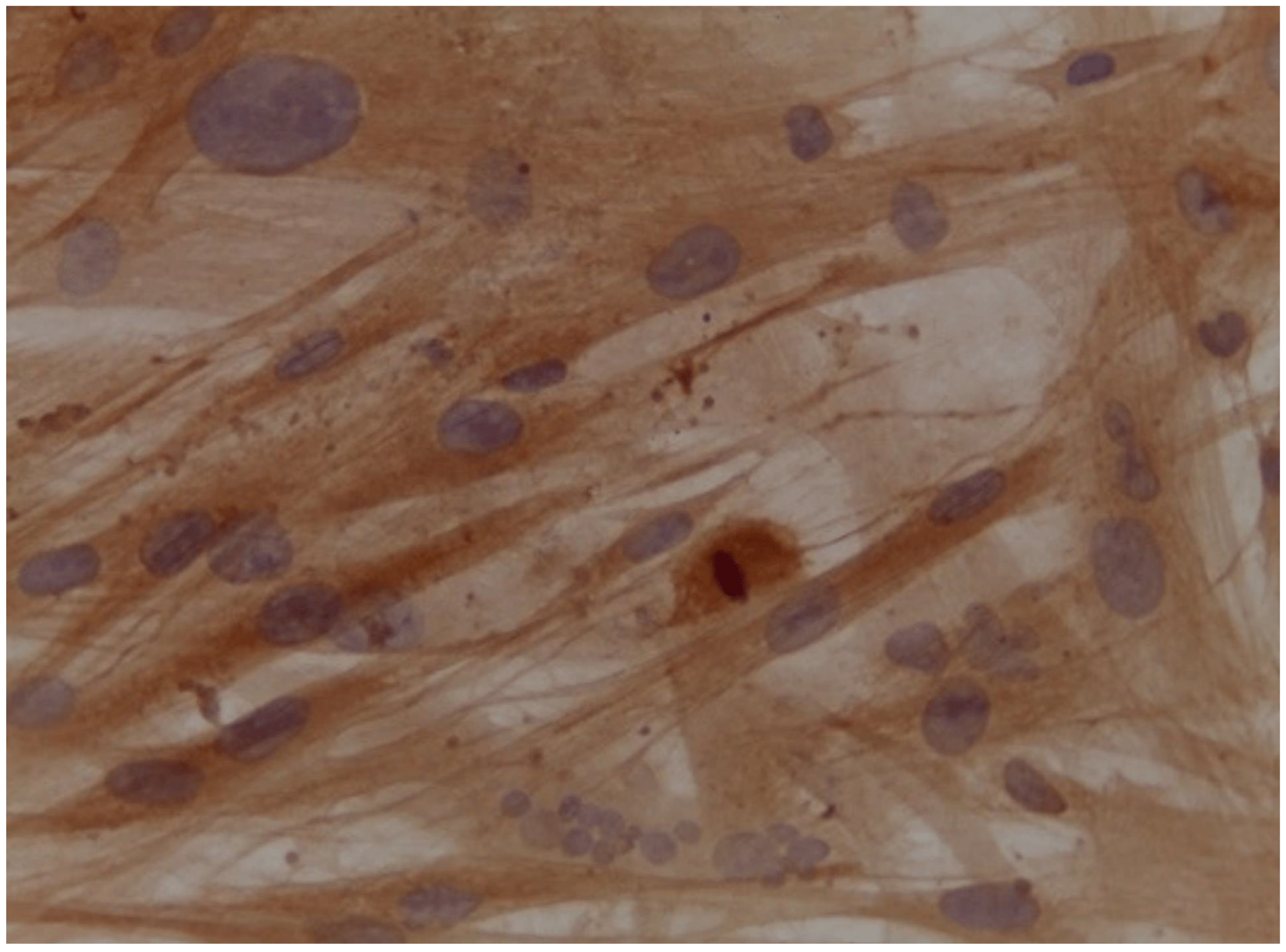
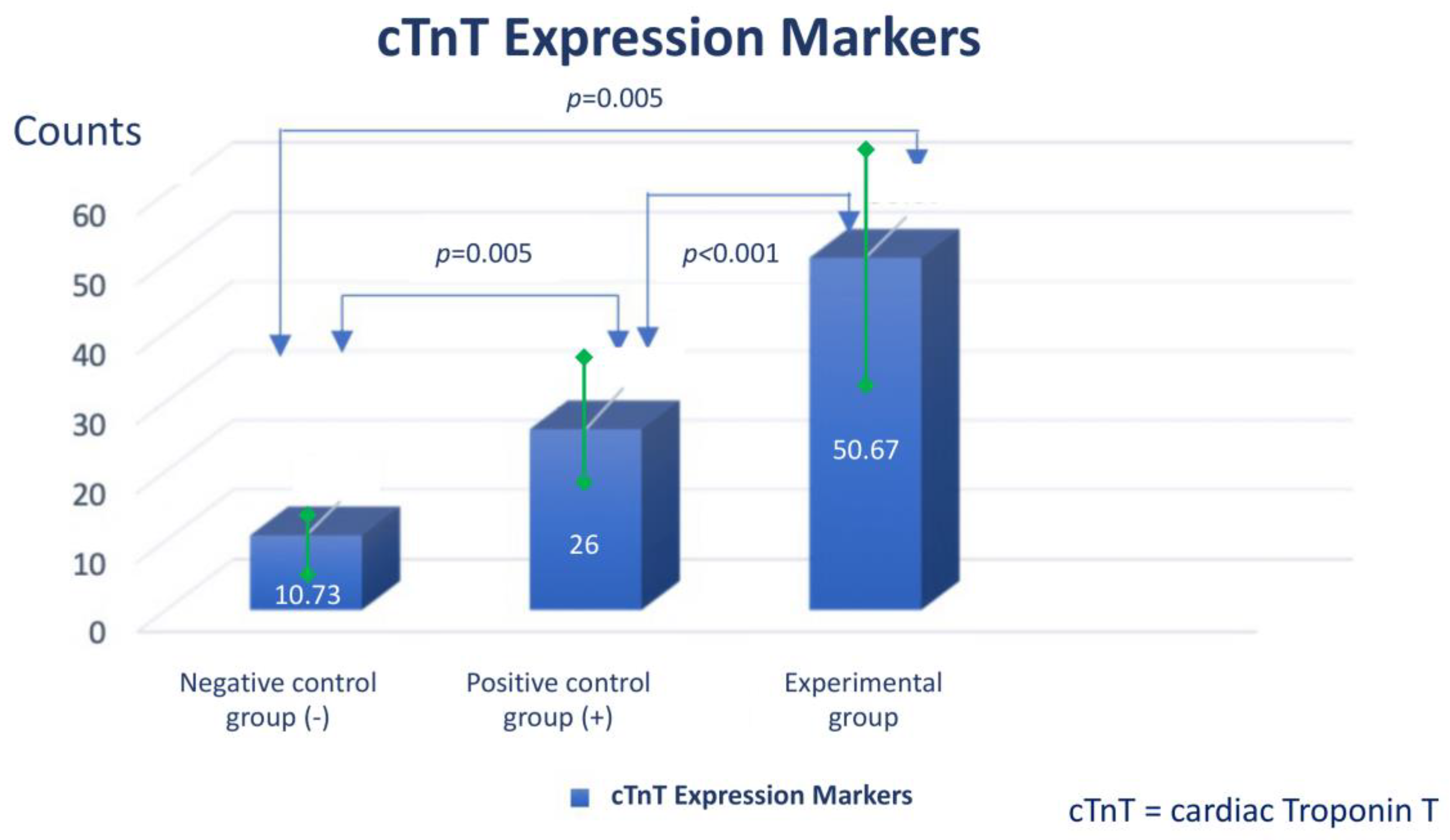
Assessment of expression of cardiomyocyte-like cells differentiation marker Troponin by Immunocytochemistry
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
SUMMARY POINTS
- ▪
- Before the beginning of the cell therapy and transplantation era, clinically there is no therapy for permanent damage of cardiomyocytes that has the effect of stimulate regenerating myocardium
- ▪
- Platelet-rich fibrin contains a variety of growth factors, thus can affect central signalling pathways, possesses an anti-inflammatory effect, and is capable of cardiomyogenesis
- ▪
- The addition of injectable platelet-rich fibrin appears to have benefit to accelerate the differentiation from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells, as can be seen by increasing the expression of GATA-4 and Troponin.
