Submitted:
10 August 2023
Posted:
11 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. C. neoformans infection causes gut microbiome disruption
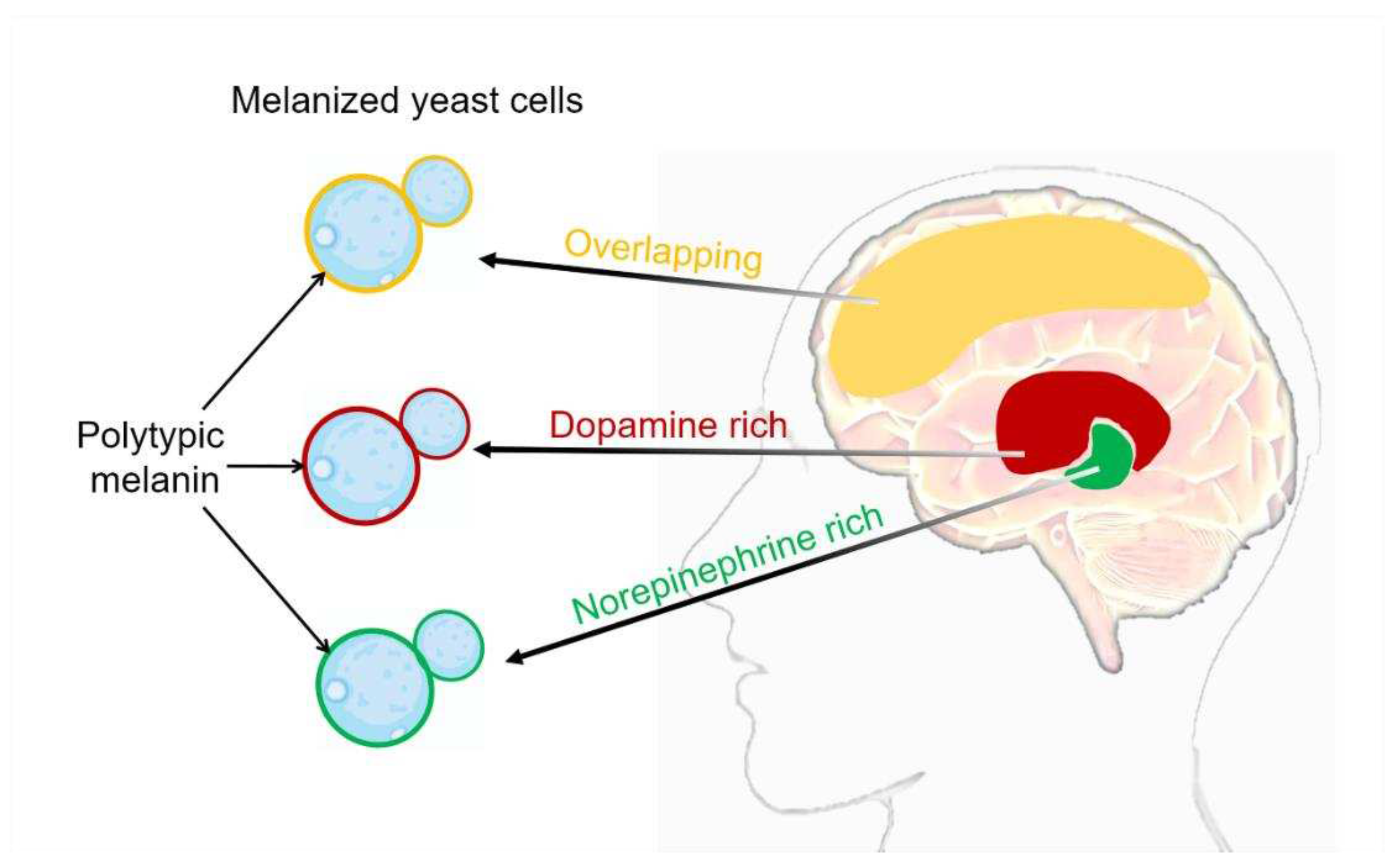
3. C. neoformans melanization in human brain tissue
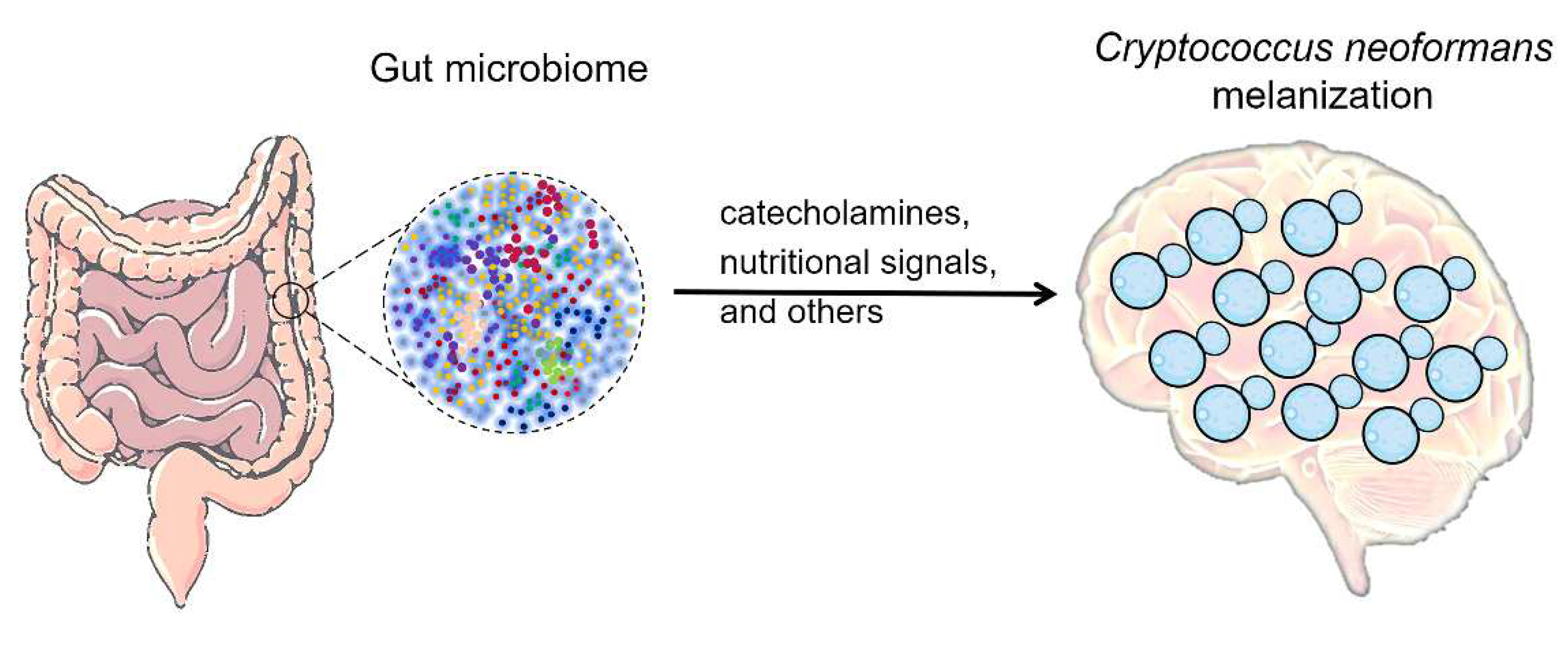
4. The possible impact of gut microbiome on C. neoformans melanization in brain
4.1. Gut microbiome influences the levels of melanin substrates
4.2. Gut microbiome impact on nutritional signals that regulate melanization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Fraser, J.A.; Doering, T.L.; Wang, Z.; Janbon, G.; Idnurm, A.; Bahn, Y.S. , Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, the etiologic agents of cryptococcosis. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine 2014, 4, a019760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, X. , Cryptococcus neoformans: Sex, morphogenesis, and virulence. Infection, genetics and evolution : journal of molecular epidemiology and evolutionary genetics in infectious diseases 2021, 89, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J. , A new species of Filobasidiella, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans B and C serotypes. Mycologia 1976, 68, 943–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J. , A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia 1975, 67, 1197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Heitman, J. From Two to One: Unipolar Sexual Reproduction. Fungal Biol Rev 2015, 29, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, X. , Mechanisms of unisexual mating in Cryptococcus neoformans. Fungal genetics and biology : FG & B 2011, 48, 651–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Heitman, J. , The biology of the Cryptococcus neoformans species complex. Annu Rev Microbiol 2006, 60, 69–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.C.; Stone, N.R.; Wiesner, D.L.; Bicanic, T.; Nielsen, K. , Cryptococcus: from environmental saprophyte to global pathogen. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016, 14, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okurut, S.; Boulware, D.R.; Olobo, J.; Meya, D.B. , Landmark clinical observations and immunopathogenesis pathways linked to HIV and Cryptococcus fatal central nervous system co-infection. Mycoses 2020, 63, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroufi, A.; Chiller, T.; Jordan, A.; Denning, D.W.; Harrison, T.S.; Govender, N.P.; Loyse, A.; Baptiste, S.; Rajasingham, R.; Boulware, D.R. , Ending deaths from HIV-related cryptococcal meningitis by 2030. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2021, 21, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.S.; Lacy, A.J.; Smith, A.T.; Shah, K.S. , Cryptococcal meningitis in an immunocompetent patient. The American journal of emergency medicine 2020, 38, 2492.e1–2492.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.M.; Montrief, T.; Ramzy, M. , Cryptococcal meningitis: a review for emergency clinicians. 2021, 16, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Chu, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M.; Liao, G.; Ding, C.; Xu, Y.; Liao, W.; Wang, L. Cryptococcus neoformans, a global threat to human health. 2023, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. , Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: an updated analysis. The Lancet infectious diseases 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.; Perfect, J.R. , The war on cryptococcosis: A Review of the antifungal arsenal. