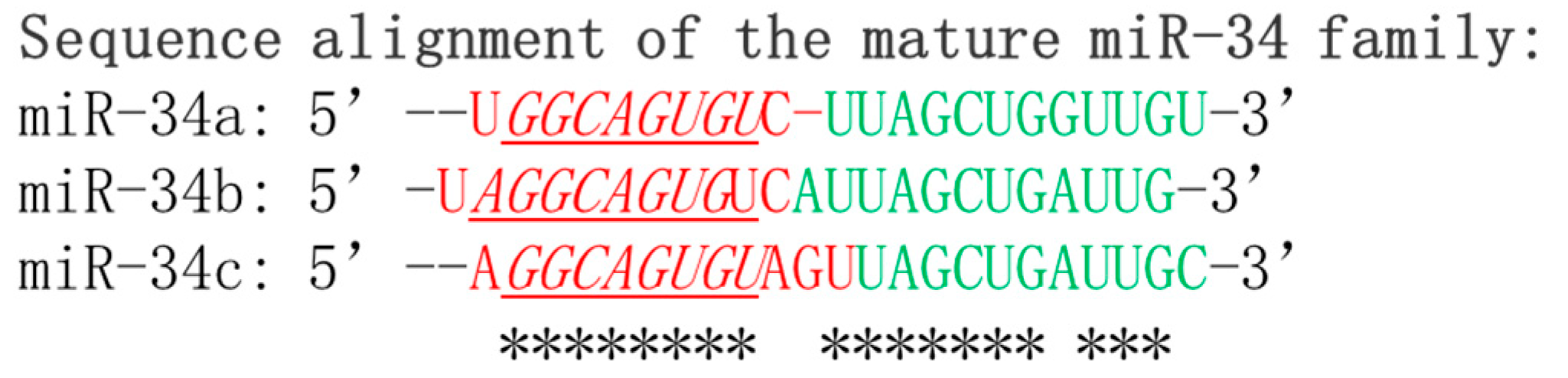1. Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs, typically consisting of 21-23 nucleotides, that exert regulatory effects on gene expression
via binding to the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of target mRNAs through a seed region (nucleotides 2-8), leading to mRNA degradation or translational inhibition [
1]. Due to their ability to regulate gene expression, miRNAs play vital roles in various biological processes, such as development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Consequently, dysregulation of miRNAs has been implicated in a wide range of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases [
2]. In the context of cancer, miRNAs have been found to modulate the expression of key oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, thereby influencing tumorigenesis, cancer cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Depending on their specific targets, miRNAs can function as either oncogenic miRNAs or tumor suppressor miRNAs, highlighting the complex and context-dependent roles of miRNAs in cancer development.
Among the tumor-suppressive miRNAs, the miR-34 family (miR-34s) has emerged as a prominent player in various human diseases, particularly cancer. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in unraveling the intricate relationship between miR-34s and cancer [
3]. This comprehensive review aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the role of miR-34 members in cancer. We will discuss the epigenetic mechanisms through which miR-34s modulate cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis. Additionally, we will explore the potential of miR-34 family members as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis, as well as their prospects as therapeutic targets in cancer treatment.
2. Biosynthesis of miR-34s and regulation of miR-34 expression
2.1. Biosynthesis of miR-34s
The miR-34 family consists of three members: miR-34a, miR-34b, and miR-34c, which are encoded by two genes located on chromosomes 1 and 11, respectively [
3]. Specifically, miR-34b and miR-34c share a common primary seed sequence found within one transcription unit on 11q23.1, while miR-34a is encoded in the second exon of a gene on 1p36.22. Comparative analysis reveals that mature form of miR-34a shares 86% identity (19/22 nt) with that of miR-34b and 82% identity (18/22 nt) with that of miR-34c, respectively [
3,
4,
5]. Notably, both miR-34a and miR-34c share identical seed sequences, suggesting a potential overlap in their target mRNAs. Additionally, the miR-34s and the miR-449 family, consisting of miR-449a, -449b, and -449c, belong to the miR-34/449 superfamily of miRNAs due to their shared seed sequence, adjacent nucleotide sequences, and mRNA targets [
6]. In most human cells, miR-34a exhibits significantly higher expression levels compared to miR-34b and miR-34c.
The biosynthesis of miRNAs, including the miR-34s, involves a complex, multi-step process occurring in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Initially, the genes encoding the miR-34 family are transcribed by RNA polymerase II or III in the nucleus, resulting in the generation of a long hairpin-shaped molecule known as pri-miRNA. Subsequently, the endonuclease DROSHA cleaves pri-miRNA to produce a stem-loop-structured miRNA precursor molecule (pre-miRNA), which is approximately 80-100 nt long. This processing step occurs within the nucleus [
7]. Next, the pre-miR-34s are actively transported to the cytoplasm through the nuclear transporter exportin-5. Once in the cytoplasm, the endonuclease DICER further processes the pre-miR-34s into double-stranded mature miR-34 molecules, which are approximately 20-23 nucleotides in length. The mature miRNA duplex then associates with the Argonaute protein to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), where one strand of the duplex becomes the mature miRNA molecule while the other is degraded [
7]. The mechanism of gene silencing by miRNAs depends on the degree of complementarity between the seed sequence and the binding site on the 3'-UTRs or 5'-UTRs of target mRNAs. If the binding sites on target mRNAs are fully complementary to the seed region of miR-34s, it may induce target mRNA degradation, resulting in the inhibition of target gene expression. However, when partially complementary sequences are present in target gene mRNAs, miR-34 can suppress gene expression through inhibiting the translation of its targets [
4,
8,
9].
The alignment of mature miR-34a, miR-34b, and miR-34c sequences is depicted in
Figure 1. It is worth mentioning that the differential expression levels of miR-34s indicate their distinct and specific functions in the regulation of gene expression. The precise mechanisms through which miRNAs exert their effects on gene expression are still under investigation, and ongoing research endeavors are expanding our knowledge of the intricate and dynamic roles played by miRNAs in cellular physiology and the development of diseases.
2.2. Regulation of miR-34 expression
The regulation of miR-34 expression involves multiple mechanisms that contribute to its dysregulation in cancer. Transcriptional regulation by various factors plays a crucial role in controlling miR-34 levels. The tumor suppressor protein p53 directly binds to the miR-34 gene promoter, activating its transcription. Additionally, other transcription factors such as ETS domain-containing protein (Elk-1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) are implicated in miR-34 regulation. EMT-TFs, including Snail, Slug, ZEB1, and ZEB2, bind to the promoter regions of miR-34 genes and repress their transcription [
4].
The dysregulation of EMT-TFs contributes to the acquisition of mesenchymal characteristics by cancer cells, resulting in increased invasiveness and migratory capacity. EMT-TFs recruit chromatin-modifying enzymes, such as histone deacetylases and DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), to the promoter regions of miR-34 genes. This recruitment leads to histone deacetylation and DNA methylation, causing a repressive chromatin state and inhibition of the miR-34 transcription [
4].
Epigenetic modifications, including CpG island methylation and histone deacetylation, further contribute to the dysregulation of miR-34 in cancers. Methylation of CpG islands in the promoter regions of miR-34 genes results in gene silencing, while histone deacetylation leads to a more compact chromatin structure that hinders transcriptional activity [
4]. These epigenetic modifications are commonly found in various cancer types, such as lung [
10,
11], multiple myeloma [
12], kidney [
13,
14], gastric [
15], breast [
16,
17], colorectal [
18], hepatocellular [
19], prostate [
20], and ovarian [
21,
22] cancers.
Understanding the intricate regulatory networks involving transcriptional factors, EMT-TFs, and epigenetic modifications provides valuable insights into the molecular processes underlying cancer progression. Targeted therapies aimed at restoring miR-34 expression and inhibiting EMT-associated metastasis may hold promise for future therapeutic interventions in cancer treatment.
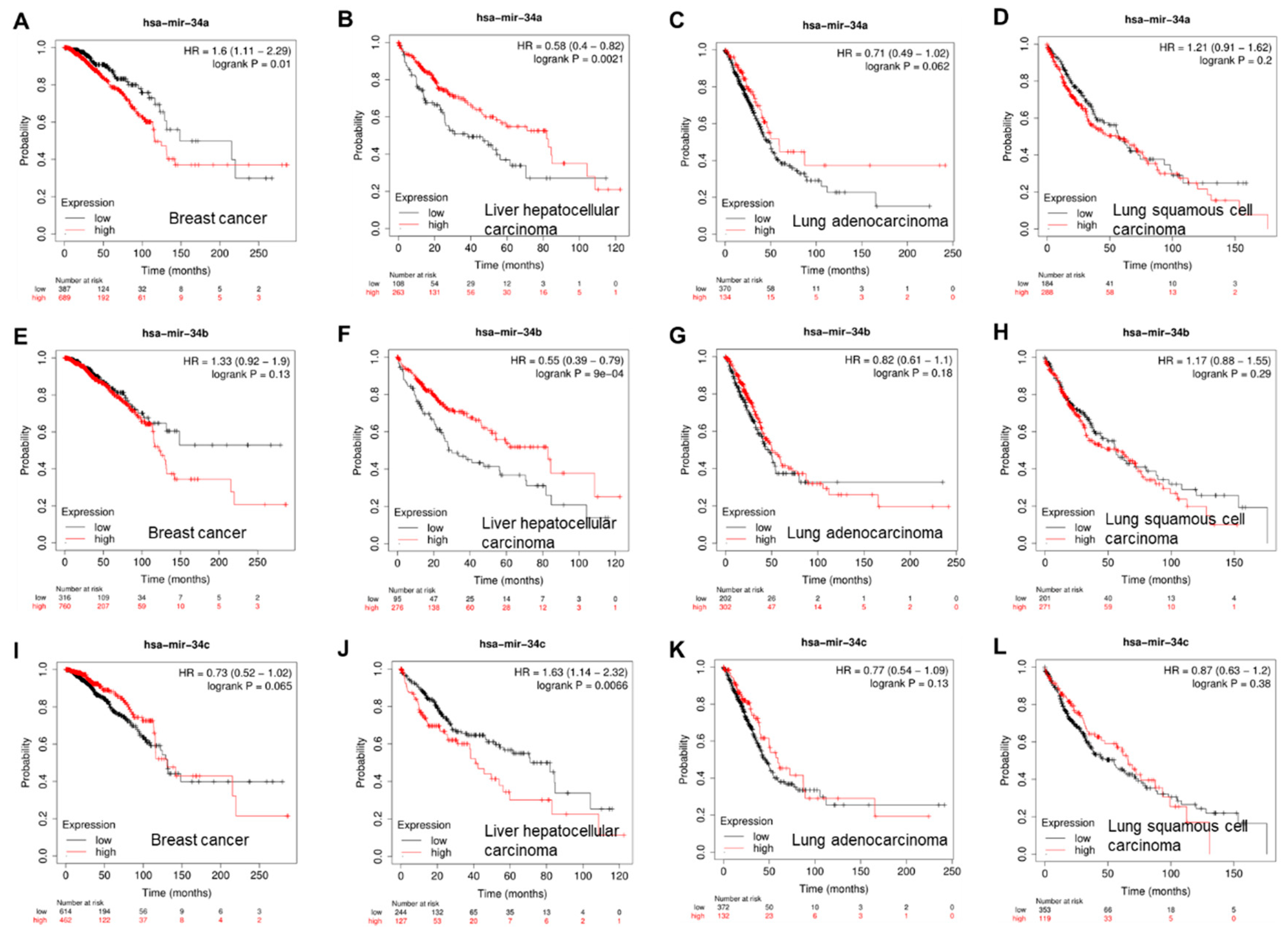
Given the tumor suppressive function of the miR-34s, correlations between the expression of miR-34s and patient survival were interrogated by the Cox proportional hazards regression and the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (
https://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=pancancer_mirna) [
23]. In multiple distinct cancer types, high expression of miR-34s, such as miR-34a (
Figure 2B, P=0.0021), miR-34b (
Figure 2F, P=0.0001), miR-34c, are correlated with longer survival of patients with liver hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). For example, Chen
et al. reported that, in serum exosome, a lower level of miR-34a was worse than that of patients with high expression in overall survival, implying it is a noninvasive marker for diagnosis and prognosis of HCC [
24].
