Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Layout
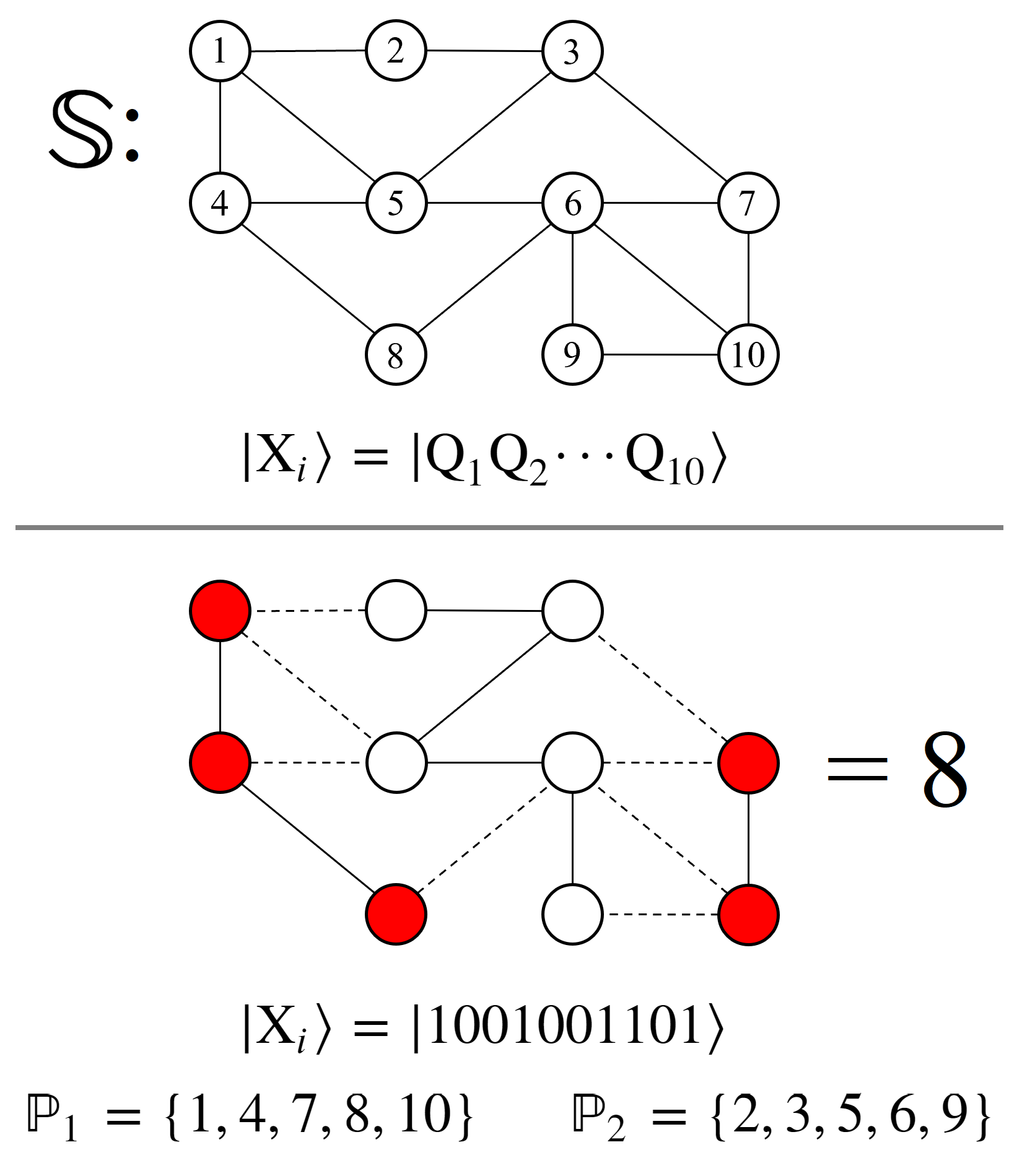
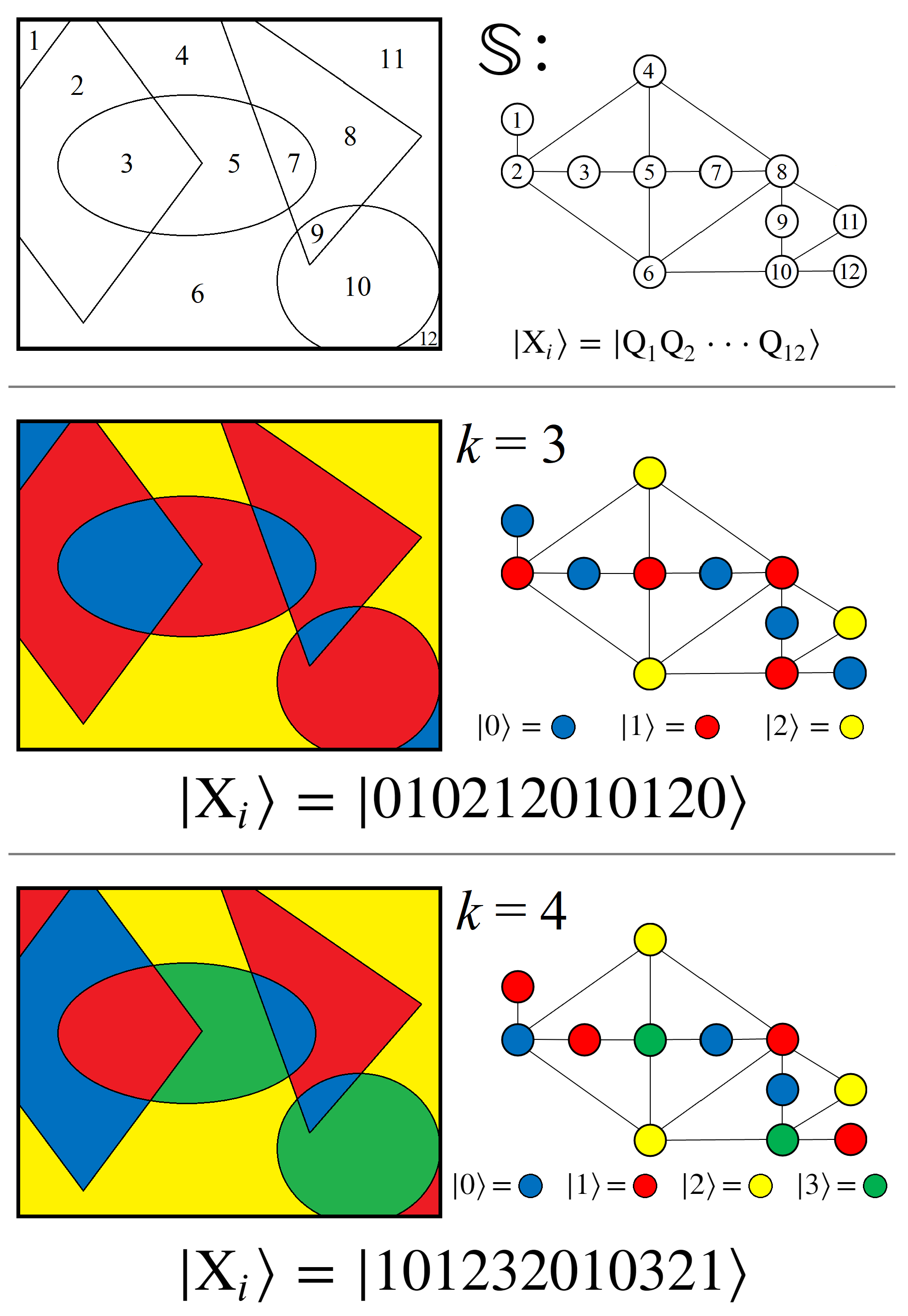
2. QUBO Definitions
2.1. Linear QUBO
3. Amplitude Amplification
| Algorithm 1 Amplitude Amplification Algorithm |
|
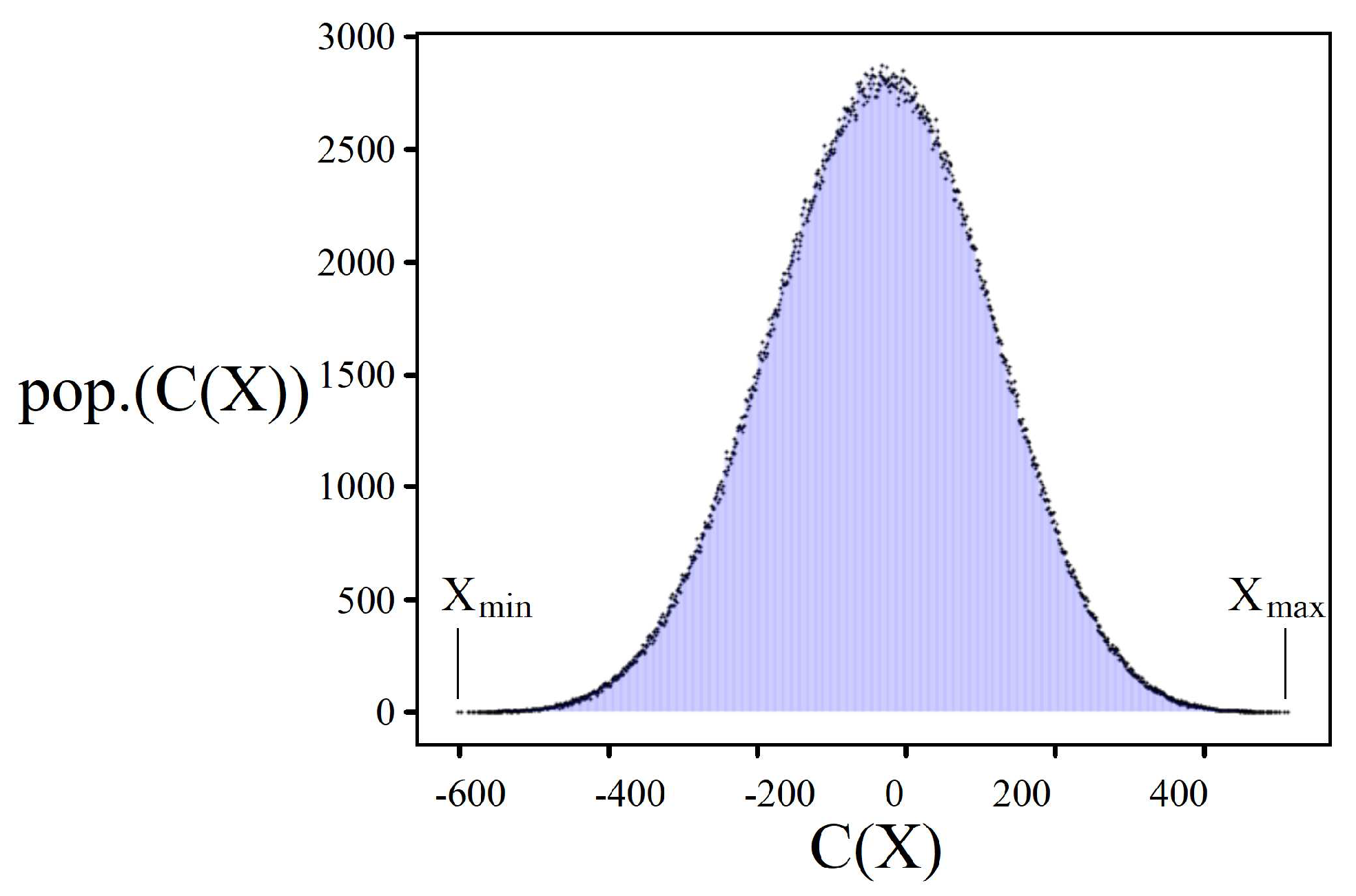
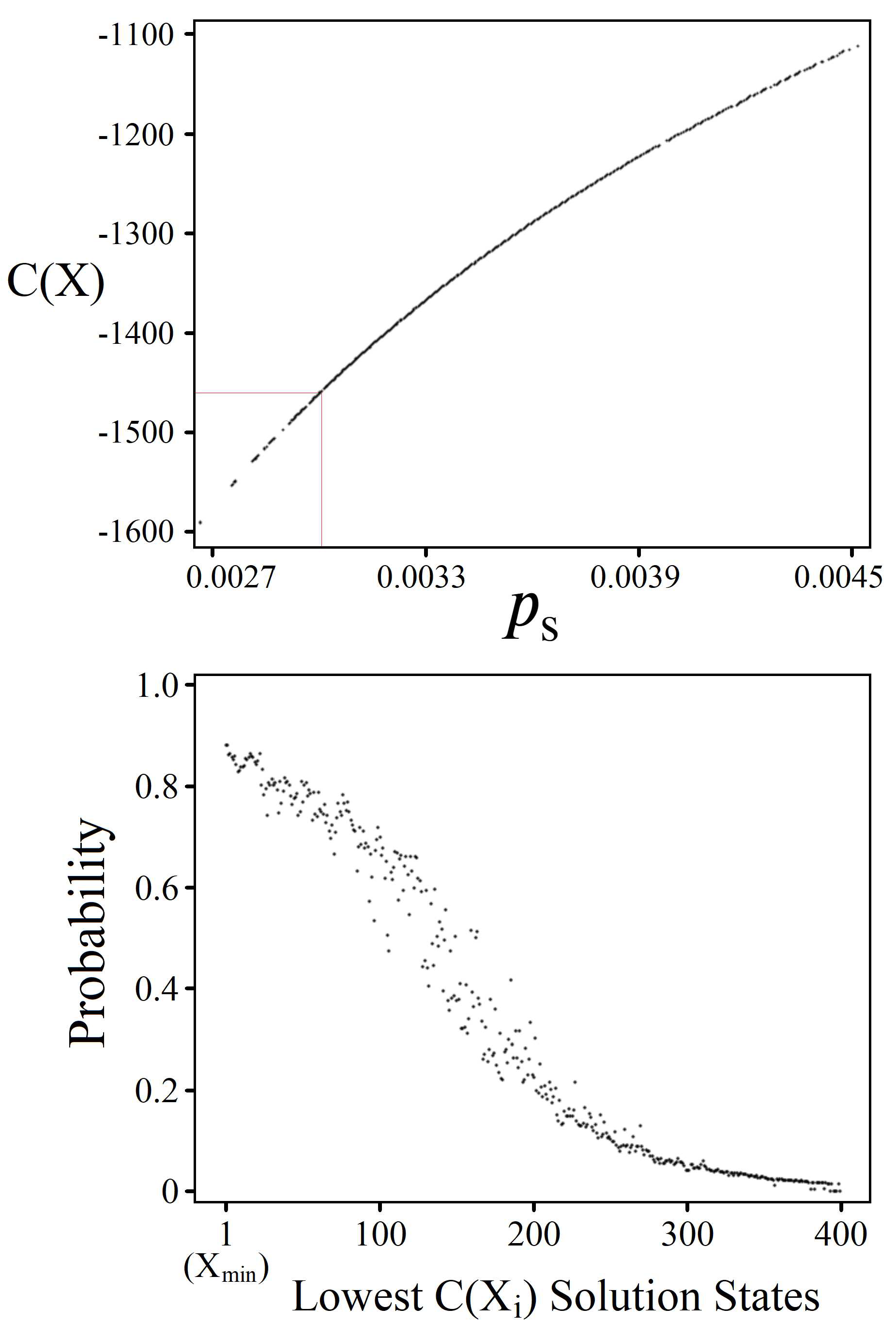
3.1. Solution Space Distribution
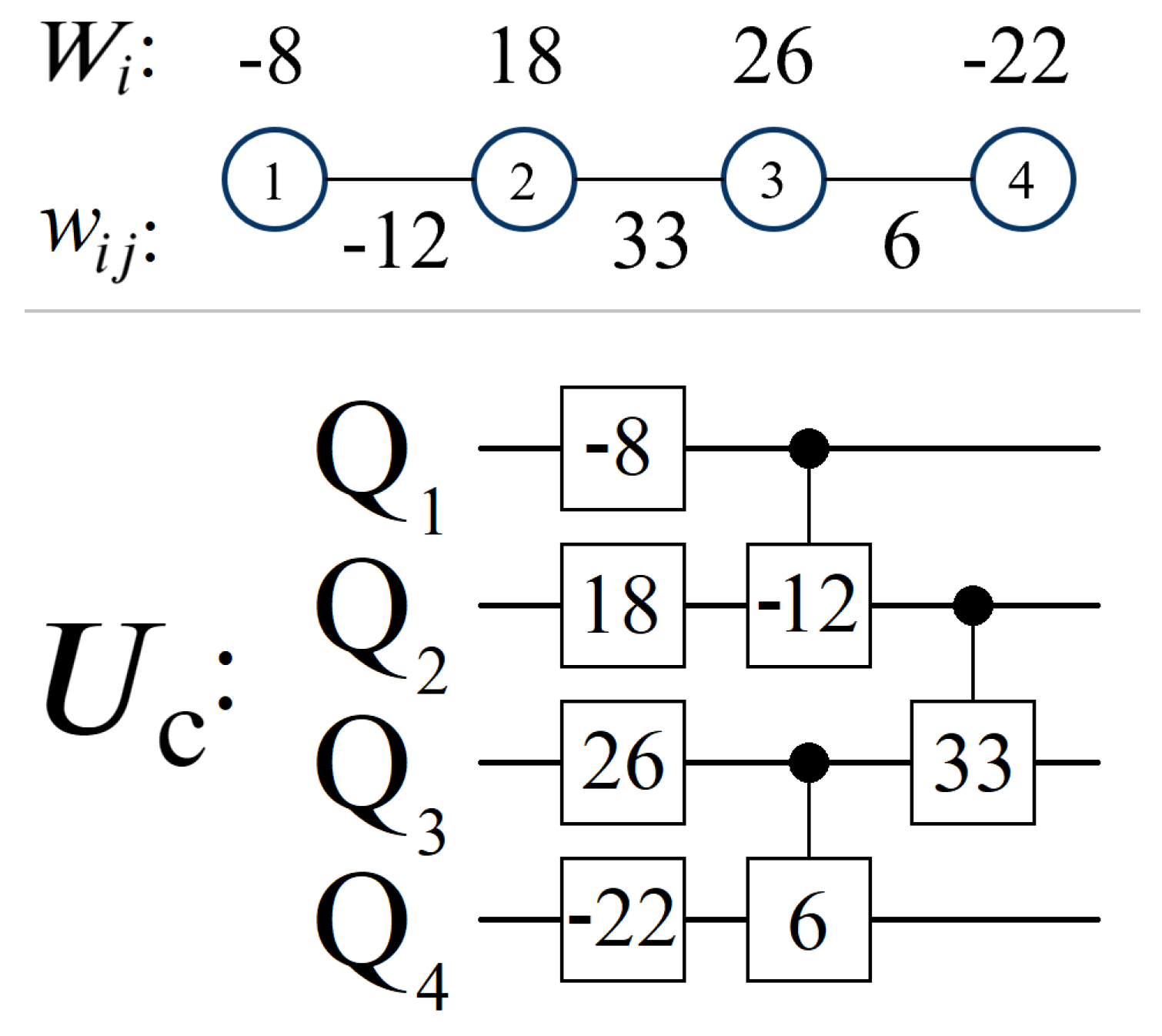
3.2. Cost Oracle
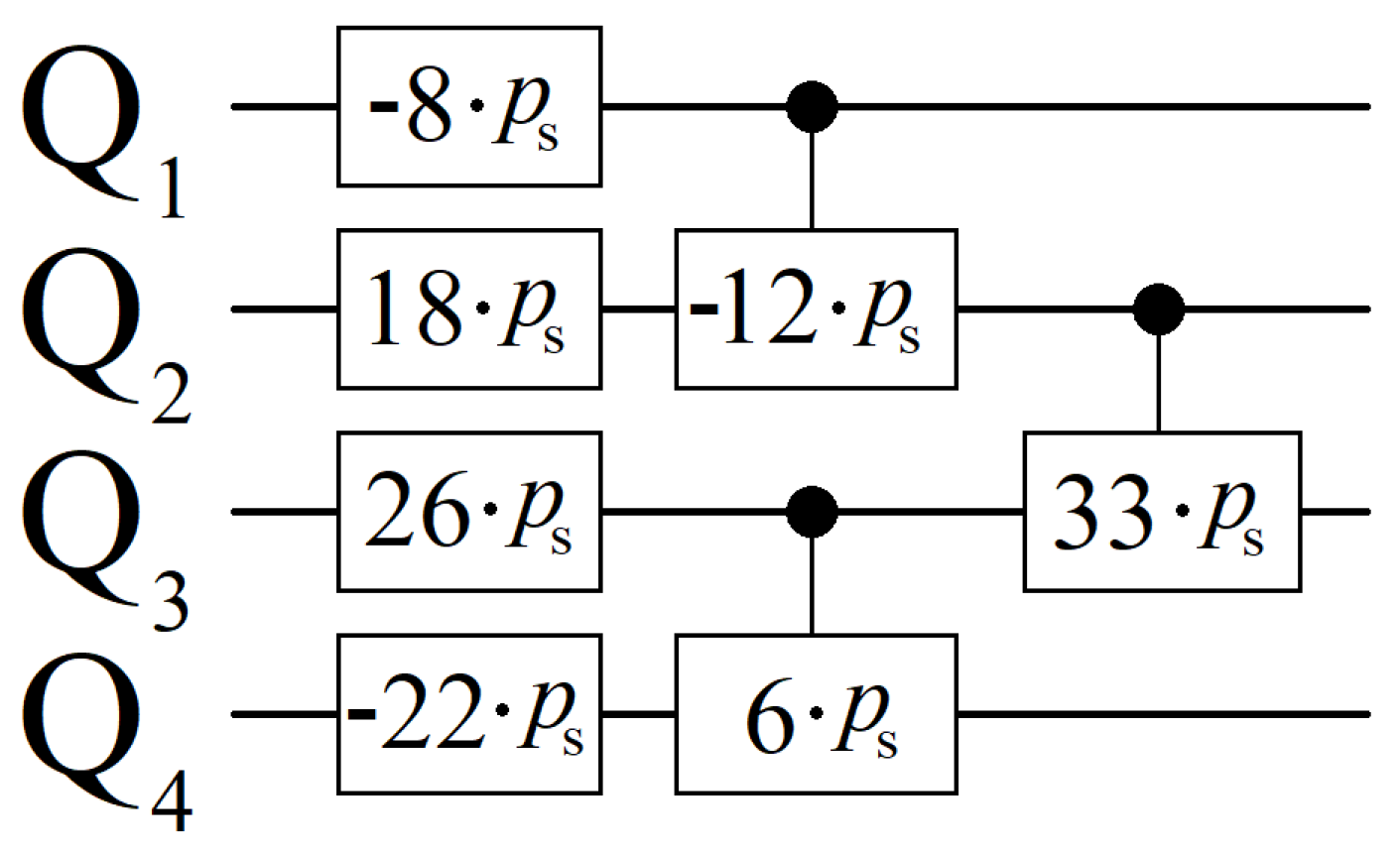
3.3. Scaling Parameter
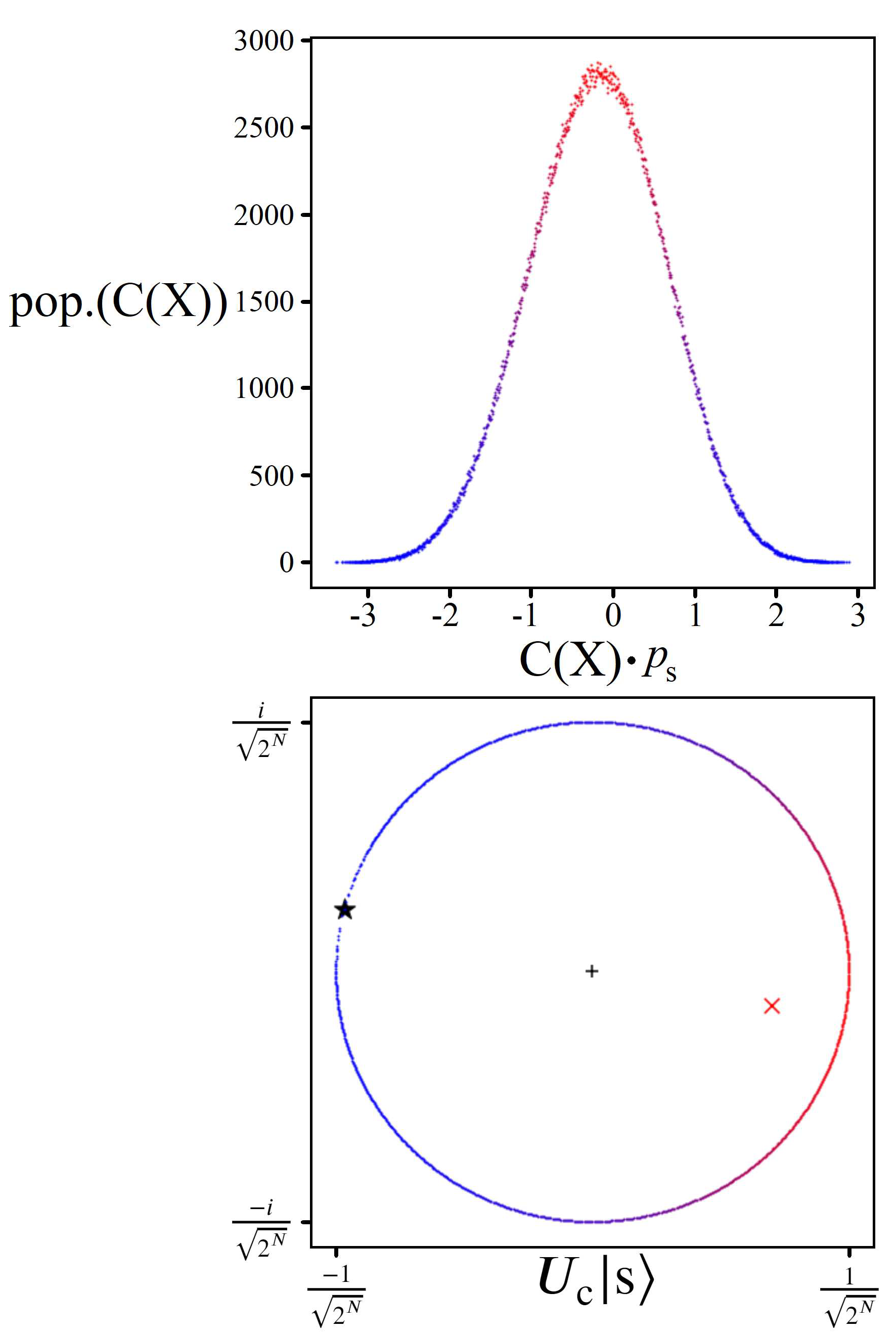
4. Gaussian Amplitude Amplification
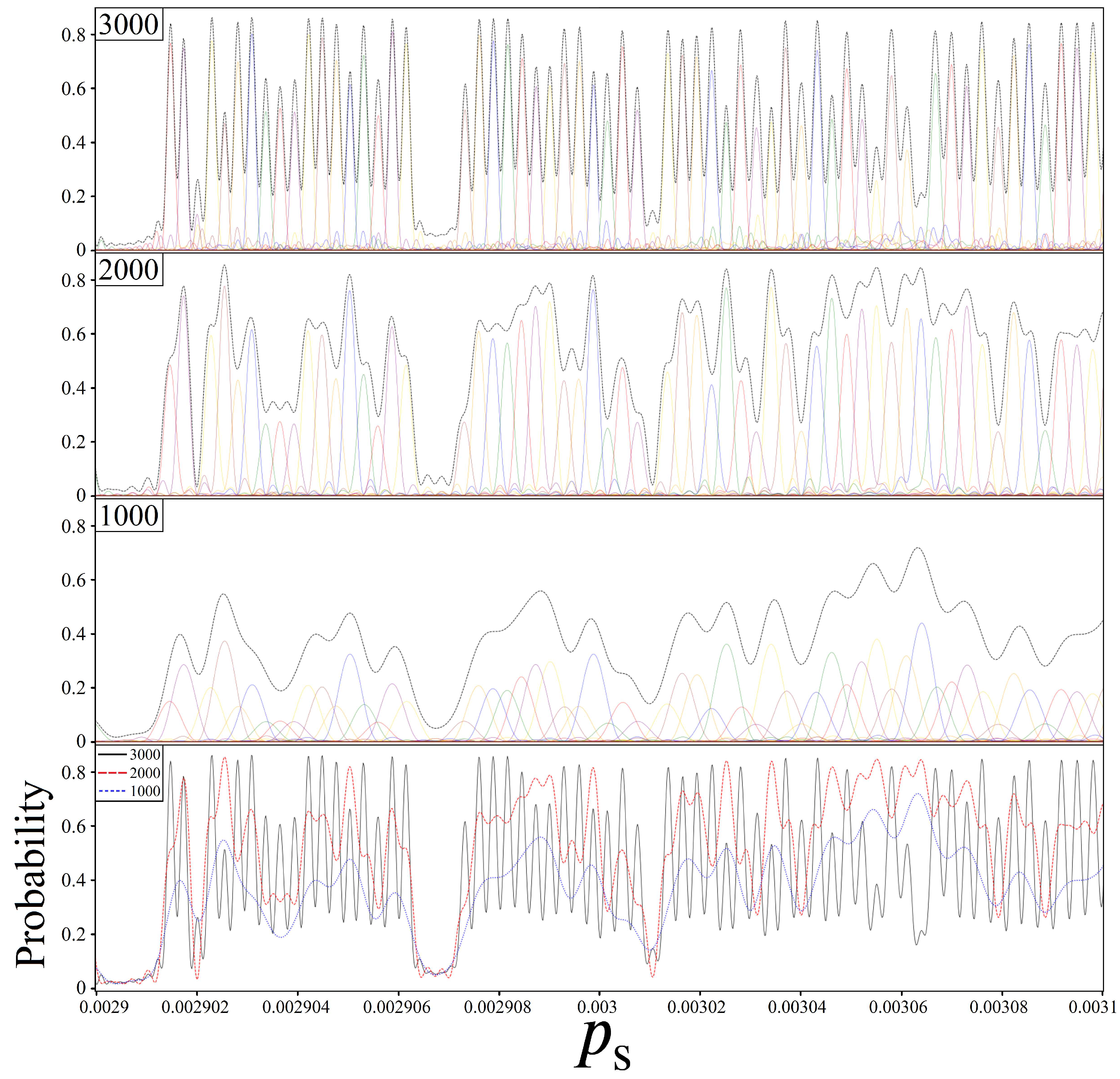
4.1. Achievable Probabilities
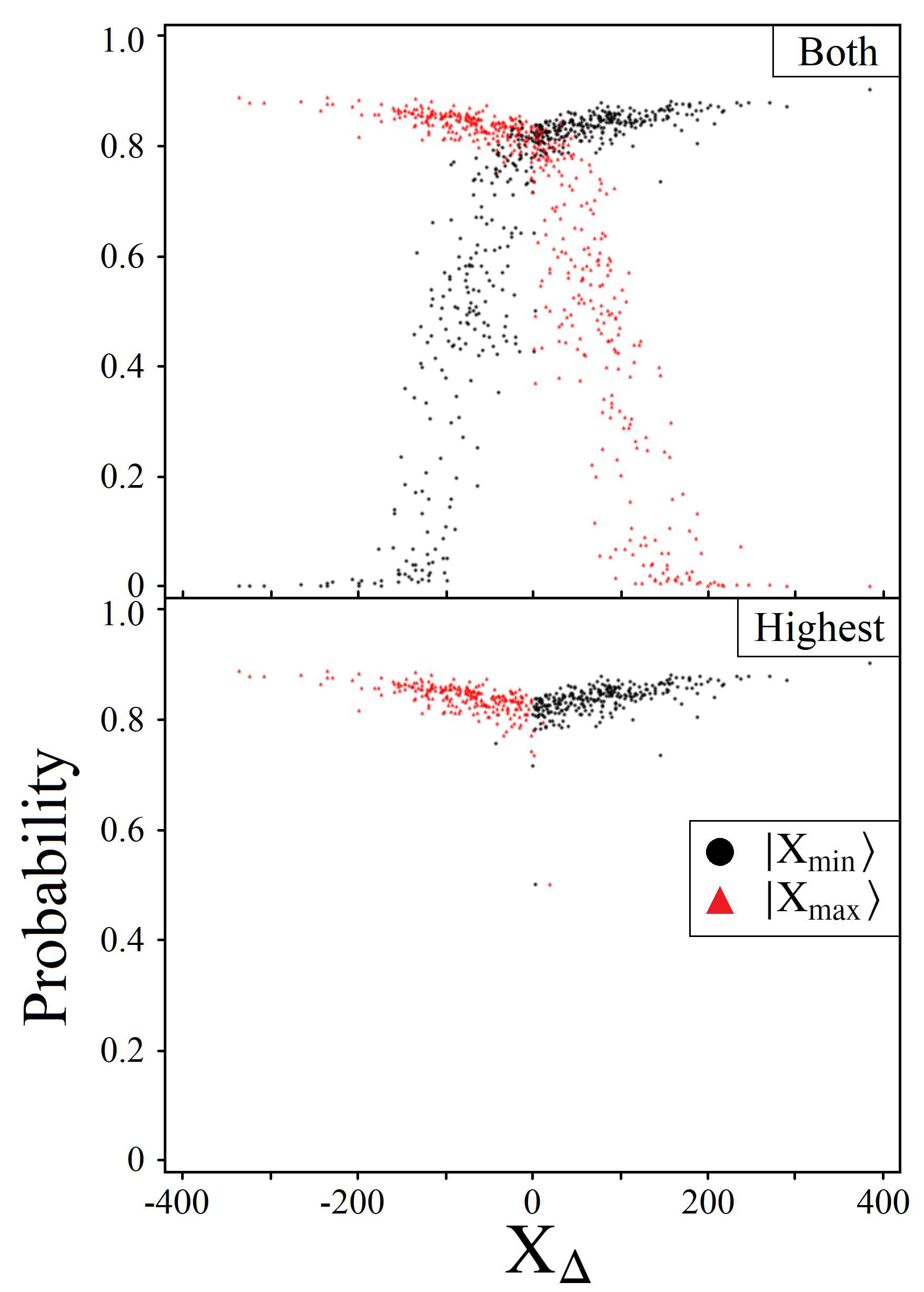
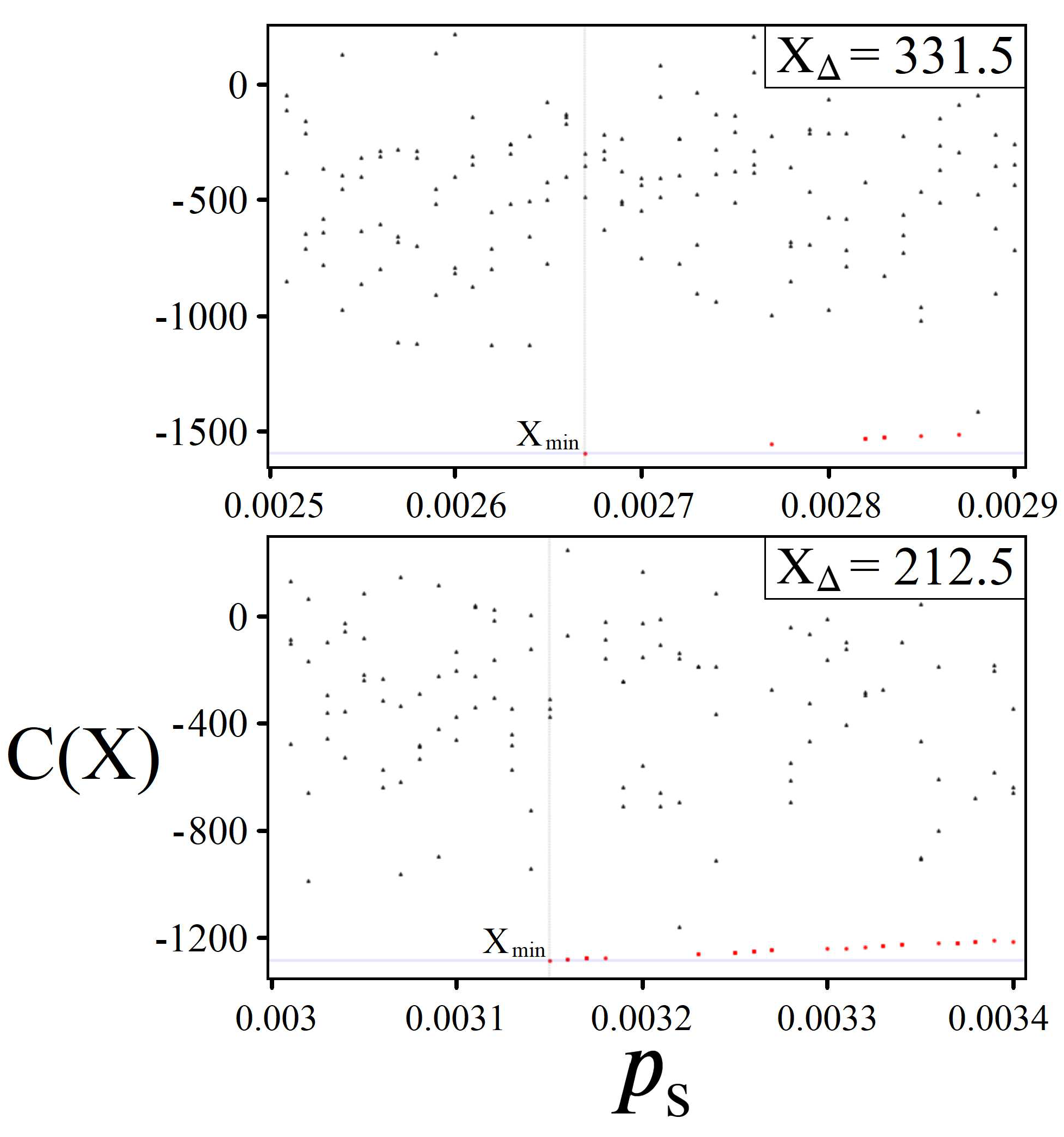
4.2. Solution Space Skewness
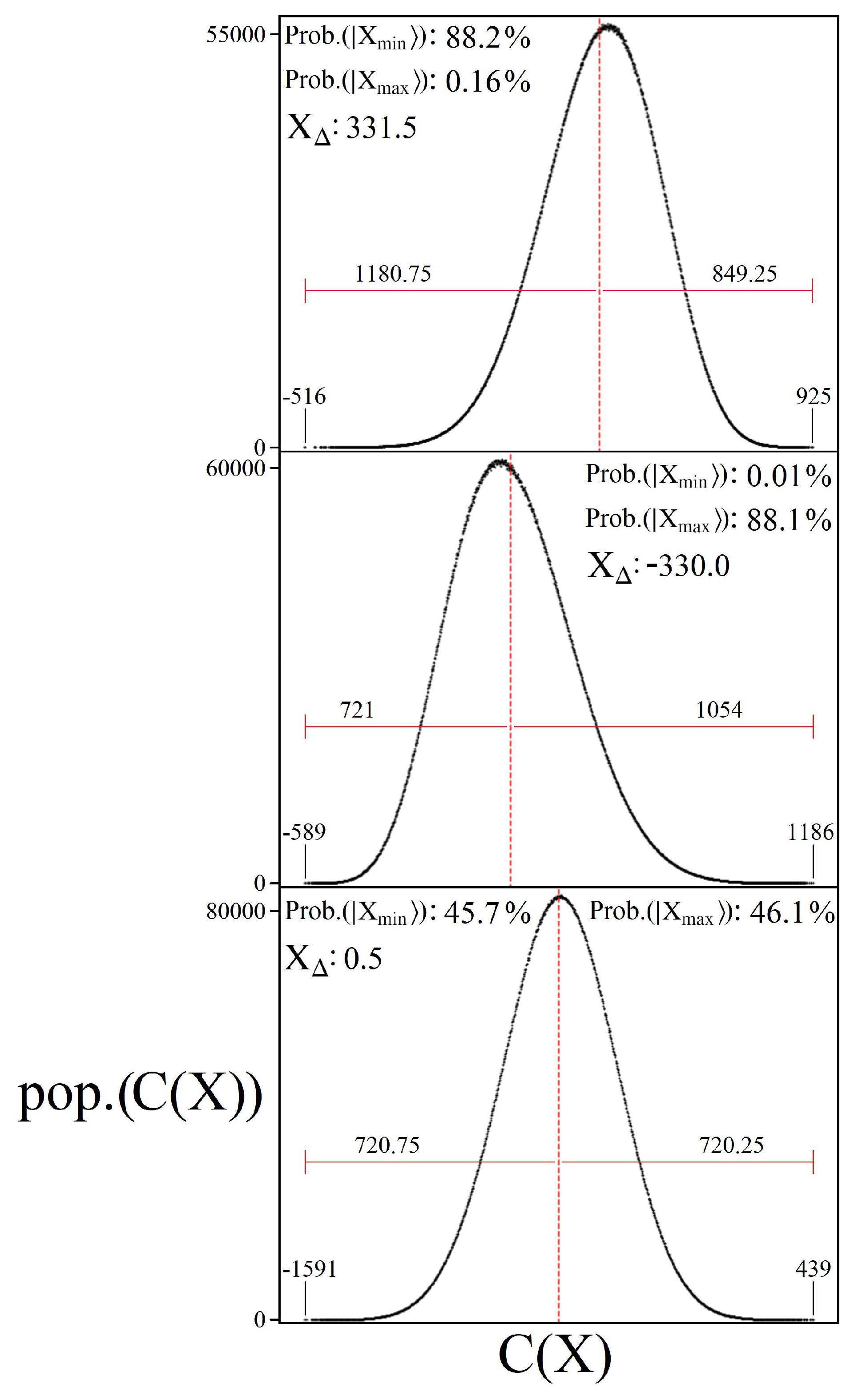
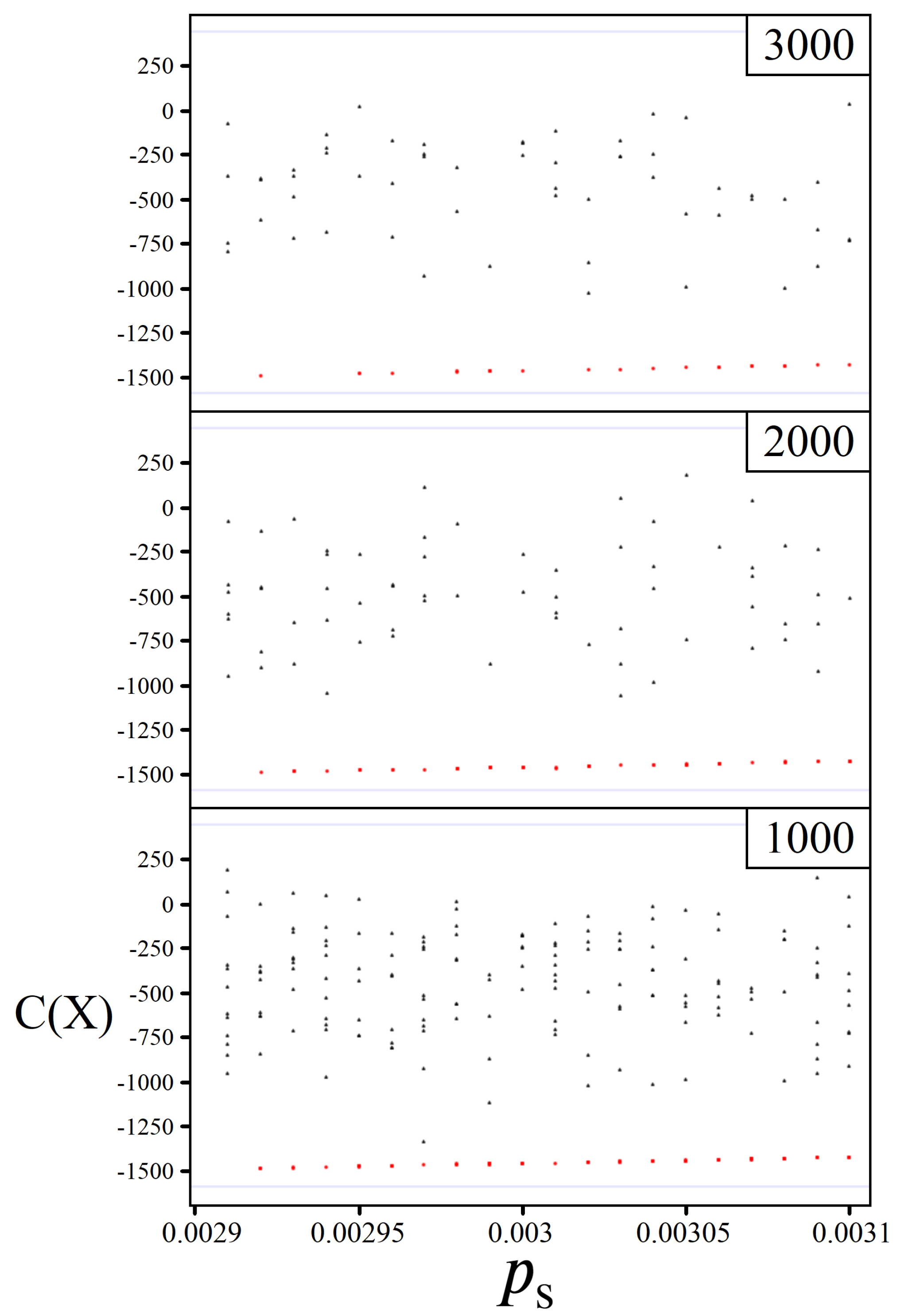
4.3. Sampling for
5. Variational Amplitude Amplification
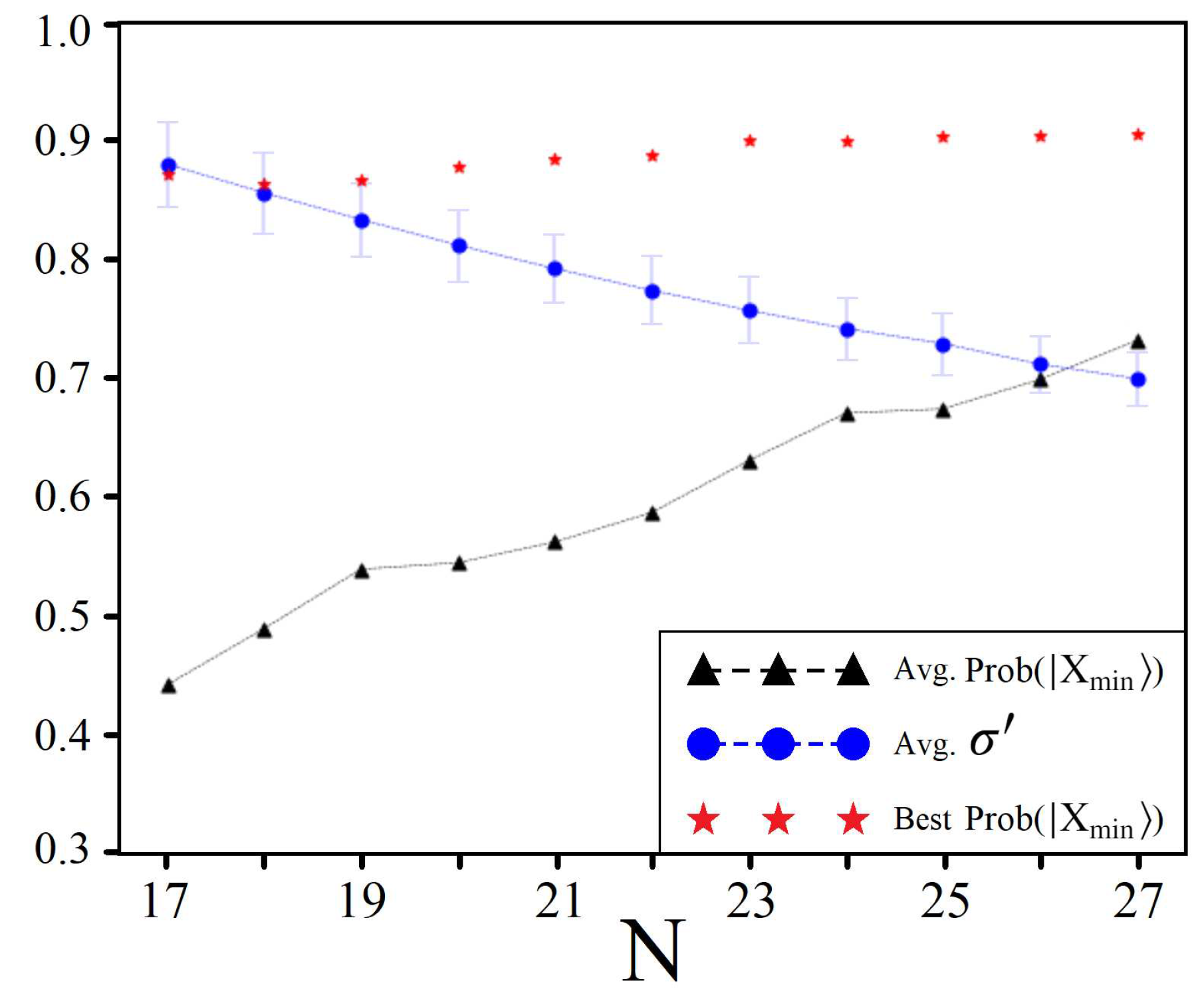
5.1. Boosting Near-Optimal Solutions
5.2. Constant Iterations
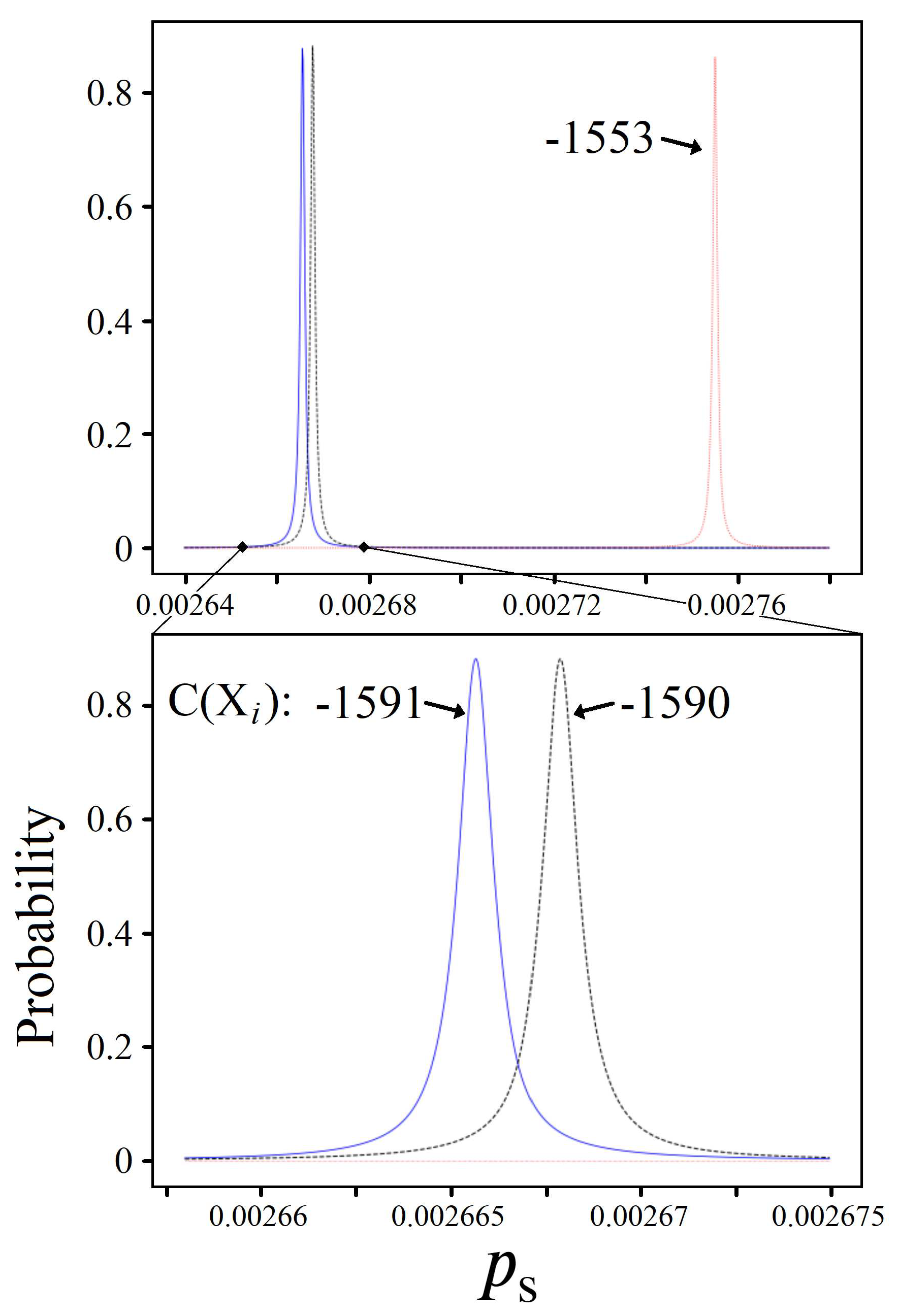
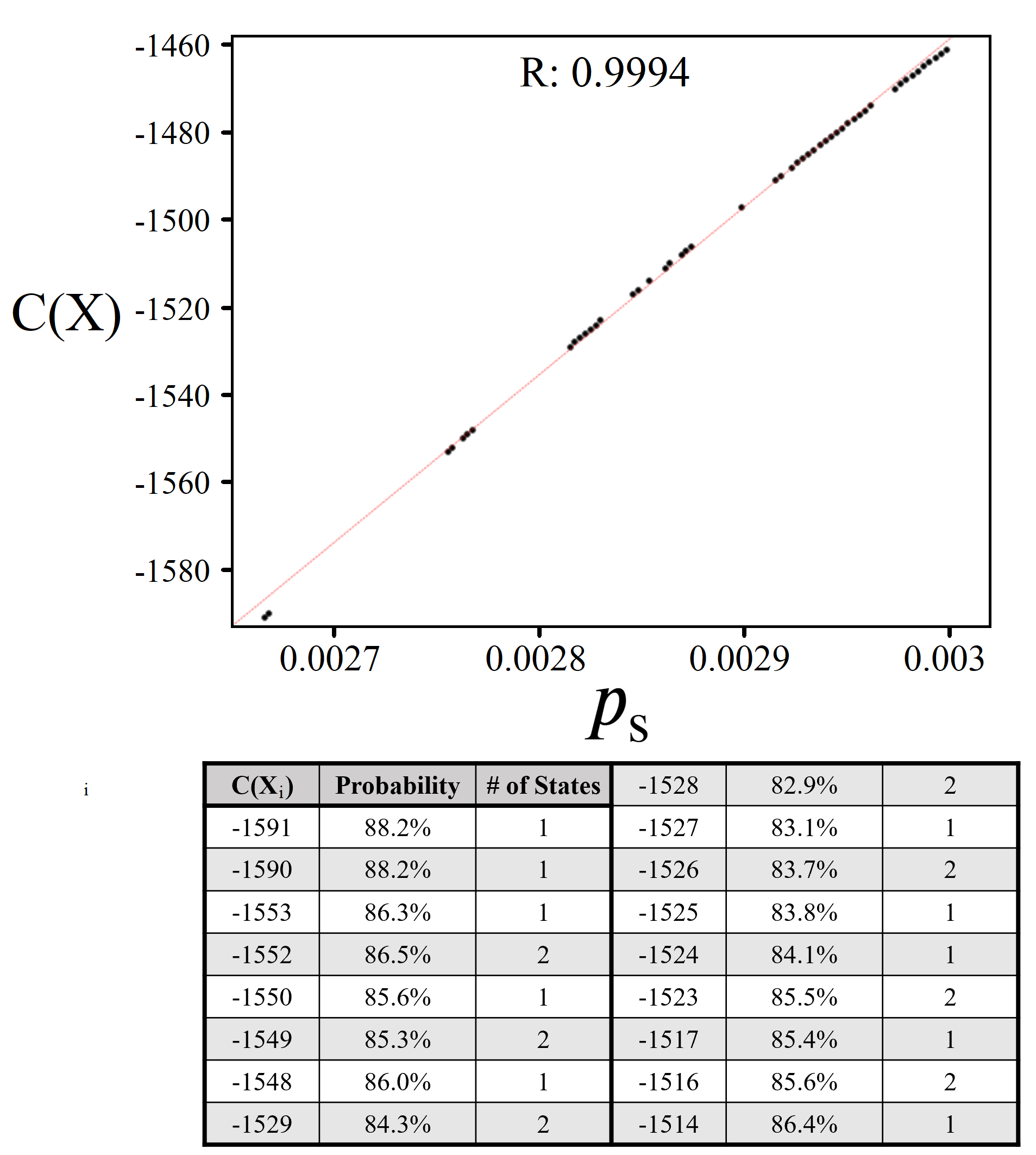
5.3. Information Through Measurements
5.4. Quantum Verification
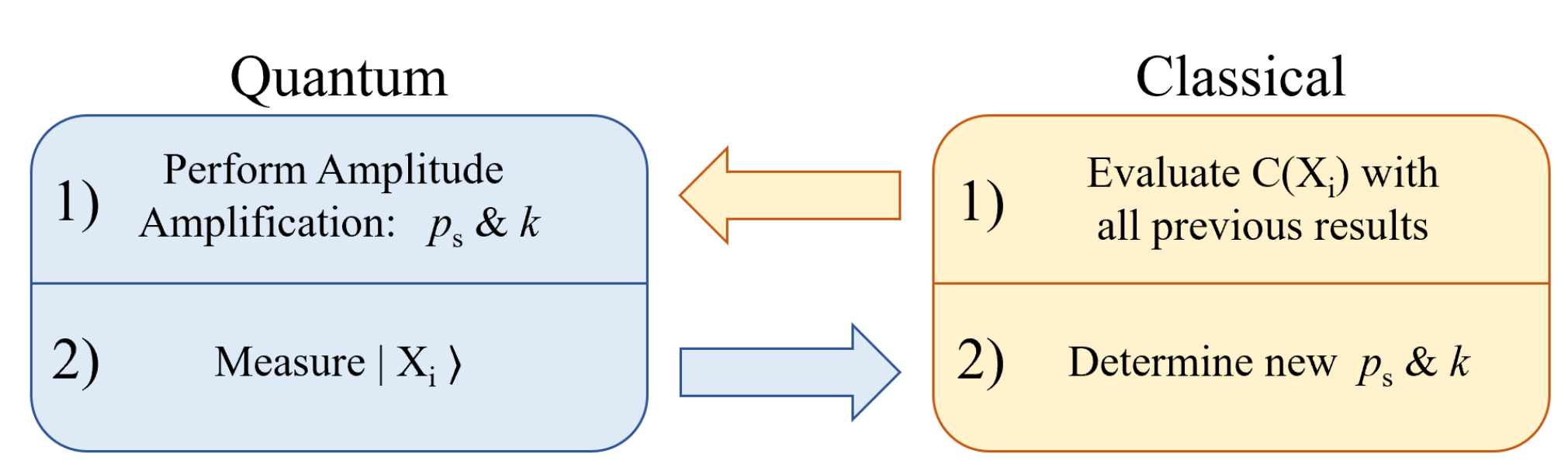