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2018, 113, e170391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronstad, J.W.; Attarian, R.; Cadieux, B.; Choi, J.; D’souza, C.A.; Griffiths, E.J.; Geddes, J.M.; Hu, G.; Jung, W.H.; Kretschmer, M. , Expanding fungal pathogenesis: Cryptococcus breaks out of the opportunistic box. Nature reviews Microbiology 2011, 9, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botts, M.R.; Hull, C.M. , Dueling in the lung: how Cryptococcus spores race the host for survival. Curr Opin Microbiol 2010, 13, 437–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, D.; Held, J.; Goerke, S.; Wagner, D.; Tintelnot, K.; Henneke, P.; Hufnagel, M. , Primary cutaneous cryptococcosis in an eight-year-old immunocompetent child: how to treat? Klinische Padiatrie 2015, 227, 41–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, E.V.; Lei, S.; Radkov, A.; Volk, R.F. , Secreted fungal virulence effector triggers allergic inflammation via TLR4. 2022, 608, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.R.; Revie, N.M.; Fu, C.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. , Treatment strategies for cryptococcal infection: challenges, advances and future outlook. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, N.T.T.; Flower, B.; Day, J.N. Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis: How Have We Got Here and Where are We Going? 2022, 82, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, S.F.; Kanyama, C.; Heyderman, R.S.; Loyse, A.; Kouanfack, C.; Chanda, D.; Mfinanga, S.; Temfack, E.; Lakhi, S.; Lesikari, S.; Chan, A.K.; Stone, N.; Kalata, N.; Karunaharan, N.; Gaskell, K.; Peirse, M.; Ellis, J.; Chawinga, C.; Lontsi, S.; Ndong, J.G.; Bright, P.; Lupiya, D.; Chen, T.; Bradley, J.; Adams, J.; van der Horst, C.; van Oosterhout, J.J.; Sini, V.; Mapoure, Y.N.; Mwaba, P.; Bicanic, T.; Lalloo, D.G.; Wang, D.; Hosseinipour, M.C.; Lortholary, O.; Jaffar, S.; Harrison, T.S. , Antifungal Combinations for Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis in Africa. The New England journal of medicine 2018, 378, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the diagnosis, prevention and management of cryptococcal disease in HIV-infected adults, adolescents and children (WHO, 2018).
- Arastehfar, A.; Gabaldón, T. , Drug-Resistant Fungi: An Emerging Challenge Threatening Our Limited Antifungal Armamentarium. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.C.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. , Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. 2022, 20, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kano, R.; Sugita, T.; Kamata, H. , Antifungal Susceptibility of Clinical Isolates and Artificially Produced Multi-azole-resistant Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans (formerly: Cryptococcus grubii) to Ravuconazole. Medical mycology journal 2020, 61, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermas, A.; Geddes-McAlister, J. , Combatting the evolution of antifungal resistance in Cryptococcus neoformans. Molecular microbiology 2020, 114, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Altamirano, S.; Ballou, E.R.; Nielsen, K. , A titanic drug resistance threat in Cryptococcus neoformans. Curr Opin Microbiol 2019, 52, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, V.; Boulware, D.R.; Bahr, N.C. , Methods for rapid diagnosis of meningitis etiology in adults. 2020, 14, 459–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasingham, R.; Wake, R.M.; Beyene, T.; Katende, A.; Letang, E.; Boulware, D.R. , Cryptococcal Meningitis Diagnostics and Screening in the Era of Point-of-Care Laboratory Testing. J Clin Microbiol 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wu, J.