Submitted:
08 August 2023
Posted:
10 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Body weight, food intake, and body composition analysis
2.3. Assessment of glucose tolerance and insulin resistance
2.4. Plasma biochemistry
2.5. Bile acid measurements
2.6. Hepatic lipid analyses
2.7. Fecal neutral sterol analyses
2.8. Determination of mRNA levels
2.9. Histology and staining of liver
2.10. Determination of fecal energy content and energy absorption
2.11. Statistical analysis
3. Results
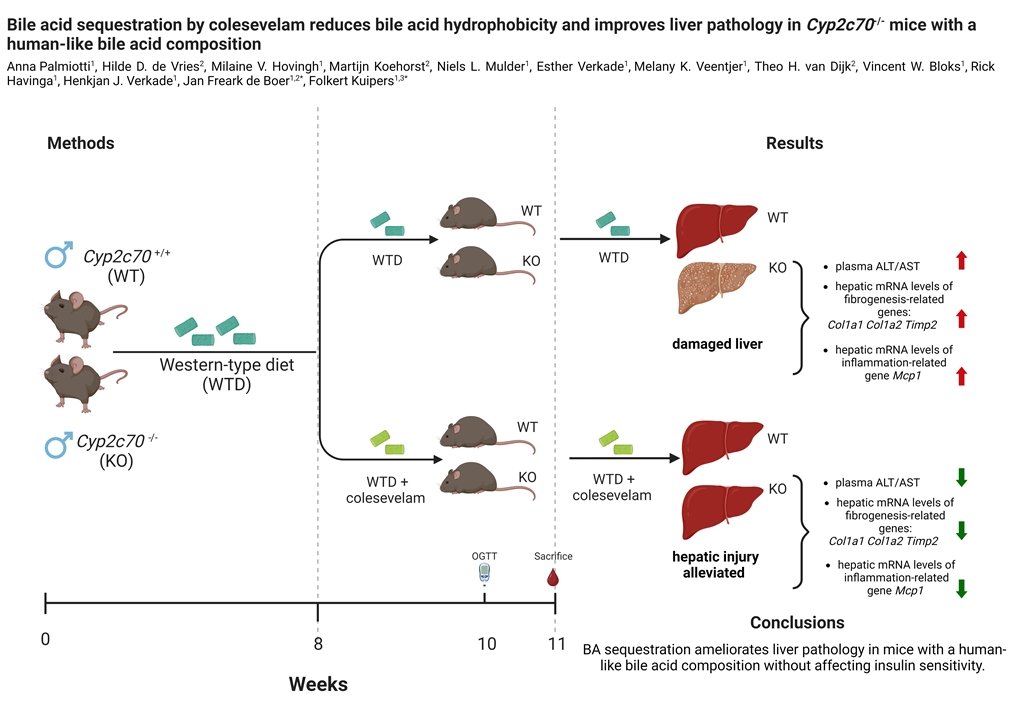
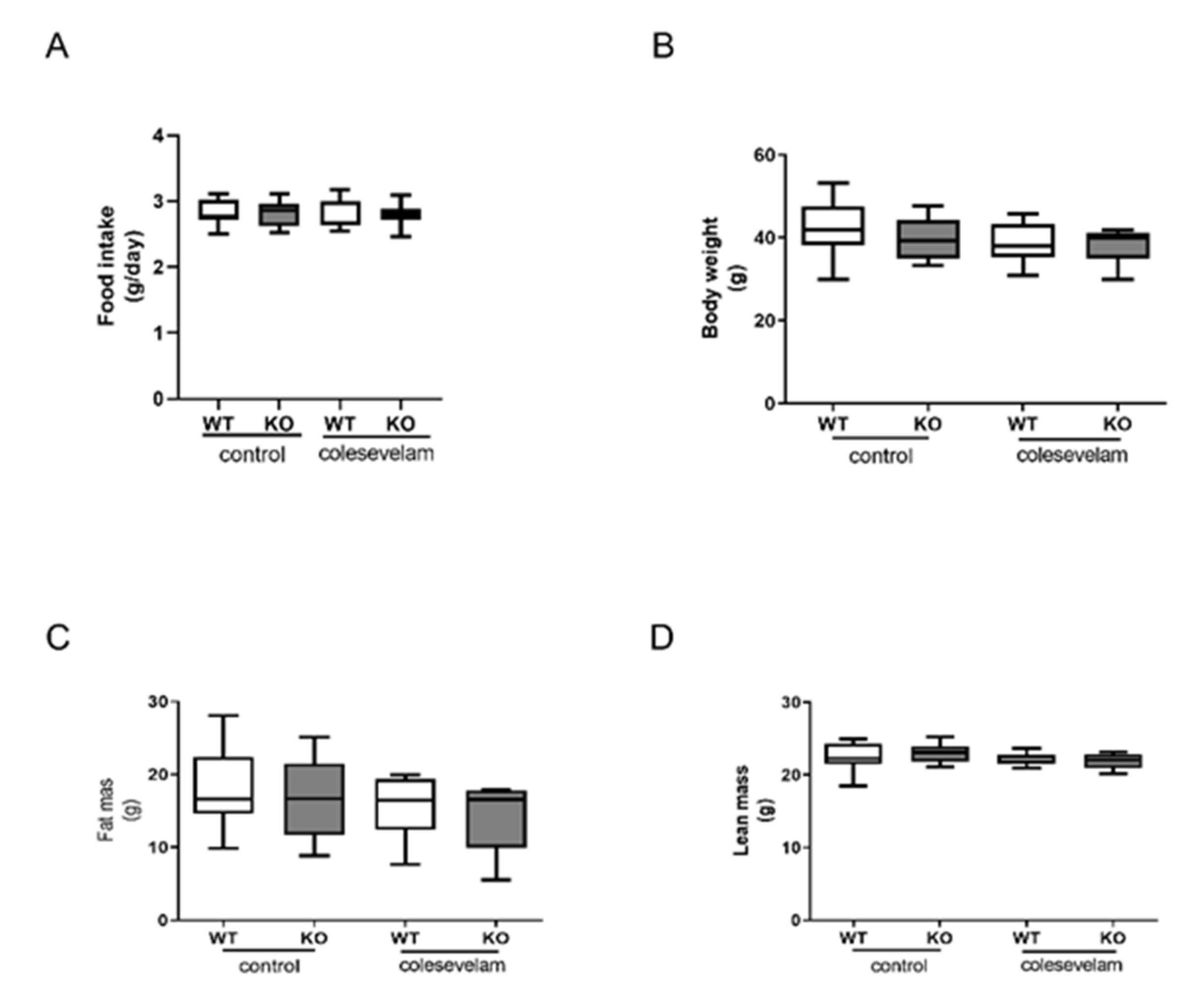
3.1. Colesevelam does not affect body weight of WTD-fed Cyp2c70-/- mice.