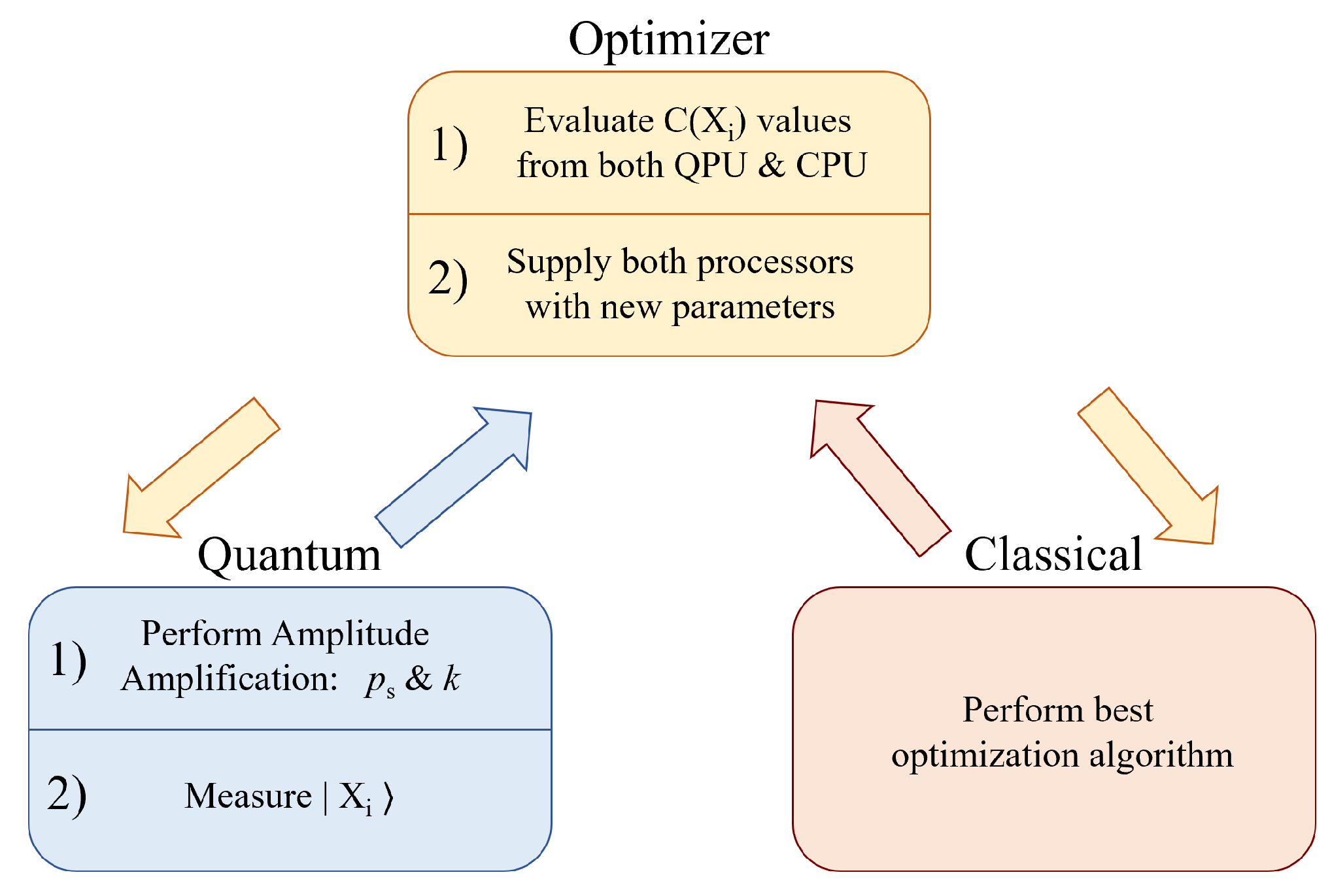
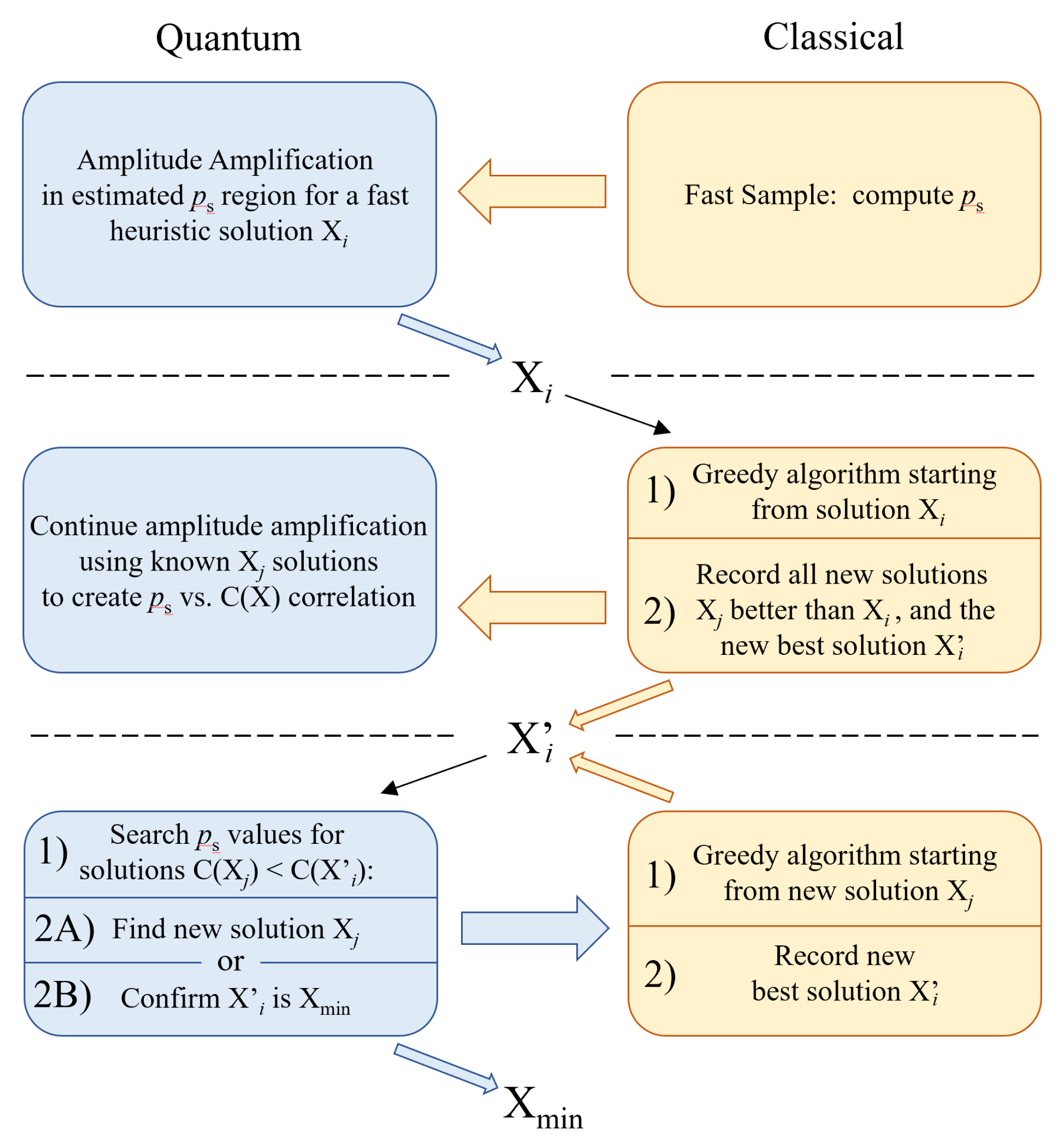
6. Hybrid Solving
6.1. Supporting Greedy Algorithms
7. More Oracle Problems
7.1. Weighted & Unweighted Max-Cut
7.2. Graph Coloring
7.3. Subset Sum
8. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Data & Code Availability
Appendix A. QUBO Data
| # of QUBOs studied | |
| 17 | 5000 |
| 18 | 3000 |
| 19 | 2000 |
| 20 | 1500 |
| 21 | 1200 |
| 22 | 1000 |
| 23 | 1000 |
| 24 | 600 |
| 25 | 500 |
| 26 | 400 |
| 27 | 100 |
Appendix B. Linear Regression
Appendix C. Max-Cut Circuit
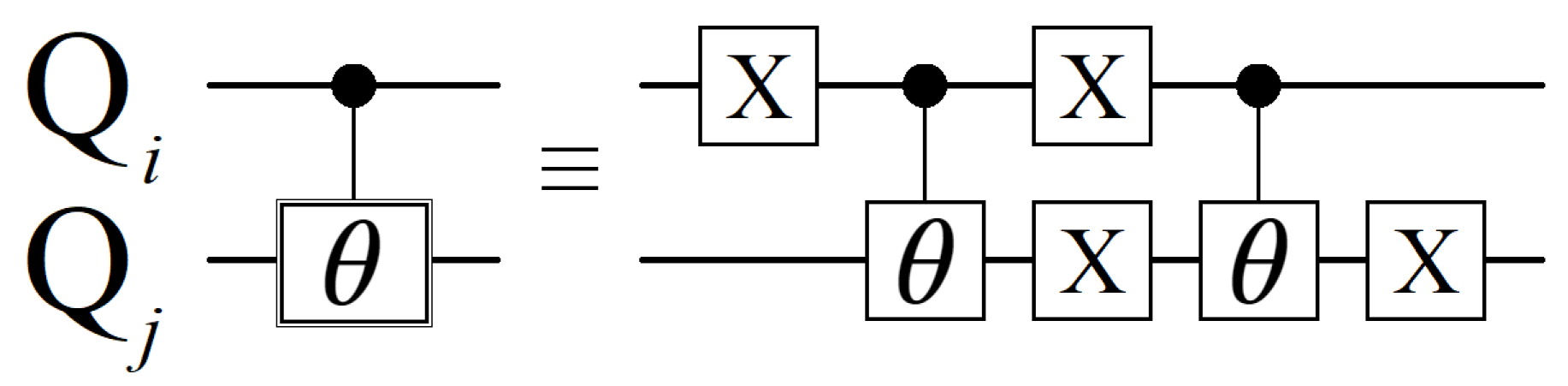
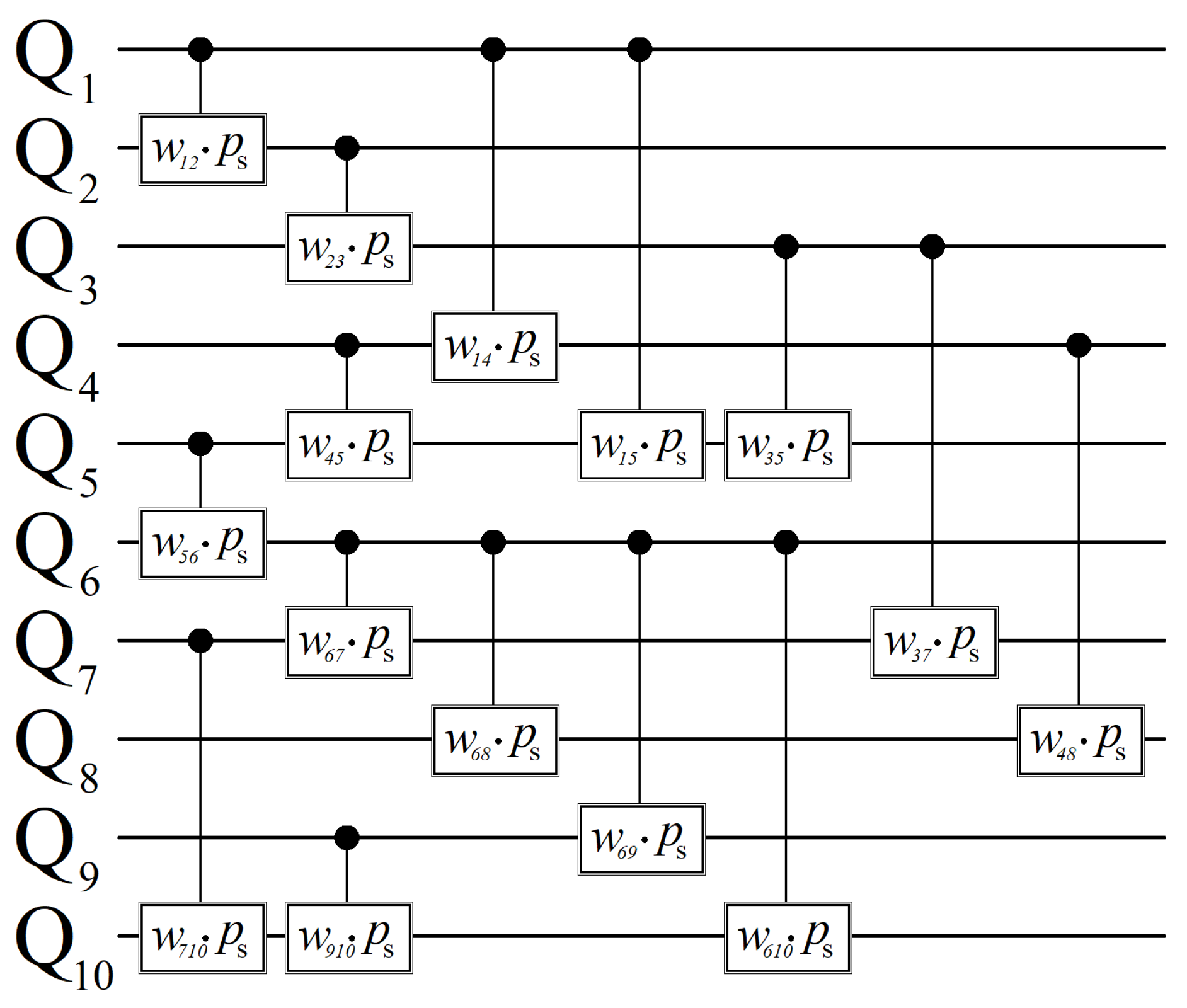
References
- L. K. Grover, A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. arXiv: 9605043 (1996). [CrossRef]
- M. Boyer, G. Brassard, P. Hoyer, A. Tapp, Tight bounds on quantum searching. Fortschritte der Physik 46, p.493-506 (1998). [CrossRef]
- C. H. Bennett, E. Bernstein, G. Brassard, U. Vazirani, Strengths and weaknesses of quantum computing. SIAM Journal on Computing 26 (5), p.1510-1523 (1997). [CrossRef]
- E. Farhi and S. Gutmann, Analog analogue of a digital quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 57, 2403 (1998). [CrossRef]