3. The roles of miR34s in cancers
Given the global health impact of cancer and its status as a leading cause of death, understanding the roles of miR-34s in cancer is crucial for the development of effective therapies [
25]. The functions of miR-34s in cancer are diverse and involve the modulation of critical signaling pathways and processes. Extensive research has identified over 700 genes that are either predicted or validated targets of the miR-34s. These genes are involved in critical signaling pathways implicated in cancer progression, including the MAPK, Notch, Wnt, PI3K/AKT, p53, and Ras pathways. Additionally, miR-34s target processes critical for cancer migration, invasion, and EMT [
26,
27,
28,
29]. Studies have demonstrated that systemic delivery of miR-34a, combined with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, can effectively inhibit tumor progression.
MiR-34s inhibit cell proliferation and survival by targeting the MAPK pathway. Similarly, miR-34s regulate the Notch and Wnt signaling pathways, which are crucial for cell fate determination, differentiation, and maintenance of stem cells. Dysregulation of these pathways is commonly observed in cancer, and miR-34s can restore normal signaling by targeting key genes within these pathways [
29].
Moreover, the PI3K/AKT pathway, which regulates cell survival and growth, is another target of the miR-34s [
30,
31]. By inhibiting genes within the PI3K/AKT pathway, miR-34s can suppress cancer cell proliferation and induce cell death. In the realm of tumor suppression, miR-34a acts as a tumor suppressor that selectively targets the p53 protein, famously known as the "guardian of the genome." The intricate interplay between p53 and miR-34 establishes positive feedback loops that facilitate tumor suppression. Specifically, activation of miR-34a enhances the functional capabilities of p53, resulting in critical cellular processes such as cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis [
32]. The miR-34 family assumes a crucial role in mediating the functions of p53, thereby significantly contributing to the preservation of genomic stability [
33,
34,
35]. miR-34a exhibits specific targeting of pro-apoptotic molecules such as SIRT1 and FasR, which are key players in p53/miR-34-induced apoptosis and the regulation of apoptotic signaling [
16,
28,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Moreover, the miR-34 family interacts with a diverse array of oncogenic regulators, including TP53, NOTCH1, and SMAD4, as well as components of the Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathways [
26,
27,
28]. These interactions form a complex regulatory network that influences cellular apoptosis and modulates crucial signaling cascades, adding to our understanding of the multifaceted roles played by the miR-34 family in cellular processes.
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms of miR-34 and its targets is essential for the development of effective cancer therapies. Continued research into the precise functions and regulatory networks of miR-34s in different types of cancer will provide valuable insights for the design of targeted treatments and personalized medicine approaches. By harnessing the potential of miR-34s, we can advance the fight against cancer and improve patient outcomes.
In the subsequent section, we will provide a concise overview of the latest progress in understanding the specific functions of miR-34 in various types of cancer.
3.1. The role of miR34s in breast cancer
Breast cancer is a significant cause of mortality in women and the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, with an estimated 297,790 new cases and 43,170 expected deaths in 2023 [
25]. Unfortunately, only a small percentage of breast cancer cases are diagnosed at an early stage when the disease is localized and more treatable. Breast cancer exhibits considerable heterogeneity and can be classified into twenty-five subtypes based on distinct histological and gene expression profiles. In breast cancer, the expression of the miR-34 family is down-regulated compared to normal tissues. Specifically, high expression of miR-34a has been correlated with less aggressive cancer behavior, although it has not been correlated with patient survival [
40].
MiR-34a plays a crucial role in maintaining mammary epithelium homeostasis. MiR-34a expression is observed during luminal commitment and differentiation, and it inhibits the expansion of mammary gland stem cells and early progenitor cells through the suppression of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Interestingly, the function of miR-34a in stem/progenitor cells is conserved in human breast cancer. When miR-34a is expressed in triple-negative mesenchymal-like cells, which are enriched in cancer stem cells (CSCs), it leads to a luminal-like differentiation, restriction of cancer stem cell pool, and inhibition of tumorigenesis [
41]. These findings highlight the potential of miR-34a in breast cancer treatment.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive subtype of breast cancer and is correlated with lower overall survival rates. New therapies for TNBC are urgently needed for this deadly disease. Inhibition of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), an immune checkpoint, has emerged as a promising treatment strategy. It has been shown that the tumor suppressor protein p53 can downregulate PD-L1 expression through miR-34a, thereby inhibiting the growth of TNBC cells [
42]. Circulating miR-34 family expression levels could serve as non-invasive prognostic biomarkers in TNBC patients. Notably, low expression of circulating miR-34c has been correlated with poor prognosis in TNBC [
43]. Recent research on single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in miRNA and target site has shed new light on the mechanistic contributions of miRNAs in carcinogenesis and their impact on cancer susceptibility and development. SNPs in miRNA and miRNA binding site of protein-coding gene further contribute to the complex and diverse roles of miRNAs in gene expression regulation. For instance, the rs4938723 C > T polymorphism in the promoter region of miR-34b/c impacts GATA-X binding and subsequently alters the miR-34b/c expression [
44]. Tsiakou
et al. reported that the rs4938723 T > C polymorphism is correlated with an unfavorable prognosis in TNBC patients [
45]. Several recent studies also demonstrated that the rs4938723 C > T polymorphism is correlated with a higher risk of hepatocellular [
46] and prostate [
47] cancers.
3.2. The role of miR34s in lung cancer
Lung cancer accounts for a significant number of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Study by Li
et al. revealed that the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) X-inactive specific transcript (XIST), upregulates the expression of PD-L1 by targeting miR-34a-5p. By influencing the viability, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and cytokine secretion of lung cancer cells, this regulatory mechanism ultimately facilitates the upregulation of immunosuppressive molecules. Consequently, it contributes to the development of an immune-suppressed tumor microenvironment, which can impede effective anti-cancer immune responses and potentially influence disease progression in lung cancer [
48]. Interestingly, miR-34a and miR-34b/c appear to have distinct functions in lung cancer cells [
49]. Kim
et al. revealed that miR-34b/c and not miR-34a enhances cell attachment and suppresses cell growth and invasion, miR-34a and miR-34b/c are capable of blocking lung metastasis in a syngeneic mouse model. Compared to miR-34a, the expression of miR-34b/c also leads to a greater reduction in the expression of mesenchymal markers such as Cdh2 and Fn1, while increasing the expression of epithelial markers including Cldn3, Dsp, and miR-200. Additionally, miR-34c has been shown to reduce the malignant characteristics of lung cancer cells
via targeting the TBL1XR1/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling [
50].
The downregulation of miR-34b-3p was confirmed in clinical specimens of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and topoisomerase 2 alpha, maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase, centromere protein F, and SRY-box 1 were identified as potential target genes of miR-34b-3p [
51]. Feng
et al. reported that miR-34b suppresses proliferation and cell cycle progression, and induces apoptosis in NSCLC cells by targeting CDK4 [
52]. Furthermore, low levels of circulating miR-34s members have been correlated with poorer prognosis in NSCLC patients, suggesting that miR-34a/c can serve as novel prognostic biomarkers for NSCLC [
11]. Knockout of miR-34a/b/c has been revealed to promote mutant Kras-driven lung tumor progression
in vivo. Significantly lower expression levels of miR-34s were found in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma samples compared to non-metastatic samples. Hypermethylation of the miR-34s promoters was predominantly observed in lung adenocarcinoma, suggesting that miR-34 methylation could be utilized as a prognostic marker for NSCLC patients [
53,
54]. Additionally, inhibition of miR-34a expression by the lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 was reported to enhance cell invasion, migration, and tumor formation in NSCLC [
55].
Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) is a novel concept that involves various RNA molecules, including mRNA, circular RNA, pseudogene transcripts, and lncRNA. These molecules regulate each other's expressions by acting as sponges for microRNAs, competing for their binding through microRNA response elements [
56]. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 has been reported to enhance cell invasion, migration, and tumor formation in NSCLC by epigenetically inhibiting miR-34a [
55]. Through this mechanism, MCM3AP-AS1 acts as a ceRNA, sequestering miR-34a and preventing its interaction with its target genes. The interruption of miR-34a with its target genes contributes to the altered behavior of cancer cells, promoting their invasive and migratory abilities. Another lncRNA, RP11-805J14.5, regulates CCND2, a gene involved in cell cycle regulation, by acting as a ceRNA/sponge for miR-34 and miR-139 in lung adenocarcinoma [
57]. By binding to these microRNAs, RP11-805J14.5 effectively reduces their availability for binding to CCND2 mRNA, thereby increasing the expression of CCND2 and potentially promoting cell cycle progression in lung cancer cells.
The ceRNA mechanism provides a complex network of interactions among different RNA molecules, allowing them to communicate and influence gene expression patterns. In lung cancer, dysregulation of ceRNA networks involving miR-34a, MCM3AP-AS1, RP11-805J14.5, and other associated molecules can have significant implications for the development and progression of the disease. Future studies on these ceRNA networks will provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of lung cancer and potentially uncover novel therapeutic targets.