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, X.; Du, M.; Chen, C.; Liao, W.; Zhi, K.; Pan, W. , Diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: challenges and recent developments. Journal of biomedical science 2023, 30, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, W. , Gut microbiota associated with cryptococcal meningitis and dysbiosis caused by anti-fungal treatment. Front Microbiol 2023, 13, 1086239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.F.; Casadevall, A. , The role of melanin in fungal pathogenesis for animal hosts. Fungal Physiology and Immunopathogenesis 2019, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Rubio, R.; de Oliveira, H.C.; Rivera, J.; Trevijano-Contador, N. , The fungal cell wall: Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus species. Frontiers in microbiology 2020, 10, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Casadevall, A. , Susceptibility of melanized and nonmelanized Cryptococcus neoformans to the melanin-binding compounds trifluoperazine and chloroquine. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 1996, 40, 541–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, P.R. , Biochemical and molecular characterization of the diphenol oxidase of Cryptococcus neoformans: identification as a laccase. J Bacteriol 1994, 176, 656–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.P.; Chrissian, C.; Stark, R.E.; Casadevall, A. , Cryptococcus neoformans melanization incorporates multiple catecholamines to produce polytypic melanin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2022, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Jang, E.-H.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.-T.; Bahn, Y.-S. , Unraveling melanin biosynthesis and signaling networks in Cryptococcus neoformans. MBio 2019, 10, e02267–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, P.R.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S. , Melanin biosynthesis in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol 1998, 180, 1570–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bi, J.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X. , Requirement of a Tsp2-type tetraspanin for laccase repression and stress resistance in the basidiomycete Cryptococcus neoformans. Applied and environmental microbiology 2012, 78, 21–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurudeen, T.A.; Ahearn, D.G. , Regulation of melanin production by Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol 1979, 10, 724–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnalová, L.; Lundgren, P.; Carty, J.R.; Goldstein, N.; Wenski, S.L.; Nanudorn, P.; Thiengmag, S.; Huang, K.-P.; Litichevskiy, L.; Descamps, H.C. , A microbiome-dependent gut–brain pathway regulates motivation for exercise. Nature 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasset, E.; Burcelin, R. , The gut microbiota to the brain axis in the metabolic control. Reviews in endocrine & metabolic disorders 2019, 20, 427–438. [Google Scholar]
- Erny, D.; Dokalis, N.; Mezö, C.; Castoldi, A.; Mossad, O.; Staszewski, O.; Frosch, M.; Villa, M.; Fuchs, V.; Mayer, A.; Neuber, J.; Sosat, J.; Tholen, S.; Schilling, O.; Vlachos, A.; Blank, T.; Gomez de Agüero, M.; Macpherson, A.J.; Pearce, E.J.; Prinz, M. , Microbiota-derived acetate enables the metabolic fitness of the brain innate immune system during health and disease. Cell Metab 2021, 33, 2260–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar]
- Mizgier, M.; Jarzabek-Bielecka, G. , The role of diet and probiotics in prevention and treatment of bacterial vaginosis and vulvovaginal candidiasis in adolescent girls and non-pregnant women. 2020, 91, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Enfert, C.; Kaune, A.K.; Alaban, L.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Cole, N.; Delavy, M.; Kosmala, D.; Marsaux, B.; Fróis-Martins, R.; Morelli, M.; Rosati, D. , The impact of the Fungus-Host-Microbiota interplay upon Candida albicans infections: current knowledge and new perspectives. 2021, 45. [Google Scholar]