- G. Brassard, P. Hoyer, A. Tapp, Quantum counting. 25th Intl. Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming (ICALP), LNCS 1443, p. 820-831, (1998).
- G. Brassard, P. Hoyer, M. Mosca, A. Tapp, Quantum amplitude amplification and estimation. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: AMS Contemporary Mathematics 305, p.53-74 (2002). [CrossRef]
- A. M. Childs, J. Goldstone, Spatial search by quantum walk. Phys. Rev. A 70, 022314 (2004). [CrossRef]
- A. Ambainis, Variable time amplitude amplification and a faster quantum algorithm for solving systems of linear equations. arXiv: 1010.4458 (2010). [CrossRef]
- R. L. Singleton Jr., M. L. Rogers, D. L. Ostby, Grover’s algorithm with diffusion and amplitude steering. arXiv: 2110.11163 (2021). [CrossRef]
- D. Koch, M. Cutugno, S. Karlson, S. Patel, L. Wessing, P. M. Alsing, Gaussian amplitude amplification for quantum pathfinding. Entropy 24 (7), 963 (2022). [CrossRef]
- S. Lloyd, Quantum search without entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 61, 010301(R) (1999). [CrossRef]
- G. F. Viamontes, I. L. Markov, J. P. Hayes, Is quantum search practical? arXiv: 0405001 (2004). [CrossRef]