3.3. miR34s in hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent form of liver cancer and one of the leading causes of deaths worldwide. The dysregulation of miR-34s has been implicated in the development and progression of HCC. The miR-34a-c-MYC-CHK1/CHK2 axis has been identified as an important regulatory pathway in HCC. It was reported that this axis inhibits cancer stem cell-like functions and enhances radiosensitivity in HCC. By targeting MYC and CHK1/CHK2, miR-34s can suppress the stemness properties of cancer cells and increase their sensitivity to radiation therapy, potentially improving treatment outcomes [
58].
A study by Jiao
et al. demonstrated that miR-34s are downregulated in tumor tissues compared to the matched noncancerous tissues of HCC. The downregulation of miR-34s in HCC is associated with poor prognosis. This suggests that the reduced expression of miR-34s may contribute to the aggressive nature of HCC and serve as a valuable prognostic marker for the disease [
59]. Furthermore, the correlation between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-miR-34b/c and the risk of HCC has been studied. The results revealed that certain genetic variations in this region are associated with increased susceptibility to HCC, highlighting the potential role of miR-34s in the genetic predisposition of HCC [
60].
In addition to tissue samples, the levels of miR-34a in the serum exosomes of HCC patients have also been evaluated as a potential biomarker. Exosomal miR-34a was revealed to be significantly down-regulated in HCC patients, suggesting its potential utility as a noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for HCC [
24]. Overall, the dysregulation of miR-34s is implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma, with their reduced expression associated with poor prognosis and increased cancer stem cell-like functions. It is expected that future studies on miR-34s and the identification of their downstream targets may contribute to the development of novel therapeutic strategies and biomarkers for HCC.
3.4. The role of miR34s in head and neck cancer
Downregulation of miR-34a has been implicated in the development of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Downregulation of miR-34a promotes cancer progression by up-regulating the mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion mechanisms [
61]. Furthermore, miR-34a is involved in regulating Flotillin-2 and the MEK/ERK1/2 pathway, which are important signaling pathways in HNSCC [
62].
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) is a rare malignancy that poses a significant health threat, particularly in regions like China. Various risk factors, including the Epstein-Barr virus, contribute to the development of NPC. Recent studies have shed light on the role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in NPC pathogenesis. CircRNAs are a unique class of single-stranded RNAs with closed-looped structures, generated through a process called back-splicing from pre-mRNA [
60]. In NPC, a circRNA known as circCRIM1 has been identified as a key player in NPC. It acts as a ceRNA by sequestering miR-34c, thereby promoting NPC progression through the miR-34c/FOSL1 pathway [
63]. This dysregulation of miR-34c and its downstream targets contributes to the tumorigenicity and aggressiveness of NPC. These findings highlight the significance of miR-34s in head and neck cancer, specifically HNSCC and NPC. Understanding the role of miR-34s and their regulatory mechanisms in these cancers can provide valuable insights into the underlying molecular pathways and potential therapeutic targets.
3.5. The role of miR34s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCC) is a highly aggressive and lethal form of cancer. Downregulation of miR-34a expression has been revealed in ESCC tissues compared to normal tissues, and its expression levels have been found to correlate with clinicopathological characteristics of the ESCC [
64]. Decreased expression of miR-34a and p53 has been reported in ESCC tissues, and overexpression of miR-34a has been shown to inhibit ESCC cell migration and invasion by directly suppressing the expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, and FNDC3B [
65]. MiR-34a exerts its inhibitory effects on ESCC migration and invasion through the regulation of different target genes, including Yin Yang-1 [
66], MMP9, MMP14 [
67], E2F5 [
68], and FOXM1 [
69]. Furthermore, hypermethylation of miR-34b/c has been correlated with early clinical stages and tumor differentiation in Kazakh ESCC patients [
70]. These findings underscore the significance of miR-34s in ESCC. The dysregulation of miR-34a and its downstream targets contributes to the aggressive nature of ESCC, including increased migration, invasion, and tumor progression. Understanding the intricate mechanisms involving miR-34s in ESCC can pave the way for novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in combating this deadly disease.
3.6. The role of miR34s in gastric cancer
Gastric cancer (GC) is a prevalent malignancy affecting the digestive system. Dysregulation of miR-34s in GC tissues is commonly observed and can be attributed to various factors, including p53 mutations, miR-34 promoter DNA methylation, and histone modifications. These alterations contribute to the downregulation of miR-34 expression in GC.
As a tumor suppressor gene, miR-34 exerts important regulatory functions in GC by inducing apoptosis, cell senescence, and cell cycle arrest, thereby inhibiting uncontrolled cell proliferation. MiR-34s also play a role in suppressing cell migration and metastasis, which are crucial steps in the spread of cancer. These effects are achieved through the regulation of several different target genes and signaling pathways [
71,
72]. For example, miR-34c has been implicated in GC progression by targeting MAP2K1, a gene involved in the MAPK pathway. By downregulating MAP2K1 expression, miR-34c inhibits the activation of MAPK pathway, which is correlated with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in GC cells. This suggests that restoration of miR-34c expression or modulation of its target genes could potentially serve as therapeutic strategies for GC treatment. Furthermore, the long non-coding RNA linc01106 has been identified as a key regulator in GC through its interaction with miR-34a. Linc01106 acts as a sponge for miR-34a, thus sequestering miR-34a and preventing its binding to target mRNAs [
73]. Silencing linc01106 was shown to suppress the malignant behaviors of GC cells by restoring the inhibitory effects of miR-34a on its downstream target gene MYCN. This indicates that targeting the linc01106/miR-34a/MYCN pathway might offer potential therapeutic benefits for GC patients [
74]. The dysregulation of miR-34s in GC underscores their critical role in the development and progression of this malignancy. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying miR-34-mediated regulation can provide valuable insights into the biology of GC and facilitate the identification of novel therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers to improve patient outcomes.
3.7. The role of miR34s in colon carcinoma
Colon carcinomais a significant contributor to cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. Dysregulation of miR-34s, specifically miR-34a, has been implicated in the development and progression of colon carcinoma. A recent study revealed that miR-34a induced immunosuppression in colon carcinoma through the SIRT1/NF-κB/B7-H3/TNF-α axis. The downregulation of miR-34a leads to increased expression of these immunosuppressive factors, contributing to tumor growth and evasion of the immune surveillance [
75]. Furthermore, miR-34a/b/c genes, whose expression is frequently silenced in colon carcinoma. They are capable of suppressing tumor formation caused by the loss of the Apc gene, which is commonly associated with colon cancer. Additionally, miR-34s help maintain the homeostasis of intestinal stem cells and secretory cells by regulating various target genes and pathways [
76]. In colon carcinoma cells, the expression of miR-34a is often reduced and restoration of miR-34a expression inhibits colony formation, proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induces cell apoptosis through regulation of SYT1. This suggests that miR-34a could serve as a potential target for colon cancer treatment [
77].
Furthermore, TP53 gene polymorphisms are associated with the methylation and expression of miR-34a/b/c in colorectal cancer tissues [
78]. This implies that miR-34s could have diagnostic and therapeutic potential in colon cancer management [
79]. In addition to miR-34s, lncRNA NONHSAG028908.3 has been identified as a modulator of colorectal cancer growth. LncRNA NONHSAG028908.3 upregulates the expression of aldolase, fructose bisphosphate A (ALDOA), a protein involved in cancer cell metabolism
via acting as a sponge for miR-34. By regulating the expression of ALDOA, lncRNA NONHSAG028908.3 can promote colorectal cancer growth [
80]. Understanding the role of miR-34s in colon carcinoma may aid in the development of targeted therapies and diagnostic approaches for improved management and outcomes in patients with colon carcinoma.
3.8. Tumor-suppressive effects of miR-34s in ovarian cancer
The role of miR34s in ovarian cancer is of significant interest in the field of cancer research. Studies have revealed that the expression levels of miR-34a, miR-34b, and miR-34c are noticeably reduced in ovarian cancer tissues compared to healthy tissues [
21]. The expression of members of the miR-34s has been identified as an independent marker for progression-free survival in ovarian cancer patients. These miRNAs play crucial roles in the progression of ovarian cancer. By targeting Notch1, miR-34 effectively hinders the proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells, while also promoting autophagy and apoptosis. This indicates that miR-34 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in ovarian cancer [
81].
Another intriguing finding is the involvement of exosomal miR-34b in ovarian cancer. It exerts its effects by suppressing ovarian cancer cell proliferation and EMT by targeting Notch2 [
82]. The ability of exosomal miRNAs to be transported between cells and influence tumor behavior has made them a potential diagnostic and therapeutic candidate. Furthermore, recent studies have identified potential prognostic markers in ovarian cancer. Overexpression of P2RY14, a G protein-coupled receptor, has been associated with improved overall survival and longer progression-free intervals in ovarian cancer patients. Interestingly, lncRNA LINC00665 acts as a sponge for miR-34c-5p, preventing its interaction with P2RY14. This leads to the maintenance of low P2RY14 expression, which, in turn, correlates with poor prognosis and increased tumor immune infiltration in ovarian carcinoma [
83]. The dysregulation of miR-34 family members and their downstream targets in ovarian cancer provides valuable insights into their significant roles in disease progression. This knowledge has the potential to contribute to the development of innovative diagnostic approaches and targeted therapies, ultimately leading to improved management and better outcomes for patients with ovarian cancer.
3.9. The role of miR34s in cervical cancer
MiR-34s exhibit differential effects in cervical cancer, with distinct functions observed for the 5p and 3p strands. In particular, miR-34a-5p has been shown to inhibit proliferation, migration, and cell invasion by reducing the activity of MMP9 and the protein expression of MAP2 [
81]. Similarly, miR-34b-5p and miR-34c-5p demonstrate inhibitory effects on proliferation and migration, while miR-34c-5p specifically suppresses MMP9 activity and MAP2 protein levels [
84]. On the other hand, miR-34a-3p and miR-34b-3p suppress proliferation and migration, with miR-34c-3p inhibiting cell invasion and MMP9 activity and reducing MAP2 protein expression [
84]. These findings imply that other regulatory genes may contribute to the varying effects of miR-34s in cervical cancer. Furthermore, specific target genes have been identified for miR-34a and miR-34c in cervical cancer. For instance, miR-34a has been reported to impede growth and migration by targeting CDC25A [
85], a key cell cycle regulator. Similarly, miR-34c exerts suppressive effects on metastasis and invasion by targeting Notch 1 [
86], a critical signaling pathway involved in cancer progression. These findings highlight the intricate regulatory roles of miR-34s in cervical cancer and provide insights into potential therapeutic targets. Overall, the dysregulation of miR-34s in cervical cancer underscores their significance as potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets in the management of this disease. Future studies are warranted to elucidate the complex interplay between miR-34s and their target genes.