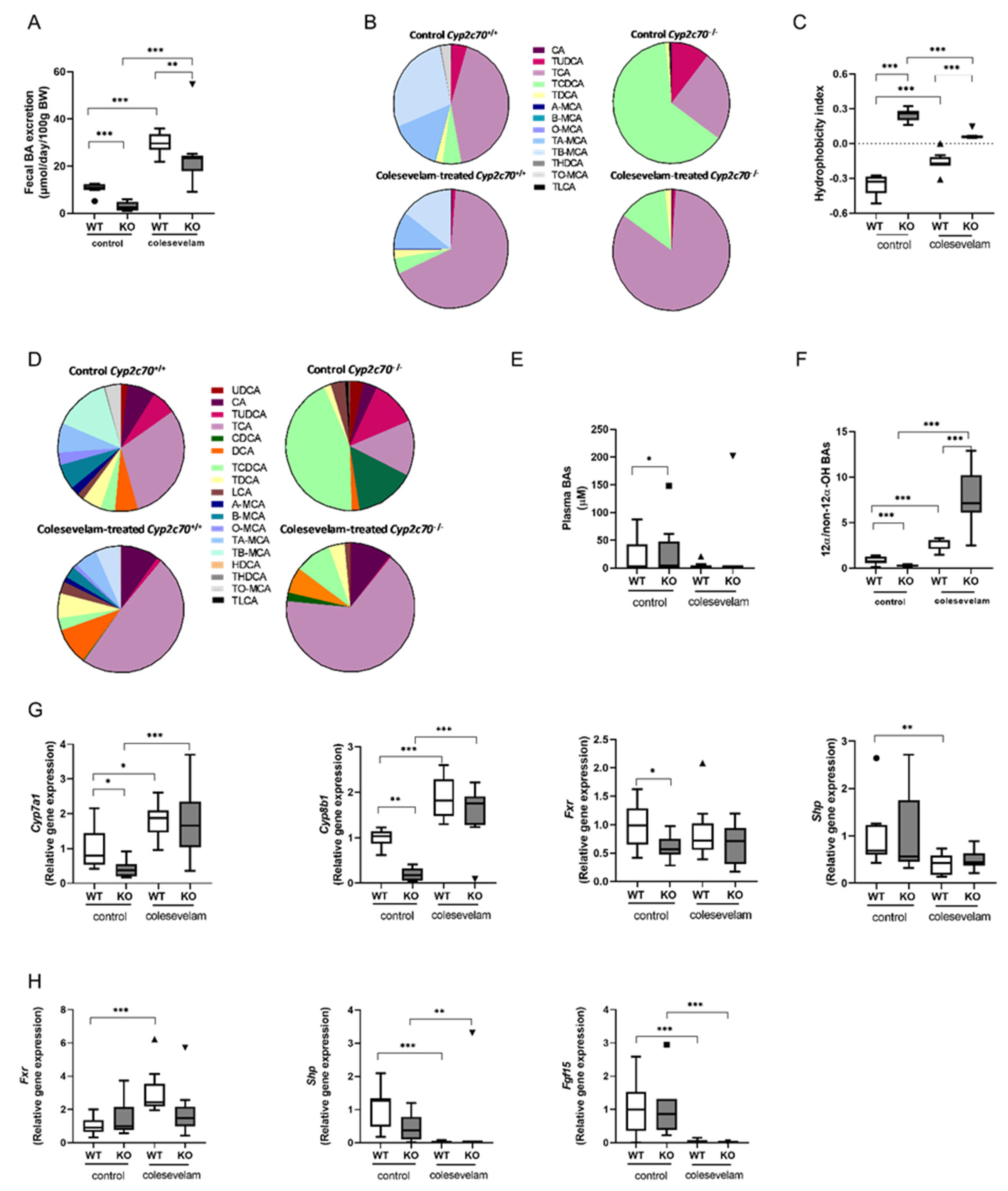
3.2. Colesevelam reduces the hydrophobicity of the bile acid pool in WTD-fed Cyp2c70-/- mice.
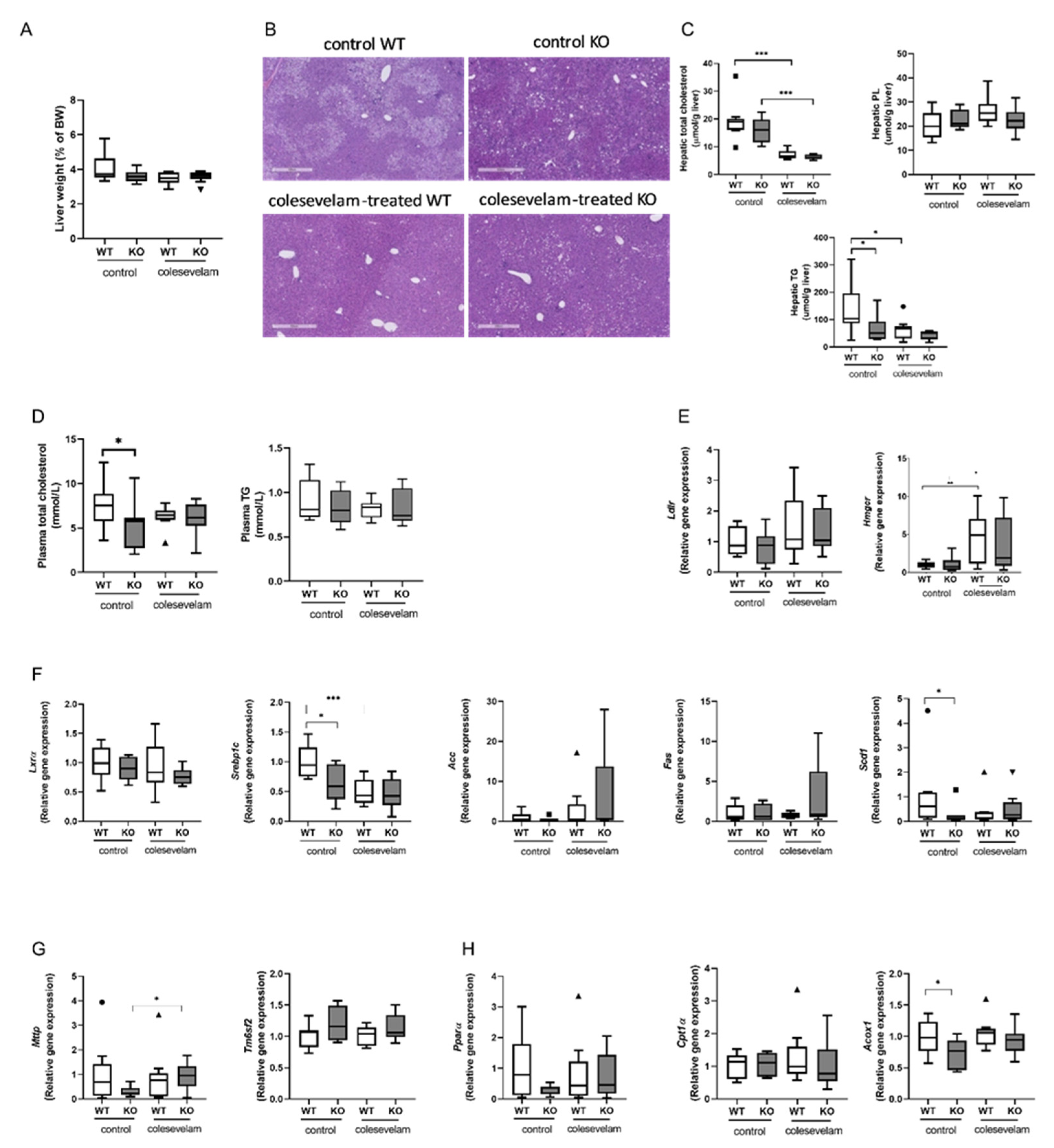
3.3. Colesevelam differentially modulates WTD-induced hepatic steatosis in WT and Cyp2c70-/- mice.
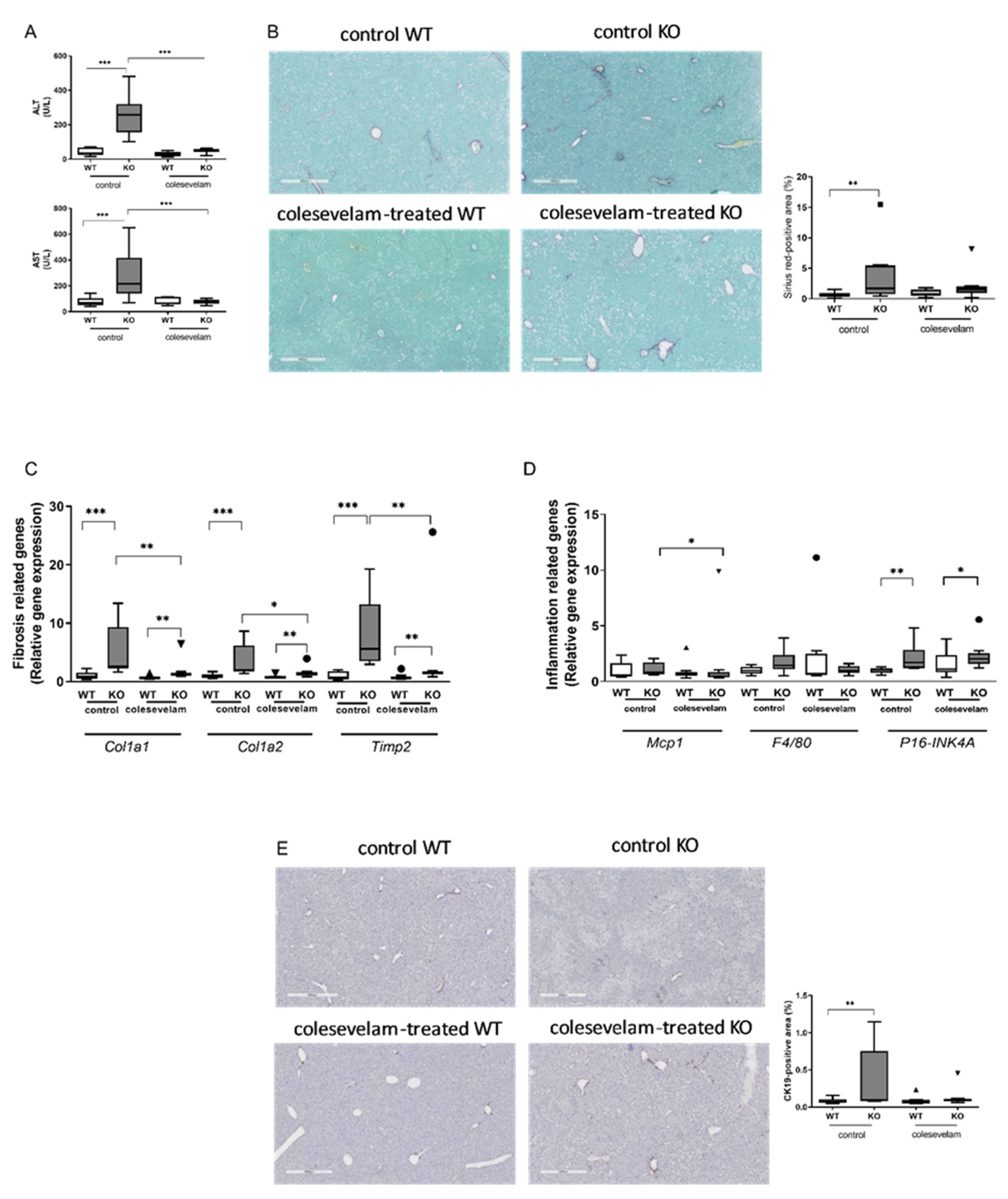
3.4. Colesevelam ameliorates liver damage in WTD-fed Cyp2c70-/- mice.
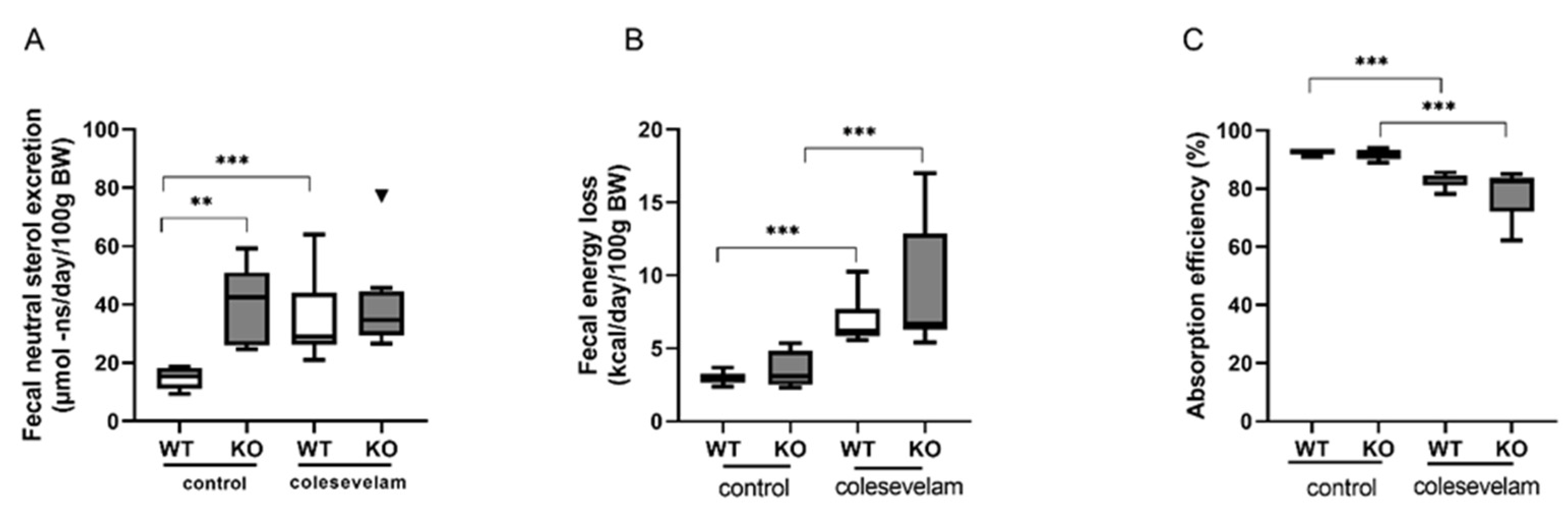
3.5. Colesevelam modulates the absorption efficiency of dietary energy in WTD-fed WT and Cyp2c70-/-mice.
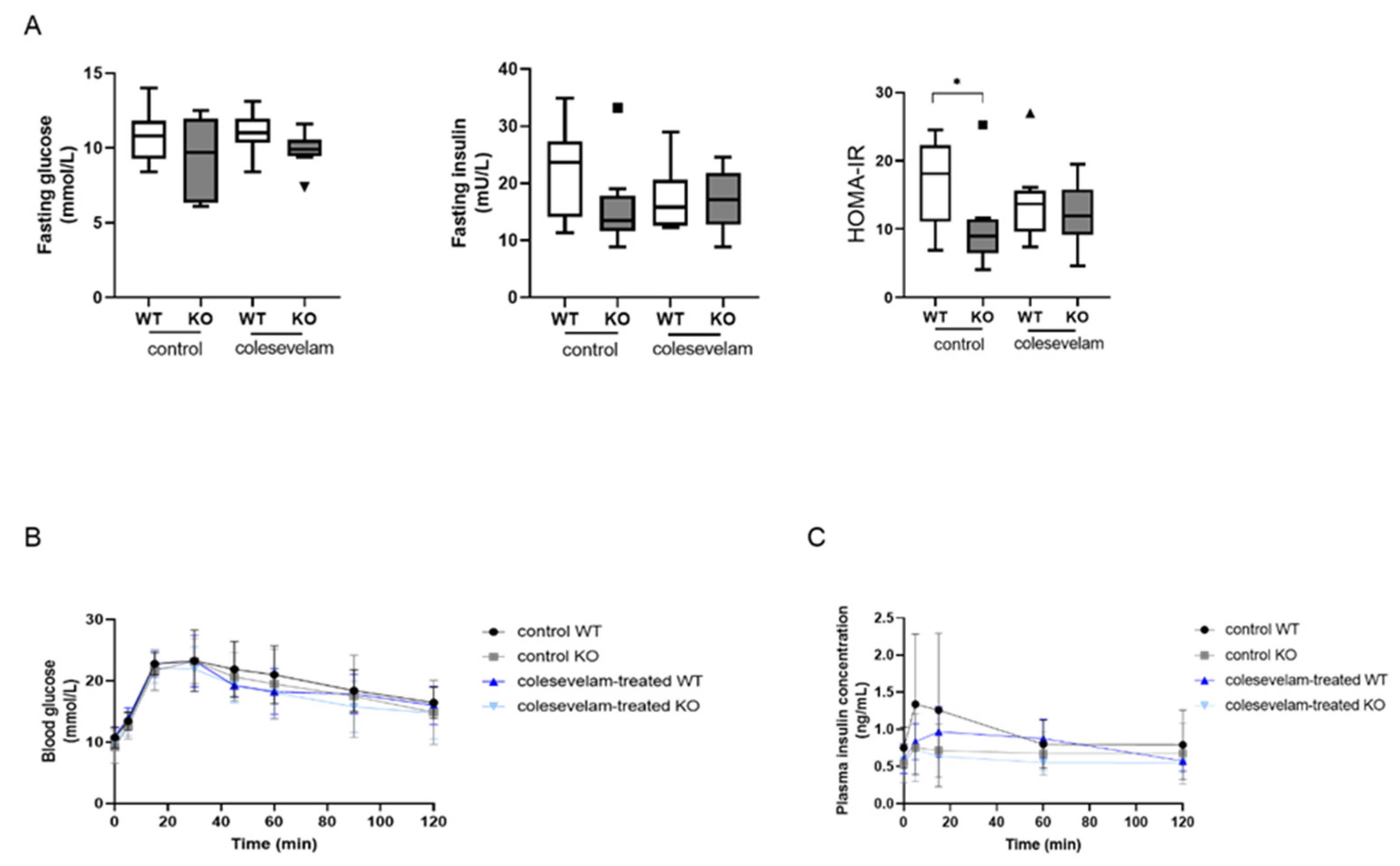