- O. Regev and L. Schiff, Impossibility of a quantum speed-up with a faulty oracle. arXiv: 1202.1027. [CrossRef]
- R. Seidel, C. K-U. Becker, S. Bock, N. Tcholtchev, I-D. Gheorge-Pop, M. Hauswirth, Automatic generation of grover quantum oracles for arbitrary data structures. arXiv: 2110.07545 (2021). [CrossRef]
- M. A. Nielsen, I. L. Chuang, Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, Cambridge University Press, p.249 (2000). [CrossRef]
- J. Bang, S. Yoo, J. Lim, J. Ryu, C. Lee, J. Lee, Quantum heuristic algorithm for traveling salesman problem. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 61, 1944 (2012). [CrossRef]
- T. Satoh, Y. Ohkura, R. V. Meter, Subdivided phase oracle for NISQ search algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering (2020). [CrossRef]
- N. Benchasattabuse, T. Satoh, M. Hajdušek, R. V. Meter, Amplitude amplification for optimization via subdivided phase oracle. arXiv: 2205.00602 (2022). [CrossRef]
- P. Shyamsundar, Non-boolean quantum amplitude amplification and quantum mean estimation. arXiv: 2102.04975 (2021). [CrossRef]
- G. L. Long, W. L. Zhang, Y. S. Li, L. Niu, Arbitrary phase rotation of the marked state cannot be used for Grover’s quantum search algorithm. Commun. Theor. Phys. 32 (3), p.335 (1999). [CrossRef]
- G. L. Long, Y. S. Li, W. L. Zhang, L. Niu, Phase matching in quantum searching. Phys. Lett. A 262, p.27-34 (1999). [CrossRef]
- P. Hoyer, Arbitrary phases in quantum amplitude amplification. Phys. Rev. A 62, 052304 (2000). [CrossRef]
- A. Younes, Towards more reliable fixed phase quantum search algorithm. Applied Math. & Info. Sciences 1 (7), 10 (2013). [CrossRef]
- T. Li, W-S. Bao, W-Q. Lin, H. Zhang, X-Q. Fu, Quantum search algorithm based on multi-phase. Chinese Phys. Lett. 31 (5), 050301 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Y. Guo, W. Shi, Y. Wang, J. Hu, Q-learning-based adjustable fixed-phase quantum Grover search algorithm. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan 86 (2), 024006 (2017). [CrossRef]
- P. H. Song and I. Kim, Computational leakage: Grover’s algorithm with imperfections. European Phys. Jour. D 23 (2000). [CrossRef]
- A. A. Pomeransky, O. V. Zhirov, D. L. Shepelyansky, Phase diagram for the Grover algorithm with static imperfections. European Phys. Jour. D 31 (2004). [CrossRef]