3.10. The tumor suppressive function of miR34s in prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men, with an estimated 288,300 new cases and 34,700 expected prostate cancer deaths in 2023 [
25]. Prostate cancer incidence increased by 3% annually from 2014 through 2019 after two decades of decline, which translate into an additional 99,000 new cases per year [
25]. Recent studies showed the involvement of genetic and epigenetic alterations, as well as microRNAs, including miR-34a, in prostate cancer development [
87,
88]. Notably, miR-34a has been found to exert tumor-suppressive effects in prostate cancer. In PC3 prostate cancer cells, miR-34a has been shown to inhibit cell growth and migration while promoting G2 cell cycle arrest by targeting the Wnt signaling pathway [
89].
The intricate network of lncRNAs has also been implicated in prostate cancer progression by interacting with miR-34a. For instance, lncRNA LINC00662 promotes prostate cancer tumorigenesis by acting as a sponge for miR-34a [
90]. Similarly, LINC01006 upregulates the expression of DAAM1, thereby facilitating prostate cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through its interaction with miR-34a-5p [
91]. Additionally, lncRNAs DANCR and NEAT1 contribute to docetaxel (DTX) resistance in prostate cancer by sequestering miR-34a-5p [
92,
93]. These emerging evidences underscore the significance of miR-34s, particularly miR-34a, in prostate cancer biology. Further investigations are warranted to unravel the underlying mechanisms and exploit the therapeutic potential of targeting the miR-34 family in prostate cancer management.
3.11. The role of miR34s in osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma, a highly aggressive bone malignancy primarily affecting children, adolescents, and young adults, poses significant challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment. In recent years, the role of miR-34s in osteosarcoma has emerged as a promising area of research, shedding light on the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying tumor development and progression. Among the members of the miR-34 family, miR-34a has garnered considerable attention due to its involvement in crucial cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. Studies in nude mice have demonstrated the tumor-suppressive effects of miR-34s in osteosarcoma. It was shown that by regulating the expression of the TGIF2 gene, miR-34s effectively inhibit tumor growth and promote apoptosis, thereby impeding the progression of osteosarcoma [
94,
95,
96].
In addition to its direct impact on tumor cells, miR-34a exerts its influence through intricate signaling pathways within the tumor microenvironment. Notably, the DNMT1/miR-34a/Bcl-2 axis has emerged as a key regulatory pathway in osteosarcoma. Isovitexin, a natural compound has shown promising potential in disrupting this axis. By targeting DNMT1 and modulating miR-34a expression, isovitexin effectively hampers cancer stemness properties and induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. This finding holds great promise for the development of novel therapeutic strategies that could potentially overcome the treatment challenges posed by osteosarcoma [
97,
98].
Moreover, the dysregulation of miR-34a has been linked to various target genes and pathways involved in osteosarcoma progression. For instance, miR-34a has been shown to target DUSP1, a protein implicated in cell signaling pathways, as well as the MALAT1/cyclin D1 axis, which plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation. The dysregulation of these targets contributes to the uncontrolled growth, progression, and metastasis observed in osteosarcoma. In addition, many lncRNAs, such as HCG18 [
99], DICER1-AS1 [
100], NEAT1 [
101], CASC11 [
102], MALAT1 [
103], and SNHG7 [
104], have been identified as miR-34a sponges and can promote osteosarcoma progression by sequestering miR-34a and diminishing its tumor-suppressive effects. Additionally, lncRNA HCG9 has been found to act as a sponge for miR-34b, thereby facilitating osteosarcoma progression through the regulation of RAD51 [
105]. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponged miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth through ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis [
106]. The intricate network of miR-34s and their target genes underscores the multifaceted role of miR-34a in osteosarcoma pathogenesis. Continued research efforts are essential to fully comprehend the complexity of miR-34s in osteosarcoma and exploit their therapeutic potential in combating this aggressive bone malignancy.
3.12. The role of miR34s in leukemia
Leukemia, particularly acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), is a widespread and challenging form of acute leukemia that accounts for approximately 80% of all cases worldwide [
107]. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), a regulatory circuit has been discovered. The tumor suppressor protein p53 has been found to regulate the expression of miR-34a, which in turn, controls the expression of MDM4. This regulatory circuit plays a pivotal role in orchestrating cancer cell apoptosis and the survival of CLL cells [
108]. In the context of AML, miR-34a's dysregulation has been linked to a circular RNA called circ_POLA2. This circular RNA has been found to impede the maturation of miR-34a, resulting in increased cell proliferation and the aggressiveness of AML [
108]. Circular RNA ATAD1, which is upregulated in AML, has been implicated in cancer cell proliferation by downregulating miR-34b
via promoter methylation [
109]. Furthermore, miR-34c-5p has emerged as a promising target in combating AML stem cells. Its unique mechanism involves inhibiting the shedding of exosomes and inducing cellular senescence through regulation of RAB27B expression. This finding opens up new avenues for targeting AML stem cells to improve treatment outcomes [
110].
These captivating findings underscore the significant role of miR-34s in the intricate landscape of leukemia. By unraveling the dysregulation of miR-34s and their intricate interactions with target genes, we gain invaluable insights into the pathogenesis of leukemia. Ultimately, this knowledge paves the way for the development of innovative and targeted therapeutic strategies, providing hope for improved outcomes for leukemia patients. Continued research into the precise mechanisms and cross-talk of miR-34s within the leukemia context holds tremendous promise for advancing our understanding of this complex disease and translating it into tangible clinical benefits.
3.13. The role of miR34s in bladder cancer
Bladder cancer ranks as the 10th most common cancer globally, with high morbidity and mortality rates. In 2023, it is estimated that there will be approximately 19,870 new cases and 4,550 expected deaths among women, and 62,420 new cases and 12,160 expected deaths among men in the United States alone [
25]. One of the key players in bladder cancer is miR-34a, which has been shown to regulate crucial cellular processes such as cell cycle control, migration, invasion, and autophagy [
111]. MiR-34a exhibits a dual effect in bladder cancer by upregulating the expression of PTEN, a tumor suppressor gene while downregulating MPP2, a gene associated with tumor progression [
112,
113]. Additionally, silencing of DNMT3B, a DNA methyltransferase, was found to promote the expression of miR-34a, resulting in the suppression of cancer migration and invasion [
114]. In non-muscle-invasive bladder tumors, expression of miR-34a has emerged as an independent predictor of recurrence, and in conjunction with the EORTC nomogram, the levels of miR-34a can further improve the predictive capabilities of EORTC [
115]. This highlights the potential of miR-34a as a valuable biomarker for prognostic assessment and treatment decision-making in bladder cancer. Moreover, a panel of four miRNAs, including miR-34a, miR-182, miR-196a, and miR-124, has been identified as a promising non-invasive biomarker for bladder cancer, exhibiting high diagnostic accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.985 [
116].
By elucidating the regulatory roles of miR-34a and other miRNAs in key cellular processes and their implications in diagnostic and prognostic strategies, we can enhance our ability to detect bladder cancer at early stages, predict disease progression, and develop targeted therapeutic interventions.
4. Exploring miR-34s in drug resistance
Resistance to conventional chemotherapy remains a significant challenge in cancer treatment. Therapy resistance leads to cancer relapse and poor patient outcomes. Numerous studies have demonstrated that altered levels of circulating miR-34s or tumor-specific miR-34 expressions are associated with poor response to chemotherapy [
117,
118,
119]. In patients with osteosarcoma, serum levels of miR-34a have been correlated with chemotherapy resistance, metastasis, recurrence, overall survival, and prognosis [
120]. In colorectal cancers with inactive p53, targeting the miR-34a/LRPPRC/MDR1 axis has shown promise in overcoming resistance to chemotherapeutic agents such as gossypol-acetic acid and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) [
121]. The ability of miR-34a to suppress cancer stem cell renewal has been linked to the reduction of gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer [
122]. Furthermore, miR-34a has been revealed to reverse multidrug resistance (MDR) to various chemotherapeutic agents including 5-FU, cisplatin (DDP), oxaliplatin, and epirubicin (EPI) in gastric cancer cells [
123]. In bladder cancer, exosomal lncRNA LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes resistance to DDP by targeting the miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis [
124]. MiR-34b expression has been reported to enhance paclitaxel chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer cells [
125]. MiR-34b also suppresses MDR to multiple drugs (paclitaxel, pirarubicin, EPI, hydrochloride, adriamycin, and DDP) in bladder cancer by regulating the expression of CCND2 and P2RY1 [
126].
In the case of miR-34c, its role in drug resistance is complex and context-dependent. It has been reported to protect lung cancer cells from paclitaxel-induced apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bmf (Bcl-2-modifying factor) [
127]. However, decreased miR-34c expression has also been observed in patients with NSCLC who exhibited a poor response to chemotherapy and increased metastasis. MiR-34c overexpression sensitized NSCLC cells to paclitaxel and DDP both
in vitro and
in vivo [
128]. MiR-34c also inhibits MDR to paclitaxel and DDP in gastric cancer cells [
129]. In ovarian cancer, the miR-34c/SOX9 axis regulated DDP -based drug resistance, and the miR-34c-AREG-EGFR-ERK pathway inhibited amphiregulin-induced cancer stemness and drug resistance [
130,
131].
Understanding the intricate roles of miR-34s in mediating drug resistance provides valuable insights for developing strategies to overcome treatment limitations and improve patient outcomes. Harnessing the potential of miR-34s as therapeutic targets or predictive biomarkers may lead to the development of personalized treatment approaches and the effective management of drug resistance in various cancer types.
Overcoming chemoresistance by targeting CSCs
Chemoresistance, a common hurdle in cancer treatment, has been attributed to the presence of a small population of CSCs that possess self-renewal and differentiation capabilities [
132]. These CSCs are thought to be responsible for tumor initiation, progression, and relapse. Due to its ability to suppress CSC activity, targeting CSCs using miR-34-based therapies has emerged as a promising approach to overcome chemoresistance and improve treatment outcomes [
133]. In taxane-resistant prostate cancer, co-delivery of DTX, a chemotherapy drug, and rub one (RUB), an activator of miR-34a specifically targeting CSCs showed that the combination therapy effectively suppressed CSC-related markers, reduced the CSC population, and enhanced the therapeutic response compared to DTX alone [
132,
134]. Furthermore, miR-34 mimics have been shown to sensitize CSCs to chemotherapy. A combination of miR-34a mimic and doxorubicin, a commonly used chemotherapy drug used in breast cancer synergistically inhibited breast cancer CSC properties and significantly reduced tumor growth compared to either treatment alone by sensitizing the CSCs to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis, thereby overcoming the chemoresistance [
135,
136].
