1. Introduction
In February 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) released its inaugural inventory of antibiotic-resistant "priority pathogens" (
https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed). This comprehensive compilation encompassed 12 bacterial families that provide the most significant peril to human well-being [
1]. The inventory emphasized the menace caused by Gram-negative bacteria demonstrating resistance to multiple antibiotics. The mentioned bacteria possessed inherent capacities to develop novel mechanisms of resistance against treatments while being capable of transferring genetic material that facilitated the acquisition of drug resistance by other microbes. The most noteworthy cohort encompassed multidrug-resistant bacteria, which presented a specific risk within healthcare facilities, long-term care facilities, and individualized necessitating medical interventions such as mechanical ventilation and intravenous catheterization. They included
Acinetobacter,
Pseudomonas and
Enterobacteriaceae (
Klebsiella,
E. coli,
Serratia, and
Proteus). These microorganisms could potentially induce severe and frequently fatal infections, such as bacteraemia and pneumonia. The bacteria resisted various antibiotics, such as carbapenems and third-generation cephalosporins, which were considered the most effective treatment options for combating bacteria resistant to multiple drugs. Hence, the imperative to uncover new antimicrobial drugs arose. Antimicrobial peptides have proved effective in eradicating bacteria while exhibiting a limited propensity for inducing drug resistance.
Dermaseptins represent a group of peptides extracted from the skin secretions of frogs belonging to the
Hylidae family [
2]. The two main attributes of dermaseptins are the possession of antimicrobial and anti-tumour effects. Many peptides exhibit lethality towards bacteria lacking cell walls, Gram-negative, Gram-positive bacteria, fungi and yeasts, while proving relatively lower toxicity towards mammalian cells. The antibacterial activity of these substances is attributed to their ability to bind to the plasma membrane of bacteria, inducing temporary wormholes or membrane disruption [
3]. Considering the escalating resistance exhibited by bacteria towards conventional antibiotics, there persists a significant need for novel antibacterial medications [
4]. Similarly, new antitumor therapies are needed in the Western world, where cancer is increasingly emerging as the primary cause of mortality, as conventional therapies exhibit non-selective cytotoxicity and are susceptible to the development of resistance as a result of microevolutionary processes in tumour cells. The dermaseptin family members additionally demonstrate specific cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects on human tumour cell lines and retain spermicidal and antiprotozoal characteristics [
5]. According to the APD3 Database (
https://aps.unmc.edu/), peptides from the dermaseptin family display significant antiproliferative activity against lung cancer cell lines. Dermaseptin-PS3, from
Phyllomedusa sauvagii, shows antimicrobial activity against
E. coli and
C. albicans and antiproliferative activity against lung cancer cell lines [
6]. Both dermaseptin L1 and phylloseptin L1, which were obtained from the skin secretions of the lemur leaf frog,
Agalychnis lemur (
Phyllomedusinae), following stimulation with norepinephrine, exhibited cytotoxic effects on hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells [
7].
3. Discussion
The study reported the identification of a newly discovered antimicrobial peptide, Dermaseptin-SS1, which was separated from the skin secretion of Phyllomedusa tarsius. The anticipated secondary structure of SS1 was determined to be an amphipathic α-helix configuration, which was subsequently validated by the CD spectrum analysis. To assess the potential efficacy of SS1 against drug-resistant bacteria, an in vitro investigation was conducted to examine its anti-planktonic microorganism activity.
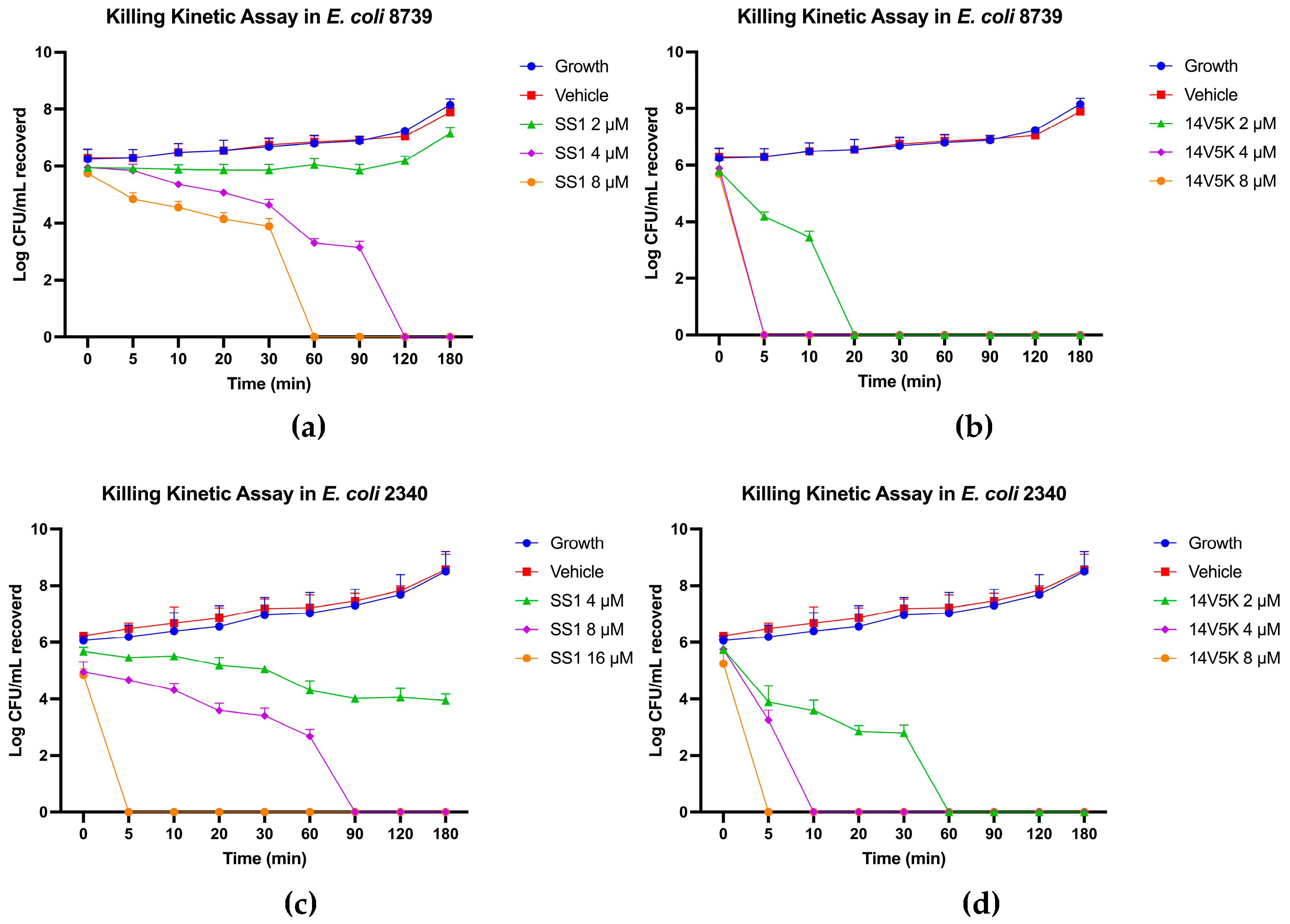
Generally, SS1 and its analogues displayed a greater range of antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria. In a comparison of the TI values of SS1 and its analogues in Table 4, 14V5K showed an obvious antimicrobial therapeutic effect. Therefore, SS1 and 14V5K were selected to measure future antimicrobial activities and mechanisms.
As peptides showed significant antimicrobial activity against
E. coli 8739, additional strains of drug-resistant
E. coli were used in the study. These were; (i)
E. coli 2340: KPC strain panel, bl
KPC+/bla
NDM-; (ii)
E. coli 2469: NDM-1 strain panel, bla
NDM+/bla
KPC-; (iii)
E. coli 2471: NDM-1 strain panel, bla
NDM+/bla
KPC-; (iv)
E. coli 13846: colistin-resistant with MCR-1 positive.
E. coli 2340, 2469 and 2471 belonged to Carbapenem-Resistant
Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) [
12]. Carbapenem antibiotics are mostly β-lactam antibiotics whose principle was to inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis [
13]. The mechanisms of carbapenem resistance were β-lactamase production combined with porin mutations to produce carbapenemase [
14]. CRE had three classifications, including KPC, NDM and OXA-48.
Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC) hydrolysed all β-lactam agents encoded by the plasmid-associated gene bla
KPC, which may be difficult to detect using higher breakpoints [
15]. New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) was encoded by the plasmid-associated gene bla
NDM [
16]. However,
E. coli 13846 was a colistin-resistant bacterium with MCR-1 positive and harboured multiple other resistance genes. The MCR-1 protein was a transmembrane protein primarily found in the cellular membrane. Its presence has potentially led to the deterioration of cell membrane integrity, decreasing the MICs of gentamicin, kanamycin, and rifampicin [
17]. The presence of MCR-1 conferred protection to the host against colistin, while simultaneously altering the permeability of the cellular membrane and diminishing resistance to hydrophobic antibiotics. The results in
Table 5 could be explained in that the antimicrobial activities of peptides against
E. coli 2340, 2469 and 2471, were better than those against
E. coli 13846 because
E. coli 13846 had the ability to change the cell membrane structure but the others did not.
14V5K showed significant superiority in salt sensitivity against both bacteria, as shown in Table 7. The results could be analysed from the perspective of the properties of the peptides. On the one hand, 14V5K had more net charges than SS1, so it was more competitive than most ions. The combination between the negatively charged LPS and peptide 14V5K produced a stronger electrostatic interaction, which was one of the factors of the membrane-targeting mechanism. On the other hand, 14V5K had a higher hydrophobic moment than SS1, and with this elevated hydrophobicity, the peptide could readily accumulate on the phospholipid bilayers of the cell membrane. Therefore, 14V5K had low salt sensitivity. Meanwhile, SS1 displayed long-duration killing for about 2 hours, while 14V5K slightly decreased killing time against bacteria because of the extra net charge and hydrophobic properties.
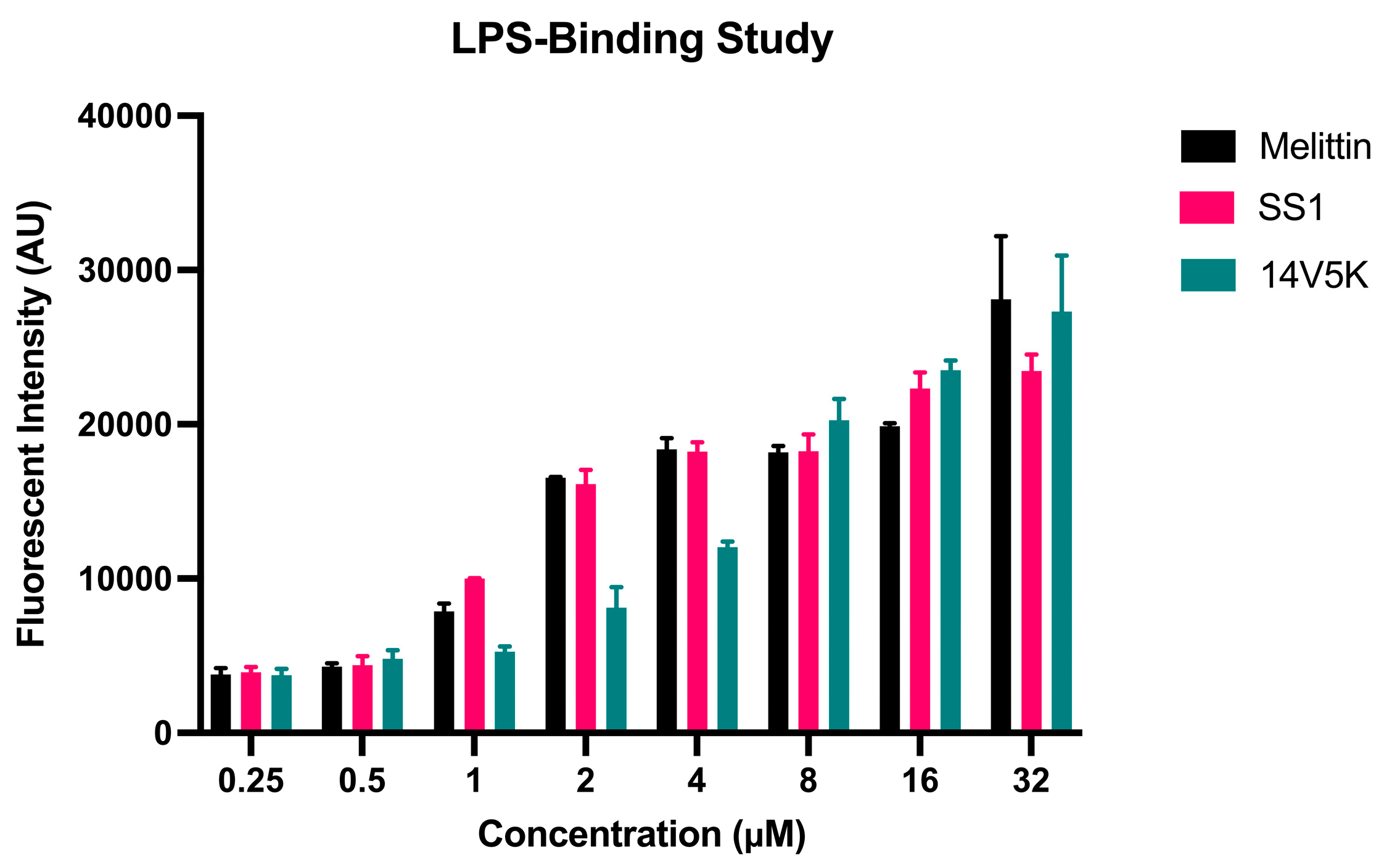
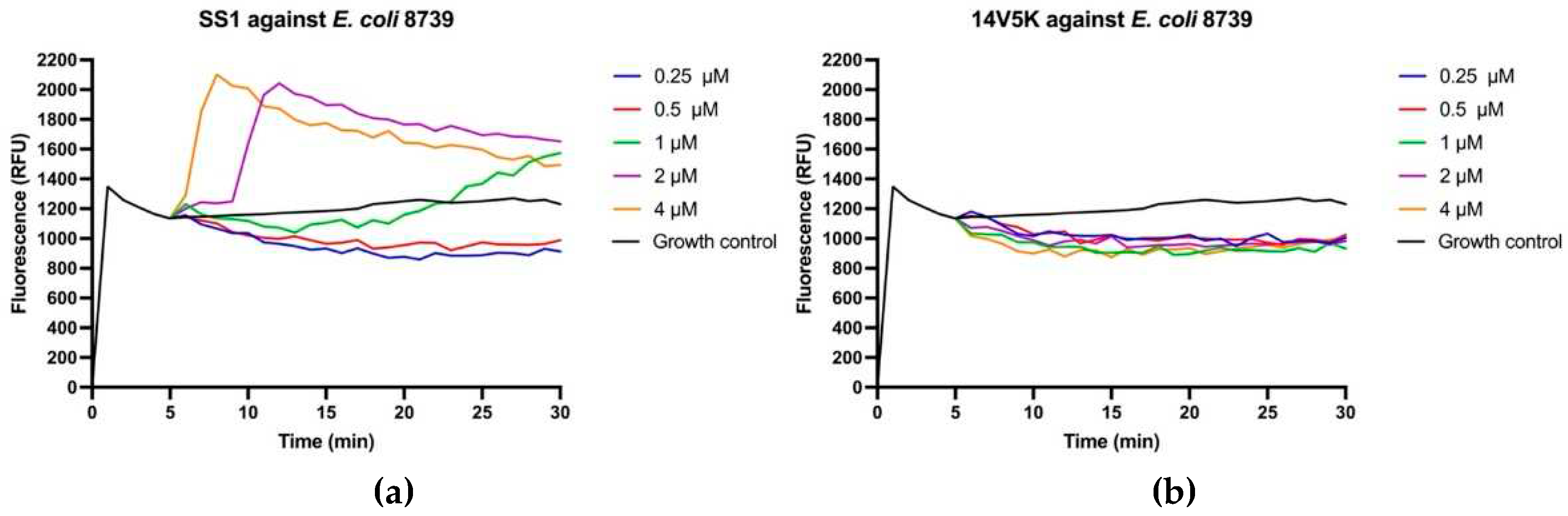
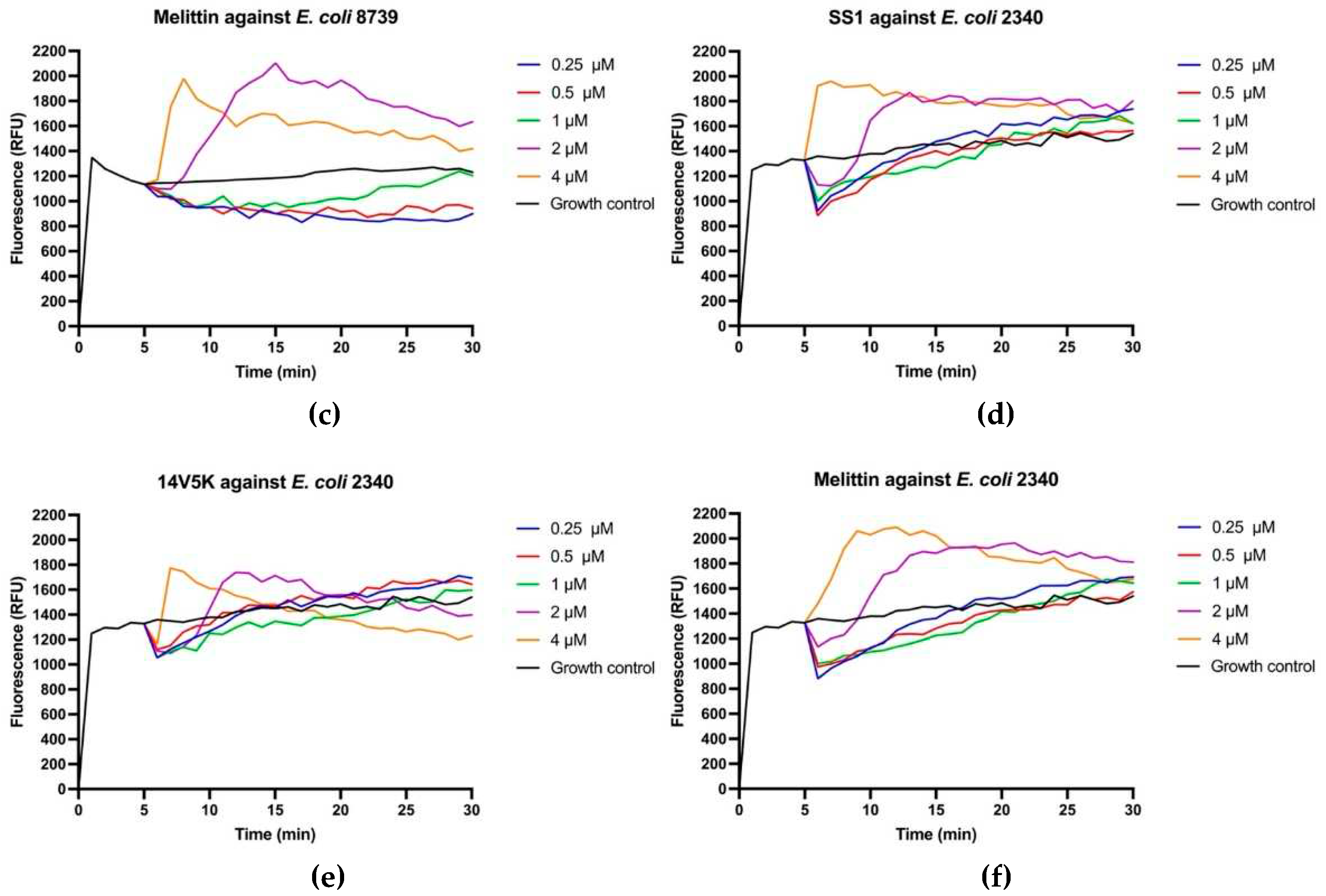
The initial reaction between peptides with positive net charges and the cell membrane occurred with the negatively charged components of the membrane. A fluorescence-based displacement assay was conducted to gauge the specificity of the binding of the peptides to LPS. As anticipated, the antimicrobial peptide SS1 exhibited comparable levels of efficiency in compulsory LPS as melittin. This well-known membrane-targeting peptide could swiftly induce pore formation in bacterial cell membranes and result in cytoplasm leakage [