- McAleer, J.P.; Nguyen, N.L.; Chen, K.; Kumar, P. , Pulmonary Th17 Antifungal Immunity Is Regulated by the Gut Microbiome. 2016, 197, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Tang, J. , Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolic profiles coincide with intestinal damage in mice with a bloodborne Candida albicans infection. Microbial pathogenesis 2021, 154, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Santos, J.R.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Freitas, G.J.; Bastos, R.W.; Ferreira, G.F.; Miranda, A.S.; Arifa, R.D.; Santos, P.C.; Martins Fdos, S.; Paixão, T.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Souza, D.G.; Santos, D.A. , The absence of microbiota delays the inflammatory response to Cryptococcus gattii. International journal of medical microbiology : IJMM 2016, 306, 187–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, E.; Vij, R. , The structural unit of melanin in the cell wall of the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. 2019, 294, 10471–10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Hu, G.; Jung, W.H.; Kronstad, J.W. , Metals and the cell surface of Cryptococcus neoformans. Curr Opin Microbiol 2023, 74, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, A.; Rosas, A.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D. , Melanin and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Curr Opin Microbiol 2000, 3, 354–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.P.; Casadevall, A. , Reciprocal modulation of ammonia and melanin production has implications for cryptococcal virulence. 2023, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosanchuk, J.D.; Rosas, A.L.; Lee, S.C.; Casadevall, A. , Melanisation of Cryptococcus neoformans in human brain tissue. Lancet (London, England) 2000, 355, 2049–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, A.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Feldmesser, M.; Cox, G.M.; McDade, H.C.; Casadevall, A. , Synthesis of polymerized melanin by Cryptococcus neoformans in infected rodents. Infect Immun 2000, 68, 2845–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregodts, P.; Michotte, Y.; Ebinger, G. , Regional differences in the distribution of norepinephrine and epinephrine in human cerebral cortex: a neurochemical study using HPLC and electrochemical detection. Neuroscience letters 1989, 98, 321–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregodts, P.; Ebinger, G.; Michotte, Y. , Distribution of monoamines in human brain: evidence for neurochemical heterogeneity in subcortical as well as in cortical areas. Brain research 1991, 542, 300–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon-Chung, K.; Tom, W.; Costa, J. , Utilization of indole compounds by Cryptococcus neoformans to produce a melanin-like pigment. Journal of clinical microbiology 1983, 18, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panepinto, J.C.; Williamson, P.R. , Intersection of fungal fitness and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. FEMS yeast research 2006, 6, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacheck, I.; Hearing, V.J.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. , Biochemical studies of phenoloxidase and utilization of catecholamines in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol 1982, 150, 1212–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Casadevall, A.; Dickson, D.W. , Immunohistochemical localization of capsular polysaccharide antigen in the central nervous system cells in cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. The American journal of pathology 1996, 148, 1267–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agirman, G.; Yu, K.B. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. 2021, 374, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Nance, K.; Chen, S. , The Gut-Brain Axis. Annual review of medicine 2022, 73, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. , Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain research 2018, (Pt B), 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Heijtz, R.