In addition to targeting CSCs directly, miR-34-based therapies have been explored for modulating the tumor microenvironment to disrupt CSC-related signaling pathways. For instance, miR-34a mimic delivery using nanocarriers was found to suppress the expression of CSC-associated factors and promote the differentiation of CSCs in hepatocellular carcinoma. This resulted in reduced tumor growth and enhanced chemosensitivity [
137]. Moreover, the combination of miR-34 mimics with natural compounds known for their anti-cancer effects has shown promise in targeting CSCs. For example, the co-delivery of miR-34a mimic with curcumin, a natural compound derived from turmeric, demonstrated synergistic effects in inhibiting CSC properties and suppressing tumor growth in colorectal cancer models [
138]. Collectively, these studies highlight the potential of miR-34-based therapies in targeting CSCs and overcoming chemoresistance. By specifically inhibiting CSCs and their associated signaling pathways, miR-34 mimics hold promise for improving treatment outcomes and address the challenges posed by CSC-mediated resistance in cancer therapy.
5. MiR-34s and cancer therapy
MiR-34s have brought about a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. Their ability to regulate gene expression and control critical processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis, has positioned miR-34s as promising candidates for targeted cancer treatment [
29,
133,
139].
Figure 3 depicts the schematic representation of the therapeutic application of miR-34s in cancer therapy and illustrates the potential impact of these molecules on combating cancer. In this section, we discuss the potential of miR-34s in cancer therapy and the diverse strategies used to harness their therapeutic potential.
5.1. Chemically synthesized miR-34: Clinical trials and beyond
The development of MRX34, a chemically synthesized miR-34a mimic, has opened up new possibilities for clinical trials to investigate the therapeutic potential of miR-34 mimics in various types of cancer. A phase I/II multicenter clinical trial (MRX34, NCT01829971) evaluated the safety and efficacy of MRX34 in patients with primary liver cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer [
140,
141,
142]. This trial includes 155 participants from seven different cancer types, including primary liver cancer, various solid tumors, and hematopoietic malignancies [
140]. The study found that patients treated with MRX34 experienced adverse events, such as fever and fatigue. The MTD was determined to be 110 mg/m
2 for non-HCC patients and 93 mg/m
2 for HCC patients [
143]. Importantly, MRX34 demonstrated antitumor activity in patients with refractory solid tumors [
144]. Additionally, the biodistribution of MRX34 was found to be broad and can be detected in various tissues including the liver, bone marrow, spleen, mammary gland, and lung [
145]. This widespread distribution of MRX34 enables its potential application in the treatment of different cancer types.
Indeed, recent studies have shown promising anti-tumor activity of MRX34 in various cancer types. In liver tumor xenograft models, systemic delivery of MRX34 led to a 1000-fold increase in miR-34a levels resulting in inhibition of tumor growth [
143] and tumor regression in more than one-third of tumor-bearing mice [
142]. These encouraging findings have prompted further investigations and sparked interest in exploring the potential of miR-34 mimics in other cancer types. The following are some additional studies to evaluate the efficacy of miR-34 mimics in diverse cancer types and explore their potential as a broad-spectrum therapeutic approach [
142].
Lung cancer: Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of miR-34 mimics in patients with lung cancer. These trials aim to assess the impact of miR-34a mimic therapy on tumor growth, metastasis, and patient outcomes in different subtypes of lung cancer [
146,
147]. Additionally, using a pre-clinical mouse model of NSCLC known as 344SQ, treatment with MRX34 led to decreased expression of PD-L1 protein, increased infiltration of tumor-fighting CD8
+ cells, and decreased infiltration of PD1
+ T-cells, macrophages, and T-regulatory cells, leading to delay in tumor growth [
141]. Furthermore, a combination of miR-34a and let-7b by the encapsulated vehicle NOV340 reduced tumor burden and prolonged survival in therapy-resistant NSCLC mouse models [
146].
Lymphoma: The initial multicenter clinical trial (NCT01829971) included patients with lymphoma and provided evidence for the feasibility and potential benefits of miR-34 mimic therapy in this type of cancer. More studies to investigate the specific effects of miR-34 mimics on different subtypes of lymphoma and patient response rates are currently ongoing [
148,
149,
150].
Breast cancer: Clinical trials are being planned or conducted to explore the role of miR-34 mimics in the treatment of breast cancer. These trials aim to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of miR-34a mimic in combination with standard treatments, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies [
143,
151].
Prostate cancer: Studies and clinical trials to investigate the potential of miR-34 mimics in the treatment of prostate cancer, including the effects of miR-34a mimic on tumor regression, metastasis, and patient survival rates in prostate cancer patients are ongoing [
144,
152].
5.2. Enhancing miR-34 efficacy: Chemical modifications and nano-delivery systems
The efficacy of miR-34 in cancer therapy has sparked significant interest in developing new strategies to enhance its therapeutic potential. Chemical modifications and the development of nano-delivery systems have emerged as promising approaches to optimize the delivery and stability of miR-34, thereby improving its efficacy. These advancements aim to overcome the challenges associated with miRNA delivery, such as poor cellular uptake, rapid degradation, and off-target effects. By incorporating chemical modifications and development of nano-delivery systems, the goal is to enhance the stability, target specificity, and therapeutic activity of miR-34, paving the way for its effective use in cancer treatment. This section describes the recent advance in enhancing miR-34 efficacy through these innovative strategies.
5.2.1. Chemical modifications to enhance the stability and potency
Chemical modifications aim to prevent nuclease degradation, reduce off-target effects, and improve the efficacy of miR-34 mimic therapy. One commonly employed strategy involves the incorporation of locked nucleic acids (LNAs) into the miR-34 mimic sequence [
153]. LNAs are modified RNA nucleotides with enhanced stability and binding affinity by locking the ribose in a ring conformation. Incorporation of LNAs into miR-34 mimics has been demonstrated to significantly improve their resistance to nucleases and increase their intracellular availability, resulting in enhanced suppression of target genes [
154]. Another approach involves the use of 2'-O-methyl modifications, where the 2'-hydroxyl group in the ribose sugar of miR-34 mimics is replaced with a methyl group. This modification enhances the stability and reduces immunostimulatory effects, thereby improving the pharmacokinetic properties of the miR-34 mimics [
155]. Furthermore, conjugating miR-34 mimics with cholesterol or other lipid moieties has been tested to improve cellular uptake and intracellular delivery. The hydrophobic nature of these modifications enables efficient association with cell membranes, facilitating endocytosis and subsequent release of the miR-34 mimics into the cytoplasm [
156,
157].
5.2.2. Nano-delivery systems for enhanced cellular uptake
Nano-delivery systems, such as liposomes or nanoparticles, have emerged as effective carriers for delivering miR-34 mimics to cancer cells. These systems offer several advantages, including protection of miR-34 mimics from enzymatic degradation, improved cellular uptake, and controlled release at the target site [
158,
159]. Liposomes, composed of lipid bilayers, have been extensively studied as delivery vehicles for the miRNAs [
159]. Liposomes can encapsulate miR-34 mimics within their aqueous core or incorporate them into the lipid membrane. Liposomes can shield miR-34 mimics from extracellular degradation, facilitate their internalization into cancer cells through endocytosis, and allow controlled release of miR-34 mimics within the cells [
143,
160]. In addition to liposomes, various types of nanoparticles, such as polymeric nanoparticles and lipid nanoparticles, have been utilized for the delivery of miR-34 mimics [
161,
162]. These nanoparticles offer advantages such as tunable particle sizes, stability, and versatile surface modifications, enabling enhanced targeting and cellular uptake. Successful delivery of miR-34 mimics and efficient gene silencing using nanoparticles has been demonstrated [
163]. Moreover, incorporating targeting ligands, such as antibodies or peptides, onto the surface of nano-delivery systems can enhance the specific uptake of miR-34 mimics by the cancer cells to improve the therapeutic outcomes [
164]. In summary, chemical modifications and nano-delivery systems represent valuable strategies for enhancing the stability, potency, and cellular uptake of miR-34 mimics. These approaches have shown promise in preclinical studies for advancing miR-34-based therapeutics in cancer treatment.
5.3. Synergistic effects of co-delivery of miR-34 strategies
The co-delivery of miR-34 mimics and other therapeutic agents has gained significant attention due to their ability to enhance the efficacy of cancer treatment. By simultaneously targeting multiple pathways involved in tumor growth and progression, the co-delivery of therapeutics targeting multiple pathways involved in tumor growth and progression can create a synergistic effect and amplify the overall therapeutic outcomes [
134]. Selection of specific co-delivery strategies should be guided by preclinical studies and clinical trials tailored to the specific cancer type and treatment options [
165,
166]. Here, we highlight the potential benefits of the co-delivery approaches.
5.3.1. Co-delivery of miR-34 Mimics with Natural Compounds
Thymoquinone (TQ, a derivative of the Chinese herbal medicine Dendrobium) possesses potent anti-tumor properties, including inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. When combined with miR-34 mimics, TQ synergistically enhances their therapeutic activity, resulting in overall better treatment outcomes [
136,
167]. Another natural compound with anti-cancer properties is curcumin. The anti-cancer effects of curcumin are derived from its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and pro-apoptotic activities. Co-delivery of miR-34 mimics with curcumin enhances their intracellular uptake and stability, leading to synergistic inhibition of tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance [
168,
169].
5.3.2. Co-Delivery with conventional chemotherapy drugs
Paclitaxel is a commonly used chemotherapy drug that disrupts microtubule dynamics, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Co-delivery of miR-34 mimics with paclitaxel can enhance the cytotoxic effects of paclitaxel by targeting different molecular pathways simultaneously. This approach has the potential to overcome chemoresistance and improves treatment outcomes in various cancer types [
170,
171]. Similarly, doxorubicin is a potent chemotherapy agent used in the treatment of several cancers. Co-delivery of miR-34 mimics with doxorubicin enhances anti-cancer efficacy by sensitizing cancer cells to the drug's cytotoxic effects. This combination has shown promise in overcoming drug resistance and improving therapeutic outcomes in preclinical studies [
172].
5.3.3. Co-delivery with targeted therapies
Co-delivery of miR-34 mimics with targeted therapies aims to elicit synergistic effects between targeted therapies and miR-34-based therapy. For example, co-delivery of miR-34 mimics with inhibitors of specific signaling pathways, such as the EGFR inhibitors or PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitors, can result in enhanced inhibition of tumor growth and improved patient response rates [
173]. The combination of miR-34 mimics with complementary therapeutic agents, whether natural compounds or conventional drugs, offers the advantage of targeting multiple pathways simultaneously. This approach can overcome drug resistance, improve treatment efficacy, and potentially reduce side effects associated with high doses of individual drugs.