18]. Once peptides form aggregates on the surface of bacteria and reach a certain concentration threshold, they could traverse the cell wall, thereby destabilising the cell membrane [
19]. However, 14V5K showed weaker LPS-binding ability at MIC concentrations. Therefore, the present study investigated the immediate impacts of peptides on both the external and internal membranes of
E. coli. The alterations in the fluorescence of NPN and the absorbance of ONPG, as observed in the presence of SS1 and 14V5K, provided initial evidence supporting the notion that these peptides illustrate an analogous process of bacterial membrane penetration to melittin, a widely explored antimicrobial peptide known for its membrane-damaging properties [
20].
The perturbation of the inner membrane through peptides was investigated utilising diSC
3-5, a probe dependent on membrane potential. According to the results in
Figure 8, peptides showed fluctuant membrane potentials. The disruption of the cytoplasmic membrane potential led to the dissipation of the proton-motivated force, which hindered the transfer of electrons along the breathing pathway and consequently reduced the synthesis of ATP. This reduction in ATP synthesis was crucial for the movement of bacteria that relied on flagella [
11].
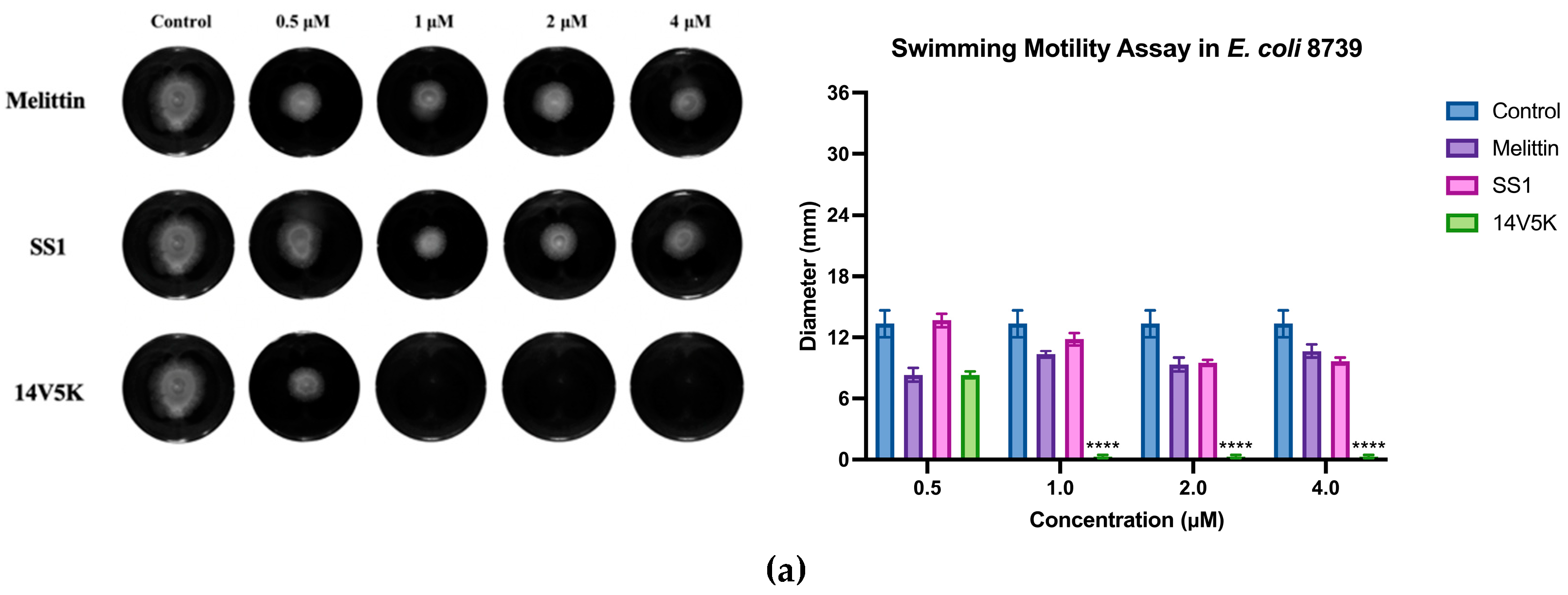
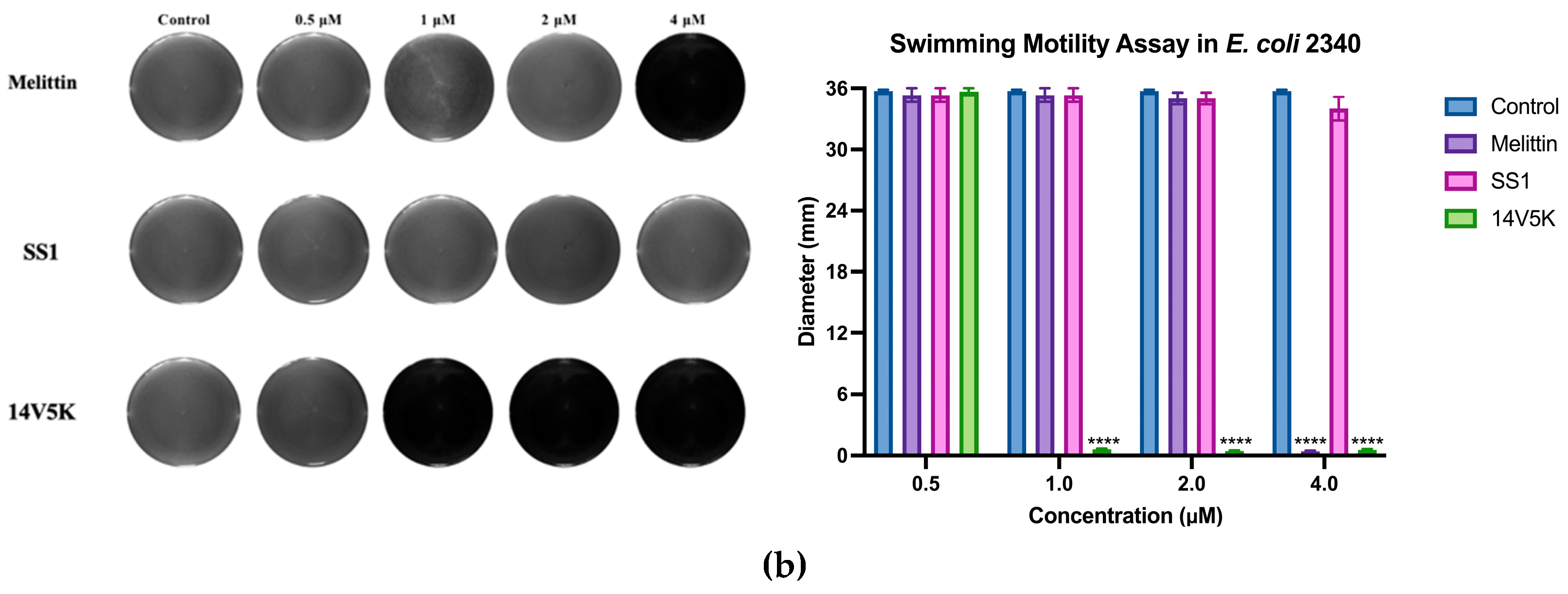
E. coli 8739 and 2340 were used to measure because of the existing flagellum. The study examined the consequences of peptides on bacterial swimming motion on swim plates with low viscosity. The peptide 14V5K demonstrated a more pronounced effect on the reduction of bacterial swimming diameter than that of melittin, whereas SS1 showed a greater capacity for membrane depolarization. Compared to 14V5K, the lower outer membrane binding ability and penetration effect of SS1 could be responsible for the less effective suppression of bacterial swimming motility. This hypothesis was supported by previous research [
21]. The belief that the electrostatic attraction between AMPs and bacterial surfaces plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of AMPs is based on the notion that it allows AMPs to reach the necessary concentrations required for disrupting the bacterial membrane. In summary,