- ▪
-
Author Contributions: please list the contributions of each author to the piece; please refer to the Author Disclosure Form for our authorship criteria.
- o
- I Gde Rurus Suryawan1* : Conceptualization, Funding, Methodology, Supervision
- o
- Andrianto2 : Project administration, Visualization, Supervision
- o
- Arisya Agita3 : Data curation, Methodology
- o
- Anudya Kartika Ratri4 : Writing – Original Draft
- o
- Ricardo Adrian Nugraha5 : Writing – Original Draft, Statistical analysis
- ▪
- Acknowledgements: We would like to show our gratitude to Prof. Dr. Fedik Abdul Rantam as Consultant of Stem Cell at Tissue Bank, Dr. Soetomo Academic General Hospital and Prof. Dr. Maria Inge Lusida as Head of Institute of Tropical Disease, Universitas Airlangga for sharing their pearls of wisdom with us during the writing process, for their comments on the later version of the manuscript, although any errors are our own and should not tarnish the reputations of these esteemed persons. We would also like to thank for anonymous residents and staffs from Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Airlangga - Dr. Soetomo Academic General Hospital for their technical contribution and so-called insights.
- ▪
- Financial disclosure: None declared.
- ▪
- Information pertaining to writing assistance: None declared.
- ▪
- Ethic statement: This research had been obtaining an ethical approval from Institutional Review Board of Dr. Soetomo Academic General Hospital - Faculty of Medicine, Airlangga University (Institution Review Board number: IORG0007195; Reference Number: 1733/KEPK/XII/2019) issued on December 27th, 2019.
- ▪
- Informed consent: Written informed consent had been obtained from study participants.
- ▪
- Data sharing statement: The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
- ▪
- Plain language summary (PLS; within article):
- ▪
- It is difficult to grow and differentiate adult stem cells such as adipose derived stem cells, to achieve perfect cardiac regeneration therapy.
- ▪
- There is a major difference between platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF). PRP injections are created by isolating the platelets from a patient's blood and concentrating them into a serum. PRF injections, on the other hand, are created by adding a fibrin matrix to the platelets, which creates a more cohesive and stable injectable product.
- ▪
- Our experiment try to evaluate the benefit of platelet-rich fibrin in various clinical scenarios, especially to grow cardiomyotes-like cells, with positive GATA-4 and Troponin expression.
- ▪
- Tweetable abstract: How to Improve Differentiation of Cardiomyocytes-like Cells Faster with the Addition of Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin in the Cell Cultures
- ▪
- Ethic statement: This research had been obtaining an ethical approval from Institutional Review Board of Dr. Soetomo Academic General Hospital - Faculty of Medicine, Airlangga University (Institution Review Board number: IORG0007195; Reference Number: 1733/KEPK/XII/2019) issued on December 27th, 2019.
- ▪
- Informed consent: Written informed consent had been obtained from study participants.
References
- Soltani L, Rahmani H, Joupari MD et al. Effects of 5-Azacytidine on Differentiation of Ovine Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Stem. Cell. Res & Transplant. 3(02), 96–100 (2015). * (this study is interesting because 5-azacytidine in culture of hMSCs for 28 days could induce differentiation towards cardiomyogenic lineage, whereas same cultural condition for a period of 24h lead to cardiac-like muscle cells).
- Ma T, Sun J, Zhao Z et al. A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. Stem. Cell. Res & Ther. 8(1), 1–8 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Castro F, Munozledo. The Mammalian limbal Stem Cell Niche : A Complex Interaction Between Cells, Growth Factors and Extracellular Matrix. Switzerland : Springer International Publishing. 23-56 (2015).
- Miron R, et al. Platelet rich fibrin and soft tissue wound healing: a systematic review. Issue Eng Part B Rev. 23, 83–99 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Al-Khawlani E, et al. Evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin versus platelet-rich plasma on the outcome of mandibular fracture: a comparative study. Egypt J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 5, 96–102 (2014).