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
The emerging roles of miR-34s as critical tumor suppressors in various cancers open up exciting possibilities for their therapeutic application. Future studies to delineate the complex signaling pathways regulated by miR-34s not only will advance our understanding of their functions but also will identify novel targets for medical intervention. In-depth studies are warranted to elucidate the specific downstream targets of miR-34s and their precise mechanisms of action in different cancer types. This knowledge will enable the development of more specific and personalized miR-34-based therapies [
174,
175].
While the therapeutic potential of miR-34 mimics is promising, several challenges need to be addressed before the successful translation into clinical practice. One challenge is the efficient and specific delivery of miR-34 mimics to cancer cells. The development of advanced nano-delivery systems to ensure effective delivery to the tumor site and chemical modifications of miR-34 mimics will further enhance the stability, cellular uptake, and intracellular release of miR-34 mimics. Overcoming issues related to biodegradation and toxicity of the delivery systems is crucial to maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing potential adverse effects [
140,
176].
Additionally, the development of miR-34-based therapies faces challenges related to their stability. MiR-34 mimics are susceptible to degradation by nucleases in the bloodstream and cellular environment [
177]. Therefore, improving the stability of miR-34 mimics through chemical modifications or encapsulation within protective carriers to achieve therapeutic levels and enhance their therapeutic effects. Another challenge is the cost associated with the production and delivery of miR-34 mimics. The synthesis process of miR-34-based therapeutics and the need for specialized delivery systems contribute to the high cost of miR-34-based therapies. Strategies to optimize and streamline the manufacturing process could help reduce the overall cost, making these therapies more accessible and affordable for patients [
56,
178].
Moreover, the identification of reliable biomarkers that predict patient response to miR-34-based therapy is essential. Biomarker discovery efforts are crucial for patient stratification, enabling the selection of individuals who are most likely to benefit from miR-34 mimics. Such personalized treatment approaches would optimize treatment outcomes, minimize potential side effects, and maximize the cost-effectiveness of miR-34-based therapies [
179,
180].
Considering the complexity of cancer and the dynamic nature of tumor progression, combination therapies that target multiple pathways hold great promise. Combining miR-34 mimics with conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or immunotherapies can potentially overcome drug resistance and improve patient responses. Synergistic effects can be achieved by simultaneously targeting CSCs and bulk tumor cells, disrupting key oncogenic pathways, and reestablishing tumor suppressor functions [
175,
181].
In conclusion, while miR-34-based therapies show tremendous potential in cancer treatment, several challenges must be overcome. Addressing issues related to delivery efficiency, stability, toxicity, and cost-effectiveness will be crucial in realizing the full therapeutic potential of miR-34 mimics. Furthermore, exploring combination therapies and uncovering novel mechanisms of action will contribute to the development of new and effective miR-34-based cancer therapeutics.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the assistance of personnel from the Research Center for Preclinical Medicine, Southwest Medical University in the preparation of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81672887, 82073263 to JF), and the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S.A (R01CA188471, R01CA266432 to RCW, and R01CA255996 to MYW).
Ethics Approval
Not applicable
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the preparation of this manuscript. S.I. and J.F. are responsible for the preparation of the figures. J.F., M.Y.W., and R.C.W. wrote the paper. J.F., S.I., and R.C.W edited and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript before publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Patient Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Data Sharing
No additional data is available.
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
References
- Meister, G. and T. Tuschl, Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature, 2004. 431(7006): p. 343-9. [CrossRef]
- Bouyssou, J.M., et al., Regulation of microRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014. 1845(2): p. 255-65. [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H., The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ, 2010. 17(2): p. 193-9. [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M. and R.A. Knight, miR-34: from bench to bedside. Oncotarget, 2014. 5(4): p. 872-81. [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M., et al., The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol, 2014. 6(3): p. 214-30. [CrossRef]
- Maroof, H., et al., Role of microRNA-34 family in cancer with particular reference to cancer angiogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol, 2014. 97(2): p. 298-304. [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.S., S.N. Bhattacharyya, and W. Filipowicz, Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol, 2007. 17(3): p. 118-26. [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P., MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell, 2009. 136(2): p. 215-33. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.C., J. Singh, and S. Barik, MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol, 2011. 3(3): p. 83-92.
- Bommer, G.T., et al., p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr Biol, 2007. 17(15): p. 1298-307. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K., et al., Circulating microRNA-34 family low expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis, 2017. 9(10): p. 3735-3746. [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H., et al., Overexpression of the miR-34 family suppresses invasive growth of malignant melanoma with the wild-type p53 gene. Exp Ther Med, 2012. 3(5): p. 793-796. [CrossRef]
- Beresneva, E.V., et al., [Methylation profile of group of miRNA genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma; involvement in cancer progression]. Genetika, 2013. 49(3): p. 366-75. [CrossRef]
- Fujino, T., et al., AU-1 from Agavaceae plants causes transient increase in p21/Cip1 expression in renal adenocarcinoma ACHN cells in an miR-34-dependent manner. J Nat Med, 2017. 71(1): p. 36-43. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q., et al., Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer, 2008. 8: p. 266. [CrossRef]
- Imani, S., et al., MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget, 2017. 8(13): p. 21362-21379. [CrossRef]
- Kaboli, P.J., et al., MicroRNA-based therapy and breast cancer: A comprehensive review of novel therapeutic strategies from diagnosis to treatment. Pharmacol Res, 2015. 97: p. 104-21. [CrossRef]
- Toyota, M., et al., Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation gene 4 is associated with CpG island methylation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res, 2008. 68(11): p. 4123-32. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J., et al., Erratum: pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a case-control study in a Chinese population. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet, 2017. 8(5): p. 59.
- Wang, L., et al., The analysis of microRNA-34 family expression in human cancer studies comparing cancer tissues with corresponding pericarcinous tissues. Gene, 2015. 554(1): p. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Welponer, H., et al., The miR-34 family and its clinical significance in ovarian cancer. J Cancer, 2020. 11(6): p. 1446-1456. [CrossRef]
- Corney, D.C., et al., Frequent downregulation of miR-34 family in human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res, 2010. 16(4): p. 1119-28. [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A., G. Munkacsy, and B. Gyorffy, Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci Rep, 2021. 11(1): p. 6047. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., et al., Serum exosomal miR-34a as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and prognostic of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer, 2022. 13(5): p. 1410-1417. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L., et al., Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023. 73(1): p. 17-48.
- Ma, W., et al., Dysregulation of the miR-34a-SIRT1 axis inhibits breast cancer stemness. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(12): p. 10432-44. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., et al., MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med, 2013. 13(2): p. 109-17. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., et al., MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene, 2013. 32(36): p. 4294-303. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., et al., The comprehensive landscape of miR-34a in cancer research. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2021. 40(3): p. 925-948. [CrossRef]
- Achari, C., et al., Expression of miR-34c induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer, 2014. 14: p. 538. [CrossRef]
- Raver-Shapira, N., et al., Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell, 2007. 26(5): p. 731-43. [CrossRef]
-
mRNA Vaccine Slows Melanoma Recurrence. Cancer Discov, 2023: p. Of1.
- Lujambio, A., et al., A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008. 105(36): p. 13556-61. [CrossRef]
- Mandke, P., et al., MicroRNA-34a modulates MDM4 expression via a target site in the open reading frame. PLoS One, 2012. 7(8): p. e42034. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G., et al., MicroRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation by targeting LMTK3 in human breast cancer mcf-7 cell line. DNA Cell Biol, 2013. 32(12): p. 699-707. [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.V., et al., MiR-34a-3p alters proliferation and apoptosis of meningioma cells in vitro and is directly targeting SMAD4, FRAT1 and BCL2. Aging (Albany NY), 2017. 9(3): p. 932-954. [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y., et al., Targeting of miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cancer Res, 2014. 74(24): p. 7573-82. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J., et al., MicroRNA-34a modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to adriamycin by targeting Notch1. Arch Med Res, 2012. 43(7): p. 514-21. [CrossRef]
- Yu, F., et al., MicroRNA 34c gene down-regulation via DNA methylation promotes self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumor-initiating cells. J Biol Chem, 2012. 287(1): p. 465-73. [CrossRef]
- Tokumaru, Y., et al., High Expression of miR-34a Associated with Less Aggressive Cancer Biology but Not with Survival in Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(9). [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, P., et al., Dual role for miR-34a in the control of early progenitor proliferation and commitment in the mammary gland and in breast cancer. Oncogene, 2019. 38(3): p. 360-374. [CrossRef]
- Deng, S., et al., p53 downregulates PD-L1 expression via miR-34a to inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells: a potential clinical immunotherapeutic target. Mol Biol Rep, 2023. 50(1): p. 577-587. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z., et al., Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Yonsei Med J, 2017. 58(4): p. 697-702. [CrossRef]
- Chou, J., S. Provot, and Z. Werb, GATA3 in development and cancer differentiation: cells GATA have it! J Cell Physiol, 2010. 222(1): p. 42-9.
- Tsiakou, A., et al., Prognostic significance of miR-34 rs4938723 T > C polymorphism in triple negative breast cancer patients. Clin Biochem, 2019. 68: p. 9-14. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J., et al., pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a case-control study in a Chinese population. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet, 2017. 8(1): p. 1-7.