- J. Janmark, D. A. Meyer, T. G. Wong, Global symmetry is unnecessary for fast quantum search. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 210502 (2014). [CrossRef]
- G. Kochenberger, J-K. Hao, F. Glover, M. Lewis, Z. Lu, H. Wang, Y. Wang, The unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem: a survey. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization 28 (1), p.58–81 (2014). [CrossRef]
- A. Lucas, Ising formulations of many NP problems. Front. Phys. 12, 2 (2014). [CrossRef]
- F. Glover, G. Kochenberger, Y. Du, A tutorial on formulating and using QUBO models. arXiv: 1811.11538 (2018). [CrossRef]
- P. Date, D. Arthur, L. Pusey-Nazzaro, QUBO formulations for training machine learning models. Scientific Reports 11 (1), 10029 (2021). [CrossRef]
- D. Herman, C. Googin, X. Liu, A. Galda, I. Safro, Y. Sun, M. Pistoia, Y. Alexeev, A survey of quantum computing for finance. arXiv: 2201.02773 (2022). [CrossRef]
- P. Date, R. Patton, C. Schuman, T. Potok, Efficiently embedding QUBO problems on adiabatic quantum computers. Quantum Inf. Process. 18 (4), 117 (2019). [CrossRef]
- H. Ushijima-Mwesigwa, C. F. A. Negre, S. M. Mniszewski, Graph partitioning using quantum annealing on the D-Wave system. arXiv: 1705.03082 (2017). [CrossRef]