E. coli 8739 and 2340 were killed by SS1 and 14V5K using the membrane-targeting mechanism.
Generally, SS1 and its analogues showed notable antiproliferative effects against both H838 and H460 lung cancer cell lines as displayed in Table 8. However, the antiproliferative activity of L2V was better than its antimicrobial activity. This was based on the membrane-targeting mechanism. A component of the membrane surface, phosphatidylserine (PS), has a higher affinity for L2V than other peptides. In cancer cells, PS is often exposed on the outer membrane leading to the development of a negative surface charge. This charge is associated with a lower pH in the surrounding environment. Membranolysis by AMPs and their selective mode of action on tumour cells can be attributed to the increased anionic nature of the cytoplasmic membrane of these cells. Another suspicion was that L2V had similar high hydrophobicity and hydrophobic moments, some of the forces required to disrupt cell membranes.
SS1 and its analogues showed cytotoxicity mostly at high concentrations in the haemolysis assays, but the IC
50 values of several peptides against HaCat cells were at low concentration levels. Meanwhile, the results of the salt stability assay supplied in
Table 7 revealed that SS1 lost antimicrobial activity partly in the environment with salts, while the salt stability of 14V5K was better than that of SS1. When a peptide bonded to red blood cells (RBCs), the activity of Na
+-K
+-ATPase on the surface of RBCs was inhibited [
22]. The imbalance of intracellular potassium ion concentration led to abnormal ion exchange between the outside and inside of the membrane. In addition, the positively charged region of the peptide interfered with the transport function of anion channels in the erythrocyte and changed the osmotic pressure of the erythrocyte membrane, causing the erythrocyte to swell and lyse. However, peptides may lose activity when potassium ions are low and may then show low cytotoxicity to RBCs. Therefore, the evidence for peptides with low cytotoxicity may be explained by their poor displacement capacity for salts.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acquisition of Phyllomedusa tarsius Dermal Secretions
The Phyllomedusa tarsius frogs were procured from an industrial supplier (PeruBiotech E.I.R.L., Lima, Peru). The epidermal secretions were collected through the process of percutaneous electrical stimulation. The skin secretions were washed away from the skin surface using deionized water and then gathered in a glass beaker. Subsequently, the accumulated secretions were subjected to freezing using liquid nitrogen and then subjected to freeze-drying. Afterwards, the samples were stored at -20 °C.
4.2‘. Shotgun’ Cloning of a cDNA Encoding Dermaseptin-SS1 Peptide Biosynthetic Precursor
To determine the nucleotide sequence of the precursor of Dermaseptin-SS1, firstly 5 mg of freeze-dried skin secretion was dissolved in 1 mL lysis/binding buffer (Dynal Biotech, Merseyside, UK). Later, the isolation process was carried out using the magnetised Dynabeads
TM mRNA Purification Kit (Invitrogen, Norway) according to the rule of Adenine-Thymine pairing. The separated mRNA was then applied as a starting point to construct the cDNA library's first strand, employing the Clontech SMARTer® RACE 5’/3’ Kit (Takara Bio, USA, Inc.). After that, the 3’-Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was carried out by applying the nested universal primer (NUP) provided by the product as an antisense primer. Additionally, the degenerate sense primer (5’-ACTTTCYGAWTTRYAAGMCCAAABATG-3’) (where Y represents C or T; W represents A or T; R represents A or G; M represents A or C; B represents T, C or G) was utilised. This primer was derived from the previously published nucleotide sequence of the extremely conserved signal peptide of dermaseptin peptides from
Phyllomedusa tarsius. The molecular weights of PCR outcomes were analysed by gel-electrophoresis with an Ultraviolet (UV) imaging system and purified by using the HiBind® DNA Mini Column (Omega Bio-Tek, USA). Then the pure products were ligated by applying a pGEM®-T Easy Vector System (Promega, Southampton, UK), and chosen via White & Blue screening. The isolated DNA plasmids were amplified by PCR, checked using gel electrophoresis and purified utilising the HiBind® DNA Mini Column. Finally, thermal cycling performed the sequencing reaction utilising a BigDye Sequencing Buffer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). An ABI 3100 automatic capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) was employed to identify the nucleotide sequence of chosen cloned samples. The nucleotide sequence was translated to amino acid sequence and analysis of this was undertaken by using NCBI-Protein BLAST (
https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi/). Sequences with high identities were aligned with the novel peptide sequence by Clustal-Omega (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/).
4.3. Physicochemical Properties and Modification of SS1
4.4. Synthesis and Identification of SS1 and its Analogues
Peptides were chemically synthesised via solid-phase Fluorenyl methoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) chemistry in the TributeTM automatic solid-phase peptide synthesiser (Protein Technologies, Tucson, AZ, USA). The utilisation of rink amide resin was implemented as a media in the synthetic procedure. The artificial peptides were liberated from the resin through the addition of a cleavage mixture solution consisting of 94% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), 2% deionized water (ddH2O), 2% thioanisole (TIS), and 2% 1,2-ethanedithiol (EDT). The process was carried out at room temperature ranging from 120 minutes to 240 minutes, which included three subsequent washes with diethyl ether. Following the approach of lyophilization, the crude peptides were subsequently subjected to purification using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP–HPLC) (Phenomenex Aeris PEPTIDE 5 μm XB-C18 column, 250 mm × 21.2 mm, Macclesfield, Cheshire, UK) with a linear gradient formed by buffer A (TFA/ddH2O = 0.05/99.95, v/v) and buffer B (TFA/ddH2O/acetonitrile = 0.05/19.95/80.0, v/v/v) at the flow rate of 5 mL/min within 80 minutes. The purity of peptides was analysed using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (Voyager DE, Perspective Biosystem, Foster City, CA, USA). The analysis was performed in positive detection mode employing α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) as the matrix. The MALDI-TOF mass spectra of peptides were constructed by mMass.
4.5. Secondary Structure Determinations by Circular Dichroism
As previously mentioned, the investigation of secondary structures of peptides was examined via a JASCO-815 circular dichroism (CD) spectrometer (Jasco, Essex, UK) [
23]. Briefly, the peptide samples, with a concentration of 100 µM, were mixed together in solutions of 10 mM NH
4Ac and 50 % TFE/NH
4Ac (v/v), correspondingly. The samples were placed into a quartz cuvette with a thickness of 1 mm, accompanied by analysis by voltage ranging from 190 to 260 nm. The scanning speed utilised in the experiment was recorded as 200 nm per minute, while the bandwidth and data pitch were determined to be 1 nm and 0.5 nm.
4.6. Anti-planktonic Microorganism Activity Study
The anti-planktonic microorganism efficacy of peptides was investigated via minimal bacterial inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) assays. Eight types of microorganisms, including Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC CRM 6538), Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (NCTC 12493), and Enterococcus faecium (NCTC 12697), Gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli (ATCC CRM 8739, ATCC BAA 2340, ATCC 13846, ATCC BAA 2469, and ATCC BAA 2471), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 43816), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC CRM 9027) and Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC BAA 747) and a yeast, Candida albicans (ATCC CRM 10231) were utilized to test the antimicrobial activity of peptides.
For the MIC assay, microorganisms were inoculated with peptides in 96-well plates. Nutrient Broth (NB) was applied for MRSA,
E. coli,
K. pneumoniae and
P. aeruginosa, Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) was applied for
S. aureus,
E. faecium and
A. baumannii, and yeast extract peptone dextrose broth (YPD-B) was used for
C. albicans. The microorganisms were cultured (bacteria: 37 °C; yeast: 26 °C) overnight at 120 rpm and subcultured to achieve the logarithmic growth stage (5 × 10
5 CFU/mL) confirmed by viable cell counts. After that, 99 µL of subculture and 1 µL of the peptide were added to the 96-well plate. The final concentration range of peptides was from 128 to 1 µmol/L (µM) using 2-fold dilution. Besides, four other groups were established simultaneously at the commencement of the test, encompassing a growth control group, a vehicle control group (Dimethyl Sulphoxide, DMSO), a positive control group utilising Norfloxacin at the concentration of 2 mg/mL for bacteria and Amphotericin B. at a concentration of 1 mg/mL for yeast, and a blank control group (sterile NB/TSB/YPD-B). The MIC values were measured after overnight incubating at 37/26 °C. The optical density (OD) values were analysed at 550 nm by a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA), and were calculated by the following equation:
where
As was the absorbance value of the sample group,
A0 was the average of the absorbance values of blank control, and
Ag was the average of the absorbance values of growth control. For the MBC assay, 10 µL of the inhibited cultures on the 96-well plate were transferred onto a corresponding medium agar plate and incubated overnight at 37/26 °C to measure MBC values. The results presented were from three independent assays.