- Hashemi, M., et al., Pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism increased the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Biomark, 2017. 18(2): p. 155-159. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., XIST/miR-34a-5p/PDL1 axis regulated the development of lung cancer cells and the immune function of CD8(+) T cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 2022. 42(5): p. 469-478. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S., et al., MiR-34a and miR-34b/c have distinct effects on the suppression of lung adenocarcinomas. Exp Mol Med, 2019. 51(1): p. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Lai, W., Y. Yue, and G. Zeng, MicroRNA-34c-5p Reduces Malignant Properties of Lung Cancer Cells through Regulation of TBL1XR1/Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling. Curr Mol Med, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K., et al., The microRNA expression signature of small cell lung cancer: tumor suppressors of miR-27a-5p and miR-34b-3p and their targeted oncogenes. J Hum Genet, 2017. 62(7): p. 671-678. [CrossRef]
- Feng, H., et al., MiR-34b-3p represses cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by targeting CDK4. J Cell Mol Med, 2019. 23(8): p. 5282-5291. [CrossRef]
- Daugaard, I., et al., The association between miR-34 dysregulation and distant metastases formation in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol, 2017. 102(3): p. 484-491. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H., et al., Combined Effect of Metastasis-Related MicroRNA, miR-34 and miR-124 Family, Methylation on Prognosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Lung Cancer, 2017. 18(1): p. e13-e20. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., et al., LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 enhances cell invasion, migration and tumor formation in non-small cell lung cancer cells by epigenetic inhibition of miR-34a. Curr Pharm Biotechnol, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nie, D., et al., Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential. Int J Mol Sci, 2019. 20(4). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H., et al., LncRNA RP11-805J14.5 functions as a ceRNA to regulate CCND2 by sponging miR-34b-3p and miR-139-5p in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep, 2022. 48(3). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., et al., The miR-34a-5p-c-MYC-CHK1/CHK2 Axis Counteracts Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties and Enhances Radiosensitivity in Hepatocellular Cancer Through Repression of the DNA Damage Response. Radiat Res, 2023. 199(1): p. 48-60. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C., et al., Combined low miR-34s are associated with unfavorable prognosis in children with hepatoblastoma: A Chinese population-based study. J Pediatr Surg, 2016. 51(8): p. 1355-61. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L., et al., Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-miR-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genet Mol Res, 2016. 15(4). [CrossRef]
- Wu, X., et al., Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor miR-34a contributes to head and neck cancer by up-regulating the MET oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021. 40(1): p. 70. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., et al., miR-34a-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in head and neck squamous cell cancer progression by targeting Flotillin-2. Int J Biol Sci, 2021. 17(15): p. 4327-4339. [CrossRef]
- He, W., et al., CircCRIM1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via the miR-34c-5p/FOSL1 axis. Eur J Med Res, 2022. 27(1): p. 59. [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M., et al., Expression Level of miR-34a in Tumor Tissue from Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer, 2019. 50(2): p. 304-307. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L., et al., Tumor suppressor microRNA-34a inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP-2/MMP-9/FNDC3B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol, 2017. 51(1): p. 378-388. [CrossRef]
- Nie, J., et al., miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1. Oncol Rep, 2015. 34(1): p. 311-7. [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.F., et al., miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting MMP9 and MMP14. PLoS One, 2014. 9(9): p. e108435. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H., et al., MicroRNA-34a inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting E2F5. J BUON, 2019. 24(6): p. 2514-2522.
- Zhou, H., et al., miR-34a inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via regulation of FOXM1. Oncol Lett, 2019. 17(1): p. 706-712. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q., et al., Hypermethylation of miR-34b/c is associated with early clinical stages and tumor differentiation in Kazakh patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019. 12(8): p. 3119-3127.
- Xiong, S., et al., Role of miR-34 in gastric cancer: From bench to bedside (Review). Oncol Rep, 2019. 42(5): p. 1635-1646. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L., et al., Human cytomegalovirus protein UL136 activates the IL-6/STAT3 signal through MiR-138 and MiR-34c in gastric cancer cells. Int J Clin Oncol, 2020. 25(11): p. 1936-1944. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q., et al., MicroRNA-34c-5p exhibits anticancer properties in gastric cancer by targeting MAP2K1 to inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Biomed Res Int, 2022. 2022: p. 7375661. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S., et al., Silencing of Long Non-coding RNA LINC01106 Represses Malignant Behaviors of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting miR-34a-5p/MYCN Axis. Mol Biotechnol, 2022. 64(2): p. 144-155. [CrossRef]
- Meng, F., et al., miR-34a induces immunosuppression in colorectal carcinoma through modulating a SIRT1/NF-kappaB/B7-H3/TNF-alpha axis. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021. 70(8): p. 2247-2259. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L. and H. Hermeking, miR-34a and miR-34b/c Suppress Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res, 2017. 77(10): p. 2746-2758. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H., et al., miRNA-34a suppresses colon carcinoma proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by targeting SYT1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019. 12(8): p. 2887-2897.
- Jun, H.H., et al., Association between TP53 genetic polymorphisms and the methylation and expression of miR-34a, 34b/c in colorectal cancer tissues. Oncol Lett, 2019. 17(5): p. 4726-4734. [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.B., J. Fichna, and P. Mosinska, One step ahead: miRNA-34 in colon cancer-future diagnostic and therapeutic tool? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2018. 132: p. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., NONHSAG028908.3 sponges miR-34a-5p to promote growth of colorectal cancer via targeting ALDOA. Oncol Rep, 2023. 49(5). [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y., et al., MicroRNA-34 suppresses proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells by triggering autophagy and apoptosis and inhibits cell invasion by targeting Notch 1. Biochimie, 2019. 160: p. 193-199. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S., et al., Exosomal miR-34b inhibits proliferation and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Notch2 in ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett, 2020. 20(3): p. 2721-2728. [CrossRef]
- Shu, C., et al., ncRNA-mediated low expression of P2RY14 correlates with poor prognosis and tumor immune infiltration in ovarian carcinoma. Ann Transl Med, 2023. 11(1): p. 10. [CrossRef]
- Cordova-Rivas, S., et al., 5p and 3p Strands of miR-34 Family Members Have Differential Effects in Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Cervical Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci, 2019. 20(3). [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. and H. Cheng, miR-34a-5p blocks cervical cancer growth and migration by downregulating CDC25A. J BUON, 2021. 26(5): p. 1768-1774.
- Wei, H., et al., miR-34c-5p targets Notch1 and suppresses the metastasis and invasion of cervical cancer. Mol Med Rep, 2021. 23(2). [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J., et al., Prostate cancer and microRNAs: New insights into apoptosis. Pathol Res Pract, 2023. 245: p. 154436. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J., et al., MicroRNA-34a, Prostate Cancer Stem Cells, and Therapeutic Development. Cancers (Basel), 2022. 14(18). [CrossRef]
- Dong, B., et al., MiR-34a affects G2 arrest in prostate cancer PC3 cells via Wnt pathway and inhibits cell growth and migration. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020. 24(16): p. 8349-8358. [CrossRef]
- Li, N., et al., Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 functions as miRNA sponge to promote the prostate cancer tumorigenesis through targeting miR-34a. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019. 23(9): p. 3688-3698. [CrossRef]
- Ma, E., et al., LINC01006 facilitates cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer through targeting miR-34a-5p to up-regulate DAAM1. Cancer Cell Int, 2020. 20: p. 515. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y., et al., Long noncoding RNA DANCR contributes to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer through targeting the miR-34a-5p/JAG1 pathway. Onco Targets Ther, 2019. 12: p. 5485-5497. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X., et al., LncRNA NEAT1 promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by regulating ACSL4 via sponging miR-34a-5p and miR-204-5p. Cell Signal, 2020. 65: p. 109422. [CrossRef]
- Xi, L., et al., miR-34 inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma in nude mice through targetly regulating TGIF2 expression. Biosci Rep, 2018. 38(3). [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., et al., Mir-34a: a regulatory hub with versatile functions that controls osteosarcoma networks. Cell Cycle, 2022. 21(20): p. 2121-2131. [CrossRef]
- Gourbault, O. and L. Llobat, MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Canine Osteosarcoma: A New Future? Vet Sci, 2020. 7(4). [CrossRef]
- Liang, X., et al., The DNMT1/miR-34a Axis Is Involved in the Stemness of Human Osteosarcoma Cells and Derived Stem-Like Cells. Stem Cells Int, 2019. 2019: p. 7028901. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X., et al., Isovitexin Suppresses Cancer Stemness Property And Induces Apoptosis Of Osteosarcoma Cells By Disruption Of The DNMT1/miR-34a/Bcl-2 Axis. Cancer Manag Res, 2019. 11: p. 8923-8936. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P., et al., LncRNA HCG18 Promotes Osteosarcoma Cells Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in by Regulating miR-34a/RUNX2 Pathway. Biochem Genet, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., et al., Long Noncoding RNA DICER1-AS1 Functions in Methylation Regulation on the Multi-Drugresistance of Osteosarcoma Cells via miR-34a-5p and GADD45A. Front Oncol, 2021. 11: p. 685881. [CrossRef]
- Ji, S., et al., Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulates the development of osteosarcoma through sponging miR-34a-5p to mediate HOXA13 expression as a competitive endogenous RNA. Mol Genet Genomic Med, 2019. 7(6): p. e673. [CrossRef]
- Song, K., et al., Long noncoding RNA CASC11 promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by suppressing degradation of snail mRNA. Am J Cancer Res, 2019. 9(2): p. 300-311.
- Sun, Z., T. Zhang, and B. Chen, Long Non-Coding RNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1) Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting c-Met and SOX4 via miR-34a/c-5p and miR-449a/b. Med Sci Monit, 2019. 25: p. 1410-1422. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y., et al., Long Noncoding RNA SNHG7 Promotes the Tumor Growth and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Regulation of miR-34a Signals in Osteosarcoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2018. 33(9): p. 365-372. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., et al., Long Noncoding RNA HCG9 Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression through RAD51 by Acting as a ceRNA of miR-34b-3p. Mediators Inflamm, 2021. 2021: p. 9978882. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y., et al., LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth via ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis, 2020. 11(4): p. 278. [CrossRef]
- Rose-Inman, H. and D. Kuehl, Acute Leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2017. 31(6): p. 1011-1028.
- Cao, L., et al., A feedback circuit of miR-34a/MDM4/p53 regulates apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Transl Cancer Res, 2020. 9(10): p. 6143-6153. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., et al., Circular RNA ATAD1 is upregulated in acute myeloid leukemia and promotes cancer cell proliferation by downregulating miR-34b via promoter methylation. Oncol Lett, 2021. 22(5): p. 799. [CrossRef]
- Peng, D., et al., miR-34c-5p promotes eradication of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by inducing senescence through selective RAB27B targeting to inhibit exosome shedding. Leukemia, 2018. 32(5): p. 1180-1188. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.I., et al., Tumor suppressive functions of hsa-miR-34a on cell cycle, migration and protective autophagy in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol, 2023. 62(5). [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.S., et al., MicroRNA-34a inhibits bladder cancer cell migration and invasion, and upregulates PTEN expression. Oncol Lett, 2019. 18(5): p. 5549-5554. [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.Y., et al., MicroRNA-34a-5p serves as a tumor suppressor by regulating the cell motility of bladder cancer cells through matrix metalloproteinase-2 silencing. Oncol Rep, 2021. 45(3): p. 911-920. [CrossRef]
- Xu, K., et al., DNMT3B silencing suppresses migration and invasion by epigenetically promoting miR-34a in bladder cancer. Aging (Albany NY), 2020. 12(23): p. 23668-23683. [CrossRef]
- Juracek, J., et al., Tumor expression of miR-34a-3p is an independent predictor of recurrence in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and promising additional factor to improve predictive value of EORTC nomogram. Urol Oncol, 2019. 37(3): p. 184 e1-184 e7. [CrossRef]
- Li, R., et al., A four-miRNA signature in serum as a biomarker for bladder cancer diagnosis. Am J Transl Res, 2022. 14(7): p. 4606-4616.