- D. Pastorello, E. Blanzieri, Quantum annealing learning search for solving QUBO problems. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 10 (2019). [CrossRef]
- W. Cruz-Santos, S. E. Venegas-Andraca, M. Lanzagorta, A QUBO formulation of minimum multicut problem instances in trees for D-Wave quantum annealers. Scientific Reports 9 (1), 17216 (2019). [CrossRef]
- E. Farhi, J. Goldstone, S. Gutmann, A quantum approximate optimization algorithm. arXiv:1411.4028 (2014). [CrossRef]
- S. Hadfield, Z. Wang, B. O’Gorman, E. G. Rieffel, D. Venturelli, R. Biswas, From the quantum approximate optimization algorithm to a quantum alternating operator ansatz. Algorithms 12 (2), 34 (2019). [CrossRef]
- G. G. Guerreschi, A. Y. Matsuura, QAOA for max-cut requires hundreds of qubits for quantum speed-up. Scientific Reports 9, 6903 (2019). [CrossRef]
- G. G. Guerreschi, Solving quadratic unconstrained binary optimization with divide-and-conquer and quantum algorithms. arXiv: 2101.07813 (2021). [CrossRef]
- M. Streif, M. Leib, Comparison of QAOA with quantum and simulated annealing. arXiv: 1901.01903 (2019).