4.7. Haemolysis Activity Study
To start, fresh defibrinated horse blood (TCS Biosciences Ltd., Buckingham, UK) was washed with PBS solution to obtain the clear supernatant. Then a 4% (v/v) suspension of red blood cells was made in PBS. After this, 100 µL of peptide solutions were incubated with 100 µL of the suspension of red blood cells in 2-mL centrifuge tubes at 37℃ for 2 hours. The ultimate concentration range of peptides was from 128 to 1 µM obtained by 2-fold dilution. Also, two other groups were set simultaneously, including a positive control group of 1% Triton X-100 and a blank control group of Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS). After incubation and centrifugation at 900
g for 10 minutes, a volume of 100 µL of the resulting supernatant from every specimen was carefully transferred into individual wells of a 96-well plate. Subsequently, the OD values were analysed via a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA) with a wavelength of 570 nm by using the following equation:
where
Hs was the absorbance value of the supernatant of the peptide group,
H0 was the average absorbance value of the blank control and
Hp was the average of the absorbance values of the positive control. The data presented were from three separate assays.
4.8. Salt Sensitivity Assay
To evaluate the salt sensitivity of peptide actions against bacteria, the peptides were incubated with S. aureus 6538 and E. coli 8739 in the presence of salts (150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 6 μM NH4Cl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 2.5 mM CaCl2, and 4 μM FeCl3). After the subculture, the peptides were incubated with the bacteria (5 × 105 CFU/mL) with salts. The MICs/MBCs were then tested as described in the MIC assay, and the findings obtained in this study were obtained from three separate assays.
4.9. Time-killing Kinetic Assay
The present study employed a time-dependent kinetics assay to assess the bactericidal activity of peptides against two strains of Escherichia coli, namely E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340. The bacteria were subcultured, as previously described, for the purpose of conducting the MIC assay. Bacterial inoculation was performed using peptide concentrations equivalent to 4-fold MIC, 2-fold MIC, and MIC, with a bacterial concentration of 5 × 105 CFU/mL. Viable cell numbers were assessed by collecting samples at various intervals (0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes). Following incubation at a temperature of 37 °C for a duration of one night, the quantification of colonies was conducted. The findings that were presented originated from three separate and distinct assays.
4.10. LPS-binding Assay
The lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding affinity of peptides was assessed using a fluorescent dye BODIPY-TR cadaverine displacement assay (BC, Sigma, USA). The trial was conducted by peptides in a 96-well black plate to achieve the expected concentrations (final concentration (c.): 0.5 μM to 32 μM) in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.4). The positive control was melittin within the same concentration range. LPS and BC dye were mixed with Tris buffer to make an ultimate concentration of 25 μg/mL for LPS and 2.5 μg/mL for BC dye. After reacting for 4 hours at room temperature, equal volumes of LPS solution were added to peptides in the black plate, and it was subjected to incubation at 37 °C for a duration of 1 hour. The fluorescence measurements were conducted via a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA) with excitation λ = 590 nm and emission λ = 645 nm. The test was performed in triplicate, with each trial carried out independently.
4.11. Outer Membrane Assay
The study encompassed the implementation of an outer membrane permeability assay employing N-Phenyl-1-naphthylamine (NPN), a fluorescent dye recognised for its susceptibility to the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. For the purpose of this study, E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340 were initially introduced into an LB medium and subjected to overnight incubation at a temperature of 37 °C. Following this, the cultures underwent subculturing at a temperature of 37 °C and a rotational speed of 120 rpm for a duration of 2 hours. The cells underwent centrifugation at a speed of 2000 rpm for 10 minutes. The cell pellets underwent a washing process and were subsequently diluted to an OD value of 0.50 at a wavelength of 600 nanometers, which corresponds to a concentration of 1 × 108 CFU/mL. This dilution was achieved using a 5 mM HEPES buffer solution supplemented with 5 mM glucose, and the pH of the buffer was adjusted to 7.4. The bacterial solution was diluted to a concentration of 1 × 107 CFU/mL. Subsequently, a volume of 100 μL of bacterial culture was combined with 50 μL of peptide solution within the black 96-well plate. The peptide concentrations were determined according to the MIC values obtained from the assay targeting planktonic microorganisms. The growth control was established using the HEPES buffer. Subsequently, a volume of 50 μL of NPN (with an ultimate concentration of 10 μM per well) was introduced into the respective wells. The fluorescence was measured in real-time by implementing a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA) with an excitation λ = 360 and emission λ = 460 for a duration of 60 minutes. The experiment was conducted in triplicate, with each trial being performed autonomously.
4.12. Inner Membrane Assay
The analysis of membrane permeabilization in E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340 involved quantifying the activity of β-galactosidase released from bacteria into the culture medium. This was achieved by using o-nitrophenol β-D-galactoside (ONPG) as the substrate. The bacteria were cultivated in LB medium supplemented with a 2% lactose concentration at a temperature of 37 °C for an extended period. Following this, the bacteria were subcultured at 37 °C and a rotational rate of 120 rpm for a duration of 2 hours. Subsequently, the bacterial culture was subjected to centrifugation at a speed of 2000 rpm for a period of 10 minutes. The cell pellets were suspended to an OD value of 600 nm of 0.5, corresponding to 1 × 108 CFU/mL concentration. The suspension was then diluted by a factor of ten using a PBS solution containing 1.5 mM ONPG at a pH of 7.4. The experimental system consisted of a mixture containing 150 μL of bacteria and 50 μL of peptides. The peptide concentrations utilised in this study were determined using the MIC values obtained from the anti-planktonic microorganism assay. The absorbance measurement was conducted at a wavelength of 460 nm at regular intervals of 5 minutes over a duration of 90 minutes. It was achieved using a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA). The temperature of the plate reader was prewarmed and set at 37°C, which is considered optimal for enzymatic reactions. This measurement aimed to assess the permeability of peptides by monitoring the influx of ONPG into the cells, with the absorbance serving as a dynamic indicator of this process. The experiment was conducted in triplicate, with each trial being performed independently.
4.13. Membrane Potential Assay
The quantification of alterations in the cytoplasmic membrane potential was conducted utilising 3,3'-Dipropylthiadicarbocyanine Iodide (diSC3-5) (Sigma), a fluorescent dye that was sensitive to membrane potential. This experiment was conducted on E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340. Initially, the bacteria were introduced into LB medium and incubated at a temperature of 37 °C for a duration of overnight. Subsequently, the bacterial culture was transferred to a fresh LB medium and subjected to incubation at a temperature of 37 °C with continuous agitation at a speed of 120 rpm for a period of 2 hours. Following this, the bacterial cells were separated from the liquid medium through centrifugation at a speed of 2000 rpm for a duration of 10 minutes. The cell pellets were rinsed using a 5 mM HEPES buffer solution including 20 mM glucose at a pH of 7.2. Subsequently, the cell pellets were diluted to an OD value of 0.05 (equivalent to a concentration of 1 × 107 CFU/mL) using a 5 mM HEPES buffer solution containing both 20 mM glucose and 0.1 M KCl at a pH of 7.2. Subsequently, a volume of 10 µL of bacterial culture was combined with 200 μL of a 20 μM disC3-5 solution, and the mixture was incubated at room temperature for a duration ranging from 30 minutes to 1 hour. The permeabilization of a 100 µL sample of bacteria was initially assessed at one-minute intervals over a period of 5 minutes using a Synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA) with excitation wavelength set at λ = 485 nm and emission wavelength set at λ = 645 nm. Subsequently, a volume of 10 μL of peptide solution, with a final concentration ranging from 0.5 μM to 4 μM, was introduced into a 90 μL suspension of bacteria. The experimental group designated as the positive control was exposed to melittin, with a final concentration ranging from 0.5 μM to 4 μM. The fluorescence emission of peptides and positively charged groups was recorded at one-minute intervals over a duration of 30 minutes. The experiment was conducted in triplicate, with each trial being performed independently.
4.14. Swimming Motility Assay
The motility of bacterial cells was assessed through the utilisation of swim plates containing a low viscosity medium (0.3% agar media, w/v) supplemented with 5 g/L tryptone and 2.5 g/L NaCl. Initially, a volume of 10 mL of molten medium was combined with a peptide solution, with a final concentration ranging from 0.5 μM to 4 μM, in a six-well plate. The mixture was subsequently subjected to a drying process lasting for a duration of 2 hours. A volume of 5 µL of bacterial culture, containing 5 × 105 CFU/mL, was introduced into the central region of the wells. The samples were then subjected to incubation at a temperature of 37 °C for a duration of 48 hours. The measurement of bacterial swimming was conducted using white light emitted by an InGenius 3, 3MP 12/16bit system (Syngene, UK), and the diameter of bacterial motility was subsequently documented. The experiment was conducted in triplicate, with each trial being performed independently.