3.6. Colesevelam does not affect glucose excursions and insulin sensitivity in WTD-fed Cyp2c70-/- mice upon 2 weeks of treatment.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, A. Palmiotti, and F. Kuipers, Emerging roles of bile acids in control of intestinal functions, CurrOpin Clin NutrMetab Care, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Kuipers, V. W. F. Kuipers, V. W. Bloks, and A. K. Groen, Beyond intestinal soap—bile acids in metabolic control, Nat Rev Endocrinol, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 488–498, Aug. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani and, C. Mangini, Primary biliary cholangitis: Old and novel therapy, Eur J Intern Med, vol. 47, pp. 1–5, Jan. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Verbeke et al., FXR agonist obeticholic acid reduces hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of toxic cirrhosis, Nature Publishing Group, 2016. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Y. Fan, W. Y. Y. Fan, W. Ding, C. Zhang, L. Fu, D. X. Xu, and X. Chen, Obeticholic acid prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis through interaction between farnesoid X receptor and Smad3, Int Immunopharmacol, vol. 77, p. 105911, Dec. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. v. Kowdleyet al., A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study of obeticholic acid for primary sclerosing cholangitis, J Hepatol, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 94–101, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Nevenset al., A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Obeticholic Acid in Primary Biliary Cholangitis, New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 375, no. 7, pp. 631–643, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- V. Manne and K. v. Kowdley, Obeticholic acid in primary biliary cholangitis: where we stand, CurrOpin Gastroenterol, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 20 May; 19. [CrossRef]
- C. L. Bowlus, Obeticholic acid for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis in adult patients: clinical utility and patient selection, Hepat Med, vol. 8, pp. 2016; 95. [CrossRef]
- B. Zhang, F. B. Zhang, F. Kuipers, J. F. de Boer, and J. A. Kuivenhoven, Modulation of bile acid metabolism to improve plasma lipid and lipoprotein profiles, J Clin Med, vol. 11, no. 1, Jan. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Fuchs et al., Colesevelam attenuates cholestatic liver and bile duct injury in Mdr2 −/− mice by modulating composition, signalling and excretion of faecal bile acids, Gut, vol. 67, pp. 1683– 1691, 2018. [CrossRef]
- et al. , Inhibition of intestinal bile acid absorption improves cholestatic liver and bile duct injury in a mouse model of sclerosing cholangitis, J Hepatol, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 674–681, Mar. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. E. Bays, R. B. H. E. Bays, R. B. Goldberg, K. E. Truitt, and M. R. Jones, Colesevelam Hydrochloride Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated With Metformin Glucose and Lipid Effects. [Online]. Available: https://jamanetwork.