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. , Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2011, 108, 3047–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; Guzzetta, K.E.; Jaggar, M.; Long-Smith, C.M.; Lyte, J.M.; Martin, J.A.; Molinero-Perez, A.; Moloney, G.; Morelli, E.; Morillas, E.; O’Connor, R.; Cruz-Pereira, J.S.; Peterson, V.L.; Rea, K.; Ritz, N.L.; Sherwin, E.; Spichak, S.; Teichman, E.M.; van de Wouw, M.; Ventura-Silva, A.P.; Wallace-Fitzsimons, S.E.; Hyland, N.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G. , The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol Rev 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Deng, H.; Qiu, J.; Ji, H.; Shen, X. , Antibiotics-induced depression in mice via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Journal of affective disorders 2022, 318, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.C.; Frawley, E.R.; Tapscott, T.; Vázquez-Torres, A. , Bacterial Stress Responses during Host Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 133–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J.; Haynes, K.; Quinn, J. , Nitrosative and oxidative stress responses in fungal pathogenicity. Curr Opin Microbiol 2009, 12, 384–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, J.C.; Bahn, Y.S.; van den Berg, B.; Heitman, J.; Xue, C. , Nutrient and Stress Sensing in Pathogenic Yeasts. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jung, W.H.; Kronstad, J.W. , The cAMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway in pathogenic basidiomycete fungi: Connections with iron homeostasis. Journal of Microbiology 2015, 53, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caza, M.; Kronstad, J.W. , The cAMP/Protein Kinase a Pathway Regulates Virulence and Adaptation to Host Conditions in Cryptococcus neoformans. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H. Gut microbiome and health: mechanistic insights. 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; Lizarbe, B.; Cerdan, S.; Brody, L.; Anastasovska, J.; Ghourab, S.; Hankir, M.; Zhang, S.; Carling, D.; Swann, J.R.; Gibson, G.; Viardot, A.; Morrison, D.; Louise Thomas, E.; Bell, J.D. , The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. , Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2015, 11, 577–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastelli, M.; Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. , The Gut Microbiome Influences Host Endocrine Functions. Endocrine reviews 2019, 40, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Jordan, B.F. , Gut microbiota-mediated inflammation in obesity: a link with gastrointestinal cancer. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology 2018, 15, 671–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, E.S.; Preston, T.; Frost, G.; Morrison, D.J. , Role of Gut Microbiota-Generated Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Current nutrition reports 2018, 7, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C.; Iglesias, M.A.; Drucker, D.J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. , Improvement of glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity by oligofructose requires a functional glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1484–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Derrien, M.; Girard, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Possemiers, S.; Van Holle, A.; François, P.; de Vos, W.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Schrenzel, J.; Cani, P.D. , Responses of gut microbiota and glucose and lipid metabolism to prebiotics in genetic obese and diet-induced leptin-resistant mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2775–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