- Miron RJ, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin and soft tissue wound healing: a systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 23, 83–99 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Neiva RF, et al. The synergistic effect of leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin and micrometer/nanometer surface texturing on bone healing around immediately placed implants: an experimental study in dogs. Biomed Res Int. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Duan X, Lin Z, Lin X et al. Study of platelet-rich fibrin combined with rat periodontal ligament stem cells in periodontal tissue regeneration. J. Cel. & Mol. Med. 22(2), 1047-1055 (2017).* (this study is interesting because this is one of the most earliest study to use platelet-rich fibrin combination to enhance stem cell regeneration).
- Apte RS, Chen DS, Ferrara N. VEGF in signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development. Cell. 176, 1248–64 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini et al published P, Samuel S, Kurkalli BG, Kumar C, Kumar BM, Shetty N, Shetty V, Vishwanath K. In vitro Comparison of Adipogenic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cultured with Collagen Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Indian J Plast Surg. 2021 Aug 26;54(3):278-283. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Z., Salehinejad, P. & Mesbah-Namin, S.A. Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells in fibrin scaffold by a histone deacetylase inhibitor. BioMed Eng OnLine 16, 134 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Badimon L, Oñate B, Vilahur G. Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Reparative Potential in Ischemic Heart Disease. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2015 Jul;68(7):599-611. (embedded AD-MSCs in PRF)) in the main manuscript to discuss the background of your work further; then proceed to clarify the novelty of your work.”. [CrossRef]
- Zuk PA and Zhu M. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells. The. Am. Society. For. Cell. Bio. (2002).
- Mazini L, Rochette L, Amine M et al. Regenerative Capacity of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs), Comparison with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(10), 2523 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Strauss FJ, Nasirzade J, Kargarpoor Z et al. Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, inflammation, and osteoclastogenesis: a systematic review of in vitro studies. Clin. Oral. Investig. 24(2):569-584 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I et al. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 8(4), 315–317 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Talman V and Ruskoaho H. Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction—from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell. Tissue. Res. 365(3), 563–581 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto H, Olson EN, Bassel-Duby R. Therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 15(10), 585–600 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Masoudi E, Ribas J, Kaushik G et al. Platelet-Rich Blood Derivatives for Stem Cell-Based tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Current. Stem. Cell. Reports. 2(1), 33-42 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Meshram VS, Lambade PN, Tiwari ST. The Autologous Platelet Rich Fibrin: A novel approach in osseus regeneration after cystic enucleation: A pilot study. Ind. J. Dental. Res. 26, 560- 564 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Naik B, Karunakar P, Jayadev M et al. Role of Platelet richfibrin in wound healing : A critical review. J. Conservatives. Dentist. 16(4) (2013). [CrossRef]
- Shah R, Triveni MG, Thomas R, et al. An Update on the Protocols and Biologic Actions of Platelet Rich Fibrin in Dentistry. Eur. J. Prosthodontics. & Restorative. Dentist. 25, 64-72 (2017).
- Soffer E, Ouhayoun JP, Anagnostou F. Fibrin sealants and platelet preparations in bone and periodontal healing. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 95(5), 521-8 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Ferreira JR, Teixeira GQ, Santos SG et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome: Influencing Therapeutic Potential by Cellular Pre-conditioning. Front. Immunol. 9, 2837 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Castegnaro S, Chieregato K, Maddalena M et al. Effect of platelet lysate on the functional and molecular characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from adipose tissue. Curr. Stem. Cell. Res. Ther. 6(2), 105-14 (2011) * (this study is interesting because human platelet lysate tends to share similar properties with platelet-rich fibrin in term of non-hematopoietic, adult, fibroblast-like, multipotent cells that are plastic adherent in standard culture conditions). [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy V, Ronald VS, Abdullah AN et al. Differentiation of dental pulp stem cells into islet-like aggregates. J. Dent. Res. 90(5), 646-52 (2011). * (this study is interesting when studying a step and protocol to isolated, propagated, and characterized stem cells). [CrossRef]
- Planat-Benard V, Silvestre JS, Cousin B et al. Plasticity of human adipose lineage cells toward endothelial cells: physiological and therapeutic perspectives. Circulation. 109(5), 656-63 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Walsh TG, Poole AW. Platelets Protect Cardiomyocytes from Ischaemic Damage. TH Open. 1(1), e24-32 (2017) * (this study is interesting because we could learn that components of stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α and transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 in the platelet exhibit cardioprotective effects. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