4.15. Antiproliferative Activity Study
The MTT assay was employed to evaluate the antiproliferative efficacy of the peptide on human cells encompassing both cancerous and non-cancerous cell lines. The human lung cancer cell lines, namely NCI-H838 and NCI-H460, as well as the human keratinocyte HaCat cell line were procured from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Md., USA). The H838 and H460 cell lines were grown in RPMI-1640 culture medium (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), while the HaCat cell line was maintained in DMEM culture medium (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) separately in a 15 mL of medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (PS) (penicillin 100 units/mL and streptomycin 100 μg/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) beforehand. Subsequently, the samples were cultured at 37 °C supplemented with 5% carbon dioxide (CO2).
To seed cells on the 96-well plates, a suitable number of cells (H838, H460: 8000 cells/100 µL; HaCat: 5000 cells/100 µL) were introduced into individual wells and subjected to a 24-hour incubation period. The complete growth medium was withdrawn to starve cells, and 100 μL of FBS-free medium was maintained for 4 hours. The peptide ranged from a concentration of 10
-4 M to 10
-9 by 10-fold dilution using an FBS-free medium. Afterwards, the medium within the wells was extracted, and 100 μL of peptide solution at varying concentrations, along with positive control (0.1% Triton X-100), vehicle control (0.5% DMSO), growth control and blank control were loaded. Each concentration required three replications. The plates were incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO
2 for 22 hours. Later, a volume of 10 μL of a solution comprising 3- (4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) at a concentration of 5 mg/mL was introduced into the sample and incubated for an additional 2 hours. Later, the OD values were assessed utilising a synergy HT plate reader (BioTek, USA) operating a wavelength of 570 nm. The viability of cells was determined by applying the subsequent formula:
where
Ms was the absorbance of the sample group,
M0 was the average absorbance value of the blank control, and
Mg was the average value of absorbance of the growth control. The results that were presented originated from three separate and distinct tests.
4.16. Statistical Analyses
The data presented here were gained through a minimum of three replicated tests. The data were analysed by GraphPad Prism 9.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). They were displayed as the mean values ± S.E.M. The p-value was determined through the use of one-way ANOVA tests, which involved comparing the mean values of the specified data. Asterisks are used to indicate significant differences (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W., M.Z., T.C., Y.J. and T.W.; methodology, X.M., Y.J., Y.C., X.C. and T.W.; software, C.M., X.M., X.C. and A.S; validation, T.W.; formal analysis, X.M., Y.C. and A.S.; investigation, X.M.; resources, C.M. and M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.M.; writing—review and editing, T.C., Y.J., Y.C., L.W. and C.S.; supervision, T.W. and L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
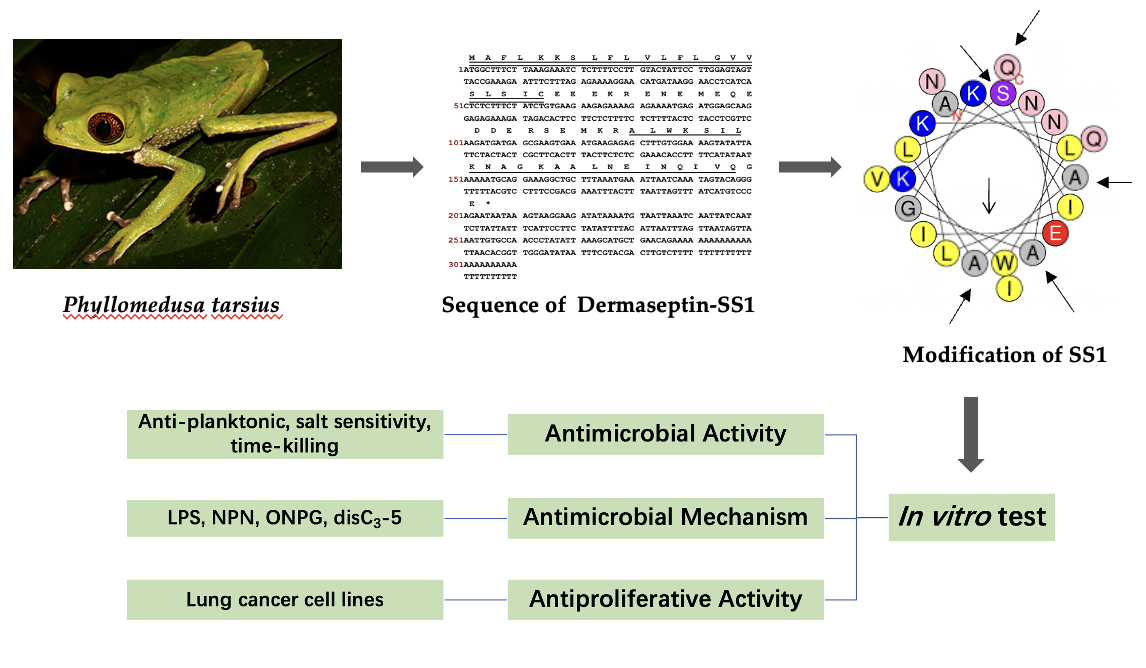
Figure 1.
The ORF of the cDNA and nucleotide sequence that encoded the biosynthetic precursor of dermaseptin-SS1 were translated. The N-terminal signal peptide sequence was denoted by double underlining, whereas the mature peptide sequence was indicated using single underlining. The stop codon was marked by the symbol “*”, signifying the termination of protein synthesis.
Figure 1.
The ORF of the cDNA and nucleotide sequence that encoded the biosynthetic precursor of dermaseptin-SS1 were translated. The N-terminal signal peptide sequence was denoted by double underlining, whereas the mature peptide sequence was indicated using single underlining. The stop codon was marked by the symbol “*”, signifying the termination of protein synthesis.
Figure 2.
The alignment of full-length nucleotide sequences of cloned encoding precursors of SS1, Dermaseptin-PS3 and Dermaseptin-B6. The identical amino acids are represented by “*”. The presence of a colon “:” denotes conservation among groups of amino acids that possess highly similar properties. The presence of a colon “.” denotes conservation among groups that exhibit weakly similar properties.
Figure 2.
The alignment of full-length nucleotide sequences of cloned encoding precursors of SS1, Dermaseptin-PS3 and Dermaseptin-B6. The identical amino acids are represented by “*”. The presence of a colon “:” denotes conservation among groups of amino acids that possess highly similar properties. The presence of a colon “.” denotes conservation among groups that exhibit weakly similar properties.
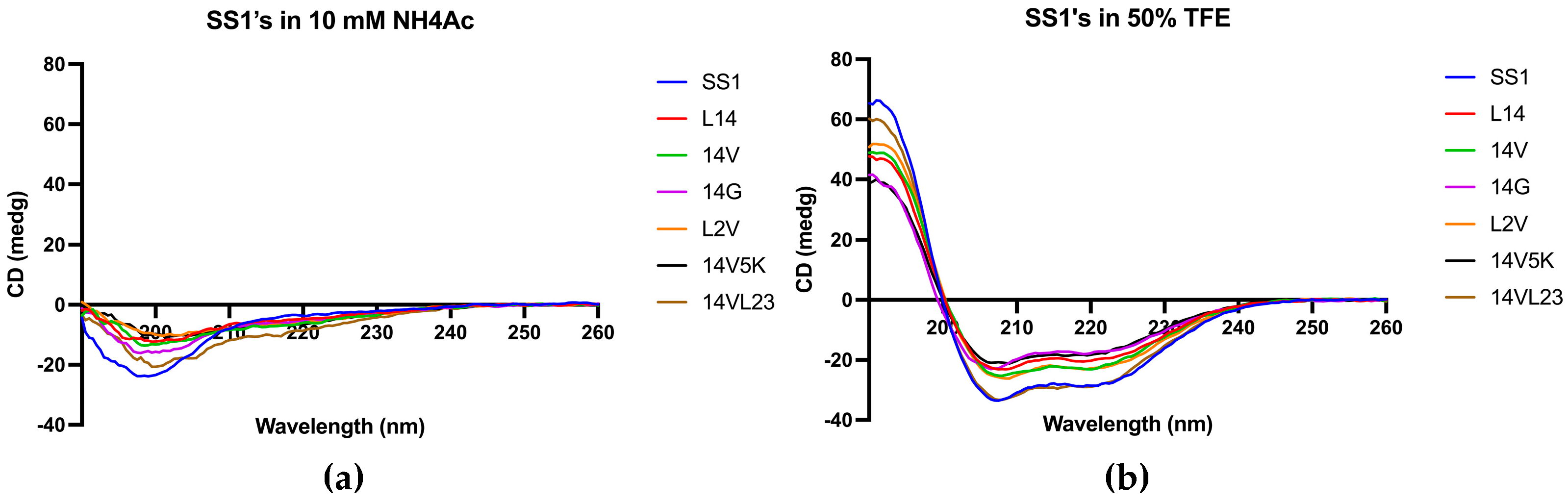
Figure 3.