- F. J. Zieve, M. F. F. J. Zieve, M. F. Kalin, S. L. Schwartz, M. R. Jones, and W. L. Bailey, Results of the glucose-lowering effect of WelChol study (GLOWS): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study evaluating the effect of Colesevelam hydrochloride on glycemic control in subjects with type 2 diabetes, Clin Ther, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 74–83, Jan. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Brufauet al., Improved Glycemic Control with Colesevelam Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Is Not Directly Associated with Changes in Bile Acid Metabolism, HEPATOLOGY, vol. 52, pp. 1455– 1464, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Meissner, H. Herrema, T. H. van Dijk, A. Gerding, and R. Havinga, Bile Acid Sequestration Reduces Plasma Glucose Levels in db/db Mice by Increasing Its Metabolic Clearance Rate, PLoS One, vol. 6, no. 11, p. 2 4564, 2011. [CrossRef]
- U. Beil, J. R. U. Beil, J. R. Crouse, K. Einarsson, and S. M. Grundy, Effects of interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids on the transport of very low density-lipoprotein triglycerides, Metabolism, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 19 May; 82. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Crouse, Hypertriglyceridemia: A contraindication to the use of bile acid binding resins, Am J Med, vol. 83, no. 2, pp. 243–248, Aug. 1987. [CrossRef]
- J. F. de Boer et al., Cholangiopathy and Biliary Fibrosis in Cyp2c70-Deficient Mice Are Fully Reversed by Ursodeoxycholic Acid, CMGH, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 1045–1069, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- et al. , Regulation of bile acid metabolism in mouse models with hydrophobic bile acid composition, J Lipid Res, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 2020; 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Straniero, A. S. Straniero, A. Laskar, C. Savva, J. Härdfeldt, B. Angelin, and M. Rudling, Of mice and men: Murine bile acids explain species differences in the regulation of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism, J Lipid Res, vol. 61, no. 4, pp. 480–491, Apr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Li et al., Low production of 12α-hydroxylated bile acids prevents hepatic steatosis in Cyp2c70-/- mice by reducing fat absorption, J Lipid Res, vol. 2021; 62. [CrossRef]
- M. B. Dommerholtet al., Short-term protein restriction at advanced age stimulates FGF21 signalling, energy expenditure and browning of white adipose tissue, FEBS Journal, vol. 288, no. 7, pp. 2257–2277, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. H. van Dijk et al., A novel approach to monitor glucose metabolism using stable isotopically labelled glucose in longitudinal studies in mice, Lab Anim, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 79–88, Apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. M. Egginket al., Chronic infusion of taurolithocholate into the brain increases fat oxidation in mice, Journal of Endocrinology, vol. 236, no. 2, pp. 85–97, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology Issued by THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF CANADA A RAPID METHOD OF TOTAL LIPID EXTRACTION AND PURIFICATION.
- A. H. O. Ronda, T. H. A. H. O. Ronda, T. H. van Dijk, H. J. Verkade, and A. K. Groen, Measurement of Intestinal and Peripheral Cholesterol Fluxes by a Dual-Tracer Balance Method, CurrProtoc Mouse Biol, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 408–434, Dec. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Stricker, BrightStat.com: Free statistics online, Comput Methods Programs Biomed, vol. 92, no. 1, pp. 135–143, Oct. 2008. [CrossRef]
- J. F. de Boer et al., A human-like bile acid pool induced by deletion of hepatic Cyp2c70 modulates effects of FXR activation in mice, J Lipid Res, vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. K. Truong et al., Ileal bile acid transporter inhibition in Cyp2c70 KO mice ameliorates cholestatic liver injury, J Lipid Res, vol. 63, no. 9, p. 100261, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Mudaliar et al., Efficacy and safety of the farnesoid x receptor agonist Obeticholic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Gastroenterology, vol. 145, no. 3, pp. 574-582.e1, Sep. 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhong et al., Haploinsufficiency of CYP8B1 associates with increased insulin sensitivity in humans, J Clin Invest, vol. 132, no. 21, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