- T. Gabor, M. L. Rosenfeld, S. Feld, C. Linnhoff-Popien, How to approximate any objective function via quadratic unconstrained binary optimization. arXiv: 2204.11035 (2022). [CrossRef]
- E. Pelofske, A. Bartschi, S. Eidenbenz, Quantum annealing vs. QAOA: 127 qubit higher-order ising problems on NISQ computers. arXiv: 2301.00520 (2023). [CrossRef]
- J. Bernoulli, Ars Conjectandi, Basileae: Thurnisiorum. (1713).
- P. S. Laplace, Mémoire sur les approximations des formules qui sont fonctions de très grands nombres et sur leur application aux probabilités. Mémoires de l’Académie Royale des Sciences de Paris, 10 (1810).
- C. F. Gauss, Theoria Motus Corporum Coelestium in Sectionibus Conicis Solem Ambientium, Hamburg: Friedrich Perthes and I.H. Besser (1809).
- A. Peruzzo, J. McClean, P. Shadbolt, M-H. Yung, X-Q. Zhou, P. J. Love, A. Aspuru-Guzik, J. L. O’Brien, A variational eigenvalue solver on a quantum processor. Nature Communications 5, 4213 (2014). [CrossRef]
- K. Nieman, H. Durand, S. Patel, D. Koch, and P. M. Alsing, Application of quantum computing amplitude amplification techniques for solving problems in control and optimization. journal pending. (2023).
- K. D. Jong, Learning with genetic algorithms: an overview. Machine Language 3, p.121-139 (1988). [CrossRef]
- S. Forrest, Genetic algorithms: principles of natural selection applied to computation. Science 261, 5123 (1993). [CrossRef]
- M. Srinivas, L. M. Patnaik, Genetic algorithms: a survey. IEEE Computer 27, p.17-26 (1994). [CrossRef]
- R. J. Parsons, S. Forrest, C. Burks, Genetic algorithms, operators, and DNA fragment assembly. Machine Learning 21, 11-33 (1995). [CrossRef]
- A. B. Finnila, M. A. Gomez, C. Sebenik, C. Stenson, J. D. Doll, Quantum annealing: a new method for minimizing multidimensional functions. Chemical Physics Letters 219, p.343-348 (1994). [CrossRef]
- Y. Koshka, M. A. Novotny, Comparison of D-Wave quantum annealing and classical simulated annealing for local minima determination. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory 1, 2 (2020). [CrossRef]
- D. Wierichs, C. Gogolin, M. Kastoryano, Avoiding local minima in variational quantum eigensolvers with the natural gradient optimizer. Phys. Rev. Research 2, 043246 (2020). [CrossRef]
- J. Rivera-Dean, P. Huembeli, A. Acin, J. Bowles, Avoiding local minima in variational quantum algorithms with neural networks. arXiv: 2104.02955 (2021). [CrossRef]
- S. H. Sack, M. Serbyn, Quantum annealing initialization of the quantum approximate optimization algorithm. Quantum 5, 491 (2021). [CrossRef]
- J. Eisert, D. Hangleiter, N. Walk, I. Roth, D. Markham, R. Parekh, U. Chabaud, E. Kashefi, Quantum certification and benchmarking. Nature Reviews Physics 2, p.382-390 (2020). [CrossRef]
- D. Willsch, M. Willsch, C. D. G. Calaza, F. Jin, H. De Raedt, M. Svensson, K. Michielsen, Benchmarking advantage and D-Wave 2000Q quantum annealers with exact cover problems. Quantum Inf. Process. 21, 141 (2022). [CrossRef]
- A. Noiri, K. Takeda, T. Nakajima, T. Kobayashi, A. Sammak, G. Scappucci, S. Tarucha, Fast universal quantum gate above the fault-tolerance threshold in silicon. Nature 601, 7893 p.338-342 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhang, S. Schwartz, L. Wagner, W. Miller, A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. Journal of Comp. Biology 7, p.203-214 (2004). [CrossRef]
- L. Lin, L. Cao, J. Wang, C. Zhang, The applications of genetic algorithms in stock market data mining optimisation. WIT Trans. on Info. and Comm. Tech. 33 (2004). [CrossRef]
- B. Korte, L. Lovasz, Mathematical structures underlying greedy algorithms. Fundamentals of Comp. Theory (1981). [CrossRef]
- J. Bang-Jensen, G. Gutin, A. Yeo, When the greedy algorithm fails. Discrete Optimization 1 (2), p.121-127 (2004). [CrossRef]
- F. Glover, G. Gutin, A. Yeo, A. Zverovich, Construction heuristics for the asymmetric TSP. European Journ. of Operational Research 129, 3 (2001). [CrossRef]
- P. Festa, P. M. Pardalos, M. G. C. Resende, C. C. Ribeiro, Randomized heuristics for the Max-Cut problem. Optimization Methods and Software 17, 6 (2002). [CrossRef]
- R. Karp, Reducibility among combinatorial problems. Proceedings of a symposium on the complexity of computer computations, Yorktown Heights, New York (1972). [CrossRef]
- M. R. Garey, D. S. Johnson, L. Stockmeyer, Some simplified NP-complete graph problems. Theoretical Computer Science 1, 3 p.237-267 (1976). [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, Z. Hu, B. C. Sanders, S. Kais, Qudits and high-dimensional quantum computing. Front. Phys. 10, 8 (2020). [CrossRef]
- B. P. Lanyon, M. Barbieri, M. P. Almeida, T. Jennewein, T. C. Ralph, K. J. Resch, G. J. Pryde, J. L. O’Brien, A. Gilchrist, A. G. White, Quantum computing using shortcuts through higher dimensions. Nature Physics 5, 134 (2009). [CrossRef]
- M-X. Luo and X-J. Wang, Universal quantum computation with qudits. Sci. China Phys. Mechanics & Astronomy 57 (9), p.1712–1717 (2014). [CrossRef]
- M. Y. Niu, I. L. Chuang, J. H. Shapiro, Qudit-Basis Universal Quantum Computation Using χ2 Interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 160502 (2018). [CrossRef]

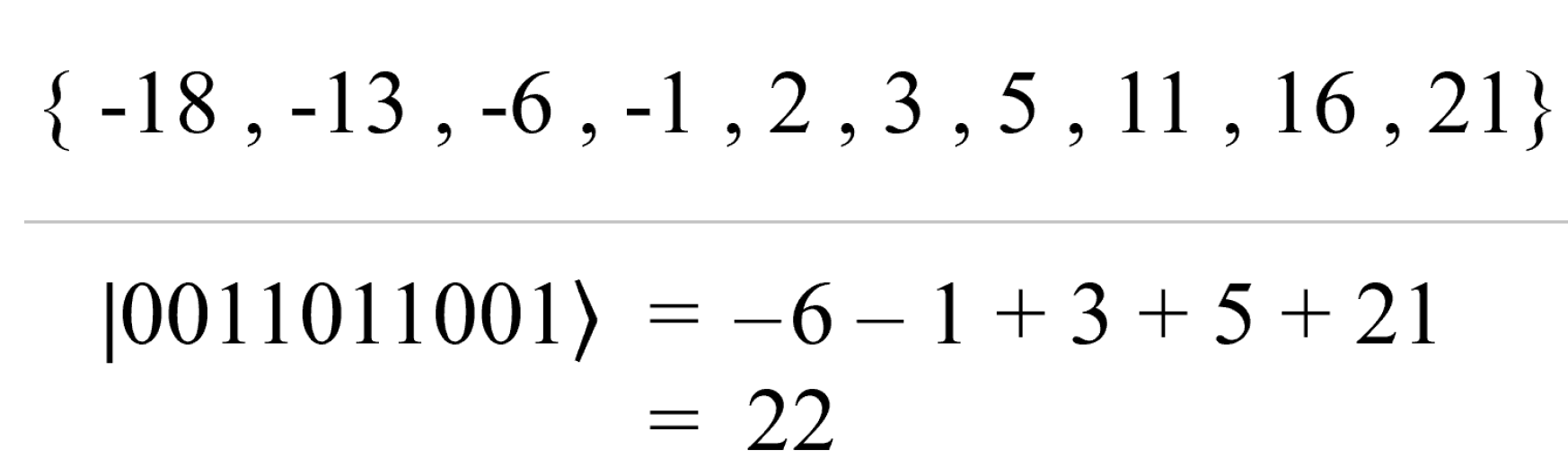
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