The CD spectra of SS1 and its analogues were obtained in two different environments: (a) a 10 mM NH4Ac buffer, encompassing an aqueous environment, and (b) a 50% TFE solution, simulating the hydrophobic conditions found in microbial membrane. Peptides demonstrated α-helical conformations in solutions that mimic membranes due to the presence of distinctive positive peaks at 193 nm and negative peaks at 208 nm and 222 nm. Inversely, in aqueous environments, they adopted a distinct random coil conformation.
Figure 3.
The CD spectra of SS1 and its analogues were obtained in two different environments: (a) a 10 mM NH4Ac buffer, encompassing an aqueous environment, and (b) a 50% TFE solution, simulating the hydrophobic conditions found in microbial membrane. Peptides demonstrated α-helical conformations in solutions that mimic membranes due to the presence of distinctive positive peaks at 193 nm and negative peaks at 208 nm and 222 nm. Inversely, in aqueous environments, they adopted a distinct random coil conformation.
Figure 4.
The kinetic time-killing curves of SS1 (a, c) and 14V5K (b, d) were assessed at three different concentrations: MIC, 2 times MIC and 4 times MIC. These experiments were conducted against two strains of Escherichia coli, namely E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340. Exponential-phase E. coli 8739 was subjected to various concentrations ranging from MIC to 4-fold MIC of SS1 (2 - 8 μM) and 14V5K (2 – 8 μM). Similarly, E. coli strain 2340 was exposed to SS1 (4 - 16 μM) and 14V5K (2 – 8 μM). The error bar represented the standard error of the mean (SEM) calculated from three replications obtained from three separate experiments.
Figure 4.
The kinetic time-killing curves of SS1 (a, c) and 14V5K (b, d) were assessed at three different concentrations: MIC, 2 times MIC and 4 times MIC. These experiments were conducted against two strains of Escherichia coli, namely E. coli 8739 and E. coli 2340. Exponential-phase E. coli 8739 was subjected to various concentrations ranging from MIC to 4-fold MIC of SS1 (2 - 8 μM) and 14V5K (2 – 8 μM). Similarly, E. coli strain 2340 was exposed to SS1 (4 - 16 μM) and 14V5K (2 – 8 μM). The error bar represented the standard error of the mean (SEM) calculated from three replications obtained from three separate experiments.
Figure 5.
The binding affinity of peptides to LPS was identified via the BC fluorescent dye displacement assay. The fluctuations of fluorescent values were observed at an λexcitation = 590 nm and λemission = 645 nm. The data presented in this study represented the means and standard deviations of three separate trials.
Figure 5.
The binding affinity of peptides to LPS was identified via the BC fluorescent dye displacement assay. The fluctuations of fluorescent values were observed at an λexcitation = 590 nm and λemission = 645 nm. The data presented in this study represented the means and standard deviations of three separate trials.
Figure 6.
The outer membrane permeabilization of SS1 and 14V5K. Exponential-phase E. coli 8739 cells were treated with MIC to 4-fold MIC concentrations of SS1 (16 - 64 μM) and 14V5K (8 – 32 μM), while E. coli 2340 cells were treated with SS1 (16 - 64 μM) and 14V5K (8 – 32 μM). The SEMs were visually represented by the error bars displayed in the graphs.
Figure 6.
The outer membrane permeabilization of SS1 and 14V5K. Exponential-phase E. coli 8739 cells were treated with MIC to 4-fold MIC concentrations of SS1 (16 - 64 μM) and 14V5K (8 – 32 μM), while E. coli 2340 cells were treated with SS1 (16 - 64 μM) and 14V5K (8 – 32 μM). The SEMs were visually represented by the error bars displayed in the graphs.
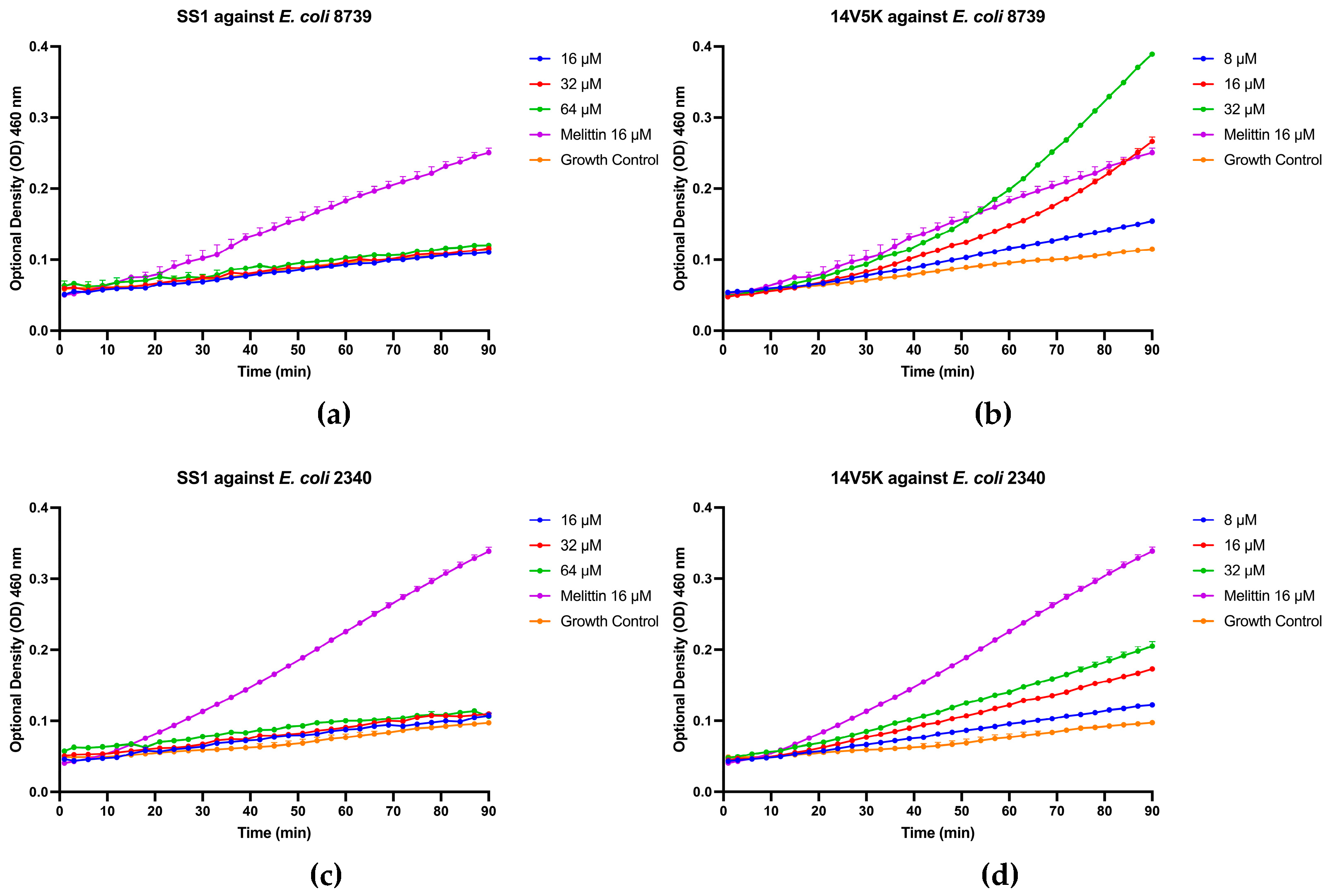
Figure 7.
Inner membrane permeabilization of E. coli 8739 and 2340 after treatment with either SS1 or 14V5K. The spectroscopic measurement of the hydrolysis of ONPG, produced by the release of cytoplasmic β-galactosidase from E. coli was measured at 460 nm over a period of 90 minutes.
Figure 7.
Inner membrane permeabilization of E. coli 8739 and 2340 after treatment with either SS1 or 14V5K. The spectroscopic measurement of the hydrolysis of ONPG, produced by the release of cytoplasmic β-galactosidase from E. coli was measured at 460 nm over a period of 90 minutes.