- Naghizadeh, S., et al., The role of miR-34 in cancer drug resistance. J Cell Physiol, 2020. 235(10): p. 6424-6440.
- Hu, Y., et al., miRNA-205 targets VEGFA and FGF2 and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis, 2016. 7(6): p. e2291. [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.L. and S. Das, The Role of MicroRNAs in Diagnosis, Prognosis, Metastasis and Resistant Cases in Breast Cancer. Curr Pharm Des, 2017. 23(12): p. 1845-1859. [CrossRef]
- Lian, H., et al., MicroRNA34a is associated with chemotherapy resistance, metastasis, recurrence, survival, and prognosis in patient with osteosarcoma. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022. 101(38): p. e30722. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., et al., Targeting the miR-34a/LRPPRC/MDR1 axis collapse the chemoresistance in P53 inactive colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ, 2022. 29(11): p. 2177-2189. [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y., et al., MicroRNA-34a Alleviates Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer by Repression of Cancer Stem Cell Renewal. Pancreas, 2021. 50(9): p. 1260-1266. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J., et al., Hsa-miR-34a-5p reverses multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting the 3'-UTR of SIRT1 and inhibiting its expression. Cell Signal, 2021. 84: p. 110016. [CrossRef]
- Luo, G., et al., Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell resistance to cisplatin by regulating miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2021. 53(5): p. 558-566. [CrossRef]
- Yanokura, M., K. Banno, and D. Aoki, MicroRNA-34b expression enhances chemosensitivity of endometrial cancer cells to paclitaxel. Int J Oncol, 2020. 57(5): p. 1145-1156. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y., et al., MiR-34b-3p Represses the Multidrug-Chemoresistance of Bladder Cancer Cells by Regulating the CCND2 and P2RY1 Genes. Med Sci Monit, 2019. 25: p. 1323-1335. [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S., et al., miR-34c may protect lung cancer cells from paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Oncogene, 2013. 32(3): p. 341-51. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z., et al., MicroRNA-34c-3p target inhibiting NOTCH1 suppresses chemosensitivity and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Int Med Res, 2020. 48(3): p. 300060520904847. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H., et al., Upregulation of miR-34c after silencing E2F transcription factor 1 inhibits paclitaxel combined with cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol, 2020. 26(5): p. 499-513. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S., et al., MiR-34c/SOX9 axis regulates the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cell to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J Cell Biochem, 2019. 120(3): p. 2940-2953. [CrossRef]
- Tung, S.L., et al., miRNA-34c-5p inhibits amphiregulin-induced ovarian cancer stemness and drug resistance via downregulation of the AREG-EGFR-ERK pathway. Oncogenesis, 2017. 6(5): p. e326. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K., Y. Yamamoto, and T. Ochiya, miRNA signaling networks in cancer stem cells. Regen Ther, 2021. 17: p. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J., et al., MicroRNA-34a: Potent Tumor Suppressor, Cancer Stem Cell Inhibitor, and Potential Anticancer Therapeutic. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021. 9: p. 640587. [CrossRef]
- Lin, F., et al., Dual responsive micelles capable of modulating miRNA-34a to combat taxane resistance in prostate cancer. Biomaterials, 2019. 192: p. 95-108. [CrossRef]
- Vares, G., et al., A multimodal treatment of carbon ions irradiation, miRNA-34 and mTOR inhibitor specifically control high-grade chondrosarcoma cancer stem cells. Radiother Oncol, 2020. 150: p. 253-261. [CrossRef]
- Imani, S., R.C. Wu, and J. Fu, MicroRNA-34 family in breast cancer: from research to therapeutic potential. J Cancer, 2018. 9(20): p. 3765-3775. [CrossRef]
- Daverey, A., K.M. Brown, and S. Kidambi, Breast Cancer/Stromal Cells Coculture on Polyelectrolyte Films Emulates Tumor Stages and miRNA Profiles of Clinical Samples. Langmuir, 2015. 31(36): p. 9991-10001. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L., et al., Exosomal miRNA-34 from cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Aging (Albany NY), 2020. 12(9): p. 8549-8564. [CrossRef]
- Kalfert, D., et al., Multifunctional Roles of miR-34a in Cancer: A Review with the Emphasis on Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Thyroid Cancer with Clinical Implications. Diagnostics (Basel), 2020. 10(8). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Y. Liao, and L. Tang, MicroRNA-34 family: a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019. 38(1): p. 53. [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A., et al., PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2016. 108(1). [CrossRef]
- Daige, C.L., et al., Systemic delivery of a miR34a mimic as a potential therapeutic for liver cancer. Mol Cancer Ther, 2014. 13(10): p. 2352-60. [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S., et al., Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer, 2020. 122(11): p. 1630-1637. [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S., et al., Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs, 2017. 35(2): p. 180-188. [CrossRef]
- Kelnar, K. and A.G. Bader, A qRT-PCR Method for Determining the Biodistribution Profile of a miR-34a Mimic. Methods Mol Biol, 2015. 1317: p. 125-33. [CrossRef]
- Kasinski, A.L., et al., A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene, 2015. 34(27): p. 3547-55. [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, J.F., et al., Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res, 2010. 70(14): p. 5923-30. [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.J., et al., Systemic microRNA-34a delivery induces apoptosis and abrogates growth of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in vivo. Leukemia, 2012. 26(11): p. 2421-4. [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.J., et al., Myc-mediated repression of microRNA-34a promotes high-grade transformation of B-cell lymphoma by dysregulation of FoxP1. Blood, 2011. 117(23): p. 6227-36. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., et al., Tumor suppressor miR-34a targets PD-L1 and functions as a potential immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Signal, 2015. 27(3): p. 443-52. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.M., M. Salvatore, and M. Incoronato, miRNA-Based Therapeutics in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Front Oncol, 2021. 11: p. 668464. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., et al., The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med, 2011. 17(2): p. 211-5. [CrossRef]
- Chabot, S., et al., LNA-based oligonucleotide electrotransfer for miRNA inhibition. Mol Ther, 2012. 20(8): p. 1590-8. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, V. and J. Winkler, miRNA-based therapies: strategies and delivery platforms for oligonucleotide and non-oligonucleotide agents. Future Med Chem, 2014. 6(17): p. 1967-84. [CrossRef]
- Soni, K., et al., Detection and knockdown of microRNA-34a using thioacetamido nucleic acid. Nucleic Acid Ther, 2013. 23(3): p. 195-202. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shushan, D., et al., Overcoming obstacles in microRNA delivery towards improved cancer therapy. Drug Deliv Transl Res, 2014. 4(1): p. 38-49. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M., T.P. Prakash, and D.R. Corey, Argonaute 2-dependent Regulation of Gene Expression by Single-stranded miRNA Mimics. Mol Ther, 2016. 24(5): p. 946-55. [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, F., et al., Delivery of biologically active miR-34a in normal and cancer mammary epithelial cells by synthetic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine, 2019. 19: p. 95-105. [CrossRef]
- Moraes, F.C., et al., miRNA Delivery by Nanosystems: State of the Art and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics, 2021. 13(11). [CrossRef]
- Hart, M., et al., Wrinkle in the plan: miR-34a-5p impacts chemokine signaling by modulating CXCL10/CXCL11/CXCR3-axis in CD4(+), CD8(+) T cells, and M1 macrophages. J Immunother Cancer, 2020. 8(2). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., et al., Folate targeted hybrid lipo-polymeric nanoplexes containing docetaxel and miRNA-34a for breast cancer treatment. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021. 128: p. 112305. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., et al., Lipoic Acid-Modified Oligoethyleneimine-Mediated miR-34a Delivery to Achieve the Anti-Tumor Efficacy. Molecules, 2021. 26(16). [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, C.H., S.A. Ioele, and E.S. Day, Layer-by-layer assembled PLGA nanoparticles carrying miR-34a cargo inhibit the proliferation and cell cycle progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2020. 108(3): p. 601-613. [CrossRef]
- Sukocheva, O.A., et al., Perspectives of using microRNA-loaded nanocarriers for epigenetic reprogramming of drug resistant colorectal cancers. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022. 86(Pt 2): p. 358-375. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., et al., Co-delivery of microRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotides and gemcitabine using nanomedicine for pancreatic cancer therapy. Cancer Sci, 2017. 108(7): p. 1493-1503. [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M., et al., Progress in Natural Compounds/siRNA Co-delivery Employing Nanovehicles for Cancer Therapy. ACS Comb Sci, 2020. 22(12): p. 669-700. [CrossRef]
- Tania, M., et al., Thymoquinone against infectious diseases: Perspectives in recent pandemics and future therapeutics. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2021. 24(8): p. 1014-1022.
- Abtahi, N.A., et al., A comparative study on biopharmaceutical function of curcumin and miR-34a by multistimuli-responsive nanoniosome carrier: In-vitro and in-vivo. Front Mol Biosci, 2022. 9: p. 1043277. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S., et al., Curcumin inhibits cancer progression through regulating expression of microRNAs. Tumour Biol, 2017. 39(2): p. 1010428317691680. [CrossRef]
- Wen, D., et al., Micellar Delivery of miR-34a Modulator Rubone and Paclitaxel in Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res, 2017. 77(12): p. 3244-3254. [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S., et al., Therapeutic Delivery of Tumor Suppressor miRNAs for Breast Cancer Treatment. Biology (Basel), 2023. 12(3). [CrossRef]
- Deng, X., et al., Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials, 2014. 35(14): p. 4333-44. [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, C. and F.J. Slack, Combinatorial Action of MicroRNAs let-7 and miR-34 Effectively Synergizes with Erlotinib to Suppress Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cell Cycle, 2015. 14(13): p. 2171-80. [CrossRef]
- Haussecker, D., Current issues of RNAi therapeutics delivery and development. J Control Release, 2014. 195: p. 49-54. [CrossRef]
- Su, D., et al., Exploring microRNAs in craniofacial regenerative medicine. Biochem Soc Trans, 2023. 51(2): p. 841-854. [CrossRef]
- Shen, T., et al., A bionic "Trojan horse"-like gene delivery system hybridized with tumor and macrophage cell membrane for cancer therapy. J Control Release, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ingle, R.G. and W.J. Fang, An Overview of the Stability and Delivery Challenges of Commercial Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics, 2023. 15(4). [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Q., et al., Small Extracellular Vesicles' miRNAs: Biomarkers and Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics, 2023. 15(4). [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E., et al., Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis, 2017. 8(10): p. e3100. [CrossRef]
- Samuel, N., et al., Transcriptome-wide characterization of the endogenous miR-34A-p53 tumor suppressor network. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(31): p. 49611-49622. [CrossRef]
- Nalls, D., et al., Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS One, 2011. 6(8): p. e24099. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).