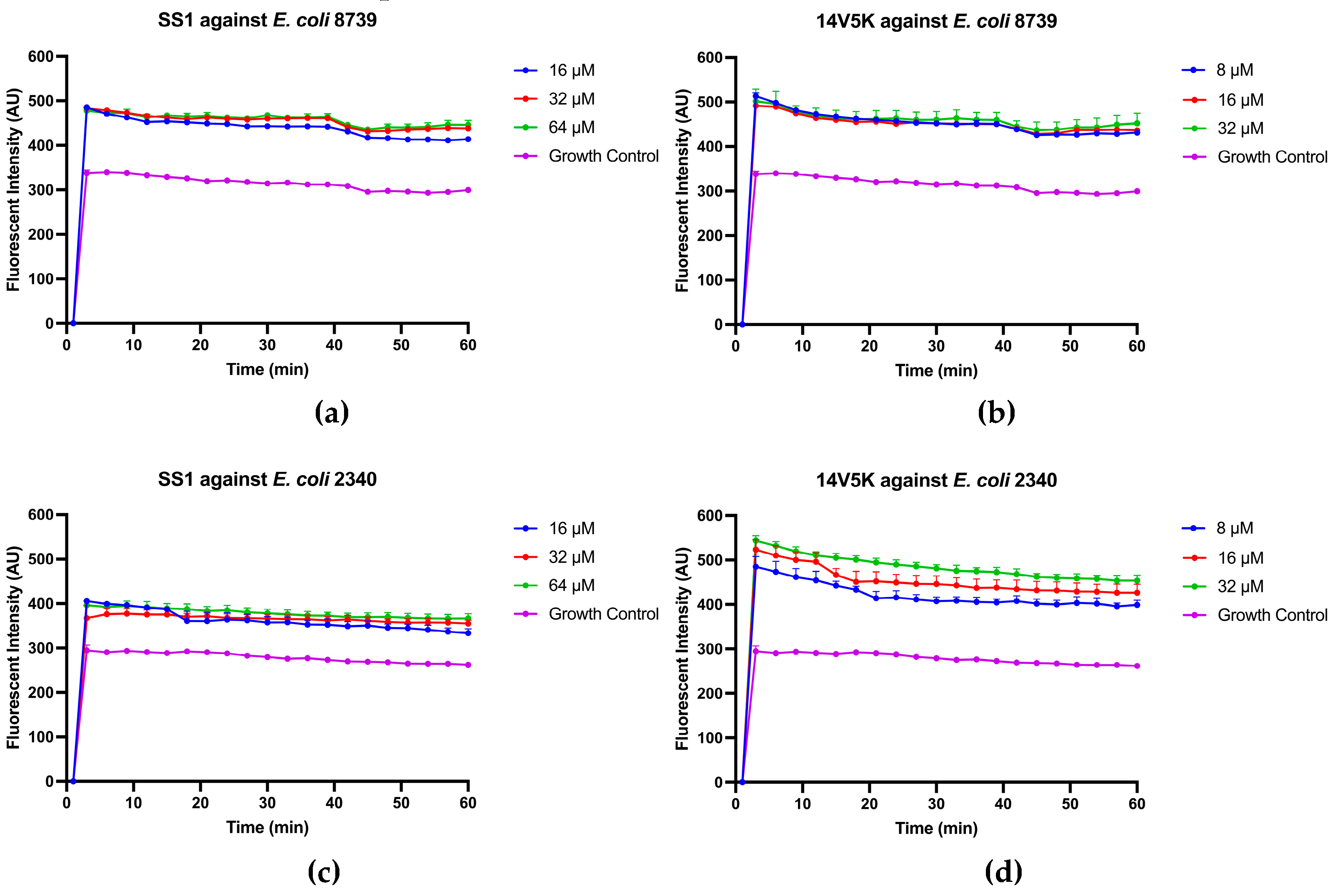
Figure 8.
Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization of E. coli 8739 (a-c) and 2340 (d-f). SS1, 14V5K and melittin were measured at concentrations spanning from 0.5 μM to 4 μM.
Figure 8.
Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization of E. coli 8739 (a-c) and 2340 (d-f). SS1, 14V5K and melittin were measured at concentrations spanning from 0.5 μM to 4 μM.
Figure 9.
The histogram presented in this study displayed the swimming motility data of E. coli strains 8739 and 2340. The values depicted in the histogram represented the means ± standard deviations, which were calculated based on three separate experiments. The statistical significance (****) was established by employing a threshold of a P-value lower than 0.0001, associated with the bacterial swimming diameter observed in the control group that did not receive any antimicrobial treatment.
Figure 9.
The histogram presented in this study displayed the swimming motility data of E. coli strains 8739 and 2340. The values depicted in the histogram represented the means ± standard deviations, which were calculated based on three separate experiments. The statistical significance (****) was established by employing a threshold of a P-value lower than 0.0001, associated with the bacterial swimming diameter observed in the control group that did not receive any antimicrobial treatment.
Table 1.
The mature amino acid sequences of peptide SS1 and its analogues.
Table 1.
The mature amino acid sequences of peptide SS1 and its analogues.
| Peptide |
Length |
Sequence |
| SS1 |
23 |
ALWKSILKNAGKAALNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| L14 |
22 |
ALWKSILKNAGKALNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| 14V |
23 |
ALWKSILKNAGKAVLNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| 14G |
23 |
ALWKSILKNAGKAGLNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| L2V |
22 |
ALWKSILKNVGKVLNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| 14V5K |
23 |
ALWKKILKNAGKAVLNEINQIVQ-NH2
|
| 14VL23 |
22 |
ALWKSILKNAGKAVLNEINQIV-NH2
|
Table 2.
The physicochemical parameters of peptide SS1 and its analogues.
Table 2.
The physicochemical parameters of peptide SS1 and its analogues.
| Peptide |
Hydrophobicity (H) |
Hydrophobic moment (μH) |
Net Charge (z) |
| SS1 |
0.405 |
0.406 |
+3 |
| L14 |
0.410 |
0.591 |
+3 |
| 14V |
0.445 |
0.445 |
+3 |
| 14G |
0.392 |
0.392 |
+3 |
| L2V |
0.492 |
0.659 |
+3 |
| 14V5K |
0.403 |
0.486 |
+4 |
| 14VL23 |
0.475 |
0.455 |
+3 |
Table 3.
Antimicrobial activity of SS1 and its analogues against various microorganisms.
Table 3.
Antimicrobial activity of SS1 and its analogues against various microorganisms.
| Microorganisms |
MIC/MBC (μM*) |
| SS1 |
L14 |
14V |
14G |
L2V |
14V5K |
14VL23 |
| Gram-positive bacteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S. aureus ATCC CRM 6538 |
8/8 |
>128 |
4/4 |
>128 |
>128 |
4/4 |
>128 |
| MRSA NCTC 12493 |
>128 |
32/32 |
8/8 |
>128 |
4/4 |
4/4 |
>128 |
|
E. faecalis NCTC 12697 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
| Gram-negative bacteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E. coli ATCC CRM 8739 |
2/4 |
4/4 |
2/2 |
16/16 |
>128 |
2/2 |
8/16 |
|
K. pneumoniae ATCC 43816 |
16/16 |
16/16 |
8/8 |
>128 |
8/>128 |
2/2 |
4/4 |
|
P. aeruginosa ATCC CRM 9027 |
32/32 |
16/>128 |
16/>128 |
32/>128 |
>128 |
8/8 |
>128 |
|
A. baumannii ATCC BAA 747 |
16/16 |
32/>128 |
4/4 |
>128 |
4/4 |
8/8 |
>128 |
| Yeast |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C. albicans ATCC CRM 10231 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
8/8 |
>128 |
Table 4.
HC50, GM and TI values of SS1 and its analogues.
Table 4.
HC50, GM and TI values of SS1 and its analogues.
| Peptide |
HC50a |
|
GMb (μM) |
|
TI valuec |
| |
Gram + |
Gram - |
Yeast |
|
Gram + |
Gram - |
Yeast |
| SS1 |
256.00 |
|
80.63 |
11.31 |
256.00 |
|
3.17 |
22.63 |
1.00 |
| L14 |
256.00 |
|
128.00 |
13.45 |
256.00 |
|
2.00 |
19.03 |
1.00 |
| 14V |
256.00 |
|
20.16 |
5.66 |
256.00 |
|
12.70 |
45.23 |
1.00 |
| 14G |
256.00 |
|
256.00 |
76.11 |
256.00 |
|
1.00 |
3.36 |
1.00 |
| L2V |
256.00 |
|
64.00 |
38.05 |
256.00 |
|
4.00 |
6.73 |
1.00 |
| 14V5K |
256.00 |
|
16.00 |
4.00 |
8.00 |
|
16.00 |
64.00 |
32.00 |
| 14VL23 |
256.00 |
|
256.00 |
38.05 |
256.00 |
|
1.00 |
6.73 |
1.00 |
Table 7.
MICs/MBCs (µM) of SS1 and 14V5K against S. aureus 6538 and E. coli 8939 in salts.
Table 7.
MICs/MBCs (µM) of SS1 and 14V5K against S. aureus 6538 and E. coli 8939 in salts.
| Salts |
S. aureus 6538 |
|
E. coli 8739 |
| SS1 |
14V5K |
|
SS1 |
14V5K |
| MIC/MBC (μM) |
8/8 |
4/4 |
|
2/4 |
2/2 |
| NaCl (150 mM) |
>128 |
8/8 |
|
4/4 |
2/2 |
| KCl (5 mM) |
>128 |
4/4 |
|
4/4 |
2/2 |
| MgCl2 (1.5 mM) |
>128 |
4/4 |
|
16/16 |
2/2 |
| CaCl2 (2.5 mM) |
>128 |
8/8 |
|
>128 |
8/8 |
| FeCl3 (4 μM) |
>128 |
4/4 |
|
4/4 |
1/1 |
| NH4Cl (6 μM) |
>128 |
4/4 |
|
2/2 |
1/1 |